Abstract
The review of modern methodological approaches to assessing the sustainable development of an industrial enterprise revealed the absence of generally accepted integral tools and the connection sustainable development trends with financial flows. To fill this gap this, taking into account the principle of balanced development economic, environmental and social components aimed. The purpose of the study is the development of a financial flow management model for the sustainable development of an industrial enterprise (using the example of a large Russian petrochemical enterprise). To achieve the goal of the purpose, the following methods implemented systematic approach, analysis and synthesis, comparative analysis, analysis of dynamics series, correlation analysis, regression analysis, solving the linear programming problem. As a result of the study, we came to conclusion about the shift of the enterprise’s focus on environmental issues; the growth of the integral indicator of sustainable development of an industrial enterprise; the negative impact of credit resources on the aggregate indicator. The novelty of the study lies in the development of a new methodological solution, which is the basis of the financial management model for the sustainable development of the enterprise: it is adequate to the level of microeconomic system; covers three ways of measuring sustainable development and the possibility of choosing the best quality; allows to implement a proactive approach to managing financial flows with the principles of sustainable development of the enterprise (existing approaches either represent only a set of indicators or addressed the diagnosis of a specific subsystem, either do not consider the relationship between financial flows and the aggregated indicator of sustainable development of the enterprise).
1. Introduction
Modern industrial systems have adapted development strategies to the challenges of primary importance: sustainable development, ESG-transformation (Environmental, Social, Governance), green economy, circular economy, low-carbon economy (decarbonized economy). The structural transformation of industry, the implementation of import substitution policy and the urgent need for breakthrough technologies in the Russian economy have opened up new opportunities and capacity building in the field of sustainable development and related aspects. These trends provided an impetus to the development of industry at the macro-, meso- and microlevels of management through innovation (process, institutional, technological), digitalization and cognitive technologies (artificial intelligence, robotics, «digital twin»).
In 2021, Cambridge University Press published a comprehensive report on the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals in the world (Sachs et al. 2021). According to the research results, Finland (score—85.9), Sweden (85.6) and Denmark (84.9) topped the rating. The top ten also includes Germany, Belgium, Austria, Norway, France, Slovenia, and Estonia. The Russian Federation took only 46th place (score—73.8) and achieved two (Goal 1 «No poverty» and Goal 4 «Quality education») of the 17 Sustainable Development Goals. The weakest positions were recorded for such goals as Goal 14 «Life below water», Goal 15 «Life on land» and Goal 16 «Peace, justice and strong institutions».
In the context of industrial development, Goals 9 «Industry, innovation and infrastructure» and 12 «Responsible consumption and production» are particularly important. In these areas, the Russian economy still shows significant problems («The Decade of Action for the Sustainable Development Goals: Sustainable Development Report 2021»), which actualizes the search for promising tools to manage the sustainable development of industry and industrial enterprises.
At the same time, an integral element the improvement of industrial systems are financial resources involved in the process of transition enterprises to sustainable development through investment and innovation projects. As a result, the financial flows management plays a fundamental role in ensuring the sustainable development of industry.
At the global level in 2021, the Russian economy significantly lags behind a number of countries (including China, Algeria, Uzbekistan, Rep. Korea, Austria, Czechia, Japan, United States, etc.) in terms of «Gross fixed capital formation» (% of GDP). Therefore, in Russia the figure was 20%, in the United States—21%, in Japan—25%, Uzbekistan—35%, China—42% (The World Bank Website n.d.). The presence of unrealized potential of investment in the Russian industry is the second argument in favor the relevance of the study.
Summarizing the highlighted emphases, we formulated the goal and objectives of the study. The goal is to develop a model of financial flow management for sustainable development of an industrial enterprise. In turn, the sustainable development of an industrial enterprise is assessed by diagnosing the economic (Iecon), social (Isoc) and environmental factor (Iecol). Achievement of the purpose assumes solving a number of tasks, in particular, to propose an improved methodology for assessing sustainable development at the micro level, to test and verify it on the example of a large petrochemical enterprise. This study is characterized by theoretical and practical significance, which is due to the contribution the development of sustainable development methodology at the level of an industrial enterprise, the identification of new (on the example of a single enterprise) patterns of financial flows influence on sustainable development and the possibility of applying the methodology in general practice.
The reliability of the presented research is due to the study of an extensive array of scientific papers devoted to the study of the problems of sustainable development of industrial enterprises and the financial flows management as a part of achieving sustainable development goals; processing of a reliable array of data on the activities of an industrial enterprise, placed in an open source.
The problems of sustainable development are deeply entrenched in the scientific literature and are widely represented in various aspects of research. The basic provisions of the concept in a number of works of scientists from different countries—Russian Federation, Belgium, Canada, Egypt, Italy, Norway, Sweden, Taiwan, Japan, United Kingdom and other countries (Waas et al. 2011; Holden et al. 2014; Shinkevich et al. 2015; Chen 2017; Dyrdonova and Lin’kova 2019; Esposito and Dicorato 2020; Shinkevich 2020; Schulte et al. 2020; Linnerud et al. 2021; Samarina et al. 2021a, 2021b) are covered. The approaches of scientists at understanding the essence of sustainable development, the need and inevitability of awareness of the benefits and prospects of the concept in the context of concern for future generations, the need for cooperation of science, business, government and society against the background of achieving the Sustainable Development Goals aimed.
The focus of our attention is the methodological profile of the concept of sustainable development, the transformation of industrial enterprises, taking into account the reduction of the negative impact on the environment while balancing the interests of economic, environmental and social. Of course, the methodological aspects of sustainable development are also widely represented in the world scientific literature.
- At the level of macroeconomic systems the category of «economic complexity» is highlighted and evaluated in relation to the environmental impact (Tauseef Hassan et al. 2023); proposed «integrated resource efficiency index», IRE-index, the multiple regression method was used (Koh et al. 2016); the Advanced Human Development Index, determined by the geometric mean method of the four feathers—«Life», «Education», «Income» and «Environment» (Karnitis et al. 2021); the regional sustainable development index (RSDI), calculated also by the geometric mean formula and including 6 indicators—economic growth rates, open unemployment, poverty rate, human development index, Gini index and environmental quality index (Rahma et al. 2019); systematized a wide range of sustainable development assessment techniques, including WDI (world development indicators), Eurostat sustainable development indicators, HDI (human development index), EF (ecological footprint), EPI (environmental performance index), SSI (sustainable society index), EISD (energy indicators for sustainable development), which is reflected in the study (Andriuškevičius et al. 2022); proposed weighting method for energy sustainability analysis of renewable energy production (Tsai 2010).
- At the level of municipalities, 13 private indicators of sustainable development (poverty ratio, physician density, mortality rate, under −5, +15 literacy rate, % total enrolment rate in basic education and others) have been assessed (Salem et al. 2020); other scientists applied the grey entropy method and formed the sustainable urban development system, which covers not 3 classic elements (economic, social and environmental), but 5 (society, the economy, the environment, resources, and technology) (Gong et al. 2019); systematized indicators of sustainable urban development by blocks: environment, transport, economic development, land use, demography, construction, health care, civic engagement (Hassan and Kotval-K 2019). (Awan et al. 2022; Liu et al. 2022b) revealed a U-shaped (nonlinear) relationship between urbanization and the environment (i.e., CO2 emissions).
- At the mesolevel (industry level) an indicator of production reliability at the level of industries was developed, based on the weighting of normalized indicators of economic, social and environmental reliability (Lubnina et al. 2016); an extensive set of key performance indicators (48 social indicators, 30 environmental indicators, and 39 economic indicators) presented in the context of three factors of sustainable industrial development (Contini and Peruzzini 2022); an aggregate indicator of sustainable industrial development based on discriminant analysis and principal component method (Shinkevich et al. 2022) was proposed, etc. Among our own research, we noted the methodology to assess the sustainable development of innovative mesosystems based on a composite indicator ISDI: calculated as a geometric mean of three factors (environmental, economic and social), includes indicators of environmental innovation, the share of enterprises with high pollution levels, the quality index of patent applications, return on assets, the number of researchers in the industry, the index of recycled and subsequently used water in the mesosystem, the share of catchment (Shinkevich et al. 2021b).
- At the microeconomic level, the issue under study through the SAM4SIP method (Self-Assessment Method of capabilities for Sustainability Implementation in the Product innovation process) of assessing an organization’s capacity to implement sustainability (Schulte and Hallstedt 2018) is revealed, the author’s solution is based on empirical research; the formation of Sustainable Development Map of the enterprise (Patalas-Maliszewska and Łosyk 2020); the development of an indicator the maturity of organization in the sustainable development management Leading Sustainability (LeadSUS), which is calculated as the average of six Relevant Domains—General Requirements/Aspects, Resource Management, Sustainable Products and Services, Social Responsibility, Implementation and Operation, Management/Leadership and Strategy (Negulescu et al. 2022), etc.
