Abstract
Financial and administrative management models are crucial to the success of digital ventures, providing practices that optimize resource management and support strategic decision-making in dynamic digital environments. This study presents an original systematic literature review (SLR) following the PRISMA guidelines, analyzing 354 articles extracted from Scopus and Web of Science databases. Bibliometric techniques, including VOSViewer 1.6.19 version and R-Bibliometrix software 4.3.3 version, were used to identify key research themes, emerging trends, and future directions in the field. A notable 114.29% increase in academic output from 2019 to 2024 underscores the growing importance of these management models. The analysis reveals a focus on financial management tools (e.g., Valuation, Discounted Cash Flow models) and administrative models (e.g., RocaSalvatella, INCIPY), while also exploring the challenges and opportunities present in digital environments. The interaction between external variables (resource management, operational efficiency, adaptability, financial planning, technological innovation) and internal variables (market conditions, government regulations, economic trends) is discussed. This study highlights the integration of agile methodologies, such as Lean Startup, and the growing emphasis on digital resilience, organizational agility, and the impact of digital transformation on business models. The theoretical contribution of this study lies in offering a comprehensive framework that synthesizes existing models, highlights key research gaps, and emphasizes the need for future studies on the dynamic interaction between financial planning, technological innovation, and organizational agility. From a practical perspective, the findings provide digital entrepreneurs and managers with valuable insights into implementing financial tools and administrative frameworks that enhance decision-making, while also underscoring the importance of agility, operational efficiency, and market adaptability to navigate digital disruptions.
1. Introduction
The management of financial and administrative resources plays a decisive role in the success and sustainability of digital ventures, which are characterized by the intensive use of digital technologies for the creation, marketing, and distribution of products and services (Franco et al., 2021; Redondo-Rodríguez et al., 2023). These ventures operate in environments marked by uncertainty, rapid technological evolution, and globalization, which present specific challenges related to financial planning, resource control, and strategic decision-making (Alfarizi et al., 2024; Kreiterling, 2023). As digital businesses evolve, they must adapt or reconfigure traditional financial and administrative management structures to address these new challenges. The growing interest in studying digital ventures reflects their significant impact on the viability and growth of digital start-ups (Fonts-Fernández & Stable-Rodriguez, 2024; Townsend & Figueroa, 2022).
Historically, financial and administrative management models in digital ventures were initially grounded in classical theories such as agency theory, the technology acceptance model, and human capital theory to better understand organizational internal and external relationships (Ghi et al., 2022; Ilyas et al., 2023; Muldoon et al., 2024). However, the rise of disruptive digital businesses has necessitated a reassessment of these theories. The unique characteristics of digital ventures—such as scalability, immateriality of products, and the need for agile decision-making—have led to the development of new models (Cueto et al., 2022; Zhai et al., 2023). For example, the integration of emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), big data analytics, and cloud-based financial models is reshaping how financial decisions are made in real-time and optimizing administrative processes (Han et al., 2024; Ladeira et al., 2019).
Despite the growing corpus of literature on financial and administrative management in digital ventures, a significant research gap remains. While a number of financial management models, tools, and administrative practices have been identified, these are often fragmented, lacking a unified theoretical framework for consistent application in the digital venture context (Bertoni et al., 2022; Ji et al., 2024). Furthermore, there is a paucity of consensus on the integration of traditional financial instruments with emerging technologies, which hinders digital entrepreneurs from adapting to an ever-evolving environment (Alkasassbeh, 2023; Franco et al., 2021). This integration gap prevents ventures from fully leveraging technological advancements while maintaining traditional practices that ensure stability. A number of studies have identified the most commonly used financial tools in digital ventures, such as valuation techniques and performance measurement systems (Fonts-Fernández & Stable-Rodriguez, 2024; Jaloliddin, 2023; Niemand et al., 2021), along with emerging technologies like blockchain for payment processing and smart contracts (Block et al., 2021, 2024). However, many of these contributions lack a comprehensive framework that merges traditional and emerging models. As digital ventures evolve, integrating these models to enhance sustainability and competitiveness becomes increasingly crucial (Bican & Brem, 2020; Tkachenko et al., 2021).
The theoretical framework of this study is based on the convergence of the digital economy, which analyses value creation through disruptive technologies and scalable, data-driven business models, and contemporary dynamic capabilities, focused on the agile reconfiguration of resources through AI and automation. The orchestration of innovation networks coordinates decentralized ecosystems (Lokuge et al., 2025), while platform governance addresses regulatory and ethical mechanisms to balance scalability with social responsibility, in accordance with regulations such as the EU Digital Services Act (Decarolis & Li, 2023; Kun, 2024). Furthermore, transformational leadership models are integrated, linking strategic goal setting with organizational adaptation and smart organization principles, where human–AI collaboration optimizes real-time decision making (Foster et al., 2025; Wang & Zhang, 2025). The ethical dilemmas under consideration are based on stakeholder theory, which prioritizes multidimensional value creation (Nguyen et al., 2024). The extant literature demonstrates a paucity of attention to the manner in which the interaction between internal and external variables, such as resource management and market conditions, affects the success of digital firms (Alfarizi et al., 2024; Alkasassbeh, 2023).
This study conducts a systematic literature review (SLR) in accordance with PRISMA guidelines, analyzing 354 scientific articles published between 2019 and 2024. Utilizing bibliometric techniques with VOSViewer and R-Bibliometrix software, it identifies key trends, research trajectories, and emerging themes in financial and administrative management models for digital ventures. The primary contribution of this study is the consolidation of various management models, tools, and variables, offering a unified framework that integrates traditional management practices with emerging technologies to optimize decision-making and efficiency. Furthermore, the study provides practical insights into how digital entrepreneurs can use AI and big data to address challenges and improve competitiveness, resilience, and sustainability in the digital landscape, emphasizing the importance of understanding the interplay between technological and behavioral factors.
2. Materials and Methods
The present study employs an SLR methodology that integrates bibliometric analysis in order to identify emerging trends and gain insight into the intellectual structure of a specific field (Donthu et al., 2021; Mukherjee et al., 2022). A citation and co-occurrence analysis were conducted using the PRISMA methodology of Page et al. (2021) and tools such as VOSviewer and R-Bibliometrix, which facilitate the construction of bibliometric networks and the visualization of connections in the literature (Aria & Cuccurullo, 2017; Van Eck & Waltman, 2010). The process involved the collection and organization of bibliographic data in Excel, with reference to articles such as Echchakoui (2020) and databases including Scopus and Web of Science. This methodological approach facilitated a comprehensive exploration of the knowledge structure and its interconnections, thereby providing a global perspective on the research conducted.
2.1. Question Formulation
The approach of the study is based on defined review questions, which guide the search strategy, the selection of studies, and the type of data extraction. To this end, the following research questions were formulated as shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Research questions.
2.2. Search Equation
Figure 1 shows the design of the search equation, and the search databases used, including Scopus and Web of Science.
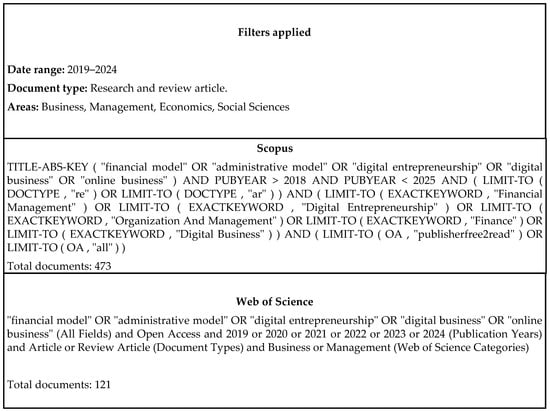
Figure 1.
Search equation design. Source: Authors.
2.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
In the analysis, inclusion and exclusion criteria were defined considering the availability of the full text (Table 2). As previously noted by Moher et al. (2015), the criteria carry a considerable degree of subjectivity in the decision-making process.

Table 2.
Inclusion/exclusion criteria.
