Abstract
Abdominal pain represents a frequent symptom for referral to emergency departments and/or internal medicine outpatient setting. Similarly, fever, fatigue and weight loss are non-specific manifestations of disease. The present case describes the diagnostic process in a patient with abdominal pain and a palpable abdominal mass. Abdominal ultrasonography confirmed the presence of a mass in the mesogastrium. Computed Tomography (CT) and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scans oriented toward calcific lymphadenopathies with increased metabolism in the positron emission tomography–computed tomography (PET-CT) scan. Laboratory examinations were inconclusive, although serology for Brucella and the Quantiferon test were positive. After multidisciplinary discussion, the patient underwent surgical excision of the abdominal mass. Histological examination excluded malignancies and oriented toward brucellosis in a patient with latent tuberculosis. The patient was treated with rifampin 600 mg qd and doxycycline 100 mg bid for 6 weeks with resolution of the symptoms. In addition, rifampin was continued for a total of 6 months in order to treat latent tuberculosis. This case underlines the need for a multidisciplinary approach in the diagnostic approach to abdominal lymphadenopathies.
1. Introduction
Abdominal pain represents one of the main reasons for referral to emergency department (ED) [1] and to internal medicine outpatient setting [2]. Given that the etiology of abdominal symptoms can be due to a wide range of diseases, a systematic approach is pivotal to reach the correct diagnosis. In fact, it has been shown that clinical history and physical examination alone are able to discriminate between organic and non-organic causes of abdominal pain in 79% of patients [1].
Enlarged lymph nodes can be a manifestation of infective, autoimmune and neoplastic diseases [3]. Similarly, fever, fatigue and weight loss are non-specific symptoms. Thus, clinicians should be guided by semiotics in the preliminary evaluation of patients in order to decide on the optimal diagnostic workup to reach the diagnosis [4].
Brucellosis is an old disease, widely distributed across the globe. Its incidence has re-emerged in the last decade [5]. Brucellae are Gram-negative, aerobic, facultative intracellular rods or coccobacilli [6], with 12 recognized species, 4 of which cause disease in humans. Clinical manifestations can range from asymptomatic presentations to multiorgan involvement [7]. The most common symptoms are fever, night sweats, chills, headaches and abdominal pain. However, although rare, isolated lymphadenopathy is a possible presentation.
Even tuberculosis (TB) represents a re-emerging disease [8]. Similarly to Brucellosis, its clinical manifestations can be non-specific, including fever, night sweats, weight loss or hemoptysis [9]. Isolated abdominal lymphadenopathies represent about 1% of TB cases [10].
The present report describes the diagnostic approach to a patient with abdominal pain and a palpable abdominal mass; an integration of clinical history together with laboratory, radiology and histology was needed to reach a diagnosis and to establish treatment.
2. Case Description
A 65-year-old Italian woman with significant past medical history of chronic hydrocephalus, Addison’s disease, osteoporosis and depression was referred to our outpatient clinic because of abdominal pain. The pain was prevalently nocturnal, requiring a painkiller (ketoprofen) almost every night. She reported regular hive and no association of symptoms with a meal.
At physical examination, the abdomen was soft. A non-tender but painful mass was palpable in the hypogastrium. No other significant signs were found. Abdominal ultrasound (US) scan revealed, in the mesogastrium, the presence of a hypoechoic dishomogeneous round mass, with internal calcifications, surrounded by thickened bowel loops. The patient was admitted to our inpatient unit for further examination.
Laboratory tests showed normocytic anemia, elevated inflammatory indices with a trend toward leukopenia. The other laboratory tests were normal (Table 1).

Table 1.
Results of main laboratory examinations performed; altered values in bold. (Abbreviations: MCV = mean corpuscular volume; PLT = platelet count; WBC = white blood cell count; ESR = erythrocyte sedimentation rate; PCR = polymerase chain reaction).
Colonoscopy and gynecological examination with endocavitary pelvic US scan were negative.
