Efficacy of Phrenic Nerve Block and Suprascapular Nerve Block in Amelioration of Ipsilateral Shoulder Pain after Thoracic Surgery: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Search Strategies and Data Extraction
2.2. Inclusion Criteria
2.3. Study Outcomes
2.4. Data Extraction and Data Retrieval
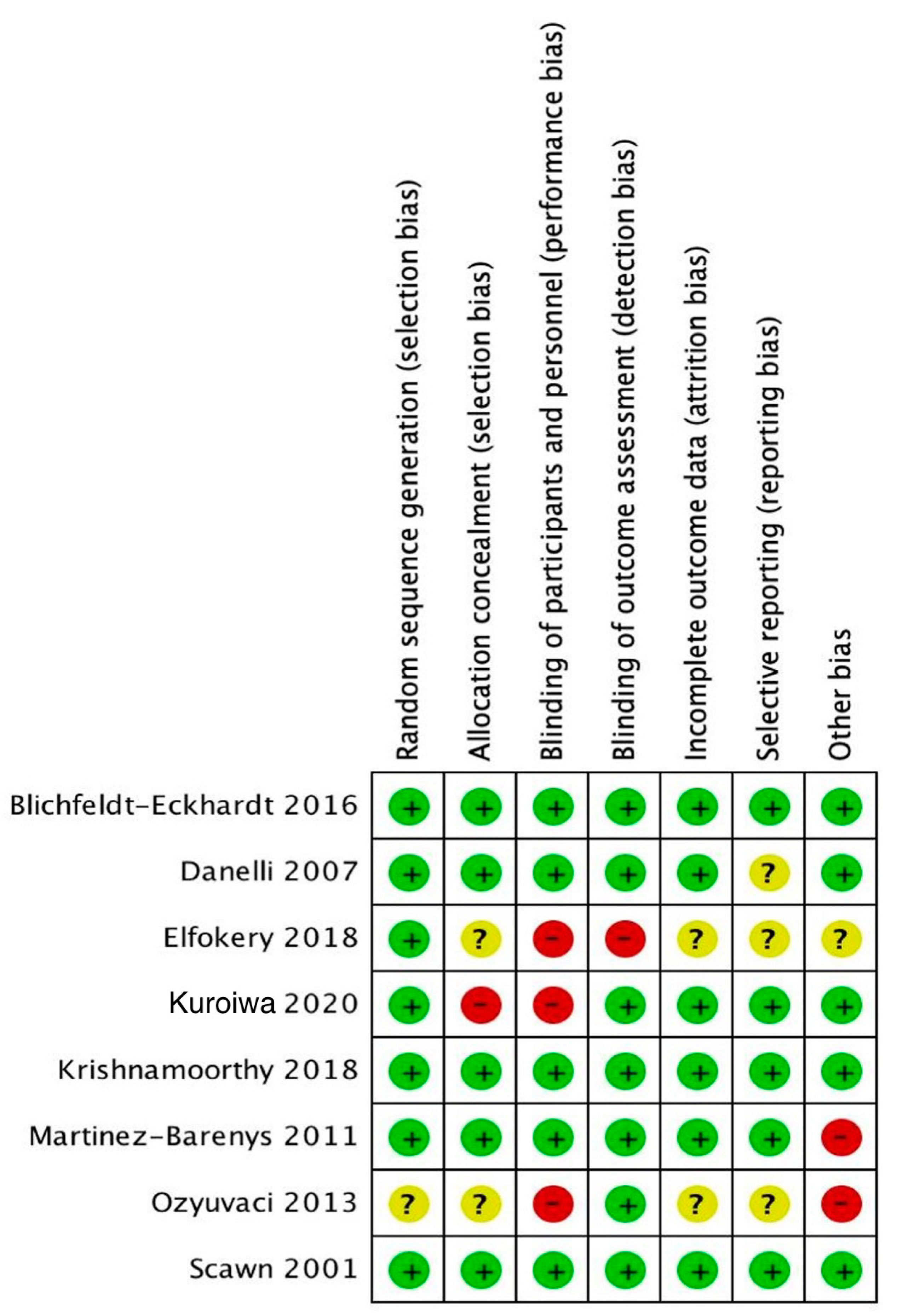
2.5. Quality Assessment
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics and Quality of Included Studies
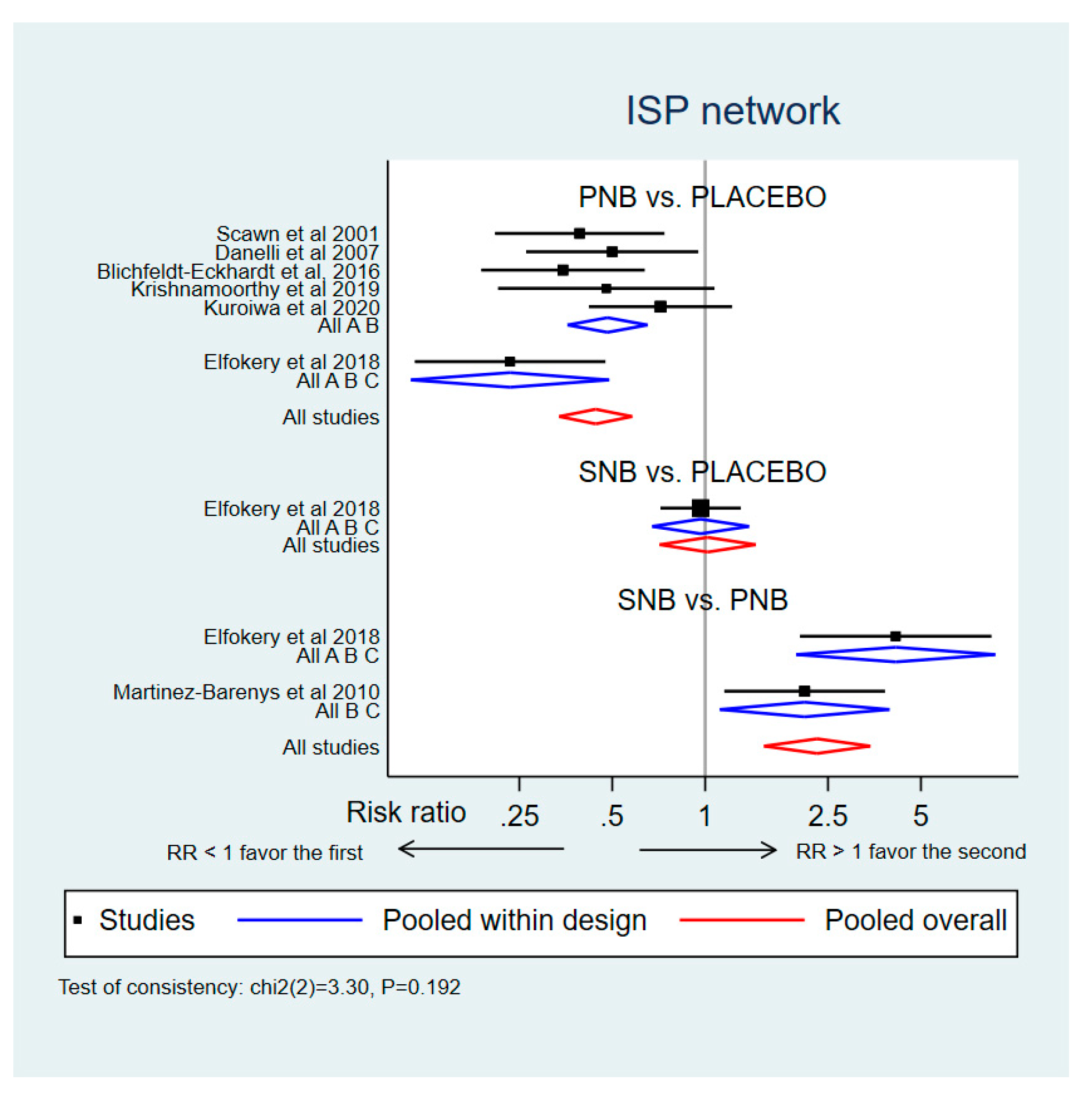
3.2. Meta-Analysis and Network Meta-Analysis
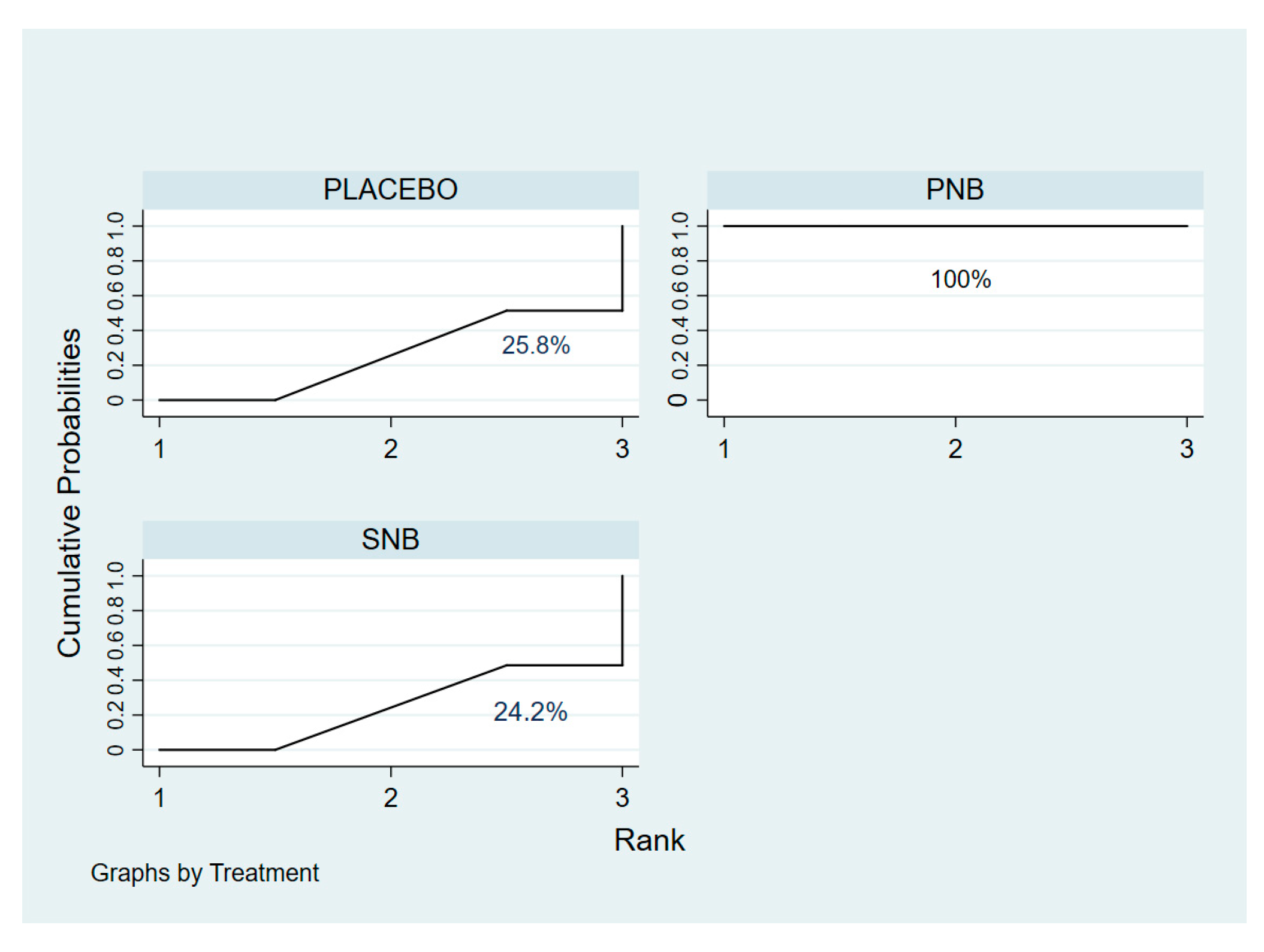
3.2.1. Incidence of ISP (Network Meta-Analysis)
3.2.2. ISP Severity (Network Meta-Analysis)
3.2.3. Postoperative Ventilatory Status Indicated by PaCO2 (Meta-Analysis)
3.2.4. Sensitivity Analysis and Publication Bias
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scawn, N.D.; Pennefather, S.H.; Soorae, A.; Wang, J.Y.; Russell, G.N. Ipsilateral shoulder pain after thoracotomy with epidural analgesia: The influence of phrenic nerve infiltration with lidocaine. Anesth. Analg. 2001, 93, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunchungmongkol, N.; Pipanmekaporn, T.; Paiboonworachat, S.; Saeteng, S.; Tantraworasin, A. Incidence and risk factors associated with ipsilateral shoulder pain after thoracic surgery. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2014, 28, 979–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barak, M.; Iaroshevski, D.; Poppa, E.; Ben-Nun, A.; Katz, Y. Low-volume interscalene brachial plexus block for post-thoracotomy shoulder pain. