The Spatio-Temporal Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Covid-19 Spread in Shenzhen, China—An Analysis Based on 417 Cases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
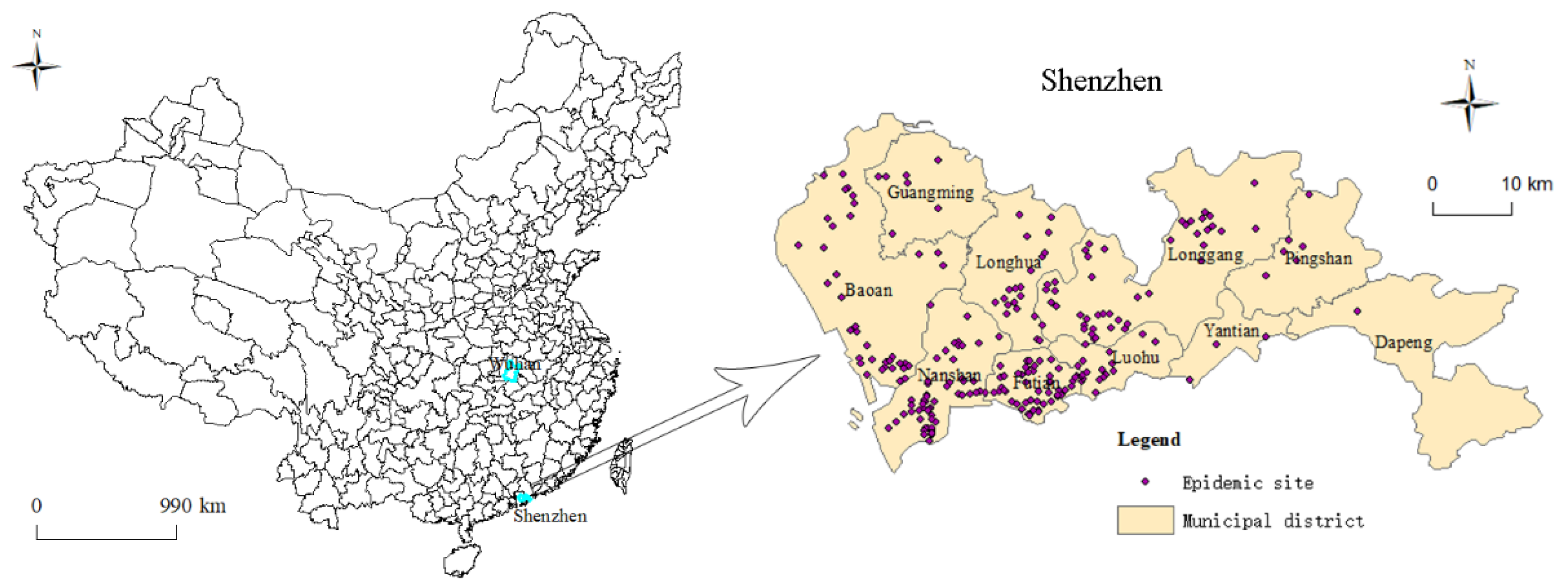
