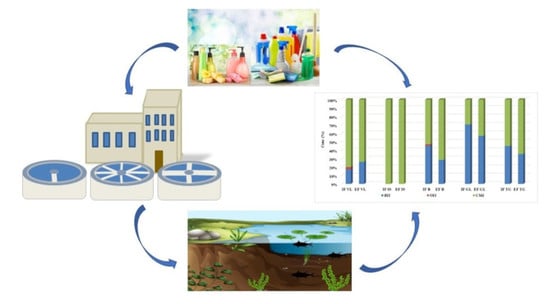
Occurrence and Transport of Isothiazolinone-Type Biocides from Commercial Products to Aquatic Environment and Environmental Risk Assessment
Abstract
Share and Cite
Paun, I.; Pirvu, F.; Iancu, V.I.; Chiriac, F.L. Occurrence and Transport of Isothiazolinone-Type Biocides from Commercial Products to Aquatic Environment and Environmental Risk Assessment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7777. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19137777
Paun I, Pirvu F, Iancu VI, Chiriac FL. Occurrence and Transport of Isothiazolinone-Type Biocides from Commercial Products to Aquatic Environment and Environmental Risk Assessment. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(13):7777. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19137777
Chicago/Turabian StylePaun, Iuliana, Florinela Pirvu, Vasile Ion Iancu, and Florentina Laura Chiriac. 2022. "Occurrence and Transport of Isothiazolinone-Type Biocides from Commercial Products to Aquatic Environment and Environmental Risk Assessment" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 13: 7777. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19137777
APA StylePaun, I., Pirvu, F., Iancu, V. I., & Chiriac, F. L. (2022). Occurrence and Transport of Isothiazolinone-Type Biocides from Commercial Products to Aquatic Environment and Environmental Risk Assessment. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(13), 7777. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19137777