Abstract
Background: Pancreatic organoids are a rapidly advancing field of research with new discoveries being made every day. A literature review was performed to answer the question of how relevant 3D pancreatic organoids are for surgery. Materials and Methods: We started our investigation by identifying articles in PubMed within the last 5 years using the keywords ((“pancreatic organoid”, OR “organ-on-a-chip”, OR “pancreatic chip” OR “3D culture methods”) AND pancreatic surgery). Only English articles were included in this literature review. This literature review was performed in a non-systematic way; articles were chosen without a predetermined protocol of inclusion and were based on the aim of the review. Results and Conclusions: There are many promising innovations in the field of 3D cultures. Drug sensitivity testing in particular holds great potential for surgical application. For locally advanced PDAC, EUS-FNB obtained cancer tissue can be cultured as organoids, and after 4 weeks, neoadjuvant treatment could be adjusted for each patient individually. Utilizing this approach could increase the number of R0 resections and possibly cure the disease. Furthermore, microfluidic devices, as a platform for pancreatic islet pre-transplant evaluation or cultivation of beta cells derived from HiPSC in vitro, promise broad application of islet transplantation to T1DM patients in the near future.
1. Introduction
The pancreas serves as an exocrine and endocrine organ. Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) develops from the exocrine part of the gland and is one of the deadliest types of cancer. It accounts for about 93% of all malignancies arising from the pancreas [1,2]. Every year more than 510,000 new cases of pancreatic cancer are diagnosed worldwide, and 467,000 deaths are reported [3]. Although a rather uncommon type of cancer, PDACs prevalence increases by 0.5% to 1.0% annually. Regardless of the systemic treatment advances in the last decades, the 5-year survival rate is still below 10% [4]. The majority of patients diagnosed with pancreatic cancer for the first time have disseminated disease with a mean survival of only 8–11 months despite aggressive chemotherapy [5,6]. Combining surgery with chemotherapy is the only curative option in localized PDAC and increases the 5-year survival to 20–25% [7]. Despite a high number of new drugs in preclinical trials, the molecular heterogeneity and mutations among PDAC limit their effectiveness [8]. To identify which systemic therapy could be the most beneficial to every individual, a more personalized approach and accurate biomarkers are needed.
In recent years, research involving patient-derived 3D organoids has made significant advancements [9,10,11]. Patient-derived cancer organoids (PDO’s) can be cultured ex vivo through multiple passages, allowing enough biomass of the tumor to study the genetic alterations of cancer clone’s DNA and sensitivity to clinically most relevant combinations of chemotherapy [12,13,14]. Originally, organoids were characterized as differentiated progenitor cells (stem cells) with the structure and function matching the tissue of interest for research purposes [15]. The more clinically relevant method is culturing pancreatic tumor organoids obtained from surgical specimens or from endoscopic ultrasound fine needle aspiration or biopsy (EUS-FNA/FNB) [16,17,18,19]. However, since pancreatic organoids after a few passages are composed only of epithelial cells, they lack the tumor microenvironment (TME) in vivo, which is primarily composed of fibroblasts and immune cells and plays a vital role in tumor biology [20]. Therefore, some groups utilize microfluidic devices to co-culture PDAC organoids with mesenchymal or immune cells to study carcinogenesis processes in vitro [21].
If the critical volume of endocrine beta cells is damaged by autoimmune disease, T1DM follows [22]. Traditional treatment includes daily insulin injections, continuous glucose monitoring, and hybrid closed-loop systems [23]. Despite this advanced treatment, some patients still suffer from constant hyperglycemia or severe, life-threatening hypoglycemia episodes. Beta cell replacement is an option in this situation. Although pancreas transplantation provides long-term normoglycemia, this procedure is associated with significant morbidity and mortality [24]. Islet transplantation is a less invasive option [25]. To add more, islet autotransplantation has improved outcomes in glycemia control after total pancreatectomy due to chronic pancreatitis [26]. We cannot offer islet transplantation for every patient with indications due to a shortage of donors. Therefore, new technologies are implemented for islet research in vitro, including microfluidic devices [27]. A new possible source of beta cells—embryonic stem cells (ESC) and human-induced pluripotent stem cells (HiPSC)—poses a great potential to solve the beta cell shortage problem [28]. Microfluidic devices can be utilized to create the same size HiPSC-derived beta cell organoids (pseudoislets) in a scalable manufacturing manner [29,30].
Within this review, the current literature is analyzed regarding pancreatic organoids and microfluidic systems’ utilization in surgery.
2. Materials and Methods
A literature search in the Medline database was conducted to identify relevant articles from the past 5 years using the keywords ((“pancreatic organoid”, OR “organ-on-a-chip”, OR “pancreatic chip” OR “3D culture methods”) AND pancreatic surgery). Only English articles were included in this literature review, in a non-systematic way.
The focus of this review was on these questions: (i) what are the main advantages of organoids?; (ii) how can we implement pancreatic 3D organoids in surgery?; and (iii) microfluidic systems as a platform for pancreatic organoid applications.
3. Discussion
3.1. Culture Types
Since the first cell culture was established by Harrison in 1907 [31], their development has progressed steadily. This enabled the proper investigation of the mechanisms of formation and function and the pathology of organs and their tissues. Until today, 2D cell cultures are the most common cell culture method being used. In a 2D cell culture system, the cells are grown as a monolayer in a culture flask or flat dish embedded into extracellular matrix (ECM) [32]. Furthermore, there is the suspension cell culture method, in which single cells or cell aggregates multiply in a nutrient fluid until further processing takes place [32]. They do not represent the normal in vivo cell environment since they do not mimic the natural structures of tissues found in the body. Therefore, cell-to-cell and cell-to-ECM interactions are not comparable to those occurring in vivo. Because of this circumstance, the predictive value of 2D culture is limited for drug discovery, testing, or research outcome [33]. Another disadvantage is the unlimited access to all ECM ingredients, which is not representative for tumor cells, i.e., in vivo cancer cells have variable access to these ingredients due to the architecture of the tumor [34]. Based on all these concerning disadvantages, there is a necessity for alternative culturing methods that would be more feasible, mimicking the ECM.
3D cell culture is the next step in cancer research [35,36]. It allows cells to grow in any direction and interact with the ECM or other aggregate cells, resulting in growth that is not limited to the 2D culture medium structure of classical cultures [37]. The main advantages of 3D cultures are that they form complex systems and show significantly better cell-to-cell and cell-to-ECM interaction while also creating “niches”. Cells can obtain signals from the surrounding environment, as it also happens in vivo. Another improvement is the maintenance of characteristics of the cell [38]. In a 3D environment, the cell can retain its unique morphology and mode of division, leading to a more viable organoid. These exclusive properties allow a more intense study of healthy tissue-derived cultures for regenerative medicine, cancer research and drug testing, or testing of the effectiveness of cell response to radiation.
In addition to that, 3D cell cultures can reduce utilization of animal testing in research and are therefore more ethical. [34,39].
There are several types of 3D cultures [40]. The simplest are aggregates or spheroids, which are mainly a collection of cells usually obtained from cell line monocultures [41]. Spheroids are described as 3D cell spontaneous aggregates that do not have contact with the culture substrate (ECM), which results in cell–cell interaction without cell/matrix interaction [42]. Two main culturing methods are utilized in spheroid creation: hanging-drop and ultra-low attachment cultures [43]. Although there is no pre-defined ECM in a spheroid culture to adhere to, it is observed that cells themselves secrete ECM molecules (for example, tripeptide Arg-Gly-Asp) to aid in cell aggregation and a stable structure of a 3D sphere [41].
