The Impact of Coagulation Biomarkers on Survival Outcomes in Adult Glioblastoma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection
2.2. Treatment Protocol and Follow-Up Procedures
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Statistical Analyses
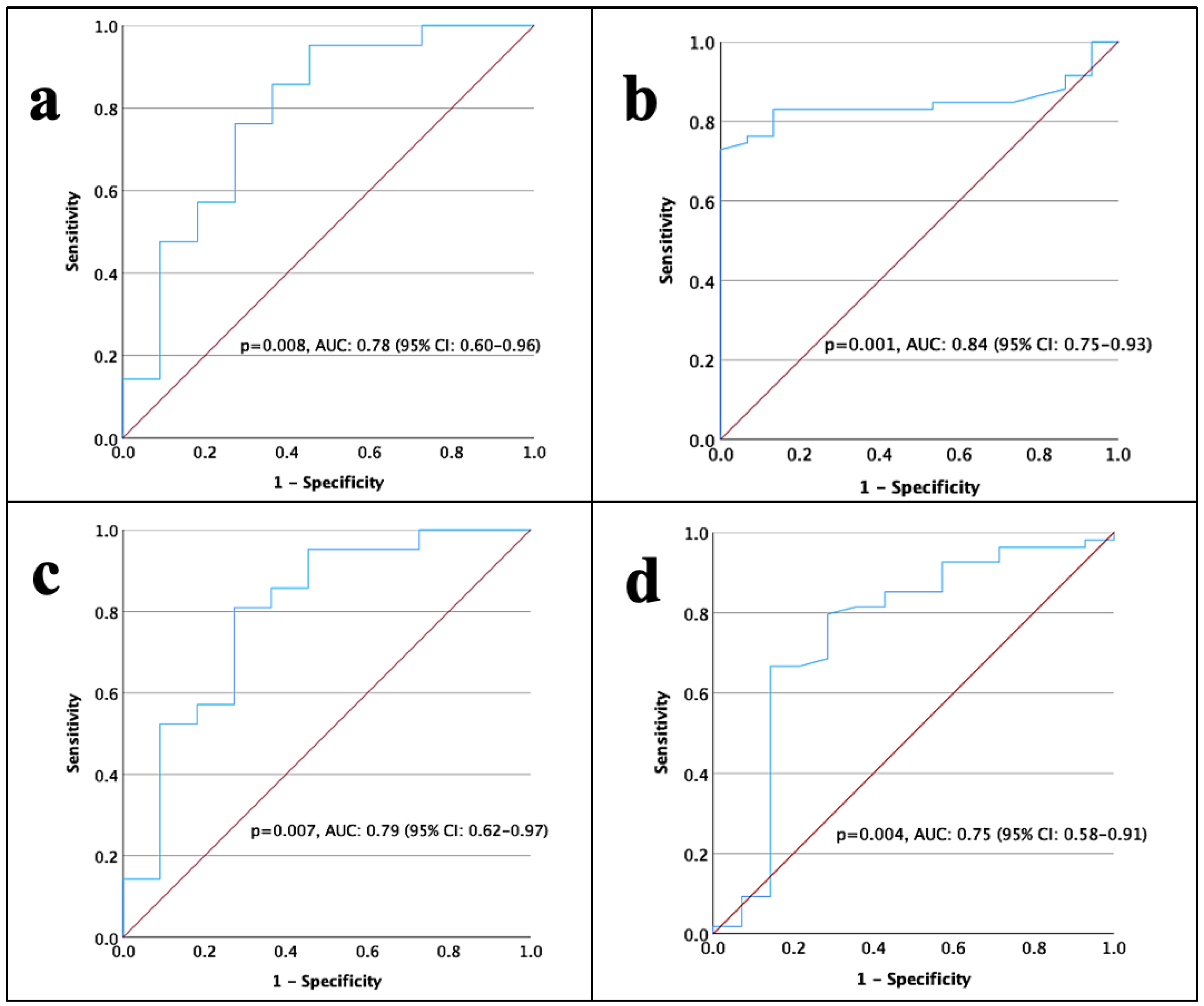
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Gittleman, H.; Truitt, G.; Boscia, A.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2011–2015. Neuro Oncol. 2018, 20 (Suppl. 4), iv1–iv86, Erratum in Neuro Oncol. 2018, 23, 508–522. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/noy171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stupp, R.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Weller, M.; Fisher, B.; Taphoorn, M.J.B.; Belanger, K.; Brandes, A.A.; Marosi, C.; Bogdahn, U.; et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, A.C.; Ashley, D.M.; López, G.Y.; Malinzak, M.; Friedman, H.S.; Khasraw, M. Management of glioblastoma: State of the art and future directions. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakkar, J.P.; Dolecek, T.A.; Horbinski, C.; Ostrom, Q.T.; Lightner, D.D.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S.; Villano, J.L. Epidemiologic and molecular prognostic review of glioblastoma. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2014, 23, 1985–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, A.; McKelvey, K.J.; Lee, A.; Hudson, A.L. The intertwined fates of inflammation and coagulation in glioma. Mamm. Genome 2018, 29, 806–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Yang, M.; Jin, C.; Hou, S.; Shi, B.; Shi, J.; Lin, N. Preoperative Hematologic Inflammatory Markers as Prognostic Factors in Patients with Glioma. World Neurosurg. 2018, 119, e710–e716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.F.; Meng, Z.; Song, H.W.; Yao, K.; Duan, Z.-J.; Yu, C.-J.; Li, S.-W.; Yan, C.-X. Preoperative Changes in Hematological Markers and Predictors of Glioma Grade and Survival. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topkan, E.; Kucuk, A.; Selek, U. Pretreatment Pan-Immune-Inflammation Value Efficiently Predicts Survival Outcomes in Glioblastoma Multiforme Patients Receiving Radiotherapy and Temozolomide. J. Immunol. Res. 2022, 2022, 1346094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydin, A.A.; Yuceer, R.O. Unraveling the Predictive Value of the Novel Global Immune-Nutrition-Inflammation Index (GINI) on Survival Outcomes in Patients with Grade 4 Adult-Type Diffuse Gliomas. Curr. Oncol. 