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2007, 21, 554–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barak, M.; Zise, A.; Katz, Y. Thoracic epidural local anesthetics are ineffective in alleviating post-thoracotomy ipsilateral shoulder pain. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2004, 18, 458–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danelli, G.; Berti, M.; Casati, A.; Bobbio, A.; Ghisi, D.; Mele, R.; Rossini, E.; Fanelli, G. Ipsilateral shoulder pain after thoracotomy surgery: A prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled evaluation of the efficacy of infiltrating the phrenic nerve with 0.2%wt/vol ropivacaine. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2007, 24, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Barenys, C.; Busquets, J.; de Castro, P.E.; Garcia-Guasch, R.; Perez, J.; Fernandez, E.; Mesa, M.A.; Astudillo, J. Randomized double-blind comparison of phrenic nerve infiltration and suprascapular nerve block for ipsilateral shoulder pain after thoracic surgery. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2011, 40, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennefather, S.H.; Akrofi, M.E.; Kendall, J.B.; Russell, G.N.; Scawn, N.D. Double-blind comparison of intrapleural saline and 0.25% bupivacaine for ipsilateral shoulder pain after thoracotomy in patients receiving thoracic epidural analgesia. Br. J. Anaesth. 2005, 94, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Brish, E.L.; Lowry, A.M.; Boddu, K. In select patients, ipsilateral post-thoracotomy shoulder pain relieved by suprascapular nerve block. Am. J. Ther. 2011, 18, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, N.; Agnew, N.M.; Scawn, N.D.; Pennefather, S.H.; Chester, M.; Russell, G.N. Suprascapular nerve block for ipsilateral shoulder pain after thoracotomy with thoracic epidural analgesia: A double-blind comparison of 0.5% bupivacaine and 0.9% saline. Anesth. Analg. 