The next step in 3D cell cultivation is organoids [15,44,45]. According to some authors, there is a distinction among the terms “spheroid” and “organoid” [46]. Spheroid is only a method of 3D cell culturing, while organoids must meet specific requirements to be called so. According to consensus by Marsee et al., an organoid is defined as a “three-dimensional structure derived from (pluripotent) stem cells, progenitor, and/or differentiated cells that self-organize through cell–cell and cell–matrix interactions to recapitulate aspects of the native tissue architecture and function in vitro” [46]. A spheroid can be called an organoid only if it is composed of organ-specific cells and recapitulates the original structure and function of the organ it is mimicking in vitro.
Organoids were originally derived from stem cells; however, during the past decade it has been observed that differentiated cells (for example, primary patient tissue or tumor cells) can be successfully cultured and passaged to study in vitro as well [47]. It is possible to produce a variety of organoids mimicking different organ structures and functions in vitro, including small and large intestine [48], pancreas [49], kidney [50], brain [51], and liver [52]. In contrast to spheroids, organoids can be propagated for a long-term ex vivo study [53]. Although cultivating organoids offers great potential, it is not an easy task [54]. Organoids can be derived from a variety of cells, but they must be carefully isolated and supplied with a specific culture medium including nutrients and growth factors. If embryonic stem cells are utilized, they are first proliferated, and once the predefined number of cells is reached, they are subsequently differentiated in a multistep protocol to mature functional organoids [55].
ECM is essential to maintain a niche for the stem cells during differentiation with physical and chemical stimulation [56,57]. Together with natural ECM, the most widespread type is Matrigel purified from Engelbreth-Holm Swarm mouse sarcoma [39]. Specific growth factors and differentiation modulators are added to the growth media for differentiation and controlled growth [58]. Also, organoids can be established from induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) or adult stem cells (ASCs) taken from normal tissue. Tissue-derived stem cells are able to reorganize themselves into organoids, mostly composed of epithelial cells [59]. The cell source, the culturing media, and the ECM should be chosen according to the organ and the result that is intended to be achieved. Compared to other organs such as the liver, the pancreas in vivo has a very limited ability to regenerate, neither in homeostasis nor when injured. This circumstance complicates the production of pancreatic organoids [60], which is why iPSCs are often used to achieve good results. Organoids differentiated from iPSCs are complex structures and pose a possibility to include multiple germ layer cell types: endothelial, epithelial, or mesenchymal cells. Supporting cells in complex pancreatic organoids usually result in enhanced viability and function in vitro [61]. The main differences between 2D and 3D cultures are provided in Figure 1.
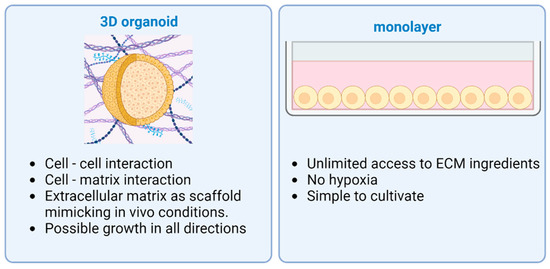
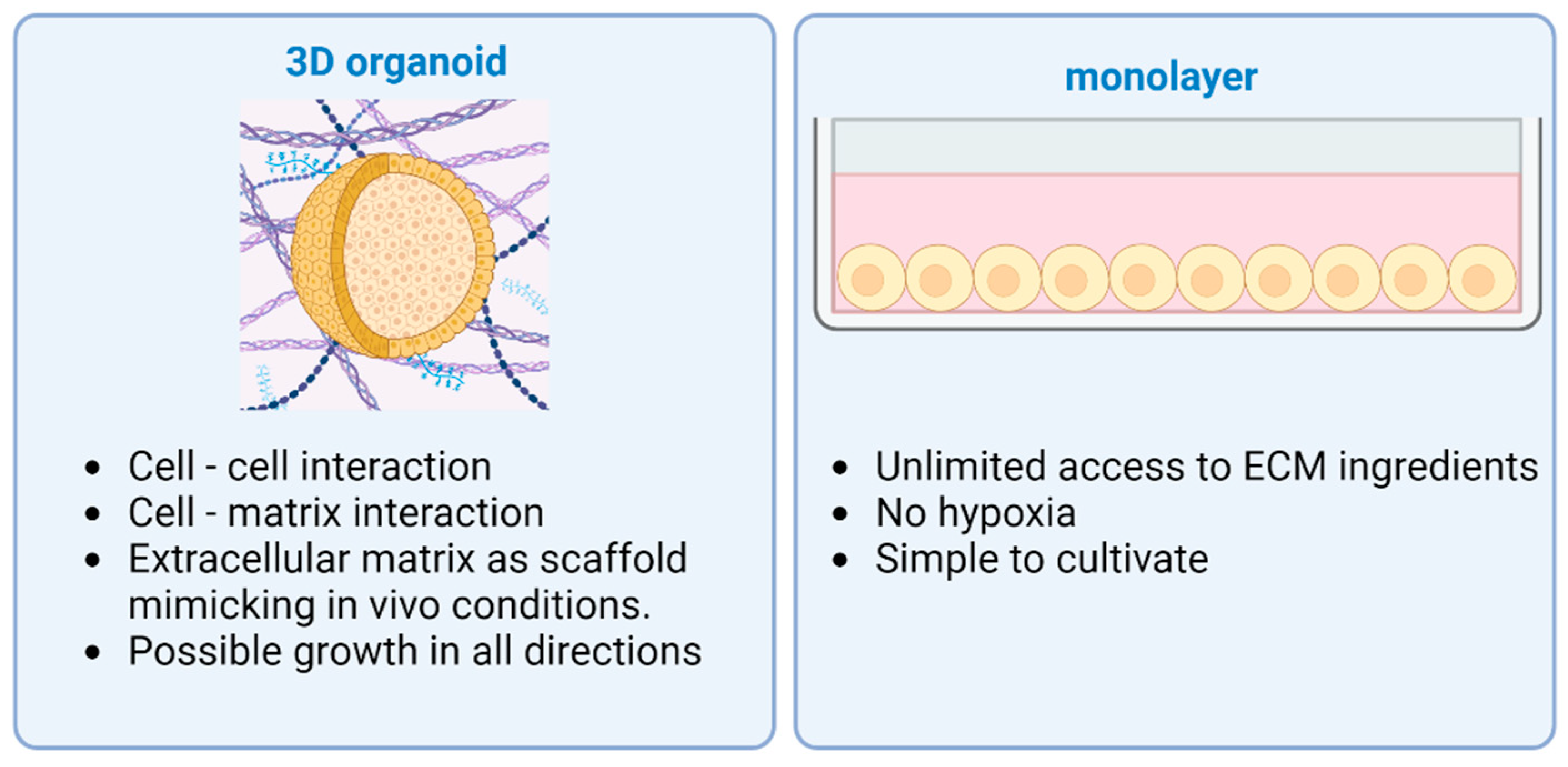
Figure 1.
Advantages of different cell culturing methods: 3D organoid vs. 2D monolayer. Two-dimensional monolayers of cells have unlimited access to ECM ingredients, suffer less from hypoxia, and are simple to cultivate. Three-dimensional organoids are more complex structures with cell–cell and cell–matrix interaction, as well as possible growth in every direction. Created with BioRender.com.
