Abstract
Migraine is a prevalent neurological disorder that significantly impacts the quality of life for affected individuals. The pathogenesis behind migraines is not yet fully understood, but hormonal changes, especially fluctuations in, estrogen and progesterone levels, have a significant role in the susceptibility of women to migraines. Pregnancy introduces a unique set of challenges for women who experience migraines, as they must navigate the complexities of managing their condition while safeguarding the health of both them and their unborn child. Pharmacological options for treating migraines during pregnancy are limited, and, therefore, there is a growing interest in exploring alternative approaches to migraine symptom relief and management. Physical activity during pregnancy provides a range of benefits, and it has gained attention as a potentially valuable tool for alleviating migraine symptoms in pregnant patients. This review explores the intricate relationship between migraines and pregnancy, emphasizing how physical activity and other alternative approaches may influence the frequency, severity, and overall experience of migraines during pregnancy. Through collaboration with healthcare providers and the adoption of personalized management strategies, women can strike a balance that supports both their own well-being and the healthy development of their unborn child. By examining existing research and emerging insights, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of the potential benefits and considerations of incorporating physical activity and other treatment options into migraine management strategies for pregnant women. Further research is needed to elucidate the specific mechanisms linking migraines, pregnancy, and physical activity, enabling the development of more targeted interventions and guidelines.
1. Introduction
Pregnancy is a transformative journey characterized by the joyful anticipation of a new life, which, unfortunately, may be interrupted by various physical and emotional challenges, including health-related concerns [1]. Neurological disorders during pregnancy can have varying consequences, and they are associated with significant maternal morbidity, accounting for approximately 20% of maternal deaths in the United States [2]. They may occur during all three trimesters of pregnancy, but each trimester has its own specificities and susceptibilities. Arterial–venous malformations usually occur early in pregnancy, unlike in most other neurological conditions, where they are more likely to happen later in pregnancy. The third trimester of pregnancy is associated with the highest risk of stroke, aneurysm rupture, and cerebral vein thrombosis [3]. The most prevalent neurological disorder during pregnancy is a migraine, and it affects many pregnant women worldwide [4].
Understanding the intricate relationship between migraines and pregnancy is crucial for providing expectant mothers with the best possible care. Migraine attacks during pregnancy can significantly impact a woman’s quality of life and may even raise concerns about the potential risks to both maternal and fetal health [5]. Additionally, the management of migraine symptoms becomes even more complex during pregnancy due to restrictions on medication use and the need to balance relief with the safety of the developing fetus [6].
While pharmacological options for treating migraines are limited during pregnancy, there is growing interest in exploring alternative approaches to symptom relief and management. Physical activity, including exercise and relaxation techniques, has gained attention as a potentially valuable tool for alleviating migraine symptoms in pregnant patients. However, the relationship between physical activity and migraines during pregnancy is complex and not yet fully understood [7,8].
This review aims to shed light on the interplay between migraines and pregnancy, emphasizing how physical activity and other alternative approaches may influence the frequency, severity, and overall experience of migraines during this transformative phase of life. By examining existing research and emerging insights, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of the potential benefits and considerations of incorporating physical activity and other treatment options into migraine management strategies for pregnant women. Such knowledge can empower healthcare providers and pregnant individuals alike to make informed decisions that promote both maternal well-being and the healthy development of the fetus.
2. Migraine Impact on Women’s Health and Life Quality
Migraines are complex, genetically determined conditions that are characterized by recurrent, moderate to severe, and usually unilateral headaches, which are commonly accompanied by vomiting, nausea, and sound and light sensitivity [9].
According to the third edition of the International Classification of Headache Disorders (ICHD-3), migraines are divided into six categories: migraine without aura (MWA), migraine with aura (MA), chronic migraine, complications of migraine, probable migraines, and episodic syndromes that may be associated with migraine [10]. Most of these categories can be subcategorized, but from the clinical aspect of view, MWAs appear to be the most relevant. MWAs are primarily associated with hormone level changes and are accountable for approximately 80% of all cases of migraines [11].
More than 15% of the world’s population report some of migraine attack symptoms at some point of their life [12]. Notable sex dimorphism in migraine prevalence is present worldwide (Table 1). Even though migraines can affect individuals of any gender and age, women are disproportionately affected in significantly higher proportions and prevalence across all age groups [13]. The peak prevalence of migraine onset among women is the reproductive age, with hormonal fluctuations playing a significant role in migraine onset and symptom severity [14]. Furthermore, functional as well as structural differences in the central nervous system have been found between women and men with migraines by magnetic resonance imaging [15].

Table 1.
The sex dimorphism in migraine patients.
Before puberty, migraines are two to three times more prevalent among girls, and after puberty, migraines are three to four times more frequent in adult women compared with men [16]. According to the Global Burden of Disease study, they are categorized as the fourth leading cause of years living with disability (YLD) for women, unlike for men, among whom they are categorized as the eighth leading cause of YLD [17]. Migraine was estimated to have caused more than 45 million cumulative years of YLDs, exceeding USD 19 billion a year in the US in indirect costs alone [17,18].
The teens and early twenties are the usual age for the onset of migraines, and peak prevalence is usually reached in the early forties, with a tendency for migraine symptom reduction after menopause. According to the age prevalence distribution, menstruation appears to be one of the key factors initiating the vicious cycle of migraine symptoms. More than 50% of women affected by migraines report an association between menstruation and migraine onset, describing it as most likely to occur in the time range from two days before the menstruation until the first three days of the menstrual cycle [19]. In favor of the hormonal impact on migraine onset, epidemiological data reveals that in prepubertal children aged 7–9 years, there is no change in migraine prevalence. First, but still insignificant, differences appear among children aged 10–12 years (5.4% of girls compared with 3.9% of boys) [20], the age that usually coincides with the occurrence of menarche.
Starting from puberty and the onset of intensive sex hormonal changes, the overall prevalence of migraines begins to increase, affecting primarily girls. Up to 20% of women suffering from migraines report their first migraine attack at the age of menarche [21].
Migraines have a bimodal prevalence pattern; they reach their initial peak at the age of 35, and the second one at the age of 50. Afterwards, the frequency and symptoms manifested start to decrease [22]. Conversely to migraine prevalence, migraine peak incidence in women is observed between the age of 20 and 24, and in men between the age of 15 and 19 [23].
Despite significant differences in the migraine occurrence between women and men, there seems to be no sex-related difference in migraine attack frequency between the genders. Both women and men appear to suffer from migraine-related symptoms on average one to four days monthly [24]. Migraine studies have proved that migraine-associated symptoms significantly impact everyday life activities for both men and women. They are responsible for family and relationship disruptions and educational, career, and financial problems among women and men in similar ratios [25].
Both men and women experience similar clinical manifestations. In the case of migraine with aura, an attack typically consists of four stages: prodrome, aura, attack, and post-drome. The prodrome phase usually begins one or two days before an upcoming migraine. Most commonly, patients experience it as constipation, changes of mood, neck stiffness, food cravings, fluid retention or increased urination. Aura might occur before or during a migraine attack. An aura is usually visual, but other sensations might be involved as well. Typically, they evolve gradually, and can last for up to 60 min. Migraine attacks usually last between 4 and 72 h, while the frequency of their occurrence widely ranges. A migraine attack is characterized by pain accompanied by nausea and vomiting. Throbs are typical pain manifestations, along with sound and light sensitivity, but smell and taste sensitivity might occur as well. A migraine postdrome phase is not uncommon. In the postdrone period, patients might experience vide range of symptoms, such as exhaustion, difficulty concentrating, mood changes, digestive issues, neck stiffness, and aches [26].
Patterns are one of the main characteristics of migraines and they consist of attacks, remissions, and relapses. Compared with women, men appear to have a more favorable pattern set, since the remission period for men seems to last longer [27].
Migraine can be classified as active and inactive as well. The occurrence of grain migraine symptoms within the last year is diagnostic for an active migraine. Study results coming from Germany imply that women of older age are less commonly affected by active migraines compared with men. The prevalence of inactive migraine in Germany is 25.7% for women, compared with only 16.5% for men aged 60 or more. This discrepancy changes the balance of migraine prevalence between men and women once again and suggests that female-sex-hormone depletion interferes significantly with the migraine prevalence [28].
Along with migraines, tension-type headaches (TTHs) are the most common primary headaches. During pregnancy, hormonal changes may influence the clinical manifestation, and due to symptom overlaps, it is not always easy to distinguish migraine from an episodic TTH. Unlike migraines, TTHs usually tend to be bilateral in location, and they typically cause a steady ache, but, most importantly, they are not correlated with any adverse pregnancy outcome [29]. TTHs do not worsen with routine physical activity. Lifestyle interventions are effective in headache prevention and treatment, but pharmacotherapy remains the mainstay of clinical management [30,31].