At the same time, we consider it is important to clarify that there is also an emphasis on environmental issues of sustainable development economic systems of different levels, which acts as a question of discussion, since sustainable development is not a significant prevalence of environmental issues, but rather the balanced development of all three components—economic, environmental and social.
Since the subject of this study is financial flows, as a part of analytical review, we studied the scientific works devoted to investment issues in the framework of sustainable development. Some papers deal mainly with the economic aspects of the relationship between an enterprise’s investment strategy and its sustainable development (Zhuravlyov et al. 2019). Other studies focus on financial risks and NPV assessment in the context of enterprise sustainability (Tobisova et al. 2022). The third area of research is investments in renewable energy sources, the consequence of which is not only the achievement of enterprise sustainability goals, but also the formation of a positive brand image (Liczmańska-Kopcewicz et al. 2020). The authors also evaluated the relationship between investments in renewable energy sources and the creation of value in a sustainable enterprise, understood as the realization of environmental, economic and social goals. Scientists from China and Pakistan address the issues of investment risk associated with the transition to a new energy supply technology—biogas production technology (at the household level) (Ahmad et al. 2023), declare the need to adopt an appropriate economic strategy (Ali et al. 2022). An important thesis (at the macroeconomic systems level) is formulated in studies (Azam et al. 2023; Khan et al. 2022; Liu et al. 2022a), which note that investment in fixed assets and energy consumption are positively associated with environmental quality and environmental sustainability. And environmental sustainability is one of the principles of sustainable development of the economic system. Other scholars have evaluated investments in environmental measures in relation to financial performance, which generally contributes to the sustainable development of the macroeconomic system (Yang et al. 2020). Another area is R&D investments for sustainable development, “green investments” (Hou et al. 2021). The topic of green investments also revealed in a study (Lyeonov et al. 2019), where the authors evaluate pairwise relationships between green investments and indicators such as GDP per capita, emissions of harmful substances, the share of renewable energy use. The impact of green lending and borrowing, green bonds, and green investment on green development and sustainable industrial development has been assessed in (Shen and Zhang 2022; Osipov et al. 2022).
Summing up the study, we note the high interest of the scientific community in the study of methodological aspects of sustainable development of enterprises and the financing of the relevant areas of activity. This is due to the lack of a standardized approach to the assessment of sustainable development due to the specifics, size and scope of enterprises. At the same time, the layer of research devoted to the problems of sustainable development (macro-, meso- and microeconomic systems) cannot solve all the problems of methodological nature, which opens up limitless opportunities to improve the existing approaches.
The literature review allows to state the prevalence of scientific approaches in the form of systematization of sustainable development indicators; lack of a clear and universal methodology of integral assessment of sustainable development of the enterprise (which takes into account social, environmental and economic indicators); coverage of investment policy and sustainable development goals of the enterprise, but with emphasis on the economic component or taking into account investment in a specific project; fragmented assessment of the relationship between financial flows and sustainable development of the enterprise. Our study at filling these methodological gaps aimed.
2. Materials and Methods
The development of methodological toolkit for the formation of a financial flows model for sustainable development of an industrial enterprise based on the collection, processing and analysis of data on the functioning of one of the largest petrochemical enterprises in Europe—PJSC «Nizhnekamskneftekhim». The company holds a leading position in the production of synthetic rubbers, plastics and ethylene in the Russian Federation. It plays a strategically important role in the development of petrochemical and related industries in the country and in the world, in particular, providing a high share of added value. The array of annual data on the functioning of the enterprise covers a 5-year period—2016–2020, the sources of which were the annual reports and consolidated financial statements of the enterprise (The Smart-lab Website n.d.). The choice of this enterprise as an object of research is due to the following factors:
- significant strategic role in the development of Russian industry;
- high level of environmental pollution due to the scale and specifics of production;
- a key place in our scientific research (Shinkevich et al. 2021a);
Taking into account the significant impact of the enterprise’s production on the environment, the need becomes obvious:
- research on the regularity of the sustainable development the industrial system of PJSC «Nizhnekamskneftekhim»;
- identifying the relationship between financial investments in the industrial system modernization and the level of its sustainable development;
- modeling and optimization of financial flows to ensure the sustainable development of an industrial enterprise.
- In this regard, the study covers several phases.
- Development of a universal methodological approach to assessing the sustainable development of an industrial enterprise. At this stage, we have formulated a system of three-way diagnostics of sustainable development. The calculation foundation develops the mesolevel approach for the assessment of the sustainable development of innovative mesosystems based on a comprehensive indicator ISDI (Shinkevich et al. 2021b) proposed earlier. However, in this case we focus on the microeconomic system and propose to expand the list of indicators accounted for the economic, environmental and social aspects. For this we propose to use the geometric average formula to estimate the economic factor of the sustainable development of an industrial enterprise (Iecon), the social factor (Isoc) and the environmental factor (Iecol):where Vi—variable (sub-indices); VRoE—returns on energy, ruble per ruble; VMP—material productivity, ruble per ruble; VRoS—return on sales (coefficient); VSP—social policy and charity expenses per 1 employee, million rubles per person; VRGW—rate of growth of tariff rates/wages, %; VSTR—average staff turnover rate, % (due to its negative nature, the indicator is calculated as the inverse of the average staff turnover rate); VREP—the volume of reduction of emissions of pollutants into the atmospheric air, thousand tons; VRWD—the volume of reduction of wastewater discharges in volume, million cubic meters.
The higher the value of each three factors, the more sustainable development demonstrated by the industrial system.
Based on these three factors, evaluating the integral indicator of sustainable development the enterprise SDIE in three ways proposed. In all three cases, the positive dynamics corresponds to the growth of the SDIE indicator.
Method 1. The first method based on a similar approach—the calculation of the average geometric. Such a methodical approach is conditioned by the harmonious management of three components—economic, environmental and social. In this case, the indicator of sustainable development of the industrial enterprise calculated by the Formula (2):
Method 2. In the second case, the method based on the weighting of three factors. The weight determined depending on the importance of economic, social and environmental factors. Calculation the index of sustainable development of an industrial enterprise to carry out by the formula proposed (3):
where Ij—is the value of the j-th sustainable development factor calculated according to Formula (1); wj—is the weighting factor of the j-th sustainable development factor. In our study, we determined the weighting coefficients based on the degree of problematic achievement of sustainable development goals in the Russian economy. Achievement of Goal 9 “Industry, innovation and infrastructure” in Russia is less than 75%, therefore, this direction of development is more in need of industry concentration (Sachs et al. 2021). The achievement of Goal 12 «Responsible consumption and production» was more than 75%, which made the environmental factor the second most important for the Russian industry (Sachs et al. 2021). The third place in the ranking system of the sustainable development factors of the enterprise assigned to the social factor. Thus, the weight coefficients of the sustainable development factors of the industrial enterprise calculated according to the Formula (4):
Then the sum of weight coefficients (denominator of Formula (3)) will be equal to 2.
Thus, method 2 consists in the following: indicators of sustainable development of an enterprise (Iecon, Isoc, Iecol), are calculated, then the three indicators are ranked, after which the weighting coefficient is determined. Thus, the methodology is based on the inclusion of indicators of a given enterprise.
Method 3. The third alternative method of assessing the sustainable development of an industrial enterprise is also lying on weighing, but based on rationing the factors of sustainable development using the standard normal distribution function according to the Formula (5):
Then the indicator of sustainable development of the industrial enterprise will calculated by the Formula (6):
- 2.
- Verification of the proposed methodological approaches by assessing the closeness of the relationship between the calculated values of SDIE (according to the three methods) and the volume of reduction of pollutant emissions VREP and wastewater discharges VRWD. Based on the evaluation results of the pair correlation coefficients, the choice in favor of the best the three methods made. The emphasis on environmental indicators is due to the positive dynamics of the development the indicators, in this regard, this factor chosen as the basis for the verification the methodology.
- 3.
- The construction of an economic-mathematical model of the sustainable development dependence indicator from the industrial enterprise on financial flows:
- acquisition of fixed assets, million rubles (investment activities) (VIA);
- attraction of long-term credits and loans, million rubles (VLTF);
- attraction of short-term credits and loans, million rubles (VSTF).
- 4.
- The emphasis on investments is due to the following: they are aimed at modernization of fixed assets (modern development programs of industries and industrial enterprises), corporate information systems, which contributes to increasing industrial safety, improving working conditions (lean production, 5S), improving the quality of products, saving resources. All of this is a sign of sustainable development.
- 5.
- Determination the optimal values of financial flows that determine, among other things, the sustainable development of the microeconomic system.
The standard features of Microsoft Excel, in particular, correlation, regression, solution search used as a means of data processing, modeling and optimization. Due to free access to this program, there are no restrictions on the application of the proposed methodology or its improvement by other researchers.
As a result of the content analysis, we revealed, firstly, the prevalence of methods for macro- and mesoeconomical systems; secondly, for the microeconomical level, the prevalence of works aimed at systematization the indicators, and not at the formation of a generalized evaluation criterion. In our study, we proposed and tested a new integral indicator, which is based on a set of private indicators of economic, environmental and social development of the enterprise.
