A Review of Electro Conductive Textiles Utilizing the Dip-Coating Technique: Their Functionality, Durability and Sustainability
Abstract
:1. Introduction
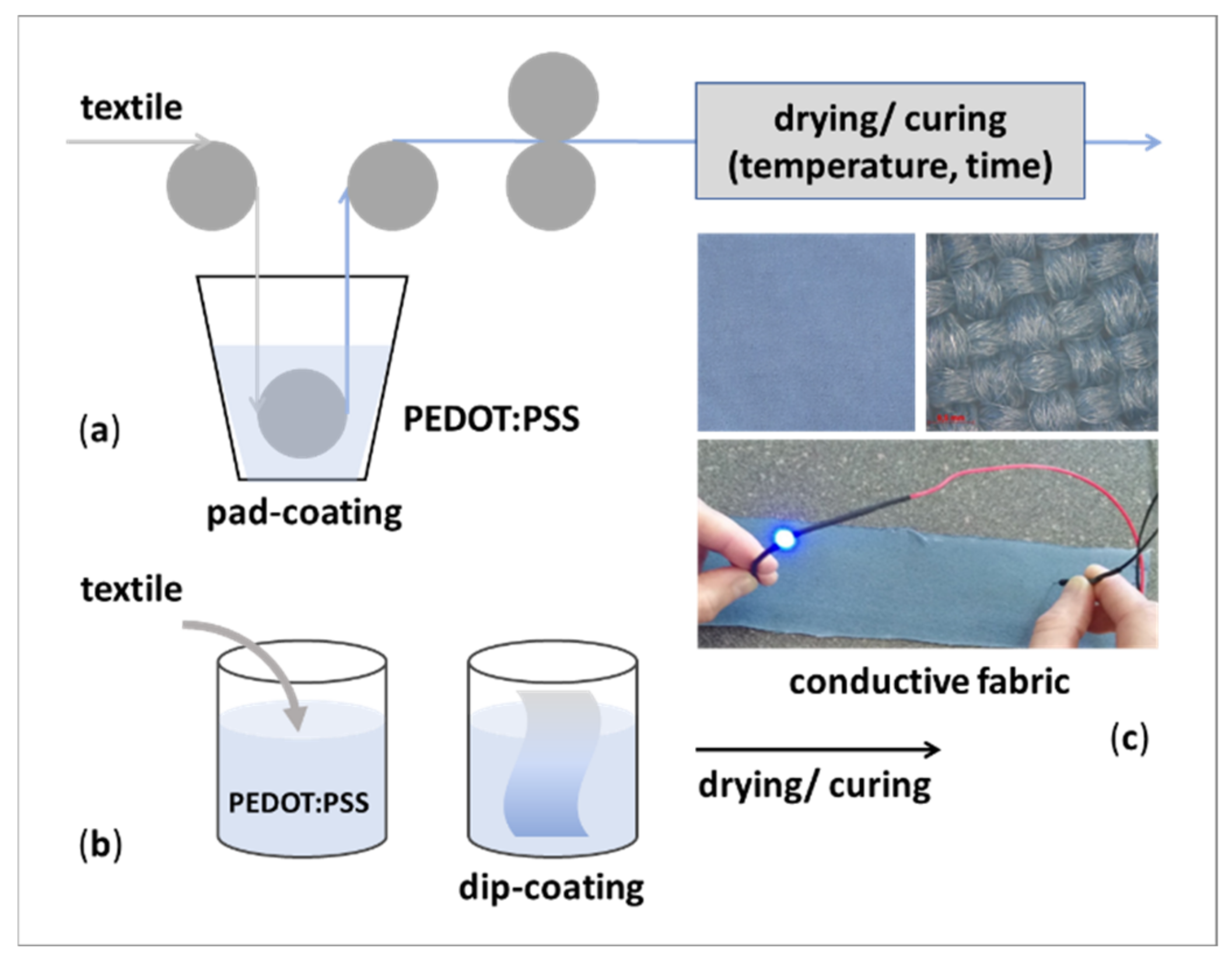
2. Dip-Coating to Obtain Electro Conductive Textiles
2.1. Electro Conductive Polymers
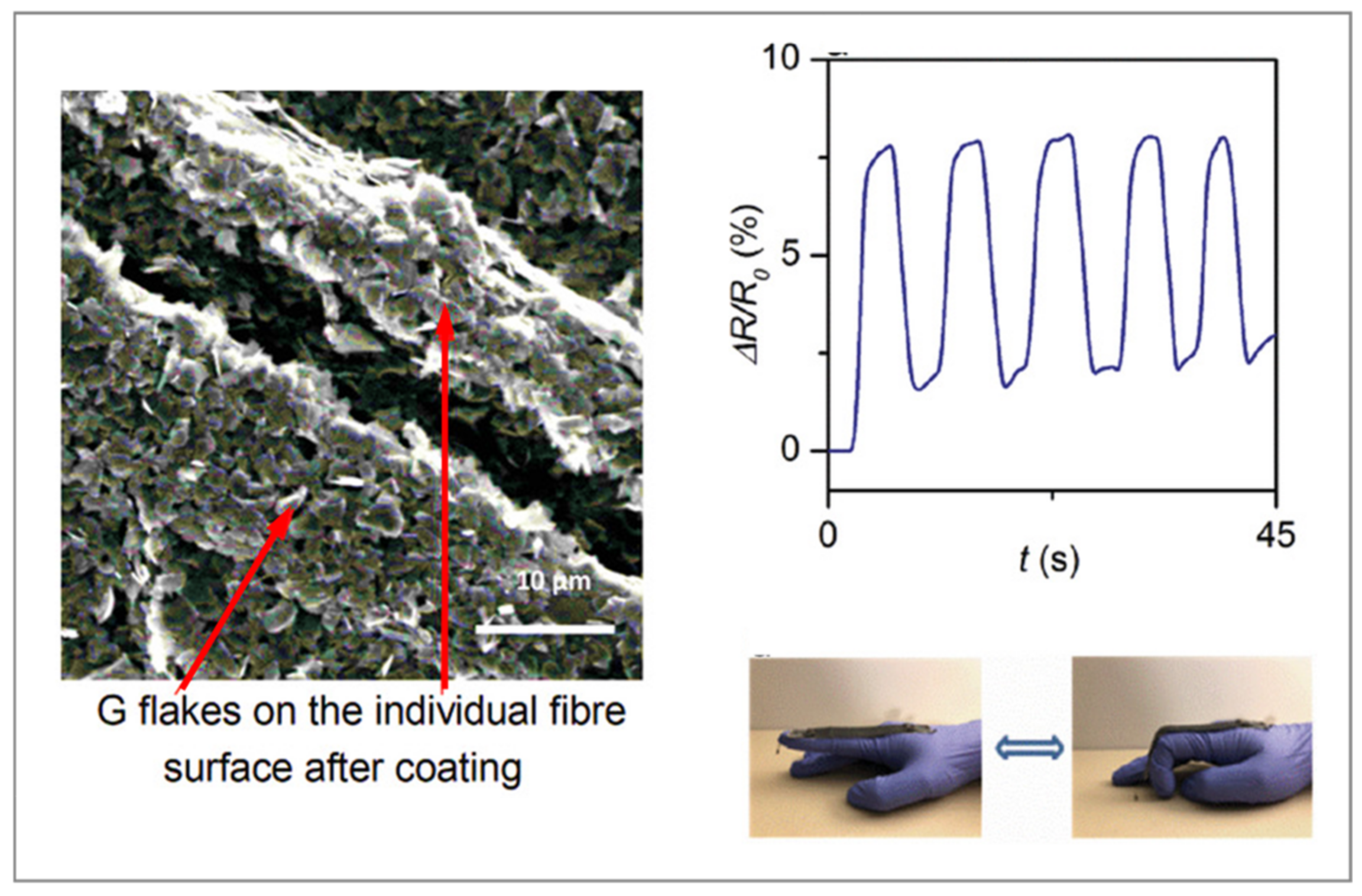
2.2. Carbon-Based Materials
2.3. Metals and Metal-Based Materials
2.4. Combinations of Different Types of Conductive Compounds
3. Characterization of Conductive Textiles
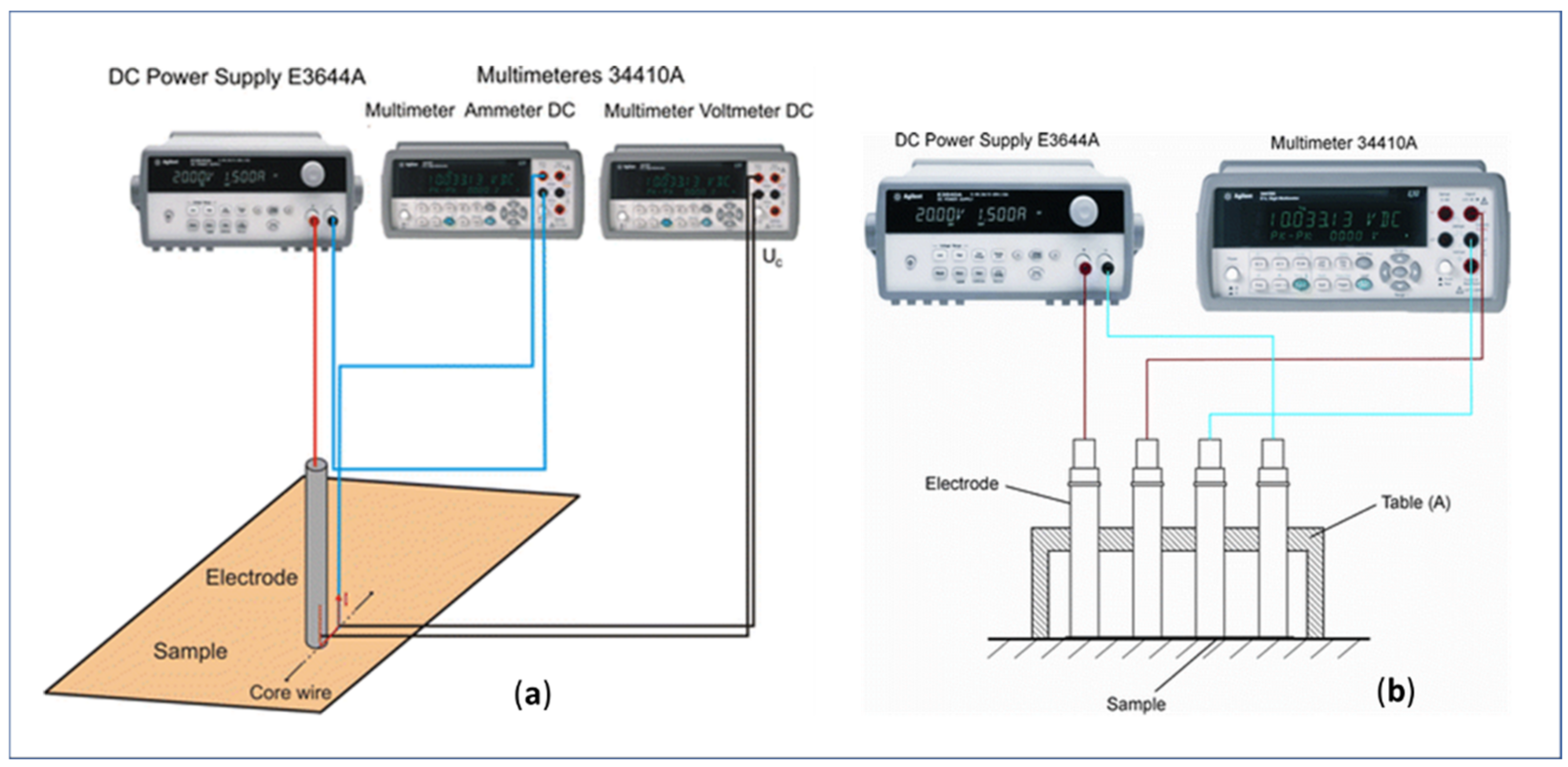
3.1. Electrical Conductivity
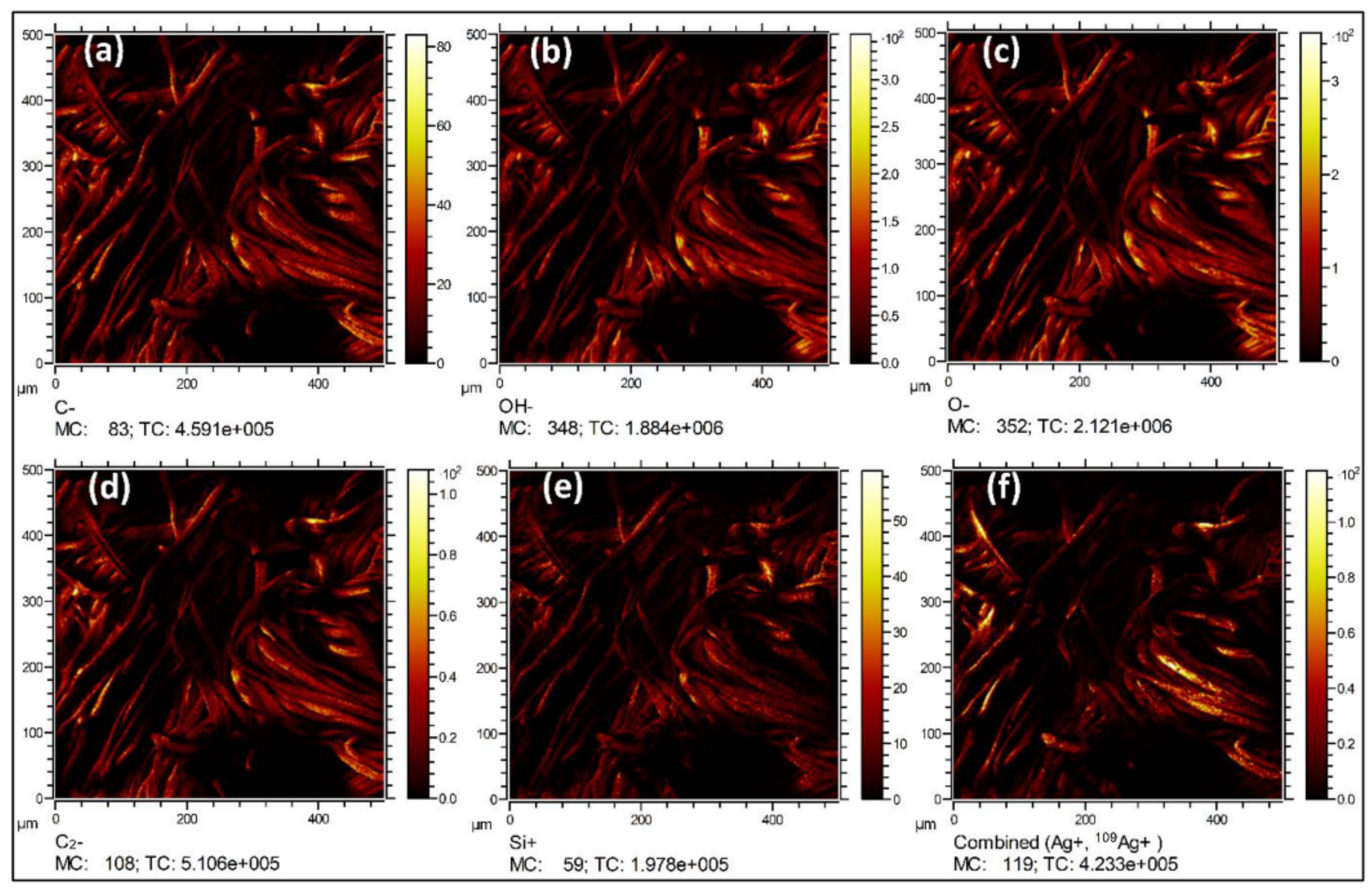
3.2. Morphological and Chemical Properties
3.3. Physical-Mechanical Properties
3.4. Comfort Properties (Moisture Absorption, Transport, Thermal Behavior)
4. Wash and Wear Durability
5. Multifunctionality of Conductive Textiles
6. Sustainability and End-Of-Life of Conductive Textiles
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fernández-Caramés, T.; Fraga-Lamas, P. Towards The Internet-of-Smart-Clothing: A Review on IoT Wearables and Garments for Creating Intelligent Connected E-Textiles. Electronics 2018, 7, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choudhry, N.A.; Arnold, L.; Rasheed, A.; Khan, I.A.; Wang, L. Textronics—A Review of Textile-Based Wearable Electronics. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2021, 23, 2100469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Du, X.; Luo, Y.; Lin, S.; Zhou, M.; Du, Z.; Cheng, X.; Wang, H. Hierarchical design of waterproof, highly sensitive, and wearable sensing electronics based on MXene-reinforced durable cotton fabrics. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 408, 127363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherston, J.; Paradiso, J.A.; Wang, K.-W.; Sohn, H.; Huang, H.; Lynch, J.P. SpaceSkin: Development of aerospace-grade electronic textile for simultaneous protection and high velocity impact characterization. In Proceedings of the Sensors and Smart Structures Technologies for Civil, Mechanical, and Aerospace Systems, Denver, CO, USA, 4–7 March 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ojstrsek, A.; Virant, N.; Fox, D.; Krishnan, L.; Cobley, A. The Efficacy of Polymer Coatings for the Protection of Electroless Copper Plated Polyester Fabric. Polymers 2020, 12, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Wang, M.; Qiang, Z.; Song, J.; Wang, Y.; Fan, Y.; You, Z.; Liao, Y.; Zhu, M.; Ye, C. Multi-functional and highly conductive textiles with ultra-high durability through ‘green’ fabrication process. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 406, 127140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehsanimehr, S.; Sonnier, R.; Najafi, P.; Ducos, F.; Badawi, M.; Formela, K.; Saeb, M.R.; Vahabi, H. Layer-by-layer polymer deposited fabrics with superior flame retardancy and electrical conductivity. React. Funct. Polym. 2022, 173, 105221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Yan, X. Dip-coating for fibrous materials: Mechanism, methods and applications. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2016, 81, 378–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseghai, G.B.; Malengier, B.; Fante, K.A.; Nigusse, A.B.; Van Langenhove, L. Development of a Flex and Stretchy Conductive Cotton Fabric Via Flat Screen Printing of PEDOT:PSS/PDMS Conductive Polymer Composite. Sensors 2020, 20, 1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gualandi, I.; Tessarolo, M.; Mariani, F.; Possanzini, L.; Scavetta, E.; Fraboni, B. Textile Chemical Sensors Based on Conductive Polymers for the Analysis of Sweat. Polymers 2021, 13, 894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acar, G.; Ozturk, O.; Golparvar, A.J.; Elboshra, T.A.; Böhringer, K.; Yapici, M.K. Wearable and Flexible Textile Electrodes for Biopotential Signal Monitoring: A review. Electronics 2019, 8, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, L.; Hoxie, S.; Andrew, T.L. Towards seamlessly-integrated textile electronics: Methods to coat fabrics and fibers with conducting polymers for electronic applications. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 7182–7193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Shu, L.; Li, Q.; Chen, S.; Wang, F.; Tao, X.M. Fiber-based wearable electronics: A review of materials, fabrication, devices, and applications. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 5310–5336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafalu, P.; Akbari, M.; Alberti, K.A.; Xu, Q.; Khademhosseini, A.; Sonkusale, S.R. A toolkit of thread-based microfluidics, sensors, and electronics for 3D tissue embedding for medical diagnostics. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2016, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, S.; Chatterjee, A. Conductive polymer-based electro-conductive textile composites for electromagnetic interference shielding: A review. J. Ind. Text. 2018, 47, 2228–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grancarić, A.M.; Jerković, I.; Koncar, V.; Cochrane, C.; Kelly, F.M.; Soulat, D.; Legrand, X. Conductive polymers for smart textile applications. J. Ind. Text. 2017, 48, 612–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grothe, T. Soft capacitor fibers using conductive polymers for electronic textiles. In Nanosensors and Nanodevices for Smart Multifunctional Textiles; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 189–202. [Google Scholar]
- Alhashmi Alamer, F.; Badawi, N.M.; Alodhayb, A.; Okasha, R.M.; Kattan, N.A. Effect of dopant on the conductivity and stability of three different cotton fabrics impregnated with PEDOT: PSS. Cellulose 2020, 27, 531–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseghai, G.B.; Mengistie, D.A.; Malengier, B.; Fante, K.A.; Van Langenhove, L. PEDOT:PSS-Based Conductive Textiles and Their Applications. Sensors 2020, 20, 1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Onggar, T.; Kruppke, I.; Cherif, C. Techniques and Processes for the Realization of Electrically Conducting Textile Materials from Intrinsically Conducting Polymers and Their Application Potential. Polymers 2020, 12, 2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojstrsek, A.; Gorgieva, S. Tailoring of Durable Conductive and UV-Shielding Properties on Cotton and Polyester Fabrics by PEDOT:PSS Screen-Printing. Polymers 2020, 12, 2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Lee, S.; Kim, H. Electrical heating performance of electro-conductive para-aramid knit manufactured by dip-coating in a graphene/waterborne polyurethane composite. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Yuan, Q.; Du, H.; Ma, M.-G.; Si, C.; Wan, P. Multiresponsive MXene (Ti3C2T x)-decorated textiles for wearable thermal management and human motion monitoring. ACS Appl. Mater. Interf. 2020, 12, 34226–34234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadesse, M.G.; Mengistie, D.A.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Loghin, C.; Nierstrasz, V. Electrically conductive highly elastic polyamide/lycra fabric treated with PEDOT:PSS and polyurethane. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 9591–9602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, L.; Sun, B.; Li, W.; Jiang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, J.; Chen, S.; Ning, X.; Zhou, F.L. Flexible and Highly Conductive AgNWs/PEDOT:PSS Functionalized Aramid Nonwoven Fabric for High-Performance Electromagnetic Interference Shielding and Joule Heating. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2021, 306, 2100365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Kim, M. Intrinsically conducting polymer (ICP) coated aramid fiber reinforced composites for broadband radar absorbing structures (RAS). Compos. Sci. Technol. 2021, 211, 108827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Ganguly, S.; Remanan, S.; Das, N.C. Fabrication and investigation of 3D tuned PEG/PEDOT: PSS treated conductive and durable cotton fabric for superior electrical conductivity and flexible electromagnetic interference shielding. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2019, 181, 107682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indarit, N.; Kim, Y.H.; Petchsang, N.; Jaisutti, R. Highly sensitive polyaniline-coated fiber gas sensors for real-time monitoring of ammonia gas. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 26773–26779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lund, A.; Darabi, S.; Hultmark, S.; Ryan, J.D.; Andersson, B.; Ström, A.; Müller, C. Roll-to-Roll Dyed Conducting Silk Yarns: A Versatile Material for E-Textile Devices. Advan. Mater. Technol. 2018, 3, 1800251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lv, J.; Zhou, P.; Zhang, L.; Zhong, Y.; Sui, X.; Wang, B.; Chen, Z.; Xu, H.; Mao, Z. High-performance textile electrodes for wearable electronics obtained by an improved in situ polymerization method. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 361, 897–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Cai, K.; Chen, S.; Wang, H.; Shen, S.Z.; Donelson, R.; Lin, T. Thermoelectric fabrics: Toward power generating clothing. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zulan, L.; Zhi, L.; Lan, C.; Sihao, C.; Dayang, W.; Fangyin, D. Reduced Graphene Oxide Coated Silk Fabrics with Conductive Property for Wearable Electronic Textiles Application. Adv. Elect. Mat. 2019, 5, 1800648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, S.; Macintyre, C.R.; Wen, X.; Bahl, P.; Kumar, U.; Chughtai, A.A.; Joshi, R. Nanoparticles incorporated graphene-based durable cotton fabrics. Carbon 2020, 166, 148–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, N.; Afroj, S.; Tan, S.; He, P.; Fernando, A.; Carr, C.; Novoselov, K.S. Scalable Production of Graphene-Based Wearable E-Textiles. ASC Nano 2017, 11, 12266–12275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, B.; Facchetti, A. Mechanically Flexible Conductors for Stretchable and Wearable E-Skin and E-Textile Devices. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, e1901408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Zheng, X.; Chen, M.; Sun, L.; Chen, J.; Wang, F.; Ma, Y. Enhancing the Linearity and Stability of a Fabric-Based Strain Sensor with Microfolded Graphene Structures. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yapici, M.K.; Alkhidir, T.; Samad, Y.A.; Liao, K. Graphene-clad textile electrodes for electrocardiogram monitoring. Sens. Actuat. B Chem. 2015, 221, 1469–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaev, D.V.; Evseev, Z.I.; Smagulova, S.A.; Antonova, I.V. Electrical Properties of Textiles Treated with Graphene Oxide Suspension. Materials 2021, 14, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.; Zhao, R.; Qu, L.; Chen, Z.; Chen, S.; Zhu, S.; Song, W.; Zhang, X.; Sun, Y.; Fu, R. Stretchable and designable textile pattern strain sensors based on graphene decorated conductive nylon filaments. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2019, 304, 1900244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montazerian, H.; Rashidi, A.; Dalili, A.; Najjaran, H.; Milani, A.S.; Hoorfar, M. Graphene-Coated Spandex Sensors Embedded into Silicone Sheath for Composites Health Monitoring and Wearable Applications. Small 2019, 15, e1804991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afroj, S.; Tan, S.; Abdelkader, A.M.; Novoselov, K.S.; Karim, N. Highly Conductive, Scalable, and Machine Washable Graphene-Based E-Textiles for Multifunctional Wearable Electronic Applications. Adv. Funct. Mat. 2020, 30, 2000293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, J.; Zhou, S. Highly conductive and ultra-durable electronic textiles via covalent immobilization of carbon nanomaterials on cotton fabric. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 12273–12282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhai, H.; Chen, X.; Sun, R.; Lyu, S.; Fan, Y.; Yi, Y.; Chen, Z.; Jin, L.; et al. Moisture-Resilient Graphene-Dyed Wool Fabric for Strain Sensing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 13265–13274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Sun, Y.; Xu, J. (3-Mercaptopropyl) triethoxysilane-Modified Reduced Graphene Oxide-Modified Polyurethane Yarn Enhanced by Epoxy/Thiol Reactions for Strain Sensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 34865–34876. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Nie, W.; Hu, Q.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Zou, L.; Hong, X.; Yang, H.; Shen, J.; Li, C. Multifunctional RGO/Ti3C2Tx MXene fabrics for electrochemical energy storage, electromagnetic interference shielding, electrothermal and human motion detection. Mat. Des. 2021, 200, 109442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadi, M.S.; Pan, J.; Xu, A.; Cheng, D.; Cai, G.; Wang, X. Direct dip-coating of carbon nanotubes onto polydopamine-templated cotton fabrics for wearable applications. Cellulose 2019, 26, 7569–7579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.