2002, 94, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pipanmekaporn, T.; Punjasawadwong, Y.; Charuluxananan, S.; Lapisatepun, W.; Bunburaphong, P.; Boonsri, S. The effectiveness of intravenous parecoxib on the incidence of ipsilateral shoulder pain after thoracotomy: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2018, 32, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mac, T.B.; Girard, F.; Chouinard, P.; Boudreault, D.; Lafontaine, E.R.; Ruel, M.; Ferraro, P. Acetaminophen decreases early post-thoracotomy ipsilateral shoulder pain in patients with thoracic epidural analgesia: A double-blind placebo-controlled study. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2005, 19, 475–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodge, A.; Rapchuk, I.L.; Gurunathan, U. Postoperative pain management and the incidence of ipsilateral shoulder pain after thoracic surgery at an Australian tertiary-care hospital: A prospective audit. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2021, 35, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoor, S.; Khan, T.; Zahoor, S.A.; Wani, S.Q.; Rather, J.M.; Yaqoob, S.; Ali, Z.; Hakeem, Z.A.; Dar, B.A. Post-thoracotomy ipsilateral shoulder pain: What should be preferred to optimize it–phrenic nerve infiltration or paracetamol infusion? Ann. Card. Anaesth. 2019, 22, 291–296. [Google Scholar]