2.1. Overview of the Research Area
2.2. Data and Variables
2.2.1. Data Source
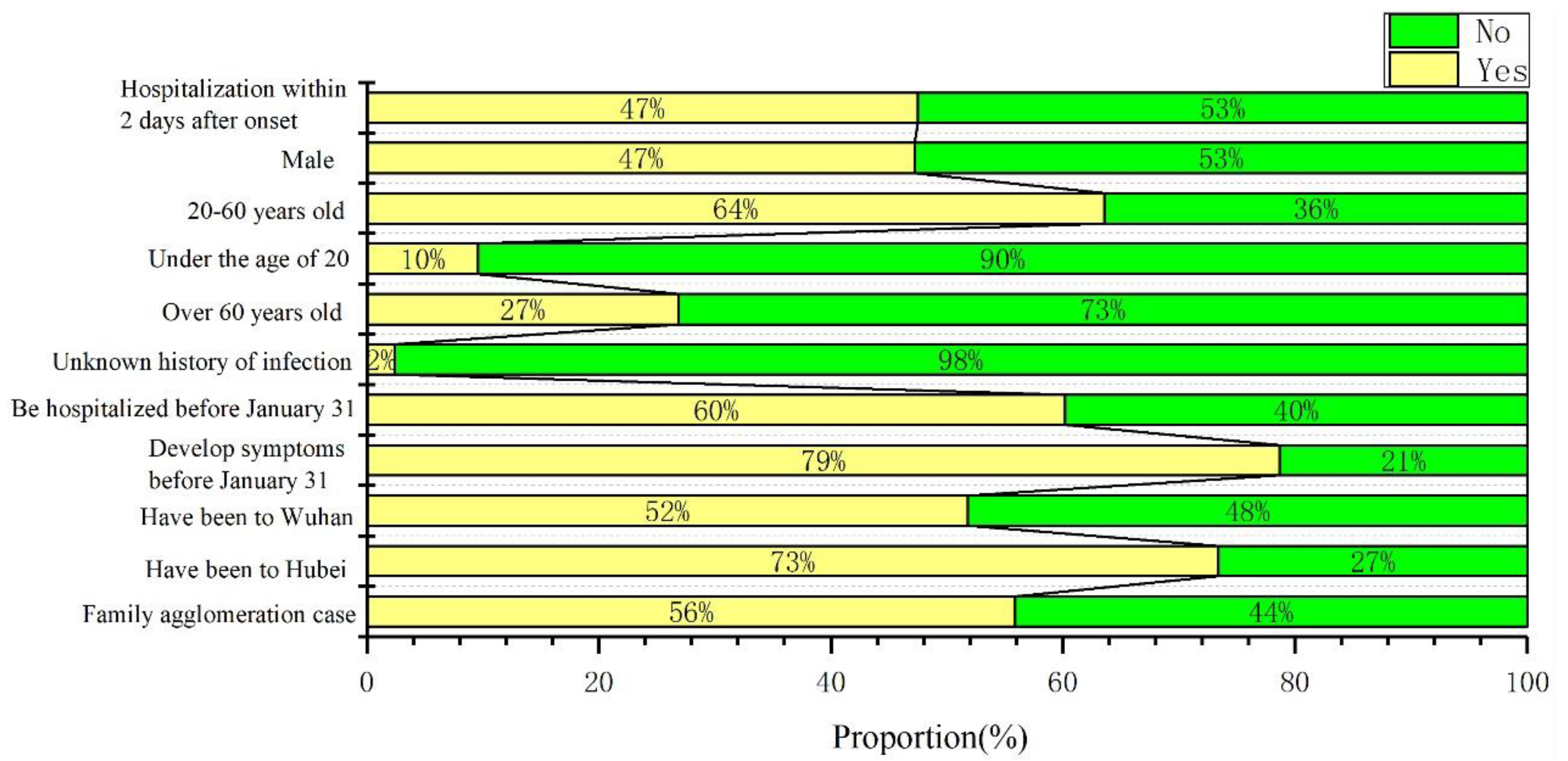
2.2.2. Variable Selection
2.3. Research Methods
2.3.1. Nearest Neighbor Index
2.3.2. Kernel Density Analysis