All symbols are presented in Appendix A.
3. Results
3.1. Stage 1: Analysis of Individual Aspects of Sustainable Development of an Industrial Enterprise
3.1.1. Diagnostics of the Main Indicators of Economic, Ecological and Social Development of PJSC «Nizhnekamskneftekhim»
Before we proceed to the analysis of the company’s activities, we note that by the end of 2020, in the rating of investment efficiency it was among the top 10 Russian companies (The National Credit Ratings Website n.d.). The company with capital expenditures of $744 million and an overall score of 60.6 was ranked 7th. The company is the leader in the Russian petrochemical industry in terms of investment efficiency.
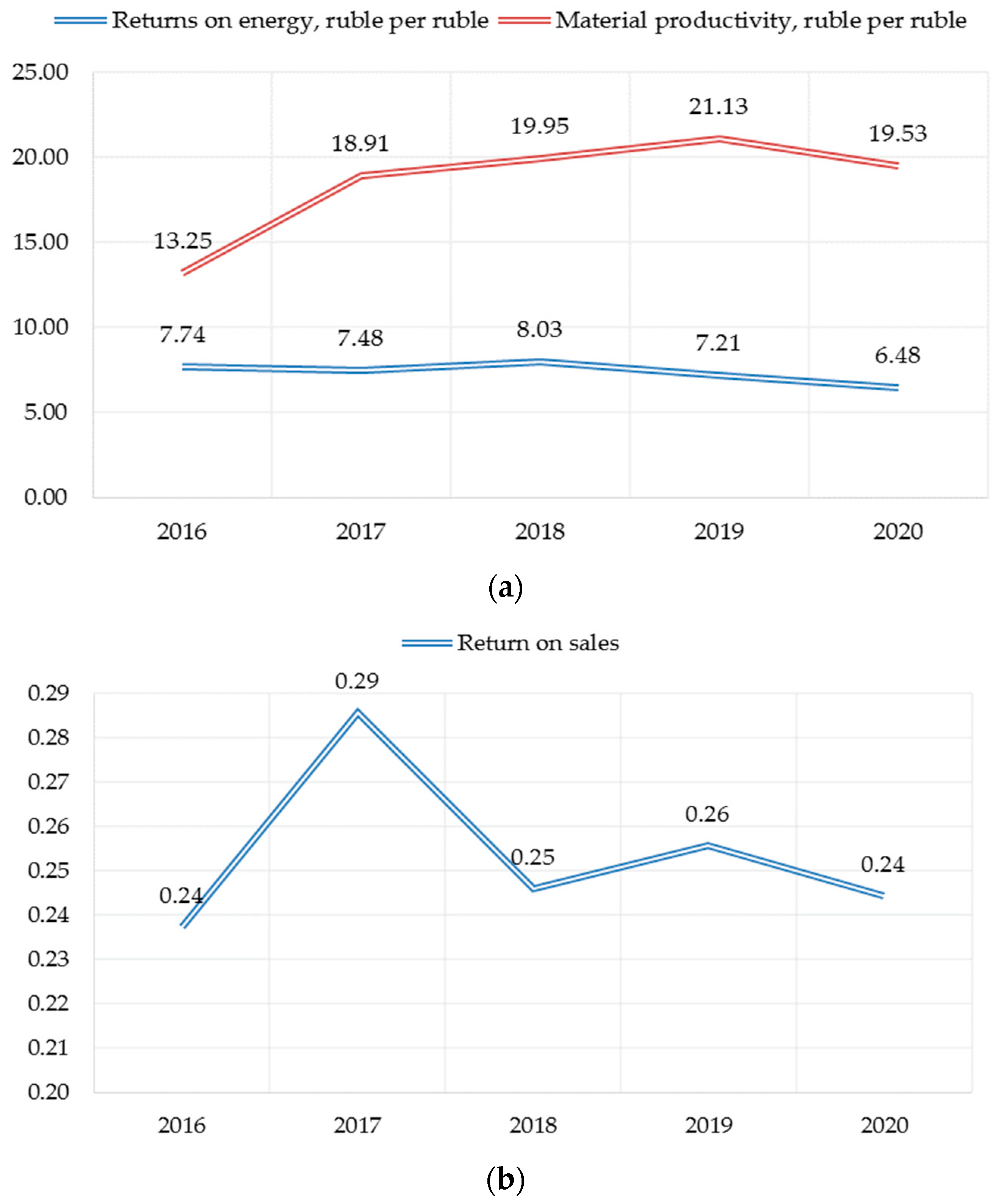
In order to assess the impact of enterprise investments on sustainable development indicators, the trends of changes in the sub-indices of sustainable development factors identified. From the perspective of economic development, there is a slight decrease in the efficiency of energy resources consumption relative to revenue, a growing trend of material efficiency and unstable dynamics of profitability the sales (Figure 1). The decrease in the energy efficiency indicator also confirmed by the assessment of the company’s readiness for the energy transition: experts evaluate the company’s adaptation potential as low, and its energy efficiency over 15 years as average (The Sustainability Monitoring Russia Website n.d.).
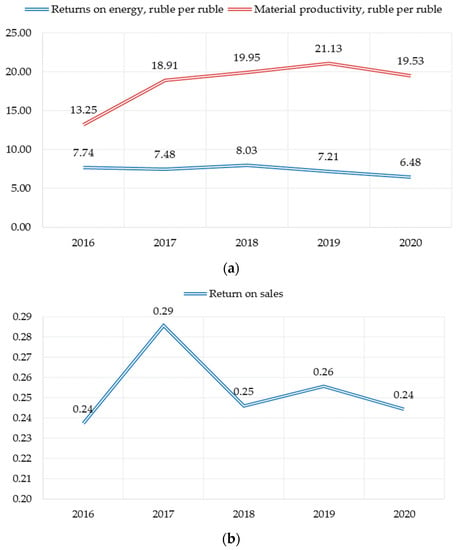
Figure 1.
Sub-indices of PJSC «Nizhnekamskneftekhim economic sustainability factor assessment»: (a) Energy and materials efficiency indicators, ruble per ruble; (b) Return on sales indicator (coefficient).
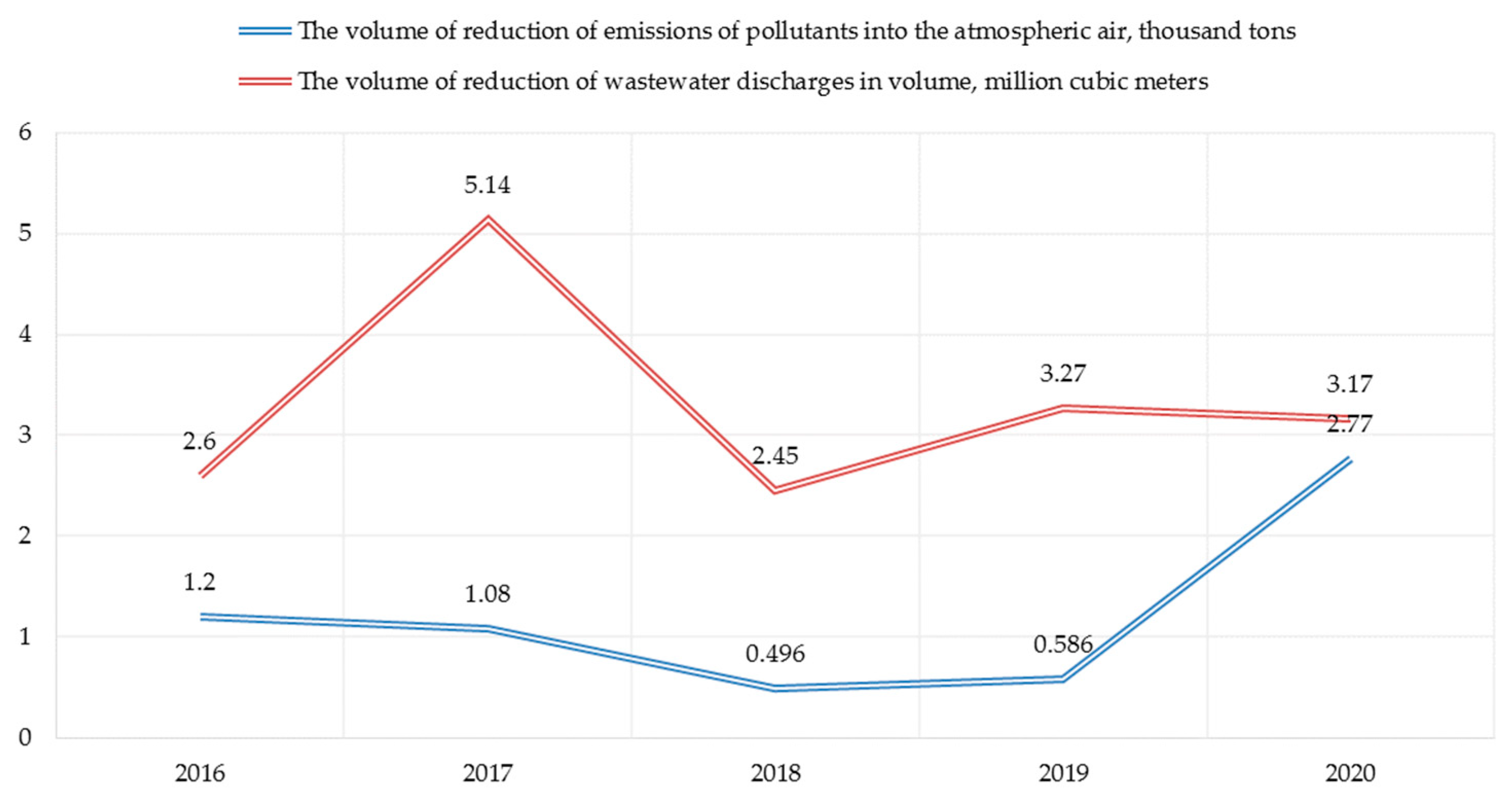
In the context of greening production, positive dynamics observed in the reduction of emissions of harmful substances into the atmosphere, the reduction of the indicator by the end of 2020 amounted to 2.77 thousand tons (Figure 2). Less positive dynamics observed in terms of wastewater discharges, the reduction in the volume of discharges is a less stable indicator.