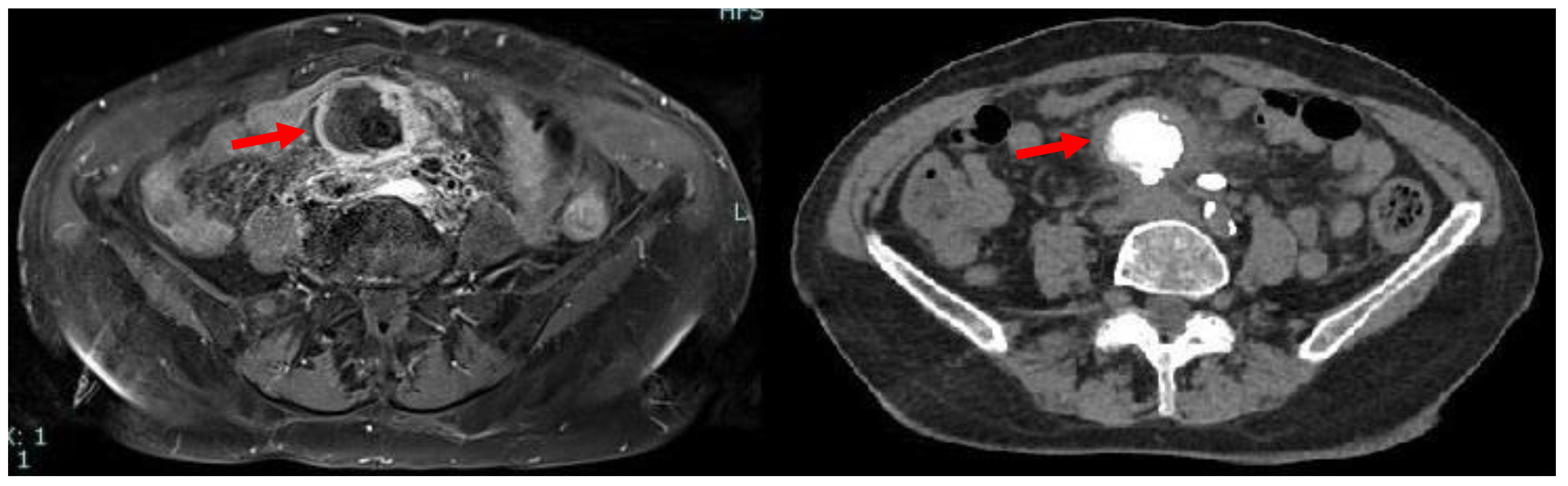
Due to iodinated contrast agent allergy, the patient underwent abdominal contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (CE-MRI) scan complete with computed tomography (CT) scans documenting, in the hypogastrium, the presence of voluminous multilobular lymphadenopathies (about 45 mm of maximum diameter) with calcific nucleus surrounding the mesenteric vessels and infiltrating the mesenteric fat (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Axial MRI (left) and CT (right) scan showing the presence, in mesogastrium, of a nodular mass (red arrows) with contrast enhancement at MRI and internal calcifications at CT.