Even though conventional organoid types are very similar to in vivo organs, it remains difficult to precisely control their development. Another limitation is the inability of conventional organoids to provide a complex micro-environment. For this reason, microfluidic systems were implemented in cell culturing and provide controllable experimental conditions for the organoid [62]. This combination of 3D cell culturing and microfluidic devices is called organ-on-a-chip (OOAC) [63]. As described by Qirui Wu et al. [64], OOAC cultures have the ability to mimic the organ much better than other culture types. By adding a microfluidic channel network, it is possible to influence important parameters of the culture such as concentration gradient and tissue-organ interactions. The design is different depending on the organ studied, but every device contains chambers for cells to grow while constantly being perfused by culture media [65]. It differs from classical organoid cultures on Matrigel, where culture medium is changed only every 5 days [66].
In vivo epithelial cells are always supported and interacting with surrounding tissues, including endothelium, mesenchymal, or immune cells [67]. These are essential elements to replicate in vitro physiological environment if tumorigenesis is studied, for example, cancer potential to metastasize or immune cell-induced tumor necrosis. The multi-organ-on-a-chip model provides great possibilities. However, the complexity of the system results in reduced reproducibility and challenges to be solved in the future [68].
3.2. PDAC Organoid Clinical Applications
3.2.1. Drug Sensitivity Testing
Pancreatic cancer, and especially PDAC, has high heterogeneity, and multiple cancer cell clones cause the aggressive systemic treatment to be ineffective with many side effects [69]. Nowadays, two main chemotherapy schemes are used to treat disseminated PDAC. Gemcitabine/nab paclitaxel (G/A) compared to FOLFIRINOX (5-fluorouracil, leucovorin, irinotecan, and oxaliplatin) is a less toxic combination but provides inferior efficacy [70]. Furthermore, if the patient received neoadjuvant chemotherapy, organoids derived from surgical specimens usually manifest with resistance to previous therapy due to emerging new PDAC clones and mutations [71,72].
PDAC is already a disseminated disease in 75–80% of patients; therefore, chemotherapy is the only possible treatment option to slow down the tumor progression and prolong survival for a few months [70]. Since PDAC is a very fast-growing tumor, speed is of utmost importance, especially for borderline tumors for which surgical resection is possible. Nowadays, we do not have sensitive and specific biomarkers to guide clinical decision-making to choose the most effective chemotherapy regimen for the individual patient. Historically, patient-derived xenografts (PDX) in vivo were the gold standard in drug sensitivity testing for PDAC [67]. However, this is a laborious and time-consuming method and lasts 6–8 months, which is clinically irrelevant [69]. To overcome this limitation, patient-derived organoids (PDO) were established [71,73]
Organoid cultures can be utilized even in predicting treatment response [74]. Organoid technology can recapitulate the original tumor genetics and structure with astonishing precision, not inferior to PDX. A study carried out by Frappart et al. [75] compared PDX organoids with patient-derived organoids with a small-scale sensitivity test. The authors concluded that organoids demonstrate the same feasibility for sensitivity testing as PDXs. In addition, organoids have higher predictive value because they do not have unwanted interactions between xenografts and animal cells.
Hervé Tiriac et al. [76] generated a patient-derived organoid library that is able to summarize the mutational spectrum and transcriptional subtypes of primary pancreatic cancer. Furthermore, they defined new oncogenes, and continued analysis showed unique clusters, which could be used to improve treatment. A case study was performed that predicted improved response for patients due to organoid-based gene expression signatures. Finally, Tiriac et al. propose that it is possible to predict clinical response by combined molecular and therapeutic profiling, which could result in a more accurate therapy. Other research groups have also come to similar results. It is possible to find concordance between patient-derived organoids and thus enable a more targeted therapy [77].
Organoid development consists of three phases: establishment, expansion, and characterization [69]. Dantes et al. report that a small biomass of organoids can be tested just after the organoid establishment phase. The supernatant is collected, and cell-free DNA is analyzed to guide specific immunotherapy in just 2 weeks after sample collection [78]. Further pharmacotyping requires larger biomass, so the expansion phase has to be completed; usually it lasts 4 weeks [69]. Success of organoid cultures obtained from surgical specimens or EUS-FNB to at least five passages and subsequent pharmacotyping in the leading world laboratories reaches over 80% [13,19].
It is even possible to establish organoid cultures non-invasively from circulating tumor cells obtained from a patient’s blood sample. Wu and colleagues reported culture efficiency of 87% in just 3 weeks of cultivation [79].
For patients who went through surgery, effective postoperative chemotherapy is an important adjunct to increase survival [80]. Seppälä et al. [81] established patient-derived organoids from surgical specimens and endoscopic biopsies for high-throughput drug testing to explore if drug sensitivity testing could be performed within a clinically meaningful timeframe. Single cells were placed in liquid Matrigel and supplied with culture medium. For sensitivity testing, single cells were placed on a 384-well assay plate in 10% Matrigel and tested for different chemotherapeutics. It was possible to obtain results rapidly within 18 days with a mean time of 49 days. The median time between surgery and initiation of chemotherapy was set to be 62 days according to a pancreatectomy database survey. This and other studies show that there is also a possibility to utilize organoids in the postoperative phase and that the results obtained can be used to choose the potent chemotherapy [82,83].
Despite the advantages of PDOs, there are still many challenges remaining for this technology to be an important part of clinical decision-making [69]. First of all, PDAC is a paucicellular tumor—the majority of the specimen consists of stromal cells, and only 15% of epithelial tumor cells [84]. A meta-analysis recently conducted by Grützmeier et al. reported that actual organoid procurement success with pharmacotyping is 60% for EUS-FNB, 36% for percutaneous biopsies, and 62% for surgical specimens [85]. Many patients are diagnosed with advanced disease, and sometimes they receive neoadjuvant systemic treatment prior to organoid establishment. It is observed that neoadjuvant chemotherapy and radiotherapy reduce chances to culture PDOs substantially [86]. This real-world data suggests that one-third of patients will not receive personalized treatment for PDAC. Unfortunately, specific immunotherapy today is applied only to a few percent of PDAC patients [69]. To add more, during PDO’s culture expansion, the stromal compartment is lost during the first two passages due to specific growth factors in the culture medium supporting only epithelial cell proliferation. Consequently, tumor microenvironment (TME) is lost, and PDOs no longer mimic in vivo cancer biology. Another interesting phenomenon was observed during the expansion phase of organoids.
Before the first passage, the most abundant genetic clone of PDAC usually is not the same after 5 passages [81]. The dominant clone requires time to overwhelm the remaining tumor variants. This means that after the last PDO’s passage, specific systemic treatment is directed only against one variant of the tumor, ignoring the rest. Finally, there are still no RCTs conducted to confirm PDO’s real impact in clinical setting.
Microfluidic technology provides some solutions for PDO’s culturing limitations. To begin with, a continuous flow of fresh culture medium provides essential growth factors and oxygen to organoids and prolongs viability. Also, microfluidic system design aids in uniform-size PDOs compared to 3D culturing methods on Matrigel [9].
Zhang et al. [87] introduced a scalable multiplexed drug-combination screening platform which uses 3D microtumor models. They produced a chip with a “Christmas tree mixer” structure with the ability to provide a large drug concentration range for screening. This high-throughput combination screening scheme has the potential to test nearly any number of drugs and their pairwise combination with multiple logarithmic mixing ratios. To test for efficacy and applicability of this chip, a 8-drug combination chip was implemented. The drug combination screening was performed with breast and pancreatic cancer cell lines [88]. For pancreatic testing MIA PaCa-2 cell lines were used. Seven chemo-drugs and one media only as a positive control were screened, resulting in 172 different treatment settings. While testing cisplatin, docetaxel, doxorubicin, gemcitabine, irinotecan, oxaliplatin and fluorouracil as a single drug or in different combinations, they saw a few treatment combinations which showed higher effectiveness compared to single drug therapy. Even though this study was based on MIA PaCa-2 cell lines, the relevance of OOAC can be inferred i.e., the possibility to test not only single drugs, but even interactions of several drugs, shows great potential.