-S.; Moon, M.S.; Kim, B.H. Electronic Textiles Fabricated with Graphene Oxide-Coated Commercial Textiles. Coatings 2021, 11, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Qi, K.; Xin, J.H. Functionalization of cotton with carbon nanotubes. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 3454–3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, C.C.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, J. Flexible wearable sensors-an update in view of touch-sensing. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2021, 22, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Y.; Yu, H.; Wang, M.; Yang, X.; Li, Z.; Yang, F.; Wang, Y.; Tai, H.; Liao, Y.; Wu, J.; et al. A multifunctional wearable E-textile via integrated nanowire-coated fabrics. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 8399–8409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tian, W.; Liu, L.; Cheng, W.; Wang, W.; Liew, K.M.; Wang, B.; Hu, Y. Eco-friendly flame retardant and electromagnetic interference shielding cotton fabrics with multi-layered coatings. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 372, 1077–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojstrsek, A.; Plohl, O.; Gorgieva, S.; Kurecic, M.; Jancic, U.; Hribernik, S.; Fakin, D. Metallisation of Textiles and Protection of Conductive Layers: An Overview of Application Techniques. Sensors 2021, 21, 3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, A.; Wu, Y.; Fenech-Salerno, B.; Torrisi, F.; Carmichael, T.B.; Müller, C. Conducting materials as building blocks for electronic textiles. MRS Bull. 2021, 46, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghdi, S.; Rhee, K.Y.; Hui, D.; Park, S.J. A review of conductive metal nanomaterials as conductive, transparent, and flexible coatings, thin films, and conductive fillers: Different deposition methods and applications. Coatings 2018, 8, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.; Yu, W.; Du, Z. Study of electrothermal properties of silver nanowire/polydopamine/cotton-based nanocomposites. Cellulose 2019, 26, 5995–6007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azari, A.; Nabizadeh, R.; Nasseri, S.; Mahvi, A.H.; Mesdaghinia, A.R. Comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis of dyes adsorption by carbon-based adsorbent materials: Classification and analysis of last decade studies. Chemosphere 2020, 250, 126238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Feng, P.; Chen, X.; Chen, B.; Gonzalez, K.; Liu, J.; Kim, I.; Li, X. Cu coated soft fabric as anode for lithium metal batteries. Ener. Storage Mater. 2020, 26, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamun, M.A.A.; Islam, M.T.; Islam, M.M.; Sowrov, K.; Hossain, M.A.; Ahmed, D.M.; Shahariar, H. Scalable Process to Develop Durable Conductive Cotton Fabric. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2020, 2, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbič, A.; Gorjanc, M.; Simončič, B. Zinc Oxide for Functional Textile Coatings: Recent Advances. Coatings 2019, 9, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dudem, B.; Kim, D.H.; Yu, J.S. Triboelectric nanogenerators with gold-thin-film-coated conductive textile as floating electrode for scavenging wind energy. Nano Res. 2017, 11, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Pang, Z.; Ge, M. Sol-gel preparation and properties of electroconductive Sn–Al co-doped ZnO coated TiO2 whisker and its applications in textiles. Mater. Sci. Semic. Proc. 2021, 124, 105607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseghai, G.B.; Malengier, B.; Fante, K.A.; Nigusse, A.B.; Van Langenhove, L. Integration of Conductive Materials with Textile Structures, an Overview. Sensors 2020, 20, 6910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogotsi, Y.; Huang, Q. MXenes: Two-Dimensional Building Blocks for Future Materials and Devices. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 5775–5780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Wang, P.; Zhang, X.; Hu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Nie, W.; Zou, L.; Li, C.; Han, X. Breathable, durable and bark-shaped MXene/textiles for high-performance wearable pressure sensors, EMI shielding and heat physiotherapy. Compos. Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2022, 152, 106700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzun, S.; Seyedin, S.; Stoltzfus, A.L.; Levitt, A.S.; Alhabeb, M.; Anayee, M.; Strobel, C.J.; Razal, J.M.; Dion, G.; Gogotsi, Y. Knittable and washable multifunctional mxene-coated cellulose yarns. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1905015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faruk, M.O.; Ahmed, A.; Adak, B.; Marzana, M.; Hossain, M.M.; Mukhopadhyay, S. High performance 2D MXene based conducting polymer hybrids: Synthesis to emerging applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2021, 9, 10193–10215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Yin, R.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, D.; Shi, X.; Zhang, B.; Liu, C.; Shen, C. Conductive MXene/cotton fabric based pressure sensor with both high sensitivity and wide sensing range for human motion detection and E-skin. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 420, 127720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, B.; Lund, A.; Tian, Y.; Darabi, S.; Muller, C. Machine-Washable Conductive Silk Yarns with a Composite Coating of Ag Nanowires and PEDOT:PSS. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 27537–27544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirabad, R.; Ramazani Saadatabadi, A.; Siadati, M.H. Preparation of polyaniline/graphene coated wearable thermoelectric fabric using ultrasonic-assisted dip-coating method. Mater. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2020, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamer, F.A. Structural and electrical properties of conductive cotton fabrics coated with the composite polyaniline/carbon black. Cellulose 2018, 25, 2075–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Hu, J. Waterborne polyurethane based thermoelectric composites and their application potential in wearable thermoelectric textiles. Compos. Part B 2016, 107, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Jalil, M.A.; Hossain, M.M.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Adak, B.; Islam, M.T.; Parvez, M.S.; Mukhopadhyay, S. A PEDOT: PSS and graphene-clad smart textile-based wearable electronic Joule heater with high thermal stability. J. Mater. Chem. 2020, 8, 16204–16215. [Google Scholar]