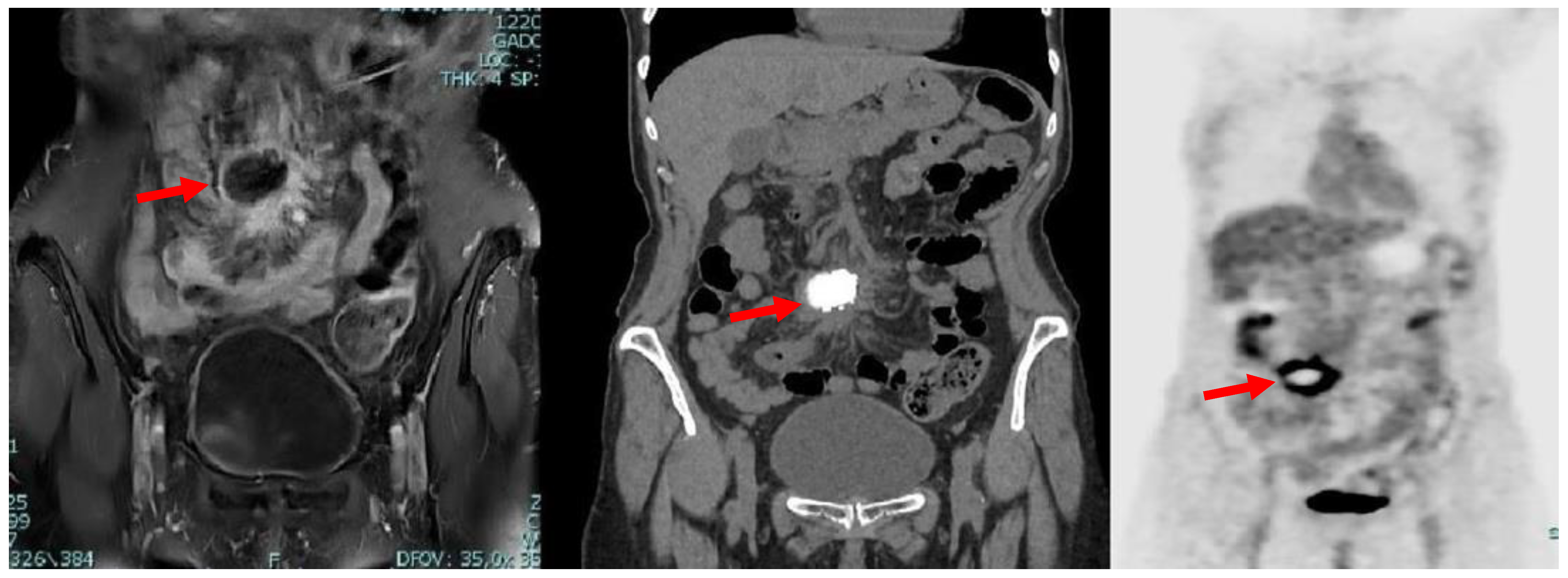
A subsequent positron emission tomography–computed tomography (PET-CT) scan revealed the presence of diffuse and pathological accumulation of the radiotracer (max SUV 13.6) in correspondence with the lymphatic nodules seen in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) (Figure 2).
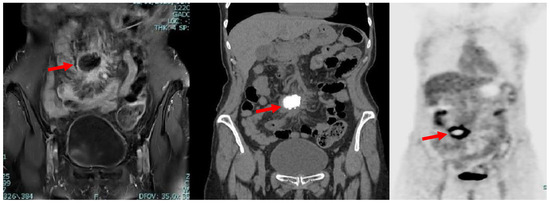
Figure 2.
Coronal MRI (left), CT (middle) and PET (right) scans showing the presence, in mesogastrium, of a nodular mass (red arrows) with contrast enhancement at MRI and internal calcifications at CT, with thickened mesenterial fat and significant uptake of the radiotracer at PET-CT.
These results—abdominal lymphadenopathies of unknown origin—required further diagnostic evaluations.
First of all, upon deeper collection of medical history, the patient reported a 7-day fever associated with chills and night sweats, occurring about 3 months before the appearance of abdominal symptoms. This symptomatology was self-limiting.
Serologies for the Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) and cytomegalovirus (CMV) were consistent with previous infection, while hepatitis B virus (HBV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) antibodies were negative (Table 2A).

Table 2.
(A) Antibody profile of the main infectious diseases (Abbreviations: EBV: Epstein–Barr Virus, CMV: Cytomegalovirus, IgM: Immunoglobulin M, IgG: Immunoglobulin G). (B) Antibody profile of the main infectious diseases.
Quantiferon-TB Gold Plus emerged as positive, in absence of pulmonary lesions in the PET-CT scan; the Wright test for brucellosis was positive (1/400) (Table 2B).
