Gramicidin, a Bactericidal Antibiotic, Is an Antiproliferative Agent for Ovarian Cancer Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Cell Proliferation Assay
2.3. TUNEL Assay
2.4. DNA Agarose Gel Electrophoresis
2.5. Cell Cycle Analysis Using Propidium Iodine (PI) Staining
2.6. Western Blot Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
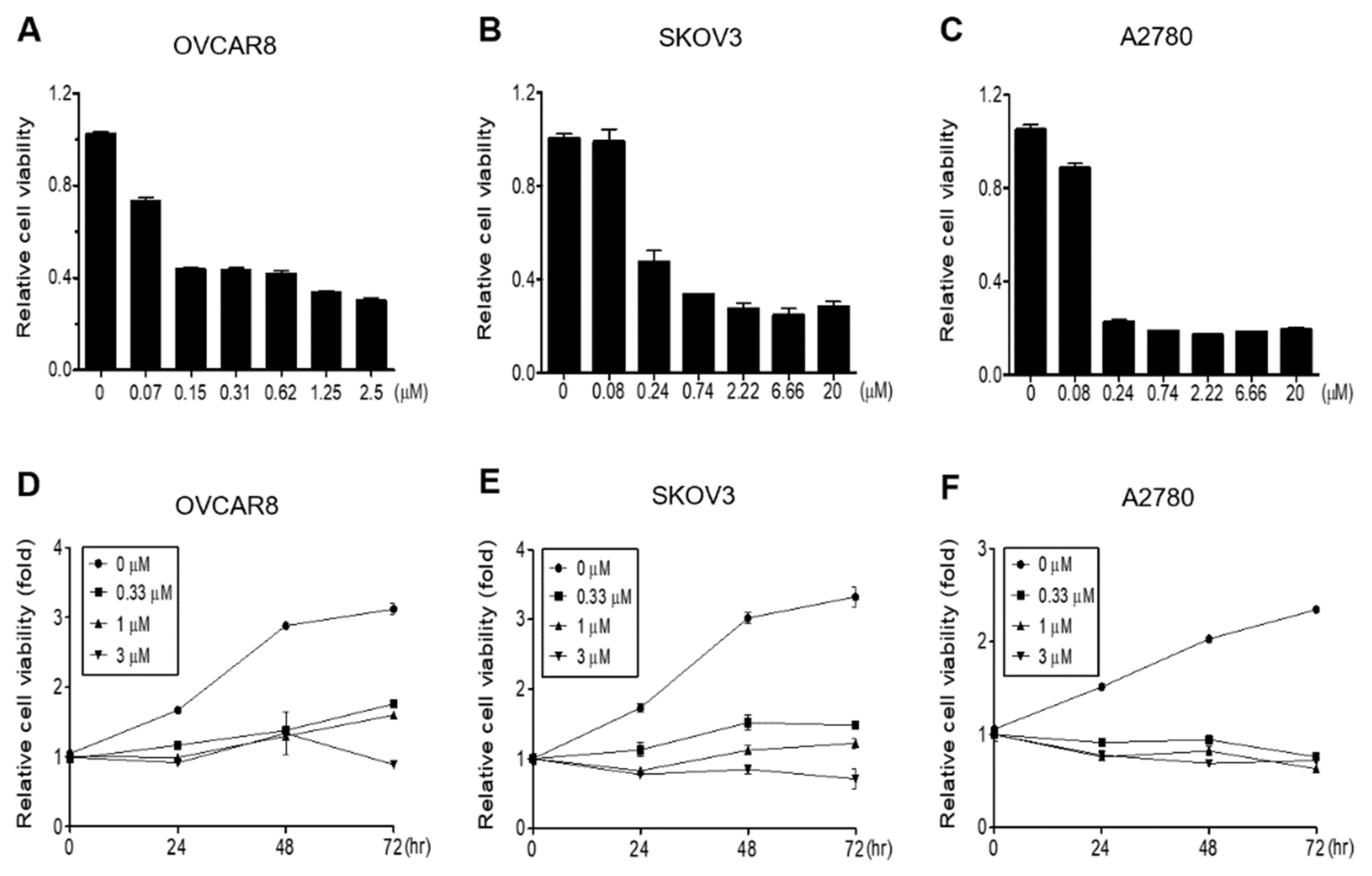
3.1. Gramicidin Inhibits the Proliferation of Ovarian Cancer Cells
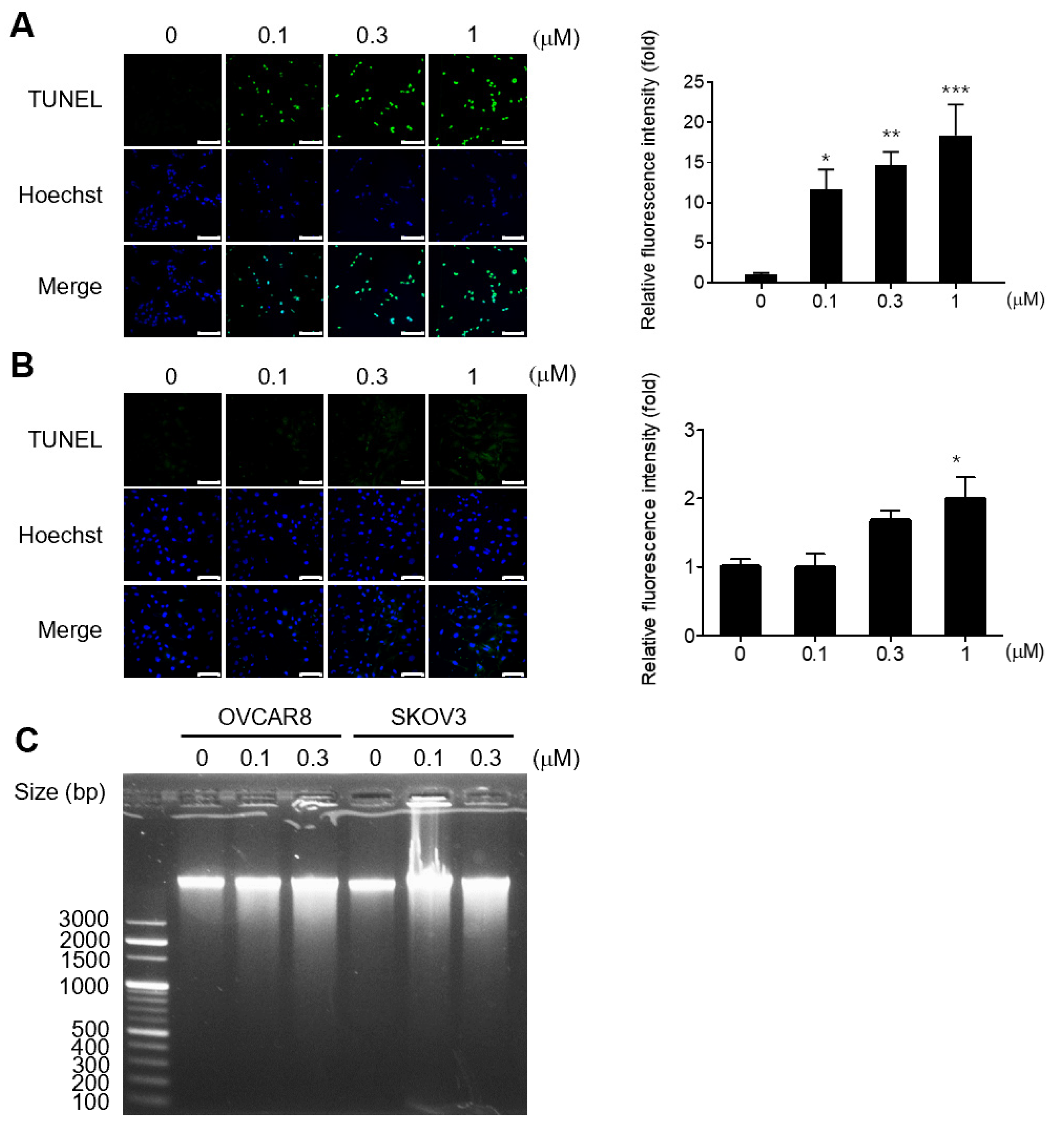
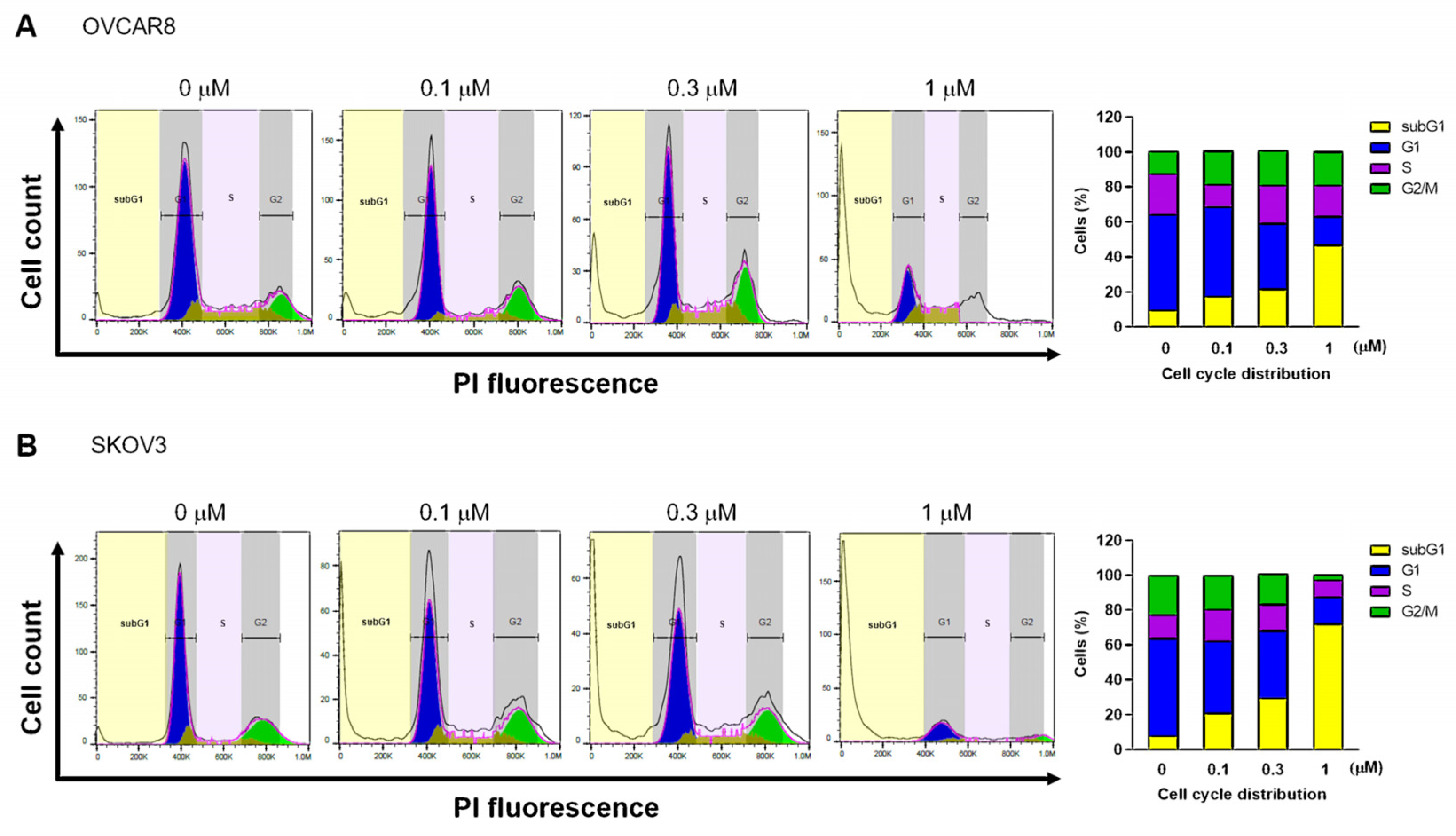
3.2. Gramicidin Induces Apoptosis by Mediating DNA Fragmentation in Ovarian Cancer Cells
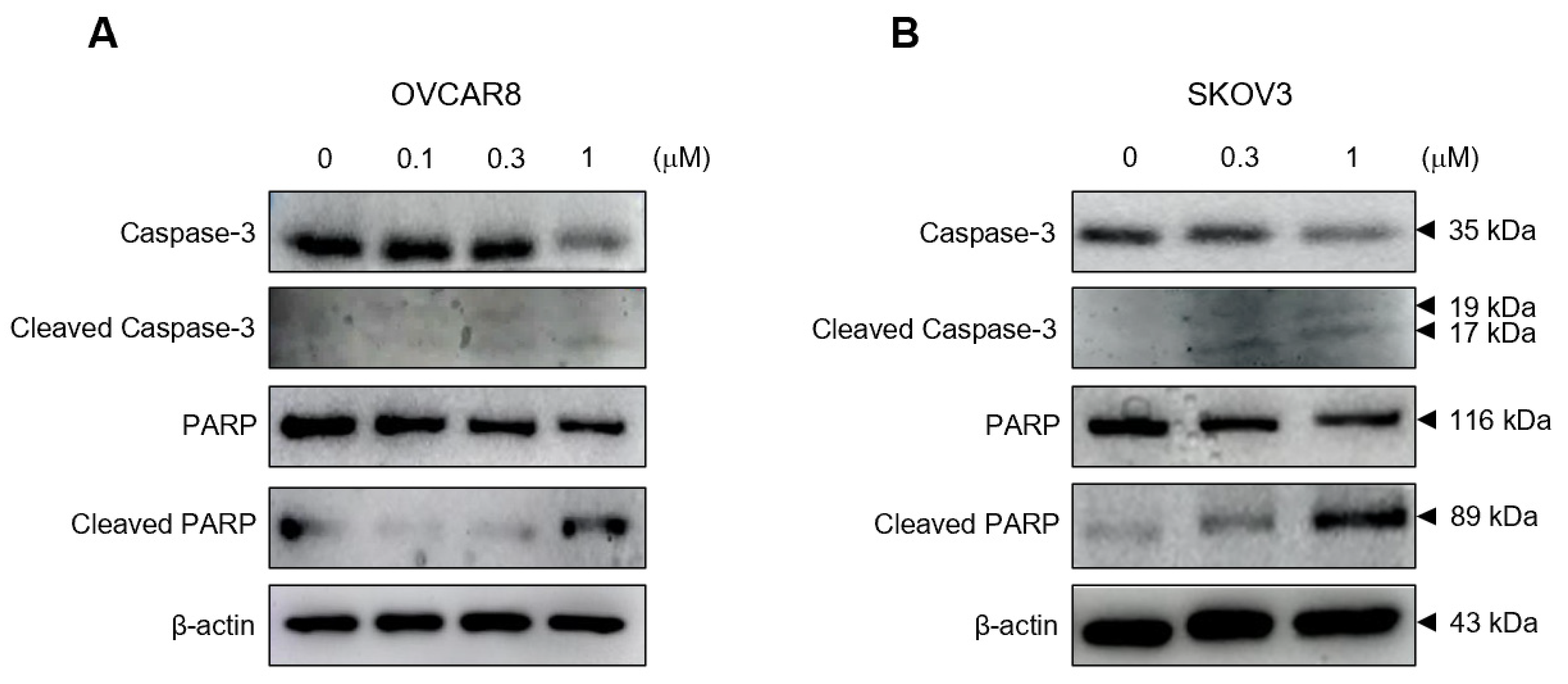
3.3. Gramicidin Mediates Apoptosis of Ovarian Cancer Cells via the Activation of Caspase-3
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schoutrop, E.; Moyano-Galceran, L.; Lheureux, S.; Mattsson, J.; Lehti, K.; Dahlstrand, H.; Magalhaes, I. Molecular, cellular and systemic aspects of epithelial ovarian cancer and its tumor microenvironment. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 86, 207–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torre, L.A.; Trabert, B.; DeSantis, C.E.; Miller, K.D.; Samimi, G.; Runowicz, C.D.; Gaudet, M.M.; Jemal, A.; Siegel, R.L. Ovarian cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 284–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biegala, L.; Gajek, A.; Marczak, A.; Rogalska, A. PARP inhibitor resistance in ovarian cancer: Underlying mechanisms and therapeutic approaches targeting the ATR/CHK1 pathway. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2021, 1876, 188633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.D.; Xia, B.R.; Jin, M.Z.; Lou, G. Organoid of ovarian cancer: Genomic analysis and drug screening. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2020, 22, 1240–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouberhan, S.; Bar-Peled, L.; Matoba, Y.; Mazina, V.; Philp, L.; Rueda, B.R. The evolving role of DNA damage response in overcoming therapeutic resistance in ovarian cancer. Cancer Drug Resist. 2023, 6, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Li, X.; Li, W.; Bai, H.; Zhang, Z. PARP inhibitors in ovarian cancer: Sensitivity prediction and resistance mechanisms. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 2303–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, T.; Tsuruda, Y.; Matsumoto, Y.; Uchida, H.; Nakayama, K.I.; Mimori, K. Drug repositioning in cancer: The current situation in Japan. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Banno, K.; Kunitomi, H.; Tominaga, E.; Aoki, D. Current state and outlook for drug repositioning anticipated in the field of ovarian cancer. J. Gynecol. Oncol. 2019, 30, e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armando, R.G.; Gomez, D.L.M.; Gomez, D.E. New drugs are not enough-drug repositioning in oncology: An update. Int. J. Oncol. 2020, 56, 651–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jourdan, J.P.; Bureau, R.; Rochais, C.; Dallemagne, P. Drug repositioning: A brief overview. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2020, 72, 1145–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.; He, S.; Bennett, W.F.D.; Bilodeau, C.L.; Andersen, O.S.; Lightstone, F.C.; Ingolfsson, H.I. Atomistic Characterization of Gramicidin Channel Formation. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2021, 17, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kessler, N.; Schuhmann, H.; Morneweg, S.; Linne, U.; Marahiel, M.A. The linear pentadecapeptide gramicidin is assembled by four multimodular nonribosomal peptide synthetases that comprise 16 modules with 56 catalytic domains. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 7413–7419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Qin, L.H.; Pace, C.J.; Wong, P.; Malonis, R.; Gao, J.M. Solubilized Gramicidin A as Potential Systemic Antibiotics. Chembiochem 2012, 13, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yu, K.; Cao, X.; Su, F.; Xu, H.; Peng, Y.; Hu, Y.; Qian, F.; et al. Gramicidin inhibits human gastric cancer cell proliferation, cell cycle and induced apoptosis. Biol. Res. 2019, 52, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, J.M.; Rajasekaran, A.K. Gramicidin A: A New Mission for an Old Antibiotic. J. Kidney Cancer VHL 2015, 2, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, J.M.; Owens, T.A.; Barwe, S.P.; Rajasekaran, A.K. Gramicidin A induces metabolic dysfunction and energy depletion leading to cell death in renal cell carcinoma cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 2296–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelkar, D.A.; Chattopadhyay, A. The gramicidin ion channel: A model membrane protein. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1768, 2011–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Zou, L.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, S.; Zhong, M.; Zhou, J.; Li, X.; Ma, X. Gramicidin inhibits cholangiocarcinoma cell growth by suppressing EGR4. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2020, 48, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.Q.; Geng, J.; Sheng, W.J.; Liu, X.J.; Jiang, M.; Zhen, Y.S. The ionophore antibiotic gramicidin A inhibits pancreatic cancer stem cells associated with CD47 down-regulation. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haoyang, W.W.; Xiao, Q.; Ye, Z.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, D.W.; Li, J.; Xiao, L.; Li, Z.T.; Hou, J.L. Gramicidin A-based unimolecular channel: Cancer cell-targeting behavior and ion transport-induced apoptosis. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 1097–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmore, S. Apoptosis: A review of programmed cell death. Toxicol. Pathol. 2007, 35, 495–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, R.S. Apoptosis in cancer: From pathogenesis to treatment. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 30, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.H.; Xu, M. DNA fragmentation in apoptosis. Cell Res. 2000, 10, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, J.M.; Owens, T.A.; Inge, L.J.; Bremner, R.M.; Rajasekaran, A.K. Gramicidin A Blocks Tumor Growth and Angiogenesis through Inhibition of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor in Renal Cell Carcinoma. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2014, 13, 788–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Du, Z.