Water Environment Characteristics and Water Quality Assessment of Water Source of Diversion System of Project from Hanjiang to Weihe River
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
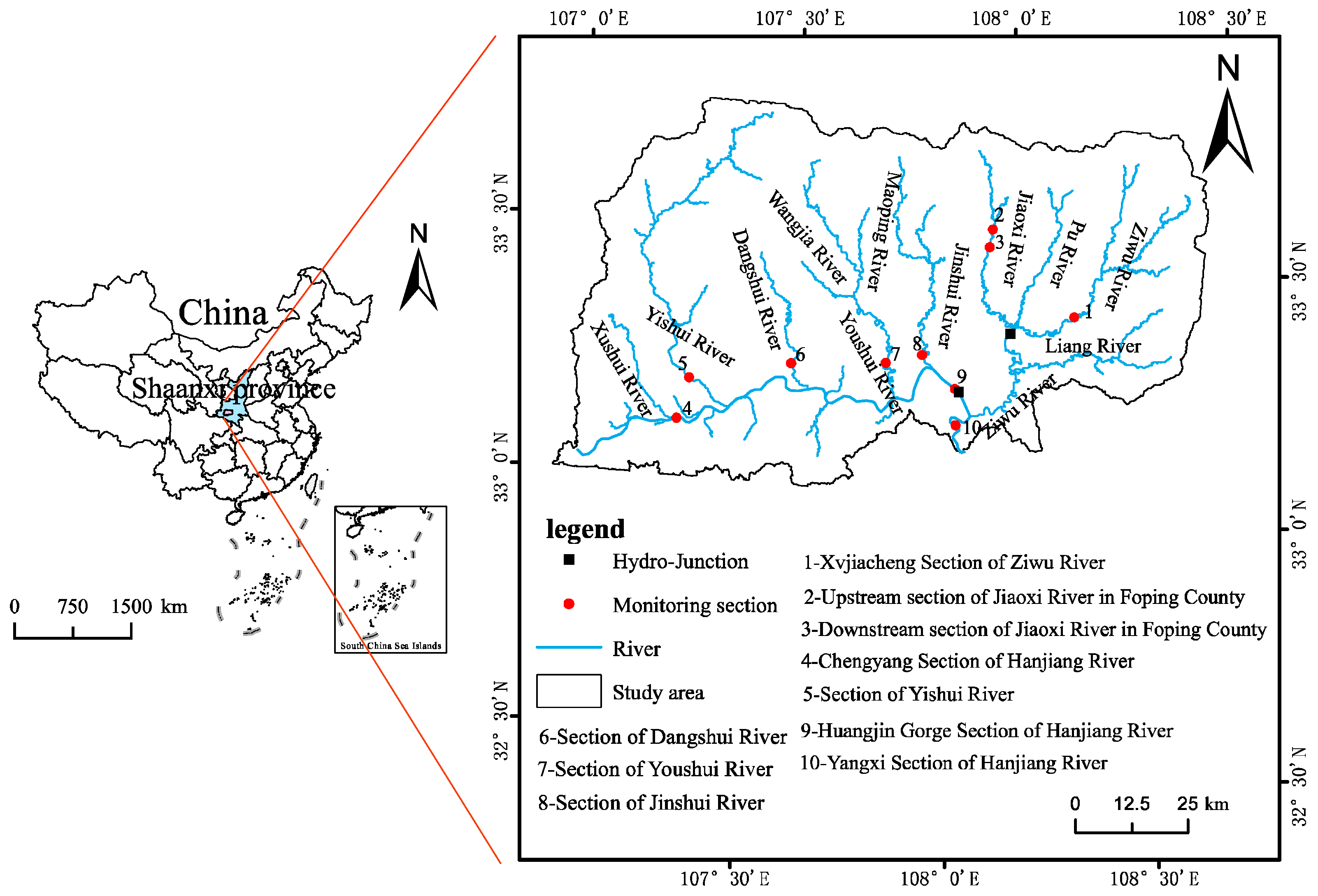
2.1. General Situation of the Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Analysis Method
2.3.1. ANOVA
2.3.2. Cluster Analysis
2.3.3. Analysis of Comprehensive Water Quality Indicator
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
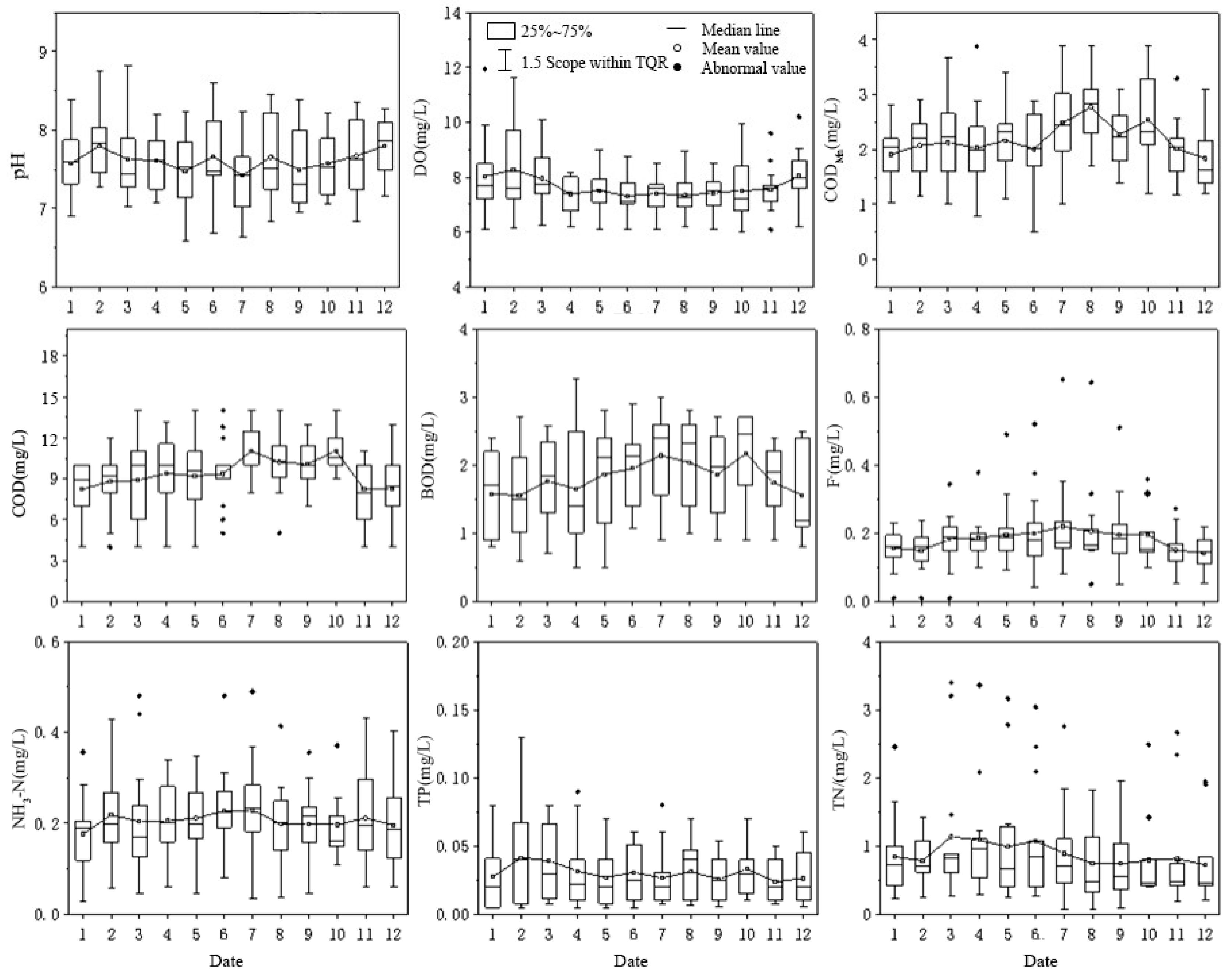
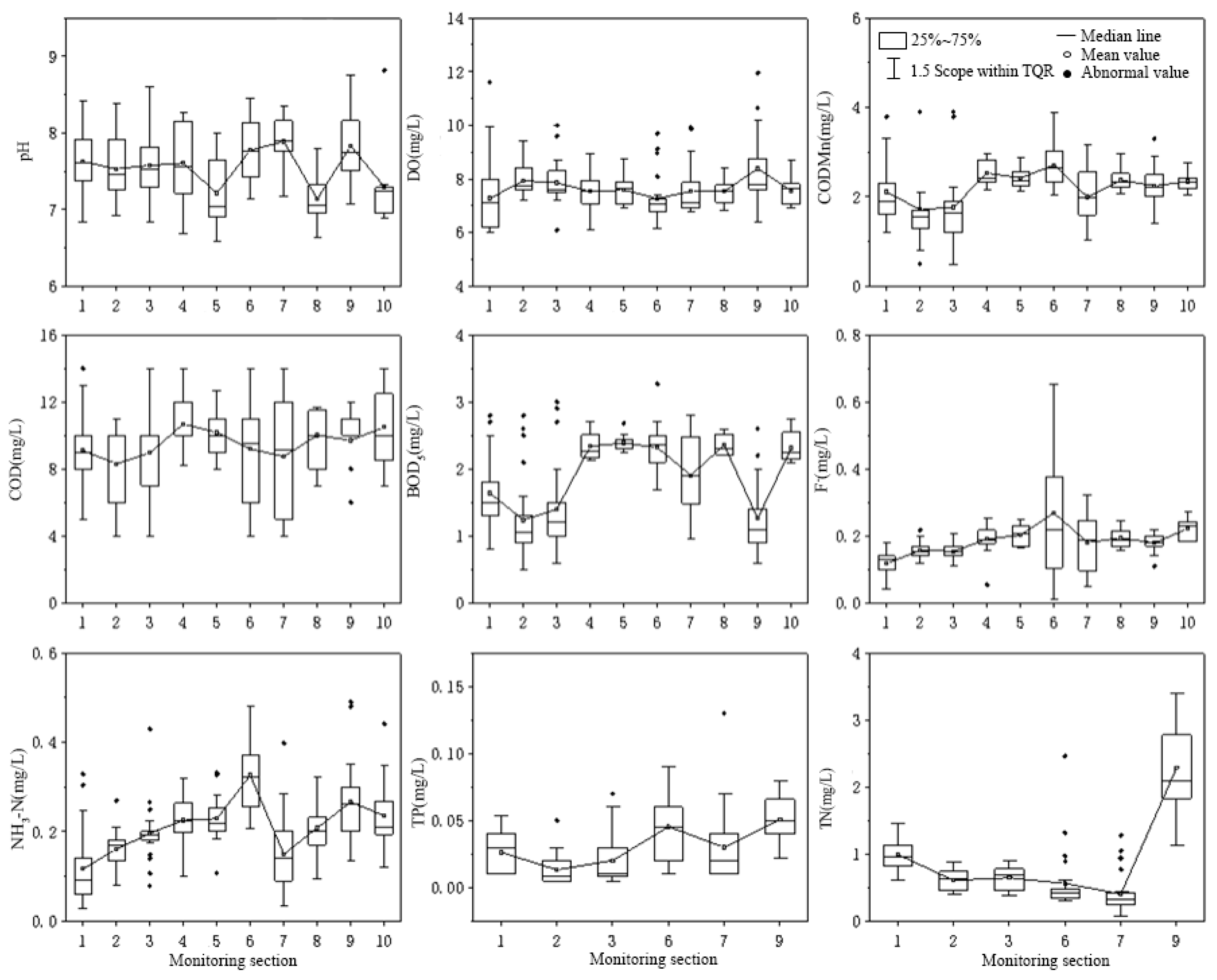
3.1. Analysis of Spatio-Temporal Distribution Characteristics
3.2. Analysis of Correlation and Clusters
3.2.1. Correlation Analysis
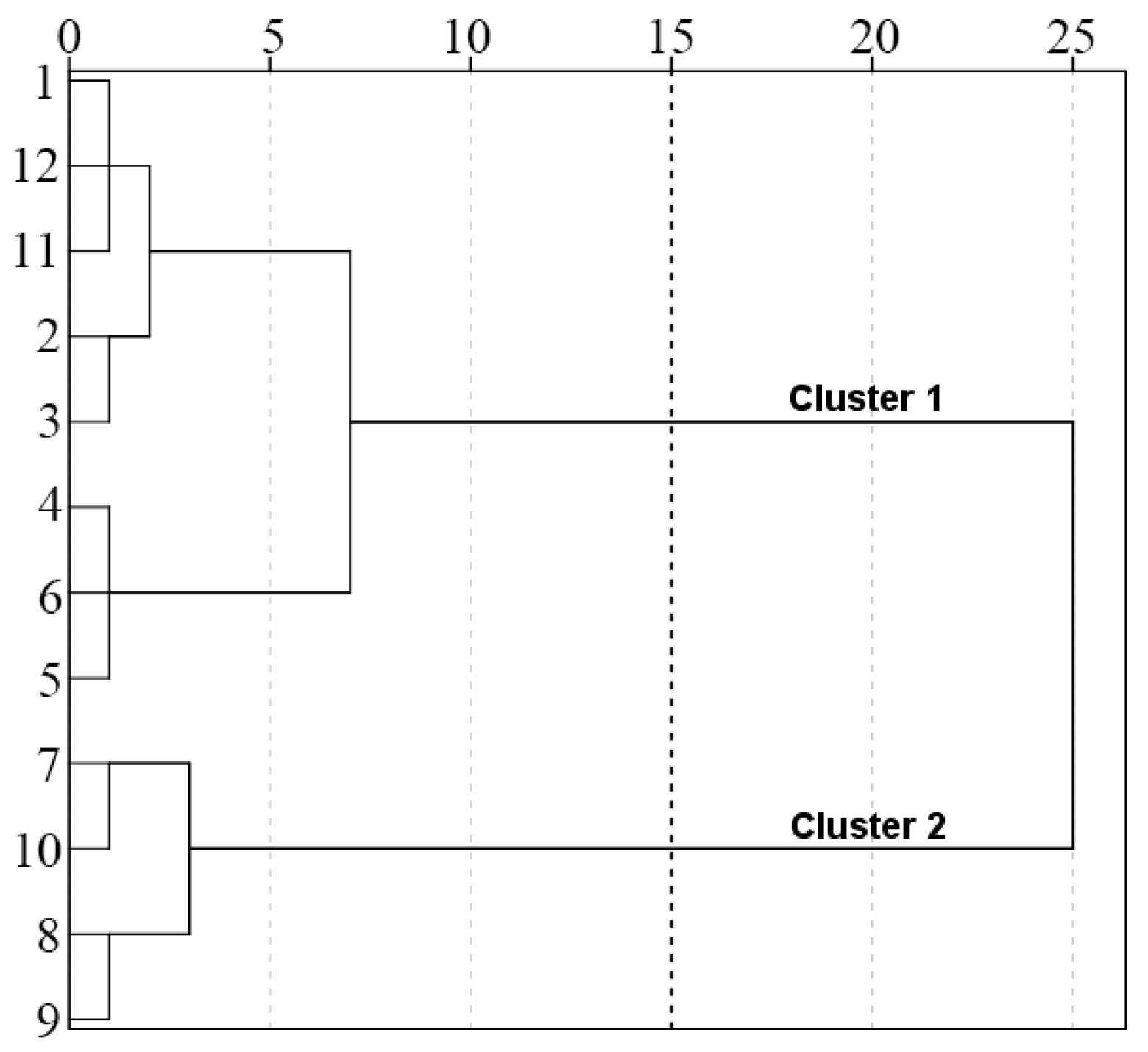
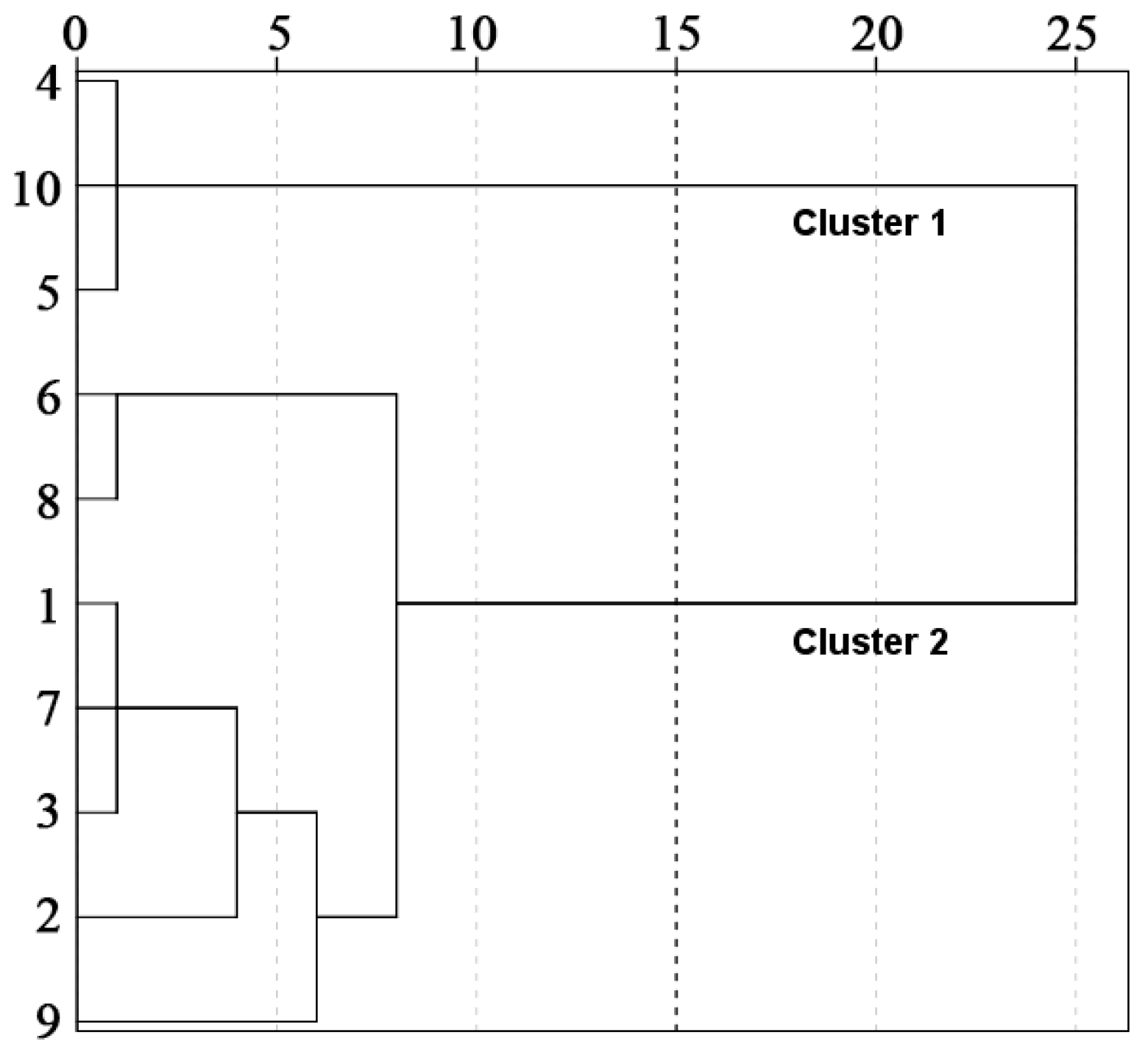
3.2.2. Cluster Analysis
3.3. Analysis of Comprehensive Assessment of Water Quality
4. Discussion
4.1. Driving Factors of Temporal and Spatial Changes in Water Quality Characteristics
4.2. Analysis of Water Quality Characteristic Factors
4.3. Law and Cause of Water Quality Comprehensive Evaluation Index
5. Conclusions
- The physical and chemical parameters of the water body in the water source area have spatio-temporal heterogeneity, showing that the concentrations of CODMn, COD, BOD5 and F− are higher in the flood season than in the non-flood season, while the concentrations of DO, TP and TN are higher in the non-flood season than in the flood season. Spatially, the concentrations of the water’s physical and chemical parameters in the Huangjinxia Reservoir Area are higher than those in the Sanhekou Reservoir Area.
- The evaluation results of the water quality in the water source area of the Hanjiang to Weihe River Water Diversion Project by the comprehensive water quality identification index method show that the comprehensive water quality category of each section meets the water quality requirements of surface water environmental quality class II. In terms of time, the water quality of the water source in the non-flood season is better than that in the flood season. Spatially, the water quality of the branch water source is better than that of the main stream. According to the single-factor water quality index, the main pollution factor is total nitrogen.