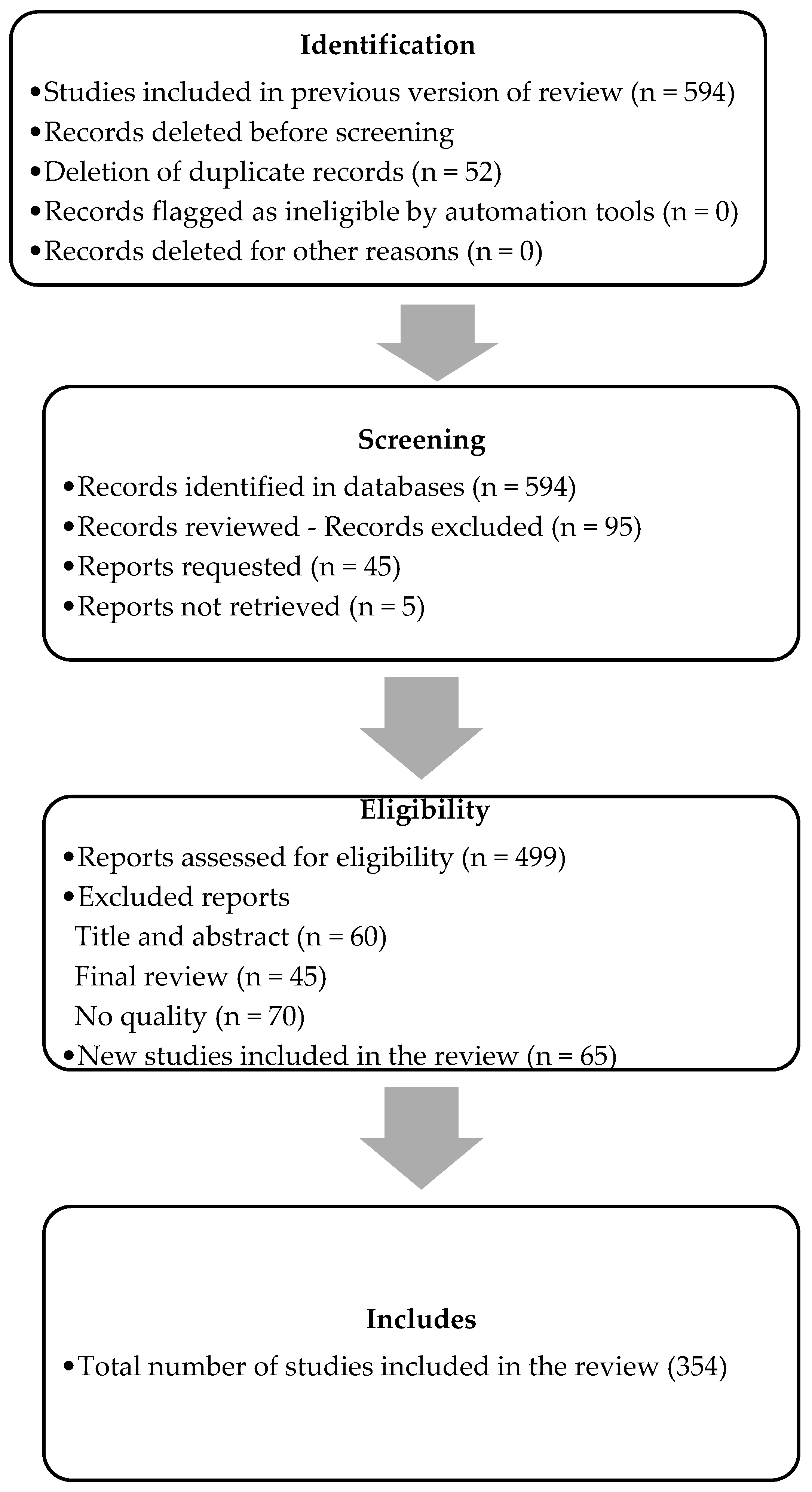
The initial search was conducted in Scopus and Web of Science resulting in a total of 594 articles, then a time horizon was established for the study between 2019 and 2024 to capture the most recent and relevant publications on administrative and financial management models in digital ventures given their relevance since 2019. Consequently, articles that did not meet the criteria of availability, domain area, year range and document type were excluded, resulting in a total of 354 articles. Figure 2 illustrates the refinement process that was carried out with the PRISMA method.
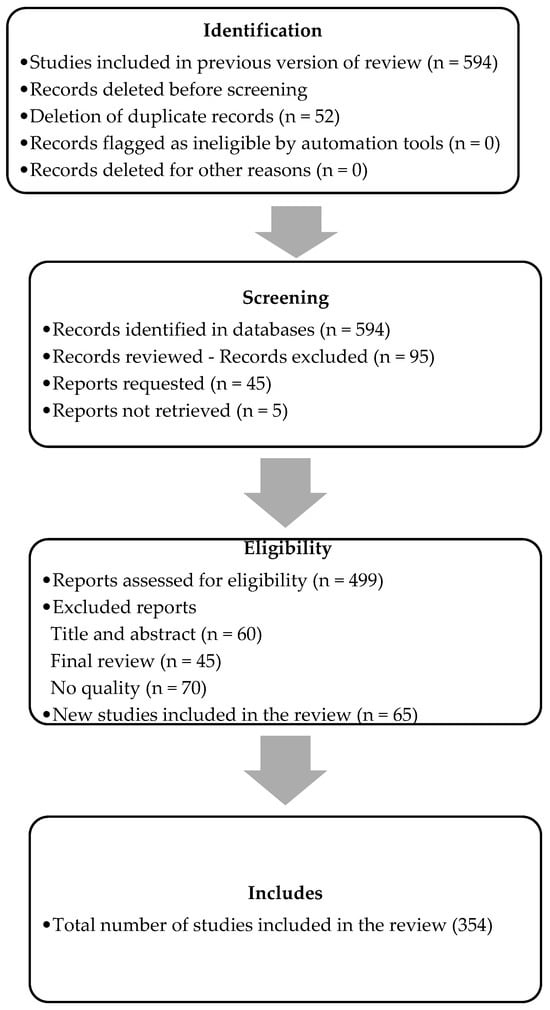
Figure 2.
PRISMA refinement procedure. Source: Authors.
The selection process for the study commenced with a total of 594 studies from the previous version of the review. A total of 52 duplicate records were then removed prior to the screening phase, with no records marked as automatically ineligible or removed for other reasons. Subsequently, 594 records were identified in the databases, encompassing both previous and new studies found in this version of the review. Following an initial review of titles and abstracts, 95 records were excluded, leaving 499 for assessment of eligibility. An additional 45 reports were requested; however, 5 could not be retrieved and were therefore not considered. Subsequently, in the evaluation of the 499 reports, 175 were excluded: 60 were discarded during the title and abstract review, 45 during the final review for not meeting quality or relevance criteria, and 70 more were excluded due to quality issues. This process resulted in the final selection of 324 reports deemed eligible for further consideration. Furthermore, 65 new studies were incorporated, resulting in a total of 354 studies finally included in the review. This rigorous selection process ensures that only the most relevant and high-quality studies are included in the final analysis.
2.4. Analysis and Synthesis
In the process of collating and organizing the analysis of the articles, Microsoft Excel was used to compile and systematize the data and bibliographic information in a spreadsheet. The methodology allowed a logical sequence to be established that ensured the coherence, consistency, and validity of the review.
3. Results
This section presents the results of the analysis in relation to the previously defined research questions. The analysis was conducted on the basis of the data extracted from the 354 primary studies selected to answer the six research questions.
- RQ1:
- Which articles, countries, and keywords address financial and administrative management models for digital ventures?
- Articles
In this study, a citation analysis of the most influential articles in the field was performed, where the ten most influential articles out of 354 were selected based on their number of citations (Table 3). The articles were then ranked according to the total number of citations they had received, and the top ten were selected for further analysis. This approach was adopted to ensure that the articles with the highest citation rates, reflecting their significant impact within the field, were included in the review. The selection was based exclusively on the number of citations, without consideration of additional criteria such as journal impact factor or age of publication.

Table 3.
Most influential articles.
The studies incorporated within the review, as demonstrated in Table 3, demonstrate the direct influence of digitization and innovation on the financial and administrative management models of digital ventures. The table highlights the total citations of key papers addressing fundamental topics such as DT, digital innovation in business models, and organizational adaptation. The substantial number of citations directed towards seminal works, including those by Hanelt et al. (2021) and Verhoef et al. (2021), serves as a testament to the profound impact of these research endeavors within the academic discourse. These studies underscore the significance of integrating digital and organizational capabilities within management models, emphasizing that digital ventures necessitate a multifaceted approach encompassing both digital strategies and organizational flexibility and continuous innovation capabilities. Furthermore, the extant literature demonstrates that effective integration of digital technologies and organizational adaptability are essential factors for optimizing performance and ensuring the long-term sustainability of such ventures.