2024, 31, 5027–5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falanga, A.; Panova-Noeva, M.; Russo, L. Procoagulant mechanisms in tumour cells. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 2009, 22, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, S.; Xiao, Y.; Baschin, M.; Splittstöhser, M.; Altmann, R.; Moritz, E.; Jedlitschky, G.; Bien-Möller, S.; Schroeder, H.W.; Rauch, B.H. The Role of Platelets in Cancer Pathophysiology: Focus on Malignant Glioma. Cancers 2019, 11, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semrad, T.J.; O’Donnell, R.; Wun, T.; Chew, H.; Harvey, D.; Zhou, H.; White, R.H. Epidemiology of venous thromboembolism in 9489 patients with malignant glioma. J. Neurosurg. 2007, 106, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwin, N.C.; Khoury, M.N.; Sohal, D.; McCrae, K.R.; Ahluwalia, M.S.; Khorana, A.A. Recurrent venous thromboembolism in glioblastoma. Thromb. Res. 2016, 137, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navone, S.E.; Guarnaccia, L.; Locatelli, M.; Rampini, P.; Caroli, M.; La Verde, N.; Gaudino, C.; Bettinardi, N.; Riboni, L.; Marfia, G.; et al. Significance and Prognostic Value of The Coagulation Profile in Patients with Glioblastoma: Implications for Personalized Therapy. World Neurosurg. 2019, 121, e621–e629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoke, M.; Dieckmann, K.; Koppensteiner, R.; Schillinger, M.; Marosi, C.; Mlekusch, W. Prognostic value of plasma d-dimer levels in patients with glioblastoma multiforme—Results from a pilot study. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2011, 123, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koudriavtseva, T.; Villani, V.; Lorenzano, S.; Giannarelli, D.; Di Domenico, E.G.; Stefanile, A.; Maschio, M.L.; D’Agosto, G.; Pimpinelli, F.; Tanzilli, A.; et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, Factor VIII and Antithrombin III: Inflammatory-clotting biomarkers in glioma. EXCLI J. 2021, 20, 1152–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.; Lis, C.G. Pretreatment serum albumin as a predictor of cancer survival: A systematic review of the epidemiological literature. Nutr. J. 2010, 9, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Huang, Y.; Li, Z.; Hou, H.; Wu, A. The prognostic role of preoperative serum albumin levels in glioblastoma patients. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, H.; Li, F.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y. Prognostic Value of Albumin to D-Dimer Ratio in Advanced Gastric Cancer. J. Oncol. 2021, 2021, 9973743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Khorobrykh, T.V.; He, M.; et al. Albumin-to-D-dimer ratios: A novel prognostic factor for evaluating first-line chemotherapy efficacy in advanced lung adenocarcinoma patients. Neoplasma 2024, 71, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McShane, L.M.; Altman, D.G.; Sauerbrei, W.; E Taube, S.; Gion, M.; Clark, G.M. REporting recommendations for tumour MARKer prognostic studies (REMARK). Br. J. Cancer 2005, 93, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruf, W.; Disse, J.; Carneiro-Lobo, T.C.; Yokota, N.; Schaffner, F. Tissue factor and cell signalling in cancer progression and thrombosis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2011, 9 (Suppl. S1), 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yunpeng, P.; Lingdi, Y.; Xiaole, Z.; Dongya, H.; Le, H.; Zipeng, L.; Kai, Z.; Chaoqun, H.; Yi, M.; Feng, G.; et al. Establishment and validation of a nomogram based on coagulation parameters to predict the prognosis of pancreatic cancer. BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, M.; Kassim, S.A.; Wang, Z.C.; Shi, M.; Hu, Y.; Zhu, H. Clinical evaluation of plasma coagulation parameters in patients with advanced-stage non-small cell lung cancer treated with palliative chemotherapy in China. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2020, 74, e13619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Yuan, M.; Chen, G. The clinical association between coagulation indexes, platelet-related parameters, and bone metastasis of newly diagnosed prostate cancer. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2023, 28, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Liu, X.; Gao, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Men, J.; Ren, J.; Wang, J.; Li, F.; Li, Y.; et al. Glioblastoma Cells Express and Secrete Alternatively Spliced Transcripts of Coagulation Factor X. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, S.; Singh, S.; Banerjee, M.; Modi, D.R.; Prakash, A. Coagulation proteases and neurotransmitters in pathogenicity of glioblastoma multiforme. Int. J. Neurosci. 