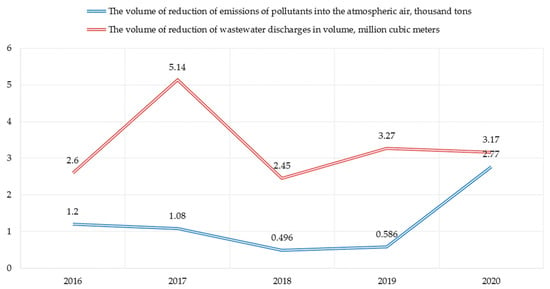
Figure 2.
Dynamics of reducing the negative impact of the enterprise’s activities on the environment.
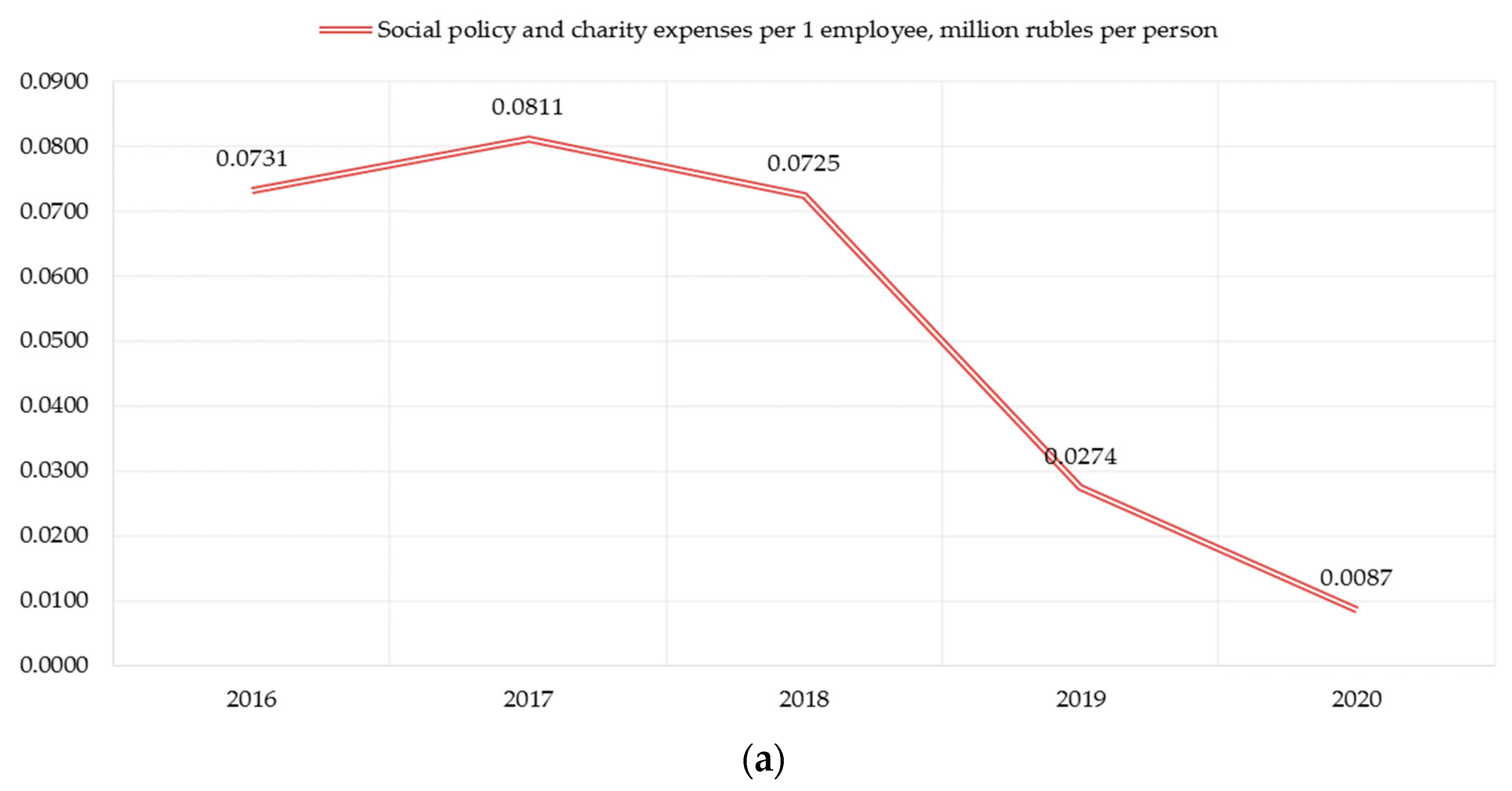
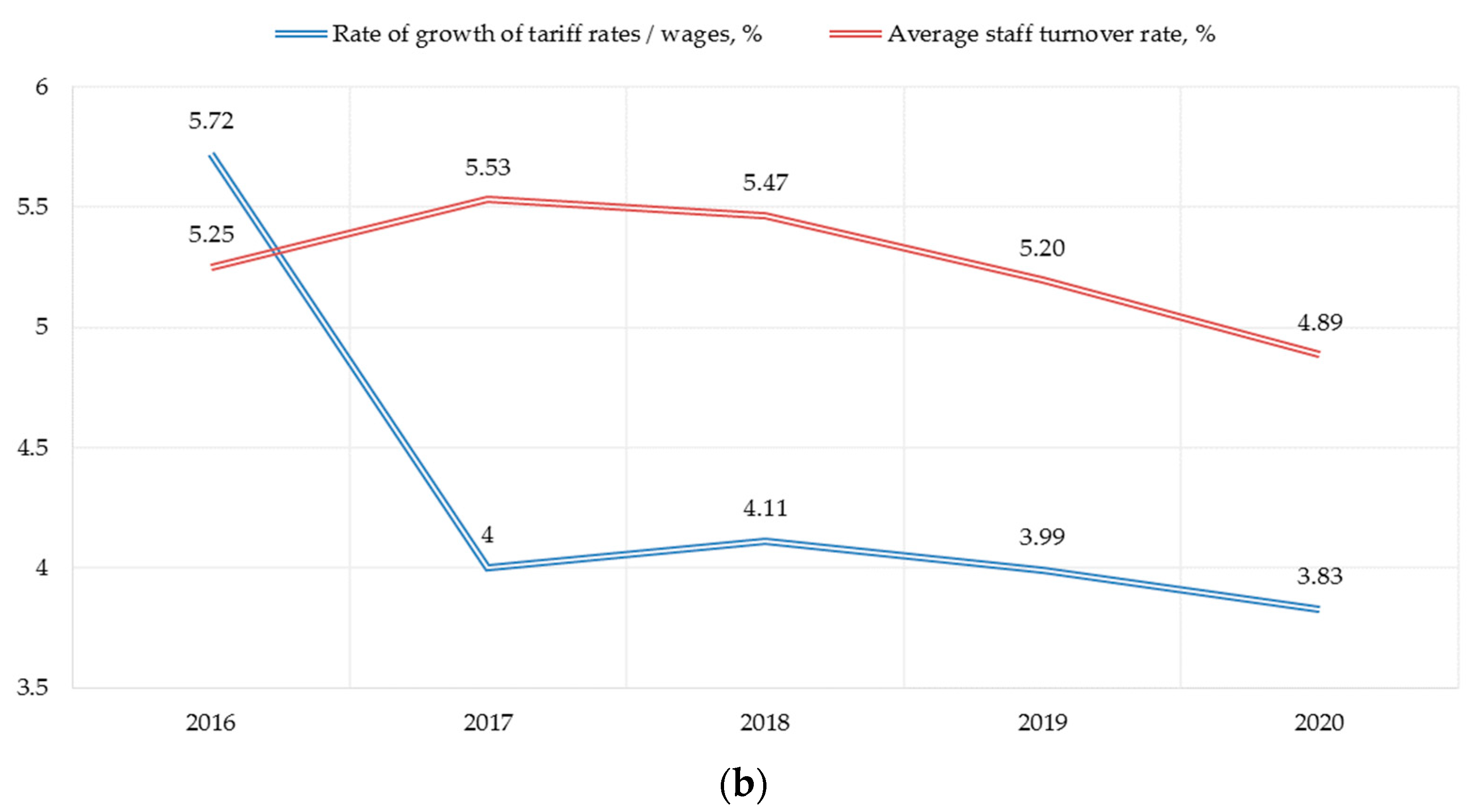
We examine the social factor through indicators of expenditures on social policy, the growth rate of wages and staff turnover. The importance of the latter is due to the satisfaction/dissatisfaction of the personnel with working conditions, which, in turn, is a consequence of the implemented social policy at the enterprise. There is an obvious weakening of the indicator reflecting the activity in the field of social policy (Figure 3a). The indicator has been visibly decreasing for 5 years (the growth rate in 2020 was—88% compared to 2016). At the same time, the indicator of personnel movement is stabilizing, but the growth rate of wages is decreasing, which in the context of high inflation is a negative factor in the social development of the enterprise (Figure 3b).