3. Migraines and Hormones: How Does the Pregnancy Interfere?
The pathogenesis underlying migraines, a complex neuromuscular disorder, is not yet fully understood. Undoubtedly it is mediated by hormones, and hormonal differences, especially fluctuations in estrogen and progesterone levels, have a significant role in the susceptibility of women to migraines [32]. Determining the exact pathophysiology mechanism that explains migraines is a matter for extensive research. Most of the results are based on animal models [23], and due to the lack of studies performed in humans, especially males, it remains a challenge to draw conclusions [24]. Aside from estrogen and progesterone fluctuations, it is known that inflammatory mediators affecting the trigeminovascular system have a prominent role in migraine pathogenesis as well as in sex-related differences in migraine occurrence [33]. Prolactin, a pituitary-derived hormone, and oxytocin, a hypothalamic neuropeptide, have become the recent focus of research interest, since it appears that they interfere with the migraine onset and symptom development [34,35]. Prolactin and oxytocin are nociceptive triggers that are involved in opposite ways. Prolactin is a pronociceptive agent, while oxytocin appears to have an antinociceptive role [33]. Changes in prolactin and oxytocin levels are closely related to pregnancy and symptom management; therefore, their potential use as agonists and antagonists creates a promising possibility for targeted migraine therapy [33].
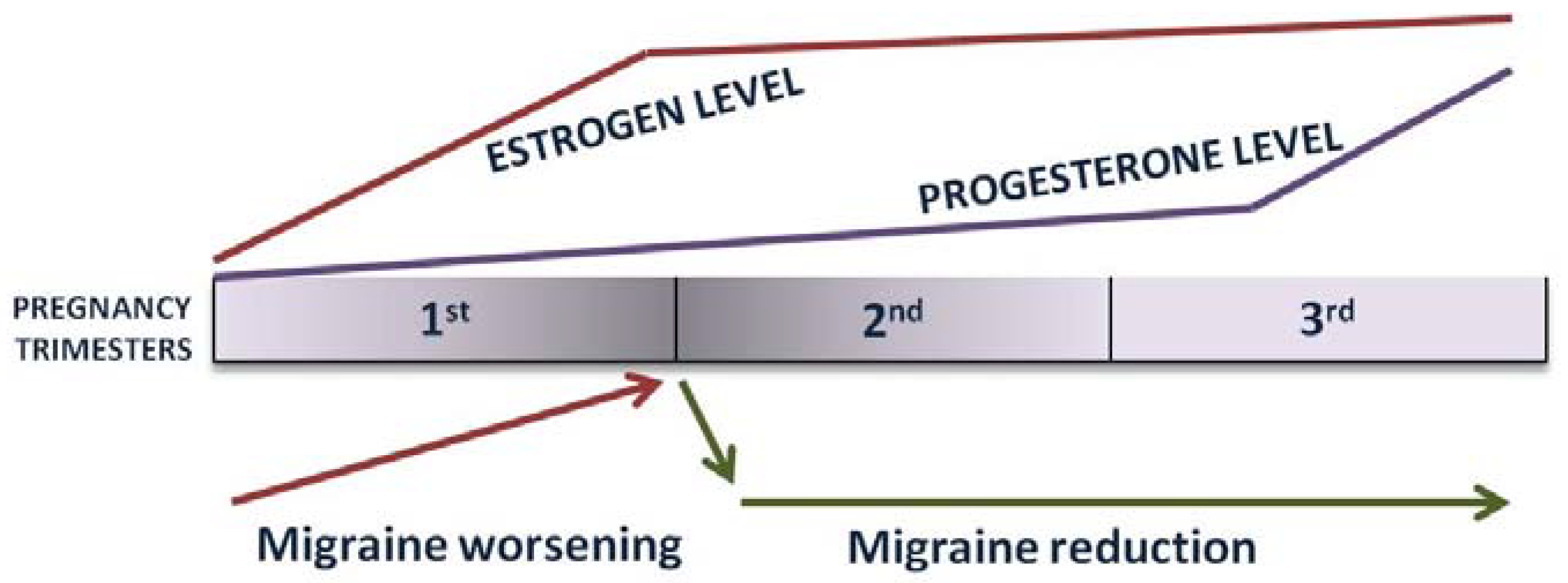
Pregnancy, marked by dramatic hormonal changes, poses a unique challenge for women with pre-existing migraines, necessitating a careful balance between managing their condition and ensuring the well-being of the developing fetus. Estrogen, progesterone, and other hormonal changes; disrupted sleep; stress; nausea; and dehydration during pregnancy can influence the frequency and severity of migraines. While some women experience migraine symptom relief during pregnancy, others may experience an exacerbation of their symptoms, particularly in the first trimester of pregnancy. MWAs have a general tendency to improve compared with MAs, which are also more likely to occur during de novo pregnancy [36]. The first trimester of pregnancy is the time when estrogen levels rise; therefore, during this stage of pregnancy, it is possible for some women to experience transient symptom worsening. The second and the third trimesters are usually known for their tendency for symptom relief, and a nearly 90% symptom reduction is expected during this time of pregnancy [37]. During this stage of pregnancy, hormone levels are stable, estrogen and endogenous opioid levels are elevated, and, most importantly, there are no more hormone fluctuations, which eliminates one of the major attack triggers (Figure 1) [36].
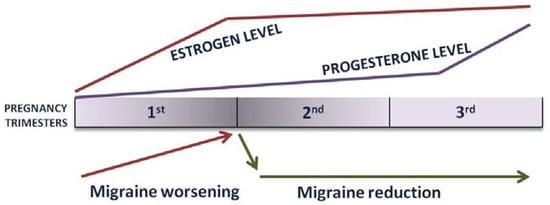
Figure 1.
Estrogen fluctuations and migraine course during pregnancy.
Acute migraine affects pregnancy outcomes in several different ways. A retrospective study conducted in the US revealed that in a case of severe acute migraine during pregnancy, more than half of the study participants were more likely to develop at least one adverse pregnancy outcome, such as pre-eclampsia, preterm delivery, or low birthweight [38]. Therefore, patients experiencing acute migraine symptoms must be considered high-risk patients, and in a case of a new headache onset, other pregnancy-related complications, such as a hypertensive disorder of pregnancy, should undoubtedly be excluded first [39].
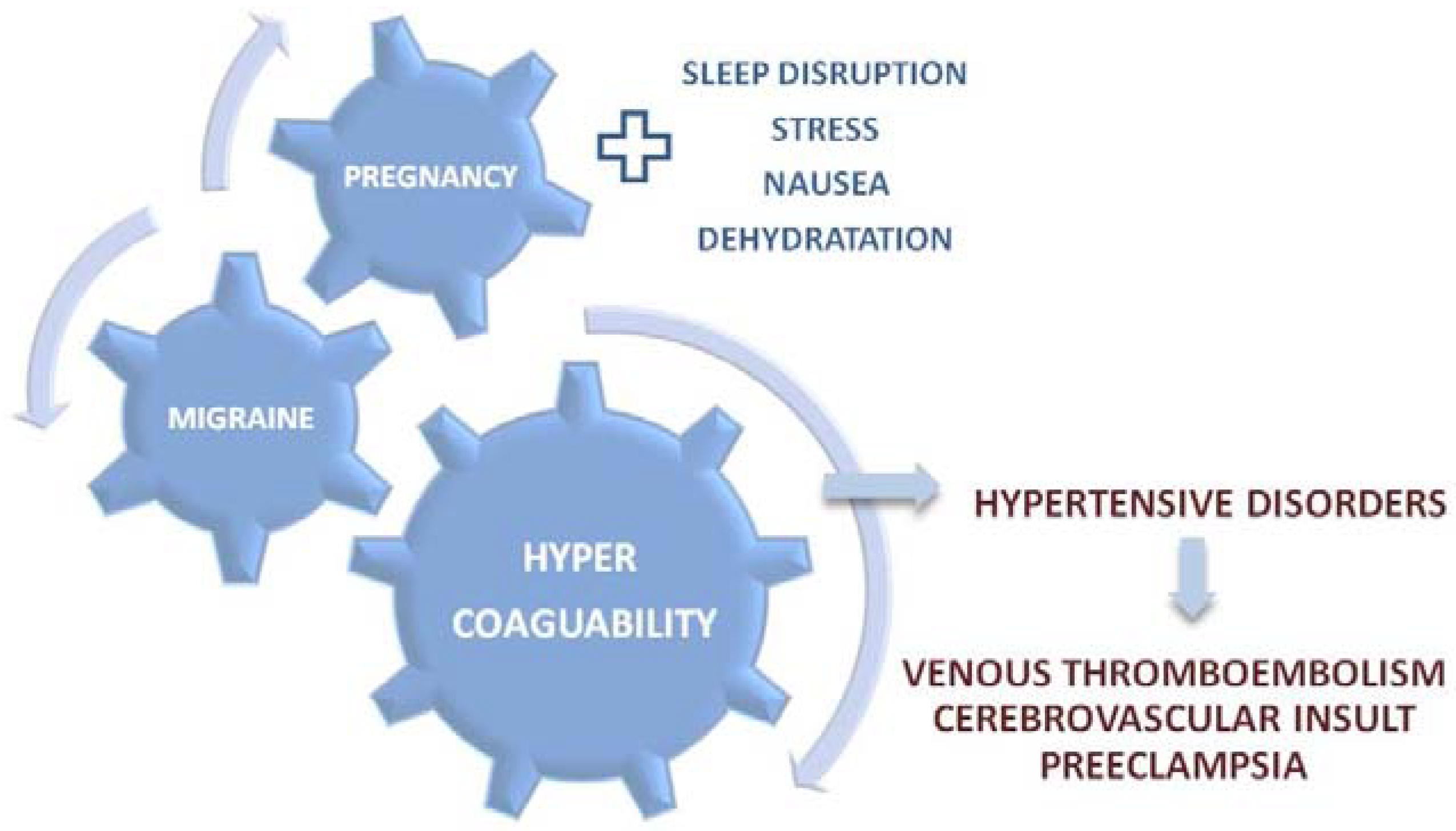
Pregnancy and migraine have another common characteristic, hypercoagulability (Figure 2). During pregnancy, hypercoagulability is a significant risk factor for some of the most serious cardiovascular incidents, including venous thromboembolism and cerebrovascular insult [36]. Furthermore, interference between hypercoagulability, cardiovascular disorders, and pre-eclampsia present another significant risk factor for the maternal, fetal, and neonatal morbidity and mortality [40]. Among patients with persistent migraine symptoms during pregnancy, symptom deterioration is associated with a 13-fold higher risk of a hypertensive disorder in pregnancy compared with the patients who experience migraine symptom improvement, or whose symptoms are remitted [41].