- The spatio-temporal differences in water quality in water source areas are mainly controlled by factors such as rainfall, temperature and human activities, and human activities with different intensities will affect the water quality in the watershed to varying degrees.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xiang, X.; Li, Q.; Khan, S.; Khalaf, O.I. Urban Water Resource Management for Sustainable Environment Planning Using Artificial Intelligence Techniques. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2021, 86, 106515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Chen, J.; Liu, G.; Wang, H.; Alatalo, J.M.; Yang, Z.; Mu, E.; Bai, Y. Framework of Basin Eco-Compensation Standard Valuation for Cross-Regional Water Supply—A Case Study in Northern China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 279, 123630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Xu, J.; Yang, F. Scalar Configuration, Power Strategies and Water Governance: Insights from the Politics of the Yangtze-to-Huai Water Transfer Project. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2022, 38, 658–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.G.; Nash, S.; Olbert, A.I. A Review of Water Quality Index Models and Their Use for Assessing Surface Water Quality. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 122, 107218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adimalla, N.; Qian, H. Groundwater Quality Evaluation Using Water Quality Index (Wqi) for Drinking Purposes and Human Health Risk (Hhr) Assessment in an Agricultural Region of Nanganur, South India. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 176, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nong, X.; Shao, D.; Zhong, H.; Liang, J. Evaluation of Water Quality in the South-to-North Water Diversion Project of China Using the Water Quality Index (Wqi) Method. Water Res. 2020, 178, 115781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, G.; Molina, J.L.; Patino-Alonso, M.C.; Castillo, M.D.C.; Vicente-Galindo, M.P.; Galindo-Villardón, M.P. Water Quality Evaluation through a Multivariate Statistical Hj-Biplot Approach. J. Hydrol. 