Harnessing Polyethylene Glycol 3350 for Enhanced Peripheral Nerve Repair: A Path to Accelerated Recovery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Model
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Operative Intervention
2.4. Electrophysiological Evaluations
2.5. Assessment of Motor Function Utilizing the Inclined Plate Technique
2.6. Histological and Immunohistochemical Analysis
2.7. Biochemical Examination of Sciatic Nerve Tissue
2.8. Assessment of Lipid Peroxidation (MDA Concentrations)
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Electrophysiological Evaluations
3.2. Restoration of Functionality
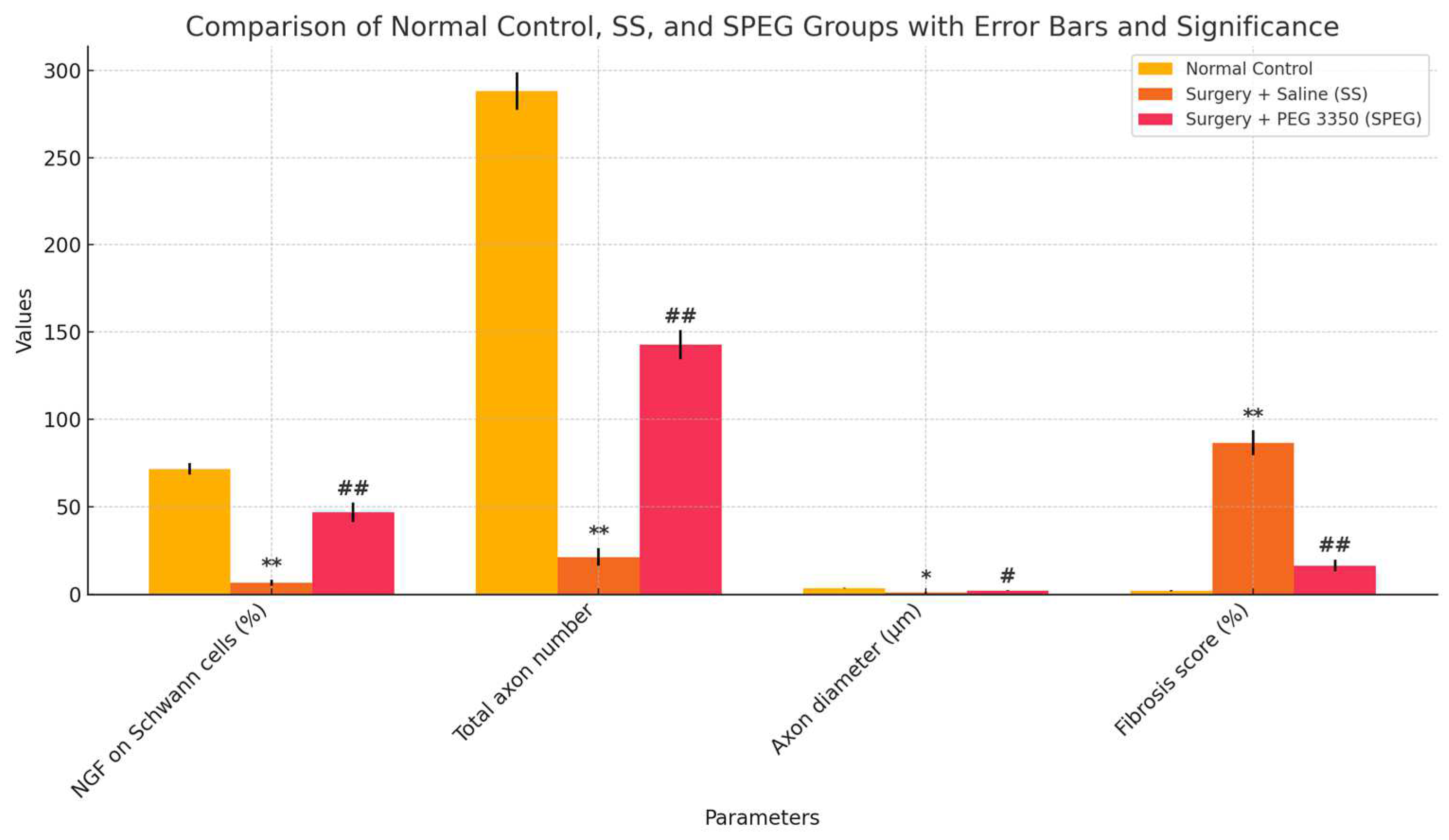
3.3. Nerve Biochemical Examination
3.4. Histopathological and Immunohistochemical Observations
4. Discussion
Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Juckett, L.; Saffari, T.M.; Ormseth, B.; Senger, J.-L.; Moore, A.M. The Effect of Electrical Stimulation on Nerve Regeneration Following Peripheral Nerve Injury. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willand, M.P.; Nguyen, M.-A.; Borschel, G.H.; Gordon, T. Electrical Stimulation to Promote Peripheral Nerve Regeneration. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2015, 30, 490–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padovano, W.M.; Dengler, J.; Patterson, M.M.; Yee, A.; Snyder-Warwick, A.K.; Wood, M.D.; Moore, A.M.; Mackinnon, S.E. Incidence of Nerve Injury After Extremity Trauma in the United States. Hand 2020, 17, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, N.; Acharya, A.M.; Bhat, A.K.; Upadhya, D.; Punja, D.; Suhani, S. The outcome of polyethylene glycol fusion augmented by electrical stimulation in a delayed setting of nerve repair following neurotmesis in a rat model. Acta Neurochir. 2023, 165, 3993–4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikesh, M.; Ghergherehchi, C.L.; Hastings, R.L.; Ali, A.; Rahesh, S.; Jagannath, K.; Sengelaub, D.R.; Trevino, R.C.; Jackson, D.M.; Bittner, G.D. Polyethylene glycol solutions rapidly restore and maintain axonal continuity, neuromuscular structures, and behaviors lost after sciatic nerve transections in female rats. J. Neurosci. Res. 2018, 96, 1223–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Mackinnon, S.E.; Wood, M.D. Advances in the repair of segmental nerve injuries and trends in reconstruction. Muscle Nerve 2020, 61, 726–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, C.R.; Reis, R.L.; Oliveira, J.M. Fundamentals and Current Strategies for Peripheral Nerve Repair and Regeneration. In Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; Volume 1249, pp. 173–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Nest, D.S.; Kahan, D.M.; Ilyas, A.M. Polyethylene Glycol Fusion of Nerve Injuries: Review of the Technique and Clinical Applicability. J. Hand Microsurg. 2020, 13, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.