- Burgess, F.W.; Anderson, D.M.; Colonna, D.; Sborov, M.J.; Cavanangh, D.G. Ipsilateral shoulder pain following thoracic surgery. Anesthesiology 1993, 78, 365–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.W.; Lee, T.W.; Yim, A.P. Shoulder function after thoracic surgery. Thorac. Surg. Clin. 2004, 14, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamoorthy, B.; Critchley, W.R.; Soon, S.Y.; Birla, R.; Begum, Z.; Nair, J.; Devan, N.; Mohan, R.; Fildes, J.; Morris, J.; et al. A randomized study comparing the incidence of postoperative pain after phrenic nerve infiltration vs. nonphrenic nerve infiltration during thoracotomy. Semin. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2019, 31, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mark, J.B.; Brodsky, J.B. Ipsilateral shoulder pain following thoracic operations. Anesthesiology 1993, 79, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamgbade, O.A.; Dorje, P.; Adhikary, G.S. The dual etiology of ipsilateral shoulder pain after thoracic surgery. J. Clin. Anesth. 2007, 19, 296–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feray, S.; Lubach, J.; Joshi, G.P.; Bonnet, F.; Van de Velde, M.; the PROSPECT Working Group of the European Society of Regional Anaesthesia and Pain Therapy. PROSPECT guidelines for video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery: A systematic review and procedure-specific postoperative pain management recommendations. Anaesthesia 2022, 77, 311–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The European Society of Regional Anesthesia and Pain Therapy. Procedure Specific Postoperative Pain Management. Available online: https://esraeurope.org/prospect/procedures/thoracotomy-2015/intra-operative-7 (accessed on 5 December 2022).
