Necrotizing Fasciitis—Severe Complication of Bullous Pemphigoid: A Systematic Review, Risk Factors, and Treatment Challenges
Abstract
:1. Introduction
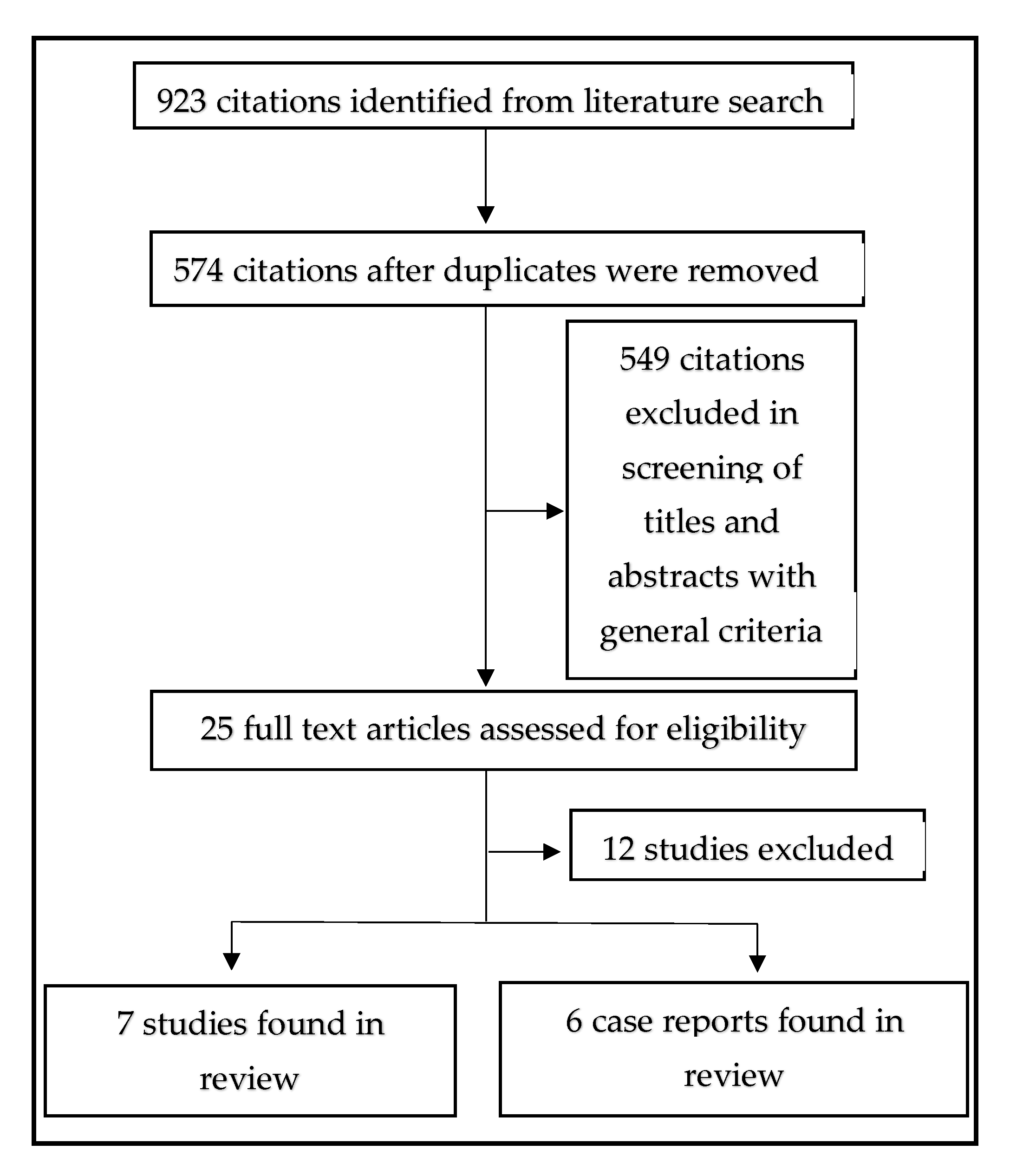
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Immunosuppression
4.2. Comorbidities
4.3. Necrotizing Fasciitis in Immunocompromised Patients
4.4. Surgical Reconstruction of Defects after Management of NF
4.5. Intravenous Immunoglobulin (IVIG)
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Langan, S.M.; Smeeth, L.; Hubbard, R.; Fleming, K.M.; Smith, C.J.P.; West, J. Bullous pemphigoid and pemphigus vulgaris--incidence and mortality in the UK: Population based cohort study. BMJ 2008, 337, a180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Milinković, M.; Janković, S.; Medenica, L.; Nikolić, M.; Reljić, V.; Popadić, S. Incidence of autoimmune bullous diseases in Serbia: A 20-year retrospective study. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2016, 14, 995–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joly, P.; Baricault, S.; Sparsa, A.; Bernard, P.; Bédane, C.; Duvert-Lehembre, S.; Courville, P.; Bravard, P.; Rémond, B.; Doffoel-Hantz, V.; et al. Incidence and Mortality of Bullous Pemphigoid in France. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 1998–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bertram, F.; Brocker, E.B.; Zillikens, D.; Schmidt, E. Prospective analysis of the incidence of autoimmune bullous disorders in Lower Franconia, Germany. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2009, 7, 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marazza, G.; Pham, H.; Schärer, L.; Pedrazzetti, P.; Hunziker, T.; Trüeb, R.; Hohl, D.; Itin, P.; Lautenschlager, S.; Naldi, L.; et al. Incidence of bullous pemphigoid and pemphigus in Switzerland: A 2-year prospective study. Br. J. Dermatol. 2009, 161, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammers, C.M.; Stanley, J.R. Mechanisms of Disease: Pemphigus and Bullous Pemphigoid. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2016, 11, 175–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Agostino, G.M.; Rizzetto, G.; Marani, A.; Marasca, S.; Candelora, M.; Gambini, D.; Gioacchini, H.; De Simoni, E.; Maurizi, A.; Campanati, A.; et al. Bullous pemphygoid and novel therapeutic approaches. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, M.S.M.; Begum, N.; Grainge, M.J.; Harman, K.E.; Grindlay, D.; Gran, S. The global incidence of bullous pemphigoid: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2022, 186, 414–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Shen, S.; Zheng, X.; Dang, E.; Zhang, J.; Shao, S.; Qiao, P.; Li, Q.; Wang, H.; Li, C.; et al. Association of HLA class I and class II alleles with bullous pemphigoid in Chinese Hans. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2018, 89, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stavropoulos, P.G.; Soura, E.; Antoniou, C. Drug-induced pemphigoid: A review of the literature. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2014, 8, 1133–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dănescu, S.; Chiorean, R.; Macovei, V.; Sitaru, C.; Baican, A. Role of physical factors in the pathogenesis of bullous pemphigoid: Case report series and a comprehensive review of the published work. J. Dermatol. 2016, 43, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Wu, H.; Zhao, M.; Chang, C.; Lu, Q. The pathogenesis of bullous skin diseases. J. Transl. Autoimmun. 2019, 2, 100014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moro, F.; Fania, L.; Sinagra, J.L.M.; Salemme, A.; Di Zenzo, G. Bullous pemphigoid: Trigger and predisposing factors. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.B.; Hashim, M.J.; King, J.K.; Govender, R.D.; Mustafa, H.; Al Kaabi, J. Epidemiology of Type 2 Diabetes—Global Burden of Disease and Forecasted Trends. J. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2020, 10, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.G.; Lee, H.J.; Yoon, M.S.; Kim, D.H. Association of Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 Inhibitor Use with Risk of Bullous Pemphigoid in Patients with Diabetes. JAMA Dermatol. 2019, 155, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomayko, M.M.; Damsky, W.; Fathy, R.; McMahon, D.E.; Turner, N.; Valentin, M.N.; Rallis, T.; Aivaz, O.; Fox, L.P.; Freeman, E.E. Subepidermal blistering eruptions, including bullous pemphigoid, following COVID-19 vaccination. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 148, 750–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, D.E.; Amerson, E.; Rosenbach, M.; Lipoff, J.B.; Moustafa, D.; Tyagi, A.; Desai, S.R.; French, L.E.; Lim, H.W.; Thiers, B.H.; et al. Cutaneous reactions reported after Moderna and Pfizer COVID-19 vaccination: A registry-based study of 414 cases. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2021, 85, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, K.Y.; Yu, H.S.; Yu, S. Current and innovated managements for autoimmune bullous skin disorders: An overview. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaul, R.; McGeer, A.; Low, D.E.; Green, K.; Schwartz, B.; Simor, A.E. Population-Based Surveillance for Group a Streptococcal Necrotizing Fasciitis: Clinical Features, Prognostic Indicators, and Microbiologic Analysis of Seventy-Seven Cases. Am. J. Med. 1997, 103, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tantraworasin, A.; Khamnuan, P.; Chongruksut, W.; Jearwattanakanok, K.; Patumanond, J. Necrotizing fasciitis: Epidemiology and clinical predictors for amputation. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2015, 14, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sablone, S.; Lagouvardou, E.; Cazzato, G.; Carravetta, F.; Maselli, R.; Merlanti, F. Necrotizing fasciitis of the thigh as unusual colonoscopic polypectomy complication: Review of the literature with case presentation. Medicina 2022, 58, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puvanendran, R.; Huey, J.C.M.; Pasupathy, S. Necrotizing fasciitis. Can. Fam. Physician. 2009, 55, 981–987. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.H.; Chang, H.C.; Pasupathy, S.; Khin, L.W.; Tan, J.L.; Low, C.O. Necrotizing fasciitis: Clinical presentation, microbiology, and determinants of mortality. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2003, 85, 1454–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stevens, D.L.; Bryant, A.E.; Goldstein, E.J. Necrotizing Soft Tissue Infections. Infect. Dis. Clin. North Am. 2021, 35, 135–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, D.L.; Bisno, A.L.; Chambers, H.F.; Dellinger, E.P.; Goldstein, E.J.C.; Gorbach, S.L.; Hirschmann, J.V.; Kaplan, S.L.; Montoya, J.G.; Wade, J.C.; et al. Practice Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Skin and Soft Tissue Infections: 2014 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 59, e10–e52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stevens, D.L.; Bryant, A.E. Necrotizing Soft-Tissue Infections. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2253–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aromataris, E.; Munn, Z. JBI Manual for Evidence Synthesis.; 2020; Available online: https://synthesismanual.jbi.global (accessed on 5 September 2022). [CrossRef]
