Abstract
Electronic cigarettes (e-cigarettes) use is becoming increasingly common, especially among adolescents and young adults, and there is little evidence on the impact of e-cigarettes use on never-smokers. With a meta-analysis method, we explore the association between e-cigarettes use and smoking intention that predicts future cigarette smoking. Studies were identified by searching three databases up to January 2016. The meta-analysis results were presented as pooled odds ratio (OR) with 95% confidence interval (CI) calculated by a fixed-effects model. A total of six studies (91,051 participants, including 1452 with ever e-cigarettes use) were included in this meta-analysis study. We found that never-smoking adolescents and young adults who used e-cigarettes have more than 2 times increased odds of intention to cigarette smoking (OR = 2.21, 95% CI: 1.86–2.61) compared to those who never used, with low evidence of between-study heterogeneity (p = 0.28, I2 = 20.1%). Among never-smoking adolescents and young adults, e-cigarettes use was associated with increased smoking intention.
1. Introduction
Although reductions in the smoking prevalence were observed at global level since 1980, the tobacco pandemic remains a threat to the health of the world’s population [1]. As the second most important risk factor for global disease burden, tobacco use accounted for 6.1 million deaths and 143.5 million disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs) across the world in 2013 [2]. Currently, nations are striving to curb tobacco use and reduce its harm. Considering that the majority of smokers begin to smoke during their adolescence [3], preventing youth initiation and transition to established smoking are critical public health issues that deserve more attention.
Smoking intention, defined as the lack of a firm commitment not to smoke among never-smokers, is strongly predictive of future established smoking [4,5,6]. A growing body of literature has identified varying factors associated with smoking intention, such as parental or peer smoking, exposure to secondhand smoke inside or outside the home, pro-tobacco advertising, and school connectedness [7,8,9]. However, additional studies are warranted in this direction with the advent of electronic cigarettes (e-cigarettes).
E-cigarettes are battery-powered nicotine-delivery devices that mimic conventional cigarettes by vaporizing a liquid mixture consisting of propylene glycol, glycerin, flavorings, nicotine, and other chemicals. Since invented in 2003, e-cigarettes have been hotly debated regarding the safety and efficacy for smoking cessation [10,11,12,13,14]. While arguments between both sides of advocates and critics persist, e-cigarettes use has rapidly increased globally [15], especially among youth [16,17]. Moreover, given the majority of users among youth are never-smokers [18,19], whether youth use of e-cigarettes may serve as a gateway to cigarette smoking has been discussed in previous studies [20,21]. However, up to date, the effect of youth e-cigarettes use on subsequent cigarette smoking remains unclear. In the present study, we use meta-analysis method to explore the association between e-cigarettes use and smoking intention among adolescents and young adults to contribute to the much-needed evidence.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature and Search Strategy
Epidemiological studies on the association between e-cigarettes use and smoking intention were searched through three databases (PubMed, Springer Link, and Elsevier) from 2003 to January 2016. Smoking intention was defined as the lack of a firm commitment not to smoke among never-smokers, with the answer yes to one or two questions derived from previous studies [4,5,6]: “Do you think you will smoke a cigarette in the next year (or two years)?” and “If one of your best friends were to offer you a cigarette, would you smoke it?” Detailed definitions were shown in Table 1. The main search terms included “electronic cigarette”, “e-cigarette”, “electronic nicotine delivery systems”, “vaping”, “vaper”, “vapor”, “smoking intention”, “susceptibility to smoke”, “openness to smoke”, and “willingness to smoke”. Reference lists of retrieved literature were also screened.

Table 1.
Information of the studies included in the meta-analysis.
The present study was carried out following the Meta-analysis of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) guidelines [28].