One of the main advantages of OOAC is co-culturing PDAC organoids with essential TME cells, for example stellate cells or lymphocytes [89,90]. These interactions observed iv vitro could lead to specific stroma or immune system targeting therapy.
Davenport et al. [91] co-cultured multiple cell types (patient-derived pancreatic organoids, human fibroblasts, and endothelial cells), placed on a flow controlled OOAC platform and tested drug sensitivity. Their results demonstrate that the value of a perfusable vascular network showed better reaction for drug screening compared to stiffened matrix.
3.2.2. Regenerative Medicine
Another area of research which is getting more attention is the study of diabetes mellitus (DM). Mortality rates in lower-middle-income countries increased by 13% between 2000 and 2019 [92]. Therefore, sufficient treatment is more important than ever. The idea of culturing pancreatic islets for transplantation has been around for a while. However, there have been some problems in producing these islets, i.e., they are more dependent on external factors, such as blood flow and interactions between cells, than other cell structures. Without these factors, cells are unable to maintain a good blood-glucose homeostasis. The introduction of 3D and OOAC models solved some of these issues. A comparative study between different types of spheroid production demonstrated that islet cell spheroids, generated either in locally fabricated silicon microwells or in Sphericalplate 5D, yielded highly functional insulin-producing constructs with minimal labor [93]. Although providing better results than previous culturing methods, spheroids have limited application abilities. Due to their structure, spheroids are very susceptible to oxygen. When they reach a certain size (approximately 150 µm in diameter), it is no longer possible to achieve sufficient oxygenation of the inner cells leading to necrosis, limiting the size and usability of such cultures.
Pancreas transplantation is an option to treat T1DM in the long term. However, it is a major surgical procedure with high morbidity and mortality [94]. Pancreatic islet transplantation is therefore a good alternative with lower morbidity [95]. For islet transplantation several OOAC models have been designed, which could bring further prospects [96]. Culturing pancreatic islets on microfluidic chips involves trapping sides, mostly micro-wells, where islets are immobilized and cultured under continuous flow [97]. It has been shown that the size of the islets should be as consistent as possible, where smaller islets are more viable and produce more insulin if normalized for their mass than the larger ones [98]. Nowadays hiPSC differentiation protocols produce viable and functional beta cells in vitro comparable to native islets [99]. Furthermore, there are promising bioengineering solutions for massive islet production such as microwells (with centrifugation) [29] and hanging drop systems [30]. Before transplantation of the islets, they need to be tested for purity, function and viability. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is still the predominant method used, which requires the separation of the cells, making this method very time and cost-consuming. On-chip testing could therefore save a lot of resources. Hori et al. [100] developed a compact fluidic system for the assessment of islet functionality called g-STAR. This novel system uses a micromesh sheet-embedded chip. Islets which are easily placed on the mesh are trapped and held in place. Culture medium was pumped through the chip. The system was complemented by a sample fraction chip for fluid collection. The functional test with high and low glucose levels was performed with murine pancreatic islets to test the performance of the system. The results have indicated that the system successfully analyzes insulin secretion, which confirms that it is able to evaluate the quality of islets cheaply and quickly. Thanks to improved islet cell assessment methods, pancreatic islet transplantation is becoming safer and more successful.
3.3. Current Trends and Future Directions
Three-dimentional culture systems have been under research for quite some time, with new systems being released and new fields of applicability can be seen everywhere. With increasing cellular complexity, culture systems are more error-prone and less reproducible than traditional cultures. The in-troduction of OOAC devices increased the effectiveness of organoids by combining microfluidic systems and organoid cultures. The key directions for organoid applicability in research and clinical setting are provided in Figure 2. What is important to remember is that any culturing device needs to be appropriate for its specific purpose, since every organ needs its unique setup. Until now there is no device which can replace animal testing totally. Another drawback of organoid systems is the lack of interorgan communication. However, research is currently underway to address these challenges as well, and promising novel multi-organ-on-a-chip devises will represent the human body even more accurately in the future than previous systems [47]. In the treatment of pancreatic tumors, a great challenge lies within the low resectability rates. Organoids can reduce this problem through high-throughput sensitivity testing methods, enabling a more individualized medication. Even though PDAC has high heterogeneity, organoid sensitivity testing can hopefully lead to successful treatment results, subsequently resulting in tumor shrinkage. With the implementation of rapidly evolving technology, an unresectable PDAC might be curable in the near future. To add more, in the field of pancreatic islet transplantation, organoids could be used with great advantage for production and evaluation of islets. In particular, using OOAC devices, it is possible to produce small size islets in large numbers, making islet transplantation utilizing pluripotent stem cells a relevant alternative to pancreas transplantation. We confirmed the great advantages and potential which 3D culture systems hold. Further research has to demonstrate whether these advantages can also be applied in clinical practice.
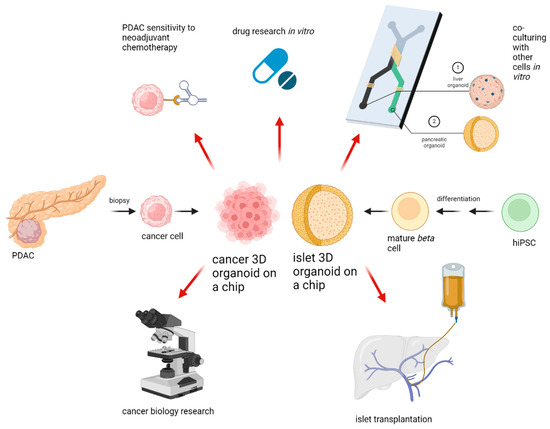
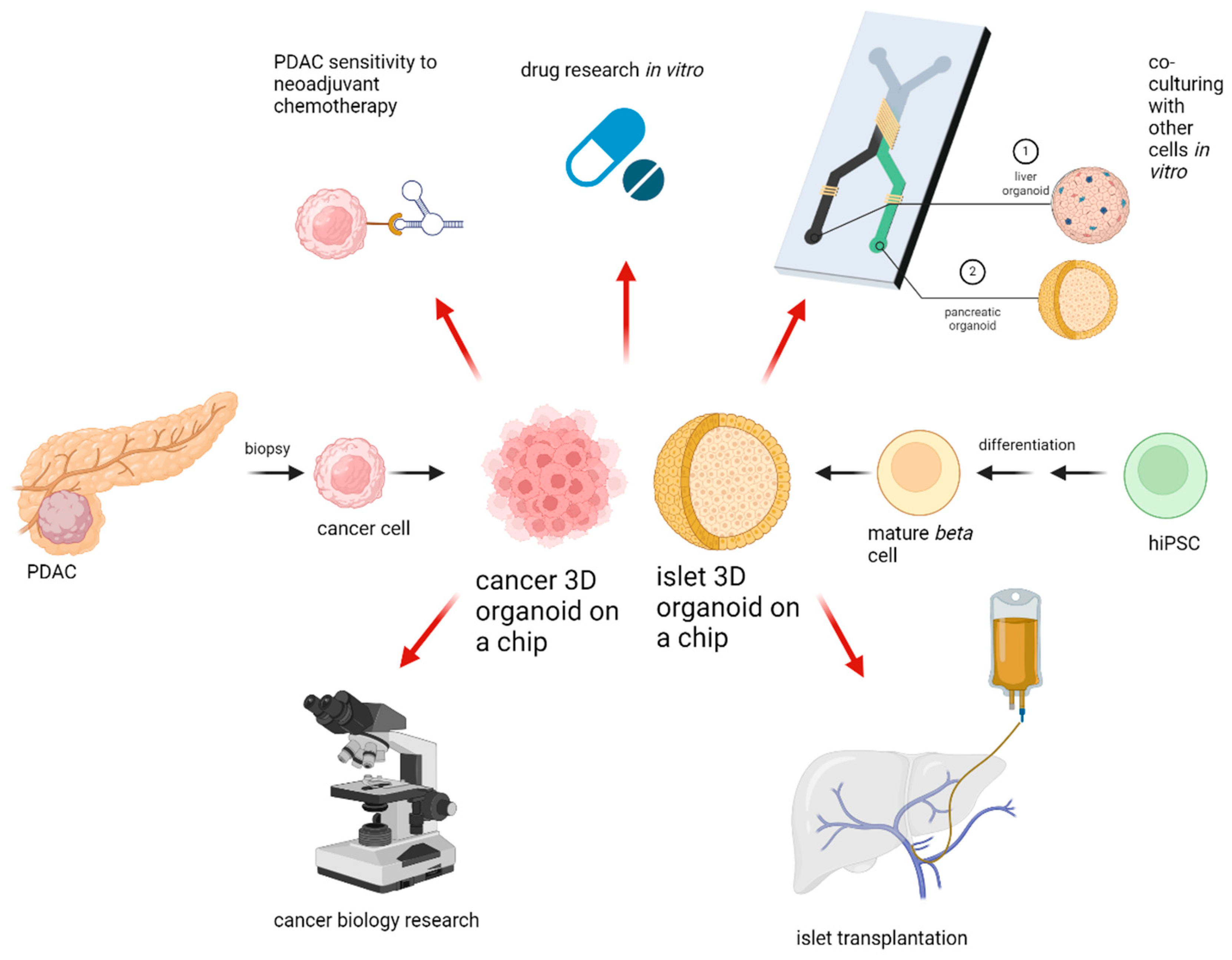
Figure 2.