2019, 577, 123993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, C.T.; Giang, N.T.H.; Thao, T.P.; Nui, N.H.; Lam, N.T.; Cong, V.H. Assessment of Cau River Water Quality Assessment Using a Combination of Water Quality and Pollution Indices. J. Water Supply Res. Technol.-Aqua 2020, 69, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimi, S.; Azhdary Moghaddam, M.; Hashemi Monfared, S.A. Prediction of Annual Drinking Water Quality Reduction Based on Groundwater Resource Index Using the Artificial Neural Network and Fuzzy Clustering. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2019, 220, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustaoğlu, F.; Tepe, Y. Water Quality and Sediment Contamination Assessment of Pazarsuyu Stream, Turkey Using Multivariate Statistical Methods and Pollution Indicators. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2019, 7, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalmaijer, E.S.; Nord, C.L.; Astle, D.E. Statistical Power for Cluster Analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2022, 23, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caruso, G.; Gattone, S.A.; Fortuna, F.; Di Battista, T. Cluster Analysis for Mixed Data: An Application to Credit Risk Evaluation. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2021, 73, 100850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Dong, M.; Xu, D.; Liu, Y.; Xu, X. Using a Water Quality Index to Assess the Water Quality of the Upper and Middle Streams of the Luanhe River, Northern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 667, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department of Rural Socio-Economic Investigation, National Bureau of Statistics. Agricultural Statistics of China (1949–2019); China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China. Environmental Quality Standard for Surface Water (GB 3838-2002); China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, R.A. Analysis of Variance with Multiple Factors. In Multivariate Statistics Made Simple: A Practical Approach; Talylor Francis Group: Abingdon, UK, 2018; Volume 51. [Google Scholar]