After interdisciplinary discussion, the patient was scheduled for surgical excision of the abdominal neoformation. The surgical procedure is summarized as follows:
“Pneumoperitoneum with open technique in the supraumbilical site. Introduction of 2 trocars. Exploration of the abdominal cavity reveals a voluminous nodule at the level of the meso-ileum; multiple ileal loops and a section of the transverse colon are attracted to the nodule. Considering the anatomical-surgical picture, laparotomic conversion is necessary. Supra-sub-umbilical midline incision. Release of the afore-mentioned intestinal loops from the neoformation and removal of the nodule which is sent for extemporaneous histological examination (non-neoplastic process, possibly infectious)…”.
The definitive histological examination is reported below:
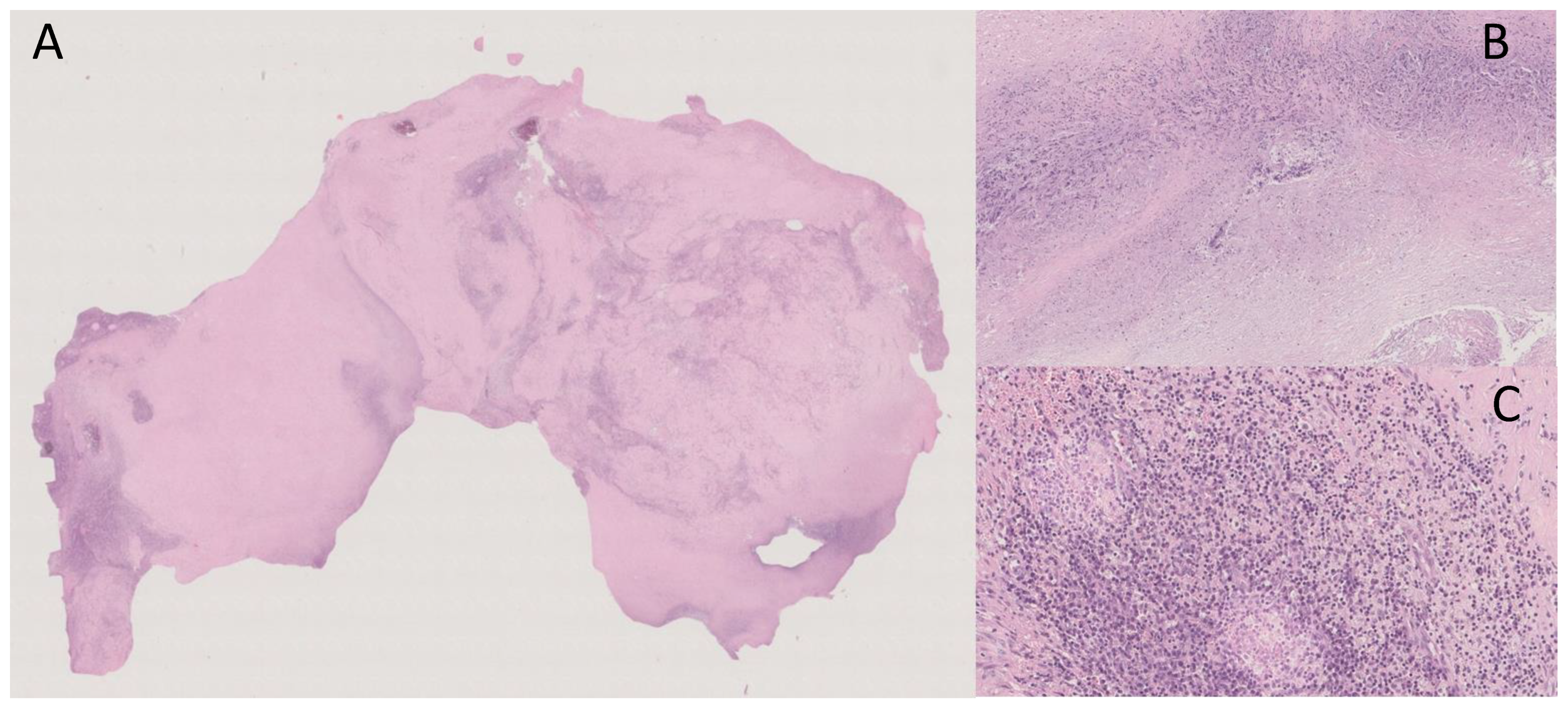
“Macroscopically, the surgical specimen consisted of solid nodular fragment, whitish in color, 4 × 3.5 × 3 cm in size, homogeneous in cut surface, partially calcified. Microscopically, Hematoxylin and Eosin stained sections documented extensive fibrosis with dystrophic calcifications and foci of lymphomonocytic, plasma cell and granulocytic infiltrate, mixed with areas of necrosis. To investigate the presence of fungi and/or mycobacteria, histochemistry was performed with Periodic Acid-Schiff (PAS), PAS-D (Periodic Acid-Schiff with diastase), Grocott’s and Ziehl- Neelsen stains in seriate sections. No fungi and mycobacteria were detected. A descriptive final diagnosis of fibro-hyaline nodule with mixed inflammatory infiltrate and suppurative necrosis was made, advising to carry out culture tests and integration with clinical-serological data” (Figure 3).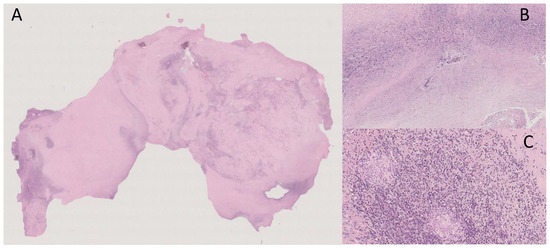 Figure 3. (A) Extensive fibrosis and dystrophic calcification (Hematoxylin and Eosin, 0.5×); (B) Suppurative necrosis (Hematoxylin and Eosin, 5×); (C) Lymphomonocytic, plasma cell and granulocytic infiltrate (Hematoxylin and Eosin, 20×).
Figure 3. (A) Extensive fibrosis and dystrophic calcification (Hematoxylin and Eosin, 0.5×); (B) Suppurative necrosis (Hematoxylin and Eosin, 5×); (C) Lymphomonocytic, plasma cell and granulocytic infiltrate (Hematoxylin and Eosin, 20×).