Applications for 3D organoids. After PDAC biopsy, 3D cultures of cancer cells can be established. If pharmacotyping is successful, personalized chemotherapy or immunotherapy can be initiated. HiPSC can be differentiated to mature beta cells followed by same-size organoid formation in microfluidic devices with subsequent islet transplantation into the portal vein. Pancreatic cancer or islet organoids can be co-cultured with other cells in vitro to create a multiple organ-on-a-chip model for further drug or cell biology research. Created with BioRender.com.
4. Conclusions
Despite difficulties in 3D organoid cultures or microfluidic systems, these technological advances will alter management of pancreatic diseases. If the majority of patients with borderline resectable PDAC could be treated with personalized neoadjuvant chemotherapy or immunotherapy, more patients would benefit from R0 resection. To add more, microfluidic device utilization in proliferating, differentiating, and preparing same-size pseudoislets derived from HiPSC would increase islet transplantation numbers substantially. Further research in these technologies is necessary to make a significant impact in pancreatic surgery.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.G. and V.P.; methodology, A.G.; software, V.P.; validation, A.G.; formal analysis, V.P.; investigation, R.D.; resources, V.P.; data curation, V.P. and R.D.; writing—original draft preparation, R.D.; writing—review and editing, V.P.; visualization, V.P.; supervision, A.G.; project administration, A.G.; funding acquisition, V.P. and A.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Vilnius University.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| ASC | Adult stem cells |
| DM | Diabetes mellitus |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| ESC | Embryonic stem cells |
| HiPSC | Human induced pluripotent stem cells |
| OOAC | Organ-on-a-chip |
| PDAC | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma |
| T1DM | Type 1 diabetes mellitus |
| TME | Tumor microenvironment |
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, D.; Fuchs, E.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 7–33. [Google Scholar]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global Cancer Statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bengtsson, A.; Andersson, R.; Ansari, D. The actual 5-year survivors of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma based on real-world data. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16425. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, W.; Wang, J.; Chen, H.; Ye, L.; Qiu, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, R.; Weng, G.; Liu, T.; Su, D.; et al. Epidemiology of pancreatic cancer: New version, new vision. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 2023, 35, 438–450. [Google Scholar]
- Park, W.; Chawla, A.; O’Reilly, E.M. Pancreatic Cancer: A Review. JAMA 2021, 326, 851–862. [Google Scholar]
- Vincent, A.; Herman, J.; Schulick, R.; Hruban, R.H.; Goggins, M. Pancreatic cancer. Lancet 2011, 378, 607–620. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Laura Gutiérrez, M.; Muñoz-Bellvís, L.; Orfao, A. Genomic Heterogeneity of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma and Its Clinical Impact. Cancers 2021, 13, 4451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foglizzo, V.; Cocco, E.; Marchiò, S. Advanced Cellular Models for Preclinical Drug Testing: From 2D Cultures to Organ-on-a-Chip Technology. Cancers 2022, 14, 3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Q.; Xu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Fan, Z.; Kong, D. Progress in the Application of Organoids-On-A-Chip in Diseases. Organogenesis 2024, 20, 2386727. [Google Scholar]
- Piro, G.; Agostini, A.; Larghi, A.; Quero, G.; Carbone, C.; Esposito, A.; Rizzatti, G.; Attili, F.; Alfieri, S.; Costamagna, G.; et al. Pancreatic Cancer Patient-Derived Organoid Platforms: A Clinical Tool to Study Cell- and Non-Cell-Autonomous Mechanisms of Treatment Response. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 793144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, M.; Meng, H.; Tan, D.; Li, P.; Qin, J.; An, Q.; Shi, C.; An, J. Establishment of organoid models for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and screening of individualized therapy strategy. Anim. Model Exp. Med. 2023, 6, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Houchen, C.W.; Li, M. Patient-Derived Organoid Pharmacotyping Guides Precision Medicine for Pancreatic Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 3176–3178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäkinen, L.; Vähä-Koskela, M.; Juusola, M.; Mustonen, H.; Wennerberg, K.; Hagström, J.; Puolakkainen, P.; Seppänen, H. Pancreatic Cancer Organoids in the Field of Precision Medicine: A Review of Literature and Experience on Drug Sensitivity Testing with Multiple Readouts and Synergy Scoring. Cancers 2022, 14, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Chen, X.; Dowbaj, A.M.; Sljukic, A.; Bratlie, K.; Lin, L.; Fong, E.L.S.; Balachander, G.M.; Chen, Z.; Soragni, A.; et al. Organoids. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 2022, 2, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Wang, M.; Liu, L.; Wang, G.; Wang, L.; Zhong, C.; Gao, C.; Wu, W.; Li, L. Ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration/biopsy-based pancreatic organoids establishment: An alternative model for basic and preclinical research. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2023, 11, goad019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.; Lee, S.H.; Ku, J.L.; Chun, J.W.; Seo, H.Y.; Kim, S.C.; Paik, W.H.; Ryu, J.K.; Lee, S.K.; et al. Establishment of Patient-Derived Pancreatic Cancer Organoids from Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine-Needle Aspiration Biopsies. Gut Liver 2022, 16, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johannes Roman Wiessner, A.; Orben, F.; Schäfer, A.; Fricke, L.; Schneider, G.; Reichert, M.; Herner, A.; Mayr, U.; Phillip, V.; Treiber, M.; et al. Comparison of endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration and fine-needle biopsy to generate pancreatic cancer organoids: Randomized trial. Endosc. Int. Open 2024, 12, E361. [Google Scholar]
- Tiriac, H.; Bucobo, J.C.; Tzimas, D.; Grewel, S.; Lacomb, J.F.; Rowehl, L.M.; Nagula, S.; Wu, M.; Kim, J.; Sasson, A.; et al. Successful creation of pancreatic cancer organoids by means of EUS-guided fine-needle biopsy sampling for personalized cancer treatment. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2018, 87, 1474–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shik Mun, K.; Arora, K.; Huang, Y.; Yang, F.; Yarlagadda, S.; Ramananda, Y.; Abu-El-Haija, M.; Palermo, J.J.; Appakalai, B.N.; Nathan, J.D.; et al. Patient-derived pancreas-on-a-chip to model cystic fibrosis-related disorders. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, S.; McOlash, L.; Palen, K.; Johnson, B.; Duris, C.; Yang, Q.; Dwinell, M.B.; Hunt, B.; Evans, D.B.; Gershan, J.; et al. Development of primary human pancreatic cancer organoids, matched stromal and immune cells and 3D tumor microenvironment models. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mobasseri, M.; Shirmohammadi, M.; Amiri, T.; Vahed, N.; Fard, H.H.; Ghojazadeh, M. Prevalence and incidence of type 1 diabetes in the world: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Health Promot. Perspect. 2020, 10, 98–115. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Holt, R.I.G.; Devries, J.H.; Hess-Fischl, A.; Hirsch, I.B.; Kirkman, M.S.; Klupa, T.; Ludwig, B.; Nørgaard, K.; Pettus, J.; Renard, E.; et al. The Management of Type 1 Diabetes in Adults. A Consensus Report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetes Care 2021, 44, 2589–2625. [Google Scholar]
