A High-Throughput Biosensing Approach for Rapid Screening of Compounds Targeting the hNav1.1 Channel: Marine Toxins as a Case Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Optimization of Concentration of Veratridine in Inhibition Mode
2.2. Feasibility of Method
2.3. Application to Marine Toxins—Initial Screening
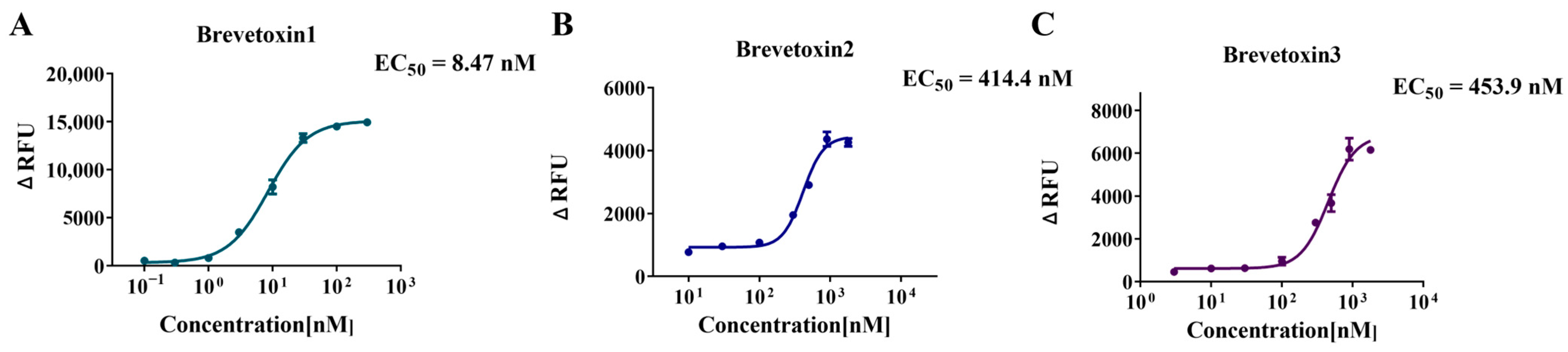
2.4. Application to Marine Toxins—Activation Curve and EC50 Determination
2.5. Application to Marine Toxins—Inhibition Curve and IC50 Determination
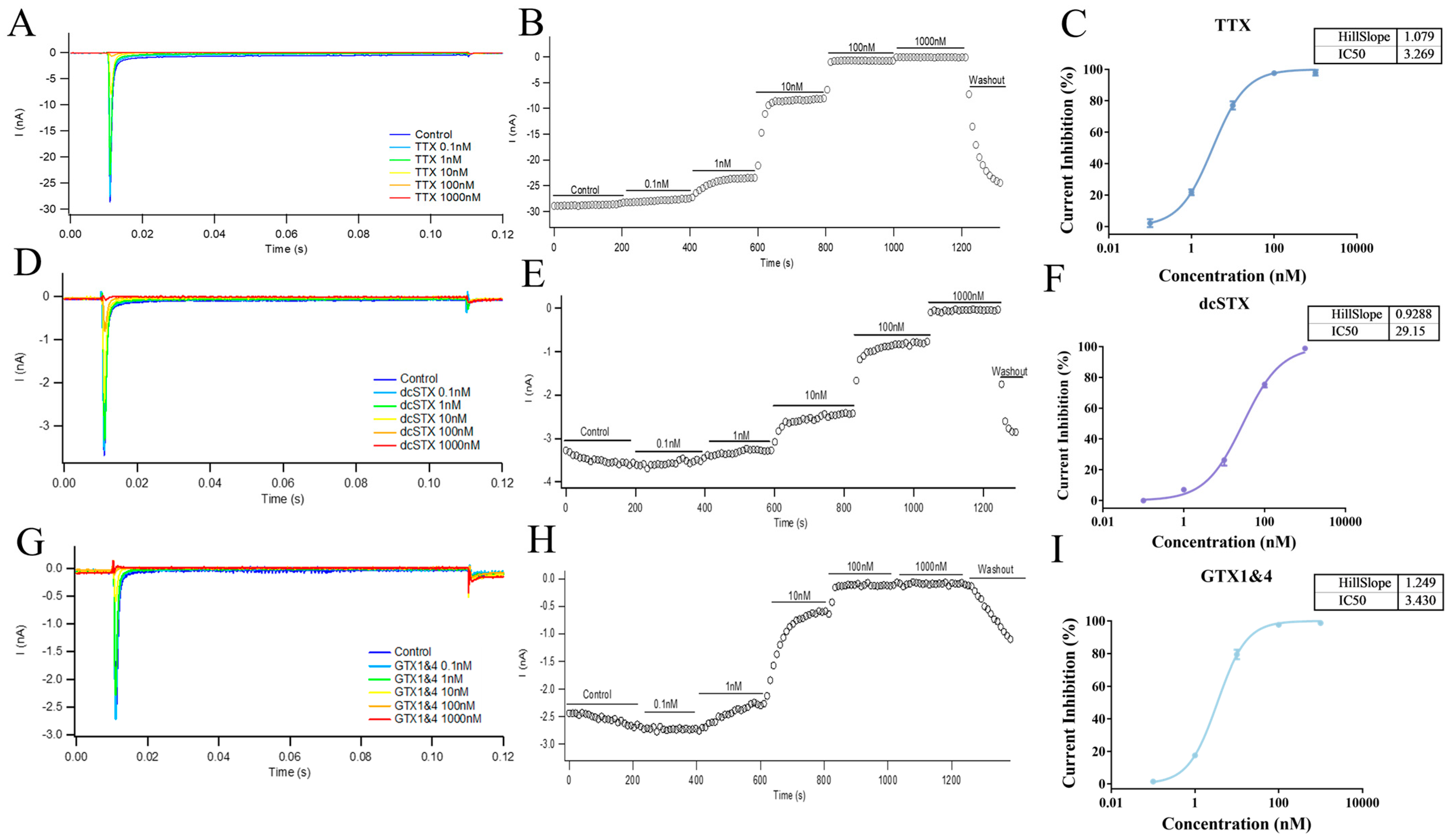
2.6. Validation of the Method by Comparison with the Patch-Clamp Technique
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. hNav1.1-CHO Cell Culture
4.3. Initial Screening of Agonists
4.4. Initial Screening of Inhibitors
4.5. Agonist Activation Curve and EC50 Determination
4.6. Inhibition Curve and IC50 Determination
4.7. Electrophysiology
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Nav | Voltage-gated sodium. |
| hNav1.1 | Human Nav1.1. |
| hNav1.1-CHO | CHO cells stably expressing hNav1.1 α-subunit. |
| VSD | Voltage-sensing domain. |
| TTX | Tetrodotoxin. |
| STX | Saxitoxin. |
| HEK | Human Embryonic Kidney. |
| CHO | Chinese Hamster Ovary. |
| GTX1/4 | Gonyautoxin ¼. |
| dcGTX 2&3 | Decarbamoylgonyautoxin 2&3. |
| dcSTX | Decarbamoylsaxitoxin. |
| C1&C2 | N-sulfocarbamoylgonyautoxin 2 and 3. |
| DTX1 | Dinophysistoxin 1. |
| DSP | Diarrhetic shellfish poisoning. |
| SBFI/AM | Sodium-binding BenzoFuran Isophthalate/AcetoxyMethyl Ester. |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. |
| LC-MS | Liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum. |
| HBSS | Hank’s Balanced Salt Solution. |
| HHBS | HBSS supplemented with 20 mM HEPES. |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline. |
| PLL | Poly-L-lysine. |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide. |
| EGTA | Ethylene Glycol Bis(2-aminoethylether)-N,N,N′,N′-tetra acetic acid. |
References
- Manning, D.; Santana, L.F. Regulating voltage-gated ion channels with nanobodies. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wisedchaisri, G.; Tonggu, L.; McCord, E.; El-Din, T.M.G.; Wang, L.; Zheng, N.; Catterall, W.A. Resting-state structure and gating mechanism of a voltage-gated sodium channel. Cell 2019, 178, 993–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sula, A.; Hollingworth, D.; Ng, L.C.; Larmore, M.; DeCaen, P.G.; Wallace, B.A.J. A tamoxifen receptor within a voltage-gated sodium channel. Mol. Cell 2021, 81, 1160–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kschonsak, M.; Jao, C.C.; Arthur, C.P.; Rohou, A.L.; Bergeron, P.; Ortwine, D.F.; McKerrall, S.J.; Hackos, D.H.; Deng, L.; Chen, J.J. Cryo-EM reveals an unprecedented binding site for NaV1. 7 inhibitors enabling rational design of potent hybrid inhibitors. Elife 2023, 12, e84151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Li, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Pan, X.; Wu, J.; Cristofori-Armstrong, B.; Smith, J.J.; Chin, Y.K.; Lei, J.; Zhou, Q.J. Structural basis for the modulation of voltage-gated sodium channels by animal toxins. Science 2018, 362, 2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, C.Y.; Chin, Y.K.-Y.; Walker, A.A.; Guo, S.; Blomster, L.V.; Ward, M.J.; Herzig, V.; Rokyta, D.R.; King, G.F.J. Venom peptides with dual modulatory activity on the voltage-gated sodium channel NaV1. 1 provide novel leads for development of antiepileptic drugs. Science 2019, 3, 119–134. [Google Scholar]