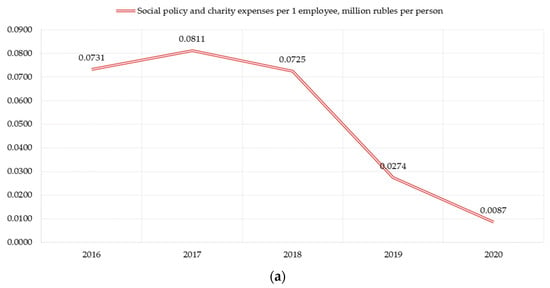
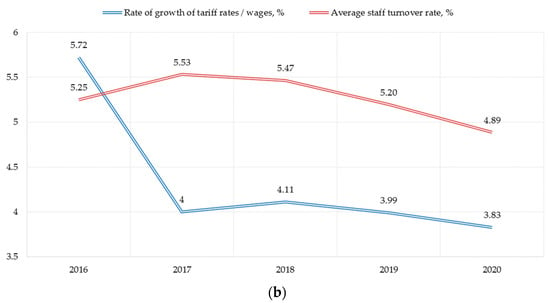
Figure 3.
Sub-indices of assessing the social factor of PJSC «Nizhnekamskneftekhim» sustainable development: (a) Social policy costs, million rubles per person; (b) Wages and staff turnover rate.
Thus, it is necessary to summarize the unbalanced development of enterprise sustainable development components—economic, environmental and social. According to the analysis results, it was revealed that in 2020 the company’s revenue fell, the profitability of sales decreased, the rate of wage growth decreased, per capita spending on social policy and charity decreased, but environmental indicators improved (which is to some extent due to a decrease in production volumes in 2020). Despite the large investments of the enterprise in fixed assets, sustainable development potential of PJSC «Nizhnekamskneftekhim» has not revealed yet.
3.1.2. Assessment of Sustainable Development Factors of PJSC «Niznekaskneftekhim»
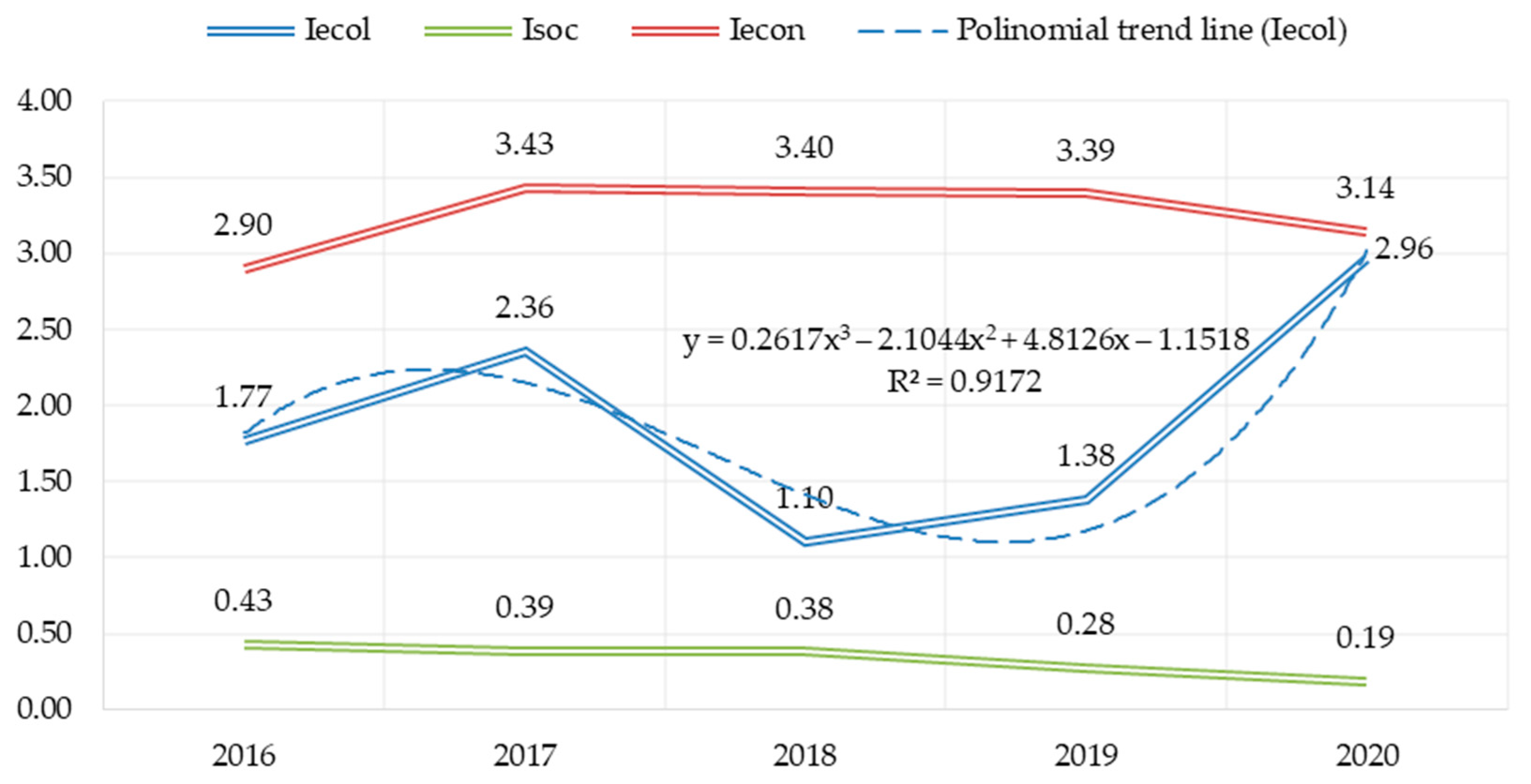
At this stage, the results based on the author’s methodology and calculation of the values factors of sustainable development of the enterprise by Formula (1) obtained. The change in the aggregate indicators in Figure 4 shown.
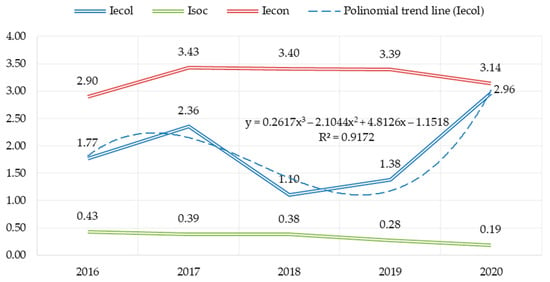
Figure 4.
Values of sustainable development factors of PJSC «Nizhnekamskneftekhim» (calculated according to the author’s methodology).
The best development vector in the environmental component observed, for 5 years the growth rate of the index was 67.7%. Less noticeable improvement at the enterprise occurred in the part of the economy (the growth restraint caused by a decrease in energy efficiency and unstable profitability of sales. A downward trend observed on the social component.
The revealed dynamics confirms the above conclusion about the disharmonization the elements of sustainable development at the enterprise, and can serve as a basis for the development of corrective measures as a part of the implementation the corporate strategy for the development of the industrial system. In this case by disharmonization we mean the diverging trends in the three sustainable development factors.
3.2. Stage 2: Three-Way Diagnostics of Sustainable Development of an Industrial Enterprise
Based on the Formulas (2)–(6), let us compare the values of the integral indicator of sustainable development of an industrial enterprise SDIE, obtained by three methods (Table 1). In two of the three cases, we observe a decrease in the composite indicator, in the first case—the most significant, in the second and third—less significant, but multidirectional.