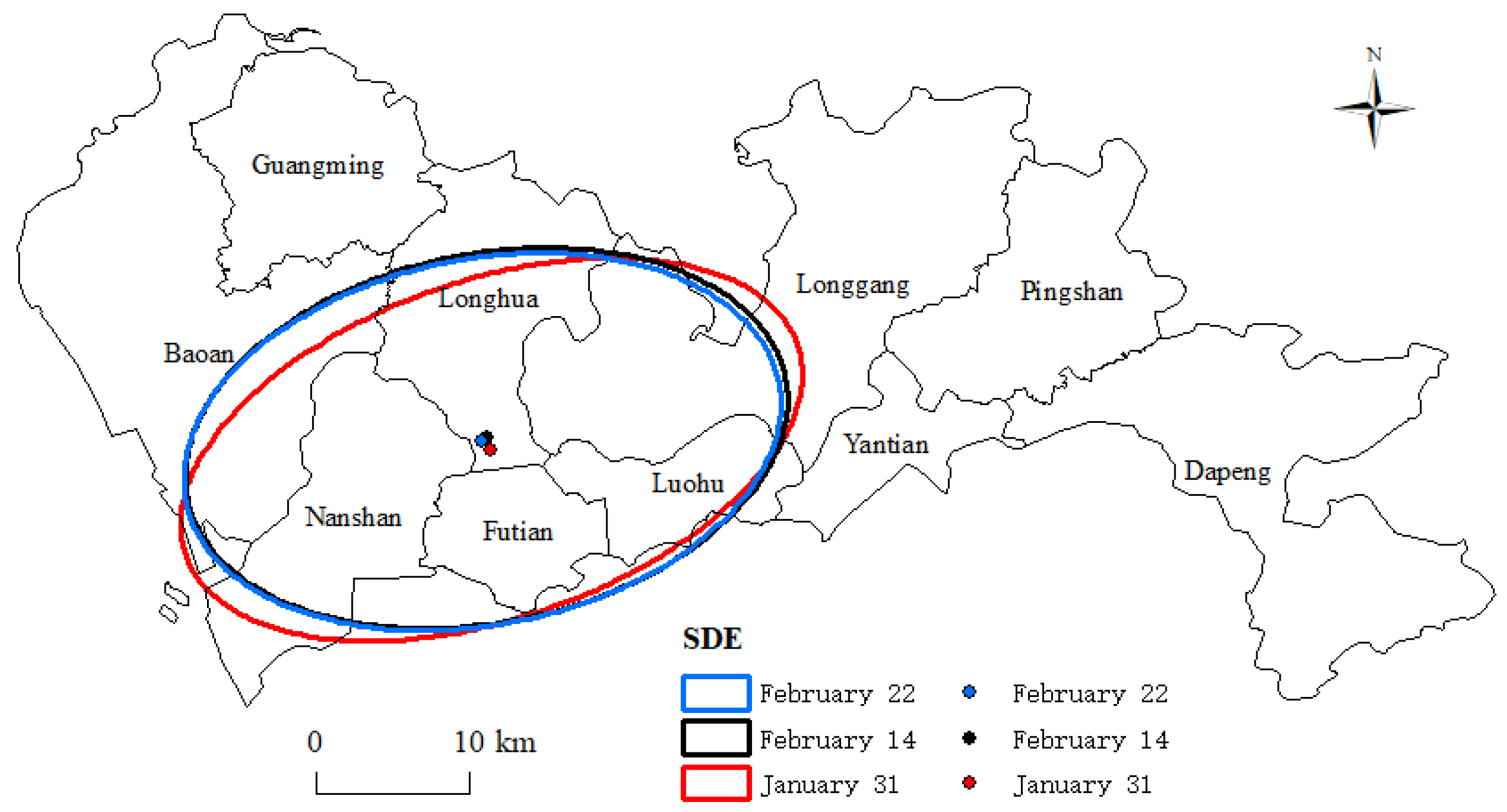
2.3.3. Standard Deviational Ellipse
2.3.4. Multiple Linear Regression
3. Results
3.1. Structural Features of Cases
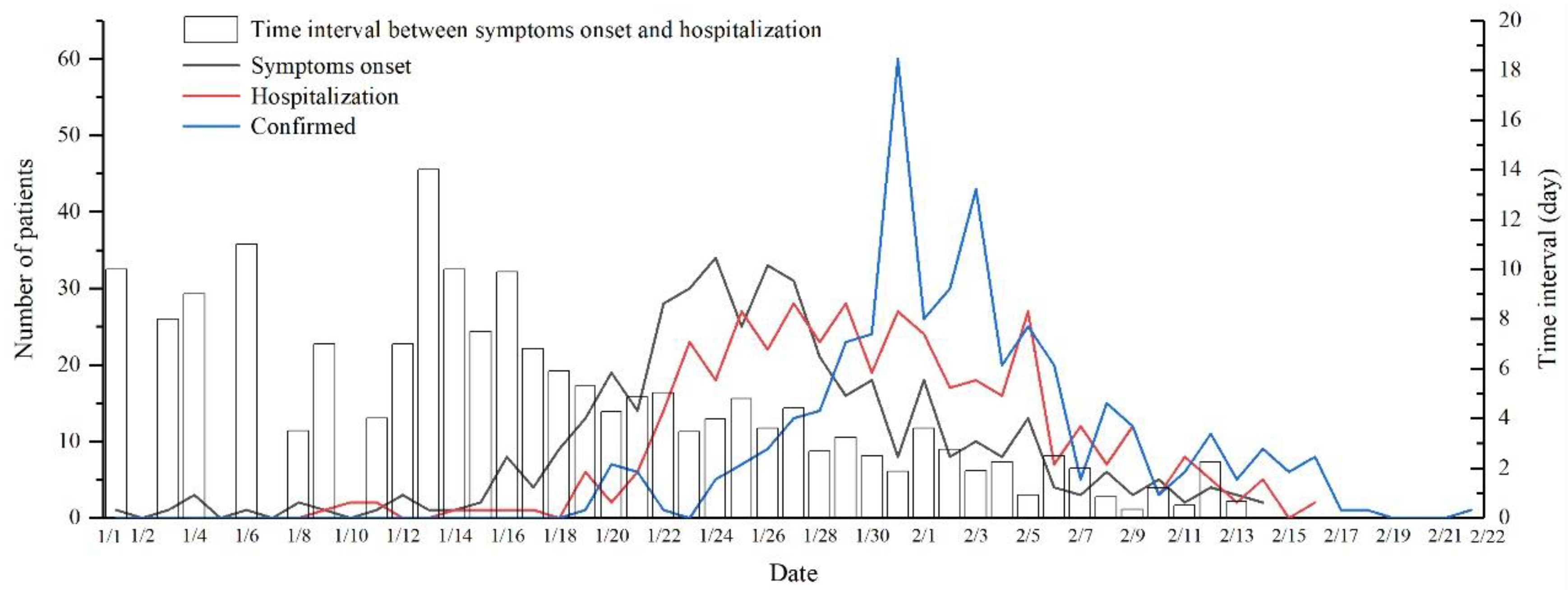
3.2. Time Series Variation Characteristics
