Synovial Fluid Markers and Extracellular Vesicles in Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Synovial Fluid Markers
3. Newly Established Markers
3.1. Aggrecan
3.2. Matrix Metalloproteinases
3.3. Glucosyl–Galactosyl–Pyridinoline
3.4. Hyaluronic Acid
3.5. S100 Proteins
3.6. Cytokines/Inhibitors/Adipocytokines
3.7. Immunological Markers
4. Novel Markers
4.1. ADAMEDC1
4.2. MAGE-I-mRNA
4.3. Non-Coding RNAs
4.4. GFAP and A1BG
4.5. ORM2
4.6. 14-3-3η Protein
5. Specific Applications of Extracellular Vesicles
5.1. Heat Shock Proteins
5.2. Lysophosphatidylcholine, Sphingolipids, and Cholesterol
5.3. Proteomic Analysis of EVs
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Majka, D.S.; Holers, V.M. Can We Accurately Predict the Development of Rheumatoid Arthritis in the Preclinical Phase? Arthritis Rheum. 2003, 48, 2701–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landewé, R.B.M. The Benefits of Early Treatment in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Confounding by Indication, and the Issue of Timing. Arthritis Rheum. 2003, 48, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lard, L.R.; Visser, H.; Speyer, I.; Vander Horst-Bruinsma, I.E.; Zwinderman, A.H.; Breedveld, F.C.; Hazes, J.M.W. Early versus Delayed Treatment in Patients with Recent-Onset Rheumatoid Arthritis: Comparison of Two Cohorts Who Received Different Treatment Strategies. Am. J. Med. 2001, 111, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almutairi, K.B.; Nossent, J.C.; Preen, D.B.; Keen, H.I.; Inderjeeth, C.A. The Prevalence of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review of Population-Based Studies. J. Rheumatol. 2021, 48, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamin, O.; Goyal, A.; Lappin, S.L. Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARD). In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: St. Petersburg, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnan, Y.; Grodzinsky, A.J. Cartilage Diseases. Matrix Biol. 2018, 71–72, 51–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goekoop-Ruiterman, Y.P.M.; De Vries-Bouwstra, J.K.; Allaart, C.F.; Van Zeben, D.; Kerstens, P.J.S.M.; Hazes, J.M.W.; Zwinderman, A.H.; Ronday, H.K.; Han, K.H.; Westedt, M.L.; et al. Clinical and Radiographic Outcomes of Four Different Treatment Strategies in Patients with Early Rheumatoid Arthritis (the Best Study): A Randomized, Controlled Trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52, 3381–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, U.; Anwar, A.; Savage, R.S.; Costa, M.L.; MacKay, N.; Filer, A.; Raza, K.; Watts, R.A.; Winyard, P.G.; Tarr, J.; et al. Biomarkers of Early Stage Osteoarthritis, Rheumatoid Arthritis and Musculoskeletal Health. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, S.F.; Bojesen, S.E.; Schnohr, P.; Nordestgaard, B.G. Elevated Rheumatoid Factor and Long Term Risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Prospective Cohort Study. BMJ 2012, 345, e5244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, E.A.; Crawford, A.; English, A.; Henshaw, K.; Mundy, J.; Corscadden, D.; Chapman, T.; Emery, P.; Hatton, P.; McGonagle, D. Synovial Fluid Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Health and Early Osteoarthritis: Detection and Functional Evaluation at the Single-Cell Level. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58, 1731–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, D.S.; Rooney, M.E. The Human Synovial Fluid Proteome: A Key Factor in the Pathology of Joint Disease. Proteom.—Clin. Appl. 2007, 1, 889–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, A.Y.; McCarty, W.J.; Masuda, K.; Firestein, G.S.; Sah, R.L. A Systems Biology Approach to Synovial Joint Lubrication in Health, Injury, and Disease. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Syst. Biol. Med. 2012, 4, 15–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choy, E. Understanding the Dynamics: Pathways Involved in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatology 2012, 51, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, A.D.; Turner, A.L.; Braine, E.L.; Pobjoy, J.; Lenzo, J.C.; Hamilton, J.A. Regulation of Systemic and Local Myeloid Cell Subpopulations by Bone Marrow Cell-Derived Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor in Experimental Inflammatory Arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 2340–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonezawa, I.; Okuda, T.; Won, J.; Sakoda, J.; Nakahara, D.; Nojiri, H.; Muto, O.; Momomura, R.; Kaneko, K. Retrodental Mass in Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Spinal Disord. Tech. 2013, 26, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, M.; Raju, R.; Radhakrishnan, A.; Nanjappa, V.; Muthusamy, B.; Singh, K.; Kuppusamy, D.; Lingala, B.T.; Pan, A.; Mathur, P.P.; et al. A Bioinformatics Resource for TWEAK-Fn14 Signaling Pathway. J. Signal Transduct. 2012, 2012, 376470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, C.E.; Borchers, C.H. Mass Spectrometry Based Biomarker Discovery, Verification, and Validation—Quality Assurance and Control of Protein Biomarker Assays. Mol. Oncol. 2014, 8, 840–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, L.; Bhattacharjee, M.; Ahmad, S.; Nirujogi, R.S.; Renuse, S.; Subbannayya, Y.; Marimuthu, A.; Srikanth, S.M.; Raju, R.; Dhillon, M.; et al. Differential Proteomic Analysis of Synovial Fluid from Rheumatoid Arthritis and Osteoarthritis Patients. Clin. Proteom. 