2.2. Inclusion Criteria and Data Extraction
Selected studies in this meta-analysis met the following criteria: (1) reporting the association between e-cigarettes use and smoking intention; (2) providing the effect value with 95% confidence interval (CI) or data to calculate these; (3) the study population must be never-smokers. Two authors independently assessed the eligibility of studies and extracted information from each eligible study. The information included (1) name of the first author; (2) year of publication; (3) participants and sample size; (4) data source and location; (5) study type; (6) measures definition; (7) variables adjusted.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
Heterogeneity between studies was assessed using a Q-test and the I2 statistic [29]. For the Q-test, p value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. The low, moderate, and high degrees of heterogeneity correspond to I2 values of 25%, 50%, and 75%, respectively. If there was significant heterogeneity, a random-effects model would be used to assign the weight of each study according to the DerSimonian-Laird method [30]. If there was evidence of no heterogeneity, we used a fixed-effects model with effect estimates that were given equal weight to the inverse variance of the study. To test robustness of the present meta-analysis result, a sensitivity analysis was performed with excluding outliers. Publication bias was assessed by Egger’s regression asymmetry test (p value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant). All the statistical analyses were conducted with STATA Version 11 software (StataCorp LP, College Station, TX, USA).
3. Results
3.1. Study Characteristics
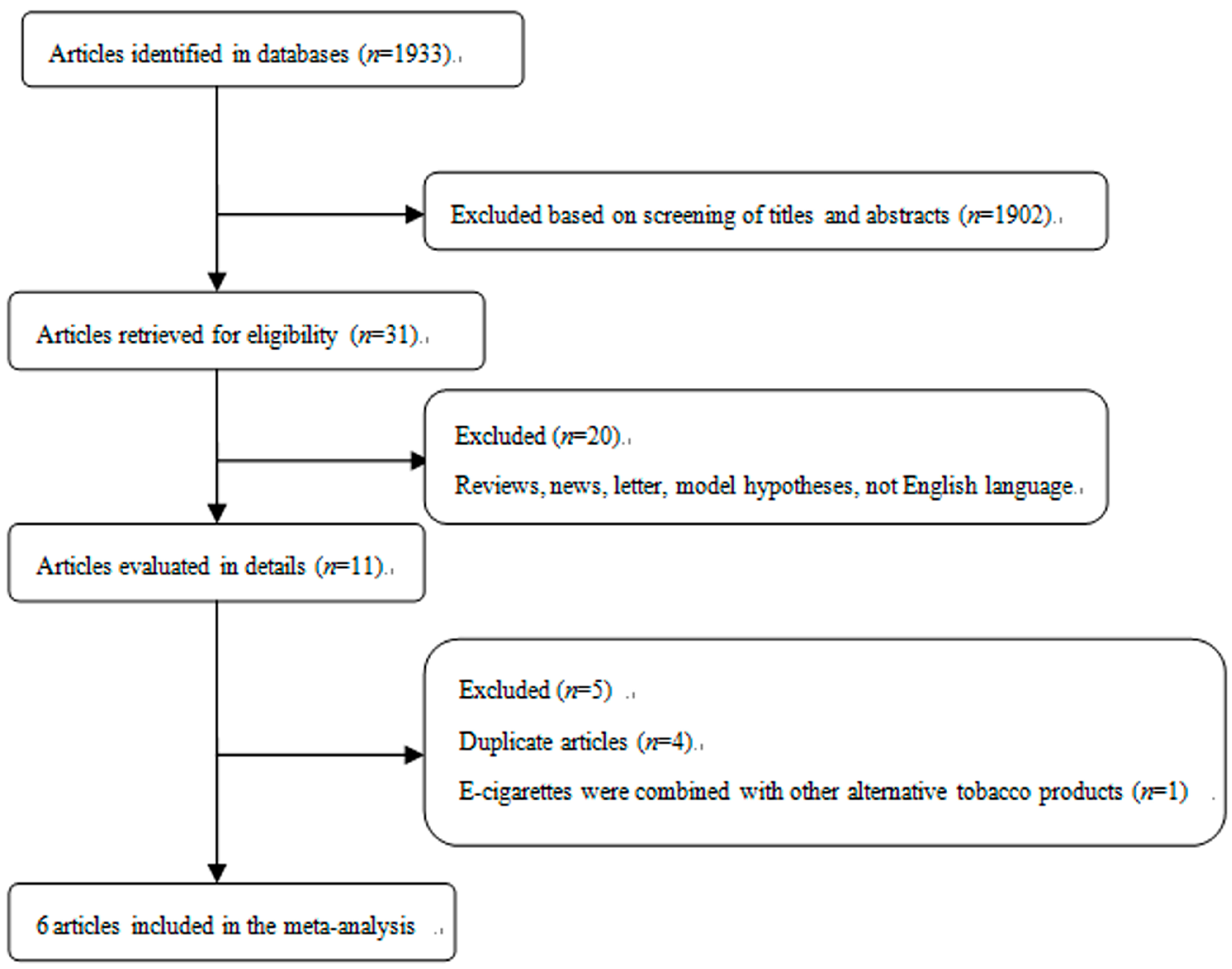
The process of study selection for this meta-analysis is shown in Figure 1. 20 articles were excluded from 31 potentially eligible studies because they were reviews, news, studies on model hypotheses, and/or published without English language. Additionally, it should be noted that four duplicate articles and one article that combined e-cigarettes with other alternative tobacco products were also excluded. The detailed information of studies was shown in Table 1. Briefly, a total of six studies were included in this meta-analysis of e-cigarettes use and smoking intention [22,23,24,25,26,27]. Among them, four studies were from the USA, one from China, and one from the UK. All the included studies reported the final estimates with adjustment for specified confounders.