3.3. Spatial Distribution Characteristics
3.3.1. Nearest Neighbor Index Analysis
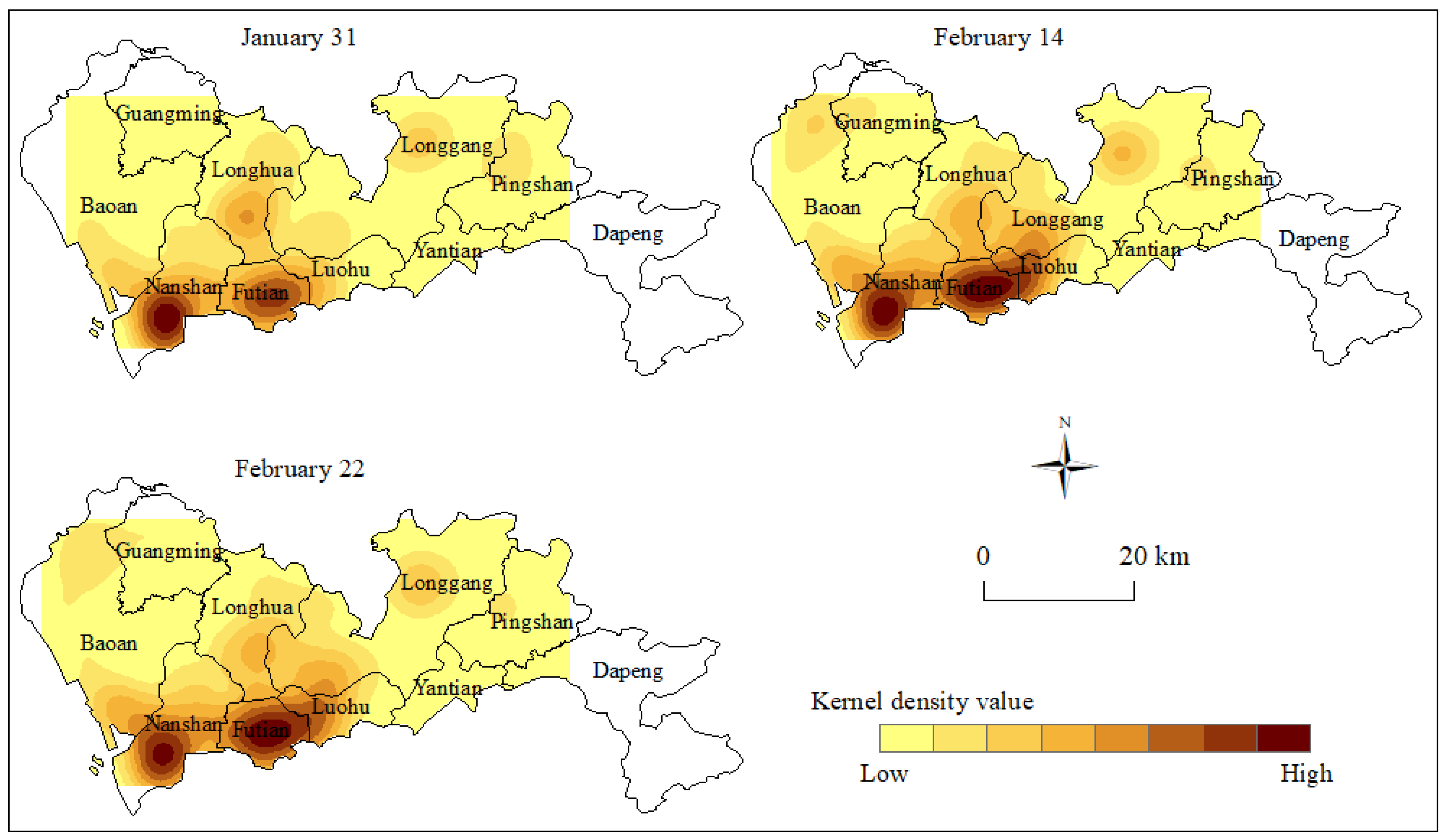
3.3.2. Kernel Density Analysis
3.3.3. Standard Deviational Ellipse Analysis
3.4. Analysis of Factors Influencing the Spread of COVID-19
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- COVID-19 Map—Johns Hopkins Coronavirus Resource Center. Available online: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html (accessed on 12 August 2020).