2014, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cretu, D.; Prassas, I.; Saraon, P.; Batruch, I.; Gandhi, R.; Diamandis, E.P.; Chandran, V. Identification of Psoriatic Arthritis Mediators in Synovial Fluid by Quantitative Mass Spectrometry. Clin. Proteom. 2014, 11, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, K.; Xiang, Y.; Nakamura, H.; Masuko, K.; Yudoh, K.; Noyori, K.; Nishioka, K.; Saito, T.; Kato, T. Identification of Novel Citrullinated Autoantigens of Synovium in Rheumatoid Arthritis Using a Proteomic Approach. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2006, 8, R175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamachi, Y.; Uto, K.; Hayashi, S.; Okano, T.; Morinobu, A.; Kuroda, R.; Kawano, S.; Saegusa, J. Exosomes Derived from Synovial Fibroblasts from Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Promote Macrophage Migration That Can Be Suppressed by miR-124-3p. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, K.; Xiang, S.; Li, Z.; Weng, X. Emerging Role of Exosomes in the Joint Diseases. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 47, 2008–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skriner, K.; Adolph, K.; Jungblut, P.R.; Burmester, G.R. Association of Citrullinated Proteins with Synovial Exosomes. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 3809–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bugatti, S.; Manzo, A.; Caporali, R.; Montecucco, C. Assessment of Synovitis to Predict Bone Erosions in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2012, 4, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.; Manolios, N. Proteomics in Rheumatology: A New Direction for Old Diseases. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 35, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, P.R.; Clayton, D.G.; Cardon, L.R.; Craddock, N.; Deloukas, P.; Duncanson, A.; Kwiatkowski, D.P.; McCarthy, M.I.; Ouwehand, W.H.; Samani, N.J.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study of 14,000 Cases of Seven Common Diseases and 3000 Shared Controls. Nature 2007, 447, 661–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurreeman, F.A.; Padyukov, L.; Marques, R.B.; Schrodi, S.J.; Seddighzadeh, M.; Stoeken-Rijsbergen, G.; van der Helm-van Mil, A.H.; Allaart, C.F.; Verduyn, W.; Houwing-Duistermaat, J.; et al. A Candidate Gene Approach Identifies the TRAF1/C5 Region as a Risk Factor for Rheumatoid Arthritis. PLoS Med. 2007, 4, e278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppe, B.; Häupl, T.; Egerer, K.; Gruber, R.; Kiesewetter, H.; Salama, A.; Burmester, G.R.; Dörner, T. Influence of Peptidylarginine Deiminase Type 4 Genotype and Shared Epitope on Clinical Characteristics and Autoantibody Profile of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2009, 68, 898–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Tuyl, L.H.D.; Voskuyl, A.E.; Boers, M.; Geusens, P.; Landewe, R.B.M.; Dijkmans, B.A.C.; Lems, W.F. Baseline RANKL:OPG Ratio and Markers of Bone and Cartilage Degradation Predict Annual Radiological Progression over 11 Years in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 1623–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syversen, S.W.; Goll, G.L.; Van Der Heijde, D.; Landewé, R.; Gaarder, P.I.; Ødegård, S.; Haavardsholm, E.A.; Kvien, T.K. Cartilage and Bone Biomarkers in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Prediction of 10-Year Radiographic Progression. J. Rheumatol. 2009, 36, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansson, B. Release of Cartilage and Bone Macromolecules into Synovial Fluid: Differences between Psoriatic Arthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2001, 60, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, R.M. Progress in the Use of Biochemical and Biological Markers for Evaluation of Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2000, 14, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Den Broek, T.; Tesser, J.R.; Albani, S. The Evolution of Biomarkers in Rheumatoid Arthritis: From Clinical Research to Clinical Care. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2008, 8, 1773–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skoumal, M.; Haberhauer, G.; Feyertag, J.; Kittl, E.M.; Bauer, K.; Dunky, A. Serum Levels of Cartilage Oligomeric Matrix Protein Are Elevated in Rheumatoid Arthritis, but Not in Inflammatory Rheumatic Diseases Such as Psoriatic Arthritis, Reactive Arthritis, Raynaud’s Syndrome, Scleroderma, Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, Vasculitis and Sjögren’s Syndrome. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2004, 6, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garnero, P.; Gineyts, E.; Christgau, S.; Finck, B.; Delmas, P.D. Association of Baseline Levels of Urinary Glucosyl-Galactosyl-Pyridinoline and Type II Collagen C-Telopeptide with Progression of Joint Destruction in Patients with Early Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2002, 46, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraser, A.; Fearon, U.; Billinghurst, R.C.; Ionescu, M.; Reece, R.; Barwick, T.; Emery, P.; Poole, A.R.; Veale, D.J. Turnover of Type II Collagen and Aggrecan in Cartilage Matrix at the Onset of Inflammatory Arthritis in Humans: Relationship to Mediators of Systemic and Local Inflammation. Arthritis Rheum. 