The articles reviewed offer a comprehensive understanding of financial and administrative management models for digital ventures. A recurrent theme in the studies is the interplay between digital business strategies and organizational capabilities. The findings indicate that financial performance, particularly in the context of SMEs, is influenced by the alignment of managerial and operational capabilities with digital strategies. This suggests that effective management in digital ventures requires a balance between strategic decision-making and operational execution. Furthermore, the importance of digital culture and information technology (IT) capabilities is emphasized as crucial factors for the successful implementation of digital product/service strategies, which directly impact a firm’s ability to compete in the digital economy. It is also vital for organizational structures to adapt, moving towards more flexible and dynamic models that support continuous adaptation in response to evolving digital ecosystems. The findings suggest that digital ventures must not only focus on the adoption of digital technologies but also integrate them within a broader administrative framework that emphasizes agility, sustainability, and technological competence. Consequently, the models of financial and administrative management in digital ventures must be multifaceted, incorporating elements of digital strategy, organizational flexibility, and continuous innovation to optimize performance and ensure long-term sustainability.
- b.
- Countries
The analysis presented indicates the number of documents related to the subject in different countries and territories. In this case, a list of 10 countries and the number of documents related to the research in each of them is presented. China leads with the highest number of articles with 37, followed by Germany with 27, and the United Kingdom with 23; the production of articles is geographically distributed among countries in different continents. Table 4 shows the influential countries in the literature.

Table 4.
The ten most relevant countries in the literature.
There is a high degree of variability in the collaborative approaches to financial and administrative management models employed in digital ventures. The variability is evident in the difference between SCP and MCP. China is the leading country in this field, with 37 articles published to date; its research output focuses on SCP, which accounts for 97.3% (36 articles) of its studies. Countries such as the United Kingdom, Italy, Finland, and Germany show a greater predominance of research devoted to MCP, with Italy standing out with 41.2% of articles in this field; the United Kingdom has a high percentage of MCP (39.1%), indicating a more global approach to management models. In general, countries such as the United States and Germany show a more balanced approach between SCP and MCP, suggesting a dual strategy as SCP is also prioritized, while others seek to expand their links and knowledge through MCP.
- c.
- Keywords
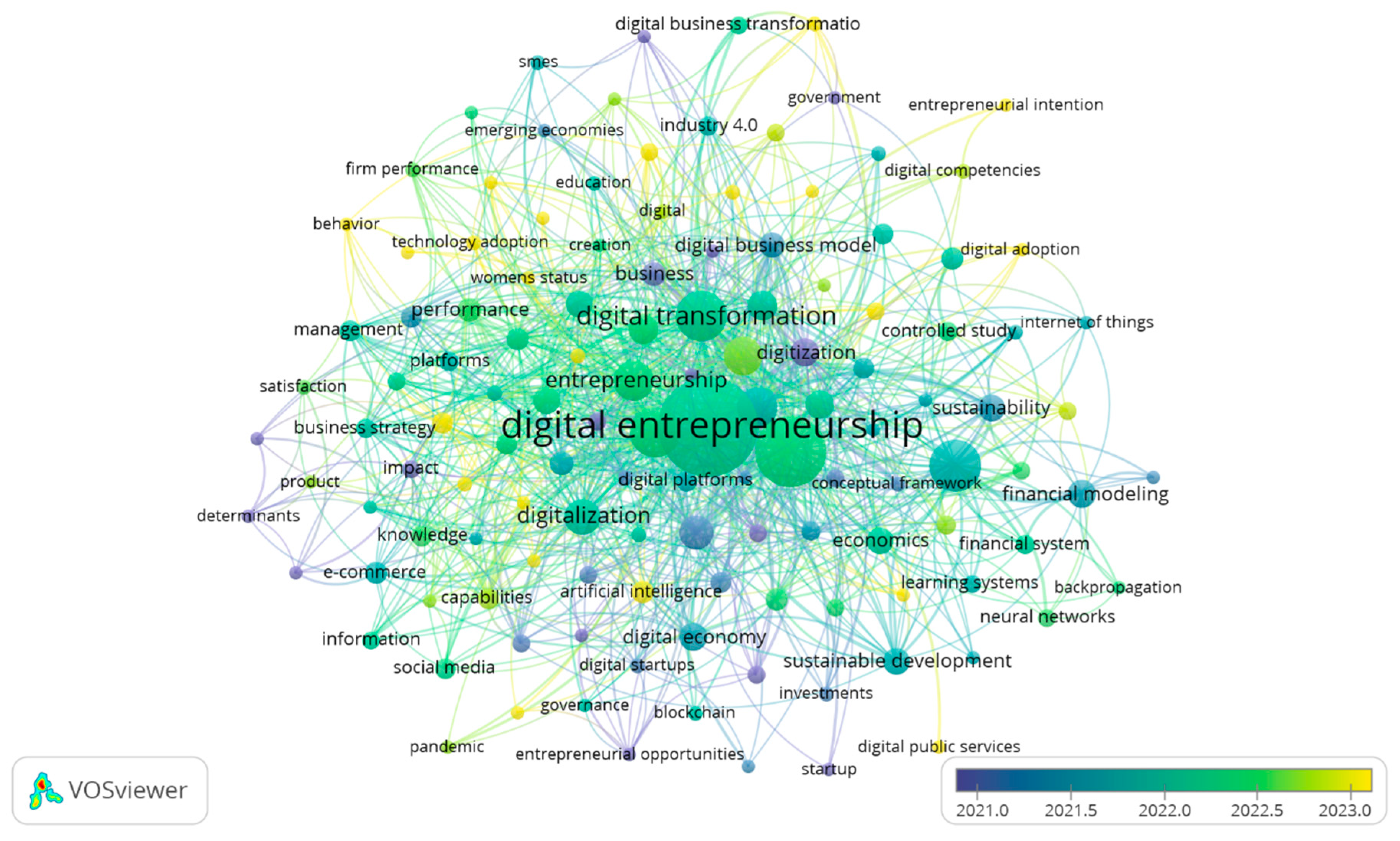
The cooccurrence analysis of high-frequency keywords allows for understanding of the thematic growth of literature. For this purpose, a minimum occurrence criterion set equal to five was established, as shown in Figure 3 and Table 5. The keywords reflect research topics in a specific field.
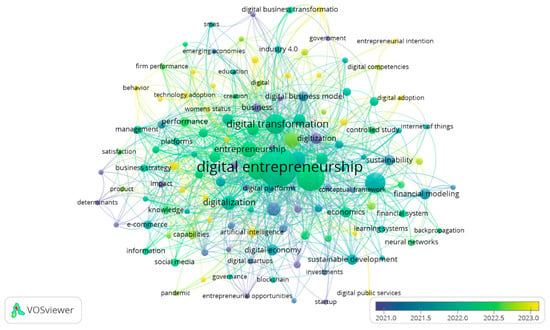
Figure 3.
Map of keyword co-occurrences. Source: VOSviewer.

Table 5.
Theme keywords.
Figure 3 highlights the most influential keywords in the research field. The analysis criteria were established so that each trend consisted of a minimum of five occurrences; the number of words selected was 128 out of 2127.
The keywords in financial and administrative management models for digital ventures, as shown in Table 5 and Figure 3, reveal an interconnected structure reflecting the dynamics of innovation, sustainability, and management. Terms like “Innovation” (539.198), “Entrepreneur” (95.502), and “Business models” (71.05) highlight the critical roles of innovation and entrepreneurship in building sustainable digital businesses. “Finance” stands out as the key concept in financial management, underscoring its importance in strategic and operational decisions. The terms “Sustainability” (41.649) and “sustainable development” (46.402) show the growing emphasis on incorporating responsible practices in management models.
Additionally, terms like “Digital business” (54.217) and “Digital entrepreneurship” (79.983) highlight the integration of business evolution with financial management in the digital age. While “Management” and “Financial management” remain relevant, emerging terms such as “Digital transformation” (0.739), “Technology” (13.175), and “Big data” (57.722) reflect the impact of new technologies on business models. “Risk assessment” and “Decision making” also emerge, emphasizing the importance of risk management in a dynamic environment. Together, these keywords indicate that digital ventures are influenced by technological innovation, sustainability, and the need for adaptability in management models.
- RQ2:
- What theoretical models exist for financial and administrative management in digital environments, and how do they compare with each other?
Table 6 presents an overview of theoretical models of financial and administrative management in digital environments, which fall into two main categories: financial models and administrative models. Financial models are concerned with evaluating and projecting the economic performance of companies, while administrative models emphasize organizational transformation and adaptation to digital challenges.

Table 6.
Main theoretical models of financial and administrative management.
Financial models in digital environments are designed with the objective of evaluating and projecting the economic performance of a company under various circumstances. The valuation model is used to determine the value of an investment or business and is fundamental to investment decision making (Arefmanesh et al., 2024; Kim-Duc & Nam, 2024). On the other hand, the DCF model calculates present value from projected future cash flows, making it useful in business or investment valuation (Arefmanesh et al., 2024; Kim-Duc & Nam, 2024).