- Samoylova, M.L.; Borle, D.; Ravindra, K.V. Pancreas Transplantation: Indications, Techniques, and Outcomes. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 99, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barton, F.B.; Rickels, M.R.; Alejandro, R.; Hering, B.J.; Wease, S.; Naziruddin, B.; Oberholzer, J.; Odorico, J.S.; Garfinkel, M.R.; Levy, M.; et al. Improvement in outcomes of clinical islet transplantation: 1999–2010. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 1436–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-El-Haija, M.; Anazawa, T.; Beilman, G.J.; Besselink, M.G.; Del Chiaro, M.; Demir, I.E.; Dennison, A.R.; Dudeja, V.; Freeman, M.L.; Friess, H.; et al. The role of total pancreatectomy with islet autotransplantation in the treatment of chronic pancreatitis: A report from the International Consensus Guidelines in chronic pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2020, 20, 762–771. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Lo, J.F.; Mendoza-Elias, J.E.; Adewola, A.F.; Harvat, T.A.; Kinzer, K.P.; Lee, D.; Qi, M.; Eddington, D.T.; Oberholzer, J. Application of microfluidic technology to pancreatic islet research: First decade of endeavor. Bioanalysis 2010, 2, 1729–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mccall, M.D.; Toso, C.; Baetge, E.E.; Shapiro, A.M.J. Are stem cells a cure for diabetes? Clin. Sci. 2009, 118, 87–97. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Gamble, A.; Pawlick, R.; Pepper, A.R.; Salama, B.; Toms, D.; Razian, G.; Ellis, C.; Bruni, A.; Gala-Lopez, B.; et al. Bioengineered human pseudoislets form efficiently from donated tissue, compare favourably with native islets in vitro and restore normoglycaemia in mice. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 2016–2029. [Google Scholar]
- Tung, Y.C.; Hsiao, A.Y.; Allen, S.G.; Torisawa, Y.S.; Ho, M.; Takayama, S. High-throughput 3D spheroid culture and drug testing using a 384 hanging drop array. Analyst 2011, 136, 473–478. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, R.G.; Greenman, M.J.; Mall, F.P.; Jackson, C.M. Observations of the living developing nerve fiber. Anat. Rec. 1907, 1, 116–128. [Google Scholar]
- Kapałczyńska, M.; Kolenda, T.; Przybyła, W.; Zajączkowska, M.; Teresiak, A.; Filas, V.; Ibbs, M.; Bliźniak, R.; Łuczewski, Ł.; Lamperska, K. 2D and 3D cell cultures—A comparison of different types of cancer cell cultures. Arch. Med. Sci. 2016, 14, 910. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Vega, V.; Hou, S.; Plenker, D.; Tiriac, H.; Baillargeon, P.; Shumate, J.; Scampavia, L.; Seldin, J.; Souza, G.R.; Tuveson, D.A.; et al. Lead identification using 3D models of pancreatic cancer. SLAS Discov. 2022, 27, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kolenda, T.; Kapałczyńska, M.; Przybyła, W.; Zajączkowska, M.; Teresiak, A.; Filas, V.; Ibbs, M.; Bliźniak, R.; Łuczewski, Ł.; Lamperska, K. State of the art paper 2D and 3D cell cultures-a comparison of different types of cancer cell cultures. Arch. Med. Sci. 2018, 14, 910–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson, A.; Andersson, R.; Rahm, J.; Ganganna, K.; Andersson, B.; Ansari, D. Organoid technology for personalized pancreatic cancer therapy. Cell Oncol. 2021, 44, 251. [Google Scholar]
- Tiriac, H.; French, R.; Lowy, A.M. Isolation and Characterization of Patient-derived Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Organoid Models. J. Vis. Exp. 2020, 155, e60364. [Google Scholar]
- Edmondson, R.; Broglie, J.J.; Adcock, A.F.; Yang, L. Three-Dimensional Cell Culture Systems and Their Applications in Drug Discovery and Cell-Based Biosensors. Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 2014, 12, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yao, J.; Yang, M.; Atteh, L.; Liu, P.; Mao, Y.; Meng, W.; Li, X. A pancreas tumor derived organoid study: From drug screen to precision medicine. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 398. [Google Scholar]
- Gunti, S.; Hoke, A.T.K.; Vu, K.P.; London, N.R. Organoid and Spheroid Tumor Models: Techniques and Applications. Cancers 2021, 13, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barroso, M.; Chheda, M.G.; Clevers, H.; Elez, E.; Kaochar, S.; Kopetz, S.E.; Li, X.N.; Meric-Bernstam, F.; Meyer, C.A.; Mou, H.; et al. A path to translation: How 3D patient tumor avatars enable next generation precision oncology. Cancer Cell 2022, 40, 1448–1453. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, X.; Hartanto, Y.; Zhang, H. Advances in multicellular spheroids formation. J. R. Soc. Interface 2017, 14, 20160877. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fennema, E.; Rivron, N.; Rouwkema, J.; van Blitterswijk, C.; De Boer, J. Spheroid culture as a tool for creating 3D complex tissues. Trends Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achilli, T.M.; Meyer, J.; Morgan, J.R. Advances in the formation, use and understanding of multi-cellular spheroids. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2012, 12, 1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, K.; Fujimori, N.; Ichihara, K.; Takeno, A.; Murakami, M.; Ohno, A.; Kakehashi, S.; Teramatsu, K.; Ueda, K.; Nakata, K.; et al. Patient-derived organoids of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma for subtype determination and clinical outcome prediction. J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 59, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, S.; Yogo, A.; Otsubo, T.; Umehara, H.; Oishi, J.; Kodo, T.; Masui, T.; Takaishi, S.; Seno, H.; Uemoto, S.; et al. Establishment of patient-derived organoids and a characterization-based drug discovery platform for treatment of pancreatic cancer. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 489. [Google Scholar]
- Marsee, A.; Roos, F.J.M.; Verstegen, M.M.A.; Roos, F.; Verstegen, M.; Clevers, H.; Vallier, L.; Takebe, T.; Huch, M.; Peng, W.C.; et al. Building consensus on definition and nomenclature of hepatic, pancreatic, and biliary organoids. Cell Stem Cell 2021, 28, 816–832. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Koo, B.K.; Knoblich, J.A. Human organoids: Model systems for human biology and medicine. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 571–584. [Google Scholar]