- Wang, D.W.; Hu, B.; Hu, C.; Zhu, F.F.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, B.B.; Xiang, H.; Cheng, Z.S.; Xiong, Y.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of 138 Hospitalized Patients With 2019 Novel Coronavirus–Infected Pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA 2020, 323, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.; Zhang, D.Y.; Wang, W.L.; Li, X.W.; Yang, B.; Song, J.D.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B.Y.; Shi, W.F.; Lu, R.J.; et al. A Novel Coronavirus from Patients With Pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhamees, A.A.; Alrashed, S.A.; Alzunaydi, A.A.; Ahmed, S.A.; Moath, S.A. The Psychological Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on the General Population of Saudi Arabia. Compr. Psychiatry 2020, 102, 152192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhu, J.F.; Yang, S.Y.; Lin, H.J.; Fu, C.W. Prevalence and Associated Factors of Poor Sleep Quality Among Chinese Returning Workers During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Sleep Med. 2020, 73, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Guan, X.H.; Wu, P.; Wang, X.Y.; Zhou, L.; Tong, Y.Q.; Ren, R.Q.; Kathy, S.M.L.; Eric, H.Y.L.; Jessica, Y.W.; et al. Early Transmission Dynamics in Wuhan, China, of Novel Coronavirus–Infected Pneumonia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prem, K.; Liu, Y.; Russell, T.W.; Adam, J.K.; Joel, H. The Effect of Control Strategies to Reduce Social Mixing on Outcomes of the COVID-19 Epidemic in Wuhan, China: A modelling study. Lancet Public Health 2020, 5, e261–e270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Lu, H.; Chen, R. Effect of a Bundle of Intervention Strategies for the Control of COVID-19 in Henan, a Neighboring Province of Wuhan, China. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2020, 132, 396–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.J.; Xie, J.G.; Huang, F.M.; Cao, L.Q. Association Between Short-term Exposure to Air Pollution and COVID-19 Infection: Evidence from China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 727, 138704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.J.; Cheng, S.S.; Wu, D.G.; Wu, T.C.; Lin, X.H.; Wang, C.L. Reconstruction of the Full Transmission Dynamics of COVID-19 in Wuhan. Nature 2020, 584, 420–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, A.; Liu, L.; Wang, C.L.; Guo, H.; Hao, X.J.; Wang, J.H.; He, N.; Yu, H.J.; Lin, X.H. Association of Public Health Interventions With the Epidemiology of the COVID-19 Outbreak in Wuhan, China. JAMA 2020, 323, 1915–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.Y.; Pei, S.; Chen, B.; Song, Y.; Zhang, T.; Yang, W.; Shaman, J. Substantial Undocumented Infection Facilitates the Rapid Dissemination of Novel Coronavirus (SARS-CoV2). Science 2020, 368, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, B.; Zheng, Z.G.; Liu, S.Y.; Chen, X.; Alon, S.; Li, J.; Li, D.; Shlomo, H. Spatio-temporal Propagation of COVID-19 Pandemics. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Struthers, J.; Min, L. Spatiotemporal Characteristics of COVID-19 Epidemic in the United States. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moh, A.A.; Sarah, A.Y.; Mohammad, M.K.; Nour, B.H.; Salman, K.A. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of COVID-19 Epidemic in the State of Kuwait. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 98, 153–160. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, K.; Marcia, C. Spatiotemporal Pattern of COVID-19 and Government Response in South Korea (as of 31 May 2020). Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 98, 328–333. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.L.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, Y.; Guo, Z.M.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.J.; Cheng, G.; Liao, C.H.; Li, Q.L.; Han, X.H.; et al. Distribution of the COVID -19 Epidemic and Correlation with Population Emigration from Wuhan, China. Chin. Med. J. 2020, 133, 1044–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.Y.; Choi, H.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, J. Spatial Epidemic Dynamics of the COVID-19 Outbreak in China. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 94, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenzhen Municipal Health Commission. Available online: http://wjw.sz.gov.cn/ (accessed on 12 August 2020).
- Gralinski, L.E.; Menachery, V.D. Return of the Coronavirus: 2019-nCoV. Viruses 2020, 12, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ning, X.L.; Tong, B.Q. Spatial Differentiation of Residential Areas in the Farming—Pastoral Ecotone on the North Foot of Yinshan Mountain. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2020, 34, 78–84. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Hu, W.P.; Wang, H.L.; Wu, C.; He, L. The Road Network Evolution of Guangzhou-Foshan Metropolitan Area Based on Kernel Density Estimation. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2011, 31, 81–86. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T.; Ma, J.J.; Xu, S.J. Spatial Patterns and Spatial Autocorrelations of Wetland Changes in China During 2003–2013. Environ. Sci. 2020, 41, 2496–2504. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Finance of the People’s Republic of China. Available online: http://www.mof.gov.cn/index.htm (accessed on 12 August 2020).