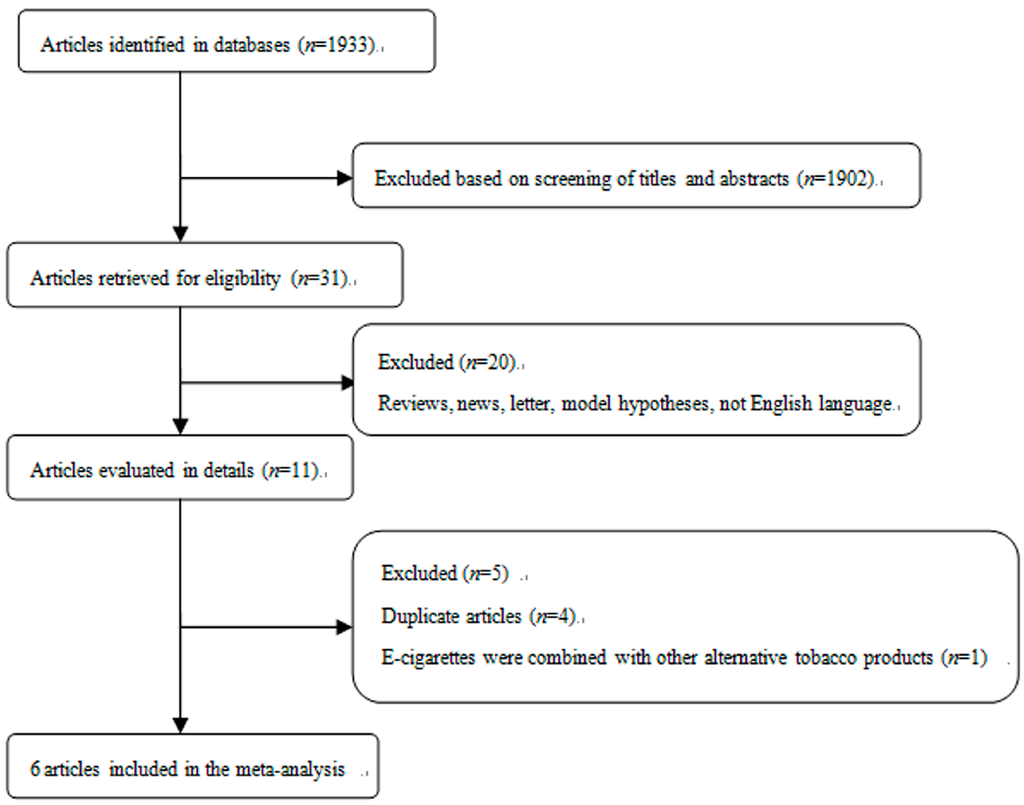
Figure 1.
Selection of studies for inclusion in meta-analysis.