- Lima, R.; Alcaraz-Espinoza, J.J.; da Silva, F.A.G., Jr.; de Oliveira, H.P. Multifunctional Wearable Electronic Textiles Using Cotton Fibers with Polypyrrole and Carbon Nanotubes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 13783–13795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, S.; Hou, L.; Lu, Y. An integrated wearable strain, temperature and humidity sensor for multifunctional monitoring. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manufac. 2021, 149, 106504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazani, I.; De Mey, G.; Hertleer, C.; Banaszczyk, J.; Schwarz, A.; Guxho, G.; Van Langenhove, L. About the collinear four-point probe technique´ s inability to measure the resistivity of anisotropic electroconductive fabrics. Text. Res. J. 2013, 83, 1587–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.; Bechtold, T. Conductive Fibers. Handb. Fibr. Mater. 2020, 13, 4298. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, A.; Nguyen, N.H.A.; Baheti, V.; Ashraf, M.; Militky, J.; Mansoor, T.; Noman, M.T.; Ahmad, S. Electrical conductivity and physiological comfort of silver coated cotton fabrics. J. Text. Inst. 2017, 109, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokarska, M.; Frydrysiak, M.; Zięba, J. Electrical properties of flat textile material as inhomegeneous and anisotropic structure. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Elect. 2013, 24, 5061–5068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tokarska, M. Characterization of electro-conductive textile materials by its biaxial anisotropy coefficient and resistivity. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 4093–4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kazani, I.; Hylli, M.; Berberi, P. Electrical Resistivity of Conductive Leather and Influence of Air Temperature and Humidity. Tekstilec 2021, 64, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Lu, H.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y. Electronic fibers and textiles: Recent progress and perspective. IScience 2021, 24, 102716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S.; Laing, R.; Tan, E.W.; Wilson, C. Encapsulation of Electrically Conductive Apparel Fabrics: Effects on Performance. Sensors 2020, 20, 4243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisung, G. Method evaluation: Electrical Surface Resistance Measurements on Coated Conductive Textiles. Master’s Theisis, University of Borås, Borås, Sweden, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Raji, R.K.; Miao, X.; Boakye, A. Electrical conductivity in textile fibers and yarns. AATCC J. Res. 2017, 4, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varnaitė-Žuravliova, S. The Types, Properties, and Applications of Conductive Textiles; Cambridge Scholars Publishing: Newcastle, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Lee, K.; Lin, J.; Koch, M. Comparison of electromagnetic shielding effectiveness properties of diverse conductive textiles via various measurement techniques. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2007, 192, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hearle, J. Fibre structure: Its formation and relation to performance. In Handbook of Textile Fibre Structure; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 3–21. [Google Scholar]