In ALM management it encompasses long-term risk and solvency and is employed by financial institutions in making decisions that ensure stability in volatile markets (Bhat, 2020). The sensitivity analysis model evaluates organizational competitiveness using key criteria such as performance and innovation and, in turn, improves long-term strategies and performance (Nguyen Ngoc et al., 2024). On the other hand, the asset allocation model optimizes the allocation of resources considering unified risks and allows banks to maximize risk-adjusted profitability (Júdice et al., 2021).
At the administrative level, it facilitates organizational transformation and adaptation to technological change. The RocaSalvatella model employs a holistic approach to DT, incorporating elements such as strategic vision, operational processes and organizational culture (Townsend & Figueroa, 2022). The MIT Center for Digital Business Model & Capgemini Consulting emphasizes the repercussions of digitalization on customer experience, operational processes, and business models, and its contribution to business performance in a digital environment (Townsend & Figueroa, 2022). The INCIPY model, on the other hand, reorients the customer experience through DT (Townsend & Figueroa, 2022). The TETR4DIG model, with its focus on telecommunications, offers a tailored framework that addresses the unique needs of this sector (Fonts-Fernández & Stable-Rodriguez, 2024).The RBV Model posits that organizations can attain a competitive advantage by cultivating distinct resources that enable their adaptation to a perpetually evolving digital environment (Ahn et al., 2022; Estensoro et al., 2022).
In a similar vein, the models proposed by De Clerck et al. (2021) and Kassim et al. (2011) in the context of management in administration offer key approaches to optimizing organizational performance. The RGM emphasizes strategic planning and the establishment of clear objectives, prioritizing the attainment of results. The HRM places significant emphasis on the cultivation of a positive work environment, promoting effective communication and employee participation. The OSM underscores the significance of organizational adaptability in responding to internal and external changes. The ICPM standardizes the control of internal processes to ensure efficiency and compliance, while the TMM encourages the integration of advanced technologies that improve decision-making and productivity. The application of these models enables organizations to enhance their effectiveness and adaptability in a dynamic environment (De Clerck et al., 2021; Kassim et al., 2011).
Theoretical models of financial and administrative management in digital environments have been shown to facilitate the assessment and management of financial risks, improve operational efficiency, and facilitate strategic decision-making. Utilizing simulations and optimization techniques, these models furnish a dynamic evaluation of profitability and sustainability within uncertain environments, thereby enhancing risk management (De Clerck et al., 2021; Fonts-Fernández & Stable-Rodriguez, 2024).
- RQ3:
- What key variables affect the effectiveness of a financial and administrative management model in digital ventures?
The effectiveness of a financial and administrative management model in digital ventures is influenced by key variables classified into internal and external factors (Table 7), and fundamental variables to ensure the sustainability and growth of organizations in a competitive digital environment.

Table 7.
Key variables of financial and administrative management models.
The effectiveness of financial and administrative management models in digital ventures is contingent upon the management of internal variables, including financial, human, and technological resources, operational efficiency, and adaptability (Shalihah et al., 2024). Such management optimizes costs, improves profitability, and ensures the proper use of available resources. Bertoni et al. (2022) and Ji et al. (2024) emphasize that proper financial planning should integrate accounting processes and control activities to support efficient resource management, which in turn supports performance in a venture. In a similar vein, the judicious allocation of human and technological resources is instrumental in achieving strategic objectives (Ladeira et al., 2019).
It is imperative that operational efficiency and adaptability are integrated into the internal variables of a successful management model. The implementation of digital technologies, including accounting software, financial analytics platforms, and AI, has been shown to facilitate process automation, reduce errors, and enhance decision-making capabilities (Elia et al., 2020). In addition, Hommel and Bican (2020) and Samara and Terzian (2021) posit that the adoption of technologies optimizes internal processes and strengthens the ability of companies to adapt to an ever-changing digital environment. Technological innovation plays a pivotal role in this context through the continuous adoption of new tools that optimize financial results, innovative products, and services (Redondo-Rodríguez et al., 2023). Consequently, financial planning is imperative for the forecasting of revenues, expenses and cash flows, thereby enabling companies to anticipate potential financial crises (Xiao et al., 2022).
As for external variables, a number of factors are beyond the direct control of the company, as they exert considerable influence on its financial and administrative management. Fluctuations in market conditions, including changes in demand and competition, have a direct impact on the firm’s profitability and financial strategy (Audretsch et al., 2024). As Fauzi et al. (2020) and Ghezzi and Cavallo (2020) note, companies must be agile in reconfiguring their resources and processes to adapt to changes in the market environment. Also, government regulations, such as those related to taxation and trade, have the potential to affect the profitability and sustainability of business initiatives; it is incumbent upon companies to be aware of the regulations that apply to them to avoid penalties or legal problems (Kreiterling, 2023).
On the other hand, local and global economic trends play a significant role, as fluctuations in macroeconomic conditions affect access to finance and investment opportunities (Alfarizi et al., 2024). As suggested by Luo et al. (2021) and Townsend and Figueroa (2022), the implementation of a financial and management plan allows anticipating potential crises and maximizing long-term profitability.
The interaction of internal and external variables is pivotal in optimizing the implementation of financial and administrative management models in digital ventures, thereby enabling organizations to adapt to competitive and volatile environments (de Mattos et al., 2024). The alignment of these variables has been shown to enhance decision-making processes, optimize resource allocation, and refine operational procedures (Hommel & Bican, 2020; Samara & Terzian, 2021). This, in turn, has the potential to increase immediate profitability and long-term competitiveness. Furthermore, it has been demonstrated that this alignment fosters strategic flexibility and the sustainability of management practices (Fauzi et al., 2020; Ghezzi & Cavallo, 2020).
- RQ4:
- How does the SLR observe the adaptation of a traditional financial and administrative management model to the specific needs of digital ventures?
Adapting a traditional financial and administrative management model to the demands of digital ventures requires a holistic approach that encompasses the internal operations as well as the external interactions of the organization. The SLR reveals a number of theoretical models, including the RocaSalvatella model, which provide a solid framework to guide this transition (Townsend & Figueroa, 2022). This model identifies six fundamental axes for DT, namely strategic vision, processes, customer touch points, organizational culture, service design, and business model; crucial elements for adapting traditional management approaches to the dynamics of digital business (Townsend & Figueroa, 2022).
The strategic vision represents the initial step, as it defines the objectives and goals of the organization in a digital context, facilitating the identification of new opportunities arising from the digital environment and enabling the realignment of organizational leadership with these changing demands (Niemand et al., 2021). Redefining the vision results in organizations moving from a traditional approach to a more dynamic and adaptive perspective (Reuter & Floyd, 2024), optimizing processes involving digitization and automation of administrative tasks (Han et al., 2024).
The integration of technological solutions has been demonstrated to contribute to a reduction in operating expenses, the identification and correction of inefficiencies, and an enhancement in agility. As highlighted by Dana et al. (2024) and Zhai et al. (2023), fundamental changes are imperative to enhance operational efficiency within a digital environment. Consequently, the transformation of customer touchpoints emerges as a pivotal concern, particularly in a digital context where touchpoints proliferate and diversify through channels such as social networks, mobile applications, online service platforms, and others. Consequently, organizations must design strategies that enhance the customer experience through personalization and the incorporation of technologies such as AI (Upadhyay et al., 2022).
Consequently, organizational culture fosters innovation and continuous learning, as companies must adapt effectively to the constantly evolving digital landscape (Bican & Brem, 2020). Consequently, service design in digital business must be reconfigured to align with the demands and opportunities presented by the digital marketplace (Hommel & Bican, 2020; Luo et al., 2021). In this regard, organizations are compelled to rethink their services, ensuring that they are more personalized and better aligned with customer expectations. This necessitates the use of new technologies to offer more targeted solutions. Cueto et al. (2022) and Russo-Spena et al. (2022) identify the use of digital platforms and the implementation of subscription-based digital business as strategies employed by digital businesses.
In this context, Rogers’ (2016) model, which emphasizes continuous adaptation in response to changes in customer preferences, the competitive landscape, and technological advances, serves to reinforce the perspective of the RocaSalvatella model. The integration of these elements ensures that organizations adapt their financial and administrative management in order to ensure their sustainability and competitiveness in the digital environment.
- RQ5:
- What role do technological tools play in optimizing financial and administrative management in digital ventures?