These findings, coupled with the high count of Brucella antibodies, excluded malignancies (i.e., lymphoma) and oriented toward a subacute/chronic infectious disease. With this in mind, real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) to determine Brucella deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) or mycobacteria was required. Unfortunately, these procedures were not possible after paraffin fixation.
A specific re-evaluation of clinical history was necessary; the patient confirmed the consumption of unpasteurized milk about 15 days before the appearance of fever.
Clinical, microbiological and histological data were consistent with mesenteric lymphadenopathies due to Brucella infection. For this reason, treatment with rifampin 600 mg daily and doxycycline 100 mg twice a day for 6 weeks was prescribed. Considering the positivity of Quantiferon, rifampin was continued for a total of 6 months in order to also treat latent tuberculosis (TB). After 4 weeks of treatment, blood exams and the abdominal US scan were normal. At the end of treatment course, the Wright serology became negative, and Quantiferon TB was indeterminate. The abdominal CT scan performed three months after the end of treatment was within normality.
3. Discussion
The present case describes the finding of mesenteric lymphadenopathies in a patient with abdominal pain and a previous history of fever, night sweats and consumption of unpasteurized milk. First-line lab tests were non-specific, while radiological exams could orient toward a suspicion of lymphoma. However, the Wright serology and Quantiferon were positive, and histology led to the diagnosis of brucellosis in a patient with latent TB.
According to the literature, the most common causes of mesenteric lymphadenopathies are inflammatory, infectious and neoplastic diseases [11]. In the present case, the inflammatory state shown in first-line lab examinations was not specific. The common causes of infectious diseases involving lymph nodes were consistent with brucellosis and TB (Table 2B). Finally, histology excluded malignancies (e.g., lymphoma and cancer).