- Chamberlain, A.J.; Wojnarowska, F. Bullous pemphigoid complicated by nonfatal necrotizing fasciitis. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2003, 28, 448–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boughrara, Z.; Ingen-Housz-Oro, S.; Legrand, P.; Duong, T.A.; Roujeau, J.C. Cutaneous infections in bullous pemphigoid patients treated with topical corticosteroids. Ann. Dermatol. Venereol. 2010, 137, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doffoel-Hantz, V.; Longueville, C.; Durox, H.; Bédane, C.; Sparsa, A.; Bonnetblanc, J.M. Purpura rétiforme et pemphigoïde bulleuse: Une association fatale? Rev. Med. Interne 2011, 32, 132–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekiz, Ö.; Şen, B.B.; Rifaioğlu, E.N.; Özgür, T.; İnan, M.U.; Doğramacı, Ç.A. Necrotizing fasciitis in a patient with bullous pemphigoid treating with systemic steroid. Cutan. Ocul. Toxicol. 2013, 32, 252–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sené, T.; Regnier, S.; Robert, N.; Dupuy, A.; Morel, P.; Tancrede, E.; Rybojad, M. Early necrotizing fasciitis following initiation of mycophenolate mofetil in two patients with bullous pemphigoid. Int. J. Dermatol. 2014, 53, e236–e239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noguchi, E.; Kamiya, K.; Maekawa, T.; Komine, M.; Murata, S.; Ohtsuki, M. Bullous pemphigoid complicated by necrotising fasciitis successfully treated with systemic corticosteroids and antibiotics in combination with i.v. immunoglobulin. Australas J. Dermatol. 2018, 59, e313–e314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurišić, M.; Nikolić, G.; Nikolić Živanović, M.; Stojičić, M. Necrotizing fasciitis-a complication of autoimmune skin blistering diseases? Case report and literature review. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries 2023, (in press). [Google Scholar]
- Joly, P.; Roujeau, J.-C.; Benichou, J.; Picard, C.; Dreno, B.; Delaporte, E.; Vaillant, L.; D'Incan, M.; Plantin, P.; Bedane, C.; et al. A Comparison of Oral and Topical Corticosteroids in Patients with Bullous Pemphigoid. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehman, J.S.; Khunger, M.; Lohse, C.M. Infection in autoimmune bullous diseases: A retrospective comparative study. J. Dermatol. 2013, 40, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.C.S.; Allen, J.C.; Lim, Y.L.; Chua, S.H.; Tan, S.H.; Tang, M.B.Y. Mortality of bullous pemphigoid in Singapore: Risk factors and causes of death in 359 patients seen at the National Skin Centre. Br. J. Dermatol. 2014, 170, 1319–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phoon, Y.W.; Fook-Chong, S.M.C.; Koh, H.Y.; Thirumoorthy, T.; Pang, S.M.; Lee, H.Y. Infectious complications in bullous pemphigoid: An analysis of risk factors. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2015, 72, 834–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Hsu, D.Y.; Brieva, J.; Silverberg, N.B.; Langan, S.M.; Silverberg, J.I. Hospitalization, inpatient burden and comorbidities associated with bullous pemphigoid in the U.S.A. Br. J. Dermatol. 2017, 176, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Mao, X.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, B.; Chen, X.; Yu, C.; Zheng, Z.; Jin, H.; Li, L. Assessment of the Characteristics and Associated Factors of Infectious Complications in Bullous Pemphigoid. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottlieb, G.J.; Ragaz, A.; Vogel, J.V.; Friedman-Kien, A.; Rywlin, A.M.; Weiner, E.A.; Ackerman, A.B. A preliminary communication on extensively disseminated Kaposi’s sarcoma in young homosexual men. Am. J. Dermatopathol. 1981, 3, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Léauté-Labrèze, C.; de la Roque Dumas, E.; Hubiche, T.; Boralevi, F. Propranolol for severe hemangiomas of infancy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 2649–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gual, A.; Mascaró, J.M.; Rojas-Farreras, S.; Guilabert, A.; Julià, M.; Iranzo, P. Mortality of bullous pemphigoid in the first year after diagnosis: A retrospective study in a Spanish medical centre. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2014, 28, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Z.; Narla, S.; Hsu, D.Y.; Silverberg, J.I. Association of serious infections with pemphigus and pemphigoid: Analysis of the Nationwide Inpatient Sample. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2018, 32, 1768–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrick, B.J.; Lohse, C.M.; Lehman, J.S. Specific causes of death in patients with bullous pemphigoid as measured by death certificate data: A retrospective cohort study. Int. J. Dermatol. 2015, 54, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramakrishnan, K.; Salinas, R.C.; Agudelo Higuita, N.I. Skin and Soft Tissue Infections. Am. Fam. Physician 2015, 92, 474–483. [Google Scholar]
- Thatayatikom, A.; White, A.J. Rituximab: A promising therapy in systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmun. Rev. 2006, 5, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Looney, R.J.; Anolik, J.; Campbell, D.; Felgar, R.E.; Young, F.; Arend, L.J.; Sloand, J.A.; Rosenblatt, J. B cell depletion as a novel treatment for systemic lupus erythematosus: A phase I/II dose-escalation trial of rituximab. Arthritis. Rheum. 2004, 50, 2580–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulkareem, A.; D’Souza, R.S.; Shogbesan, O.; Donato, A. A Case of Rituximab-Induced Necrotizing Fasciitis and a Review of the Literature. Case. Rep. Hematol. 2017, 2017, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rashid, O.M.; Nagahashi, M.; Takabe, K. Management of massive soft tissue defects: The use of INTEGRA® artificial skin after necrotizing soft tissue infection of the chest. J. Thorac. Dis 2012, 4, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keung, E.Z.; Liu, X.; Nuzhad, A.; Adams, C.; Ashley, S.W.; Askari, R. Immunocompromised Status in Patients with Necrotizing Soft-Tissue Infection. JAMA Surg. 2013, 148, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Savin, J.A.; Noble, W.C. Immunosuppression and skin infection. Br. J. Dermatol. 1975, 93, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginzler, E.; Diamond, H.; Kaplan, D.; Weiner, M.; Schlesinger, M.; Seleznick, M. Computer analysis of factors influencing frequency of infection in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1978, 21, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuck, A.E.; Minder, C.E.; Frey, F.J. Risk of Infectious Complications in Patients Taking Glucocorticosteroids. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1989, 11, 954–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rzany, B.; Partscht, K.; Jung, M.; Kippes, W.; Mecking, D.; Baima, B.; Prudlo, C.; Pawelczyk, B.; Messmer, E.M.; Schuhmann, M.; et al. Risk Factors for Lethal Outcome in Patients with Bullous Pemphigoid. Arch. Dermatol. 2002, 138, 903–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dropulic, L.K.; Lederman, H.M. Overview of Infections in the Immunocompromised Host. Microbiol. Spectr. 2016, 4, 3–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polansky, M.; Eisenstadt, R.; DeGrazia, T.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Y.; Feldman, R. Rituximab therapy in patients with bullous pemphigoid: A retrospective study of 20 patients. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol 2019, 81, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamberts, A.; Euverman, H.I.; Terra, J.B.; Jonkman, M.F.; Horváth, B. Effectiveness and Safety of Rituximab in Recalcitrant Pemphigoid Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2018, 19, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Goh, T.; Goh, L.G.; Ang, C.H.; Wong, C.H. Early diagnosis of necrotizing fasciitis. Br. J. Surg. 2013, 101, e119-25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenhalgh, D.G. Wound healing and diabetes mellitus. Clin. Plast. Surg. 2003, 30, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donihi, A.C.; Raval, D.; Saul, M.; Korytkowski, M.T.; DeVita, M.A. Prevalence and Predictors of Corticosteroid-Related Hyperglycemia in Hospitalized Patients. Endocr. Pract. 