2024, 134, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, X.; Yan, B.; Gu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Jiao, J.; Sun, D.; Wang, N.; Yue, X. Elevated plasma D-dimer levels correlate with long term survival of gastric cancer patients. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schorling, R.M.; Pfrepper, C.; Golombek, T.; Cella, C.A.; Muñoz-Unceta, N.; Siegemund, R.; Engel, C.; Petros, S.; Lordick, F.; Knödler, M. Evaluation of Biomarkers for the Prediction of Venous Thromboembolism in Ambulatory Cancer Patients. Oncol. Res. Treat. 2020, 43, 414–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Tang, Y.; Song, Y.; Chen, S.H.; Sisliyan, N.; Ni, M.; Zhang, H.; Zeng, Q.; Hou, B.; Xie, X.; et al. Prognostic Role of Pretreatment Plasma D-Dimer in Patients with Solid Tumors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 45, 1663–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Shi, Q.; Li, S.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, H. Clinical characteristics of glioblastoma with metastatic spinal dissemination. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2022, 11, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danan, D.; Shonka, D.C., Jr.; Selman, Y.; Chow, Z.; Smolkin, M.E.; Jameson, M.J. Prognostic value of albumin in patients with head and neck cancer. Laryngoscope 2016, 126, 1567–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borg, N.; Guilfoyle, M.R.; Greenberg, D.C.; Watts, C.; Thomson, S. Serum albumin and survival in glioblastoma multiforme. J. Neurooncol. 2011, 105, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, L. Prognostic significance of preoperative serum albumin, albumin-to-globulin ratio, and prognostic nutritional index for patients with glioma: A meta-analysis. Medicine 2020, 99, e20927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Ye, J.; Luo, Q.; Kuang, M.; Mao, M.; Dai, S.; Wang, X. Prediction of Poor Outcomes in Patients with Colorectal Cancer: Elevated Preoperative Prothrombin Time (PT) and Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time (APTT). Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 5373–5384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.P.; Mao, M.J.; He, Z.L.; Zhang, L.; Chi, P.-D.; Su, J.-R.; Dai, S.-Q.; Liu, W.