3.2. Meta-Analysis of Association between E-Cigarettes Use and Smoking Intention
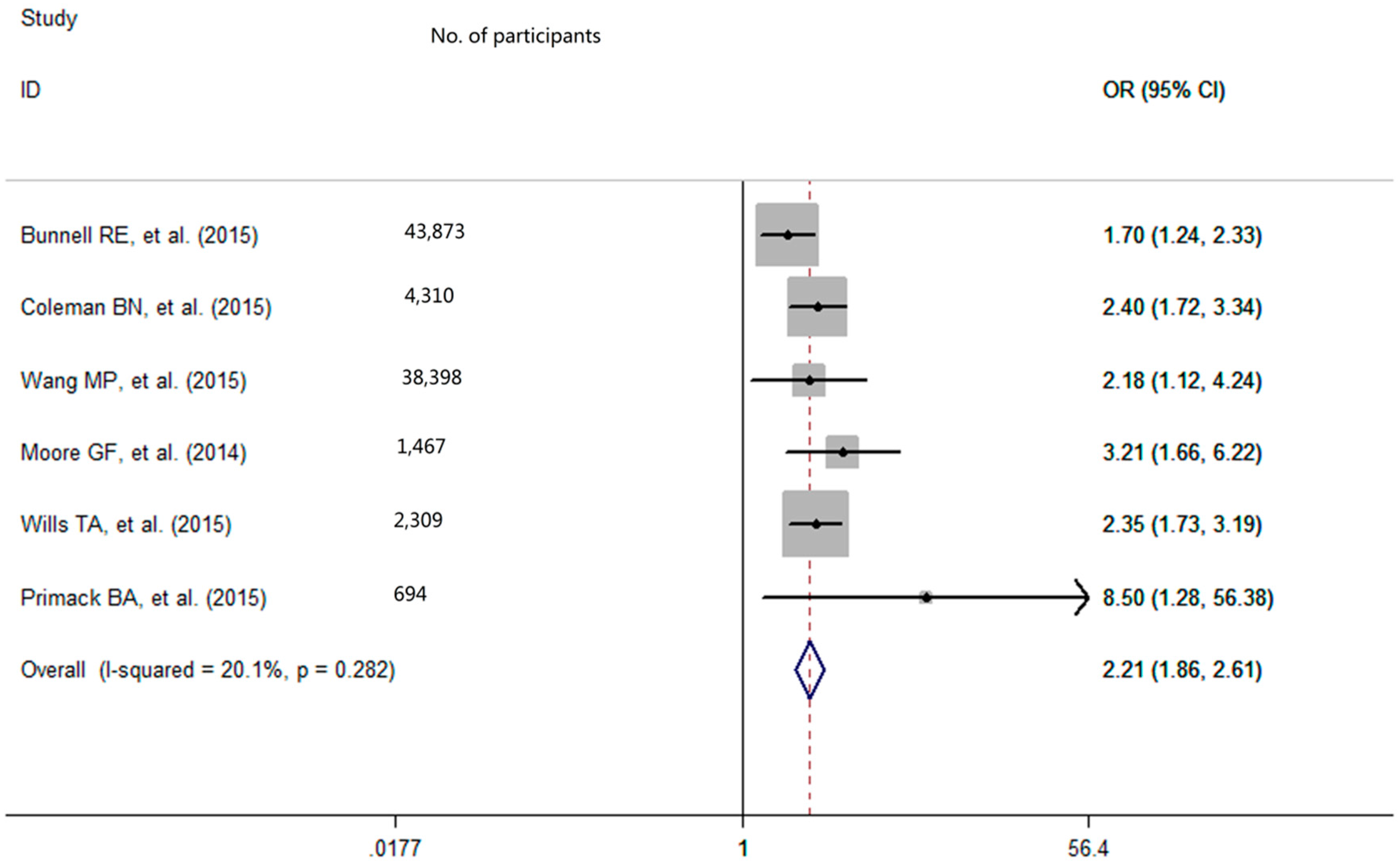
With low degree of heterogeneity (p = 0.28, I2 = 20.1%), a fixed-effects model was used to calculate the pooled odds ratio (OR) with 95% confidence interval (CI) for e-cigarettes use. The pooled analysis showed that among never-smoking adolescents and young adults, individuals who used e-cigarettes had a greater smoking intention in the future (OR = 2.21, 95% CI: 1.86–2.61; Figure 2). After excluding the outlier, the sensitivity analysis result showed that the pooled OR was 2.46 (95% CI = 2.01–3.01) and there was no significant study heterogeneity (p = 0.64, I2 = 0%).
