The Influence of COVID-19 Pandemic Lockdown on the Physical Performance of Professional Soccer Players: An Example of German and Polish Leagues
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
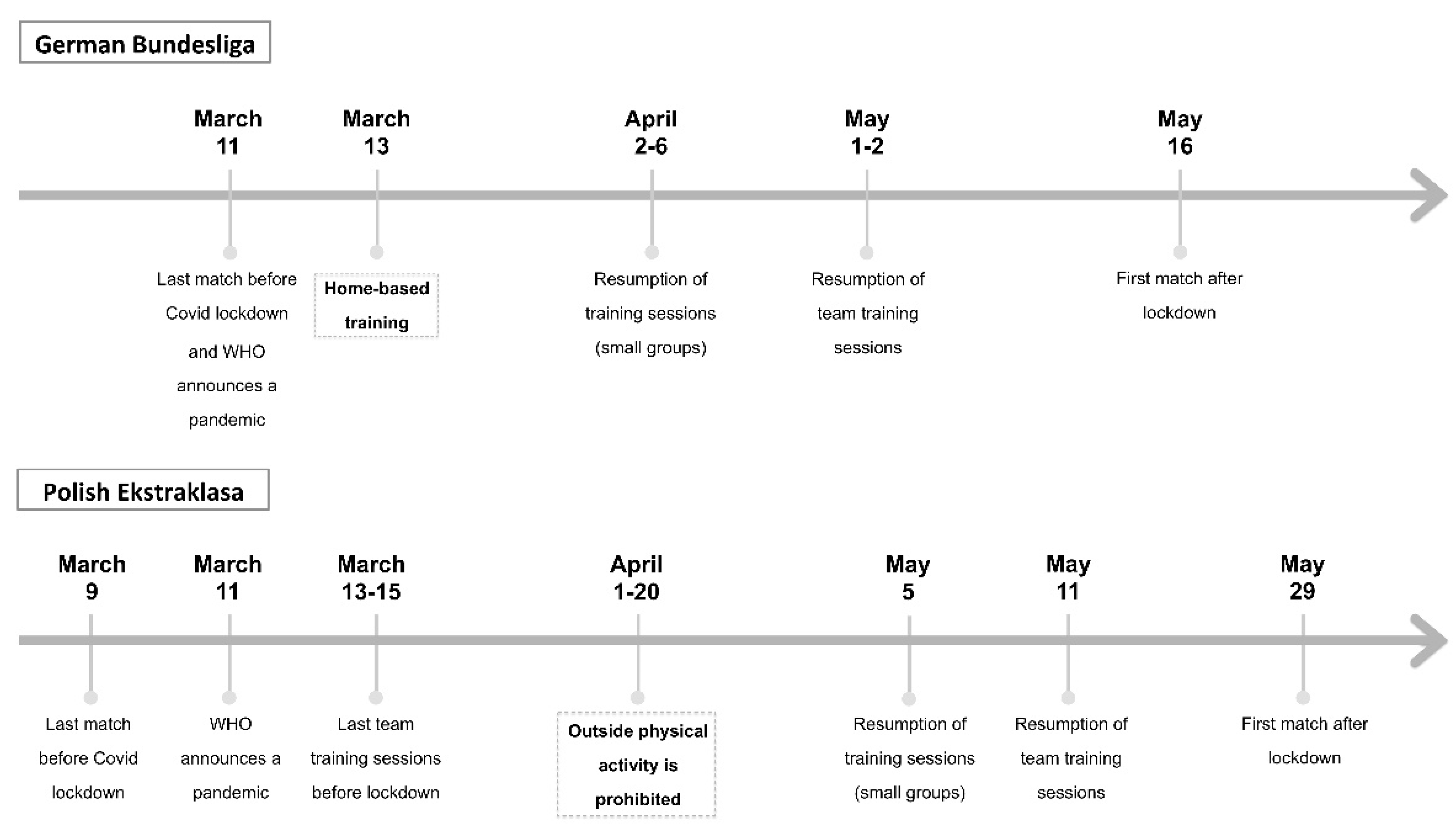
2.2. German Bundesliga Schedule
2.3. Polish Ekstraklasa Schedule
2.4. Methodology
2.4.1. German Bundesliga
2.4.2. Polish Ekstraklasa
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
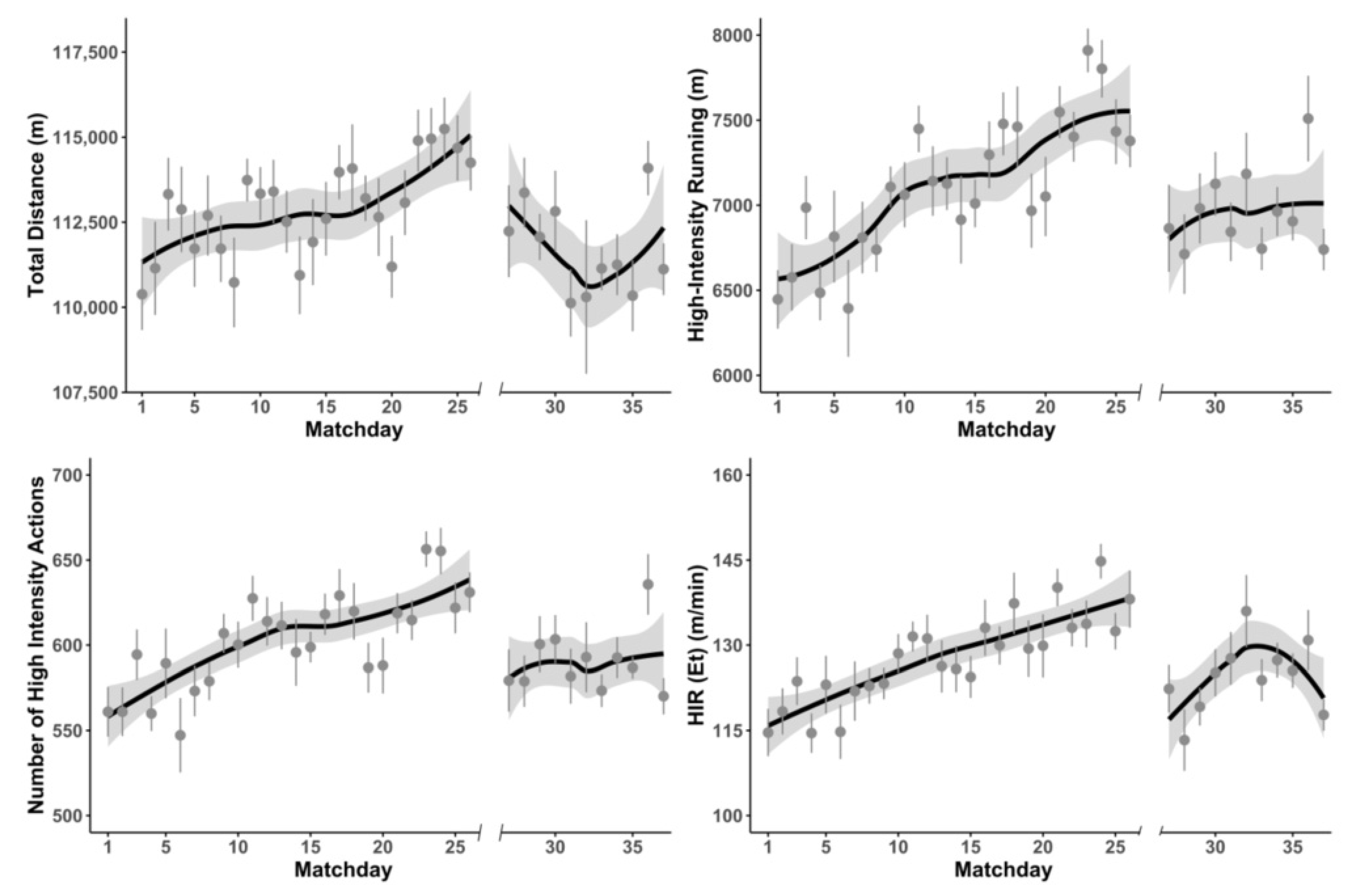
3.1. German Bundesliga
3.2. Polish Ekstraklasa
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Salata, C.; Calistri, A.; Parolin, C.; Palù, G. Coronaviruses: A paradigm of new emerging zoonotic diseases. Pathog. Dis. 2019, 77, ftaa006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, T.; Du, Z.; Zhu, F.; Cao, Z.; An, Y.; Gao, Y.; Jiang, B. Comorbidities and multi-organ injuries in the treatment of COVID-19. Lancet 2020, 395, e52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Zhou, M.; Dong, X.; Qu, J.; Gong, F.; Han, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wei, Y.; et al. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A descriptive study. Lancet 2020, 395, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, Y.-Y.; Ma, Y.-T.; Zhang, J.-Y.; Xie, X. COVID-19 and the cardiovascular system. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2020, 17, 259–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Su, H.; Yang, M.; Wan, C.; Yi, L.-X.; Tang, F.; Zhu, H.-Y.; Yi, F.; Yang, H.-C.; Fogo, A.B.; Nie, X.; et al. Renal histopathological analysis of 26 postmortem findings of patients with COVID-19 in China. Kidney Int. 2020, 98, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.R.; Brito, J.; Akenhead, R.; Nassis, G.P. The Transition Period in Soccer: A Window of Opportunity. Sports Med. 2016, 46, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koundourakis, N.; Androulakis, N.; Malliaraki, N.; Tsatsanis, C.; Venihaki, M.; Margioris, A.N. Discrepancy between Exercise Performance, Body Composition, and Sex Steroid Response after a Six-Week Detraining Period in Professional Soccer Players. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisciotti, G.N.; Eirale, C.; Corsini, A.; Baudot, C.; Saillant, G.; Chalabi, H. Return to football training and competition after lockdown caused by the COVID-19 pandemic: Medical recommendations. Biol. Sport 2020, 37, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buldú, J.M.; Antequera, D.R.; Aguirre, J. The resumption of sports competitions after COVID-19 lockdown: The case of the Spanish football league. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2020, 138, 109964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrero-Gonzalez, H.; Martín-Acero, R.; Del Coso, J.; Lalín-Novoa, C.; Pol, R.; Martin-Escudero, P.; De La Torre, A.I.; Hughes, C.; Mohr, M.; Biosca, F.; et al. Position statement of the Royal Spanish Football Federation for the resumption of football activities after the COVID-19 pandemic (June 2020). Br. J. Sports Med. 2020, 54, 1133–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, T.; Mack, D.; Donde, K.; Harzer, O.; Krutsch, W.; Rössler, A.; Kimpel, J.; Von Laer, D.; Gärtner, B.C. Successful return to professional men’s football (soccer) competition after the COVID-19 shutdown: A cohort study in the German Bundesliga. Br. J. Sports Med. 2021, 55, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, E.; Costa, P.B.; Corredoira, F.J.; de Rellan Guerra, A.S. Effects of Age on Physical Match Performance in Professional Soccer Players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo-Martinez, M.; Kalén, A.; Rey, E.; Campo, R.L.-D.; Resta, R.; Lago-Peñas, C. Do elite soccer players cover less distance when their team spent more time in possession of the ball? Sci. Med. Footb. 2020, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellano, J.; Blanco-Villaseñor, A.; Álvarez, D. Contextual Variables and Time-Motion Analysis in Soccer. Int. J. Sports. Med. 2011, 32, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Andrzejewski, M.; Konefał, M.; Chmura, P.; Kowalczuk, E.; Chmura, J. Match outcome and distances covered at various speeds in match play by elite German soccer players. Int. J. Perform. Anal. Sport 2016, 16, 817–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepschy, H.; Wäsche, H.; Woll, A. How to be Successful in Football: A Systematic Review. Open Sports Sci. J. 2018, 11, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radzimiński, Ł.; Szwarc, A.; Padrón-Cabo, A.; Jastrzębski, Z. Correlations between body composition, aerobic capacity, speed and distance covered among professional soccer players during official matches. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2020, 60, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradley, P.S.; Ade, J.D. Are Current Physical Match Performance Metrics in Elite Soccer Fit for Purpose or Is the Adoption of an Integrated Approach Needed? Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2018, 13, 656–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, C.; Archer, D.T.; Hogg, B.; Bush, M.; Bradley, P.S. The Evolution of Physical and Technical Performance Parameters in the English Premier League. Int. J. Sports Med. 2014, 35, 1095–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konefał, M.; Chmura, P.; Tessitore, A.; Melcer, T.; Kowalczuk, E.; Chmura, J.; Andrzejewski, M. The Impact of Match Location and Players’ Physical and Technical Activities on Winning in the German Bundesliga. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Calderón, B. The effect of short-term and long-term coronavirus quarantine on physical performance and injury incidence in high-level soccer. Soccer Soc. 2021, 22, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, D.B.; González-García, J.; Campo, R.L.-D.; Resta, R.; Buldú, J.M.; Wilk, M.; Coso, J. Players’ physical performance in LaLiga when the competition resumes after COVID-19: Insights from previous seasons. Biol. Sport 2021, 38, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Aliaga, A.; Marquina, M.; Cordón-Carmona, A.; Sillero-Quintana, M.; de la Rubia, A.; Román, I.R. Comparative Analysis of Soccer Performance Intensity of the Pre–Post-Lockdown COVID-19 in LaLiga™. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konefał, M.; Chmura, P.; Zając, T.; Chmura, J.; Kowalczuk, E.; Andrzejewski, M. A New Approach to the Analysis of Pitch-Positions in Professional Soccer. J. Hum. Kinet. 2019, 66, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siegle, M.; Stevens, T.; Lames, M. Design of an accuracy study for position detection in football. J. Sports Sci. 2012, 31, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linke, D.; Link, D.; Lames, M. Football-specific validity of TRACAB’s optical video tracking systems. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2017; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 22 June 2020).
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 133468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; Lawrence Erlbaum: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Chmura, P.; Konefał, M.; Wong, D.P.; Figueiredo, A.J.; Kowalczuk, E.; Rokita, A.; Chmura, J.; Andrzejewski, M. Players’ Physical Performance Decreased After Two-Thirds of the Season: Results of 3 Consecutive Seasons in the German First Bundesliga. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grazioli, R.; Loturco, I.; Baroni, B.M.; Oliveira, G.S.; Saciura, V.; Vanoni, E.; Dias, R.; Veeck, F.; Pinto, R.S.; Cadore, E.L. Coronavirus Disease-19 Quarantine Is More Detrimental Than Traditional Off-Season on Physical Conditioning of Professional Soccer Players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2020, 34, 3316–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkmaz, S.; Aslan, C.S.; Eyuboglu, E.; Celebi, M.; Kir, R.; Karakulak, I.; Akyuz, O.; Ozer, U.; Geri, S. Impact of detraining process during the COVID-19 pandemic on the selected physical and motor features of football players. Prog. Nutr. 2020, 22, e2020029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabre, J.-B.; Grelot, L.; Vanbiervielt, W.; Mazerie, J.; Manca, R.; Martin, V. Managing the combined consequences of COVID-19 infection and lock-down policies on athletes: Narrative review and guidelines proposal for a safe return to sport. BMJ Open Sport Exerc. Med. 2020, 6, e000849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, M.; Nassis, G.P.; Brito, J.; Randers, M.B.; Castagna, C.; Parnell, D.; Krustrup, P. Return to elite football after the COVID-19 lockdown. Manag. Sport Leis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, P.S.; Lago-Peñas, C.; Rey, E. Evaluation of the Match Performances of Substitution Players in Elite Soccer. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2014, 9, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padrón-Cabo, A.; Rey, E.; Vidal, B.; García-Nuñez, J. Work-rate Analysis of Substitute Players in Professional Soccer: Analysis of Seasonal Variations. J. Hum. Kinet. 2018, 65, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lorenzo-Martínez, M.; Padrón-Cabo, A.; Rey, E.; Memmert, D. Analysis of Physical and Technical Performance of Substitute Players in Professional Soccer. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Before | After | ∆ (%) | ES (CI 95%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Distance (m) | 115,501.1 ± 4444.2 | 114,822.2 ± 4530.9 | −0.59 | −0.15 (−0.33 to 0.03) |
| Distance covered at 21–24 km/h (m) | 3946.7 ± 480.1 | 3961.7 ± 442.6 | 0.38 | 0.03 (−0.14 to 0.21) |
| Distance covered at speeds >24 km/h (m) | 3074.4 ± 555.0 | 3110.5 ± 564.2 | 1.17 | 0.06 (−0.11 to 0.24) |
| Et (min) | 56.8 ± 4.2 | 57.0 ± 4.8 | 0.35 | −0.05 (−0.13 to 0.22) |
| TD (m/min) | 1213.42 ± 49.05 | 1207.68 ± 49.20 | −0.46 | −0.12 (−0.30 to 0.06) |
| TD (Et) (m/min) | 2042.3 ± 134.3 | 2025.2 ± 149.5 | −0.84 | −0.12 (−0.30 to 0.06) |
| Distance covered at 21–24 km/h (m/min) | 41.48 ± 5.20 | 41.68 ± 4.80 | 0.48 | 0.04 (−0.14 to 0.22) |
| Distance covered at 21–24 km/h (Et) (m/min) | 69.8 ± 9.8 | 69.9 ± 10.3 | 0.14 | 0.01 (−0.16 to 0.19) |
| Distance covered at speeds >24 km/h (m/min) | 32.32 ± 5.96 | 32.73 ± 6.02 | 1.27 | 0.07 (−0.11 to 0.25) |
| Distance covered at speeds >24 km/h (Et) (m/min) | 54.2 ± 10.7 | 55.3 ± 11.6 | 2.03 | 0.10 (−0.08 to 0.28) |