-Q.; Jiang, B.-G.; Zhang, P.-X.; Zhang, H.-B. The rule of proliferation after sciatic injury of rats: Immunohistological observation. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi 2006, 44, 268–270. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Pušnik, L.; Lechner, L.; Serša, I.; Cvetko, E.; Haas, P.; Jengojan, S.A.; Snoj, Ž. 3D fascicular reconstruction of median and ulnar nerve: Initial experience and comparison between high-resolution ultrasound and MR microscopy. Eur. Radiol. Exp. 2024, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sąsiadek, M.J.; Szewczyk, P.; Bladowska, J. Application of diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) in pathological changes of the spinal cord. Med. Sci. Monit. 2012, 18, RA73–RA79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alper, A.; Pashankar, D.S. Polyethylene Glycol: A game-changer laxative for children. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2013, 57, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasut, G.; Veronese, F.M. PEGylation of proteins as tailored chemistry for optimized bioconjugates. In Polymer Therapeutics I; Satchi-Fainaro, R., Duncan, R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 95–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemani, S.; Chaker, S.B.; Ismail, H.M.; Yao, J.; Chang, M.; Kang, H.; Desai, M.; Weikert, D.; Bhandari, P.L.; Drolet, B.; et al. Polyethylene Glycol–Mediated Axonal Fusion Promotes Early Sensory Recovery after Digital Nerve Injury: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2024, 154, 1247–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Britt, J.M.; Kane, J.R.; Spaeth, C.S.; Zuzek, A.; Robinson, G.L.; Gbanaglo, M.Y.; Estler, C.J.; Boydston, E.A.; Schallert, T.; Bittner, G.D. Polyethylene Glycol Rapidly Restores Axonal Integrity and Improves the Rate of Motor Behavior Recovery After Sciatic Nerve Crush Injury. J. Neurophysiol. 2010, 104, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bamba, R.; Waitayawinyu, T.; Nookala, R.M.; Riley, D.C.; Boyer, R.B.; Sexton, K.W.; Boonyasirikool, C.; Niempoog, S.; Kelm, N.D.; Does, M.D.; et al. A novel therapy to promote axonal fusion in human digital nerves. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2016, 81, S177–S183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarac, B.A.; Wordsworth, M.; Schmucker, R.W. Polyethylene Glycol Fusion and Nerve Repair Success: Practical Applications. J. Hand Surg. Glob. Online 2024, 6, 740–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.A.; Zhou, L.; Ghergherehchi, C.L.; Mikesh, M.; Yang, C.Z.; Tucker, H.O.; Allgood, J.; Bushman, J.S.; Bittner, G.D. Polyethylene glycol has immunoprotective effects on sciatic allografts, but behavioral recovery and graft tolerance require neurorrhaphy and axonal fusion. Neural Regen. Res. 2024, 20, 