Brucellosis is a common zoonosis, affecting half a million people annually [12]. The most common route of infection is consumption of unpasteurized milk or milk products. Four species of Brucella have been reported to cause human disease: Brucella melitensis (being the most common), Brucella abortus, Brucella suis and Brucella canis [5,13].
Brucellosis has a wide spectrum of clinical manifestations, ranging from asymptomatic presentations to multiorgan involvement [7]. In addition, Brucellosis can mimic any disease, making its diagnosis difficult [14]. The most common symptoms are fever, night sweats, chills, headaches and joint pain, although any organ can be affected. Moreover, brucellosis can manifest with isolated abdominal lymphadenopathies [15]. This last presentation is more common among children than adults [16].
Table 3 summarizes, in chronological order, the clinical and diagnostic features of case reports describing isolated abdominal lymphadenopathies associated with brucellosis, as reported in the English literature. Although rare, this presentation has been reported to account for 2.4–19% of cases [7,15,17].

Table 3.
Cases of isolated abdominal lymphadenopathies associated with brucellosis reported in the literature (chronological order). (Abbreviations: CRP: C-reactive protein; CT: Computed tomography; ELISA: Enzyme Linked ImmunoSorbent Assay; ESR: Erythrocyte sedimentation rate; IgM: Immunoglobulin M; IgG: Immunoglobulin G; WBC: White blood cell; M: Male; F: Female; n.a.: Not available).
In a retrospective evaluation of 1028 brucellosis cases, lymphadenopathy was present in 2.4% of cases [15]. Of these, 15 patients were affected by acute brucellosis, 6 patients by subacute and 4 by the chronic form of disease [15]. In a different series of 72 patients, the prevalence of lymphadenopathies was 6.9% [7]. Descriptions coming from endemic areas report a higher prevalence of lymphadenopathies. For example, in a systematic review and meta-analysis of epidemiology and clinical manifestations of brucellosis in China, lymphadenectases were present in 19% of cases [17]. This percentage considers all lymph node stations, but cases with isolated involvement of abdominal lymph nodes are even more rare [12,18,19,20].
The English literature reports a few cases similar to the present one. In fact, Massoud et al. [12] and Jayakumar et al. [18] reported cases of patients suffering abdominal pain with clinical data consistent with lymphoma. In both cases, histology concluded reactive lymphadenitis caused by B. melitensis [12,18]. Rodrigues Dos Santos et al. [20] even described a case of brucellosis with enlarged abdominal lymph nodes and possible ileal involvement. Acute abdominal pain itself can be read as a symptom of brucellosis, as suggested by Göke et al. in their case [19]. In this regard, US scan seems to be promising for supporting the diagnosis. In fact, in a Turkish study evaluating the role of abdominal sonography in a series of 251 cases of Brucellosis, Pourbagher et al. found that the frequency of enlarged abdominal (periportal) lymph nodes in patients with acute, subacute and chronic disease was 9.2% [21]. Considering these data, careful clinical history analysis and differential diagnosis are necessary for the correct approach.
It is noteworthy to underline that the immune response to Brucella infection involves both innate and adaptive immunity [22]. Macrophages are active participants in this process because B. melitensis can survive to their phagocytosis, evading the innate immunity [23]. This leads to lymphocytes recruitment and interferon (IFN) gamma production, finally contributing to lymph node enlargement. All these pathophysiological mechanisms are shared with TB. In particular, the molecular strategies to escape to macrophage killing (e.g., inhibition of phagosome–lysosome fusion) are similar between these two diseases [24,25]. Interestingly, Masoudian et al. [26] found the expression of similar genes in THP-1 macrophages of both diseases [26]. Finally, even several clinical features are common in TB and Brucellosis (e.g., fever, lymphadenopathy, hepato-splenomegaly) [27]. In this regard, vertebral osteomyelitis and posterior abscess can be found as extrapulmonary manifestations of TB (Pott’s disease) or spinal localization of Brucella (pseudo-Pott’s disease). As already stated, fever is a non-specific symptom. However, its feature can be seen as a potential tool for distinction. In fact, TB generally causes low-grade sub-continuous fever, whereas Brucella spp. are known to provoke intermittent fever [28]. Finally, both TB and Brucella spp. can cause hepato-splenomegaly (mainly Brucella spp.) and central nervous system (CNS) infections [29]. The sharing of common cytokines, immunity cells, molecular pathways can justify the presentation with granuloma in both pathological settings. However, TB typically produces caseous necrosis, while Brucella spp. does not [30]. However, differential diagnosis is not easy and requires laboratory and radiology.