The role of technological tools in optimizing financial and administrative management in digital ventures is critical, as these tools enable more efficient, real-time management of financial resources and administrative tasks. These technologies empower business leaders to make informed, data-driven decisions, which are crucial in the fast-paced digital landscape (Zhang et al., 2022). The ability to access data in real-time enables companies to respond more swiftly to market dynamics, thereby helping them to maintain competitiveness and flexibility in a constantly evolving business environment (Steininger, 2019).
Specialized financial planning tools, including forecasting software, enhance the precision of financial projections and budgets, thereby empowering businesses to proactively anticipate potential liquidity concerns or resource deficiencies. This proactive approach facilitates the development of strategies aimed at mitigating financial risks and ensuring long-term financial stability (Alkasassbeh, 2023; Leong et al., 2022). A significant benefit of these tools is their capacity to automate processes that have historically been manual, including accounting, invoicing, and expense tracking. This has two main benefits. Firstly, it reduces the time and cost associated with these tasks. Secondly, it reduces the risk of human error, improving the overall efficiency of financial operations (Leong et al., 2022).
Furthermore, technological tools enhance document management by providing secure, cloud-based storage solutions (Leong et al., 2022). These solutions enhance the accessibility of financial documentation, thereby ensuring that businesses can comply with legal requirements while simultaneously improving the effectiveness of audit processes. Furthermore, the integration of interactive dashboards empowers financial managers to monitor the company’s financial health in real-time, facilitating the decision-making process informed by current data (Franco et al., 2021).
However, it is important to note that the implementation of these tools necessitates ongoing staff training, as digital ventures must ensure that their teams are proficient with the new technologies. Continuous training helps personnel to stay up to date with advancements and optimizes their ability to leverage the full potential of the technologies, ultimately improving operational efficiency (Braune & Dana, 2022).
AI-powered tools have had a profound impact on financial and administrative management, leading to the development of models such as predictive management (Abdullah & Almaqtari, 2024; Guerrero-Martin et al., 2024; Hassan et al., 2023; Ostapenko et al., 2024; Sayari et al., 2025). This model utilizes machine learning algorithms and big data to anticipate financial trends and market behavior. This facilitates proactive decision-making by businesses, enhancing their strategic positioning (Kunduru, 2023). Robotic process automation (RPA) is another significant innovation, automating repetitive administrative tasks such as account reconciliation and invoice management, which reduces the burden on human workers and increases operational efficiency (Kunduru, 2023).
Furthermore, the incorporation of business intelligence (BI) models that are augmented with AI has been shown to enhance financial decision-making capabilities by facilitating the analysis of voluminous data sets, thereby offering businesses a more profound understanding of their financial performance (Kunduru, 2023). This information can then be used to optimize strategic planning, allocate resources more effectively, and improve overall decision-making (Di Vaio et al., 2022; Kumar et al., 2024). Furthermore, AI-based financial risk management models help identify, assess, and mitigate potential risks before they materialize, significantly reducing the likelihood of fraud and protecting a company’s assets from potential threats (Estep et al., 2024).
In a variety of sectors, including but not limited to financial technology, e-commerce, healthcare, and logistics, AI has become integral to the optimization of financial and administrative processes. Within the domain of fintech, AI has been instrumental in the automation of payment management, the enhancement of fraud detection mechanisms, and the personalization of services. Within the domain of e-commerce, AI has been instrumental in enhancing user experience by optimizing inventory management and customer interactions (Di Vaio et al., 2022; Singh & Thirumoorthi, 2019). In a similar vein, AI has been instrumental in the field of medical diagnostics, enhancing healthcare technology. Furthermore, AI has been employed to optimize logistics through enhanced delivery route management and demand forecasting (Al-Ababneh et al., 2024; de Mattos et al., 2024; Koebe, 2025; Mauro et al., 2024).
The integration of AI in financial and administrative management brings numerous benefits, such as the automation of processes, the enhancement of decision-making, and the prediction of trends (Aloulou et al., 2024; Barone et al., 2024). These benefits lead to improved operational efficiency, reduced financial costs, and better risk management (de Mattos et al., 2024; Kumar et al., 2024). Consequently, AI is transforming key sectors and enhancing customer experiences, which could result in a more agile, efficient, and competitive business environment (Hassan et al., 2023; Kumar et al., 2024).
- RQ6:
- What future work do the authors consider should be done regarding financial and administrative management models for digital ventures?
The study presents a relevant boom for academic research and the business world. Based on the literature review, a framework for future research is outlined in Table 8.

Table 8.
Future research directions.
In the context of AI, several studies have been conducted that emphasize its relevance in strategic decision-making and investment management. Specifically, AI has been demonstrated to enhance project selection, risk analysis and opportunity assessment, facilitated by technologies such as machine learning. Research by Bertoni et al. (2022) and Han et al. (2024) explores the potential of AI to optimize these processes, while also addressing ethical and operational biases. AI is presented as a key enabler of DT, especially in strategic decision making and process optimization in digital enterprises. Furthermore, research on digital agility, integration of innovative technologies (such as AI) and sustainability in digital startups is critical (Bican & Brem, 2020; Ghezzi, 2019; Hanelt et al., 2021; Verhoef et al., 2021).
It is imperative that future research endeavors concentrate on the manner in which organizations traverse the phases of DT and cultivate digital resilience in response to competitive pressures. The investigation of organizational structures in promoting digital agility and the evolution of metrics during DT is of paramount importance for strategic decision-making. Subsequent studies should explore the integration of Lean Startup (LS) and Agile methodologies, their impact on business model innovation, and the application of these approaches in startup contexts. Expanding research to regions with different levels of digitization and exploring the regulation of digital technologies, privacy concerns, and AI’s role in investment decisions will also provide valuable insights. Lastly, interdisciplinary research that addresses the socio-economic impact of DT and its influence on business management will be essential for understanding its long-term effects.
4. Discussions
The results of this study provide a comprehensive view of financial and administrative management models in digital ventures, considering both internal and external variables that impact the operational efficiency and success of these organizations. A pivotal finding is the dynamic interplay between internal variables, such as operational capability and digital strategy, and external variables, such as market conditions, technology, and government regulations. This analysis underscores the pivotal role of effective alignment between these variables, emphasizing organizational agility and technological innovation in shaping the financial stability and competitiveness of digital ventures (Ghezzi, 2019; Ghezzi & Cavallo, 2020; Ukko et al., 2019).
A seminal model identified in the extant literature is financial management based on AI and machine learning. These models have been shown to be instrumental in improving decision-making by predicting financial trends and market behaviors, allowing companies to proactively adapt to changes. For instance, the utilization of machine learning algorithms to forecast cash flow and investment needs has been shown to enhance the financial planning capabilities of digital companies (Estep et al., 2024; Kunduru, 2023). These findings align with the extant literature, which demonstrates that AI applied to financial management optimizes processes and offers competitive advantages by predicting and mitigating risks with greater accuracy (Aloulou et al., 2024; Kumar et al., 2024).
Another model that emerges as relevant in this study is process automation through RPA, which uses AI to automate repetitive administrative tasks such as account reconciliation and invoice management. This approach enables digital organizations to enhance operational efficiency and reduce human intervention, leading to a reduction in costs and errors, thereby promoting organizational agility and risk reduction (Franco et al., 2021; Kunduru, 2023). This finding is further substantiated by prior studies that have demonstrated the efficacy of automation in enhancing efficiency within pivotal sectors such as accounting and payment management (Barone et al., 2024; Leong et al., 2022).
Furthermore, this study underscores the significance of agile methodologies, such as Lean Startup, which have gained recognition as a valuable model for enhancing the flexibility and adaptability of digital ventures in the face of competitive challenges. The capacity of these models to expeditiously recalibrate business strategies and function efficaciously is paramount in a digital milieu, where celerity and adaptability are indispensable for success (Bican & Brem, 2020; Hommel & Bican, 2020). The findings of the study indicate that enterprises that adopt these agile methodologies not only demonstrate responsiveness to market changes but also enhance their innovation and decision-making capabilities (Rangaswamy et al., 2020).
In terms of practical implications, the results indicate that entrepreneurs and managers of digital companies must understand and apply these models to optimize their financial and administrative processes. The integration of AI and automation tools must be accompanied by a continuous focus on staff training, as the successful implementation of these technologies depends on the team’s ability to adapt to new tools and processes (Braune & Dana, 2022). Furthermore, it is recommended that entrepreneurs take into account external variables, such as market conditions and government regulations, in order to design strategies that adequately respond to changes in the environment (Ghezzi & Cavallo, 2020; Steininger, 2019).