2003, 48, 3085–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gineyts, E.; Garnero, P.; Delmas, P.D. Urinary Excretion of Glucosyl-galactosyl Pyridinoline: A Specific Biochemical Marker of Synovium Degradation. Rheumatology 2001, 40, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, T. Predictive Value of Rheumatoid Factor Isotypes for Radiological Progression in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 1996, 25, 189–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedesco, A.; D’Agostino, D.; Soriente, I.; Amato, P.; Piccoli, R.; Sabatini, P. A New Strategy for the Early Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Combined Approach. Autoimmun. Rev. 2009, 8, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vossenaar, E.R.; Després, N.; Lapointe, E.; Van Der Heijden, A.; Lora, M.; Senshu, T.; Van Venrooij, W.J.; Ménard, H.A. Rheumatoid Arthritis Specific Anti-Sa Antibodies Target Citrullinated Vimentin. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2004, 6, R142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, C.; Serre, G.; Lapeyre, F.; Fournie, B.; Ayrolles, C.; Fournie, A.; Soleilhavoup, J.P. High Diagnostic Value in Rheumatoid Arthritis of Antibodies to the Stratum Corneum of Rat Oesophagus Epithelium, so-Called “Antikeratin Antibodies”. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1989, 48, 712–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Leeuwen, M.A.; van Rijswijk, M.H.; van der Heijde, D.M.F.M.; Meerman, G.J.T.; van Riel, P.L.C.M.; Houtman, P.M.; van de Putte, L.B.A.; Limburg, P.C. The Acute-Phase Response in Relation to Radiographic Progression in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Prospective Study During the First Three Years of the Disease. Rheumatology 1993, 32, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammer, H.B.; Odegard, S.; Fagerhol, M.K.; Landewe, R.; Heijde, D.V.D.; Uhlig, T.; Mowinckel, P.; Kvien, T.K. Calprotectin (a Major Leucocyte Protein) Is Strongly and Independently Correlated with Joint Inflammation and Damage in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2007, 66, 1093–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokubun, M.; Imafuku, Y.; Okada, M.; Ohguchi, Y.; Ashikawa, T.; Yamada, T.; Yoshida, H. Serum Amyloid A (SAA) Concentration Varies among Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Estimated by SAA/CRP Ratio. Clin. Chim. Acta 2005, 360, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldmann, M.; Brennan, F.M.; Maini, R.N. Role of Cytokines in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1996, 14, 397–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotake, S.; Udagawa, N.; Takahashi, N.; Matsuzaki, K.; Itoh, K.; Ishiyama, S.; Saito, S.; Inoue, K.; Kamatani, N.; Gillespie, M.T.; et al. IL-17 in Synovial Fluids from Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Is a Potent Stimulator of Osteoclastogenesis. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 103, 1345–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlson, E.W.; Chibnik, L.B.; Tworoger, S.S.; Lee, I.; Buring, J.E.; Shadick, N.A.; Manson, J.E.; Costenbader, K.H. Biomarkers of Inflammation and Development of Rheumatoid Arthritis in Women from Two Prospective Cohort Studies. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 641–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rho, Y.H.; Solus, J.; Sokka, T.; Oeser, A.; Chung, C.P.; Gebretsadik, T.; Shintani, A.; Pincus, T.; Stein, C.M. Adipocytokines Are Associated with Radiographic Joint Damage in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 1906–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Vollenhoven, R.V.; Klareskog, L.; Trollmo, C.; Malmström, V. CD25brightCD4+regulatory T Cells Are Enriched in Inflamed Joints of Patients with Chronic Rheumatic Disease. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2004, 6, R335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Amelsfort, J.M.R.; Van Roon, J.A.G.; Noordegraaf, M.; Jacobs, K.M.G.; Bijlsma, J.W.J.; Lafeber, F.P.J.G.; Taams, L.S. Proinflammatory Mediator–Induced Reversal of CD4+,CD25+ Regulatory T Cell–Mediated Suppression in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 56, 732–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagase, H.; Kashiwagi, M. Aggrecanases and Cartilage Matrix Degradation. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2003, 5, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, A.R.; Ionescu, M.; Swan, A.; Dieppe, P.A. Changes in Cartilage Metabolism in Arthritis Are Reflected by Altered Serum and Synovial Fluid Levels of the Cartilage Proteoglycan Aggrecan. Implications for Pathogenesis. J. Clin. Investig. 1994, 94, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, S.; Lohmander, L.S.; Struglics, A. Synovial Fluid Level of Aggrecan ARGS Fragments Is a More Sensitive Marker of Joint Disease than Glycosaminoglycan or Aggrecan Levels: A Cross-Sectional Study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2009, 11, R92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rims, C.; Uchtenhagen, H.; Kaplan, M.J.; Carmona-Rivera, C.; Carlucci, P.; Mikecz, K.; Markovics, A.; Carlin, J.; Buckner, J.H.; James, E.A. Citrullinated Aggrecan Epitopes as Targets of Autoreactive CD 4+ T Cells in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rousseau, J.C.; Sumer, E.U.; Hein, G.; Sondergaard, B.C.; Madsen, S.H.; Pedersen, C.; Neumann, T.; Mueller, A.; Qvist, P.; Delmas, P.; et al. Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Have an Altered Circulatory Aggrecan Profile. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2008, 9, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalai, E.; Bahlous, A.; Charni, N.; Bouzid, K.; Sahli, H.; Laadhar, L.; Chelly, M.; Rajhi, H.; Zouari, B.; Makni, S.; et al. Association of Serum Levels of Aggrecan ARGS, NITEGE Fragments and Radiologic Knee Osteoarthritis in Tunisian Patients. Jt. Bone Spine 2012, 79, 610–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Månsson, B.; Carey, D.; Alini, M.; Ionescu, M.; Rosenberg, L.C.; Poole, A.R.; Heinegård, D.; Saxne, T. Cartilage and Bone Metabolism in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Differences between Rapid and Slow Progression of Disease Identified by Serum Markers of Cartilage Metabolism. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 95, 1071–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Grauw, J.C.; van de Lest, C.H.A.; van Weeren, P.R. Inflammatory Mediators and Cartilage Biomarkers in Synovial Fluid after a Single Inflammatory Insult: A Longitudinal Experimental Study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2009, 11, R35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Close, D.R. Matrix Metalloproteinase Inhibitors in Rheumatic Diseases. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2001, 60 (Suppl. 3), iii62–iii67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.; Manning, H.B.; Jain, A.; Troeberg, L.; Dudhia, J.; Essex, D.; Sandison, A.; Seiki, M.; Nanchahal, J.; Nagase, H.; et al. Membrane Type 1 Matrix Metalloproteinase Is a Crucial Promoter of Synovial Invasion in Human Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 686–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooney, T.; Roux-Lombard, P.; Veale, D.J.; FitzGerald, O.; Dayer, J.-M.; Bresnihan, B. Synovial Tissue and Serum Biomarkers of Disease Activity, Therapeutic Response and Radiographic Progression: Analysis of a Proof-of-Concept Randomised Clinical Trial of Cytokine Blockade. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 706–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-H.; Lin, I.-L.; Tsay, G.J.; Yang, S.-C.; Yang, T.-P.; Ho, K.-T.; Hsu, T.-C.; Shiau, M.-Y. Elevated Circulatory MMP-2 and MMP-9 Levels and Activities in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Clin. Biochem. 2008, 41, 955–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young-Min, S.; Cawston, T.; Marshall, N.; Coady, D.; Christgau, S.; Saxne, T.; Robins, S.; Griffiths, I. Biomarkers Predict Radiographic Progression in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis and Perform Well Compared with Traditional Markers. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 56, 3236–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edhayan, G.; Ohara, R.A.; Stinson, W.A.; Amin, M.A.; Isozaki, T.; Ha, C.M.; Haines, G.K.; Morgan, R.; Campbell, P.L.; Arbab, A.S.; et al. Inflammatory Properties of Inhibitor of DNA Binding 1 Secreted by Synovial Fibroblasts in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2016, 18, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foers, A.D.; Dagley, L.F.; Chatfield, S.; Webb, A.I.; Cheng, L.; Hill, A.F.; Wicks, I.P.; Pang, K.C. Proteomic Analysis of Extracellular Vesicles Reveals an Immunogenic Cargo in Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovial Fluid. Clin. Trans. Immunol. 2020, 9, e1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marotte, H.; Gineyts, E.; Miossec, P.; Delmas, P.D. Effects of Infliximab Therapy on Biological Markers of Synovium Activity and Cartilage Breakdown in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2009, 68, 1197–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeed, M. Relationship between Serum Hyaluronic Acid Level and Disease Activity in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2004, 63, 1166–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cylwik, B.; Gruszewska, E.; Gindzienska-Sieskiewicz, E.; Kowal-Bielecka, O.; Chrostek, L. Comparison of Hyaluronic Acid in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis, Systemic Sclerosis and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Biochem. Med. (Online) 2021, 31, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chubinskaya, S.; Frank, B.S.; Michalska, M.; Kumar, B.; Merrihew, C.A.; Thonar, E.; Lenz, M.; Otten, L.; Rueger, D.C.; Block, J.A. Osteogenic Protein 1 in Synovial Fluid from Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis or Osteoarthritis: Relationship with Disease and Levels of Hyaluronan and Antigenic Keratan Sulfate. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2006, 8, R73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, L.L.; Garrie, K.; Turner, M.D. Role of S100 Proteins in Health and Disease. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Mol. Cell Res. 2020, 1867, 118677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, A.K.; Bruserud, Ø. S100 Proteins in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Neoplasia 2018, 20, 1175–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austermann, J.; Spiekermann, C.; Roth, J. S100 Proteins in Rheumatic Diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2018, 14, 528–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristóvão, J.S.; Gomes, C.M. S100 Proteins in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.; Yang, C.; Qu, S.