- Nikolaev, M.; Mitrofanova, O.; Broguiere, N.; Geraldo, S.; Dutta, D.; Tabata, Y.; Elci, B.; Brandenberg, N.; Kolotuev, I.; Gjorevski, N.; et al. Homeostatic mini-intestines through scaffold-guided organoid morphogenesis. Nature 2020, 585, 574–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshihara, E.; O’Connor, C.; Gasser, E.; Wei, Z.; Oh, T.G.; Tseng, T.W.; Wang, D.; Cayabyab, F.; Dai, Y.; Yu, R.T.; et al. Immune-evasive human islet-like organoids ameliorate diabetes. Nature 2020, 586, 606–611. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.V.; Er, P.X.; Lawlor, K.T.; Motazedian, A.; Scurr, M.; Ghobrial, I.; Combes, A.N.; Zappia, L.; Oshlack, A.; Stanley, E.G.; et al. Kidney micro-organoids in suspension culture as a scalable source of human pluripotent stem cell-derived kidney cells. Development 2019, 146, dev172361. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.H.; Chang, M.Y. Application of Human Brain Organoids—Opportunities and Challenges in Modeling Human Brain Development and Neurodevelopmental Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mun, S.J.; Ryu, J.S.; Lee, M.O.; Son, Y.S.; Oh, S.J.; Cho, H.S.; Son, M.Y.; Kim, D.S.; Kim, S.J.; Yoo, H.J.; et al. Generation of expandable human pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatocyte-like liver organoids. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 970–985. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Y.; Eglen, R.M. Three-Dimensional Cell Cultures in Drug Discovery and Development. Slas Discov. 2017, 22, 456. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roberto de Barros, N.; Wang, C.; Maity, S.; Peirsman, A.; Nasiri, R.; Herland, A.; Ermis, M.; Kawakita, S.; Gregatti Carvalho, B.; Hosseinzadeh Kouchehbaghi, N.; et al. Engineered organoids for biomedical applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2023, 203, 115142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takasato, M.; Er, P.X.; Becroft, M.; Vanslambrouck, J.M.; Stanley, E.G.; Elefanty, A.G.; Little, M.H. Directing human embryonic stem cell differentiation towards a renal lineage generates a self-organizing kidney. Nat. Cell Biol. 2013, 16, 118–126. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, T.; Du, W.L.; Chen, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.N. Organoid models of the tumor microenvironment and their applications. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 5829–5841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, J.T.; Li, X.; Zhu, J.; Giangarra, V.; Grzeskowiak, C.L.; Ju, J.; Liu, I.H.; Chiou, S.H.; Salahudeen, A.A.; Smith, A.R.; et al. Organoid Modeling of the Tumor Immune Microenvironment. Cell 2018, 175, 1972–1988.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swayden, M.; Soubeyran, P.; Iovanna, J. Upcoming Revolutionary Paths in Preclinical Modeling of Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2020, 9, 1443. [Google Scholar]
- Haque, M.R.; Wessel, C.R.; Leary, D.D.; Wang, C.; Bhushan, A.; Bishehsari, F. Patient-derived pancreatic cancer-on-a-chip recapitulates the tumor microenvironment. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2022, 8, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Melton, D.A. Pancreas regeneration. Nature 2018, 557, 351. [Google Scholar]
- Takasato, M.; Er, P.X.; Chiu, H.S.; Maier, B.; Baillie, G.J.; Ferguson, C.; Parton, R.G.; Wolvetang, E.J.; Roost, M.S.; Chuva, S.M.; et al. Kidney organoids from human iPS cells contain multiple lineages and model human nephrogenesis. Nature 2015, 526, 564–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Zhou, T.T.; Cao, L. Use and application of organ-on-a-chip platforms in cancer research. J. Cell Commun. Signal 2023, 17, 1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, D.; Gonzalez-Suarez, A.M.; Dumbrava, M.G.; Medlyn, M.; de Hoyos-Vega, J.M.; Cichocki, F.; Miller, J.S.; Ding, L.; Zhu, M.; Stybayeva, G.; et al. Microfluidic Organoid Cultures Derived from Pancreatic Cancer Biopsies for Personalized Testing of Chemotherapy and Immunotherapy. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2303088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Feng, L.; Wu, J.; Zhu, X.; Wen, W.; Gong, X. Organ-on-a-chip: Recent breakthroughs and future prospects. Biomed. Eng. Online 2020, 19, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glieberman, A.L.; Pope, B.D.; Zimmerman, J.F.; Liu, Q.; Ferrier, J.P.; Kenty, J.H.R.; Schrell, A.M.; Mukhitov, N.; Shores, K.L.; Tepole, A.B.; et al. Synchronized stimulation and continuous insulin sensing in a microfluidic human Islet on a Chip designed for scalable manufacturing. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 2993–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, J.E.; Muthuswamy, L.; Huang, L.; Akshinthala, D.; Perea, S.; Gonzalez, R.S.; Tsai, L.L.; Cohen, J.; Bockorny, B.; Bullock, A.J.; et al. Organoid Sensitivity Correlates with Therapeutic Response in Patients with Pancreatic Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 708–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhuo, Q.; Ye, Z.; Xu, X.; Ji, S. Organoid model: A new hope for pancreatic cancer treatment? Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2021, 1875, 188466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picollet-D’hahan, N.; Zuchowska, A.; Lemeunier, I.; le Gac, S. Multiorgan-on-a-Chip: A Systemic Approach To Model and Decipher Inter-Organ Communication. Trends Biotechnol. 2021, 39, 788–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seppälä, T.T.; Burkhart, R.A. Can Pancreatic Organoids Help in the Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer? Adv. Surg. 2021, 55, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conroy, T.; Castan, F.; Lopez, A.; Turpin, A.; Ben Abdelghani, M.; Wei, A.C.; Mitry, E.; Biagi, J.J.; Evesque, L.; Artru, P.; et al. Five-Year Outcomes of FOLFIRINOX vs Gemcitabine as Adjuvant Therapy for Pancreatic Cancer: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2022, 8, 1571–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennig, A.; Baenke, F.; Klimova, A.; Drukewitz, S.; Jahnke, B.; Brückmann, S.; Secci, R.; Winter, C.; Schmäche, T.; Seidlitz, T.; et al. Detecting drug resistance in pancreatic cancer organoids guides optimized chemotherapy treatment. J. Pathol. 2022, 257, 607–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farshadi, E.A.; Chang, J.; Sampadi, B.; Doukas, M.; Van’t Land, F.; van der Sijde, F.; Vietsch, E.E.; Pothof, J.; Koerkamp, B.G.; van Eijck, C.H.J. Organoids Derived from Neoadjuvant FOLFIRINOX Patients Recapitulate Therapy Resistance in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 6602–6612. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.C.; Seo, H.Y.; Lee, J.O.; Maeng, J.E.; Shin, Y.K.; Lee, S.H.; Jang, J.Y.; Ku, J.L. Establishment, characterization, and biobanking of 36 pancreatic cancer organoids: Prediction of metastasis in resectable pancreatic cancer. Cell. Oncol. 2024, 47, 1627–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beutel, A.K.; Schütte, L.; Scheible, J.; Roger, E.; Müller, M.; Perkhofer, L.; Kestler, A.M.T.U.; Kraus, J.M.; Kestler, H.A.; Barth, T.F.E.; et al. A Prospective Feasibility Trial to Challenge Patient-Derived Pancreatic Cancer Organoids in Predicting Treatment Response. Cancers 2021, 13, 2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frappart, P.O.; Walter, K.; Gout, J.; Beutel, A.K.; Morawe, M.; Arnold, F.; Breunig, M.; Barth, T.F.E.; Marienfeld, R.; Schulte, L.; et al. Pancreatic cancer-derived organoids—A disease modeling tool to predict drug response. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2020, 8, 594. [Google Scholar]
- Tiriac, H.; Belleau, P.; Engle, D.D.; Plenker, D.; Deschênes, A.; DSomerville, T.D.; MFroeling, F.E.; Burkhart, R.A.; Denroche, R.E.; Jang, G.H.; et al. Organoid Profi ling Identifi es Common Responders to Chemotherapy in Pancreatic Cancer. Available online: www.aacrjournals.org (accessed on 24 January 2023).