- Elfokery, B.M.; Tawfic, S.A.; Abdelrahman, A.M.; Abbas, D.N.; Abdelghaffar, I.M. Comparative study on the analgesic effect of acute ipsilateral shoulder pain after open thoracotomy between preoperative ultrasound guided suprascapular nerve block (SNB) and intraoperative phrenic nerve infiltration (PNI) in cancer lung patients. J. Egypt. Natl. Canc. Inst. 2018, 30, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blichfeldt-Eckhardt, M.R.; Laursen, C.B.; Berg, H.; Holm, J.H.; Hansen, L.N.; Ørding, H.; Andersen, C.; Licht, P.B.; Toft, P. A randomised, controlled, double-blind trial of ultrasound-guided phrenic nerve block to prevent shoulder pain after thoracic surgery. Anaesthesia 2016, 71, 1441–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanahan, E.M.; Ahern, M.; Smith, M.; Wetherall, M.; Bresnihan, B.; FitzGerald, O. Suprascapular nerve block (using bupivacaine and methylprednisolone acetate) in chronic shoulder pain. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2003, 62, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozyuvaci, E.; Akyol, O.; Sitilci, T.; Dübüs, T.; Oglu, H.T.; Leblebici, H.; Ikgöz, A.A. Preoperatıve ultrasound-guided suprascapular nerve block for postthoracotomy shoulder paın. Curr. Ther. Res. Clin. Exp. 2013, 74, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, S.; Yoon, B.H.; Shin, I.S.; Bae, J.M. Network meta-analysis: Application and practice using Stata. Epidemiol. Health. 2017, 39, e2017047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salanti, G.; Higgins, J.P.; Ades, A.E.; Ioannidis, J.P. Evaluation of networks of randomized trials. Stat. Methods. Med. Res. 2008, 17, 279–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulrow, C.; Peter, C.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, A.J.P.; Clarke, M.; Devereaux, P.J.; Kleijnen, J.; et al. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: Explanation and elaboration. BMJ 2009, 339, b2700. [Google Scholar]
- Pipanmekaporn, T.; Leurcharusmee, P.; Punjasawadwong, Y.; Khorana, J.; Samerchua, A.; Sukhupragarn, W.; Sukuam, I.; Bunchungmongkol, N.; Saokaew, S. Comparative Effectiveness of Phrenic Nerve Block and Suprascapular Nerve Blockfor Amelioration of Ipsilateral Shoulder Pain after Open Thoracotomy: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. 2020. Available online: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?RecordID=204473 (accessed on 24 September 2020).