4. Conclusions
Fever and abdominal pain represent non-specific symptoms, requiring a complete medical workup. Both Brucellosis and TB can manifest with isolated lymph node enlargement. The integration of medical history, laboratory and instrumental examinations is required to reach the correct diagnosis. The criterion ex juvantibus could be adopted when a definite diagnosis cannot be made.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.M., P.P. (Pamela Piscitelli) and S.D.C.; clinical management, A.M., N.R., A.D., A.d.M., L.P., P.P. (Paola Parente), D.P.C., A.B., A.A., I.C., E.S., P.G. and F.B.; writing—original draft preparation, A.M., N.R. and A.D.; writing—review and editing, A.M., N.R., A.D., P.P. (Pamela Piscitelli) and S.D.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient.
Data Availability Statement
Data supporting reported results may be provided on reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Natesan, S.; Lee, J.; Volkamer, H.; Thoureen, T. Evidence-Based Medicine Approach to Abdominal Pain. Emerg. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 34, 165–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Addolorato, G.; Mirijello, A.; D’Angelo, C.; Leggio, L.; Ferrulli, A.; Abenavoli, L.; Vonghia, L.; Cardone, S.; Leso, V.; Cossari, A.; et al. State and trait anxiety and depression in patients affected by gastrointestinal diseases: Psychometric evaluation of 1641 patients referred to an internal medicine outpatient setting. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2008, 62, 1063–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaddey, H.L.; Riegel, A.M. Unexplained Lymphadenopathy: Evaluation and Differential Diagnosis. Am. Fam. Physician 2016, 94, 896–903. [Google Scholar]
- Mirijello, A.; D’Errico, M.M.; Notarangelo, S.; De Cosmo, S. The role of medical history in the diagnostic process of unexplainable weight loss. BMJ. Case. Rep. 2019, 12, e231182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakir, R. Brucellosis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 15, 117280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khurana, S.K.; Sehrawat, A.; Tiwari, R.; Prasad, M.; Gulati, B.; Shabbir, M.Z.; Chhabra, R.; Karthik, K.; Patel, S.K.; Pathak, M.; et al. Bovine brucellosis—A comprehensive review. Vet. Q. 2021, 41, 61–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köse, Ş.; Serin Senger, S.; Akkoçlu, G.; Kuzucu, L.; Ulu, Y.; Ersan, G.; Oğuz, F. Clinical manifestations, complications, and treatment of brucellosis: Evaluation of 72 cases. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2014, 44, 220–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; Available online: https://www.who.int/tb/publications/global_report/en/ (accessed on 30 January 2023).