| Before | After | ∆ (%) | ES (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TD (m) | 112,895.0 ± 4218.6 | 111,714.4 ± 4614.1 ** | −1.05 | −0.27 (−0.45 to −0.10) |
| HIR (m) | 7107.3 ± 838.5 | 6961.2 ± 786.6 * | −2.06 | −0.18 (−0.35 to −0.01) |
| Sprint (m) | 1752.9 ± 357.7 | 1720.6 ± 332.6 | −1.84 | −0.09 (−0.27 to −0.01) |
| Number of HIR | 602.3 ± 62.5 | 590.5 ± 60.3 * | −1.96 | −0.20 (−0.37 to −0.02) |
| Et (min) | 55.9 ± 4.7 | 56.3 ± 4.6 | 0.71 | 0.09 (−0.09 to 0.26) |
| TD (m/min) | 1166.1 ± 49.3 | 1162.3 ± 50.8 | −0.33 | −0.08 (−0.25 to 0.10) |
| TD (Et) (m/min) | 2030.1 ± 159.8 | 1995.3 ± 162.3 * | −1.72 | −0.21 (−0.39 to −0.04) |
| HIR (m/min) | 73.53 ± 8.59 | 72.43 ± 8.34 | −1.50 | −0.13 (−0.31 to 0.05) |
| HIR (Et) (m/min) | 127.95 ± 17.86 | 124.45 ± 17.78 * | −2.74 | −0.20 (−0.37 to −0.02) |
| Sprint (m/min) | 18.13 ± 3.65 | 17.90 ± 3.48 | −1.27 | −0.06 (−0.24 to 0.11) |
| Sprint (Et) (m/min) | 31.57 ± 6.94 | 30.71 ± 6.41 | −2.72 | −0.13 (−0.30 to 0.05) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Radzimiński, Ł.; Padrón-Cabo, A.; Konefał, M.; Chmura, P.; Szwarc, A.; Jastrzębski, Z. The Influence of COVID-19 Pandemic Lockdown on the Physical Performance of Professional Soccer Players: An Example of German and Polish Leagues. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8796. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18168796
Radzimiński Ł, Padrón-Cabo A, Konefał M, Chmura P, Szwarc A, Jastrzębski Z. The Influence of COVID-19 Pandemic Lockdown on the Physical Performance of Professional Soccer Players: An Example of German and Polish Leagues. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(16):8796. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18168796
Chicago/Turabian StyleRadzimiński, Łukasz, Alexis Padrón-Cabo, Marek Konefał, Paweł Chmura, Andrzej Szwarc, and Zbigniew Jastrzębski. 2021. "The Influence of COVID-19 Pandemic Lockdown on the Physical Performance of Professional Soccer Players: An Example of German and Polish Leagues" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 16: 8796. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18168796
APA StyleRadzimiński, Ł., Padrón-Cabo, A., Konefał, M., Chmura, P., Szwarc, A., & Jastrzębski, Z. (2021). The Influence of COVID-19 Pandemic Lockdown on the Physical Performance of Professional Soccer Players: An Example of German and Polish Leagues. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(16), 8796. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18168796