- Driehuis, E.; van Hoeck, A.; Moore, K.; Kolders, S.; Francies, H.E.; Gulersonmez, M.C.; Stigter, E.C.A.; Burgering, B.; Geurts, V.; Gracanin, A.; et al. Pancreatic cancer organoids recapitulate disease and allow personalized drug screening. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 26580–26590. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dantes, Z.; Yen, H.Y.; Pfarr, N.; Winter, C.; Steiger, K.; Muckenhuber, A.; Hennig, A.; Lange, S.; Engleitner, T.; Öllinger, R.; et al. Implementing cell-free DNA of pancreatic cancer patient-derived organoids for personalized oncology. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e137809. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.H.; Hung, Y.P.; Chiu, N.C.; Lee, R.C.; Li, C.P.; Chao, Y.; Shyr, Y.M.; Wang, S.E.; Chen, S.C.; Lin, S.H.; et al. Correlation between drug sensitivity profiles of circulating tumour cell-derived organoids and clinical treatment response in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Eur. J. Cancer 2022, 166, 208–218. [Google Scholar]
- Strobel, O.; Neoptolemos, J.; Jäger, D.; Büchler, M.W. Optimizing the outcomes of pancreatic cancer surgery. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 16, 11–26. [Google Scholar]
- Seppälä, T.T.; Zimmerman, J.W.; Sereni, E.; Plenker, D.; Suri, R.; Rozich, N.; Blair, A.; Thomas, D.L.; Teinor, J.; Javed, A.; et al. Patient-derived organoid pharmacotyping is a clinically tractable strategy for precision medicine in pancreatic cancer. Ann. Surg. 2020, 272, 427. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzocchi, A.; Soker, S.; Skardal, A. 3D bioprinting for high-throughput screening: Drug screening, disease modeling, and precision medicine applications. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2019, 6, 011302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.; Tiriac, H.; Sridharan, B.P.; Scampavia, L.; Madoux, F.; Seldin, J.; Souza, G.R.; Watson, D.; Tuveson, D.; Spicer, T.P. Advanced Development of Primary Pancreatic Organoid Tumor Models for High-Throughput Phenotypic Drug Screening. Slas Discov. 2018, 23, 574. [Google Scholar]
- Pishvaian, M.J.; Bender, R.J.; Halverson, D.; Rahib, L.; Hendifar, A.E.; Mikhail, S.; Chung, V.; Picozzi, V.J.; Sohal, D.; Blais, E.M.; et al. Molecular Profiling of Patients with Pancreatic Cancer: Initial Results from the Know Your Tumor Initiative. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 5018–5027. [Google Scholar]
- Grützmeier, S.E.; Sodal, H.M.M.; Kovacevic, B.; Vilmann, P.; Karstensen, J.G.; Klausen, P. EUS-guided biopsies versus surgical specimens for establishing patient-derived pancreatic cancer organoids: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2024, 100, 750–755. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Demyan, L.; Habowski, A.N.; Plenker, D.; King, D.A.; Standring, O.J.; Tsang, C.; St Surin, L.; Rishi, A.; Crawford, J.M.; Boyd, J.; et al. Pancreatic Cancer Patient-derived Organoids Can Predict Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy. Ann. Surg. 2022, 276, 450–462. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y.C.; Urs, S.; Chen, L.; Simeone, D.M.; Yoon, E. Scalable Multiplexed Drug-Combination Screening Platforms Using 3D Microtumor Model for Precision Medicine. Small 2018, 14, e1703617. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jaaks, P.; Coker, E.A.; Vis, D.J.; Edwards, O.; Carpenter, E.F.; Leto, S.M.; Dwane, L.; Sassi, F.; Lightfoot, H.; Barthorpe, S.; et al. Effective drug combinations in breast, colon and pancreatic cancer cells. Nature 2022, 603, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, S.K.; Khawar, I.A.; Jeong, S.Y.; Chung, S.; Kuh, H.J. Microfluidic co-culture of pancreatic tumor spheroids with stellate cells as a novel 3D model for investigation of stroma-mediated cell motility and drug resistance. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, S.R.; Kang, M. Exploring Tumor–Immune Interactions in Co-Culture Models of T Cells and Tumor Organoids Derived from Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport Huyer, L.; Radisic, M.; Dou, W.; Sun, Y.; Radulovich, N.; Tsao, M.S.; Fook Lun Lai, B.; Xing Ze Lu, R.; Hu, Y.; Dou, W.; et al. Recapitulating Pancreatic Tumor Microenvironment through Synergistic Use of Patient Organoids and Organ-on-a-Chip Vasculature. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2000545. [Google Scholar]
- Diabetes. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/diabetes (accessed on 22 December 2022).
- Wassmer, C.H.; Bellofatto, K.; Perez, L.; Lavallard, V.; Cottet-Dumoulin, D.; Ljubicic, S.; Parnaud, G.; Bosco, D.; Berishvili, E.; Lebreton, F. Engineering of Primary Pancreatic Islet Cell Spheroids for Three-dimensional Culture or Transplantation: A Methodological Comparative Study. Cell Transplant. 2020, 29, 963689720937292. [Google Scholar]
- Kandaswamy, R.; Skeans, M.A.; Gustafson, S.K.; Carrico, R.J.; Prentice, M.A.; Israni, A.K.; Snyder, J.J.; Kasiske, B.L. Pancreas. Am. J. Transplant. 2016, 16 (Suppl. S2), 47–68. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wassmer, C.H.; Lebreton, F.; Bellofatto, K.; Bosco, D.; Berney, T.; Berishvili, E. Generation of insulin-secreting organoids: A step toward engineering and transplanting the bioartificial pancreas. Transpl. Int. 2020, 33, 1577–1588. [Google Scholar]
- Jeon, S.; Lee Ysun Oh, S.R.; Jeong, J.; Lee, D.H.; So, K.H.; Hwang, N.S. Recent advances in endocrine organoids for therapeutic application. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2023, 199, 114959. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, J.S.; Wang, Y.; Harvat, T.A.; Oberholzer, J.; Eddington, D.T. Microfluidic device for multimodal characterization of pancreatic islets. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abadpour, S.; Aizenshtadt, A.; Olsen, P.A.; Shoji, K.; Wilson, S.R.; Krauss, S.; Scholz, H. Pancreas-on-a-Chip Technology for Transplantation Applications. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2020, 20, 72. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Khawaga, S.; Memon, B.; Butler, A.E.; Taheri, S.; Abou-Samra, A.B.; Abdelalim, E.M. Pathways governing development of stem cell-derived pancreatic β cells: Lessons from embryogenesis. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2018, 93, 364–389. [Google Scholar]
- Hori, T.; Yamane, K.; Anazawa, T.; Kurosawa, O.; Iwata, H. Compact fluidic system for functional assessment of pancreatic islets. Biomed. Microdevices 2019, 21, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).