- Sbert, M.; Havran, V.; Szirmay-Kalos, L. Variance Analysis of Multi-sample and One-sample Multiple Importance Sampling. Comput. Graph. Forum 2019, 35, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Mili, L.; Zhao, J. Probabilistic Power Flow Calculation and Variance Analysis Based on Hierarchical Adaptive Polynomial Chaos-Anova Method. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2019, 34, 3316–3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukate, S.; Wagh, V.; Panaskar, D.; Jacobs, J.A.; Sawant, A. Development of New Integrated Water Quality Index (Iwqi) Model to Evaluate the Drinking Suitability of Water. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 101, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Guo, L.; Deng, Z.; Wang, D.; Liu, L. Assessment of Heavy Metal Pollution and Water Quality Characteristics of the Reservoir Control Reaches in the Middle Han River, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 799, 149472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Li, C.; Zeng, C.; Zhang, F.; Raymond, P.A.; Hur, J. Immobilization of Relic Anthropogenic Dissolved Organic Matter from Alpine Rivers in the Himalayan-Tibetan Plateau in Winter. Water Res. 2019, 160, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Li, L.; Gao, J. Framework for Quantifying Rural Nps Pollution of a Humid Lowland Catchment in Taihu Basin, Eastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 688, 983–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wang, P.; Sheng, H.; Wang, D.; Huang, M.; Cao, C. Sustainability of Riparian Zones for Non-Point Source Pollution Control in Chongming Island: Status, Challenges, and Perspectives. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 244, 118804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhang, P.; Xiao, Y.C.; Hou, X.S.; Shen, Z.Y. Construction of a Cellular Automata-Based Model for Rainfall-Runoff and Nps Pollution Simulation in an Urban Catchment. J. Hydrol. 2019, 568, 929–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Hou, K.; Wu, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, J. A Conceptual Framework for Establishing the Index System of Ecological Environment Evaluation–a Case Study of the Upper Hanjiang River, China. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 107, 105568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Liang, R.; Li, K.; Wang, Y.; Pu, X. Study on the Coupling Model of Urbanization and Water Environment with Basin as a Unit: A Study on the Hanjiang Basin in China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 131, 108130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, Q. Transformation and Source Identification of N in the Upper Reaches of the Han River Basin, China: Evaluated by a Stable Isotope Approach. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Ge, H.-G.; Zhao, H.; Liu, Z.; Si, J.; Tang, B. Pollution Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in the Sediments of Upstream Hanjiang River, China. Earth Sci. Inform. 2021, 14, 655–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Fuenzalida, R.A.; Molins-Legua, C.; Calabria, D.; Mirasoli, M.; Guardigli, M.; Roda, A.; Campíns-Falcó, P. Sustainable and Green Persulfate-Based Chemiluminescent Method for on-Site Estimation of Chemical Oxygen Demand in Waters. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1223, 340196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Thomson, N. Estimation of the Maximum Consumption of Permanganate by Aquifer Solids Using a Modified Chemical Oxygen Demand Test. J. Environ. Eng. Asce 2008, 134, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Shen, J.; Feng, J.; Sun, Z.; Sun, T.; Liu, D.; Xi, M.; Li, R.; Wang, X. The Estimation of Chemical Oxygen Demand of Erhai Lake Basin and Its Links with Dom Fluorescent Components Using Machine Learning. Water 2021, 13, 3629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Yang, L.; Liu, E. A Holistic Framework of Water Quality Evaluation Using Water Quality Index (Wqi) in the Yihe River (China). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 80937–80951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lele, D.; Kebing, C.; Zhangjun, L.; Boyang, W.; Zekun, C.; Shaokun, H. Spatiotemporal Variation Evaluation of Water Quality in Middle and Lower Han River, China. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhen, G.; Chi, J.; Liu, X.; Lu, Y.; Wang, X.; Yao, R.; Chen, J.; Zhang, W. Nutrient Loads Flowing into Coastal Waters from the Main Rivers of China (2006–2012). Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, S.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Ding, X.; Zhou, J. A Comprehensive Method for Water Environment Assessment Considering Trends of Water Quality. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2021, 2021, 5548113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Hu, Z.; Liu, X.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, W. Spatio-Temporal Variation of Total Nitrogen and Ammonia Nitrogen in the Water Source of the Middle Route of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project. Water 2020, 12, 2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filazzola, A.; Mahdiyan, O.; Shuvo, A.; Ewins, C.; Moslenko, L.; Sadid, T.; Blagrave, K.; Imrit, M.A.; Gray, D.K.; Quinlan, R.; et al. A Database of Chlorophyll and Water Chemistry in Freshwater Lakes. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Xue, B.; Wang, G.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q. Deep Learning-Based Water Quality Retrieval in an Impounded Lake Using Landsat 8 Imagery: An Application in Dongping Lake. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Cai, H.; Zhang, X.; Fu, Y. Water Quality in Relation to Land Use in the Junshan Lake Watershed and Water Quality Predictions. Water Supply 2021, 21, 3602–3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Ma, T.; Shen, S.; Du, Y.; Wu, X.; Liu, W. Distribution Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Poor-Quality Native Groundwater in River Percolation System in the Lower Reaches of the Hanjiang Rive. Earth Sci. Front. 2021, 28, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Li, Z.; Zhang, R.; Pan, J.; Liu, Y. Does Water Diversion Project Deteriorate the Water Quality of Reservoir and Downstream? A Case-Study in Danjiangkou Reservoir. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 24, e01235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.j.; Dong, F.; Huang, A.P.; Lian, Q.Y.; Peng, W.Q. The Migration and Transformation of Nitrogen in the Danjiangkou Reservoir and Upper Stream: A Review. Water 2021, 13, 2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, Y.M.; Liu, W.w.; Zhao, E.; Li, R.; Muñoz-Carpena, R. Water Quality Variability in the Middle and Down Streams of Han River under the Influence of the Middle Route of South-North Water Diversion Project, China. J. Hydrol. 2019, 569, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Strokal, M.; van Vliet, M.T.H.; Fu, X.; Wang, M.; Ma, L.; Kroeze, C. In-Stream Surface Water Quality in China: A Spatially-Explicit Modelling Approach for Nutrients. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 334, 130208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Liu, D.; Guo, S.; Xiong, L.; Liu, P.; Yin, J.; Tian, J.; Deng, L.; Zhang, J. Impacts of Water Resources Allocation on Water Environmental Capacity under Climate Change. Water 2021, 13, 1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Ma, R.; Ma, T.; Sun, Z. Modeling the Effects of Water Diversion Projects on Surface Water and Groundwater Interactions in the Central Yangtze River Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 830, 154606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W. Impacts of Human Activities in the Hanjiang River Basin, China. J. Coast. Res. 2019, 96, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| pH | DO | CODMn | COD | BOD5 | F− | NH3-N | TP | TN | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spatial | 6.22 ** | 2.28 * | 4.79 ** | 1.60 | 16.63 ** | 6.20 ** | 15.26 ** | 12.36 ** | 95.99 ** |
| Time | 0.80 | 1.78 * | 2.58 ** | 2.96 ** | 2.79 ** | 1.46 | 0.61 | 1.35 | 2.74 ** |
| Index | pH | DO | CODMN | COD | BOD5 | F− | NH3-N | TP | TN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 1 | ||||||||
| DO | −0.196 | 1 | |||||||
| CODMN | −0.175 | −0.271 | 1 | ||||||
| COD | −0.104 | −0.054 | 0.451 ** | 1 | |||||
| BOD5 | 0.193 | −0.288 * | 0.723 ** | 0.650 ** | 1 | ||||
| F− | −0.223 | −0.337 * | 0.073 | −0.274 | −0.176 | 1 | |||
| NH3-N | −0.075 | −0.375 ** | −0.261 | −0.077 | −0.274 | −0.153 | 1 | ||
| TP | −0.001 | −0.228 | 0.060 | −0.098 | −0.053 | −0.255 | 0.278 | 1 | |
| TN | 0.076 | −0.244 | −0.193 | 0.224 | 0.024 | −0.134 | 0.372 ** | 0.238 | 1 |
| Time | Single-Factor Water Quality Labeling Index | Iwq | Category | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DO | CODMN | COD | BOD5 | F− | NH3-N | TP | TN | |||
| T1 | 1.80 | 2.00 | 1.60 | 1.60 | 1.20 | 2.20 | 2.10 | 3.91 | 2.010 | Ⅰ |
| T2 | 2.10 | 2.30 | 1.70 | 1.70 | 1.20 | 2.20 | 2.10 | 3.61 | 2.110 | Ⅱ |
| Spatial | Single-Factor Water Quality Labeling Index | Iwq | Category | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DO | CODMN | COD | BOD5 | F− | NH3-N | TP | TN | |||
| S-1 | 2.10 | 2.10 | 1.60 | 1.50 | 1.10 | 1.80 | 2.10 | 4.01 | 2.010 | Ⅰ |