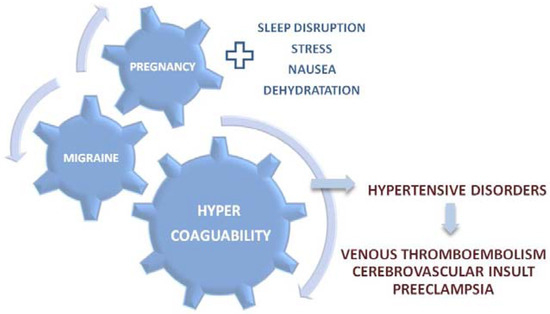
Figure 2.
Hypercoagulability as a crosslink between migraine, pregnancy, and maternal/fetal morbidity.
4. Physical Activity—Are There Two Sides to the Coin?
4.1. Physical Activity and Pregnancy
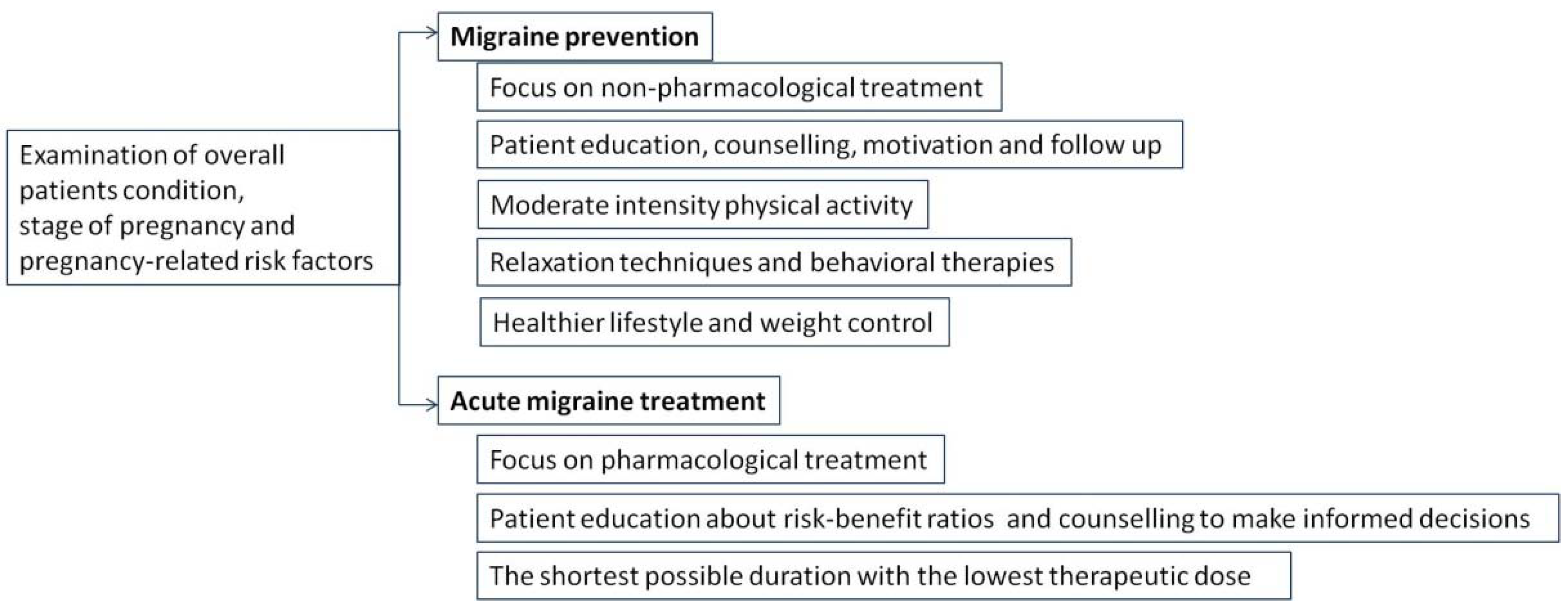
It appears that pharmacotherapy has only a moderate impact in migraine management, and pharmacological treatment options available for pregnant migrainous women seem to be very limited [42]. Non-pharmacological treatment, such as physical activity (PA), is usually recommended for mild migraine sufferers during pregnancy, and it is usually the therapy of choice for patients suffering from migraines during pregnancy. In order maximize the benefits of such a treatment, healthcare providers should motivate women of reproductive age to adopt healthy lifestyles that include regular PA, and migrainous women should be encouraged to engage in regular PA before becoming pregnant [43]. Furthermore, since pregnancy is recognized as a “teachable moment”, pregnant women are usually motivated to adapt healthy behavior changes, and physicians should take this opportunity as an advantage to motivate, encourage, and support their patients (Figure 3) [44]. Moderate-intensity PA is strongly recommended during pregnancy, and, according to the Royal College of Obstetrics and Gynecologists (RCOG), it should last at least 150 min per week. It may include climbing stairs, yoga, swimming, carrying grocery shopping bags, cycling, dancing, using the treadmill, or simply taking a walk [45].
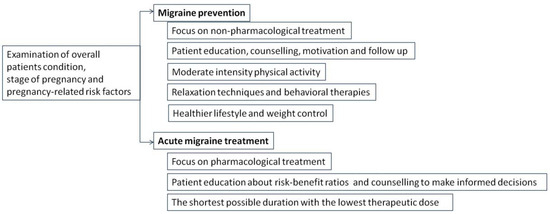
Figure 3.
Recommendations for migraine management during pregnancy.