- Deuis, J.R.; Dekan, Z.; Wingerd, J.S.; Smith, J.J.; Munasinghe, N.R.; Bhola, R.F.; Imlach, W.L.; Herzig, V.; Armstrong, D.A.; Rosengren, K.J. Pharmacological characterisation of the highly NaV1. 7 selective spider venom peptide Pn3a. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40883. [Google Scholar]
- Osteen, J.D.; Herzig, V.; Gilchrist, J.; Emrick, J.J.; Zhang, C.; Wang, X.; Castro, J.; Garcia-Caraballo, S.; Grundy, L.; Rychkov, G.Y.J. Selective spider toxins reveal a role for the Nav1. 1 channel in mechanical pain. Nature 2016, 534, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, J.; Milescu, M.; Salvatierra, J.; Wagner, J.; Klint, J.K.; King, G.F.; Olivera, B.M.; Bosmans, F.J. From foe to friend: Using animal toxins to investigate ion channel function. J. Mol. Biol. 2015, 427, 158–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernov-Rogan, T.; Li, T.; Lu, G.; Verschoof, H.; Khakh, K.; Jones, S.W.; Beresini, M.H.; Liu, C.; Ortwine, D.F.; McKerrall, S.J.J. Mechanism-specific assay design facilitates the discovery of Nav1. 7-selective inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E792–E801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, M.; Peigneur, S.; Tytgat, J.J. Neurotoxins and their binding areas on voltage-gated sodium channels. Front. Pharmacol. 2011, 2, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Ou, S.-W.; Wang, Y.-J.J.C. Distribution and function of voltage-gated sodium channels in the nervous system. Channels 2017, 11, 534–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Yang, Q.; Wu, W. Ensuring seafood safe to spoon: A brief review of biosensors for marine biotoxin monitoring. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2020, 62, 2495–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, R.-C.; Kong, F.-Z.; Li, C.; Dai, L.; Chen, Z.-F.; Geng, H.-X.; Zhou, M.-J. Contamination status of lipophilic marine toxins in shellfish samples from the Bohai Sea, China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katikou, P.; Gokbulut, C.; Kosker, A.R.; Campàs, M.; Ozogul, F.J. An updated review of tetrodotoxin and its peculiarities. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, V.G.; Khan, E.J. Freshwater neurotoxins and concerns for human, animal, and ecosystem health: A review of anatoxin-a and saxitoxin. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 736, 139515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amzil, Z.; Derrien, A.; Terre Terrillon, A.; Duval, A.; Connes, C.; Marco-Miralles, F.; Nézan, E.; Mertens, K.N.J. Monitoring the emergence of algal toxins in shellfish: First report on detection of brevetoxins in French mediterranean mussels. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo-Garcia, S.; Castro, D.; Lence, E.; Estévez, P.; Leão, J.M.; González-Bello, C.; Gago-Martínez, A.; Louzao, M.C.; Vale, C.; Botana, L.M.J. In silico simulations and functional cell studies evidence similar potency and distinct binding of Pacific and Caribbean ciguatoxins. Expo. Health 2023, 15, 641–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boente-Juncal, A.; Raposo-García, S.; Vale, C.; Louzao, M.C.; Otero, P.; Botana, L.M.J. In vivo evaluation of the chronic oral toxicity of the marine toxin palytoxin. Toxins 2020, 12, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arteaga-Sogamoso, E.; Riobo, P.; Rodríguez, F.; Mancera-Pineda, J.E.; Franco-Angulo, J.J. First record of the dinoflagellate Prorocentrum borbonicum in the continental coast of Colombian Caribbean: A new 42 hydroxi-palytoxin producer. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 973250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyasaka, T.; Adachi, M.; Nishikawa, T.J. Synthesis of the 8-deoxy analogue of 4, 9-anhydro-10-hemiketal-5-deoxy-tetrodotoxin, a proposed biosynthetic precursor of tetrodotoxin. Org. Lett. 2021, 23, 9232–9236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metz, T.T.; Putnam, S.P.; Scott, G.I.; Ferry, J.L.J. Shoreline drying of microseira (lyngbya) wollei biomass can lead to the release and formation of toxic saxitoxin analogues to the water column. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 16866–16872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackieh, R.; Abou-Nader, R.; Wehbe, R.; Mattei, C.; Legros, C.; Fajloun, Z.; Sabatier, J. Voltage-gated sodium channels: A prominent target of marine toxins. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elleman, A.V.; Devienne, G.; Makinson, C.D.; Haynes, A.L.; Huguenard, J.R.; Du Bois, J.J. Precise spatiotemporal control of voltage-gated sodium channels by photocaged saxitoxin. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.-J.; Harootunian, A.; Maher, M.P.; Quan, C.; Raj, C.D.; McCormack, K.; Numann, R.; Negulescu, P.A.; González, J. Characterization of voltage-gated sodium-channel blockers by electrical stimulation and fluorescence detection of membrane potential. Nat. Btechnol. 2006, 24, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Li, X.; Jin, L.; Zhang, F.; Inoue, M.; Yu, B.; Cao, Z.J. Development of a rapid throughput assay for identification of hNav1. 7 antagonist using unique efficacious sodium channel agonist, antillatoxin. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finol-Urdaneta, R.K.; Zhorov, B.S.; Baden, D.G.; Adams, D.J. Brevetoxin versus brevenal modulation of human Nav1 channels. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunlop, J.; Bowlby, M.; Peri, R.; Vasilyev, D.; Arias, R.J. High-throughput electrophysiology: An emerging paradigm for ion-channel screening and physiology. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felix, J.P.; Williams, B.S.; Priest, B.T.; Brochu, R.M.; Dick, I.E.; Warren, V.A.; Yan, L.; Slaughter, R.S.; Kaczorowski, G.J.; Smith, M.M.J. Functional assay of voltage-gated sodium channels using membrane potential-sensitive dyes. Asay Drug. Dev. Techn. 2004, 2, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klint, J.K.; Smith, J.J.; Vetter, I.; Rupasinghe, D.B.; Er, S.Y.; Senff, S.; Herzig, V.; Mobli, M.; Lewis, R.J.; Bosmans, F.J. Seven novel modulators of the analgesic target Nav1.7 uncovered using a high-throughput venom-based discovery approach. Bit J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 2445–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukamoto, T.; Chiba, Y.; Wakamori, M.; Yamada, T.; Tsunogae, S.; Cho, Y.; Sakakibara, R.; Imazu, T.; Tokoro, S.; Satake, Y.J. Differential binding of tetrodotoxin and its derivatives to voltage-sensitive sodium channel subtypes (Nav1. 1 to Nav1. 7). Bit Jpharmacol. 2017, 174, 3881–3892. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.-q.; Wang, L.; Zhang, W.-b.; Tang, C.-p.; Chen, X.-q.; Zheng, Y.-m.; Yao, S.; Gao, Z.-b.; Ye, Y. Naphthylisoquinoline alkaloids, a new structural template inhibitor of Nav1.7 sodium channel. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2023, 44, 1768–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yuan, H.; Yao, X.; Chen, S.J. Endogenous ion channels expressed in human embryonic kidney (HEK-293) cells. Pflug. Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2022, 474, 665–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, P.B.; Guthrie, H.R.J. Trends in ion channel drug discovery: Advances in screening technologies. Trends Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-Y.; Wang, G.K.J. Voltage-gated sodium channels as primary targets of diverse lipid-soluble neurotoxins. Cell Signal 2003, 15, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Xu, F.; Xu, H.; Zhang, S.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Dong, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, B.; Sun, J.J. Structural basis for modulation of human Nav1. 3 by clinical drug and selective antagonist. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, J.; Maddern, J.; Erickson, A.; Caldwell, A.; Grundy, L.; Harrington, A.M.; Brierley, S.M.J. Pharmacological modulation of voltage-gated sodium (NaV) channels alters nociception arising from the female reproductive tract. Pain 2021, 162, 227–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibowitz, M.D.; Sutro, J.B.; Hille, B. Voltage-dependent gating of veratridine-modified Na channels. J. Gen. Physiol. 1986, 87, 25–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippaert, K.; Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Fatehi, M.; Long, W.; Soni, S.; Byrne, N.J.; Barr, A.; Singh, J.; Wong, J.; Palechuk, T.J. Cardiac late sodium channel current is a molecular target for the sodium/glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor empagliflozin. Circulation 2021, 143, 2188–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inserra, M.C.; Israel, M.R.; Caldwell, A.; Castro, J.; Deuis, J.R.; Harrington, A.M.; Keramidas, A.; Garcia-Caraballo, S.; Maddern, J.; Erickson, A.J. Multiple sodium channel isoforms mediate the pathological effects of Pacific ciguatoxin-1. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konoki, K.; Baden, D.G.; Scheuer, T.; Catterall, W.A.J.T. Molecular determinants of brevetoxin binding to voltage-gated sodium channels. Toxin 2019, 11, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ukai, R.; Uchida, H.; Sugaya, K.; Onose, J.-i.; Oshiro, N.; Yasumoto, T.; Abe, N. Structural Assignment of the Product Ion Generated from a Natural Ciguatoxin-3C Congener, 51-Hydroxyciguatoxin-3C, and Discovery of Distinguishable Signals in Congeners Bearing the 51-Hydroxy Group. Toxins 2024, 16, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loser, D.; Schaefer, J.; Danker, T.; Möller, C.; Brüll, M.; Suciu, I.; Ückert, A.K.; Klima, S.; Leist, M.; Kraushaar, U. Human neuronal signaling and communication assays to assess functional neurotoxicity. Arch. Toxicol. 2021, 95, 229–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, L.; Qiu, J.; Li, A. Proposed biotransformation pathways for new metabolites of paralytic shellfish toxins based on field and experimental mussel samples. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 5494–5502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yau, M.S.; Lei, E.N.; Ng, I.H.; Yuen, C.K.; Lam, J.C.; Lam, M.H. Changes in the neurotransmitter profile in the central nervous system of marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma) after exposure to brevetoxin PbTx-1—A multivariate approach to establish exposure biomarkers. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 673, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botana, L.M.; Hess, P.; Munday, R.; Nathalie, A.; DeGrasse, S.L.; Feeley, M.; Suzuki, T.; van den Berg, M.; Fattori, V.; Gamarro, E.G.; et al. Derivation of toxicity equivalency factors for marine biotoxins associated with Bivalve Molluscs. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2017, 59, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, P.; Kim, N.H.; Wu, F.H.; El Kasmr, F.; Chi, Y.; Walton, W.G.; Furzer, O.J.; Lietzan, A.D.; Sunil, S.; Kempthorn, K.; et al. Plant “helper” immune receptors are Ca2+-permeable nonselective cation channels. Science 2021, 373, 420–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Takeuchi, S.; Imai, S.; Terada, T.; Ueda, T.; Nasu, Y.; Terai, T.; Campbell, R.E. Hemigenetic indicators based on synthetic chelators and green fluorescent protein. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2023, 19, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Xing, J.; Yuan, B.; He, L.; Lu, L.; Chen, N.; Cai, P.; Wu, A.; Li, J. Rganic small-molecule fluorescent probe-based detection for alkali and alkaline earth metal ions in biological systems. J. Mater. Chem. B 2023, 11, 3295–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, R.; Lin, R.; Singh, V.; Donowitz, M.; Tse, C.-M.J. SLC26A3 (DRA) is stimulated in a synergistic, intracellular Ca2+-dependent manner by cAMP and ATP in intestinal epithelial cells. Cell Physiol. 2023, 324, C1263–C1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Shafer, T.J.; Crofton, K.M.; Gennings, C.; Murray, T.F. Additivity of pyrethroid actions on sodium influx incerebrocortical neurons in primary culture. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 1236–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, X.; He, Y.; Qiao, J.; Zhang, C.; Cao, Z. The natural scorpion peptide, BmK NT1 activates voltage-gated sodium channels and produces neurotoxicity in primary cultured cerebellar granule cells. Toxicon 2016, 109, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Z.; Gerwick, W.H.; Murray, T.F. Antillatoxin is a sodium channel activator that displays unique efficacy in heterologously expressed rNav1. 2, rNav1. 4 and rNav1. 5 alpha subunits. BMC Neurosci. 2010, 11, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tay, B.; Stewart, T.A.; Davis, F.M.; Deuis, J.R.; Vetter, I. Development of a high-throughput fluorescent no-wash sodium influx assay. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0213751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iurova, E.; Beloborodov, E.; Rastorgueva, E.; Fomin, A.; Saenko, Y.J.M. Peptide Sodium Channels Modulator Mu-Agatoxin-Aa1a Prevents Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury of Cells. Molecules 2023, 28, 3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinohara, R.; Akimoto, T.; Iwamoto, O.; Hirokawa, T.; Yotsu-Yamashita, M.; Yamaoka, K.; Nagasawa, K.J. Synthesis of skeletal analogues of saxitoxin derivatives and evaluation of their inhibitory activity on sodium ion channels Nav1. 4 and Nav1. 5. Cem-Eur. J. 2011, 17, 12144–12152. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.L.; Wassall, R.D.; Takai, M.; Morinaga, H.; Nomura, M.; Cunnane, T.C.; Teramoto, N. Actions of veratridine on tetrodotoxin-sensitive voltage-gated Na+ currents, NaV1.6, in murine vas deferens myocytes. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 157, 1483–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Bi, R.Y.; Zhang, P.; Gan, Y.H. Veratridine modifies the gating of human voltage-gated sodium channel Nav1.7. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2018, 39, 1716–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Zhang, H.; Xiong, P.; Yan, X.; Liao, C.; Jiang, G. Application of electrophysiological technique in toxicological study: From manual to automated patch-clamp recording. Trac-Trend Anal. Chem. 2020, 133, 116082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, A.; Ikegaya, Y.; Matsumoto, N. In vivo whole-cell patch-clamp methods: Recent technical progress and future perspectives. Sensors 2021, 21, 1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrix, A.M.; Lefebvre, K.A.; Bowers, E.K.; Stuppard, R.; Burbacher, T.; Marcinek, D.J.J. Age and sex as determinants of acute domoic acid toxicity in a mouse model. Toxins 2023, 15, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Guan, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, L.; Yin, R.; Jiang, T.J. Protective effects of marine alkaloid neolamellarin A derivatives against glutamate induced PC12 cell apoptosis. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noirmain, F.; Dano, J.; Hue, N.; Gonzalez-Jartin, J.M.; Botana, L.M.; Servent, D.; Simon, S.; Aráoz, R.J. NeuroTorp A lateral flow test based on toxin-receptor affinity for in-situ early detection of cyclic imine toxins. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1221, 339941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo, M.; Joens, J.A.; O’Shea, K.E.J. Fundamental studies of the singlet oxygen reactions with the potent marine toxin domoic acid. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 6073–6081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Yang, J.; He, X.; Wang, J.; Pan, L.; Xin, M.; Chen, F.; Liang, S.; Wang, B.J. Prevalence of the neurotoxin domoic acid in the aquatic environments of the Bohai and Northern Yellow seas in China. Si Total Env. 2023, 876, 162732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Tabban, A.; Rhouati, A.; Fataftah, A.; Cialla-May, D.; Popp, J.; Zourob, M.J. Design of a duplex-to-complex structure-switching approach for the homogeneous determination of marine biotoxins in water. Toxin 2024, 16, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sabi, A.; McArthur, J.; Ostroumov, V.; French, R.J. Marine Toxins That Target Voltage-gated Sodium Channels. Mar. Drugs 2006, 4, 157–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, H.; Cui, Y.; Liang, S.; Zhou, S.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Song, J. A High-Throughput Biosensing Approach for Rapid Screening of Compounds Targeting the hNav1.1 Channel: Marine Toxins as a Case Study. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23030119
Shen H, Cui Y, Liang S, Zhou S, Li Y, Wu Y, Song J. A High-Throughput Biosensing Approach for Rapid Screening of Compounds Targeting the hNav1.1 Channel: Marine Toxins as a Case Study. Marine Drugs. 2025; 23(3):119. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23030119
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Huijing, Yuxia Cui, Shiyuan Liang, Shuang Zhou, Yingji Li, Yongning Wu, and Junxian Song. 2025. "A High-Throughput Biosensing Approach for Rapid Screening of Compounds Targeting the hNav1.1 Channel: Marine Toxins as a Case Study" Marine Drugs 23, no. 3: 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23030119
APA StyleShen, H., Cui, Y., Liang, S., Zhou, S., Li, Y., Wu, Y., & Song, J. (2025). A High-Throughput Biosensing Approach for Rapid Screening of Compounds Targeting the hNav1.1 Channel: Marine Toxins as a Case Study. Marine Drugs, 23(3), 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23030119