-L.; Shao, Y.-D.; Zhou, C.-Y.; Chao, R.; Huang, L.; Zhang, C. S100 Proteins in Atherosclerosis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2020, 502, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baillet, A.; Trocme, C.; Berthier, S.; Arlotto, M.; Grange, L.; Chenau, J.; Quetant, S.; Seve, M.; Berger, F.; Juvin, R.; et al. Synovial Fluid Proteomic Fingerprint: S100A8, S100A9 and S100A12 Proteins Discriminate Rheumatoid Arthritis from Other Inflammatory Joint Diseases. Rheumatology 2010, 49, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Zhang, B.; Niu, G.; Yan, Z.; Tong, X.; Zou, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, M. Neutrophil Infiltration Characterized by Upregulation of S100A8, S100A9, S100A12 and CXCR2 Is Associated With the Co-Occurrence of Crohn’s Disease and Peripheral Artery Disease. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 896645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inciarte-Mundo, J.; Frade-Sosa, B.; Sanmartí, R. From Bench to Bedside: Calprotectin (S100A8/S100A9) as a Biomarker in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1001025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odink, K.; Cerletti, N.; Brüggen, J.; Clerc, R.G.; Tarcsay, L.; Zwadlo, G.; Gerhards, G.; Schlegel, R.; Sorg, C. Two Calcium-Binding Proteins in Infiltrate Macrophages of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nature 1987, 330, 80–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menees, S.B.; Powell, C.; Kurlander, J.; Goel, A.; Chey, W.D. A Meta-Analysis of the Utility of C-Reactive Protein, Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate, Fecal Calprotectin, and Fecal Lactoferrin to Exclude Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Adults With IBS. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 110, 444–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Clark, N.; Park, K.T. Effectiveness and Cost-Effectiveness of Measuring Fecal Calprotectin in Diagnosis of Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Adults and Children. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 12, 253–262.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firestein, G.S. Evolving Concepts of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nature 2003, 423, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayer, J.-M.; Choy, E. Therapeutic Targets in Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Interleukin-6 Receptor. Rheumatology 2010, 49, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorgensen, K.T.; Wiik, A.; Pedersen, M.; Hedegaard, C.J.; Vestergaard, B.F.; Gislefoss, R.E.; Kvien, T.K.; Wohlfahrt, J.; Bendtzen, K.; Frisch, M. Cytokines, Autoantibodies and Viral Antibodies in Premorbid and Postdiagnostic Sera from Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: Case-Control Study Nested in a Cohort of Norwegian Blood Donors. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2008, 67, 860–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwamoto, T.; Okamoto, H.; Toyama, Y.; Momohara, S. Molecular Aspects of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Chemokines in the Joints of Patients. FEBS J. 2008, 275, 4448–4455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rioja, I.; Hughes, F.J.; Sharp, C.H.; Warnock, L.C.; Montgomery, D.S.; Akil, M.; Wilson, A.G.; Binks, M.H.; Dickson, M.C. Potential Novel Biomarkers of Disease Activity in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients: CXCL13, CCL23, Transforming Growth Factor α, Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor Superfamily Member 9, and Macrophage Colony-stimulating Factor. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58, 2257–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cope, A.P. T Cells in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2008, 10, S1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrenstein, M.R.; Evans, J.G.; Singh, A.; Moore, S.; Warnes, G.; Isenberg, D.A.; Mauri, C. Compromised Function of Regulatory T Cells in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Reversal by Anti-TNFα Therapy. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 200, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Londei, M. Role of Regulatory T Cells in Experimental Arthritis and Implications for Clinical Use. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2005, 7, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Amelsfort, J.M.R.; Jacobs, K.M.G.; Bijlsma, J.W.J.; Lafeber, F.P.J.G.; Taams, L.S. CD4+CD25+ Regulatory T Cells in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Differences in the Presence, Phenotype, and Function between Peripheral Blood and Synovial Fluid. Arthritis Rheum. 2004, 50, 2775–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, L.; Dai, C.; Wang, L.; Pan, X. Potential Biomarkers That Discriminate Rheumatoid Arthritis and Osteoarthritis Based on the Analysis and Validation of Datasets. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2022, 23, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, F.; Zhang, C.; He, Z.; Ding, L.; Xiao, H. Analysis of Critical Molecules and Signaling Pathways in Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2013, 7, 603–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.C.; Bai, D.L.; Xu, Y.; Chen, H.; Ma, R.; Hou, W.B.; Xu, R.J. Identification of Differentially Expressed Genes in Synovial Tissue of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Osteoarthritis in Patients. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 4533–4544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd Elsalam, E.; El-Maghawry, I.; Emerah, A. Qualitative Assay of Synovial MAGE-1 m-RNA as a New Trend in Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. BESPS 2011, 31, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qtaitat, A.; Mwafi, N.; Albtoosh, A.; Al-Dalaien, N. A New Tool for Early Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis Using Combined Biomarkers; Synovial MAGE-1 mRNA and Serum Anti-CCP and RF. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2020, 36, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, K.; Yoshitomi, H.; Tanida, S.; Ishikawa, M.; Nishitani, K.; Ito, H.; Nakamura, T. Plasma and Synovial Fluid microRNAs as Potential Biomarkers of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2010, 12, R86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahendran, S.M.; Oikonomopoulou, K.; Diamandis, E.P.; Chandran, V. Synovial Fluid Proteomics in the Pursuit of Arthritis Mediators: An Evolving Field of Novel Biomarker Discovery. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2017, 54, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, M.A.; Ludwig, R.G.; Garcia-Martin, R.; Brandão, B.B.; Kahn, C.R. Extracellular miRNAs: From Biomarkers to Mediators of Physiology and Disease. Cell Metab. 2019, 30, 656–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Li, C.; Miao, Y.-R.; Lei, Q.; Li, Q.; Guo, A.-Y. EVmiRNA: A Database of miRNA Profiling in Extracellular Vesicles. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D89–D93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhao, M.; Xu, Y.; Yu, H.; Qin, J.; Li, H. Exploration of Exosomal miRNAs from Serum and Synovial Fluid in Arthritis Patients. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, K.; Yoshitomi, H.; Furu, M.; Ishikawa, M.; Shibuya, H.; Ito, H.; Matsuda, S. MicroRNA-451 Down-Regulates Neutrophil Chemotaxis via P38 MAPK. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niimoto, T.; Nakasa, T.; Ishikawa, M.; Okuhara, A.; Izumi, B.; Deie, M.; Suzuki, O.; Adachi, N.; Ochi, M. MicroRNA-146a Expresses in Interleukin-17 Producing T Cells in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2010, 11, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, Y.; Farina, N.H.; Matzelle, M.M.; Fanning, P.J.; Lian, J.B.; Gravallese, E.M. Synovium-Derived MicroRNAs Regulate Bone Pathways in Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2017, 32, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogunia-Kubik, K.; Wysoczańska, B.; Piątek, D.; Iwaszko, M.; Ciechomska, M.; Świerkot, J. Significance of Polymorphism and Expression of miR-146a and NFkB1 Genetic Variants in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2016, 64, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Park, S.; Lee, H.; Kwon, E.J.; Park, H.R.; Kim, Y.H.; Lee, S.-G. Exosomal Hsa-miR-335-5p and Hsa-miR-483-5p Are Novel Biomarkers for Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Development and Validation Study. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 120, 110286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, C.; Jia, X.; Yu, J. Circulating Exosomal miR-17 Inhibits the Induction of Regulatory T Cells via Suppressing TGFBR II Expression in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 50, 1754–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Liang, L.; Tian, R.; Huang, Q.; Ji, Z.; Li, X.; Lin, P.; Zheng, S.; Peng, Y.; Yuan, Q.; et al. LncRNA Expression Profiling in Exosomes Derived from Synovial Fluid of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 130, 111735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, S.; Sharma, S.; Saroha, A.; Bhakuni, D.S.; Malhotra, R.; Zahur, M.; Oellerich, M.; Das, H.R.; Asif, A.R. Identification of Novel Autoantigen in the Synovial Fluid of Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Using an Immunoproteomics Approach. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.M.; Amin, S.; Jones, L.K.; Lachance, D.H.; Flanagan, E.P.; Jentoft, M.E.; Kantarci, O.H. Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein (GFAP) Autoimmunity in the Setting of Seropositive Rheumatoid Arthritis Treated With Etanercept. Neurologist 2019, 24, 152–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Atab, O.; Gupta, B.; Han, Z.; Stribny, J.; Asojo, O.A.; Schneiter, R. Alpha-1-B Glycoprotein (A1BG) Inhibits Sterol-Binding and Export by CRISP2. J. Biol. Chem. 2024, 300, 107910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brink, M.; Lundquist, A.; Alexeyenko, A.; Lejon, K.; Rantapää-Dahlqvist, S. Protein Profiling and Network Enrichment Analysis in Individuals before and after the Onset of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2019, 21, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.M.; Lee, K.G.; Lee, S.; Hong, B.K.; Yun, H.; Park, Y.J.; Yoo, S.A.; Kim, W.U. The Acute Phase Reactant Orosomucoid-2 Directly Promotes Rheumatoid Inflammation. Exp. Mol. Med. 2024, 56, 890–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dénarié, D.; Constant, E.; Thomas, T.; Marotte, H. Could Biomarkers of Bone, Cartilage or Synovium Turnover Be Used for Relapse Prediction in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients? Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 537324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermeer, M.; Kuper, H.H.; Hoekstra, M.; Haagsma, C.J.; Posthumus, M.D.; Brus, H.L.M.; Van Riel, P.L.C.M.; Van De Laar, M.A.F.J. Implementation of a Treat-to-Target Strategy in Very Early Rheumatoid Arthritis: Results of the Dutch Rheumatoid Arthritis Monitoring Remission Induction Cohort Study. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 2865–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammam, N.; Salah, S.; Kholef, E.F.; Moussa, E.M.; Marotta, A. 14-3-3η Protein in Serum and Synovial Fluid Correlates with Radiographic Damage and Progression in a Longitudinal Evaluation of Patients with Established Rheumatoid Arthritis. Mod. Rheumatol. 2020, 30, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maksymowych, W.P.; Van Der Heijde, D.; Allaart, C.F.; Landewé, R.; Boire, G.; Tak, P.P.; Gui, Y.; Ghahary, A.; Kilani, R.; Marotta, A. 14-3-3η Is a Novel Mediator Associated with the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Joint Damage. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014, 16, R99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McInnes, I.B.; Schett, G. Cytokines in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.H.M.; Sameh, A.; Essam, H.E.-N. Serum Level of 14-3-3η (Eta) Protein as a Diagnostic Marker for Rheumatoid Arthritis and Potential Correlation with Disease Activity. MOJ Orthop. Rheumatol. 2017, 7, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavasolian, F.; Moghaddam, A.S.; Rohani, F.; Abdollahi, E.; Janzamin, E.; Momtazi-Borojeni, A.A.; Moallem, S.A.; Jamialahmadi, T.; Sahebkar, A. Exosomes: Effectual Players in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Liu, Y.; Wei, W.; Liu, M.-L. Extracellular Vesicles in Autoimmune Vasculitis—Little Dirts Light the Fire in Blood Vessels. Autoimmun. Rev. 2019, 18, 593–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanczyk, J.; Ospelt, C.; Karouzakis, E.; Filer, A.; Raza, K.; Kolling, C.; Gay, R.; Buckley, C.D.; Tak, P.P.; Gay, S.; et al. Altered Expression of microRNA-203 in Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovial Fibroblasts and Its Role in Fibroblast Activation. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Hu, D.; Zhang, L.; Tang, P. Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 93, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Schwarz, E.M.; Boyce, B.F. Osteoclast Precursors, RANKL/RANK, and Immunology. Immunol. Rev. 2005, 208, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De La Poza Plaza, E.; Barykin, S.; Shishkin, V.; Shishkin, V.V.; Kudryavtseva, G.V. AB0234 prognostic potential of Exosomes (EX) as immunomodulators in Synovial Fluid (SF) in Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA). In Proceedings of the Scientific Abstracts; BMJ Publishing Group Ltd. and European League Against Rheumatism: Zürich, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 1301.1–1302. [Google Scholar]
- Varela, L.; Van De Lest, C.H.A.; Boere, J.; Libregts, S.F.W.M.; Lozano-Andrés, E.; Van Weeren, P.R.; Wauben, M.H.M. Acute Joint Inflammation Induces a Sharp Increase in the Number of Synovial Fluid EVs and Modifies Their Phospholipid Profile. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2023, 1868, 159367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, S.; Radic, M. Citrullinated Autoantigens: From Diagnostic Markers to Pathogenetic Mechanisms. Clin. Rev. Allerg. Immunol. 2015, 49, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, J.; Lee, S.K.; Lim, M.; Sheen, D.; Choi, E.-H.; Kim, S.A. Exosomal Amyloid A and Lymphatic Vessel Endothelial Hyaluronic Acid Receptor-1 Proteins Are Associated with Disease Activity in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2017, 19, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
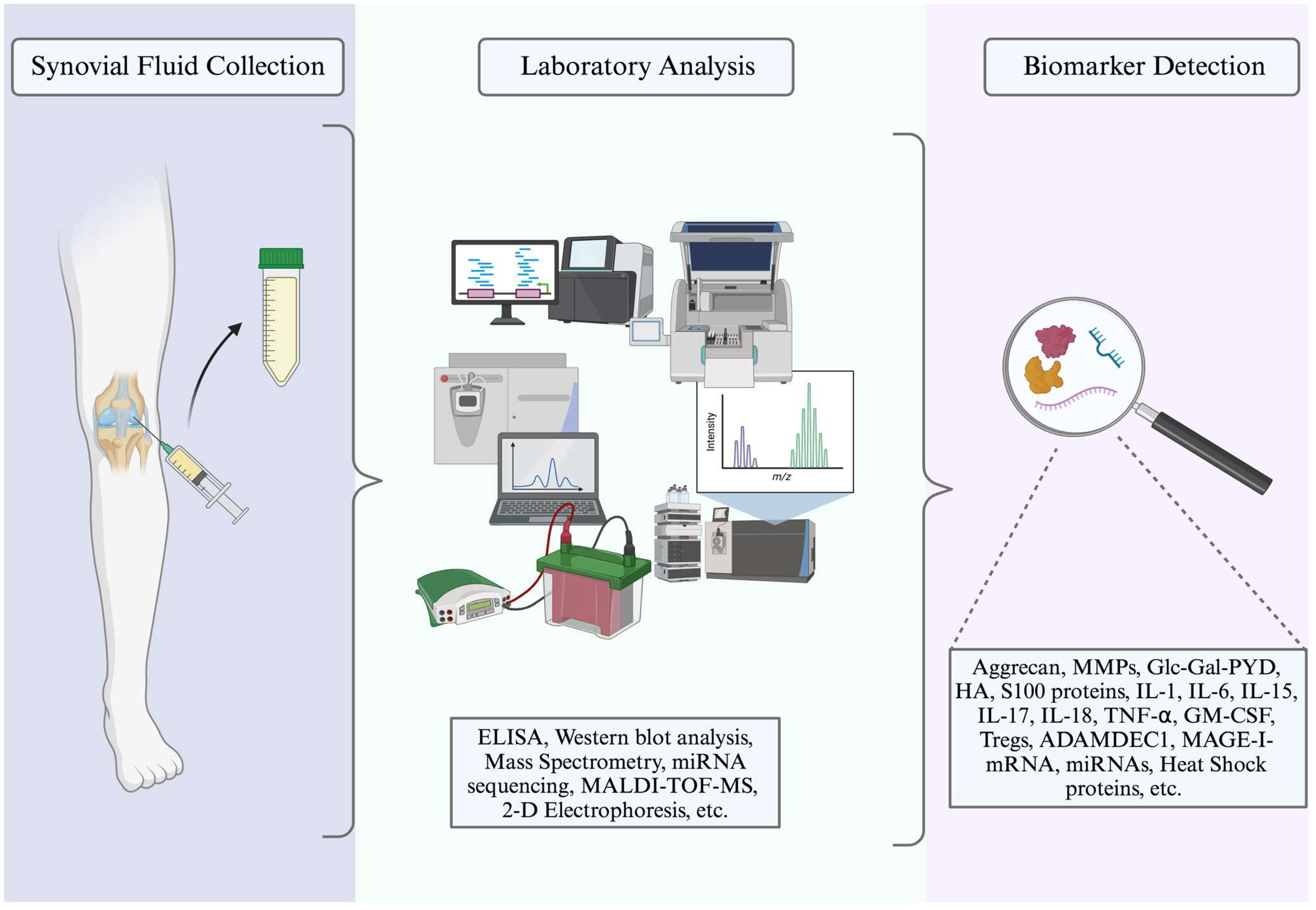
| Marker Type | Marker Name/Description | Location | Association with RA | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genetic Markers | HLA-DRB1 | Genetic–6p21.32 | The strongest association with RA risk and severity, also with anti-CCP antibodies. | [26] |
| TRAF1/C5 | Genetic–9q33-34 | Associated with erosive changes in RA, though of modest clinical utility. | [27] | |
| PADI4 | Genetic–1p36.13 | Controversial association with RA susceptibility across different populations. | [28] | |
| Bone Markers | RANKL/OPG ratio | Serum/synovium | Predicts radiographic progression of joint damage. | [29] |
| Collagen (type I) cross-linked C-telopeptide (CTX-I) | Serum/urine | High levels predict the risk of radiological progression and joint destruction. | [30] | |
| Bone sialoprotein (BSP) | Serum/synovial fluid | Elevated levels may indicate joint damage and help in the early identification of destructive RA. | [31] | |
| Cathepsin K | Serum/synovial fluid | Potential marker of bone resorption but requires further validation. | [32] | |
| Osteocalcin | Serum | Reflects bone metabolism but is less effective at predicting disease activity. | [33] | |
| Cartilage Markers | Cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (COMP) | Serum | Changes in COMP linked to cartilage destruction and joint damage in RA. | [34] |
| C-terminal cross-linking telopeptide of type II collagen (CTX-II) | Urine | High levels predict joint destruction progression in RA. | [30,35] | |