| S-2 | 1.70 | 1.90 | 1.60 | 1.40 | 1.20 | 2.00 | 1.70 | 3.21 | 1.810 | Ⅰ |
| S-3 | 1.80 | 1.90 | 1.60 | 1.50 | 1.20 | 2.10 | 2.00 | 3.31 | 1.910 | Ⅰ |
| S-6 | 2.20 | 2.40 | 1.60 | 1.80 | 1.30 | 2.50 | 2.30 | 3.11 | 2.210 | Ⅱ |
| S-7 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 1.60 | 1.60 | 1.20 | 2.00 | 2.10 | 2.70 | 1.900 | Ⅰ |
| S-8 | 2.00 | 2.20 | 1.60 | 1.80 | 1.20 | 2.20 | / | / | 1.800 | Ⅰ |
| S-9 | 1.40 | 2.10 | 1.60 | 1.40 | 1.20 | 2.30 | 2.40 | 6.14 | 2.310 | Ⅱ |
| S1 | 1.90 | 2.10 | 1.60 | 1.60 | 1.20 | 2.20 | / | / | 1.800 | Ⅰ |
| S-4 | 2.00 | 2.30 | 1.70 | 1.80 | 1.20 | 2.20 | / | / | 1.900 | Ⅰ |
| S-5 | 1.90 | 2.20 | 1.70 | 1.80 | 1.20 | 2.20 | / | / | 1.800 | Ⅰ |
| S-10 | 2.00 | 2.40 | 1.70 | 1.80 | 1.20 | 2.20 | / | / | 1.900 | Ⅰ |
| S2 | 2.00 | 2.30 | 1.70 | 1.80 | 1.20 | 2.20 | / | / | 1.900 | Ⅰ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, W.; Chen, H.; Xu, S.; Liu, T.; Wang, H.; Li, G.; Wang, J. Water Environment Characteristics and Water Quality Assessment of Water Source of Diversion System of Project from Hanjiang to Weihe River. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 2890. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20042890
Wu W, Chen H, Xu S, Liu T, Wang H, Li G, Wang J. Water Environment Characteristics and Water Quality Assessment of Water Source of Diversion System of Project from Hanjiang to Weihe River. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(4):2890. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20042890
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Wei, Hang Chen, Sheng Xu, Ting Liu, Hao Wang, Gaoqing Li, and Jiawei Wang. 2023. "Water Environment Characteristics and Water Quality Assessment of Water Source of Diversion System of Project from Hanjiang to Weihe River" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 4: 2890. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20042890
APA StyleWu, W., Chen, H., Xu, S., Liu, T., Wang, H., Li, G., & Wang, J. (2023). Water Environment Characteristics and Water Quality Assessment of Water Source of Diversion System of Project from Hanjiang to Weihe River. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(4), 2890. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20042890