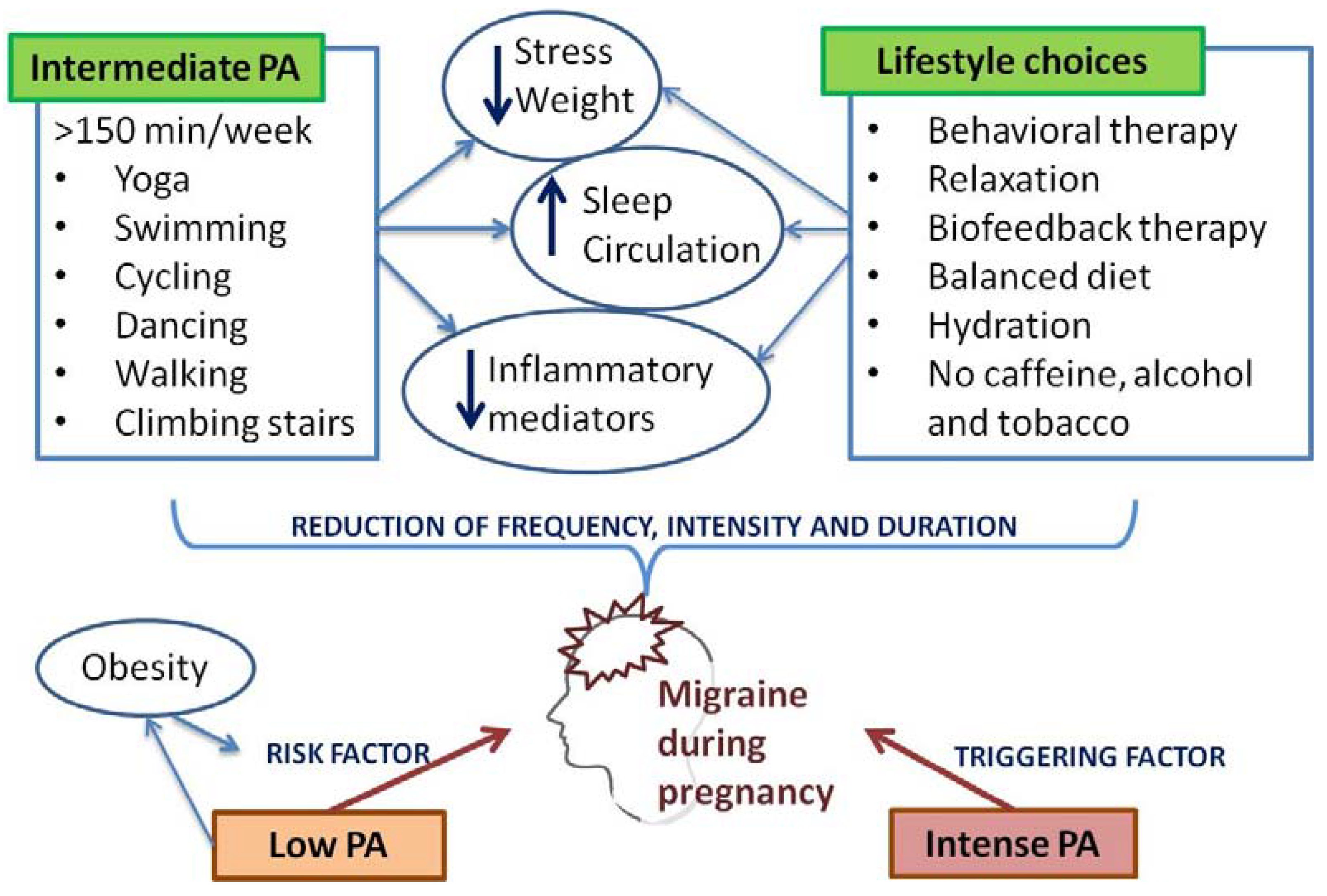
PA during pregnancy provides a range of benefits [46,47]. Regular exercise is helpful in stress reduction, better sleep, improved circulation, and weight management, all of which can be important aspects of migraine management [48]. When introduced during pregnancy for the first time, PA level must be started gradually. The patients’ overall condition, stage of pregnancy, as well as pregnancy-related risk factors should be cautiously analyzed before any type of exercise is proposed to a patient. The RCOG strongly advises patients not to engage in any activity which may involve the risk of falling or suffering a potential abdominal injury; it also stresses the danger of high-altitude environments and hot temperatures [45].
4.2. Physical Activity and Pathophysiology
PA interferes with inflammatory mediators, and it suppresses the levels of some stress hormones, including cortisol and growth hormone [49]. The migraine neuroinflammatory model implies a significant role of elevated inflammatory markers, cytokines, and adipocytokines in a migraine setting. Regular aerobic exercise has a suppressive effect on inflammatory mediators, and, eventually, it may lead to a suppression of the intensity, frequency, and duration of migraine attacks [50]. PA may activate several pathways, including endogenous opioid and cannabinoid systems, brain-derived neurotrophic factor, as well as some behavioral and psychological factors, which may eventually attenuate migraine symptoms. Hence, PA is a potentially effective strategy platform in migraine treatment and prevention [8]. Furthermore, PA stands as a promising, effective, and feasible complimentary or augmentative therapy for suboptimally treated migraineurs [50].
Integrated therapy modalities provide the highest level of care in medicine and therefore, behavioral therapy, combined with PA and pharmacotherapy, should be considered indispensable whenever possible. Cognitive behavioral therapy, relaxation, and biofeedback therapy interfere with lifestyle habits involved in the transformation of episodic to chronic migraines, a disabling condition that affects a substantial proportion of patients [51]. Relaxation exercises, such as prenatal Pilates or gentle stretching, may reduce everyday tension and pain and promote the overall wellbeing and quality of life during pregnancy, and these could be incorporated in pregnant women’s daily routine [52].
The majority of studies underline the significance of PA in migraine symptom management and acknowledge the role of PA as a relevant resource for migraine treatment. However, some authors did report ambiguous conclusions regarding the effectiveness of PA [53]. Indeed, PA was identified as a migraine-triggering factor by some authors, but this was primarily associated with intensive PA [54]. In a study published by Varkey et al., a cycle ergometer test was used until exhaustion to provoke migraine attacks. This group of authors concluded that maximal aerobic exercise may be a migraine-attack trigger, but they emphasized that it does not necessarily lead to a migraine attack [55]. Controversially, low PA, defined as less than 30 min of PA per week, was identified by Lebedeva et al. as a statistically significant risk factor for migraine development in women, but not in man [56].
A possible explanation behind PA as a migraine triggering factor is related to an increase in nitric oxide (NO) synthesis and to the consequential changes in blood flow [57,58]. PA is associated with intrinsic NO production; it augments endothelium-dependent vasodilatation [57,58], leads to cerebral arterial dilatation, and eventually it may act as a triggering factor for vascular headaches and migraines [59]. Additionally, it is a well-known fact that nitroglycerin and other drugs that generate NO are migraine triggers in the majority of migraine patients [60].
Even though some types of PA may be a triggering factor for migraines [48], regular PA has a prophylactic effect [48]. Altered thresholds triggering migraine attacks are the most likely cause of reduced attacks among migrainous people who exercise regularly [61]. Accumulated scientific evidence now provide more insight into the true connections between migraines and PA. Despite the fact that a systemic review did find moderate-quality evidence associating PA with a decreased number of migraine days, it could not draw clear conclusions regarding migraine attack duration or pain intensity [62]. Luckily, a more recent meta-analysis showed a clinically significant difference in pain intensity between patients engaged in regular PA and those who are not [63].
Finally, individuals with headaches tend to be less physically active; therefore, it remains challenging to establish clear connections between migraines and PA, since migraines are a well-known disabling condition that is commonly associated with limited social interferences and PA [64]. Cognitive decline, anxiety, depression, and sleep deprivation are frequently attributed to people suffering from migraines [65], and the advantages of PA may be used for symptom control and the management of these comorbidities as well [50].
5. Other Lifestyle Choices and Interventions
PA requires patients’ committed involvement, and it is often time consuming. Other lifestyle interventions and changes in daily habits, including a balanced daily calorie intake, hydration with non-caffeinated fluids, stress reduction, and complete alcohol and tobacco avoidance, may be an effective alternative for migraine frequency reduction as well (Figure 4) [66]. Most of these recommendations and interventions are the actual requirements of pregnancy, and their incorporation into pregnant migraineurs’ daily life could at least partially explain the tendency of frequency and severity of migraines to decrease during pregnancy [67].
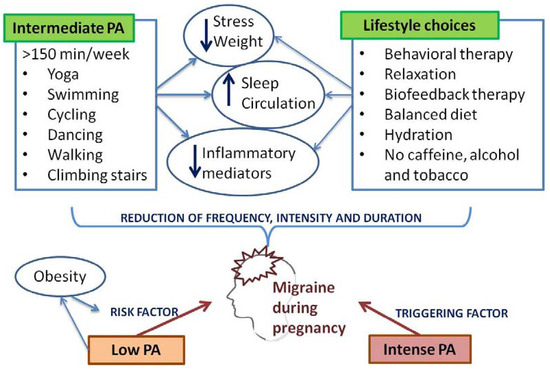
Figure 4.
Effects of physical activity and lifestyle choices on migraine during pregnancy.
Obesity is a well-known risk factor for pregnancy outcomes and for the well-being of the offspring [68,69], but it is also a risk factor associated with increased migraine prevalence and frequency [70,71]. There is no specific diet prescribed for migraine sufferers, but for all obese patients, a weight-loss diet is recommendable [72]. Diet during pregnancy should always be strictly balanced, and the required intake of micro- and macronutrients, as well as a minimum of 1600 kcal/day, ought to be provided to all patients [73]. The Mediterranean diet provides the nutritional requirements of pregnancy. In addition, it may result in weight loss, has several cardiovascular benefits, and it is the optimal diet to consume in pregnancy [74]. Other dietary regimes, such as the elimination diet, includes the identification and elimination of the migraine-provocative ingredient, and it may be an effective alternative as well [75].