2006, 12, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipsky, B.A.; Tabak, Y.P.; Johannes, R.S.; Vo, L.; Hyde, L.; Weigelt, J.A. Skin and soft tissue infections in hospitalised patients with diabetes: Culture isolates and risk factors associated with mortality, length of stay and cost. Diabetologia 2010, 53, 914–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Wu, C.; Lin, M.; Chen, T.; Liao, K.; Hwang, C.; Chu, S.; Chen, C.; Lee, D.; Chang, Y.; et al. Comorbidity profiles among patients with bullous pemphigoid: A nationwide population-based study. Br. J. Dermatol. 2011, 165, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misiakos, E.P.; Bagias, G.; Patapis, P.; Sotiropoulos, D.; Kanavidis, P.; Machairas, A. Current concepts in the management of necrotizing fasciitis. Front. Surg. 2014, 1, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goldstein, E.J.C.; Anaya, D.A.; Dellinger, E.P. Necrotizing Soft-Tissue Infection: Diagnosis and Management. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 44, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mok, M.Y.; Wong, S.Y.; Chan, T.M.; Tang, W.M.; Wong, W.S.; Lau, C.S. Necrotizing fasciitis in rheumatic diseases. Lupus 2006, 15, 380–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roje, Z.; Roje, Ž.; Matić, D.; Librenjak, D.; Dokuzović, S.; Varvodić, J. Necrotizing fasciitis: Literature review of contemporary strategies for diagnosing and management with three case reports: Torso, abdominal wall, upper and lower limbs. World J. Emerg. Surg. 2011, 6, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.-Y.; Huang, T.-Y.; Chen, J.-L.; Kuo, L.-T.; Huang, K.-C.; Tsai, Y.-H. Rational use of ceftriaxone in necrotizing fasciitis and mortality associated with bloodstream infection and hemorrhagic bullous lesions. Antibiotics 2022, 111, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.H.; Khin, L.W.; Heng, K.S.; Tan, K.C.; Low, C.O. The LRINEC (Laboratory Risk Indicator for Necrotizing Fasciitis) score: A tool for distinguishing necrotizing fasciitis from other soft tissue infections. Crit. Care Med. 2004, 32, 1535–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechar, J.; Sepehripour, S.; Hardwicke, J.; Filobbos, G. Laboratory risk indicator for necrotising fasciitis (LRINEC) score for the assessment of early necrotising fasciitis: A systematic review of the literature. Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl. 2017, 99, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brafa, A.; Grimaldi, L.; Brandi, C.; Nisi, G.; Calabrò, M.; Campa, A.; D’Aniello, C. Abdominoplasty as a reconstructive surgical treatment of necrotising fasciitis of the abdominal wall. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2009, 62, 136–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somasundaram, J.; Wallace, D.L.; Cartotto, R.; Rogers, A.D. Flap coverage for necrotising soft tissue infections: A systematic review. Burns 2021, 47, 1608–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Liu, T.; Zhao, Cq.; Lei, Y.-Z.; Fan, D.-L.; Mao, T-Ch. Negative pressure wound therapy and split thickness skin graft aided in the healing of extensive perineum necrotizing fasciitis without faecal diversion: A case report. BMC Surg. 2018, 18, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neri, I.; Antonucci, V.A.; Balestri, R.; Tengattini, V.; Iozzo, I.; Bardazzi, F. Bullous pemphigoid appearing both on thermal burn scars and split-thickness skin graft donor sites. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2013, 11, 675–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGrath, J.; Black, M. Split skin grafting and bullous pemphigoid. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 1991, 16, 72–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, D.L.; Sadhwani, A. Blistering on a squamous cell carcinoma graft site in a patient with bullous pemphigoid. Cutis 1994, 54, 40. [Google Scholar]