Table 1.
Assessment the dynamics of sustainable development of the enterprise by three ways of calculating the SDIE (according the author’s methodology).
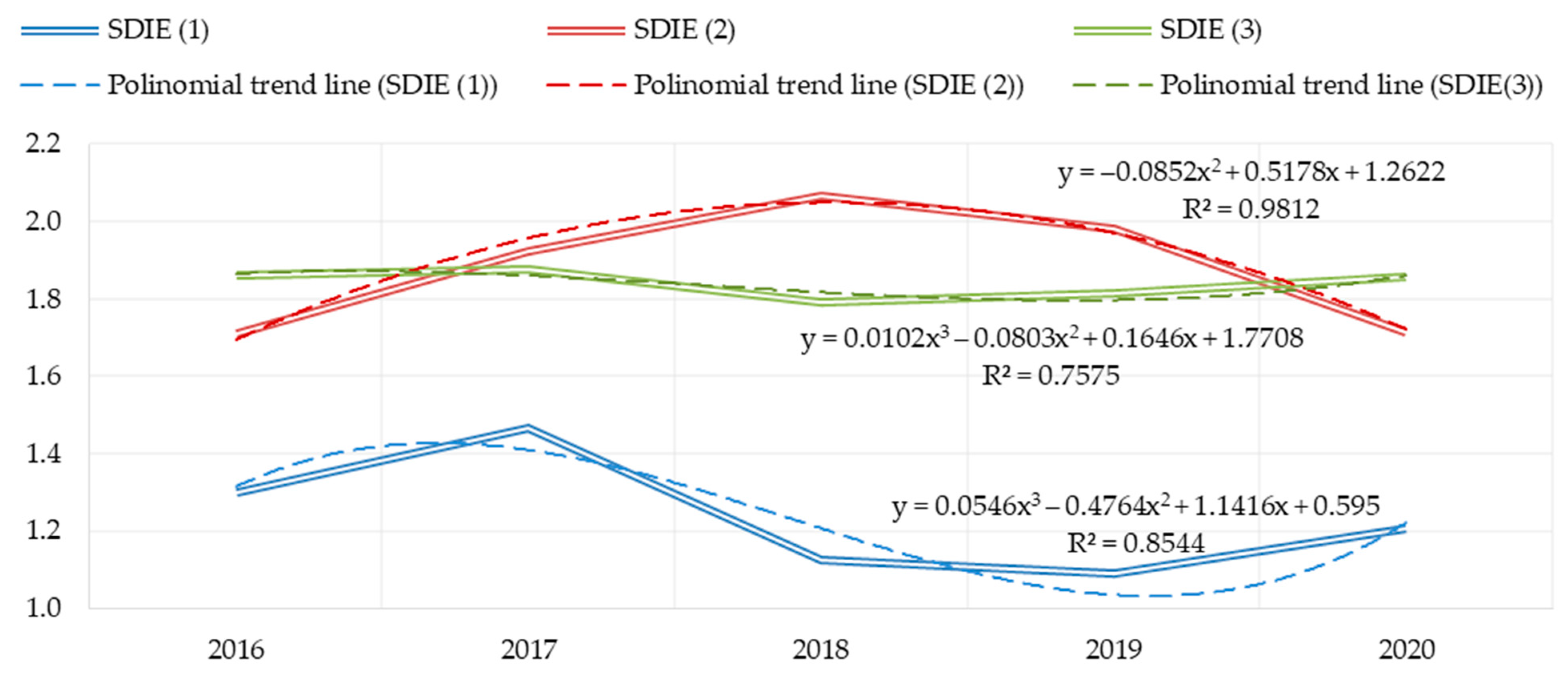
The construction of polynomial trend lines of the 2nd and 3rd degree makes it possible to verify the trajectories of sustainable development of an industrial enterprise (Figure 5). The values of the SDIE indicator, calculated by method 1, predict further growth (reliability of approximation—85%); method 2 allows to judge about future decrease of the indicator (reliability of approximation—98%); method 3 also demonstrates growth of sustainable development indicator in perspective (reliability of approximation—76%).
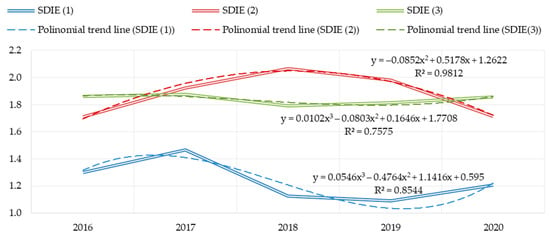
Figure 5.
Integral indicator of sustainable development of the industrial enterprise SDIE and graphs of the approximating function (polynomial).
Summarizing the intermediate results of the study, we emphasize the difference in the results of using the three developed methodological solutions. Next, we will identify the best method for assessing the sustainable development of an industrial enterprise.
3.3. Stage 3: Verification the Proposed Methods for Assessing the Sustainable Development of the Enterprise
As noted earlier, the verification based on the assessment the closeness of the relationship between the obtained values of SDIE and the environmental effect of the functioning the production system of an industrial enterprise (Table 2). The choice in favor of sub-indices of the environmental factor is due to a significant increase in dynamics (Figure 4).

Table 2.
Correlation coefficients between SDIE and environmental indicators (according the author’s methodology).
The methodology for calculating SDIE by all three methods designed in such a way that all three factors reflect positive changes in the context of sustainable development the enterprise. In addition, since the integral indicator also tends to the maximum, negative correlation coefficients are not considered. In this regard, the second method of calculation (weighting of sustainability factors without data standardization) characterized by low quality of assessment.
Method 1 and 3 are acceptable, because in both cases a direct close correlation between them revealed. Taking into account the highest value of correlation in the first case (0.737), further we will dwell on method 1, which consists in the use of techniques for calculating the geometric average.
3.4. Stage 4: Development of an Economic-Mathematical Model of Financial Flows for Sustainable Development of an Industrial Enterprise
Within the framework of economic and mathematical modeling, we estimated the coefficients of pair correlation between the values of SDIE (1) and such indicators of financial flows as acquisition of fixed assets, million rubles (investment activity) (VIA); attraction of long-term credits and loans, million rubles (VLTF); attraction of short-term credits and loans, million rubles (VSTF). It revealed that all three indicators have an inverse, but significant impact on the integral indicator of sustainable development (Table 3). This explained by the low efficiency of fixed assets renovation relative to the growing scale of production and/or inexpediency of credits and loans. An alternative is integration into network structures, as well as the search for instruments for state support of industrial development.

Table 3.
Correlations matrix between SDIE and indicators of financial flows at the enterprise.
As a result of regression analysis (multiple), the investment activity of the enterprise (VIA) in conjunction with other indicators provides low quality of the predictive model revealed. In this regard, the following multiple regression equation built:
The quality of the model is high on all parameters:
- the coefficient of determination R2 was 0.994 (or 99.4%);
- Fisher’s F-criterion is fulfilled, the hypothesis that the differences between the indicators are non-random and the regression equation is adequate is accepted, because:
Fcalc > Ftabl. (161.33 > 19);
- t-Student’s criterion is fulfilled, the significance of the obtained regression coefficients is confirmed, because:
|tcalc| > ttabl. (80.21 > 4.3);
|tcalc| > ttabl. (|−14.79| > 4.3);
|tcalc| > ttabl. (|−10.09| > 4.3).
|tcalc| > ttabl. (|−14.79| > 4.3);
|tcalc| > ttabl. (|−10.09| > 4.3).
Thus, the built model of financial flows is qualitative and can applied in the forecasting of sustainable development of an industrial enterprise, strategizing its activities by optimizing the parameters.
3.5. Stage 5: Optimization the Financial Flows for Sustainable Development of an Industrial Enterprise
In order to build a linear programming problem, the indicator dependence formula of sustainable development the enterprise on financial flows applied. Exactly this formula acts as a target function, oriented to the maximum value. The system of restrictions not provided. Relying on values of past periods, the value equal to 1.5 is set as target level of SDIE (1) indicator.
The choice in favor of this value is due to the indicators of previous periods. So, according to method 1, in 2017, the SDIE value was 1.465—the maximum observed over 5 years (Table 1). As a result of rounding in the direction of growth, the target value of SDIE is 1.5. Then optimal values of predictors will be the following:
VLTF = 0.017 billion rubles;
VSTF = 0.257 billion rubles.
VSTF = 0.257 billion rubles.
The obtained optimal sizes of credits and loans of long-term and short-term nature are significantly lower than the indicators of 2020. Thus, to improve the quality of sustainable development the enterprise needs to revise the system of financial flows, taking into account the possibility to apply the state support, network forms of interaction, private investment, project education. The latter acquires significant importance through the targeted training of highly qualified and highly qualified specialists of a narrow profile for different areas of industrial system transformation.
