Lasered Graphene Microheaters Modified with Phase-Change Composites: New Approach to Smart Patch Drug Delivery
Abstract
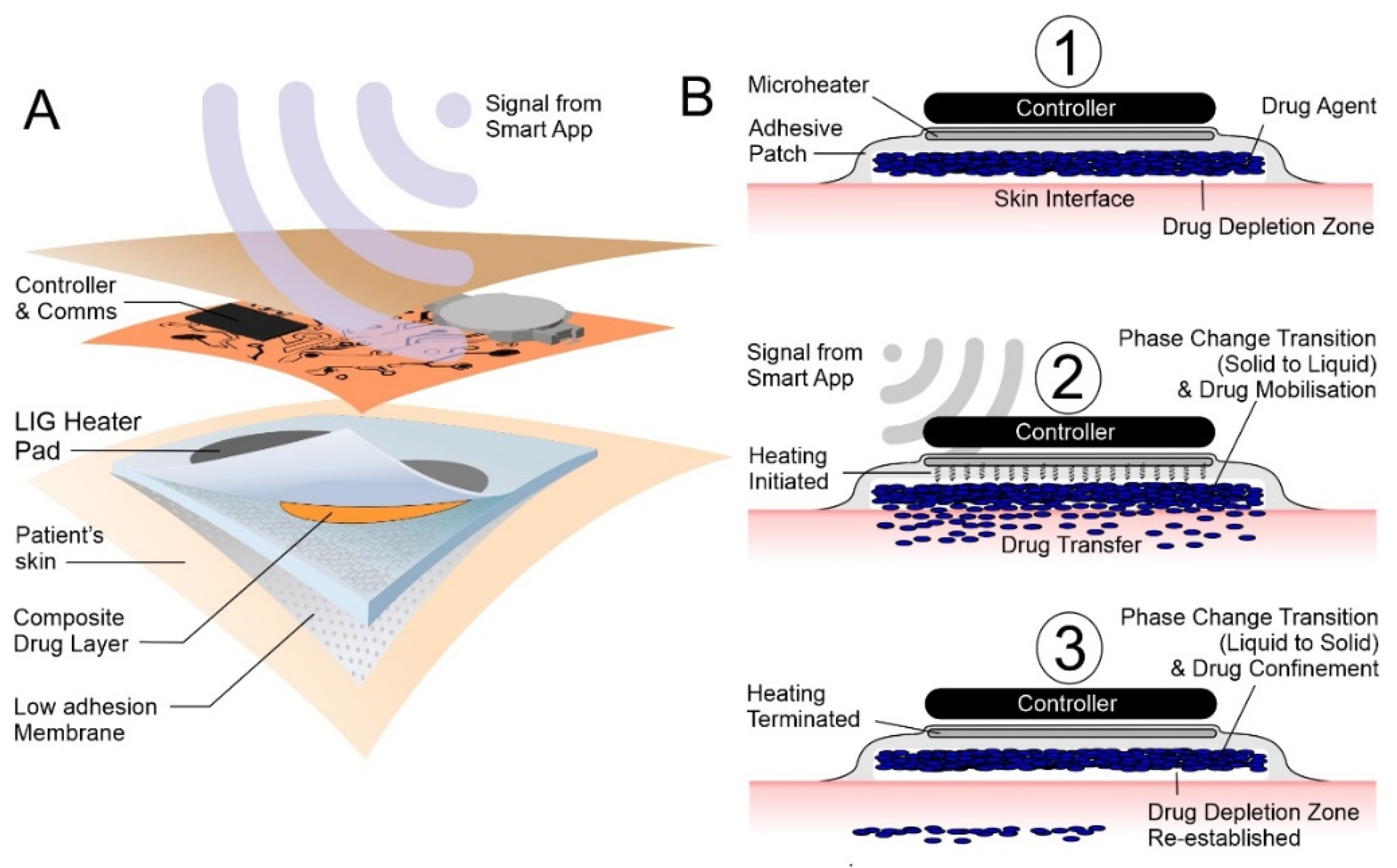
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
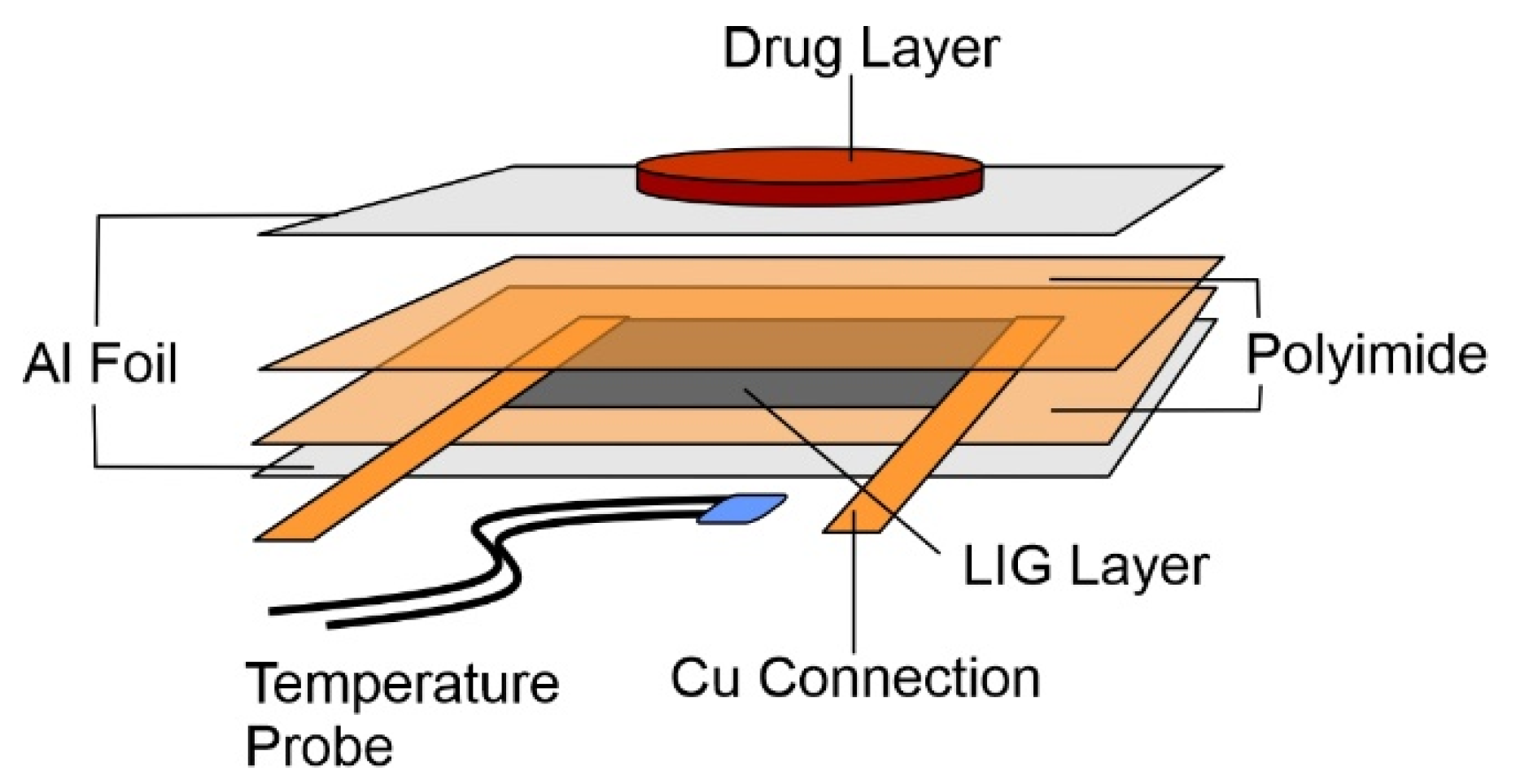
2.1. Lasered Graphene Heater Fabrication
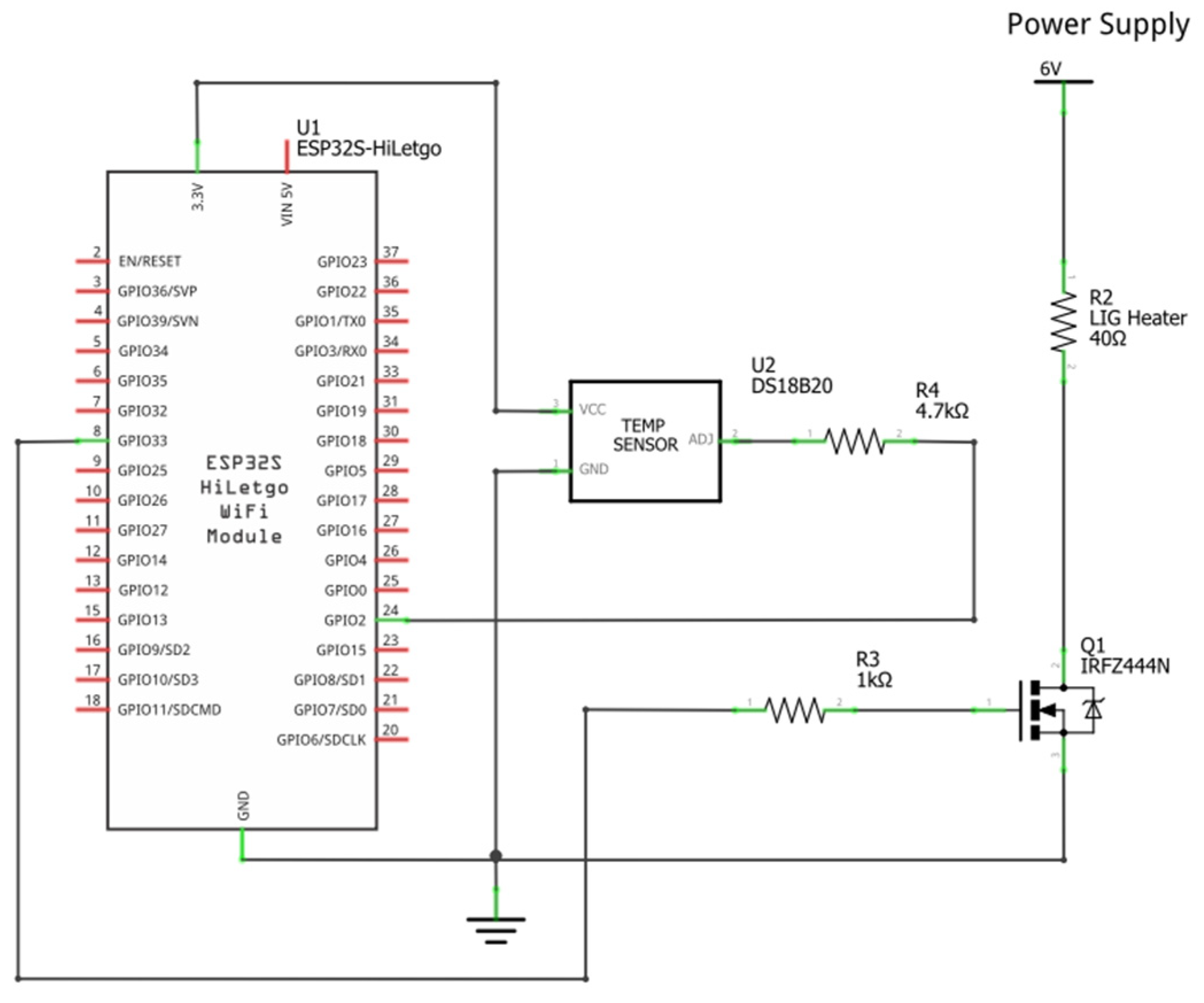
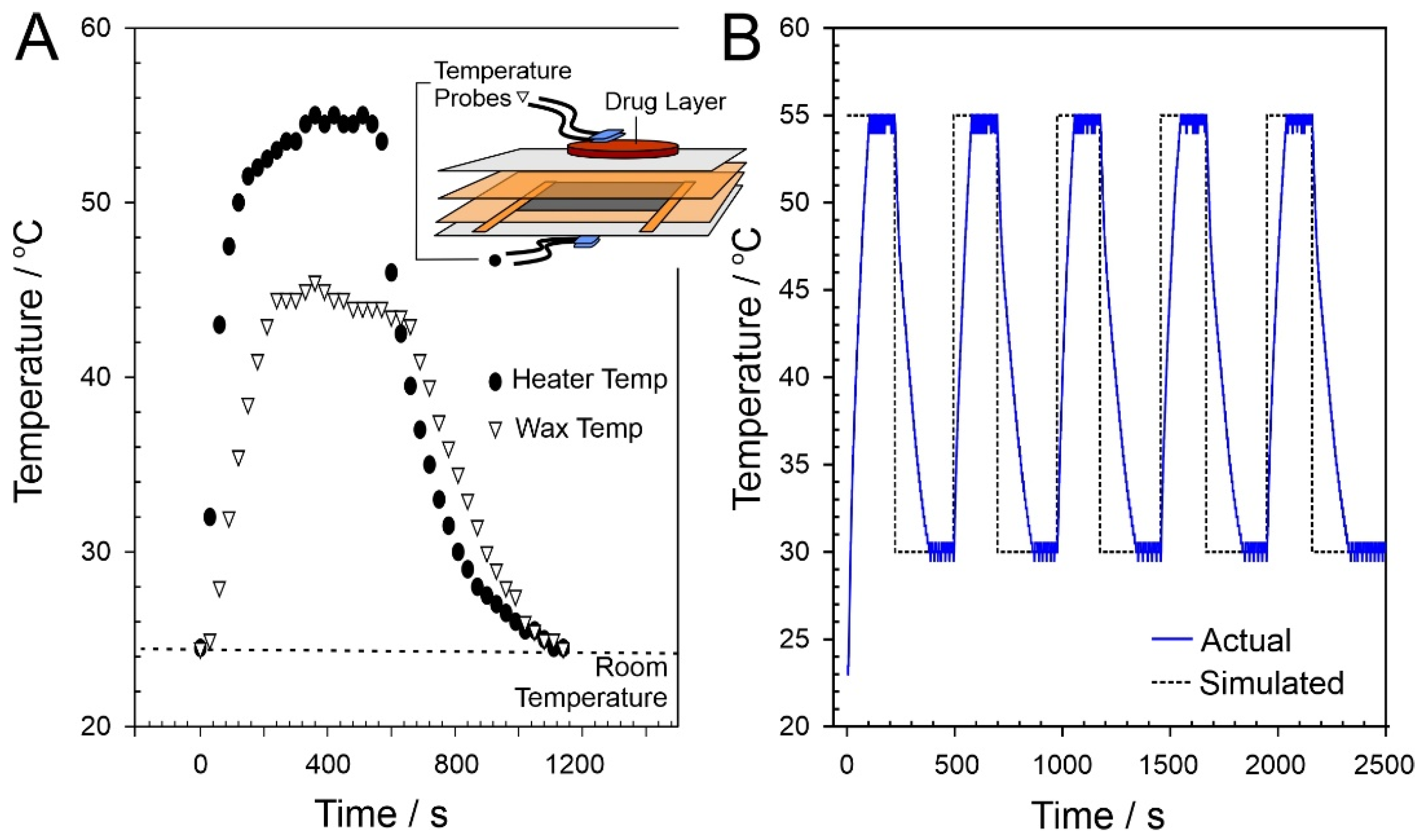
2.2. Heater Control
2.3. Phase-Change Material—Drug Composite Films
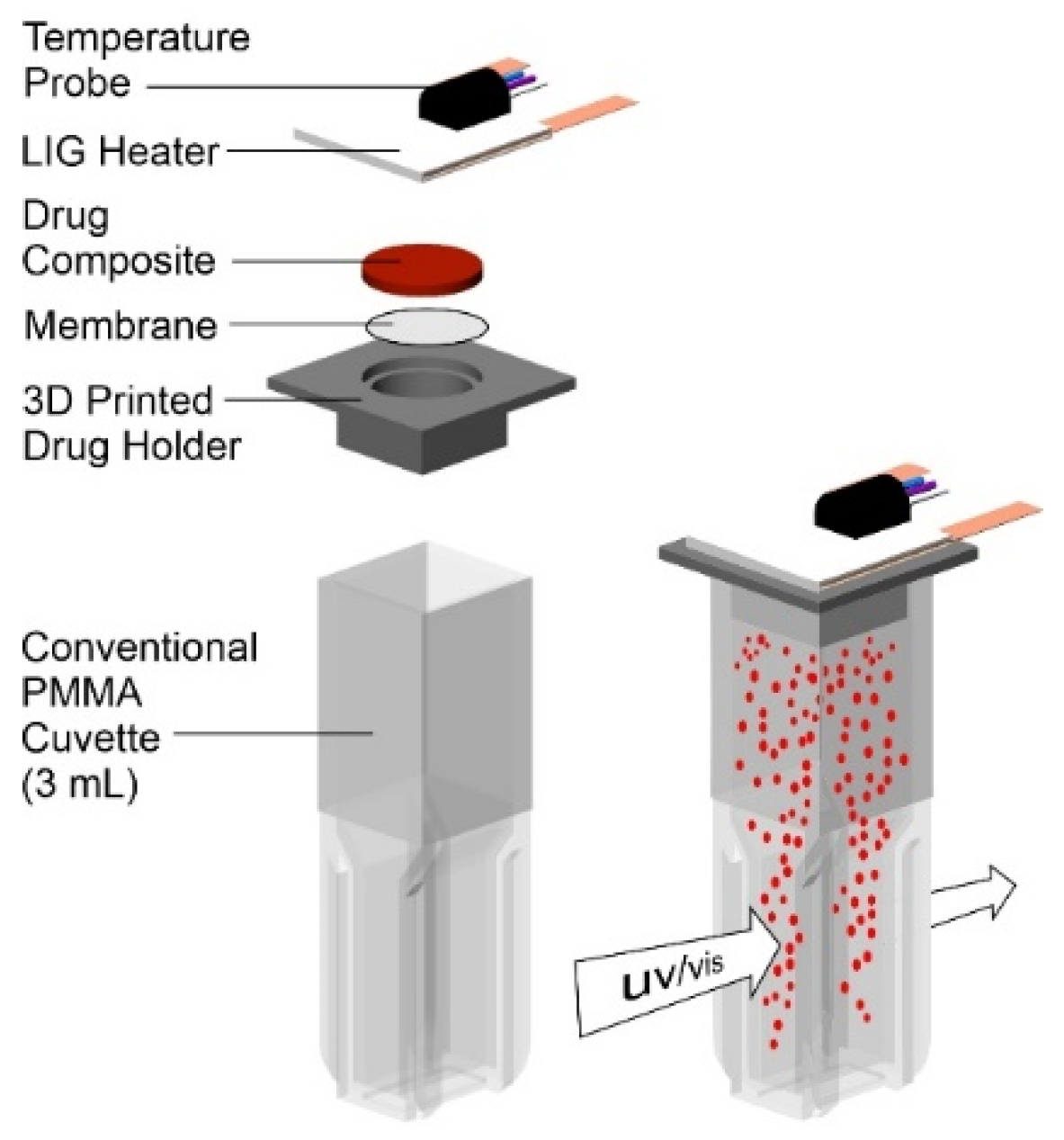
2.4. Drug Release Studies
3. Results
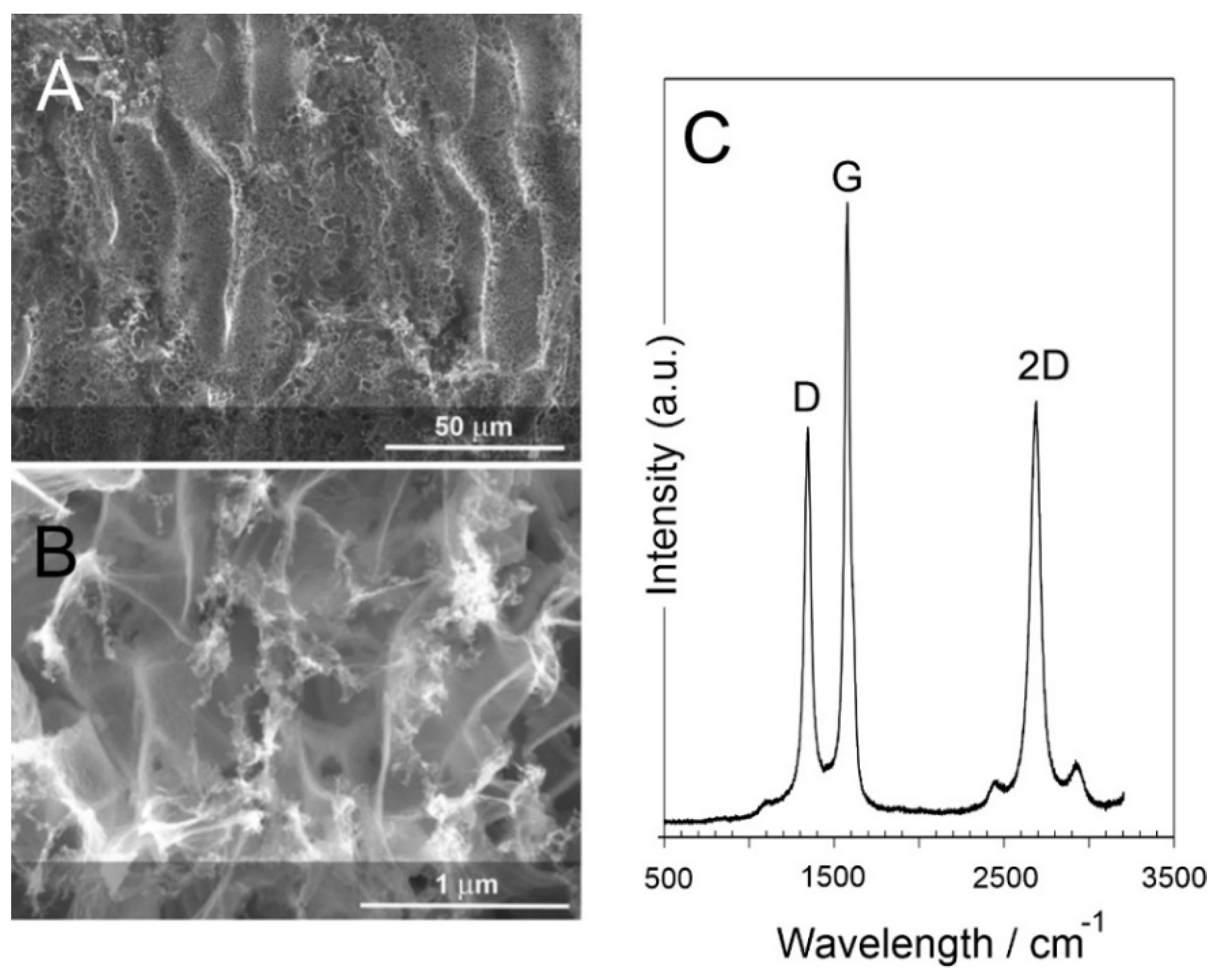
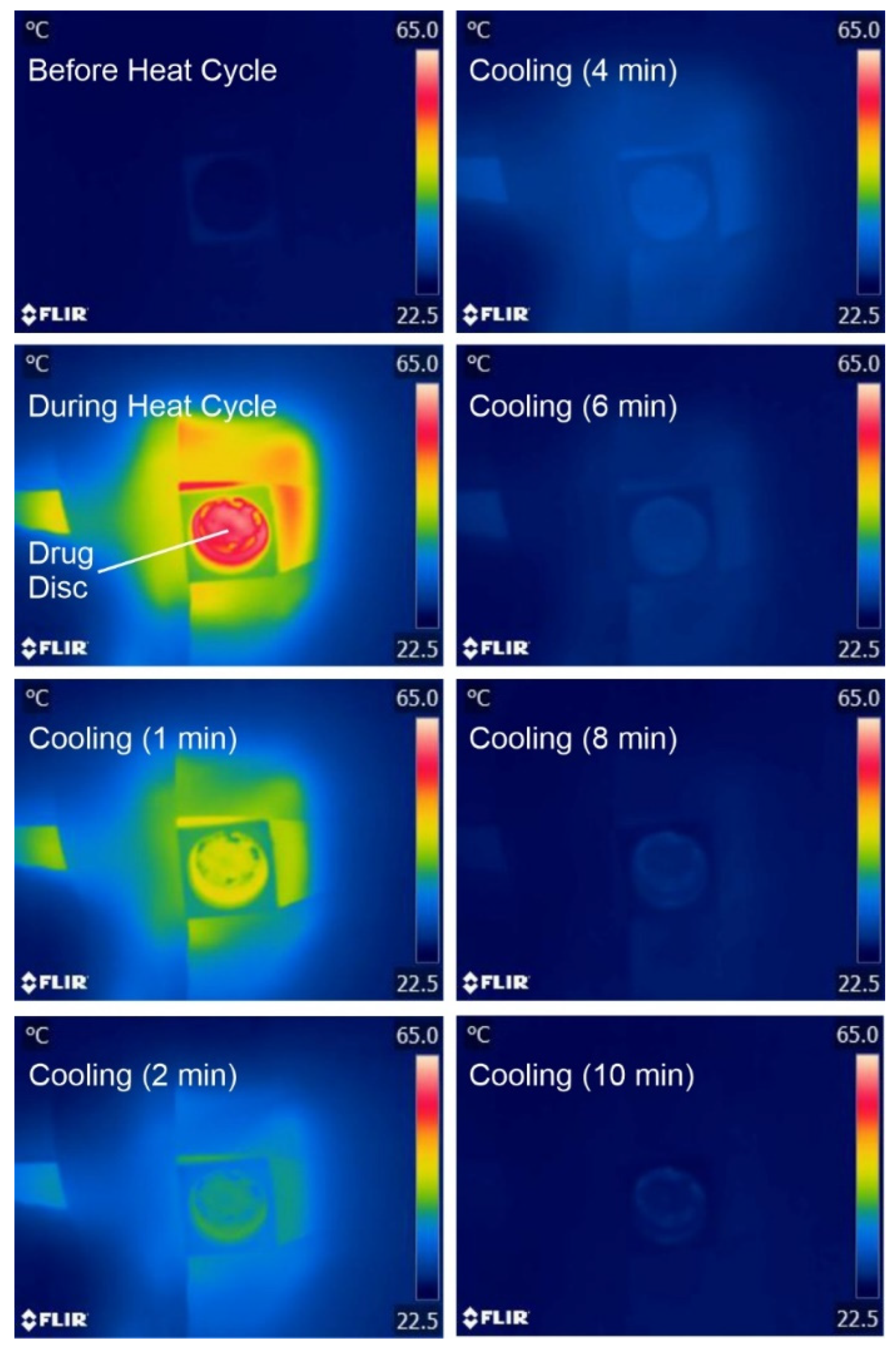
3.1. Laser-Induced Graphene (LIG) Heater Characterisation
3.2. Release Characteristics
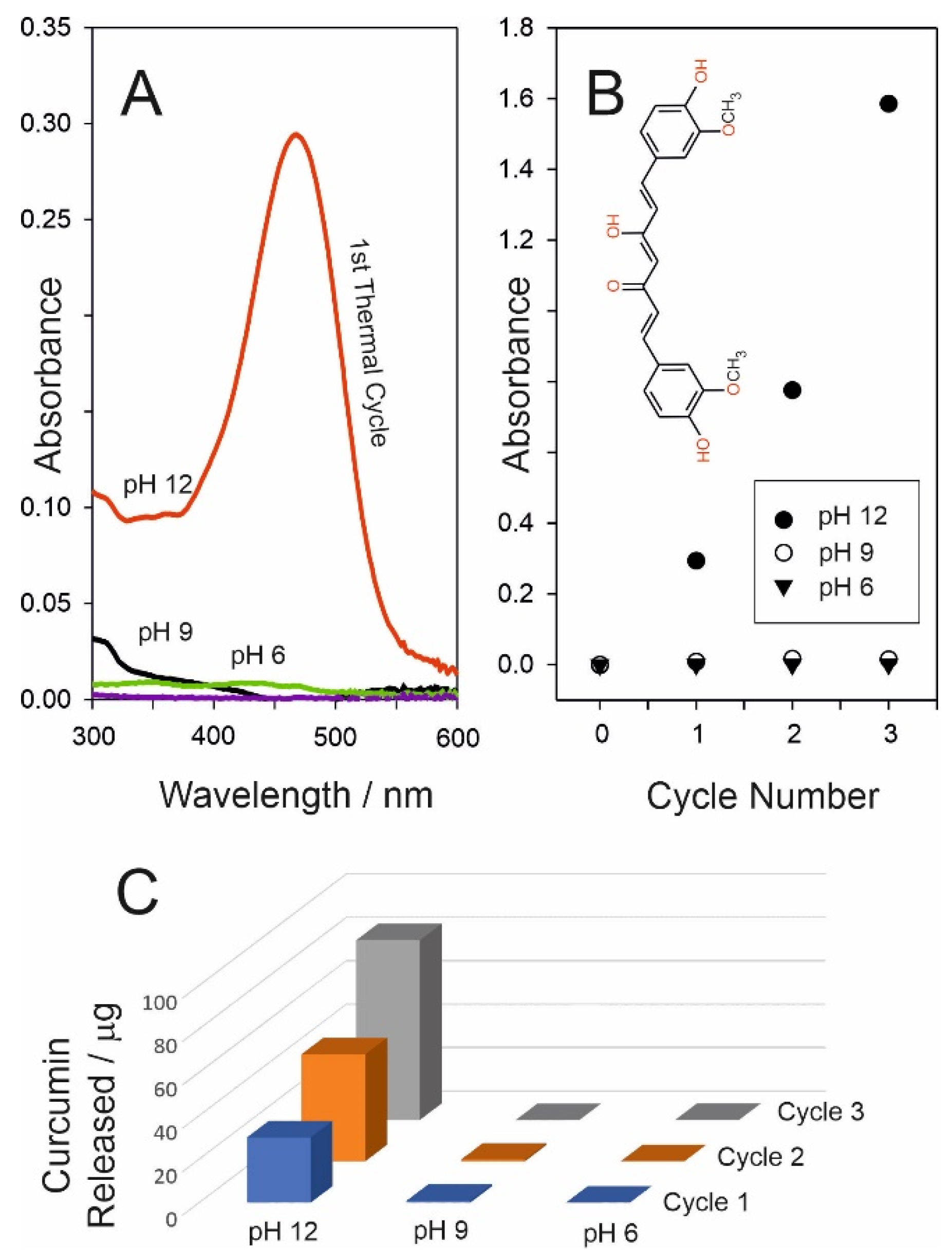
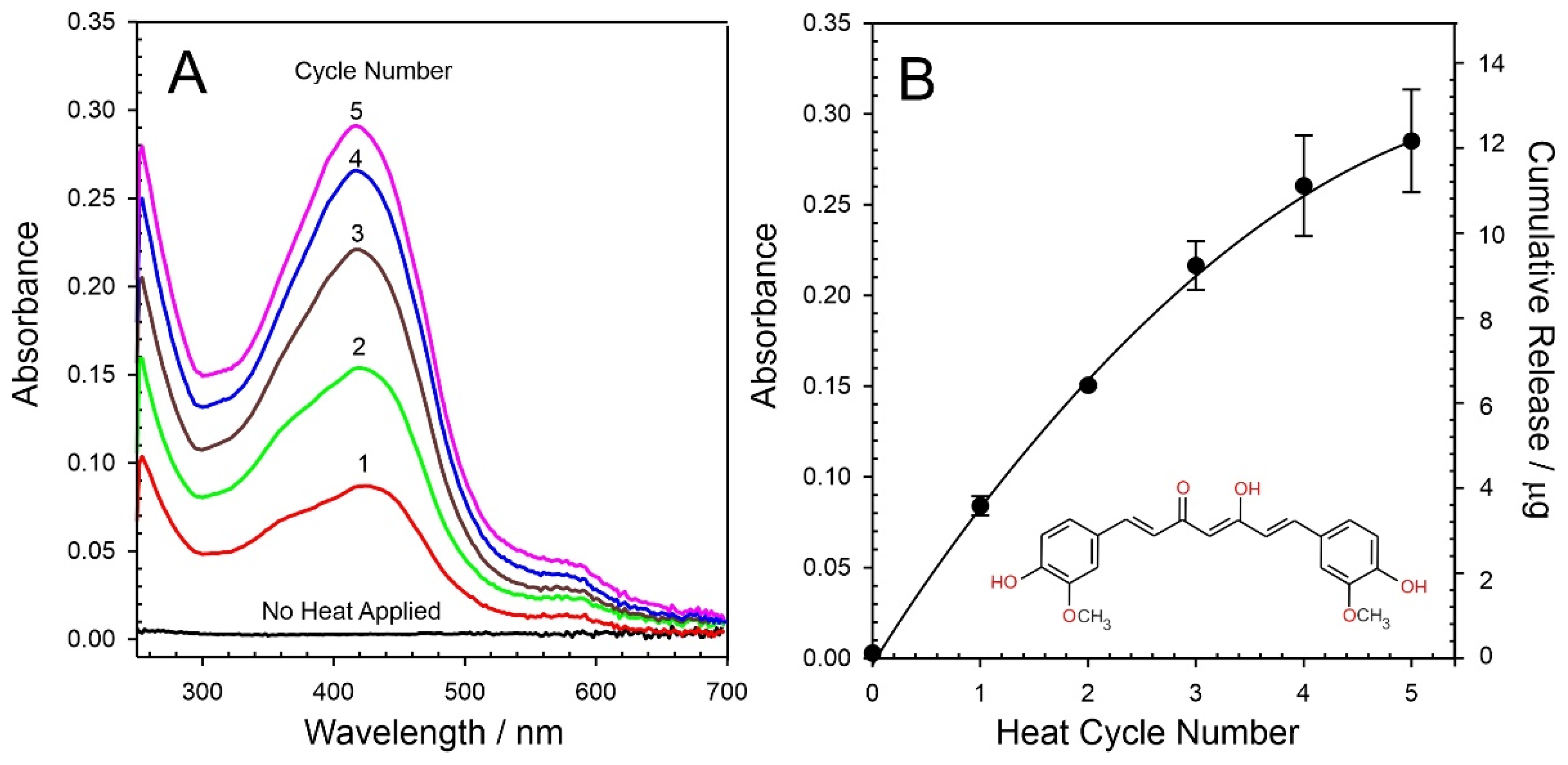
3.3. Curcumin Delivery
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alkilani, A.Z.; Nasereddin, J.; Hamed, R.; Nimrawi, S.; Hussein, G.; Abo-Zour, H.; Donnelly, R.F. Beneath the Skin: A Review of Current Trends and Future Prospects of Transdermal Drug Delivery Systems. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbagh, F.; Kim, B.S. Recent advances in polymeric transdermal drug delivery systems. J. Control. Release 2022, 341, 132–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avcil, M.; Çelik, A. Microneedles in Drug Delivery: Progress and Challenges. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handschin, J.; Hitsman, B.; Blazekovic, S.; Veluz-Wilkins, A.; Wileyto, E.P.; Leone, F.T.; Ashare, R.L.; Schnoll, R.A. Factors associated with adherence to transdermal nicotine patches within a smoking cessation effectiveness trial. J. Smok. Cessat. 2018, 13, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.H.; Thomas, S.; Raney, S.G.; Ghosh, P.; Hammell, D.C.; El-Kamary, S.S.; Chen, W.H.; Billington, M.M.; Hassan, H.E.; Stinchcomb, A.L. In vitro-in vivo correlations for nicotine transdermal delivery systems evaluated by both in vitro skin permeation (IVPT) and in vivo serum pharmacokinetics under the influence of transient heat application. J. Control. Release 2018, 270, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertonazzi, A.; Nelson, B.; Salvador, J.; Umland, E. The smallest available estradiol transdermal patch: A new treatment option for the prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Womens Health 2015, 11, 815–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padula, C.; Pescina, S.; Nicoli, S.; Santi, P. Generic patches containing fentanyl: In vitro equivalence and abuse deterrent evaluation according to EMA and FDA guidelines. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 537, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, J.S.; Lin, J.; Ogawa, S.; Yuan, C.; O’Brien, T.; Le, B.H.C.; Bothwell, A.M.; Moon, H.; Hadjiat, Y.; Ganapathi, A. Transdermal buprenorphine and fentanyl patches in cancer pain: A network systematic review. J. Pain Res. 2017, 10, 1963–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malaiya, M.K.; Jain, A.; Pooja, H.; Jain, A.; Jain, D. Controlled delivery of rivastigmine using transdermal patch for effective management of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 45, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, T.; Tolosa, E.; Badea, L.; Asgharnejad, M.; Grieger, F.; Markowitz, M.; Nondonfaz, X.; Bauer, L.; Timmermann, L. An observational study of rotigotine transdermal patch and other currently prescribed therapies in patients with Parkinson’s disease. J. Neural Transm. 2018, 125, 953–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drago, S.; Imboden, R.; Schlatter, P.; Buylaert, M.; Krahenbuhl, S.; Drewe, J. Pharmacokinetics of transdermal etofenamate and diclofenac in healthy volunteers. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2017, 121, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.G.; Lei, X.F.; Di Ren, B.; Lv, S.Y.; Zhang, J.L. Diclofenac transdermal patch versus the sustained release tablet: A randomized clinical trial in rheumatoid arthritic patients. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2017, 16, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kim, H.U.; Roh, Y.H.; Shim, M.S.; Bonga, K.W. Microfluidic fabrication of fatty alcohol-based microparticles for NIR light-triggered drug release. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 80, 778–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Wu, D.; Wang, X. Temperature and pH dual-stimuli-responsive phase-change microcapsules for multipurpose applications in smart drug delivery. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 583, 470–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConville, A.; Atchison, J.; Roddy, A.; Davis, J. A wireless smart patch for the controlled repetitive transdermal administration of therapeutic agents. Sens. Actuators B. Chem. 2019, 294, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Yang, N.; Dai, H.; Huang, H.; Song, X.; Zhang, Q.; Dong, X. Recent advances in phase change material based nanoplatforms for cancer therapy. Nanoscale Adv. 2021, 3, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, R.; James, D.K.; Tour, J.M. Laser-Induced Graphene. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 1609–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, P.; Guo, X. Laser-Induced Graphene Based Flexible Electronic Devices. Biosensors 2022, 12, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Fei, Q.; Page, M.; Zhao, G.; Ling, Y.; Chen, D.; Yan, Z. Laser-Induced Graphene for Bioelectronics and Soft Actuators. Nano Res. 2021, 14, 3033–3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Peng, Z.; Liu, Y.; Ruiz-Zepeda, F.; Ye, R.; Samuel, E.L.G.; Yacaman, M.J.; Yakobson, B.I.; Tour, J.M. Laser-Induced Porous Graphene Films from Commercial Polymers. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wathoni, N.; Motoyama, K.; Higashi, T.; Okajima, M.; Kaneko, T.; Arima, H. Enhancement of curcumin wound healing ability by complexation with 2-hydroxypropyl--cyclodextrin in sacran hydrogel film. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 98, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Nan, K.; Li, L.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, H. In vivo evaluation of curcumin nanoformulation loaded methoxy poly(ethylene glycol)-graft-chitosan composite film for wound healing application. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 88, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, S.; Zhang, B.; Li, M.; Diao, K.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Xu, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, H. In situ injectable nano-composite hydrogel composed of curcumin, N,O-carboxymethyl chitosan and oxidized alginate for wound healing application. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 437, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krausz, A.E.; Adler, B.L.; Cabral, V.; Navati, M.; Doerner, J.; Charafeddine, R.A.; Chandra, D.; Liang, H.; Gunther, L.; Clendaniel, A.; et al. Curcumin-encapsulated nanoparticles as innovative antimicrobial and wound healing agent. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2015, 11, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postolovic, K.; Ljujic, B.; Kovacevic, M.M.; Đorđevic, S.; Nikolic, S.; Zivanovic, S.; Stanic, Z. Optimization, characterization, and evaluation of carrageenan/alginate/poloxamer/curcumin hydrogel film as a functional wound dressing material. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 31, 103528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, C.; Sahoo, S.K. Curcumin and its topical formulations for wound healing applications. Drug Discov. Today 2017, 22, 1582–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Zhu, J.; Rajabpour, S.; Joshi, K.; Kowalik, M.; Croom, B.; Schwab, Y.; Zhang, L.; Bumgardner, C.; Brown, K.R.; et al. Graphene reinforced carbon fibers. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz4191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenburg, F.; Ionescu, E.; Nicoloso, N.; Riedel, R. High-temperature Raman spectroscopy of nano-crystalline carbon in silicon oxycarbide. Materials 2018, 11, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benson, J.; Xu, Q.; Wang, P.; Shen, Y.; Sun, L.; Wang, T.; Li, M.; Papakonstantinou, P. Tuning