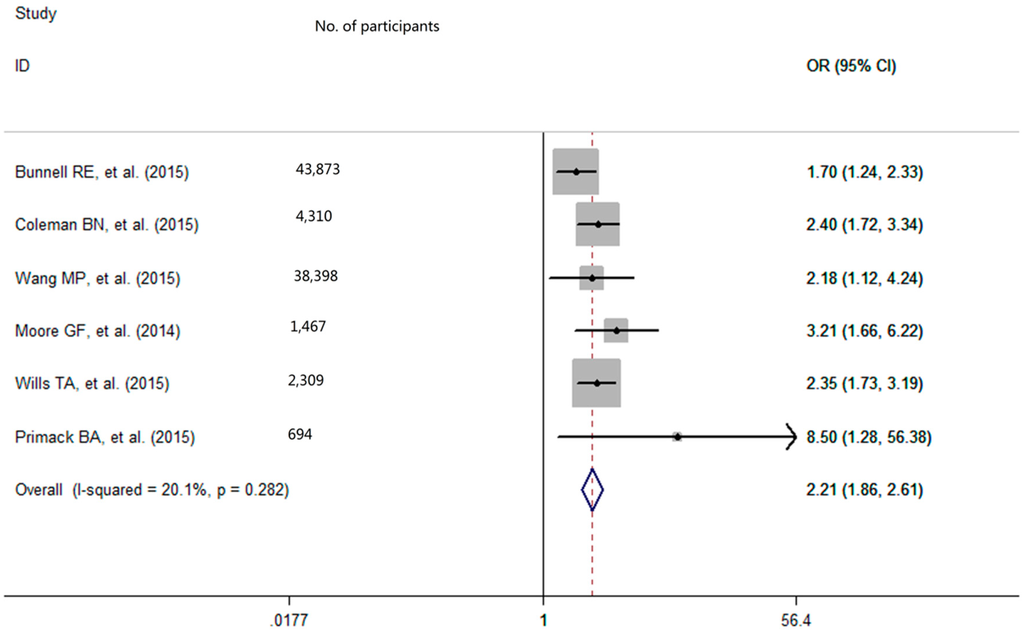
Figure 2.
Effect of e-cigarettes use on smoking intention among never-smoking adolescents and young adults. OR refers to odds ratio; CI refers to confidence interval.
3.3. Publication Bias
As for the publication bias, the Egger’s regression asymmetry test did not give a statistically significant result (p = 0.15).
4. Discussion
The present study uses meta-analysis method to provide a summary estimate of the effect of e-cigarettes use on smoking intention among never-smoking adolescents and young adults. With low evidence of between-study heterogeneity, findings from our meta-analysis confirm that never-smoking adolescents and young adults who used e-cigarettes have more than two times increased odds of intention to cigarette smoking (OR = 2.21, 95% CI: 1.86–2.61) in the future. Currently, there is considerable controversy about the health effects of e-cigarettes and one potential risk that e-cigarettes may become a new gateway to cigarette use among never-smokers has been identified as a concern by public health professionals [31,32]. As smoking intention is a strong predictor of future established smoking [4,5,6], our findings, in a way, add some tentative support for the probability that e-cigarettes use encourages the cigarette smoking initiation among never-smoking adolescents and young adults.