- Ghura, H.S.; Johnston, G.A.; Milligan, A. Development of a bullous pemphigoid after split-skin grafting. Br. J. Plast. Surg. 2001, 54, 447–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafejee, A.; Coulson, I.H. Localized bullous pemphigoid 20 years after split skin grafting. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2005, 30, 187–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzaque, A. Intravenous immunoglobulin therapy for patients with bullous pemphigoid unresponsive to conventional immunosuppressive treatment. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2001, 45, 825–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amagai, M.; Ikeda, S.; Hashimoto, T.; Mizuashi, M.; Fujisawa, A.; Ihn, H.; Matsuzaki, Y.; Ohtsuka, M.; Fujiwara, H.; Furuta, J.; et al. A randomized double-blind trial of intravenous immunoglobulin for bullous pemphigoid. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2017, 85, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darenberg, J.; Ihendyane, N.; Sjölin, J.; Aufwerber, E.; Haidl, S.; Follin, P.; Andersson, J.; Norrby-Teglund, A. The Streptlg Study Group, Intravenous Immunoglobulin G Therapy in Streptococcal Toxic Shock Syndrome: A European Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2003, 37, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parks, T.; Wilson, C.; Curtis, N.; Norrby-Teglund, A.; Sriskandan, S. Polyspecific Intravenous Immunoglobulin in Clindamycin-treated PAients With Streptococcal Toxic Shock Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 67, 1434–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Zhao, M.; Hilario-Vargas, J.; Prisayanh, P.; Warren, S.; Diaz, L.A.; Roopenian, D.C.; Liu, Z. Complete FcRn dependence for intravenous Ig therapy in autoimmune skin blistering diseases. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 3440–3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, J.H.O.; Enk, A.H. High-dose intravenous immunoglobulin in skin autoimmune disease. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leo, H.P.; Volkmann, E.R.; Ohanian, A.K. Necrotizing Soft Tissue Infection in a Patient with Bullous Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Case Report. Ann. Arthritis Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 1, 1002. [Google Scholar]
- Berkani, N.; Joly, P.; Golinski, M.-L.; Colliou, N.; Lim, A.; Larbi, A.; Riou, G.; Caillot, F.; Bernard, P.; Bedane, C.; et al. B-cell depletion induces a shift in self antigen specific B-cell repertoire and cytokine pattern in patients with bullous pemphigoid. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalowska, M.; Ciepiela, O.; Kowalewski, C.; Demkow, U.; Schwartz, R.A.; Wozniak, K. Enzyme-linked immunoassay index for anti-NC16a IgG and IgE auto-antibodies correlates with severity and activity of bullous pemphigoid. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2016, 96, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fiorino, A.S.; Baum, S.; Czernik, A.; Hall, R.; Zeeli, T.; Baniel, A.; Sinha, A.A.; Seiffert-Sinha, K.; Kolatch, B.; Zhang, Z.; et al. 570 Safety and efficacy of bertilimumab, a human anti-eotaxin-1 monoclonal antibody, in bullous pemphigoid in a phase 2a study. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2019, 139, S98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tung, C.Y.; Isenberg, D. Necrotising fasciitis in systemic lupus erythematosus: A case report and literature review. Lupus Sci. Med. 2014, 1, e000008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Authors | Age | Sex | Comorbidities | NF Onset (after BP Therapy) | Control of BP | Previous Therapy | Current Therapy | Diagnostics | Bacteriology | NF Treatment | Evolution |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chamberlain 2003 [29] | 85 | F | HTA | 9 d | Incomplete | TCP, Erythromycin 250 mg ×2 | Prednisolone 30 mg/g + Betamethasone 500 µg × 2/d mouth wash, Erythromycin 250 mg ×2 | Local findings of NF on the left leg, Laboratory, Microbiology, Ultrasound, | Strep A | Successive surgical debridement, split thickness skin grafting Initial antimicrobe therapy: Vancomycin 1 g ×2 Meropenem 1 g ×3 Additional antimicrobial therapy: cefuroxime 1.5 g ×3 clindamycin 300 mg ×4 | Survived (sequel) |
| Boughrara 2010 [30] | 73 | M | MI, benign vesical polyps | 2 years | Incomplete | ? | TCP | Local findings of NF in two localizations: left arm and dorsal side of the right hand, Microbiology | Strep A, Pseudomonas sepsis | Debridement of the left arm and amputation of the right index finger Antimicrobial therapy undisclosed. | Died |
| Boughrara 2010 [30] | 64 | F | Obesety, insulin dependant DM | 14 d | Incomplete | ? | TCP, MTX 15 mg/week | Local findings of NF on the left leg, microbiology | Strep A, MRSA, Acinetobacter | Surgical debridement of the dorsal side of the foot and amputation of two toes. Antimicrobial therapy undisclosed. | Died |
| Boughrara 2010 [30] | 81 | M | HTA, insulin ndependat DM, preterminal CRI, COPD | 14 d | Incomplete | TCP | TCP, MMF | Local finding of NF on left leg and foot, Microbiology | Strep A | Surgical debridement, Antimicrobial therapy undisclosed. | Died |
| Doffoel-Hantz 2011 [31] | 86 | F | Acheimer’s dementia | 3 weeks | Incomplete | TCP | TCP | Retiform purpura of the ancle followed by development of necrosis. | Strep A | Broad-spectrum antibiotics, no surgical debridement was performed. | Died |
| Ekiz 2013 [32] | 78 | F | HTA | 3 weeks | Tetracyclin, Niacinamid, TCP, systemic steroids | Prednisolon 48 mg/d after 2 weeks 32 mg/d, | Local finding of NF on the left leg, laboratory, MRI, Microbiology Histopathology | Strep A. | Surgical debridement, Sulbactam/ampicillin 1 g, oral ciprofloxacin 750 mg 2 × 1, tigecycline | Died | |
| Sene 2014 [33] | 52 | M | Obesity | 35 d | Incomplete | TCP | Prednisolone 100 mg/d, after 2 weeks Prednisolone 60 mg/d and MMF 2 mg/d | Local finding of NF on the left leg, laboratory, Microbiology | Strep A | Surgical debridement, pipera- cillin-tazobactam and vancomycin | Survived |
| Sene 2014 [33] | 76 | F | HTA, DM | 2 weeks | Incomplete | TCP 30 g/d | TCP 10 g/d, MMF 2 g/d | Local finding of NF on the left leg, laboratory, Microbiology | Strep A, MRSA | Surgical debridement piperacillin-tazobactam, gentamicin, and vancomycin | Died |
| Noguchi 2018 [34] | 69 | F | DM, | 4 d | Incomplete | Prednisolone 20 mg/d, Cyclosporine 100 mg/d | Prednisolone 40 mg/d, IVIG 4 days latter | Local finding of NF on the insertion point of CVC, Laboratory, Microbiology, CT scan | MSSA | Surgical debridement piperacillin-tazobactam and vancomycin | Survived |
| Jurisic 2023 [35] | 51 | M | HTA, DM, Obesity | 3 weeks | Incomplete | Undisclosed corticosteroid therapy regimen | ? | Local finding of deep tissue necrosis due to advanced disease, CT scan, laboratory, microbiology | Acinetobacter spp. Klebsiella-enterobacter Spp. Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Enterococcus spp. Acinetobacter baumannii complex sepsis (MDR) | Successive surgical debridements, Vancomycin 2 × 1.5 g, Clindamycin 900 mg 3 × 1 and Meropenem 3 × 1 g Additional antimicrobial therapy: Colistimethate-sodium 3 × 3,000,000ij | Died |