1192–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sever, I.; Ozkul, B.; Atasoy, O.; Cini, N.; Bozkurt, M.; Erdogan, M.; Yaprak, G.; Erbas, O. Neuroprotective effect of polyethylene Glycol (PEG-3350) on radiation-induced brain injury via membrane stabilization. Int. J. Radiat. Res. 2023, 21, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Borgens, R.; Shi, R. Polyethylene glycol immediately repairs neuronal membranes and inhibits free radical production after acute spinal cord injury. J. Neurochem. 2002, 83, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrero-Andrés, A.; Panisello-Roselló, A.; Roselló-Catafau, J.; Folch-Puy, E. Polyethylene glycol 35 ameliorates pancreatic inflammatory response in cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis in rats. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 5970–5982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Siddiqui, A.M.; Cui, X.; Wu, R.; Dong, W.; Zhou, M.; Hu, M.; Simms, H.H.; Wang, P. The anti-inflammatory effect of curcumin in an experimental model of sepsis is mediated by up-regulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma. Crit Care Med. 2006, 34, 1874–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Quick, E.; Leung, G.; Hamann, K.; Fu, Y.; Cheng, J.-X.; Shi, R. Polyethylene Glycol Protects Injured Neuronal Mitochondria. Pathobiology 2009, 76, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rippee, D.B.; Glassman, G.E.; Chaker, S.C.; Assi, P.E.; Black, J.; Yao, J.; Pollins, A.C.; Thayer, W.P. Polyethylene Glycol Treatment for Peripheral Nerve Repair in Preclinical Models. J. Neurol. Neuromed. 2021, 6, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, S.N.; Legato, J.M.; Liu, Y.; Vaccaro, C.N.; Da Silva, R.P.; Miskiel, S.; Gilbert, G.V.; Hakonarson, H.; Fuller, D.A.; Buono, R.J. An analysis of differential gene expression in peripheral nerve and muscle utilizing RNA sequencing after polyethylene glycol nerve fusion in a rat sciatic nerve injury model. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0304773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paskal, A.M.; Paskal, W.; Pietruski, P.; Wlodarski, P.K. Polyethylene Glycol: The Future of Posttraumatic Nerve Repair? Systemic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalçın, M.B.; Bora, E.S.; Erbaş, O. The Effect of Liraglutide on Axon Regeneration and Functional Recovery after Peripheral Nerve Lesion. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibbard, E.A.; Sengelaub, D.R. Intraneural Topography of Rat Sciatic Axons: Implications for Polyethylene Glycol Fusion Peripheral Nerve Repair. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 852933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Venkudusamy, K.; Hibbard, E.A.; Montoya, Y.; Olivarez, A.; Yang, C.Z.; Leung, A.; Gokhale, V.; Periyasamy, G.; Pathak, Z.; et al. Polyethylene glycol fusion repair of severed sciatic nerves accelerates recovery of nociceptive sensory perceptions in male and female rats of different strains. Neural Regen. Res. 2024, 20, 2667–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrero-Andrés, A.; Panisello-Roselló, A.; Serafín, A.; Roselló-Catafau, J.; Folch-Puy, E. Polyethylene Glycol 35 (PEG35) Protects against Inflammation in Experimental Acute Necrotizing Pancreatitis and Associated Lung Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackland, G.L.P.; Del Arroyo, A.G.; Yao, S.T.; Stephens, R.C.F.; Dyson, A.M.; Klein, N.J.P.; Singer, M.M.; Gourine, A.V. Low-molecular-weight polyethylene glycol improves survival in experimental sepsis. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 38, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-J.; Shu, G.-F.; Xu, X.-L.; Peng, C.-H.; Lu, C.-Y.; Cheng, X.-Y.; Luo, X.-C.; Li, J.; Qi, J.; Kang, X.-Q.; et al. Combinational protective therapy for spinal cord injury medicated by sialic acid-driven and polyethylene glycol based micelles. Biomaterials 2019, 217, 119326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Borgens, R.; Shi, R. Polyethylene Glycol Improves Function and Reduces Oxidative Stress in Synaptosomal Preparations following Spinal Cord Injury. J. Neurotrauma 2004, 21, 994–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.G.; Lee, G.B.; Vinayagam, R.; Do, G.S.; Oh, S.Y.; Yang, S.J.; Kwon, J.B.; Singh, M. Anti-Inflammatory, Antioxidative, and Nitric Oxide-Scavenging Activities of a Quercetin Nanosuspension with Polyethylene Glycol in LPS-Induced RAW 264.7 Macrophages. Molecules 2022, 27, 7432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Li, D.; Wu, C.; Ye, L.; Wu, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Yang, S.; Xie, L.; Mao, Y.; Jiang, T.; et al. Nerve growth factor activates autophagy in Schwann cells to enhance myelin debris clearance and to expedite nerve regeneration. Theranostics 2020, 10, 1649–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burstein, D.E.; Greene, L.A. Evidence for RNA synthesis-dependent and -independent pathways in stimulation of neurite outgrowth by nerve growth factor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1978, 75, 6059–6063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, B.; Lv, Y. Dual-delivery of VEGF and NGF by emulsion electrospun nanofibrous scaffold for peripheral nerve regeneration. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 82, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, J.; Coughlin, M.; Macintyre, L.; Holmes, M.; Visheau, B. Evidence that endogenous beta nerve growth factor is responsible for the collateral sprouting, but not the regeneration, of nociceptive axons in adult rats. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 6596–6600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Barua, S.; Huang, M.Y.; Park, J.; Yenari, M.A.; Lee, J.E. Heat Shock Protein 70 (HSP70) Induction: Chaperonotherapy for Neuroprotection after Brain Injury. Cells 2020, 9, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margiana, R.; Salma, N.M.; Jusuf, A.A. Impact of Platelet-Rich Plasma on Sciatic Nerve Injury in Rats: HSP 70 Expression and Histological Changes in the Anterior Horn of the Spinal Cord. South East. Eur. J. Public Health 2024, XXV, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaouali, M.A.; Bejaoui, M.; Calvo, M.; Folch-Puy, E.; Pantazi, E.; Pasut, G.; Rimola, A.; Ben Abdennebi, H.; Adam, R.; Roselló-Catafau, J. Polyethylene glycol rinse solution: An effective way to prevent ischemia-reperfusion injury. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 16203–16214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yenari, M.A.; Giffard, R.G.; Sapolsky, R.M.; Steinberg, G.K. The neuroprotective potential of heat shock protein 70 (HSP70). Mol. Med. Today 1999, 5, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalçın, M.B.; Bora, E.S.; Erdoğan, M.A.; Çakır, A.; Erbaş, O. The Effect of Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Peripheral Nerve Damage in a Rodent Model. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



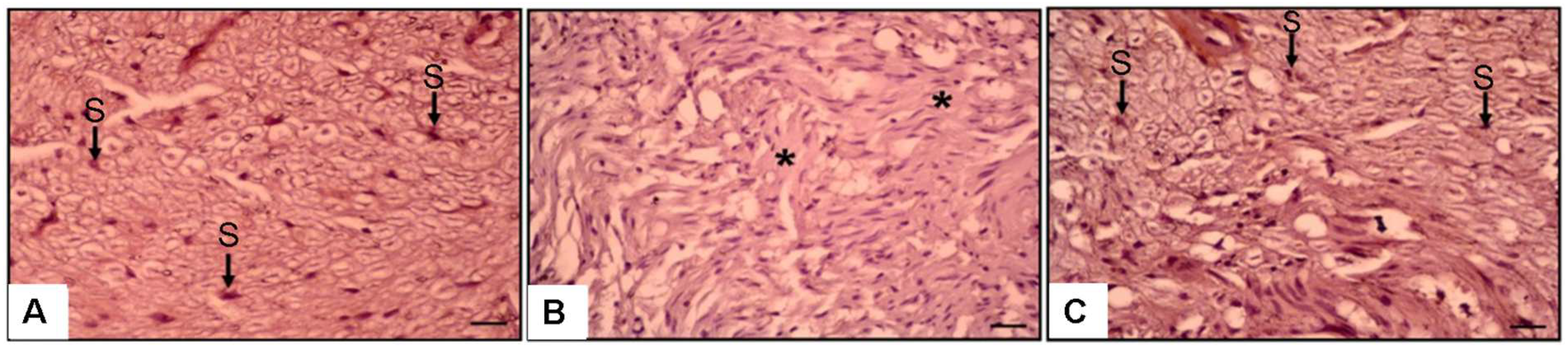
| Normal Control | Surgery and Saline (SS) Group | Surgery and PEG 3350 (SPEG) Group | |
|---|---|---|---|
| EMG CMAP latency (ms) | 2.28 ± 0.1 | 4.42 ± 0.2 * | 3.3 ± 0.17 ## |
| EMG CMAP amplitude (mV) | 13.4 ± 0.9 | 1.6 ± 0.2 ** | 4.9 ± 0.6 # |
| Inclaned plane score (°) | 88.7 ± 2.5 | 38.6 ± 8.1 ** | 76.8 ± 6.5 ## |
| Normal Control | Surgery and Saline (SS) Group | Surgery and PEG 3350 (SPEG) Group | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nevre MDA Level (nmol/g) | 82.2 ± 3.1 | 144.3 ± 4.5 * | 95.6 ± 1.8 # |
| Nerve NGF Level (pg/g) | 115.2 ± 1.9 | 30.5 ± 1.2 * | 82.9 ± 1.5 ## |
| Nerve HSP-70 Level (µg/mg) | 5.6 ± 0.3 | 6.4 ± 0.5 | 10.1 ± 0.8 # |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tunç, E.; Bora, E.S.; Erbaş, O. Harnessing Polyethylene Glycol 3350 for Enhanced Peripheral Nerve Repair: A Path to Accelerated Recovery. Medicina 2025, 61, 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040624
Tunç E, Bora ES, Erbaş O. Harnessing Polyethylene Glycol 3350 for Enhanced Peripheral Nerve Repair: A Path to Accelerated Recovery. Medicina. 2025; 61(4):624. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040624
Chicago/Turabian StyleTunç, Erdinç, Ejder Saylav Bora, and Oytun Erbaş. 2025. "Harnessing Polyethylene Glycol 3350 for Enhanced Peripheral Nerve Repair: A Path to Accelerated Recovery" Medicina 61, no. 4: 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040624
APA StyleTunç, E., Bora, E. S., & Erbaş, O. (2025). Harnessing Polyethylene Glycol 3350 for Enhanced Peripheral Nerve Repair: A Path to Accelerated Recovery. Medicina, 61(4), 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040624