The US Institute of Medicine (IoM) recommendations are based on age and gender. According to the IoM, water intake should range from 2.7 to 3.7 L, or nine to thirteen cups, per day [76]. IoM recommendations are in agreement with the requirements in pregnancy for water intake, which range from eight to twelve cups per day [77]. Adequate hydration accounts for balanced ion concentrations and plasma osmolality, which are important for migraine control and management [78]. Caffeine use may lead to an increase in migraine frequency, but its withdrawal may induce headaches as well. Migraine sufferers who choose to continue drinking caffeinated beverages should keep their daily intake consistent and should not exceed a daily consumption of 200 mg of caffeine daily [79]. Pregnant women are advised not to take more than 200 mg of caffeine per day as well. According to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), this moderate caffeine consumption is not a major contributor for a preterm birth or a miscarriage [80].
There is a well-known notion that alcohol consumption may trigger different types of headaches, but without taking into account individual dispositions and different cultural backgrounds, it is not justified to advise all patients with headaches to abstain from alcohol completely [81]. In several different pathways, alcoholic beverages may cause a migraine attack that includes an inflammatory pathophysiology mechanism, dehydration, vasodilation, toxicity, and the release of histamine, sulfites, tyramine, flavonoids and 5-HT [82]. Excessive and chronic use of alcohol is undoubtedly associated with poor migraine control and pregnancy outcome, but some reviews did find a beneficial effect of low doses of alcohol on migrainous patients [82]. Smoking can trigger migraine attacks, and this risk is dose-dependent on the total number of cigarettes smoked per day [83]. Aside from migraine management, behavioral interventions targeting alcohol and smoking cessation during pregnancy and the preconceptional period are crucial in avoiding poor pregnancy outcomes and the inevitable consequences for the offspring [84].
Neuronal and hormonal changes provoked by stress may have multiple relationships with migraines, but the exact mechanism by which stress causes migraine attacks remains unclear [85]. Sleep deprivation, insomnia, and a lower quality of life are well-known stress provokers, and by eliminating these primary causes of stress, the migraine incidence and symptom management may effectively be controlled [86].
Another helpful resource in migraine management may be the use of smartphones with installed apps and electronic diaries. A diary of attacks can give provide insight into the migraine frequency, duration, and potential triggers, and lead to better migraine management [87].
In Table 2, the types of physical activities and the outcomes associated with pregnancy are presented.

Table 2.
Type of physical activity and outcomes associated with pregnancy.
6. Pharmacotherapy
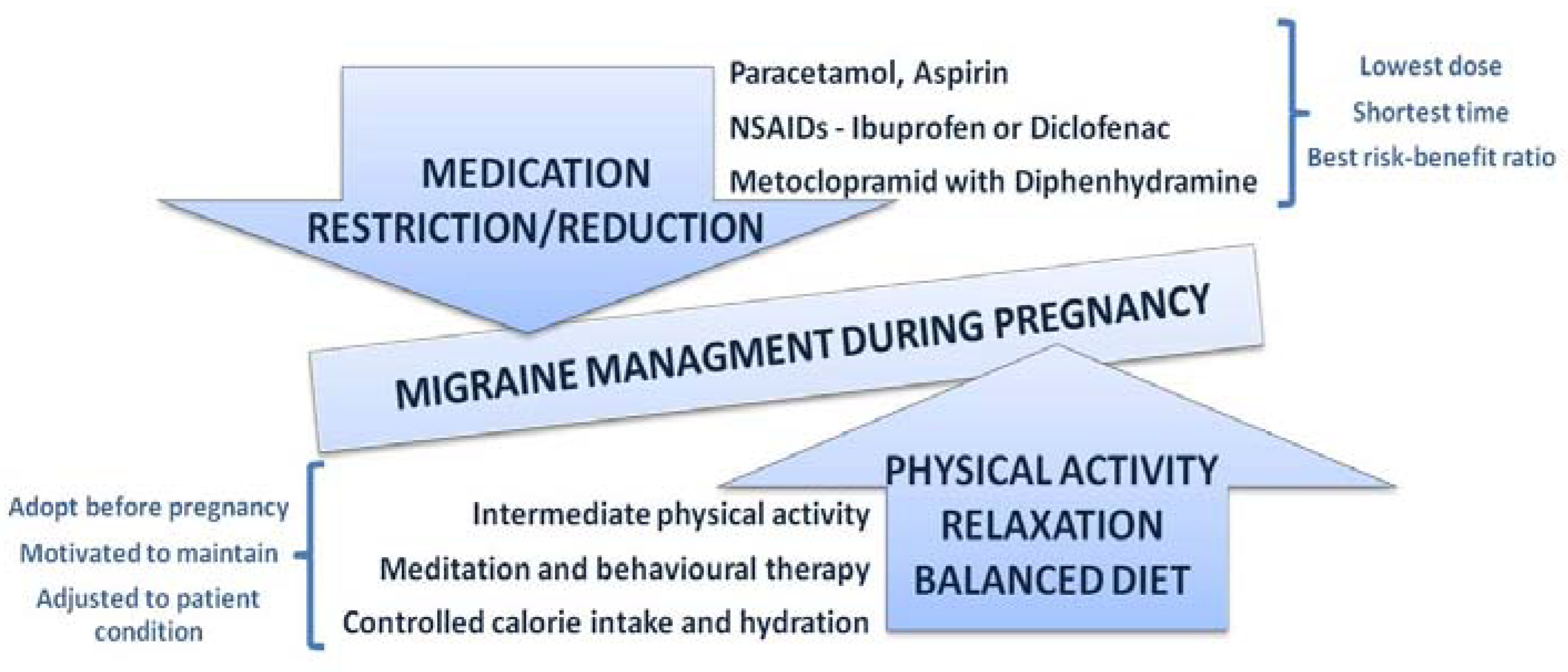
Prevention, early diagnosis, regular follow ups, and non-pharmacological treatment options are the cornerstones of migraine treatment whenever possible (Figure 5) [98]. Acute migraine often requires pharmacological treatment in order to reduce the attack frequency and duration and to provide the optimal treatment. Whenever a new drug is prescribed to a pregnant woman, treatment should be tailored to the shortest possible duration with the lowest therapeutic dose, and a risk–benefit ratio should be presented and clarified [99].

Figure 5.
Balancing migraine management in pregnancy.
Acetaminophen (paracetamol), metoclopramide, diphenhydramine, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and NSAID-triptan combinations are the usual pharmacotherapeutic options available for acute migraine attacks [100,101]. For headaches and pain management, paracetamol and NSAIDs are usually the most appropriate, although weaker opioids administrated over the short term are generally considered to be safe in pregnancy as well [102].
Paracetamol is recommended as the first choice of treatment for acute migraine during pregnancy, but the potential side effects of paracetamol use during pregnancy must not be neglected [103]. According to some study results, paracetamol might negatively interfere with the maternal hormones involved in embryonic brain development, or it might induce oxidative stress reaction, leading to neurotoxicity and to irreversible neuron loss [104].
NSAIDs are the second line of treatment, with ibuprofen and diclofenac being the most commonly used NSAIDs. The use of NSAIDs should be avoided for an extended period of time during the first and the third trimesters of pregnancy, since it is associated with certain risks and contraindications [105].
Although metoclopramide and diphenhydramine are not typically used for prolonged amounts of time, their use is considered safe during pregnancy. In pregnant women, metoclopramide administered with diphenhydramine effectively relieves migraine headaches when paracetamol fails [106].
Triptans and ergot derivates have been associated with an increased risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes, including prematurity, congenital abnormalities, miscarriages, and low birth weight [107], and only patients with severe attacks who are poor responders to other treatment options should consider the triptan approach [108].
Opioids are extremely rarely prescribed during pregnancy, and only for severe and intractable migraine pain. Opioid pain relievers can be addictive for both the mother and the newborn; their use in early pregnancy increases the risk of congenital abnormalities, and they are associated with preterm birth and fetal growth restriction [109].
Specially designed to prevent migraines, Gepants were the first oral agents ever introduced in migraine treatment. Gepants are CGRP (calcitonin-gene-related peptide) antagonists with proven activity in migraine prevention and treatment. Along with neurokinin A, NO, and substance P, CGRP leads to vasodilatation, protein extravasation, and sterile inflammation, causing nociceptor activation. Despite its effectiveness, the use of Gepants remains controversial due to possible long-term side effects, primarily those associated with vascular hemodynamic impairment [110].
Low-dose aspirin use during pregnancy has proven its benefits for some pregnancy-related disorders, and despite insufficient evidence proving its usefulness in migraine treatment during pregnancy, a 100 mg dose of aspirin seems, at least, to be harmless [111].