In conclusion, this study makes a significant contribution to the extant literature by proposing a conceptual framework for future research on the dynamic interaction between internal and external variables in the financial and administrative management models of digital ventures. The contributions of this study also have important practical implications, as they highlight the need for firms to adopt a holistic approach that combines advanced technology, agile methodologies, and organizational flexibility to ensure their long-term competitiveness and sustainability (Bican & Brem, 2020; Hassan et al., 2023; Kumar et al., 2024).
4.1. Theoretical Implications
The present study has been designed to analyze the current state of financial and administrative management models for digital ventures, with a view to providing valuable insights into the theoretical foundations of these models and their implications for research. Firstly, the study makes a significant contribution to the extant literature by offering a comprehensive review of existing models, based on 354 articles from reputable databases such as Scopus and Web of Science. Employing bibliometric techniques, it identifies key themes and trends in the research, shedding light on the evolution and future trajectory of financial and administrative management in digital ventures. While this study consolidates and synthesizes the extant literature, it also identifies gaps in the current research, particularly concerning the integration of external variables (such as resource management, operational efficiency, adaptability, technological innovation) and internal variables (market conditions, government regulations, and economic trends). By offering a conceptual framework for future research on the dynamic interaction between these variables and their impact on digital entrepreneurs, the study makes a significant contribution to the field. This framework is designed to serve as a guide for researchers, encouraging them to explore new models and test theories that explain the interplay between financial planning, technological innovation, and organizational agility in digital ventures.
4.2. Practical Implications
In addition to theoretical contributions, this study provides practical implications for digital entrepreneurs, managers, and system developers. By underscoring the mounting academic interest in financial and administrative management models, it emphasizes the significance of comprehending and implementing various financial instruments (e.g., valuation and discounted cash flow) and administrative frameworks (e.g., RocaSalvatella and INCIPY) for enhancing decision-making processes in digital contexts. The study also emphasizes the role of external and internal variables in shaping the success of digital ventures, pointing out the need for entrepreneurs to consider factors like operational efficiency, market conditions, and government regulations in their strategies. A review of the extant literature reveals a significant increase in research on agile methodologies, such as Lean Startup, which enhance organizational agility and resilience in the face of digital disruption. System designers and managers can leverage these findings to design more effective systems and strategies that support digital resilience, mitigate the challenges of the digital environment, and capitalize on emerging opportunities. It is imperative to acknowledge these factors to facilitate adaptation to rapid technological advancements and to navigate a volatile market environment.
4.3. Limitations
Whilst the present study provides valuable insights, it is not without its limitations. The selection of articles based on specific criteria may have resulted in the exclusion of significant contributions, such as industry reports, books, and conference papers, which could offer additional perspectives. Furthermore, given that research on financial and administrative management models for digital ventures is still in its early stages of development, many studies remain fragmented, which complicates the consolidation of all relevant findings and the provision of quantitative analysis of their effects. The study posits that future research should address these limitations by conducting replicative studies in diverse contexts and technological applications to refine and expand the current framework. Additionally, more comprehensive analyses integrating both qualitative and quantitative approaches could provide deeper insights into the complexities of managing digital ventures in a rapidly evolving technological landscape.
5. Conclusions
The research employs an SLR using bibliometric techniques to examine the importance of financial and administrative management models in digital entrepreneurship, focusing on articles published in Scopus and Web of Science between 2019 and 2024. The study is divided into two parts: the first part comprises a bibliometric analysis, using tools such as VOSviewer and R-Bibliometrix; and the second part consists of an analysis of the SLR results, carried out using bibliometric methods. The most relevant articles, countries, and most cited keywords were identified, as well as the theoretical models, variables, and associated technological tools.
The bibliometric analysis enabled the measurement of the impact of the literature, with particular attention to the most influential articles, including Verhoef et al. (2021), Hanelt et al. (2021), and Ghezzi and Cavallo (2020), which have been cited 778, 301, and 2021 times, respectively, and have contributed significantly to the literature on administrative and financial management models in digital entrepreneurship in the context of DT in business models. Verhoef et al. identify the key stages of DT and its impact on organizational strategies, while Hanelt et al. propose a framework on organizational change towards more flexible structures driven by digital ecosystems. Ghezzi and Cavallo demonstrate how LS approaches can foster innovation in digital startups through agile and flexible organizational structures.
China (37), Germany (27), and the United Kingdom (23) are the countries with the highest number of documents, followed by a number of Latin American countries with a comparatively low number of documents, including Brazil (9), Colombia (2), Chile (1), Ecuador (1), Mexico (1), and Peru (1).The contributions from these countries serve to broaden the knowledge of the subject and motivate other countries to research it. The keywords ‘Innovation’ (539.198), ‘Entrepreneur’ (95.502), Business models’ (71.05), and ‘Finance’ (303.075) are evidence that the extant literature focuses on understanding how the models applied in digital businesses affect their internal functioning, and their interaction with the external environment, including regulatory compliance, financial and administrative management, business innovation, and economic growth.
In the context of financial management models, it can be concluded that they provide entrepreneurs with key tools to optimize the decision-making process in digital ventures, especially in an environment characterized by high uncertainty and market fluctuations. Consequently, models such as the DCF, the ALM, and sensitivity analysis are fundamental to assess the value and financial viability of companies; in turn, they allow entrepreneurs to anticipate scenarios and manage risks. Asset allocation is also crucial to maximize return on investment, considering the specificities of the digital environment. In general, these models contribute to more accurate financial planning, although their effectiveness depends on the ability of companies to adapt them to their particular needs and conditions.
In the domain of management, the proposed models—RocaSalvatella, INCIPY, and TETR4DIG—offer conceptual frameworks for change management and innovation in digital organizations. These models address the importance of digital strategy, technology integration and adaptation to a dynamic business environment. Models such as the RBV and the RGM also emphasize the need for adequate resources and clear objectives to ensure the success of digital enterprises. Conversely, models such as the HRM, the OSM, and the TMM underscore the significance of organizational culture, flexibility, and a systemic approach in the management of digital enterprises. These management approaches provide a robust foundation for enhancing operational efficiency, adapting to rapid change, and fortifying the sustainability of digital enterprises.
In terms of external variables that have a direct impact on business management, factors such as resource management, operational efficiency, organizational adaptability, financial planning and technological innovation were identified as key determinants of a firm’s competitiveness in a globalized environment. These factors facilitate the management of risks inherent in the external environment and the identification of new growth opportunities. From an internal perspective, factors such as market conditions, government regulations and economic trends play a key role in influencing strategic decision-making processes.
The utilization of advanced technological tools, including data collection and specialized financial planning, has been demonstrated to enhance decision-making processes and optimize resource allocation. The implementation of AI and automation has been demonstrated to enhance operational efficiency, reduce expenditure, and stimulate innovation within the domain of financial management. Furthermore, cloud storage ensures the security and accessibility of data in real time. Financial management models in digital ventures empower entrepreneurs to implement effective strategies, thereby improving resource management and ensuring long-term viability in the digital environment.
The review has resulted in the proposal of ten future research projects, which aim to investigate various topics related to the management models of digital enterprises. Firstly, the impact of financial management models on the digitization of products, services, and processes will be investigated, focusing on scalability and flexibility, as well as the use of AI. Secondly, the impact of digital capabilities and organizational culture on the financial performance of start-ups will be studied. The relationship between the digitization of processes and operational efficiency is also to be analyzed, as well as exploring how external factors, such as regulation, influence financial strategies in different contexts (Asian or US). The interdependence between digital strategy, consumer behavior, and financial decisions will also be examined. Finally, the study will examine how small companies can manage the digital transition with flexible financial strategies, agile methodologies such as LS, and assess the impact of digital culture on financial sustainability.
Author Contributions
Authors L.C.G.C., L.H.A., D.R.P. and M.S.R.B. participated in the conception and design of the study. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The Universidad Cooperativa de Colombia funded this research. Project INV3663. Financial and Administrative Management Model for digital ventures.