-L. A retrospective discussion of the prognostic value of combining prothrombin time(PT) and fibrinogen(Fbg) in patients with Hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Cancer 2017, 8, 2079–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Li, W.; Liu, N.; Ding, Z.; Cai, J.; Zhang, Y. Prothrombin time (PT) and CEA as prognostic predictive biomarkers for postoperative recurrence after curative resection in patients with stage I-III colorectal cancer: A retrospective cohort study. Updates Surg. 2022, 74, 999–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockmann, M.A.; Giese, A.; Mueller, K.; Kaba, F.J.; Lohr, F.; Weiss, C.; Gottschalk, S.; Nolte, I.; Leppert, J.; Tuettenberg, J.; et al. Preoperative thrombocytosis predicts poor survival in patients with glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol. 2007, 9, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristic | n | % |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | ||
| <65 | 49 | 66.2 |
| ≥65 | 25 | 33.8 |
| Gender | ||
| Female | 28 | 37.8 |
| Male | 46 | 62.2 |
| ECOG-PS | ||
| 0 | 24 | 32.4 |
| 1 | 32 | 43.2 |
| 2 | 18 | 24.4 |
| Location | ||
| Frontal | 26 | 35.1 |
| Parietal | 26 | 35.1 |
| Temporal | 18 | 24.4 |
| Occipital | 4 | 5.4 |
| Laterality | ||
| Right | 36 | 48.6 |
| Left | 32 | 43.2 |
| Bilateral | 6 | 8.2 |
| Extent of resection | ||
| Subtotal resection | 41 | 55.4 |
| N/GTR | 33 | 44.6 |
| IDH mutation status | ||
| Wild | 45 | 60.8 |
| Mutant | 8 | 10.8 |
| Unknown | 21 | 28.4 |
| Ki-67 index | ||
| <30% | 28 | 37.8 |
| ≥30% | 24 | 32.4 |
| Unknown | 22 | 29.8 |
| Total radiotherapy dose | ||
| 40 Gy | 8 | 10.8 |
| 60 Gy | 66 | 89.2 |
| Variables | Cut-Off | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | p | HR (95% CI) | p | ||
| Age (years) | <65 vs. ≥65 | 1.7 (0.9–3.0) | 0.06 | ||
| Gender | Male vs. Female | 0.8 (0.5–1.4) | 0.54 | ||
| ECOG-PS | 0–1 vs. 2 | 2.8 (1.5–5.1) | 0.001 | 0.4 (0.1–1.6) | 0.24 |
| Tumor volume | <36.3 vs. ≥36.3 | 1.9 (0.8–4.2) | 0.11 | ||
| EoR | Subtotal vs. N/GTR | 0.7 (0.4–1.1) | 0.15 | ||
| Ki-67 index | <30% vs. ≥30% | 1.01 (0.7–1.3) | 0.96 | ||
| RT dose (Gy) | 60 vs. 40 | 1.7 (0.7–4.0) | 0.20 | ||
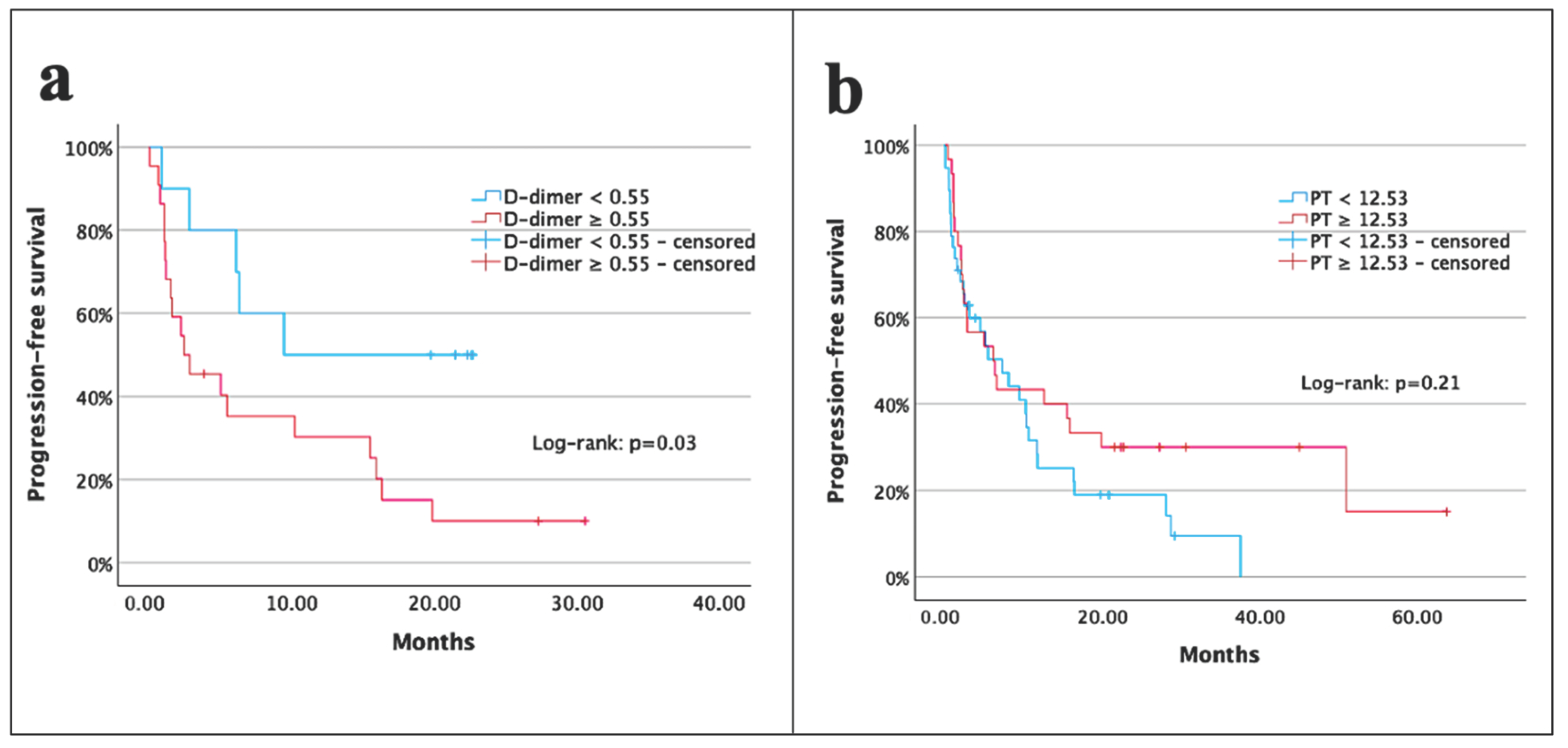
| D-dimer (μg/mL) | <0.55 vs. ≥0.55 | 2.8 (1.0–7.6) | 0.03 | 1.9 (0.6–5.9) | 0.24 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | <4.3 vs. ≥4.3 | 0.3 (0.2–0.6) | 0.001 | 0.2 (0.1–0.8) | 0.02 |