Although mechanisms accounting for the effect of e-cigarettes use on cigarette smoking initiation are complicated and still remain unclear, it is plausible that the nicotine exposure from e-cigarettes may play an important role in the “gateway effect”. As a nicotine-delivery product, e-cigarettes may serve as a “nicotine starter” [27]. Adolescents, who have developing brains, are especially sensitive to nicotine exposure [12], which can create nicotine dependence and lead youth to use tobacco products [33,34]. Currently, new-generation e-cigarettes have evolved to be more efficient and nicotine delivery from some devices may approach or even exceed that of a tobacco cigarette [35,36]. In theory, the “gateway effect” would be more apparent in the future. Additionally, secondhand tobacco smoke (SHS) is an important contributor to nicotine and may potentiate the smoking initiation. A recent systematic review reveals positive associations between smoking initiation among nonsmokers and SHS and nicotine dependence, [37]. E-cigarettes, with some of mainstream vapor exhaled, the secondhand exposure to bystanders is no doubt inevitable and has been identified as a source of nicotine [38,39]. Hence, we posit that the same process may promote youth who used e-cigarettes to cigarette smoking initiation. However, given that SHS is a significant public health problem among never-smoking adolescents [40], the effect of nicotine from e-cigarettes vapor on smoking initiation may be confounded by SHS inevitably. Except for the biological mechanism of nicotine, psychological mechanism is also possible. Studies have shown that the greater possibility of e-cigarette use is associated with increased exposure to parental or peer smoking, which may foster smoking susceptibility [40,41,42], suggesting that e-cigarette use is likely to be a proxy for influences and pressures from family and peer.
The results from our meta-analysis study are subject to several limitations. Firstly, our literature searching was conducted through only three databases and the possible bias was inevitable. Secondly, given that most of the included studies are cross-sectional studies in the current meta-analysis, we cannot infer whether the association between e-cigarettes use and cigarette smoking initiation is causal or not, and as such, more prospective studies are warranted. Thirdly, the data was self-reported and susceptible to misreporting. Fourthly, due to a limited number of participants who ever used e-cigarettes, the observed association between ever e-cigarettes use and smoking intention should be interpreted with caution.
5. Conclusions
From a public health perspective, our findings that e-cigarettes use by never-smoking adolescents and young adults is associated with cigarette smoking intention have important implications for the debates on the benefits and risks of e-cigarettes. In order to reduce the smoking intentions of youth and prevent them from initiating the first cigarette, we propose that prevention efforts around e-cigarettes restrictions should be enhanced.
Acknowledgments
The study was sponsored by “Medicine and Health Care in Zhejiang Province Science and Technology Plan” (Grant number: 2015KYB084).
Author Contributions
Meng Wang designed the study and collected, analyzed the data with Shuangshuang Cao, Weiwei Gong, and Fangrong Fei. Jieming Zhong gave much advice and directions in both study design and preparing of the manuscript. All the authors have read and approved the final submitted version.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| E-cigarettes | Electronic cigarettes |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| RR | Relative risk |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| DALYs | Disability-adjusted life-years |
| SHS | Second hand tobacco smoke |
References
- Ng, M.; Freeman, M.K.; Fleming, T.D.; Robinson, M.; Dwyer-Lindgren, L.; Thomson, B.; Wollum, A.; Sanman, E.; Wulf, S.; Lopez, A.D.; et al. Smoking prevalence and cigarette consumption in 187 countries, 1980–2012. JAMA 2014, 311, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GBD 2013 Risk Factors Collaborators; Forouzanfar, M.H.; Alexander, L.; Anderson, H.R.; Bachman, V.F.; Biryukov, S.; Brauer, M.; Burnett, R.; Casey, D.; Coates, M.M.; et al. Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 79 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks in 188 countries, 1990–2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2015, 386, 2287–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Department of Health and Human Services. Preventing Tobacco Use among Youth and Young Adults: A Report of the Surgeon General 2012. Available online: http://www.surgeongeneral.gov/library/reports/preventing-youth-tobacco-use/ (accessed on 21 February 2016).