7. Conclusions
Migraines, pregnancy, and physical activity intersect in a complex web of physiological and lifestyle factors. Pregnant women with migraines face the challenge of managing their condition while reaping the benefits of physical activity during this critical period. Through collaboration with healthcare providers and the adoption of individualized management strategies, women can strike a balance that supports both their own well-being and the healthy development of their unborn child.
Physical activity may be a reliable treatment option for pregnant women, but it is essential to approach physical activity gradually to avoid triggering migraines. In terms of future perspectives, ongoing research continues to explore the relationship between migraines, physical activity, and potential therapeutic interventions. Advances in personalized medicine may lead to tailored approaches for managing migraines based on individual’s specific triggers and responses. Engaging in regular physical activity has been linked to a potential reduction in the frequency and severity of migraines; however, this relationship is complex and varies among individuals. Some individuals find exercise helpful, while others may experience migraines that are triggered by physical activity. Therefore, further research is needed to understand the mechanisms behind this connection and to develop personalized recommendations for migraine management through physical activity.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.L., D.N. and M.J.; methodology, M.L., D.N., M.J., Z.M. and S.M.; writing—original draft preparation, M.L., D.N., M.J., Z.M. and S.M.; supervision, M.L., D.N., M.J. and S.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Pieczykolan, A.; Rzońca, E.; Grzesik-Gąsior, J.; Korżyńska-Piętas, M.; Iwanowicz-Palus, G.; Bień, A. Acceptance of Pregnancy-Induced Disease and Intrapersonal Resistance Resources of Pregnant Women-Preliminary Report. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, C.J.; Chang, J.; Callaghan, W.M.; Whitehead, S.J. Pregnancy-related mortality in the United States, 1991–1997. Obstet. Gynecol. 2003, 101, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rissardo, J.P.; Caprara, A.L. Cerebrovascular Disorders during Pregnancy. Matrix Sci. Medica 2023, 7, 82–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, R.; Schwedt, T.J.; Kim, S.K.; Dumkrieger, G.; Chong, C.D.; Dodick, D.W. Effect of Migraine on Pregnancy Planning: Insights from the American Registry for Migraine Research. In Mayo Clinic Proceedings; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Volume 95, pp. 2079–2089. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, W.; Cao, X.; Zhao, J.; Yang, J.; Cen, Y.; He, J.; Luo, J.; Zhong, Y.; Luo, Y.; Wang, X.; et al. Health-related quality of life and associated factors in Chinese menstrual migraine patients: A cross-sectional study. BMC Womens Health 2022, 22, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, K.T.; Robbins, M.S. Migraine treatment in pregnant women presenting to acute care: A retrospective observational study. Headache J. Head Face Pain 2019, 59, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seng, E.K.; Martin, P.R.; Houle, T.T. Lifestyle factors and migraine. Lancet Neurol. 2022, 21, 911–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.J.; Chu, M.K. Exercise in Treatment of Migraine Including Chronic Migraine. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2021, 25, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pescador Ruschel, M.A.; De Jesus, O. Migraine Headache. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- The International Classification of Headache Disorders 3rd Edition. Available online: https://ichd-3.org (accessed on 3 September 2023).
- Barus, J.; Sudharta, H.; Adriani, D. Study of the Mechanisms and Therapeutic Approaches of Migraine in Women and Pregnancy: A Literature Review. Cureus 2023, 15, e35284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation. GBD Results Tool; IHME, University of Washington Seattle: Seattle, WA, USA, 2020; Available online: http://ghdx.healthdata.org/gbd-results-tool (accessed on 3 September 2023).
- Safiri, S.; Pourfathi, H.; Eagan, A.; Mansournia, M.A.; Khodayari, M.T.; Sullman, M.J.M.; Kaufman, J.; Collins, G.; Dai, H.; Bragazzi, N.L.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden of migraine in 204 countries and territories, 1990 to 2019. Pain 2022, 163, e293–e309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burch, R. Epidemiology and Treatment of Menstrual Migraine and Migraine During Pregnancy and Lactation: A Narrative Review. Headache 2020, 60, 200–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, N.; Linnman, C.; Brawn, J.; Burstein, R.; Becerra, L.; Borsook, D. Her versus his migraine: Multiple sex differences in brain function and structure. Brain 2012, 135, 2546–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, M.F.; Tumminello, A.; Marconi, M.; Gualano, M.R.; Santoro, P.E.; Malorni, W.; Moscato, U. Sex and gender differences in migraines: A narrative review. Neurol. Sci. 2022, 43, 5729–5734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vos, T.; Allen, C.; Arora, M.; Barber, R.M.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Brown, A.; Carter, A.; Casey, D.C.; Charlson, F.J.; Chen, A.Z.; et al. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 310 diseases and injuries, 1990–2015: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2015. Lancet 2016, 388, 1545–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacGregor, E.A.; Gendolla, A. Hormonal Influences on Headache. In Handbook of Headache; Martelletti, P., Steiner, T.J., Eds.; Springer: Milano, Italy, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yucel, A.; Thach, A.; Kumar, S.; Loden, C.; Bensink, M.; Goldfarb, N. Estimating the economic burden of migraine on US employers. Am. J. Manag. Care 2020, 26, e403–e408. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Victor, T.W.; Hu, X.; Campbell, J.C.; Buse, D.C.; Lipton, R.B. Migraine prevalence by age and sex in the United States: A life-span study. Cephalalgia 2010, 30, 1065–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macgregor, E.A.; Rosenberg, J.D.; Kurth, T. Sex-related differences in epidemiological and clinic-based headache studies. Headache 2011, 51, 843–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonini, M.C. Gender differences in migraine. Neurol. Sci. 2018, 39 (Suppl. 1), 77–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetvik, K.G.; MacGregor, E.A. Sex differences in the epidemiology, clinical features, and pathophysiology of migraine. Lancet Neurol. 2017, 16, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaruelle, Z.; Ivanova, T.A.; Khan, S.; Negro, A.; Ornello, R.; Raffaelli, B.; Terrin, A.; Mitsikostas, D.D.; Reuter, U.; European Headache Federation School of Advanced Studies (EHF-SAS). Male and female sex hormones in primary headaches. J. Headache Pain 2018, 19, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buse, D.C.; Fanning, K.M.; Reed, M.L.; Murray, S.; Dumas, P.K.; Adams, A.M.; Lipton, R.B. Life With Migraine: Effects on Relationships, Career, and Finances From the Chronic Migraine Epidemiology and Outcomes (CaMEO) Study. Headache 2019, 59, 1286–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, A. The pathophysiology of migraine: Implications for clinical management. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vetvik, K.G. Epidemiology of Migraine in Men and Women. In Gender and Migraine. Headache; Maassen van den Brink, A., MacGregor, E., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccininni, M.; Brinks, R.; Rohmann, J.L.; Kurth, T. Estimation of migraine prevalence considering active and inactive states across different age groups. J. Headache Pain 2023, 24, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixit, A.; Bhardwaj, M.; Sharma, B. Headache in pregnancy: A nuisance or a new sense? Obstet. Gynecol. Int. 2012, 2012, 697697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashina, S.; Mitsikostas, D.D.; Lee, M.J.; Yamani, N.; Wang, S.J.; Messina, R.; Ashina, H.; Buse, D.C.; Pozo-Rosich, P.; Jensen, R.H.; et al. Tension-type headache. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negro, A.; Delaruelle, Z.; Ivanova, T.A.; Khan, S.; Ornello, R.; Raffaelli, B.; Terrin, A.; Reuter, U.; Mitsikostas, D.D.; European Headache Federation School of Advanced Studies (EHF-SAS). Headache and pregnancy: A systematic review. J. Headache Pain 2017, 18, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, R.; Tassorelli, C.; Mangione, A.S.; Smeraldi, A.; Allena, M.; Sandrini, G.; Nappi, G.; Nappi, R.E. Effect of sex and estrogens on neuronal activation in an animal model of migraine. Headache 2013, 53, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szewczyk, A.K.; Ulutas, S.; Aktürk, T.; Al-Hassany, L.; Börner, C.; Cernigliaro, F.; Kodounis, M.; Lo Cascio, S.; Mikolajek, D.; Onan, D.; et al. Prolactin and oxytocin: Potential targets for migraine treatment. J. Headache Pain 2023, 24, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, B.N.; Kallianpur, R.; Price, T.J.; Akopian, A.N.; Dussor, G.O. Prolactin signaling modulates stress-induced behavioral responses in a preclinical mouse model of migraine. Headache 2022, 62, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warfvinge, K.; Krause, D.; Edvinsson, L. The distribution of oxytocin and the oxytocin receptor in rat brain: Relation to regions active in migraine. J. Headache Pain 2020, 21, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allais, G.; Chiarle, G.; Sinigaglia, S.; Mana, O.; Benedetto, C. Migraine during pregnancy and in the puerperium. Neurol. Sci. 2019, 40 (Suppl. 