Acknowledgments
Universidad Cooperativa de Colombia, Ibagué campus.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Abdullah, A. A. H., & Almaqtari, F. A. (2024). The impact of artificial intelligence and Industry 4.0 on transforming accounting and auditing practices. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, 10(1), 100218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S., Kim, K.-S., & Lee, K.-H. (2022). Technological capabilities, entrepreneurship and innovation of technology-based start-ups: The resource-based view. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, 8(3), 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ababneh, H., Alotoum, F., Dalbouh, M., Popova, O., Myroshnychenko, G., & Mugableh, M. (2024). Managing the modification of digital marketing and logistics under the influence of artificial intelligence. Acta Logistica, 11(03), 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfarizi, M., Widiastuti, T., & Ngatindriatun. (2024). Exploration of technological challenges and public economic trends phenomenon in the sustainable performance of Indonesian digital MSMEs on Industrial Era 4.0. Journal of Industrial Integration and Management, 9(01), 65–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkasassbeh, W. A. K. (2023). Digital entrepreneurship as one of the applications of contemporary administration in the entrepreneurial orientations. Journal of Law and Sustainable Development, 11(12), e1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloulou, M., Grati, R., Al-Qudah, A. A., & Al-Okaily, M. (2024). Does FinTech adoption increase the diffusion rate of digital financial inclusion? A study of the banking industry sector. Journal of Financial Reporting and Accounting, 22(2), 289–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arefmanesh, Z., Taftiyan, A., & Darvishi, S. (2024). A comprehensive analysis of startup valuation models: Insights from meta-synthesis. Iranian Journal of Accounting, Auditing and Finance, 8(3), 43–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aria, M., & Cuccurullo, C. (2017). bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. Journal of Informetrics, 11(4), 959–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audretsch, D. B., Belitski, M., Caiazza, R., Drapeau, M. D., Menter, M., & Wales, W. J. (2024). Resilience and digitally-advanced entrepreneurship. Entrepreneurship & Regional Development, 36(1–2), 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, M., Bussoli, C., & Fattobene, L. (2024). Digital financial consumers’ decision-making: A systematic literature review and integrative framework. International Journal of Bank Marketing, 42(7), 1978–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoni, F., Bonini, S., Capizzi, V., Colombo, M. G., & Manigart, S. (2022). Digitization in the market for entrepreneurial finance: Innovative business models and new financing channels. Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice, 46(5), 1120–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, D. A. (2020). A review of asset liability management models (pp. 1–16). SocArXiv ub69x. Center for Open Science. Available online: https://osf.io/ub69x_v1 (accessed on 25 March 2025). [CrossRef]
- Bican, P. M., & Brem, A. (2020). Digital business model, digital transformation, digital entrepreneurship: Is there a sustainable “digital”? Sustainability, 12(13), 5239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, J. H., Diegel, W., & Fisch, C. (2024). How venture capital funding changes an entrepreneur’s digital identity: More self-confidence and professionalism but less authenticity! Review of Managerial Science, 18, 2287–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, J. H., Groh, A., Hornuf, L., Vanacker, T., & Vismara, S. (2021). The entrepreneurial finance markets of the future: A comparison of crowdfunding and initial coin offerings. Small Business Economics, 57(2), 865–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braune, E., & Dana, L. (2022). Digital entrepreneurship: Some features of new social interactions. Canadian Journal of Administrative Sciences/Revue Canadienne Des Sciences de l’Administration, 39(3), 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallo, A., Ghezzi, A., Dell’Era, C., & Pellizzoni, E. (2019). Fostering digital entrepreneurship from startup to scaleup: The role of venture capital funds and angel groups. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 145, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cueto, L. J., Frisnedi, A. F. D., Collera, R. B., Batac, K. I. T., & Agaton, C. B. (2022). Digital innovations in MSMEs during economic disruptions: Experiences and challenges of young entrepreneurs. Administrative Sciences, 12(1), 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dana, L.-P., Crocco, E., Culasso, F., & Giacosa, E. (2024). Mapping the field of digital entrepreneurship: A topic modeling approach. International Entrepreneurship and Management Journal, 20(2), 1011–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decarolis, F., & Li, M. (2023). Regulating online search in the EU: From the android case to the digital markets act and digital services act. International Journal of Industrial Organization, 90, 102983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Clerck, T., Aelterman, N., Haerens, L., & Willem, A. (2021). Enhancing volunteers capacity in all-volunteer nonprofit organizations: The role of volunteer leaders’ reliance on effective management processes and (de)motivating leadership. Nonprofit Management and Leadership, 31(3), 481–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mattos, C. A., Correia, F. C., & Kissimoto, K. O. (2024). Artificial intelligence capabilities for demand planning process. Logistics, 8(2), 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Vaio, A., Hassan, R., & Alavoine, C. (2022). Data intelligence and analytics: A bibliometric analysis of human–Artificial intelligence in public sector decision-making effectiveness. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 174, 121201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donthu, N., Kumar, S., Mukherjee, D., Pandey, N., & Lim, W. M. (2021). How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: An overview and guidelines. Journal of Business Research, 133, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echchakoui, S. (2020). Why and how to merge Scopus and Web of Science during bibliometric analysis: The case of sales force literature from 1912 to 2019. Journal of Marketing Analytics, 8(3), 165–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elia, G., Margherita, A., & Passiante, G. (2020). Digital entrepreneurship ecosystem: How digital technologies and collective intelligence are reshaping the entrepreneurial process. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 150, 119791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estensoro, M., Larrea, M., Müller, J. M., & Sisti, E. (2022). A resource-based view on SMEs regarding the transition to more sophisticated stages of industry 4.0. European Management Journal, 40(5), 778–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estep, C., Griffith, E. E., & MacKenzie, N. L. (2024). How do financial executives respond to the use of artificial intelligence in financial reporting and auditing? Review of Accounting Studies, 29(3), 2798–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauzi, T. H., Harits, B., Danial, D. M., & Komariah, K. (2020). Adaptive strategies of external environmental effects in digital entrepreneurship in the strategic management perspective. Academic Journal of Interdisciplinary Studies, 9(3), 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonts-Fernández, C. L., & Stable-Rodriguez, Y. (2024). Modelo para la evaluación de competencias digitales, informacionales y mediáticas para la transformación digital. Revista Gestión de Las Personas y Tecnología, 17(49), 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, C. J., Plant, K. L., & McIlroy, R. C. (2025). The never-ending nightshift: Insights into organisational adaptation during COVID-19. Safety Science, 184, 106740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, M., Godinho, L., & Rodrigues, M. (2021). Exploring the influence of digital entrepreneurship on SME digitalization and management. Small Enterprise Research, 28(3), 269–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghezzi, A. (2019). Digital startups and the adoption and implementation of lean startup approaches: Effectuation, bricolage and opportunity creation in practice. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 146, 945–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghezzi, A., & Cavallo, A. (2020). Agile business model innovation in digital entrepreneurship: Lean startup approaches. Journal of Business Research, 110, 519–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghi, T., Thu, N., Huan, N., & Trung, N. (2022). Human capital, digital transformation, and firm performance of startups in Vietnam. Management, 26(1), 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Martin, C. A., Guerrero, W. A., Camacho-Galindo, S., Guerrero-Martin, L. E., Arévalo, J. C., da Fernandes, F. A. S., Correa, E. S., & da Moura, T. R. S. (2024). Digital transformation in financial and economic engineering: Tools, challenges and opportunities for business management. Revista de Gestão e Secretariado, 15(11), e4469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X., Hu, Y., Wang, L., & Zhou, R. (2024). Enterprise digital management: Research review, current status and prospects. Management System Engineering, 3(1), 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanelt, A., Bohnsack, R., Marz, D., & Antunes Marante, C. (2021). A systematic review of the literature on digital transformation: Insights and implications for strategy and organizational change. Journal of Management Studies, 58(5), 1159–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A., Elrahman, M. G. S. A., Ali, S. A., Abdulkhaleq, N. M. S., Dahlan, M., & Shaker, G. (2023). Using Artificial Intelligence (AI) in the Management Process. In B. Alareeni, A. Hamdan, R. Khamis, & R. E. Khoury (Eds.), Digitalisation: Opportunities and challenges for business. ICBT 2022. Lecture notes in networks and systems (Vol. 620). Springer. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hommel, K., & Bican, P. M. (2020). Digital entrepreneurship in finance: Fintechs and funding decision criteria. Sustainability, 12(19), 8035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, M., ud din, A., Haleem, M., & Ahmad, I. (2023). Digital entrepreneurial acceptance: An examination of technology acceptance model and do-it-yourself behavior. Journal of Innovation and Entrepreneurship, 12(1), 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaloliddin, R. (2023). Digitalization in global trade: Opportunities and challenges for investment. Global Trade and Customs Journal, 18(10), 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H., Miao, Z., Wan, J., & Lin, L. (2024). Digital transformation and financial performance: The moderating role of entrepreneurs’ social capital. Technology Analysis & Strategic Management, 36(8), 1978–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Júdice, P., Pinto, L., & Santos, J. L. (2021). Bank strategic asset allocation under a unified risk measure. Expert Systems with Applications, 185, 115574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassim, J., Ahmad, J., Hamzah, M. I. M., & Wahab, J. A. (2011). Developing management models in malaysian context for the gallantry of national schools in West Malaysia. Procedia—Social and Behavioral Sciences, 28, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim-Duc, N., & Nam, P. K. (2024). Earnings growth rates in business valuation models: The impossible quaternity. Global Finance Journal, 60, 100930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koebe, P. (2025). How digital technologies and AI contribute to achieving the health-related SDGs. International Journal of Information Management Data Insights, 5(1), 100298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreiterling, C. (2023). Digital innovation and entrepreneurship: A review of challenges in competitive markets. Journal of Innovation and Entrepreneurship, 12(1), 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M., Raut, R. D., Mangla, S. K., Ferraris, A., & Choubey, V. K. (2024). The adoption of artificial intelligence powered workforce management for effective revenue growth of micro, small, and medium scale enterprises (MSMEs). Production Planning & Control, 35(13), 1639–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kun, E. (2024). Challenges in regulating cloud service providers in EU financial regulation: From operational to systemic risks, and examining challenges of the new oversight regime for critical cloud service providers under the Digital Operational Resilience Act. Computer Law & Security Review, 52, 105931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunduru, A. R. (2023). Effective usage of artificial intelligence in enterprise resource planning applications. International Journal of Computer Trends and Technology, 71(4), 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladeira, M. J. M., Ferreira, F. A. F., Ferreira, J. J. M., Fang, W., Falcão, P. F., & Rosa, Á. A. (2019). Exploring the determinants of digital entrepreneurship using fuzzy cognitive maps. International Entrepreneurship and Management Journal, 15(4), 1077–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, C., Tan, F. T. C., Tan, B., & Faisal, F. (2022). The emancipatory potential of digital entrepreneurship: A study of financial technology-driven inclusive growth. Information & Management, 59(3), 103384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokuge, S., Sedera, D., Grover, V., & Sarker, S. (2025). Orchestrating digital technologies with incumbent enterprise systems for attaining innovation. Information & Management, 62(1), 104066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y., Peng, Y., & Zeng, L. (2021). Digital financial capability and entrepreneurial performance. International Review of Economics & Finance, 76, 55–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauro, M., Noto, G., Prenestini, A., & Sarto, F. (2024). Digital transformation in healthcare: Assessing the role of digital technologies for managerial support processes. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 209, 123781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D., Shamseer, L., Clarke, M., Ghersi, D., Liberati, A., Petticrew, M., Shekelle, P., & Stewart, L. A. (2015). Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Systematic Reviews, 4(1), 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, D., Lim, W. M., Kumar, S., & Donthu, N. (2022). Guidelines for advancing theory and practice through bibliometric research. Journal of Business Research, 148, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muldoon, J., Skorodziyevskiy, V., Gould, A. M., & Joullié, J.-E. (2024). Agency theory and social entrepreneurship: An axe that needs sharpening. The International Journal of Entrepreneurship and Innovation. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T. M. P., Nguyen, T. M. A., Tran, M. D., Le, Q. L., & Nguyen, D. N. (2024). Determinants influencing investment decisions of individual investors: The case of the developing economy. Journal of Governance and Regulation, 13(1), 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen Ngoc, H., Mohammed Abdelkader, E., Al-Sakkaf, A., Alfalah, G., & Zayed, T. (2024). A hybrid AHP-MAUT model for assessing competitiveness of construction companies: A case study of construction companies in Vietnam and Canada. Construction Innovation, 24(5), 1320–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemand, T., Rigtering, J. P. C., Kallmünzer, A., Kraus, S., & Maalaoui, A. (2021). Digitalization in the financial industry: A contingency approach of entrepreneurial orientation and strategic vision on digitalization. European Management Journal, 39(3), 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostapenko, T., Ponomarov, O., Turlo, Y., Osypova, Y., & Onopriienko, O. (2024). Defining the directions for the impact of administrative management tools on the project management system. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 2(13), 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M. J., Moher, D., Bossuyt, P. M., Boutron, I., Hoffmann, T. C., Mulrow, C. D., Shamseer, L., Tetzlaff, J. M., Akl, E. A., Brennan, S. E., Chou, R., Glanville, J., Grimshaw, J. M., Hróbjartsson, A., Lalu, M. M., Li, T., Loder, E. W., Mayo-Wilson, E., McDonald, S., … McKenzie, J. E. (2021). PRISMA 2020 explanation and elaboration: Updated guidance and exemplars for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ, 372, n160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proksch, D., Rosin, A. F., Stubner, S., & Pinkwart, A. (2024). The influence of a digital strategy on the digitalization of new ventures: The mediating effect of digital capabilities and a digital culture. Journal of Small Business Management, 62(1), 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangaswamy, A., Moch, N., Felten, C., Van Bruggen, G., Wieringa, J. E., & Wirtz, J. (2020). The role of marketing in digital business platforms. Journal of Interactive Marketing, 51(1), 72–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redondo-Rodríguez, L., Yábar, D. C. P.-B., & Díaz-Garrido, E. (2023). Impact of technological innovation on digital entrepreneurship and the effects on the economy. International Entrepreneurship and Management Journal, 19(3), 1501–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, E., & Floyd, S. (2024). Strategic leaders’ ecosystem vision formation and digital transformation: A motivated interactional lens. Strategic Entrepreneurship Journal, 18(1), 103–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, D. L. (2016). The digital transformation playbook. Columbia University Press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo-Spena, T., Tregua, M., D’Auria, A., & Bifulco, F. (2022). A digital business model: An illustrated framework from the cultural heritage business. International Journal of Entrepreneurial Behavior & Research, 28(8), 2000–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samara, G., & Terzian, J. (2021). Challenges and opportunities for digital entrepreneurship in developing countries. Digital Entrepreneurship, 283, 283–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satalkina, L., & Steiner, G. (2020). Digital entrepreneurship and its role in innovation systems: A systematic literature review as a basis for future research avenues for sustainable transitions. Sustainability, 12(7), 2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayari, K., Jannathl Firdouse, M. K., & Al Abri, F. (2025). Artificial intelligence and machine learning adoption in the financial sector: A holistic review. IAES International Journal of Artificial Intelligence (IJ-AI), 14(1), 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalihah, A., Jaja Raharja, S., & Purnomo, M. (2024). Decoding organizational dynamics: Navigating the ambiguity between flexibility and agility in digital entrepreneurship through a systematic literature review. Journal of Economics, Finance and Management Studies, 7(2), 930–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A. K., & Thirumoorthi, P. (2019). The impact of digital disruption technologies on customer preferences: The case of retail commerce. International Journal of Recent Technology and Engineering (IJRTE), 8(3), 1255–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steininger, D. M. (2019). Linking information systems and entrepreneurship: A review and agenda for IT-associated and digital entrepreneurship research. Information Systems Journal, 29(2), 363–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkachenko, V., Klymchuk, M., & Tkachenko, I. (2021). Recursive and convergence methodology of the investment management of the enterprise digitalization processes. Management Systems in Production Engineering, 29(1), 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, J., & Figueroa, J. (2022). Una Aproximación de los modelos de transformación digital en la gestión de las empresas comerciales. Carácter—Revista Científica de La Universidad Del Pacífico, 10(1), 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukko, J., Nasiri, M., Saunila, M., & Rantala, T. (2019). Sustainability strategy as a moderator in the relationship between digital business strategy and financial performance. Journal of Cleaner Production, 236, 117626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, N., Upadhyay, S., & Dwivedi, Y. K. (2022). Theorizing artificial intelligence acceptance and digital entrepreneurship model. International Journal of Entrepreneurial Behavior & Research, 28(5), 1138–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eck, N. J., & Waltman, L. (2010). Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics, 84(2), 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoef, P. C., Broekhuizen, T., Bart, Y., Bhattacharya, A., Qi Dong, J., Fabian, N., & Haenlein, M. (2021). Digital transformation: A multidisciplinary reflection and research agenda. Journal of Business Research, 122, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S., & Zhang, H. (2025). Enhancing SMEs sustainable innovation and performance through digital transformation: Insights from strategic technology, organizational dynamics, and environmental adaptation. Socio-Economic Planning Sciences, 98, 102124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X., Yu, M., Liu, H., & Zhao, Q. (2022). How does financial literacy affect digital entrepreneurship willingness and behavior—Evidence from Chinese villagers’ participation in entrepreneurship. Sustainability, 14(21), 14103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y., Yang, K., Chen, L., Lin, H., Yu, M., & Jin, R. (2023). Digital entrepreneurship: Global maps and trends of research. Journal of Business & Industrial Marketing, 38(3), 637–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X., Liu, Y., Geng, X., & Wei, D. (2022). The digital entrepreneurship era: How to motivate innovativeness in middle management teams? The vertical organisational pervasiveness of chief executive officer entrepreneurial orientation. Frontiers in Psychology, 13, 775558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).