4. Discussion
The diagnosis of the theory and methodology of sustainable development revealed gaps in previously published studies. Thus, most scientists focus on the formation the system of indicators the sustainable development countries or industries (Hassan and Kotval-K 2019; Andriuškevičius et al. 2022; Contini and Peruzzini 2022), but not on the calculation of the integral indicator sustainable development of the enterprise, which, in our opinion, is objectively necessary and requires comprehensive coverage of economic, environmental and social factors. A similar methodology been developed at the global level (Sachs et al. 2021) and assesses the goals achievement the sustainable development of the countries in the world. However, for the microeconomic level, such an approach, in our opinion, is not universal enough and requires adaptation to the industrial enterprises, whose activities are associated only with individual Sustainable Development Goals. For the microeconomic systems the Approaches have been proposed (Schulte and Halstedt 2018; Patalas-Maliszewska and Łosyk 2020; Negulescu et al. 2022), which, in turn, reflect the system of indicators largely than an aggregated assessment. Against the background of this thesis, our proposed scientific and methodological approach is more specific in terms of efficiency (the efficiency of use the material and energy resources is taken into account), quantifiable (all indicators included in the methodology are quantitative, reflecting the performance of the enterprise), taking into account various kinds of effects (including environmental).
In addition, the presented results and the conclusions formulated complement our methodological toolkit for managing the sustainable development the economic systems of different levels. In earlier studies, the methodology developed for industrial systems (Shinkevich et al. 2021b), in the present study, we moved to the next level of decomposition the enterprise.
Separately, we would like to note the divergence of the scientists views on the structure of the system indicators the sustainable development: some scientists adhere to the classical three-element structure (Lubnina et al. 2016; Contini and Peruzzini 2022), others expand this approach with resources and technology (Gong et al. 2019). In our view, the second viewpoint contradicts the concept of sustainable balanced development. The block “resources” is an integral element of the economic subsystem and in conjunction with the block “technology” can represent a means of achieving the goals of sustainable development (in particular, through the modernization of infrastructure).
Summarizing the results of a comprehensive survey of the Russian petrochemical enterprise PJSC «Nizhnekamskneftekhim», we highlight a number of provisions.
- First, the patterns of enterprise development in the context of individual indicator identified: unbalanced development of economic, environmental and social components; the presence of unrealized potential for sustainable development of the enterprise, despite the high investment activity.
- Secondly, a methodology for assessing the sustainable development of an industrial enterprise based on the calculation the integral index as an aggregator of the three known factors of sustainable development, taking into account key aspects of the enterprise (energy consumption, material consumption, return on sales, per capita social policy costs, staff turnover, reduction of pollutant emissions and wastewater discharges), covering three methods of measurement was developed. The uniqueness of the author’s approach lies in the comparison of the results of the three methods of calculating the integral indicator and the possibility of choosing the most acceptable calculation option.
- Thirdly, the economic-mathematical model of sustainable development management of industrial enterprise developed, which allows identifying the best proportions of attracting credit resources, contributing to the increase in the integral indicator of sustainable development the industrial enterprise. The peculiarity of the approach lies in the flexibility of modeling provided by the choice of the method for calculating the aggregate indicator of sustainable development.
The novelty of the research lies in the development of sustainable development methodology, a new methodological solution underlying the management model and optimization the financial flows to promote sustainable development of an industrial enterprise. The data set noted as a limitation of the proposed methodology. The enterprise published reports on sustainable development only for 3 periods (2014, 2015, 2016). The availability of information on the structure of investments in environmental protection measures can improve the quality of the proposed economic and mathematical model. Nevertheless, our approach makes a relevant contribution to solving the problem of methodological tools in the field of diagnostics of sustainable development the industrial system, justifying the expediency of addressing these or those sources of financing activities as part of the transition to the vector of sustainable development.
5. Conclusions
This study reveals the existence of a relationship between financial flows (investment in fixed assets) and the degree of sustainable development of an enterprise, which we estimate according to a new proposed methodology. The author’s methodology is based on linear multiple regression, which allows us to formalize the linear programming problem.
This study partially solves the problem of measuring the harmonious sustainable development (meeting human needs while preserving the environment and using resources sustainably) of an industrial enterprise. The indicators presented in the work reflect the aspects of harmonization of society development at the enterprise level. The estimation of separate elements of steady development of the Russian industrial enterprise allowed revealing the following regularities: some decrease in values of economic and social factors, but positive dynamics of change of ecological factor that can testify to displacement of emphasis of the enterprise on the decision of ecological questions. At the same time, as a whole there is a growth of integral indicator of steady development of the industrial enterprise. The constructed economic-mathematical models allow to judge about presence of positive effect of modernization of industrial system (investments into the capital assets of the enterprise) and realization of nature protection actions.
The following conclusions formulated as the result of the study:
- the coronavirus pandemic of 2020 had an impact on the company’s activities (both economic and social indicators);
- the sustainable development of the enterprise is characterized by an imbalance, as evidenced by the multidirectional trends of changes in the factors Iecon, Isoc, Iecol;
- the investment flow management system of the enterprise requires optimization, restructuring of financing sources, which will help to ensure sustainable development and improve the overall picture of the enterprise development.
The formulated conclusions taken into consideration by the top management of the company in refining the corporate strategy, implementing a proactive approach to the management of financial flows, taking into account the principles of sustainable development the enterprise and the development of preventive measures to mitigate the negative impact of the production system on the environment. The proposed models of management of sustainable development of the enterprise recommended using in the organization of management of modern production systems that solve parallel tasks—import substitution and greening of production. This, in turn, requires the restructuring of funding sources, taking into account new programs to support industry in Russia.
In future studies we planned to expand the proposed methodology of diagnostics of an industrial enterprise by taking into account the costs of such environmental protection measures as the cost of air protection, protection and rational use of water resources, waste management, etc.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.F.G. and M.V.S.; methodology, F.F.G.; validation, F.F.G., M.V.S. and N.V.B.; formal analysis, N.V.B.; investigation, F.F.G.; data curation, M.V.S.; writing—original draft preparation, F.F.G.; writing—review and editing, F.F.G. and M.V.S.; visualization, N.V.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the grant of the President of the Russian Federation for state support of leading scientific schools of the Russian Federation, project number NSh-1886.2022.2.
Data Availability Statement
The authors used The Smart-lab Website data, which are publicly available.