the catalytic activity of graphene nanosheets for oxygen reduction reaction via size and thickness reduction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 19726–19736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.M.; Jin, S.-P.; Doh, E.J.; Lee, D.H.; Chung, J.H. Regional Variation of Human Skin Surface Temperature. Ann. Dermatol. 2019, 31, 349–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zebib, B.; Mouloungui, Z.; Noirot, V. Stabilization of Curcumin by Complexation with Divalent Cations in Glycerol/Water System. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2010, 2010, 292760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Matrix/Polymer | Material Type | Release 24 h/% | Curcumin Released | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Complexation with 2-hydroxypropyl--cyclodextrin in sacran hydrogel film | Film | 50 | 110 µg/cm2 | [21] |
| Curcumin nano formulation loaded methoxy poly(ethylene glycol)–graft–chitosan composite film | Film | 8.4 | 74 µg/cm2 | [22] |
| N,O-carboxymethyl chitosan and oxidised alginate | Hydrogel | 11.8 | 295 µg | [23] |
| Tetramethyl orthosilicate (TMOS) | Nanoparticles | 81.5 | 8.15 µg/mg np | [24] |
| Carrageenan/alginate/poloxamer/curcumin hydrogel film | Hydrogel | 88 | 623 µg/cm2 | [25] |
| Paraffin wax–AP-PEG composite | Film | n/a | 4.5 µg/cm2 | This work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gilpin, V.; Surandhiran, D.; Scott, C.; Devine, A.; Cundell, J.H.; Gill, C.I.R.; Pourshahidi, L.K.; Davis, J. Lasered Graphene Microheaters Modified with Phase-Change Composites: New Approach to Smart Patch Drug Delivery. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13071132
Gilpin V, Surandhiran D, Scott C, Devine A, Cundell JH, Gill CIR, Pourshahidi LK, Davis J. Lasered Graphene Microheaters Modified with Phase-Change Composites: New Approach to Smart Patch Drug Delivery. Micromachines. 2022; 13(7):1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13071132
Chicago/Turabian StyleGilpin, Victoria, Deetchaya Surandhiran, Cameron Scott, Amy Devine, Jill H. Cundell, Chris I. R. Gill, L. Kirsty Pourshahidi, and James Davis. 2022. "Lasered Graphene Microheaters Modified with Phase-Change Composites: New Approach to Smart Patch Drug Delivery" Micromachines 13, no. 7: 1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13071132
APA StyleGilpin, V., Surandhiran, D., Scott, C., Devine, A., Cundell, J. H., Gill, C. I. R., Pourshahidi, L. K., & Davis, J. (2022). Lasered Graphene Microheaters Modified with Phase-Change Composites: New Approach to Smart Patch Drug Delivery. Micromachines, 13(7), 1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13071132