- Pierce, J.P.; Choi, W.S.; Gilpin, E.A.; Farkas, A.J.; Merritt, R.K. Validation of susceptibility as a predictor of which adolescents take up smoking in the United States. Health Psychol. 1996, 15, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, W.S.; Gilpin, E.A.; Farkas, A.J.; Pierce, J.P. Determining the probability of future smoking among adolescents. Addiction 2001, 96, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakefield, M.; Kloska, D.D.; O’Malley, P.M.; Johnston, L.D.; Chaloupka, F.; Pierce, J.; Giovino, G.; Ruel, E.; Flay, B.R. The role of smoking intentions in predicting future smoking among youth: Findings from Monitoring the Future data. Addiction 2004, 99, 914–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azagba, S.; Asbridge, M. School connectedness and susceptibility to smoking among adolescents in Canada. Nicotine Tob. Res. 2013, 15, 1458–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veeranki, S.P.; Mamudu, H.M.; Anderson, J.L.; Zheng, S. Worldwide never-smoking youth susceptibility to smoking. J. Adolesc. Health 2014, 54, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dube, S.R.; Arrazola, R.A.; Lee, J.; Engstrom, M.; Malarcher, A. Pro-tobacco influences and susceptibility to smoking cigarettes among middle and high school students—United States, 2011. J. Adolesc. Health 2013, 52 (Suppl. 5), S45–S51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goniewicz, M.L.; Knysak, J.; Gawron, M.; Kosmider, L.; Sobczak, A.; Kurek, J.; Prokopowicz, A.; Jablonska-Czapla, M.; Rosik-Dulewska, C.; Havel, C.; et al. Levels of selected carcinogens and toxicants in vapour from electronic cigarettes. Tob. Control 2014, 23, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bullen, C.; Howe, C.; Laugesen, M.; McRobbie, H.; Parag, V.; Williman, J.; Walker, N. Electronic cigarettes for smoking cessation: A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2013, 382, 1629–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grana, R.; Benowitz, N.; Glantz, S.A. E-cigarettes: A scientific review. Circulation 2014, 129, 1972–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adkison, S.E.; O’Connor, R.J.; Bansal-Travers, M.; Hyland, A.; Borland, R.; Yong, H.H.; Cummings, K.M.; McNeill, A.; Thrasher, J.F.; Hammond, D.; et al. Electronic nicotine delivery systems: International tobacco control four-country survey. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2013, 44, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzoli, L.; Flacco, M.E.; Fiore, M.; La Vecchia, C.; Marzuillo, C.; Gualano, M.R.; Ligurori, G.; Cicolini, G.; Capasso, L.; D’Amario, C.; et al. Electronic Cigarettes Efficacy and Safety at 12 Months: Cohort Study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gravely, S.; Fong, G.T.; Cummings, K.M.; Yan, M.; Quah, A.C.; Borland, R.; Yong, H.H.; Hitchman, S.C.; Mc Neill, A.; Hammond, D.; et al. Awareness, trial, and current use of electronic cigarettes in 10 countries: Findings from the ITC project. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 11691–11704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMillen, R.C.; Gottlieb, M.A.; Shaefer, R.M.; Winickoff, J.P.; Klein, J.D. Trends in Electronic Cigarette Use among U.S. Adults: Use is Increasing in Both Smokers and Nonsmokers. Nicotine Tob. Res. 2015, 17, 1195–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agaku, I.T.; King, B.A.; Husten, C.G.; Bunnell, R.; Ambrose, B.K.; Hu, S.S.; Holder-Hayes, E.; Day, H.R. Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Tobacco product use among adults–United States, 2012–2013. MMWR Morb. Mortal Wkly. Rep. 2014, 63, 542–547. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reid, J.L.; Rynard, V.L.; Czoli, C.D.; Hammond, D. Who is using e-cigarettes in Canada? Nationally representative data on the prevalence of e-cigarette use among Canadians. Prev. Med. 2015, 81, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll Chapman, S.L.; Wu, L.T. E-cigarette prevalence and correlates of use among adolescents versus adults: A review and comparison. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2014, 54, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutra, L.M.; Glantz, S.A. Electronic cigarettes and conventional cigarette use among U.S. adolescents: A cross-sectional study. JAMA Pediatr. 