Acknowledgments
The research carried out within the framework of the Russian Federation Presidents grant for state support of leading scientific schools of the Russian Federation, project number NSh-1886.2022.2.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A
| Conditional Designation | Content |
| SDIE | integral indicator of sustainable development of the enterprise, coefficient |
| Iecon | the economic factor of sustainable development of the enterprise, coefficient |
| Isoc | social factor of sustainable development of the enterprise, coefficient |
| Iecol | environmental factor of sustainable development of the enterprise, coefficient |
| VRoE | returns on energy, rubles per rubles |
| VMP | material productivity, rubles per rubles |
| VRoS | return on sales, coefficient |
| VSP | social policy and charity expenses per 1 employee, million rubles per person |
| VRGW | rate of growth of tariff rates/wages, % |
| VSTR | average staff turnover rate, % |
| VREP | the volume of reduction of emissions of pollutants into the atmospheric air, thousand tons |
| VRWD | the volume of reduction of wastewater discharges in volume, million cubic meters |
| VIA | acquisition of fixed assets, million rubles |
| VLTF | attraction of long-term loans and borrowings, million rubles |
| VSTF | attraction of short-term loans and borrowings, million rubles |
References
- Ahmad, Munir, Irfan Khan, Muhammad Qaiser Shahzad Khan, Gul Jabeen, Hafiza Samra Jabeen, and Cem Işık. 2023. Households’ perception-based factors influencing biogas adoption: Innovation diffusion framework. Energy 263: 126155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, Shahid, Qingyou Yan, Asif Razzaq, Irfan Khan, and Muhammad Irfan. 2022. Modeling factors of biogas technology adoption: A roadmap towards environmental sustainability and green revolution. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 30: 11838–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andriuškevičius, Karolis, Dalia Štreimikienė, and Irena Alebaitė. 2022. Convergence between Indicators for Measuring Sustainable Development and M&A Performance in the Energy Sector. Sustainability 14: 10360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awan, Ashar, Muhammad Sadiq, Syed Tauseef Hassan, Irfan Khan, and Noor Hashim Khan. 2022. Combined nonlinear effects of urbanization and economic growth on CO2 emissions in Malaysia. An application of QARDL and KRLS. Urban Climate 46: 101342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, Waseem, Irfan Khan, and Ali Syed Ahtsham. 2023. Alternative energy and natural resources in determining environmental sustainability: A look at the role of government final consumption expenditures in France. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 30: 1949–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Toly. 2017. Competitive and sustainable manufacturing in the age of globalization. Sustainability 9: 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contini, Giuditta, and Margherita Peruzzini. 2022. Sustainability and Industry 4.0: Definition of a Set of Key Performance Indicators for Manufacturing Companies. Sustainability 14: 11004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyrdonova, Alena N., and Tatiana S. Lin’kova. 2019. Principles of petrochemical cluster’ sustainability assessment based on its members’ energy efficiency performance. E3S Web of Conferences 124: 04013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, Paolo, and Spiridione Lucio Dicorato. 2020. Sustainable Development, Governance and Performance Measurement in Public Private Partnerships (PPPs): A Methodological Proposal. Sustainability 12: 5696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Qunxi, Min Chen, Xianli Zhao, and Zhigeng Ji. 2019. Sustainable Urban Development System Measurement Based on Dissipative Structure Theory, the Grey Entropy Method and Coupling Theory: A Case Study in Chengdu, China. Sustainability 11: 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, Azad, and Zeenat Kotval-K. 2019. A Framework for Measuring Urban Sustainability in an Emerging Region: The City of Duhok as a Case Study. Sustainability 11: 5402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, Erling, Kristin Linnerud, and David Banister. 2014. Sustainable development: Our Common Future revisited. Global Environmental Change 26: 130–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Peng, Mengting Zhou, Jiaqi Xu, and Yue Liu. 2021. Financialization, Government Subsidies, and Manufacturing R&D Investment: Evidence from Listed Companies in China. Sustainability 13: 12633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnitis, Edvins, Janis Bicevskis, and Girts Karnitis. 2021. Measuring the Implementation of the Agenda 2030 Vision in Its Comprehensive Sense: Methodology and Tool. Energies 14: 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Irfan, Abdulrasheed Zakari, Vishal Dagar, and Sanjeet Singh. 2022. World energy trilemma and transformative energy developments as determinants of economic growth amid environmental sustainability. Energy Economics 108: 105884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, Lenny S. C., Jonathan Morris, Seyed M. Ebrahimi, and Raymond Obayi. 2016. Integrated Resource Efficiency: Measurement and Management. International Journal of Operations & Production Management 36: 1576–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liczmańska-Kopcewicz, Katarzyna, Paula Pypłacz, and Agnieszka Wiśniewska. 2020. Resonance of Investments in Renewable Energy Sources in Industrial Enterprises in the Food Industry. Energies 13: 4285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linnerud, Kristin, Erling Holden, and Morten Simonsen. 2021. Closing the sustainable development gap: A global study of goal interactions. Sustainable Development 29: 738–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Haiying, Irfan Khan, Abdulrasheed Zakari, and Majed Alharthi. 2022a. Roles of trilemma in the world energy sector and transition towards sustainable energy: A study of economic growth and the environment. Energy Policy 170: 113238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Haiying, Majed Alharthi, Ahmed Atil, Muhammad Wasif Zafar, and Irfan Khan. 2022b. A non-linear analysis of the impacts of natural resources and education on environmental quality: Green energy and its role in the future. Resources Policy 79: 102940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubnina, Alsu A., Alexander N. Melnik, and Marina V. Smolyagina. 2016. On modelling of different sectors of economy in terms of sustainable development. International Business Management 10: 5592–95. [Google Scholar]
- Lyeonov, Serhiy, Tetyana Pimonenko, Yuriy Bilan, Dalia Štreimikienė, and Grzegorz Mentel. 2019. Assessment of Green Investments’ Impact on Sustainable Development: Linking Gross Domestic Product Per Capita, Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Renewable Energy. Energies 12: 3891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negulescu, Oriana Helena, Anca Draghici, and Gabriela Fistis. 2022. A Proposed Approach to Monitor and Control Sustainable Development Strategy Implementation. Sustainability 14: 11066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osipov, Vladimir S., Yuriy A. Krupnov, Galina N. Semenova, and Maria V. Tkacheva. 2022. Ecologically Responsible Entrepreneurship and Its Contribution to the Green Economy’s Sustainable Development: Financial Risk Management Prospects. Risks 10: 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patalas-Maliszewska, Justyna, and Hanna Łosyk. 2020. An Approach to Assessing Sustainability in the Development of a Manufacturing Company. Sustainability 12: 8787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahma, Hania, Akhmad Fauzi, Bambang Juanda, and Bambang Widjojanto. 2019. Development of a Composite Measure of Regional Sustainable Development in Indonesia. Sustainability 11: 5861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachs, Jeffrey, Christian Kroll, Guillaume Lafortune, Grayson Fuller, and Finn Woelm. 2021. The Decade of Action for the Sustainable Development Goals: Sustainable Development Report 2021. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. [Google Scholar]
- Salem, Muhammad, Naoki Tsurusaki, Prasanna Divigalpitiya, and Emad Kenawy. 2020. An Effective Framework for Monitoring and Measuring the Progress towards Sustainable Development in the Peri-Urban Areas of the Greater Cairo Region, Egypt. World 1: 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarina, Vera P., Tatiana P. Skufina, and Diana Yu Savon. 2021a. Comprehensive assessment of sustainable development of mining and metallurgical holdings: Problems and mechanisms of their resolution. Ugol 7: 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarina, Vera P., Tatiana P. Skufina, Diana Yu Savon, and Alexey I. Shinkevich. 2021b. Management of Externalities in the Context of Sustainable Development of the Russian Arctic Zone. Sustainability 13: 7749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte, Jesko, and Sophie Isaksson Hallstedt. 2018. Self-Assessment Method for Sustainability Implementation in Product Innovation. Sustainability 10: 4336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte, Jesko, Carolina Villamil, and Sophie I. Hallstedt. 2020. Strategic Sustainability Risk Management in Product Development Companies: Key Aspects and Conceptual Approach. Sustainability 12: 10531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Yang, and Xiuwu Zhang. 2022. Study on the Impact of Environmental Tax on Industrial Green Transformation. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19: 16749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinkevich, Alexey I. 2020. Sustainable development of territories in the zone of industrial facilities. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering 890: 012190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinkevich, Marina V., Alexey I. Shinkevich, Liudmila A. Ponkratova, Natalya V. Klimova, Guzel F. Yusupova, Irina V. Lushchik, and Tatiana A. Zhuravleva. 2015. Models and Technologies to Manage the Institutionalization of Sustainable Innovative Development of Meso-Systems. Mediterranean Journal of Social Sciences 6: 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinkevich, Alexey I., Farida F. Galimulina, Yulia S. Polozhentseva, Alla A. Yarlychenko, and Naira V. Barsegyan. 2021a. Computer Analysis of Energy and Resource Efficiency in the Context of Transformation of Petrochemical Supply Chains. International Journal of Energy Economics and Policy 11: 529–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinkevich, Alexey I., Irina G. Ershova, and Farida F. Galimulina. 2021b. Innovative Mesosystems Algorithm for Sustainable Development Priority Areas Identification in Industry Based on Decision Trees Construction. Mathematics 9: 3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinkevich, Aleksey I., Alsu R. Akhmetshina, and Ruslan R. Khalilov. 2022. Development of a Methodology for Forecasting the Sustainable Development of Industry in Russia Based on the Tools of Factor and Discriminant Analysis. Mathematics 10: 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauseef Hassan, Syed, Ping Wang, Irfan Khan, and Bangzhu Zhu. 2023. The impact of economic complexity, technology advancements, and nuclear energy consumption on the ecological footprint of the USA: Towards circular economy initiatives. Gondwana Research 113: 237–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The National Credit Ratings Website. n.d. Available online: https://ratings.ru/analytics/corps/investment-efficiency-240821/ (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- The Smart-lab Website. n.d. NKNH—Financial Reports, Annual Reports, Presentations. Available online: https://smart-lab.ru/q/NKNC/f/l/ (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- The Sustainability Monitoring Russia Website. n.d. Energy Transition Readiness Rating. Available online: https://monitoring-esg.com/ratings/energy-transition-rating/ (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- The World Bank Website. n.d. Available online: https://www.worldbank.org/en/home (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Tobisova, Alica, Andrea Senova, Gabriela Izarikova, and Ivana Krutakova. 2022. Proposal of a Methodology for Assessing Financial Risks and Investment Development for Sustainability of Enterprises in Slovakia. Sustainability 14: 5068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Wen-Tien. 2010. Energy sustainability from analysis of sustainable development indicators: A case study in Taiwan. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 14: 2131–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waas, Tom, Jean Hugé, Aviel Verbruggen, and Tarah Wright. 2011. Sustainable Development: A Bird’s Eye View. Sustainability 3: 1637–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Liu, Han Qin, Quanxin Gan, and Jiafu Su. 2020. Internal Control Quality, Enterprise Environmental Protection Investment and Finance Performance: An Empirical Study of China’s A-Share Heavy Pollution Industry. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17: 6082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuravlyov, Vladimir, Tatyana Khudyakova, Natalia Varkova, Sergei Aliukov, and Svetlana Shmidt. 2019. Improving the Strategic Management of Investment Activities of Industrial Enterprises as a Factor for Sustainable Development in a Crisis. Sustainability 11: 6667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).