1), 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, S.; Dassan, P.; Piercy, C.N. Managing migraine in pregnancy. BMJ 2018, 360, k80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossman, T.B.; Robbins, M.S.; Govindappagari, S.; Dayal, A.K. Delivery Outcomes of Patients with Acute Migraine in Pregnancy: A Retrospective Study. Headache 2017, 57, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lackovic, M.; Nikolic, D.; Jankovic, M.; Rovcanin, M.; Mihajlovic, S. Stroke vs. Preeclampsia: Dangerous Liaisons of Hypertension and Pregnancy. Medicina 2023, 59, 1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, C.; Chen, Y.Y.; Dong, J.F. Prothrombotic state associated with preeclampsia. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2021, 28, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giorgione, V.; Cauldwell, M.; Thilaganathan, B. Pre-eclampsia and Cardiovascular Disease: From Pregnancy to Postpartum. Eur. Cardiol. 2023, 18, e42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dipietro, L.; Evenson, K.R.; Bloodgood, B.; Sprow, K.; Troiano, R.P.; Piercy, K.L.; Vaux-Bjerke, A.; Powell, K.E.; 2018 Physical Activity Guidelines Advisory Committee*. Benefits of Physical Activity during Pregnancy and Postpartum: An Umbrella Review. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2019, 51, 1292–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susanti, R.; Muhammad, S. Migraine and pregnancy: What should we know. J. Obgın. Emas. 2020, 4, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockliffe, L.; Peters, S.; Heazell, A.E.; Smith, D.M. Understanding pregnancy as a teachable moment for behaviour change: A comparison of the COM-B and teachable moments models. Health Psychol. Behav. Med. 2022, 10, 41–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (RCOG). Physical Activity and Pregnancy; Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (RCOG): London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Calhoun, A.H. Migraine Treatment in Pregnancy and Lactation. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2017, 21, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovcanin, M.; Jankovic, S.; Mikovic, Z.; Sipetic Grujicic, S.; Ersk, I.R.B.; Lackovic, M.; Dimitrijevic, D.; Simanic, S.; Vujcic, I. The Translation and Cross-Cultural Adaptation of the Pregnancy Physical Activity Questionnaire: Validity and Reliability of a Serbian Version (PPAQ-SRB). Healthcare 2022, 10, 1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, F.M.; Aristeidou, S.; Baraldi, C.; Czapinska-Ciepiela, E.K.; Ariadni, D.D.; Di Lenola, D.; Fenech, C.; Kampouris, K.; Karagiorgis, G.; Braschinsky, M.; et al. The association between migraine and physical exercise. J. Headache Pain 2018, 19, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, M.; Pace, A. Exercise and Migraine Prevention: A Review of the Literature. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2020, 24, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irby, M.B.; Bond, D.S.; Lipton, R.B.; Nicklas, B.; Houle, T.T.; Penzien, D.B. Aerobic Exercise for Reducing Migraine Burden: Mechanisms, Markers, and Models of Change Processes. Headache 2016, 56, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pistoia, F.; Sacco, S.; Carolei, A. Behavioral therapy for chronic migraine. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2013, 17, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraz, V.S.; Peixoto, C.; Ferreira Resstel, A.P.; Cerqueira de Paula, Y.T.; Gomes de Souza Pegorare, A.B. Effect of the pilates method on pain and quality of life in pregnancy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2023, 35, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindblad, M.; Hougaard, A.; Amin, F.M.; Ashina, M. Can migraine aura be provoked experimentally? A systematic review of potential methods for the provocation of migraine aura. Cephalalgia 2017, 37, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varkey, E.; Grüner Sveälv, B.; Edin, F.; Ravn-Fischer, A.; Cider, Å. Provocation of Migraine after Maximal Exercise: A Test-Retest Study. Eur. Neurol. 2017, 78, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyakova, E.Y.; Kapilevich, L.V.; Shylko, V.G.; Popov, S.V.; Anfinogenova, Y. Physical exercise associated with NO production: Signaling pathways and significance in health and disease. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2015, 3, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebedeva, E.R.; Kobzeva, N.R.; Gilev, D.V.; Olesen, J. Factors Associated with Primary Headache according to Diagnosis, Sex, and Social Group. Headache 2016, 56, 341–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, C.; Nishioka, K.; Umemura, T.; Jitsuiki, D.; Sakagutchi, A.; Kawamura, M.; Chayama, K.; Yoshizumi, M.; Higashi, Y. Acute moderate-intensity exercise induces vasodilation through an increase in nitric oxide bioavailiability in humans. Am. J. Hypertens. 2007, 20, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karsan, N.; Gosalia, H.; Goadsby, P.J. Molecular Mechanisms of Migraine: Nitric Oxide Synthase and Neuropeptides. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, A.C.; Hoffmann, W.; Meisinger, C.; Evers, S.; Vennemann, M.; Pfaffenrath, V.; Fendrich, K.; Baumeister, S.E.; Kurth, T.; Berger, K. Association between lifestyle factors and headache. J. Headache Pain 2011, 12, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olesen, J. The role of nitric oxide (NO) in migraine, tension-type headache and cluster headache. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 120, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ovadia, C. Prescribing for pregnancy: Managing chronic headache and migraine. Drug Ther. Bull. 2020, 59, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemmens, J.; De Pauw, J.; Van Soom, T.; Michiels, S.; Versijpt, J.; van Breda, E.; Castien, R.; De Hertogh, W. The effect of aerobic exercise on the number of migraine days, duration and pain intensity in migraine: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis. J. Headache Pain 2019, 20, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varangot-Reille, C.; Suso-Martí, L.; Romero-Palau, M.; Suárez-Pastor, P.; Cuenca-Martínez, F. Effects of Different Therapeutic Exercise Modalities on Migraine or Tension-Type Headache: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis with a Replicability Analysis. J. Pain 2022, 23, 1099–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannix, S.; Skalicky, A.; Buse, D.C.; Desai, P.; Sapra, S.; Ortmeier, B.; Widnell, K.; Hareendran, A. Measuring the impact of migraine for evaluating outcomes of preventive treatments for migraine headaches. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2016, 14, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Kang, Y.; Cho, S.J. Subjective cognitive decline in patients with migraine and its relationship with depression, anxiety, and sleep quality. J. Headache Pain 2017, 18, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbetou, M.; Adoukonou, T. Lifestyle modifications for migraine management. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 719467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kardes, G.; Hadimli, A.; Ergenoglu, A.M. Determination of the Frequency of Migraine Attacks in Pregnant Women and the Ways They Cope with Headaches: A Cross-Sectional Study. Healthcare 2023, 11, 2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lackovic, M.; Filimonovic, D.; Mihajlovic, S.; Milicic, B.; Filipovic, I.; Rovcanin, M.; Dimitrijevic, D.; Nikolic, D. The Influence of Increased Prepregnancy Body Mass Index and Excessive Gestational Weight Gain on Pregnancy Course and Fetal and Maternal Perinatal Outcomes. Healthcare 2020, 8, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihajlovic, S.; Nikolic, D.; Milicic, B.; Santric-Milicevic, M.; Glushkova, N.; Nurgalieva, Z.; Lackovic, M. Association of Pre-Pregnancy Obesity and COVID-19 with Poor Pregnancy Outcome. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thierry, A.; Mendinatou, A.; Aude, G.; Bohr, S.C.; Dismand, H. Migraine and obesity in parakou in 2017: Case-control study. Pain Stud. Treat. 2018, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gelaye, B.; Sacco, S.; Brown, W.J.; Nitchie, H.L.; Ornello, R.; Peterlin, B.L. Body composition status and the risk of migraine: A meta-analysis. Neurology 2017, 88, 1795–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazerani, P. Migraine and Diet. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marangoni, F.; Cetin, I.; Verduci, E.; Canzone, G.; Giovannini, M.; Scollo, P.; Corsello, G.; Poli, A. Maternal Diet and Nutrient Requirements in Pregnancy and Breastfeeding. An Italian Consensus Document. Nutrients 2016, 8, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaragoza-Martí, A.; Ruiz-Ródenas, N.; Herranz-Chofre, I.; Sánchez-SanSegundo, M.; Serrano Delgado, V.C.; Hurtado-Sánchez, J.A. Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet in Pregnancy and Its Benefits on Maternal-Fetal Health: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Front Nutr. 2022, 9, 813942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskatel, L.S.; Zhang, N. Migraine and Diet: Updates in Understanding. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2022, 22, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panel on Dietary Reference Intakes for Electrolytes and Water Standing Committee on the Scientific Evaluation of Dietary Reference Intakes Food and Nutrition. Board Dietary Reference Intakes for Water, Potassium, Sodium, Chloride, and Sulfate; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; p. 638. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, N.; Zhang, F.; Chen, S.; Han, F.; Lin, G.; Zhai, Y.; He, H.; Zhang, J.; Ma, G. Associations between hydration state and pregnancy complications, maternal-infant outcomes: Protocol of a prospective observational cohort study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2020, 20, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blau, J.N. Water deprivation: A new migraine precipitant. Headache 2005, 45, 757–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowaczewska, M.; Wiciński, M.; Kaźmierczak, W. The Ambiguous Role of Caffeine in Migraine Headache: From Trigger to Treatment. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ACOG Committee. Opinion No. 462: Moderate caffeine consumption during pregnancy. Obstet. Gynecol. 2010, 116 Pt 1, 467–468. [Google Scholar]