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Jacqueline, C.; Miranda, C.; Tianjing, L.; Matthew, J.P.; Vivian, A.W. (Eds.) Cochrane Handbooks for Systematic Review of Interventions, 2nd ed.; Bell & Bain Ltd.: Glasglow, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Jadad, A.R.; Moore, R.A.; Carroll, D.; Jenkinson, C.; Reynolds, D.J.; Gavaghan, D.J.; McQuay, H.J. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: Is blinding necessary? Control. Clin. Trials. 1996, 17, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Jo, J.K.; Autorino, R.; Chung, J.H.; Kim, K.S.; Lee, J.W.; Baek, E.J.; Lee, S.W. Randomized controlled trials in endourology: A quality assessment. J. Endourol. 2013, 27, 1055–1060. [Google Scholar]
- Hozo, S.P.; Djulbegovic, B.; Hozo, I. Estimating the mean and variance from the median, range, and the size of a sample. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2005, 5, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Kuroiwa, K.K.; Shiko, Y.; Kawasaki, Y.; Aoki, Y.; Nishizawa, M.; Ide, S.; Miura, K.; Kobayashi, N.; Sehmbi, H. Phrenic nerve block at the azygos vein level versus sham block for ipsilateral shoulder pain after video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery: A randomized controlled trial. Anesth. Analg. 2021, 132, 1594–1602. [Google Scholar]
- Morélot-Panzini, C.; Le Pimpec-Barthes, F.; Menegaux, F.; Gonzalez-Bermejo, J.; Similowski, T. Referred shoulder pain (C4 dermatome) can adversely impact diaphragm pacing with intramuscular electrodes. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 45, 1751–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohmori, A.; Iranami, H.; Fujii, K.; Yamazaki, A.; Doko, Y. Myofascial involvement of supra- and infraspinatus muscles contributes to ipsilateral shoulder pain after muscle-sparing thoracotomy and video-assisted thoracic surgery. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2013, 27, 1310–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blichfeldt-Eckhardt, M.R.; Andersen, C.; Ørding, H.; Licht, P.B.; Toft, P. Shoulder pain after thoracic surgery: Type and time course, a prospective cohort study. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2017, 31, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, Y.A.; Sun, C.K.; Chiang, M.H.; Chen, J.Y.; Ko, C.C.; Chen, C.C.; Chen, Y.; Teng, I.C.; Hung, K.C. Effect of intraoperative phrenic nerve infiltration on postoperative ipsilateral shoulder pain after thoracic surgeries: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled studies. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2022, 36, 3334–3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, J.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, K.C.; Kim, C.H.; Jun, J. The effect of interscalene block on ipsilateral shoulder pain and pulmonary function in patients undergoing lung lobectomy: A randomized controlled trial. Medicine 2018, 97, e11034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blichfeldt-Eckhardt, M.R.; Toft, P. Treatment of ipsilateral shoulder pain after thoracic surgery-time for comparative studies? J. Thorac. Dis. 2019, 11, S417–S419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misiołek, H.; Karpe, J.; Copik, M.; Marcinkowski, A.; Jastrzębska, A.; Szelka, A.; Czarnożycka, A.; Długaszek, M. Ipsilateral shoulder pain after thoracic surgery procedures under general and regional anesthesia–a retrospective observational study. Kardiochir. Torakochirurgia. Pol. 2014, 11, 44–47. [Google Scholar]




| Author, Period, Country | Surgical Approach (%) | Jadad Scale | Surgical Procedure (%) | Outcomes | Intervention: Study Size Injection Site, Injectate | Incidence of ISP (%) (Treat vs. Comp) | Age of Patients (Years) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treat | Comp | Treat | Comp | ||||||
| Scawn et al. 2001 [1], United Kingdom | Thoracotomy | 5 | Pneumonectomy (24.5) Lobectomy (61) Wedge resection (12), Inoperable (2.5) | Incidence Severity of ISP Safety of PNB
| PNB: (n = 21) Periphrenic fat pad at level of diaphragm, Lidocaine | PLB: (n = 20) Periphrenic fat pad at level of diaphragm, 0.9% saline | 33.3 vs. 85 (6 h) | PNB: 64 (61–67) | PLB: 67 (63–68) |
| Danelli et al. 2007 [5], Italy | Thoracotomy | 5 | NR | Incidence Severity of ISP Safety of PNB