| Col2-3/4Clong mono and Col2-3/4Cshort (Type II) | Serum | May indicate cartilage degradation and predict joint space narrowing. | [36] | |
| Hyaluronic acid (HA) | Serum/synovial fluid | Elevated levels correlate with disease activity but are variable throughout the day. | [35,37] | |
| Autoantibodies | Rheumatoid factor (RF) | Serum | Commonly detected but not specific to RA; correlates with disease activity and prognosis. | [38] |
| Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) | Serum | Highly specific for RA and predictive of joint destruction; may be detected before RA onset. | [39] | |
| Anti-mutated citrullinated vimentin (MCV) | Serum | High specificity for RA; predicts severe joint involvement. | [40] | |
| Antiperinuclear factor (APF) | Serum | Present in many RA patients; assists in early intervention. | [41] | |
| Inflammatory Markers | Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) | Blood | Reflects disease activity and can predict long-term radiological progression useful in clinical settings. | [42] |
| C-reactive protein (CRP) | Blood | Reflects short-term disease activity and is associated with joint destruction; widely used. | [32] | |
| Calprotectin | Synovial fluid | High levels correlate with joint damage and predict erosive disease. | [43] | |
| Serum amyloid-associated protein (SAA) | Blood | Correlates with clinical parameters; may not provide additional information over CRP. | [44] | |
| Cytokines, Inhibitors Adipokines | Various cytokines (e.g., IL-1, IL-6, TNF-α) | Synovial fluid | Elevated levels contribute to joint destruction; dynamic balance is necessary for predictive value. | [45,46] |
| Soluble TNF receptor II (sTNFR-II) | Blood/synovial fluid | May indicate future RA development. | [47] | |
| Adipocytokines (e.g., leptin, visfatin) | Blood | Elevated in RA; associated with radiographic joint damage. | [48] | |
| Immunological Markers | CD4 + CD25+ T-regulatory cells | Synovial fluid | Increased in inflamed joints; controversial role in RA pathology and potential biomarkers. | [49,50] |
| Marker | Prognostic | Diagnostic | Therapeutic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aggrecan | + | + | − |
| MMPs | + | − | + |
| Glc-Gal-PYD | + | − | − |
| Hyaluronic acid | − | + | − |
| S100 proteins | − | + | − |
| Calprotectin | − | + | − |
| Cytokines | + | − | + |
| Immunological markers | − | − | − |
| ADAMEDC1 | + | + | − |
| MAGE-I-mRNA | − | + | − |
| Non-coding RNAs | + | + | + |
| GFAP and A1BG | + | + | − |
| ORM2 | + | − | + |
| 14-3-3η protein | + | + | − |
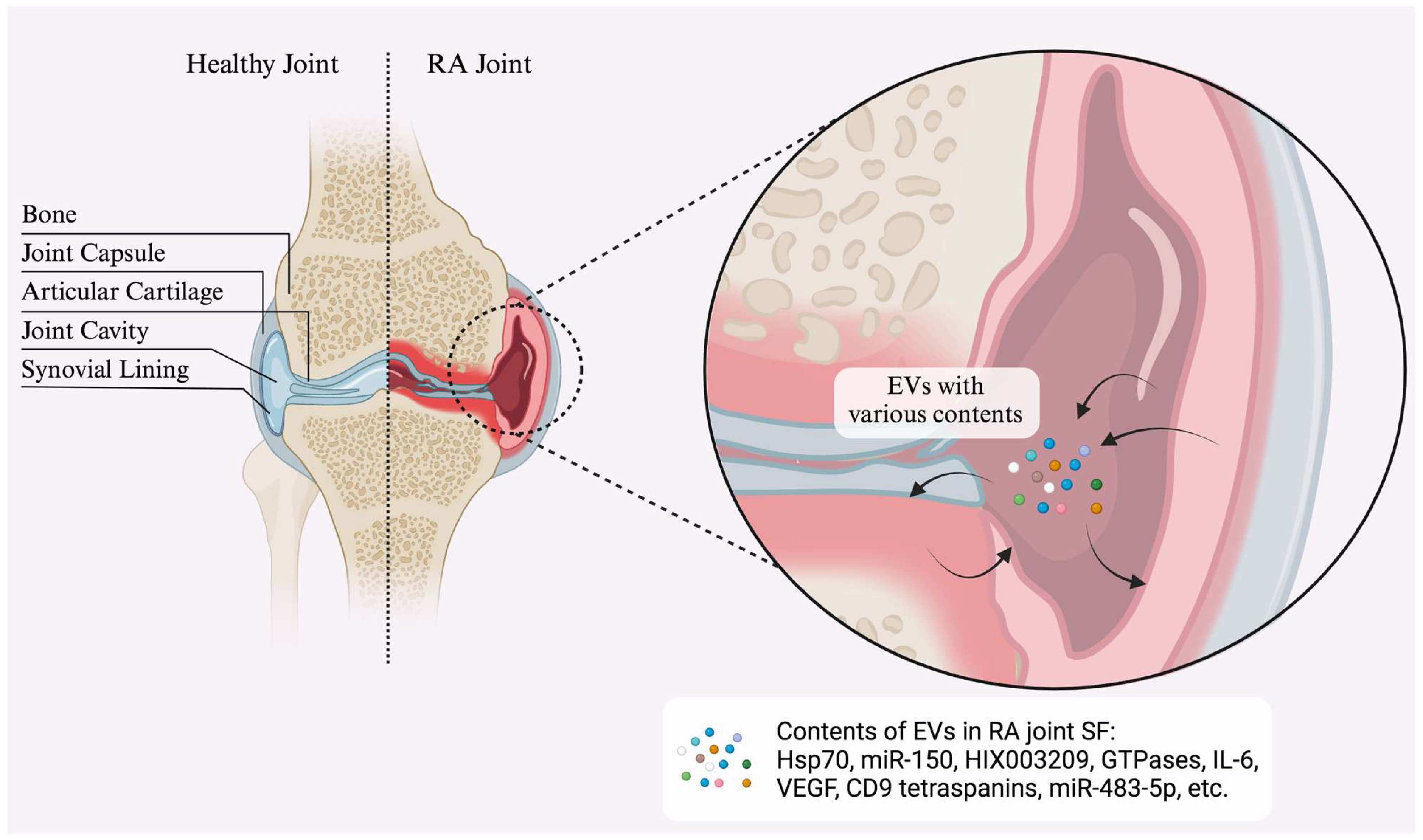
| Exosomal Content | Source/Type | Role in RA | Key Markers/Findings | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| miRNAs | Synovial fluid exosomes | Modulate inflammation, serve as biomarkers, contribute to joint damage and cartilage degradation | miR-155, miR-150, miR-146a, miR-21, miR-221-3p, miR-335p, miR-483-5p; associated with T cell differentiation and inhibition of bone repair | [97,98] |
| Autoantigens | EVs from fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) | Participate in the immune response by interacting with citrullinated proteins and presenting autoantigens | Citrullinated peptides, MHC-I/II molecules, immunological complexes, IgG, fibrin α-chain, β-chain, fibrinogen | [20] |
| Heat Shock Proteins (HSPs) | Exosomes from synovial cells | Contribute to inflammatory pathways and exosome secretion | Elevated Hsp70 and CD9 tetraspanins; increased acidic endonuclease activity and decreased alkaline activity | [123] |
| MMPs | Exosomes from FLS | Promote cartilage breakdown and angiogenesis | MMP-13, MMP-3, IL-6, VEGF; granulocyte-derived vesicles linked to pro-coagulation effects | [65] |
| Lipids | Exosomal lipid content | Involved in synovial inflammation and EV biogenesis | Hexosylceramides, sphingomyelin; increased phosphatidylethanolamines during acute inflammation | [124] |
| Proteins | EVs in synovial fluid | Associated with inflammation, bone destruction, autoantigen presentation, and signaling pathways | STAT1, STAT3, JAK1, JAK2, TLR2, MMP9, PYCARD, CCR1, HSP90AB1, F-actin, Histones H1, H2, H3; GTPases, NADPH oxidase, MPO, Rac1, Rac2 | [125,126] |
| lncRNAs | Exosomal lncRNAs | Serve as RA biomarkers; modulate inflammation via miRNA interaction | ENST00000433825.1 (correlates with CRP levels in RA); HIX003209 linked to inflammatory processes | [106] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Smolinska, V.; Klimova, D.; Danisovic, L.; Harsanyi, S. Synovial Fluid Markers and Extracellular Vesicles in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Medicina 2024, 60, 1945. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60121945
Smolinska V, Klimova D, Danisovic L, Harsanyi S. Synovial Fluid Markers and Extracellular Vesicles in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Medicina. 2024; 60(12):1945. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60121945
Chicago/Turabian StyleSmolinska, Veronika, Daniela Klimova, Lubos Danisovic, and Stefan Harsanyi. 2024. "Synovial Fluid Markers and Extracellular Vesicles in Rheumatoid Arthritis" Medicina 60, no. 12: 1945. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60121945
APA StyleSmolinska, V., Klimova, D., Danisovic, L., & Harsanyi, S. (2024). Synovial Fluid Markers and Extracellular Vesicles in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Medicina, 60(12), 1945. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina60121945