| Albumin/D-dimer | <6.5 vs. ≥6.5 | 0.5 (0.2–1.2) | 0.12 | ||
| PT (s) | <12.53 vs. ≥12.53 | 0.7 (0.3–1.1) | 0.21 | ||
| aPTT (s) | <23 vs. ≥23 | 0.6 (0.4–1.1) | 0.12 | ||
| Platelet count (103) | <313 vs. ≥313 | 0.7 (0.3–1.1) | 0.20 | ||
| Variables | Cut-Off | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | p | HR (95% CI) | p | ||
| Age (years) | <65 vs. ≥65 | 2.1 (1.2–3.7) | 0.004 | 6.5 (1.2–35.1) | 0.04 |
| Gender | Male vs. Female | 0.8 (0.5–1.5) | 0.65 | ||
| ECOG-PS | 0–1 vs. 2 | 2.5 (1.4–4.5) | 0.001 | 0.3 (0.1–14.6) | 0.58 |
| Tumor volume | <36.3 vs. ≥36.3 | 3.4 (1.4–8.3) | 0.007 | 4.1 (0.5–33.3) | 0.17 |
| EoR | Subtotal vs. N/GTR | 0.4 (0.2–0.8) | 0.01 | 0.2 (0.1–0.7) | 0.02 |
| Ki-67 index | <30% vs. ≥30% | 1.2 (0.8–1.6) | 0.23 | ||
| RT dose (Gy) | 60 vs. 40 | 3.5 (1.6–7.7) | 0.001 | 0.2 (0.1–2.9) | 0.14 |
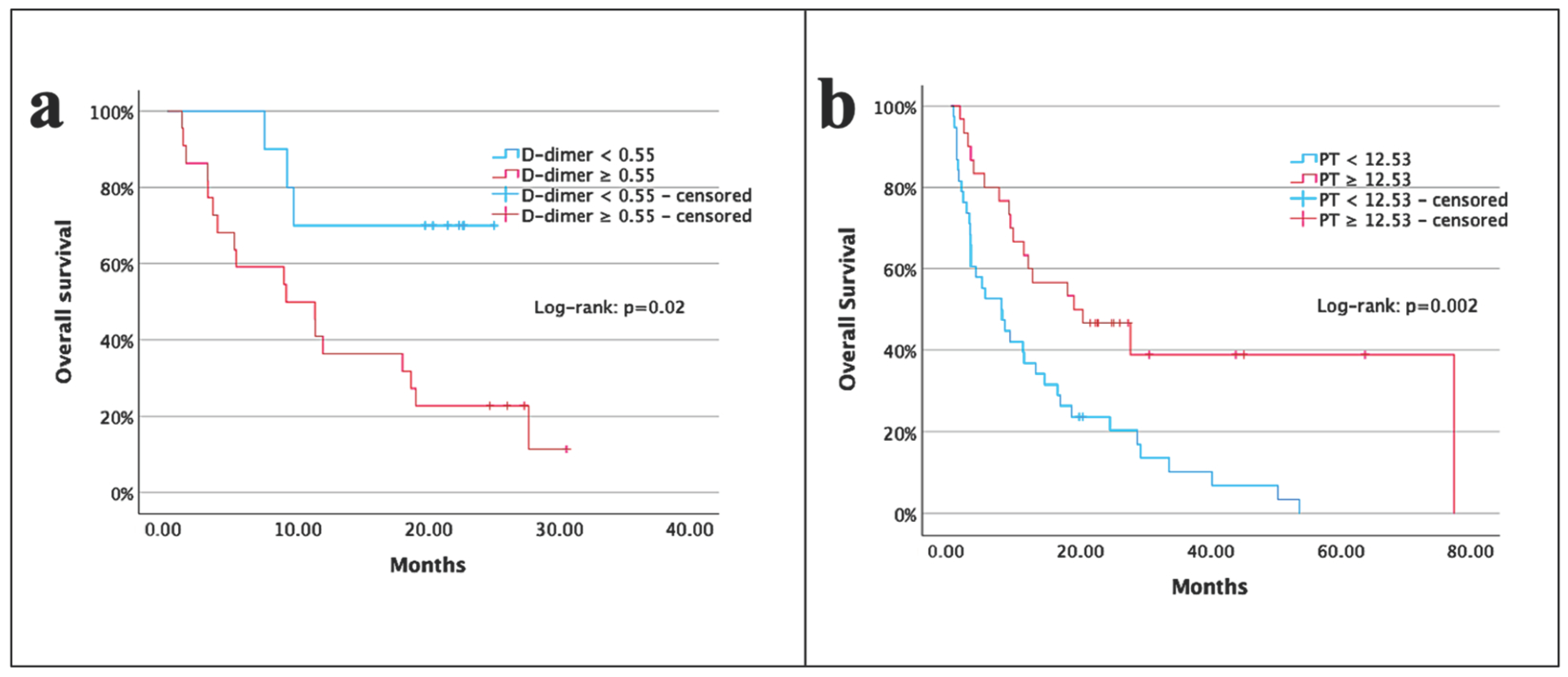
| D-dimer (μg/mL) | <0.55 vs. ≥0.55 | 3.9 (1.1–13.4) | 0.02 | 2.3 (0.1–44.8) | 0.57 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | <4.3 vs. ≥4.3 | 0.2 (0.1–0.4) | 0.001 | 0.5 (0.1–9.5) | 0.69 |
| Albumin/D-dimer | <6.5 vs. ≥6.5 | 0.2 (0.1–0.8) | 0.02 | 3.9 (0.3–44.4) | 0.27 |
| PT (s) | <12.53 vs. ≥12.53 | 0.4 (0.2–0.7) | 0.002 | 0.2 (0.1–0.8) | 0.04 |
| aPTT (s) | <23 vs. ≥23 | 0.6 (0.3–1.0) | 0.09 | ||
| Platelet count (103) | <313 vs. ≥313 | 0.6 (0.3–1.1) | 0.13 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aksoy, R.A.; Koca, T.; Şengün, Y.; Atak, E.; Korcum, A.F. The Impact of Coagulation Biomarkers on Survival Outcomes in Adult Glioblastoma. Medicina 2025, 61, 756. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040756
Aksoy RA, Koca T, Şengün Y, Atak E, Korcum AF. The Impact of Coagulation Biomarkers on Survival Outcomes in Adult Glioblastoma. Medicina. 2025; 61(4):756. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040756
Chicago/Turabian StyleAksoy, Rahmi Atıl, Timur Koca, Yasemin Şengün, Ece Atak, and Aylin Fidan Korcum. 2025. "The Impact of Coagulation Biomarkers on Survival Outcomes in Adult Glioblastoma" Medicina 61, no. 4: 756. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040756
APA StyleAksoy, R. A., Koca, T., Şengün, Y., Atak, E., & Korcum, A. F. (2025). The Impact of Coagulation Biomarkers on Survival Outcomes in Adult Glioblastoma. Medicina, 61(4), 756. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040756