| PNB: (n = 25) Periphrenic fat pad at level of diaphragm, Ropivacaine | PLB: (n = 25) Periphrenic fat pad at level of diaphragm, 0.9% saline solution | 32 vs. 64 (24 h) | PNB: 65 (32–77) | PLB: 66 (41–77) |
| Martinez Barenys et al. 2011 [6], Spain | Thoracotomy | 5 | Major resection (87), Sublobar resection (13) | Incidence Severity of ISP | PNB: (n = 37) Periphrenic fat pad 1–2 cm proximal at level of diaphragm, Lidocaine | SNB: (n = 37) Supraclavicular fossa (after chest closure), Bupivacaine | 27 vs. 56.7 (24 h) | PNB: 62.8 ± 10.5 | SNB: 63.2 ± 12.7 |
| Ozyuvaci et al. 2013 [24], Turkey | Thoracotomy | 2 | NR | Severity of ISP | SNB: (n = 18) Ultrasound guided, Levobupivacaine | NO (n = 18) | NR | SNB: 61.8 ± 8.7 | NO: 57.5 ± 8.2 |
| Blichfeldt-Eckhardt et al. 2016 [22], Denmark | Thoracotomy (72.4), VATS (27.6) | 5 | Pneumonectomy (9.5), Lobectomy (90.5) | Incidence Severity of ISP Safety of PNB
| PNB: (n = 38) Ultrasound-guided supraclavicular fossa (after chest closure), Ropivacaine | PLB: (n = 38) Ultrasound-guided supraclavicular fossa (after chest closure), 0.9% saline solution | 23.7 vs. 68 (6 h) | PNB: 68.1 ± 8.0 | PLB: 67.9 ± 8.2 |
| Elfokery et al. 2018 [21], Egypt | Thoracotomy | 3 | Pneumonectomy (5), Lobectomy (25), Metastatectomy (70) | Incidence Severity of ISP Safety of PNB
| PNB: (n = 45) Periphrenic fat pad, 1–2 cm proximal at level of diaphragm, Bupivacaine SNB: (n = 45) Ultrasound guided (before operation), Bupivacaine | NO: (n = 45) | 15.5 (PNB), 64.4 (SNB) vs. 66.7 (NO) (24 h) | PNB: 41 ± 7.8 SNB: 36.5 ± 7.2 | NO: 39 ± 7.4 |
| Krishnamoorthy et al. 2018 [16], United Kingdom | Thoracotomy | 5 | Lobectomy | Incidence Severity of ISP Safety of PNB
| PNB: (n = 50) Perinephric fat pad above and below hilum of diaphragm, Bupivacaine | NO: (n = 50) | 15.2 vs. 31.8 | PNB: 74 ± 15 | NO: 70 ± 13 |
| Kuroiwa et al. 2020 [33], Japan | Thoracotomy (10.5), VATS (89.5) | 3 | Lobectomy (80), Wedge resection (17.6), Other (2.4) | Incidence Severity of ISP Safety
| PNB: (n = 42) (Rt) proximal to junction of azygous vein and SVC (Lt) hemivenous join the azygous vein, Ropivacaine | PLB: (n = 43) (Rt) proximal to junction of azygous vein and SVC (Lt) hemivenous join the azygous vein, 0.9% saline solution | 33.3 vs. 46.5 | PNB: 66.4 ± 10.8 | PLB: 62.5 ± 18.5 |
| PNB | ||
|---|---|---|
| 0.43 (0.29,0.64) | SNB | |
| 0.44 (0.34,0.58) | 1.02 (0.71, 1.46) | PLACEBO |
| PNB | ||
|---|---|---|
| −1.14 (−3.47, 1.19) | SNB | |
| −1.75 (−3.47, −0.04) | −0.61 (−2.95, 1.72) | PLACEBO |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pipanmekaporn, T.; Leurcharusmee, P.; Punjasawadwong, Y.; Khorana, J.; Samerchua, A.; Sukhupragarn, W.; Sukuam, I.; Bunchungmongkol, N.; Saokaew, S. Efficacy of Phrenic Nerve Block and Suprascapular Nerve Block in Amelioration of Ipsilateral Shoulder Pain after Thoracic Surgery: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Medicina 2023, 59, 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59020275
Pipanmekaporn T, Leurcharusmee P, Punjasawadwong Y, Khorana J, Samerchua A, Sukhupragarn W, Sukuam I, Bunchungmongkol N, Saokaew S. Efficacy of Phrenic Nerve Block and Suprascapular Nerve Block in Amelioration of Ipsilateral Shoulder Pain after Thoracic Surgery: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Medicina. 2023; 59(2):275. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59020275
Chicago/Turabian StylePipanmekaporn, Tanyong, Prangmalee Leurcharusmee, Yodying Punjasawadwong, Jiraporn Khorana, Artid Samerchua, Wariya Sukhupragarn, Isaraporn Sukuam, Nutchanart Bunchungmongkol, and Surasak Saokaew. 2023. "Efficacy of Phrenic Nerve Block and Suprascapular Nerve Block in Amelioration of Ipsilateral Shoulder Pain after Thoracic Surgery: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis" Medicina 59, no. 2: 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59020275
APA StylePipanmekaporn, T., Leurcharusmee, P., Punjasawadwong, Y., Khorana, J., Samerchua, A., Sukhupragarn, W., Sukuam, I., Bunchungmongkol, N., & Saokaew, S. (2023). Efficacy of Phrenic Nerve Block and Suprascapular Nerve Block in Amelioration of Ipsilateral Shoulder Pain after Thoracic Surgery: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Medicina, 59(2), 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59020275