- Lewinsohn, D.M.; Leonard, M.K.; LoBue, P.A.; Cohn, D.L.; Daley, C.L.; Desmond, E.; Keane, J.; Lewinsohn, D.A.; Loeffler, A.M.; Mazurek, G.H.; et al. Official American Thoracic Society/Infectious Diseases Society of America/Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Clinical Practice Guidelines: Diagnosis of Tuberculosis in Adults and Children. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 64, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Zhang, M. Disseminated tuberculosis mimicking abdominal metastatic carcinoma: A case report. Medicine 2021, 100, e27886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucey, B.C.; Stuhlfaut, J.W.; Soto, J.A. Mesenteric lymph nodes seen at imaging: Causes and significance. Radiographics 2005, 25, 351–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massoud, M.; Kerbage, F.; Antoun, L.; Merhi, R.; Hallit, S.; Hallit, R. Brucellosis: A lymphoma-like presentation. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2017, 10, 833–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayoun, M.A.; Muco, E.; Shorman, M. Brucellosis. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ulu-Kilic, A.; Metan, G.; Alp, E. Clinical presentations and diagnosis of brucellosis. Recent Pat. Antiinfect. Drug Discov. 2013, 8, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buzgan, T.; Karahocagil, M.K.; Irmak, H.; Baran, A.I.; Karsen, H.; Evirgen, O.; Akdeniz, H. Clinical manifestations and complications in 1028 cases of brucellosis: A retrospective evaluation and review of the literature. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 14, e469–e478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Ma, J.; Chen, X.; Dong, L. A 10-year retrospective comparative analysis of the clinical features of brucellosis in children and adults. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2021, 15, 1147–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, R.; Xie, S.; Lu, X.; Sun, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, K. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Epidemiology and Clinical Manifestations of Human Brucellosis in China. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 5712920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayakumar, R.V.; Al-Aska, A.K.; Subesinghe, N.; Wright, S.G. Unusual presentation of culture positive brucellosis. Postgrad. Med. J. 1988, 64, 118–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Göke, M.; Neurath, M.; Braunstein, S.; Daniello, S.; Knolle, P.; Dippold, W.; Meyer zum Büschenfelde, K.H. Brucellosis: Differential diagnosis of acute abdominal pain. Z. Gastroenterol. 1993, 31, 671–674. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues Dos Santos, J.; Silva, R.; Nejo, P.; Vassalo, T.; Coimbra, A.; Peixoto, L. A Case of Brucellosis with Possible Ileal Involvement. GE Port. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 27, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourbagher, M.A.; Pourbagher, A.; Savas, L.; Turunc, T.; Demiroglu, Y.Z.; Erol, I.; Yalcintas, D. Clinical pattern and abdominal sonographic findings in 251 cases of brucellosis in southern Turkey. AJR. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2006, 187, W191–W194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, W.; Yang, Y. Evasion of anti-infectious immunity by Brucella—A review. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao 2016, 56, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Billard, E.; Cazevieille, C.; Dornand, J.; Gross, A. High susceptibility of human dendritic cells to invasion by the intracellular pathogens Brucella suis, B. abortus, and B. melitensis. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 8418–8424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porte, F.; Naroeni, A.; Ouahrani-Bettache, S.; Liautard, J.P. Role of the Brucella suis lipopolysaccharide O antigen in phagosomal genesis and in inhibition of phagosome-lysosome fusion in murine macrophages. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 1481–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carranza, C.; Chavez-Galan, L. Several Routes to the Same Destination: Inhibition of Phagosome-Lysosome Fusion by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 357, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masoudian, M.; Derakhshandeh, A.; Ghahramani Seno, M.M. Brucella melitensis and Mycobacterium tuberculosis depict overlapping gene expression patterns induced in infected THP-1 macrophages. Iran J. Vet. Res. 2015, 16, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dasari, S.; Naha, K.; Prabhu, M. Brucellosis and tuberculosis: Clinical overlap and pitfalls. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2013, 6, 823–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, D.; Zhou, J.; Jiang, X. Diagnosis and management of spinal tuberculosis combined with brucellosis: A case report and literature review. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 15, 3455–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdem, H.; Senbayrak, S.; Gencer, S.; Hasbun, R.; Karahocagil, M.K.; Sengoz, G.; Karsen, H.; Kaya, S.; Civljak, R.; Inal, A.S.; et al. Tuberculous and brucellosis meningitis differential diagnosis. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2015, 13, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esendagli-Yilmaz, G.; Uluoglu, O. Pathologic basis of pyogenic, nonpyogenic, and other spondylitis and discitis. Neuroimaging Clin. N. Am. 2015, 25, 159–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).