- Dueland, A.N. Headache and Alcohol. Headache 2015, 55, 1045–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panconesi, A. Alcohol and migraine: Trigger factor, consumption, mechanisms. A review. J. Headache Pain 2008, 9, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinberger, A.H.; Seng, E.K. The Relationship of Tobacco Use and Migraine: A Narrative Review. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2023, 27, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heslehurst, N.; Hayes, L.; Jones, D.; Newham, J.; Olajide, J.; McLeman, L.; McParlin, C.; de Brun, C.; Azevedo, L. The effectiveness of smoking cessation, alcohol reduction, diet and physical activity interventions in changing behaviours during pregnancy: A systematic review of systematic reviews. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stubberud, A.; Buse, D.C.; Kristoffersen, E.S.; Linde, M.; Tronvik, E. Is there a causal relationship between stress and migraine? Current evidence and implications for management. J. Headache Pain 2021, 22, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiseo, C.; Vacca, A.; Felbush, A.; Filimonova, T.; Gai, A.; Glazyrina, T.; Hubalek, I.A.; Marchenko, Y.; Overeem, L.H.; Piroso, S.; et al. Migraine and sleep disorders: A systematic review. J. Headache Pain 2020, 21, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minen, M.T.; Jalloh, A.; Ortega, E.; Powers, S.W.; Sevick, M.A.; Lipton, R.B. User Design and Experience Preferences in a Novel Smartphone Application for Migraine Management: A Think Aloud Study of the RELAXaHEAD Application. Pain Med. 2019, 20, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana Carvalho, A.P.; Dufresne, S.S.; Rogerio de Oliveira, M.; Couto Furlanetto, K.; Dubois, M.; Dallaire, M.; Ngomo, S.; da Silva, R.A. Effects of lumbar stabilization and muscular stretching on pain, disabilities, postural control and muscle activation in pregnant woman with low back pain. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2020, 56, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coll, C.V.N.; Domingues, M.R.; Stein, A.; da Silva, B.G.C.; Bassani, D.G.; Hartwig, F.P.; da Silva, I.C.M.; da Silveira, M.F.; da Silva, S.G.; Bertoldi, A.D. Efficacy of Regular Exercise During Pregnancy on the Prevention of Postpartum Depression: The PAMELA Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e186861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, R.; Refoyo, I.; Coteron, J.; Franco, E. Exercise during pregnancy has a preventative effect on excessive maternal weight gain and gestational diabetes. A randomized controlled trial. Braz. J. Phys. Ther. 2019, 23, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Blanque, R.; Aguilar-Cordero, M.J.; Marín-Jiménez, A.E.; Menor-Rodríguez, M.J.; Montiel-Troya, M.; Sánchez-García, J.C. Water Exercise and Quality of Life in Pregnancy: A Randomised Clinical Trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghandali, N.Y.; Iravani, M.; Habibi, A.; Cheraghian, B. The effectiveness of a Pilates exercise program during pregnancy on childbirth outcomes: A randomised controlled clinical trial. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2021, 21, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMillan, A.G.; May, L.E.; Gaines, G.G.; Isler, C.; Kuehn, D. Effects of Aerobic Exercise during Pregnancy on 1-Month Infant Neuromotor Skills. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2019, 51, 1671–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brik, M.; Fernández-Buhigas, I.; Martin-Arias, A.; Vargas-Terrones, M.; Barakat, R.; Santacruz, B. Does exercise during pregnancy impact on maternal weight gain and fetal cardiac function? A randomized controlled trial. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2019, 53, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alomairah, S.A.; Knudsen, S.P.; Roland, C.B.; Molsted, S.; Clausen, T.D.; Bendix, J.M.; Løkkegaard, E.; Jensen, A.K.; Larsen, J.E.; Jennum, P.; et al. Effects of Two Physical Activity Interventions on Sleep and Sedentary Time in Pregnant Women. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 5359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, S.M.; Isler, C.; Haven, K.; Newton, E.; Kuehn, D.; Kelley, G.; Chasan-Taber, L.; May, L.E. Moderate intensity aerobic exercise during pregnancy and 1-month infant Morphometry. Birth Defects Res. 2021, 113, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, L.E.; McDonald, S.; Forbes, L.; Jones, R.; Newton, E.; Strickland, D.; Isler, C.; Haven, K.; Steed, D.; Kelley, G.; et al. Influence of maternal aerobic exercise during pregnancy on fetal cardiac function and outflow. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. MFM 2020, 2, 100095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eigenbrodt, A.K.; Ashina, H.; Khan, S.; Diener, H.C.; Mitsikostas, D.D.; Sinclair, A.J.; Pozo-Rosich, P.; Martelletti, P.; Ducros, A.; Lantéri-Minet, M.; et al. Diagnosis and management of migraine in ten steps. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2021, 17, 501–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ather, A.; Zhong, S.; Rosenbaum, A.J.; Quinonez, R.B.; Khan, A.A. Pharmacotherapy during pregnancy: An endodontic perspective. J. Endod. 2020, 46, 1185–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turankar, T.; Sorte, A.; Wanjari, M.B.; Chakole, S.; Sawale, S. Relation and Treatment Approach of Migraine in Pregnancy and Breastfeeding. Cureus 2023, 15, e36828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, E.; Khor, K.E.; Kennedy, D.; Chutatape, A.; Sharma, S.; Vancaillie, T.; Demirkol, A. Medication Use and Pain Management in Pregnancy: A Critical Review. Pain Pract. 2019, 19, 875–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peck, J.; Urits, I.; Zeien, J.; Hoebee, S.; Mousa, M.; Alattar, H.; Kaye, A.D.; Viswanath, O. A Comprehensive Review of Over-the-counter Treatment for Chronic Migraine Headaches. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2020, 24, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amundsen, S.; Nordeng, H.; Nezvalová-Henriksen, K.; Stovner, L.J.; Spigset, O. Pharmacological treatment of migraine during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2015, 11, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liew, Z.; Ritz, B.; Rebordosa, C.; Lee, P.C.; Olsen, J. Acetaminophen use during pregnancy, behavioral problems, and hyperkinetic disorders. JAMA Pediatr. 2014, 168, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marhofer, D.; Jaksch, W.; Aigmüller, T.; Jochberger, S.; Urlesberger, B.; Pils, K.; Maier, B.; Likar, R.; Kayer, B.; Wallner, R.; et al. Schmerztherapie in der Schwangerschaft: Eine expertInnenbasierte interdisziplinäre Konsensus-Empfehlung [Pain management during pregnancy: An expert-based interdisciplinary consensus recommendation]. Schmerz 2021, 35, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Childress, K.M.S.; Dothager, C.; Gavard, J.A.; Lebovitz, S.; Laska, C.; Mostello, D.J. Metoclopramide and Diphenhydramine: A Randomized Controlled Trial of a Treatment for Headache in Pregnancy when Acetaminophen Alone Is Ineffective (MAD Headache Study). Am. J. Perinatol. 2018, 35, 1281–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bérard, A.; Strom, S.; Zhao, J.P.; Kori, S.; Albrecht, D. Dihydroergotamine and triptan use to treat migraine during pregnancy and the risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, W.J. Acute Migraine Treatment. Contin. Lifelong Learn. Neurol. 2015, 21, 953–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdy, M.M.; Desai, R.J.; Brogly, S.B. Prescription Opioids in Pregnancy and Birth Outcomes: A Review of the Literature. J. Pediatr. Genet. 2015, 4, 56–70. [Google Scholar]
- Rissardo, J.P.; Caprara, A.L.F. Gepants for Acute and Preventive Migraine Treatment: A Narrative Review. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afridi, S.K. Current concepts in migraine and their relevance to pregnancy. Obstet. Med. 2018, 11, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).