-W.; Xu, T.-M.; Wang, X.-J.; Li, W.; Gao, J.-L.; Li, J.; Zhu, H. HIF-1 alpha Is a Rational Target for Future Ovarian Cancer Therapies. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 785111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semenza, G.L. Defining the role of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 in cancer biology and therapeutics. Oncogene 2010, 29, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, M.S.; Lee, C.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, Y.M.; Lee, S.; Kim, H.J.; Heo, K. Gramicidin, a Bactericidal Antibiotic, Is an Antiproliferative Agent for Ovarian Cancer Cells. Medicina 2023, 59, 2059. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59122059
Choi MS, Lee CY, Kim JH, Lee YM, Lee S, Kim HJ, Heo K. Gramicidin, a Bactericidal Antibiotic, Is an Antiproliferative Agent for Ovarian Cancer Cells. Medicina. 2023; 59(12):2059. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59122059
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Min Sung, Chae Yeon Lee, Ji Hyeon Kim, Yul Min Lee, Sukmook Lee, Hyun Jung Kim, and Kyun Heo. 2023. "Gramicidin, a Bactericidal Antibiotic, Is an Antiproliferative Agent for Ovarian Cancer Cells" Medicina 59, no. 12: 2059. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59122059
APA StyleChoi, M. S., Lee, C. Y., Kim, J. H., Lee, Y. M., Lee, S., Kim, H. J., & Heo, K. (2023). Gramicidin, a Bactericidal Antibiotic, Is an Antiproliferative Agent for Ovarian Cancer Cells. Medicina, 59(12), 2059. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59122059