- Xie, Z.X.; Qin, Y.C.; Li, Y.; Shen, W.; Zheng, Z.C.; Liu, S.R. Spatial and Temporal Differentiation of COVID-19 Epidemic Spread in Mainland China and its Influencing Factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 744, 140929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zhuang, Z.; Ran, J.J.; Lin, J.; Yang, G.P.; Yang, L.; He, D.H. The Association between Domestic Train Transportation and Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) Outbreak in China from 2019 to 2020: A data-driven correlational report. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2020, 33, 101568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthew, R.L.; Sasikiran, K.; Jeffrey, S. Differential COVID-19 Case Positivity in New York City Neighborhoods: Socioeconomic Factors and Mobility. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.F.W.; Yuan, S.F.; Kok, K.H.; Kelvin, K.W.; Hin, C.; Yang, J.; Xing, F.F.; Liu, J.; Cyril, C.Y.Y.; Rosana, W.S.P.; et al. A Familial Cluster of Pneumonia Associated with the 2019 Novel Coronavirus Indicating Person-to-Person Transmission: A Study of a Family Cluster. Lancet 2020, 395, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollalo, A.; Vahedi, B.; Rivera, K.M. GIS -based Spatial Modeling of COVID -19 Incidence Rate in the Continental United States. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mario, C. Factors Determining the Diffusion of COVID-19 and Suggested Strategy to Prevent Future Accelerated Viral Infectivity Similar to COVID. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 729, 138474. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Lau, E.H.Y.; Wu, P.; Deng, X.L.; Wang, J.; Hao, X.X.; Lau, Y.C.; Wong, J.; Guan, Y.J.; Tan, X.H.; et al. Temporal Dynamics in Viral Shedding and Transmissibility of COVID-19. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 672–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Date | Sample Number | NNI | Z Value | Significance Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 31 January | 82 | 0.80 | −3.46 | 1% |
| 14 February | 230 | 0.72 | −8.03 | 1% |
| 22 February | 242 | 0.70 | −8.79 | 1% |
| Time | Rotation | X-StdDist | Y-StdDist |
|---|---|---|---|
| 31 January | 70.9° | 0.09 | 0.19 |
| 14 February | 78.5° | 0.10 | 0.18 |
| 22 February | 78.6° | 0.10 | 0.18 |
| Coefficient | 95% CI | p-Value | VIF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GDP | 0.102 | (0.000, 0.000) | 0.007 | 6.260 |
| Actual utilization of foreign capital | 0.092 | (−0.003, 0.003) | 0.004 | 7.002 |
| Per capita disposable income | −0.018 | (−0.005, 0.004) | 0.013 | 4.128 |
| Resident population | 0.137 | (−0.051, 0.042) | 0.029 | 4.068 |
| Population density | 0.479 | (−0.010, 0.010) | 0.008 | 5.823 |
| Number of industrial enterprises | 1.397 | (−0.050, 0.050) | 0.018 | 8.152 |
| Green coverage rate | −0.187 | (−4.403, 2.822) | 0.652 | 2.655 |
| Good air quality rate | −0.373 | (−12.122, 9.503) | 0.389 | 3.496 |
| Adjusted R2 | 0.985 | |||
| Significance F | 0.012 | |||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, S.; Qin, Y.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, J. The Spatio-Temporal Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Covid-19 Spread in Shenzhen, China—An Analysis Based on 417 Cases. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7450. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17207450
Liu S, Qin Y, Xie Z, Zhang J. The Spatio-Temporal Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Covid-19 Spread in Shenzhen, China—An Analysis Based on 417 Cases. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(20):7450. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17207450
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Shirui, Yaochen Qin, Zhixiang Xie, and Jingfei Zhang. 2020. "The Spatio-Temporal Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Covid-19 Spread in Shenzhen, China—An Analysis Based on 417 Cases" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 20: 7450. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17207450
APA StyleLiu, S., Qin, Y., Xie, Z., & Zhang, J. (2020). The Spatio-Temporal Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Covid-19 Spread in Shenzhen, China—An Analysis Based on 417 Cases. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(20), 7450. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17207450