2014, 168, 610–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leventhal, A.M.; Strong, D.R.; Kirkpatrick, M.G.; Unger, J.B.; Sussman, S.; Riggs, N.R.; Stone, M.D.; Khoddam, R.; Samet, J.M.; Audrain-McGoven, J. Association of Electronic Cigarette Use With Initiation of Combustible Tobacco Product Smoking in Early Adolescence. JAMA 2015, 314, 700–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunnell, R.E.; Agaku, I.T.; Arrazola, R.A.; Apelberg, B.J.; Caraballo, R.S.; Corey, C.G.; Coleman, B.N.; Dube, S.R.; King, B.A. Intentions to smoke cigarettes among never-smoking US middle and high school electronic cigarette users: National Youth Tobacco Survey, 2011–2013. Nicotine Tob. Res. 2015, 17, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleman, B.N.; Apelberg, B.J.; Ambrose, B.K.; Green, K.M.; Choiniere, C.J.; Bunnell, R.; King, B.A. Association between electronic cigarette use and openness to cigarette smoking among US young adults. Nicotine Tob. Res. 2015, 17, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.P.; Ho, S.Y.; Leung, L.T.; Lam, T.H. Electronic cigarette use and its association with smoking in Hong Kong Chinese adolescents. Addict. Behav. 2015, 50, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, G.F.; Littlecott, H.J.; Moore, L.; Ahmed, N.; Holliday, J. E-cigarette use and intentions to smoke among 10–11-year-old never-smokers in Wales. Tob. Control 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wills, T.A.; Sargent, J.D.; Knight, R.; Pagano, I.; Gibbons, F.X. E-cigarette use and willingness to smoke: A sample of adolescent non-smokers. Tob. Control 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Primack, B.A.; Soneji, S.; Stoolmiller, M.; Fine, M.J.; Sargent, J.D. Progression to Traditional Cigarette Smoking After Electronic Cigarette Use Among US Adolescents and Young Adults. JAMA Pediatr. 2015, 169, 1018–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stroup, D.F.; Berilin, J.A.; Morton, S.C.; Olkin, I.; Williamson, G.D.; Rennie, D.; Moher, D.; Becker, B.J.; Sipe, T.A.; Thacker, S.B. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: A proposal for reporting. Meta-analysis of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) group. JAMA 2000, 283, 2008–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2013, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DerSimonian, R.; Laird, N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control. Clin. Trials 1986, 7, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairchild, A.L.; Bayer, R.; Colgrove, J. The renormalization of smoking? E-cigarettes and the tobacco “endgame”. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 293–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grana, R.A. Electronic cigarettes: A new nicotine gateway? J. Adolesc. Health 2013, 52, 135–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, W.; Dierker, L.C.; Rose, J.S.; Selya, A.; Mermelstein, R.J. The natural course of nicotine dependence symptoms among adolescent smokers. Nicotine Tob. Res 2012, 14, 1445–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durmowicz, E.L. The impact of electronic cigarettes on the paediatric population. Tob. Control 2014, 23 (Suppl. 2), ii41–ii46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramôa, C.P.; Hiler, M.M.; Spindle, T.R.; Lopez, A.A.; Karaoghlanian, N.; Lipato, T.; Breland, A.B.; Shihadeh, A.; Eissenberg, T. Electronic cigarette nicotine delivery can exceed that of combustible cigarettes: A preliminary report. Tob. Control 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farsalinos, K.E.; Spyrou, A.; Tsimopoulou, K.; Stefopoulos, C.; Romagna, G.; Voudris, V. Nicotine absorption from electronic cigarette use: Comparison between first and new-generation devices. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okoli, C.T.; Kodet, J. A systematic review of secondhand tobacco smoke exposure and smoking behaviors: Smoking status, susceptibility, initiation, dependence, and cessation. Addict. Behav. 2015, 47, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czogala, J.; Goniewicz, M.L.; Fidelus, B.; Zielinska-Danch, W.; Travers, M.J.; Sobczak, A. Secondhand exposure to vapors from electronic cigarettes. Nicotine Tob. Res. 2014, 16, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAuley, T.R.; Hopke, P.K.; Zhao, J.; Babaian, S. Comparison of the effects of e-cigarette vapor and cigarette smoke on indoor air quality. Inhal. Toxicol. 2012, 24, 850–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veeranki, S.P.; Mamudu, H.M.; Zheng, S.; John, R.M.; Cao, Y.; Kioko, D.; Anderson, J.; Ouma, A.E. Secondhand smoke exposure among never-smoking youth in 168 countries. J. Adolesc. Health 2015, 56, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, K.; Forster, J. Characteristics associated with awareness, perceptions, and use of electronic nicotine delivery systems among young US Midwestern adults. Am. J. Public Health 2013, 103, 556–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonardi-Bee, J.; Jere, M.L.; Britton, J. Exposure to parental and sibling smoking and the risk of smoking uptake in childhood and adolescence: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Thorax 2011, 66, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).