| Author | Year | Type | No. Patients | Mean Age | Therapy | Events | Comorbidities | Risk Factors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jolly | 2002 [36] | Randomized multicenter trial | 341 | 80 ± 11 | TCP Oral CS | 1 necrotizing Cellulitis in oral CS group | Cardiovascular disease Neurologic disorder DementiaDiabetes mellitus Chronic lung condition | Oral corticosteroid therapy Low Karnofsky score Old age |
| Boughrara | 2010 [30] | Retrospective | 30 | 83.5 | TCP MTX MMF | 3 NF/10 SSTI | Diabetes Autoimmune diseases | / |
| Lehman | 2013 [37] | Retrospective | 54 | 75.8 | TCP Oral CS Cyclosporin MTX MMF Dapsone Rituximab Azathioprine | 43 SSTI’s | Diabetes Solid organ cancer/treatment Other autoimmune disorders | Oral corticosteroid therapy |
| Cai | 2014 [38] | Retrospective | 359 | 75.7 ± 2.6 | Corticosteroids (88%), Doxycycline and/or nicotinamide (25.9%), Dapsone (13.9%) Azathioprine (39%), Combination therapy of corticosteroids and IMA 37.6% | 5 SSTI related causes of death | Heart failure Chronic renal disease Parkinson disease Stroke | Concomitant neurologic disease Heart failure Parkinson disease |
| Phoon | 2015 [39] | Retrospective | 97 | 79 ± 11 | Prednisolone + adjuvant therapy in 53% of patients: dapsone 17% doxycycline and nicotinamide 34% azathioprine 3% MMF 6% | 7 SSTI’s | Hypertension Neurologic disorders Diabetes | Low Karnofsky score, dementia, higher CCIS |
| Ren | 2018 [40] | Retrospective | 13,342 | 77.3 | / | BP was associated with higher odds of necrotizing fasciitis, adjusted OR (95% CI) 2.91 (1.25–6.80), p = 0.0136 | Rheumatoid arthritis Systemic lupus erythematosus Diabetes Cushing’s Cancer | Older age Higher number of chronic condition Diabetes Cushing’s Cancer |
| Chen | 2020 [41] | Retrospective | 252 | 67.2 | Corticosteroids 74.6% Other immunosuppressants 52.0% IVIG 3.6% | 40 SSTI’s | Diabetes, Mucosal involvement Respiratory comorbidities | Maximal control dose of corticosteroids, Low serum albumin levels, Hospitalization, Diabetes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stojičić, M.; Jurišić, M.; Marinković, M.; Karamarković, M.; Jovanović, M.; Jeremić, J.; Jović, M.; Vlahović, A.; Jovanović, M.; Radenović, K.; et al. Necrotizing Fasciitis—Severe Complication of Bullous Pemphigoid: A Systematic Review, Risk Factors, and Treatment Challenges. Medicina 2023, 59, 745. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59040745
Stojičić M, Jurišić M, Marinković M, Karamarković M, Jovanović M, Jeremić J, Jović M, Vlahović A, Jovanović M, Radenović K, et al. Necrotizing Fasciitis—Severe Complication of Bullous Pemphigoid: A Systematic Review, Risk Factors, and Treatment Challenges. Medicina. 2023; 59(4):745. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59040745
Chicago/Turabian StyleStojičić, Milan, Milana Jurišić, Milana Marinković, Miodrag Karamarković, Milan Jovanović, Jelena Jeremić, Marko Jović, Aleksandar Vlahović, Mladen Jovanović, Kristina Radenović, and et al. 2023. "Necrotizing Fasciitis—Severe Complication of Bullous Pemphigoid: A Systematic Review, Risk Factors, and Treatment Challenges" Medicina 59, no. 4: 745. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59040745
APA StyleStojičić, M., Jurišić, M., Marinković, M., Karamarković, M., Jovanović, M., Jeremić, J., Jović, M., Vlahović, A., Jovanović, M., Radenović, K., Jovićević, N., & Vasović, D. (2023). Necrotizing Fasciitis—Severe Complication of Bullous Pemphigoid: A Systematic Review, Risk Factors, and Treatment Challenges. Medicina, 59(4), 745. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59040745