- Eichhorn, S.; Hearle, J.; Jaffe, M.; Kikutani, T. Handbook of Textile Fibre Structure: Volume 1: Fundamentals and Manufactured Polymer Fibres; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Villanueva, R.; Ganta, D.; Guzman, C. Mechanical, in-situ electrical and thermal properties of wearable conductive textile yarn coated with polypyrrole/carbon black composite. Mater. Res. Express 2018, 6, 016307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lu, Z.; Xin, B.; Liu, Y.; Cui, Y.; Hu, Y. All-solid-state flexible supercapacitor of Carbonized MXene/Cotton fabric for wearable energy storage. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 528, 146975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendjchi, A.; Khajavi, R.; Yousefi, A.A.; Yazdanshenas, M.E. Improved continuity of reduced graphene oxide on polyester fabric by use of polypyrrole to achieve a highly electro-conductive and flexible substrate. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 363, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, D.P.; Ferreira, A.; Fangueiro, R. Searching for Natural Conductive Fibrous Structures via a Green Sustainable Approach Based on Jute Fibers and Silver Nanoparticles. Polymers 2018, 10, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pei, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, S.; Dai, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, C. Facile preparation of superhydrophobic conductive textiles and the application of real-time sensor of joint motion sensor. Coll. Surf. Physicochem. Engin. Asp. 2021, 628, 127257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Siddiqui, M.O.R.; Iqbal, K. Specialty testing techniques for smart textiles. In Smart Textile Coatings and Laminates; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 99–116. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, J.; Gao, S.; Luo, H.; Wang, L.; Huang, X.; Guo, Z.; Lai, X.; Lin, L.; Li, R.K.Y.; Gao, J. Superhydrophobic and breathable smart MXene-based textile for multifunctional wearable sensing electronics. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 406, 126898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Du, Z. Preparation of a highly sensitive and stretchable strain sensor of MXene/silver nanocomposite-based yarn and wearable applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 45930–45938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.H.; Jiang, S.X.; Zheng, Y.D.; Lan, J.W. Electroless nickel deposition of a palladium-activated self-assembled monolayer on polyester fabric. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 127, 4186–4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, R.M.; Yousif, N.M.; Zohdy, M.H. Electrical conductivity and mechanical properties of conductive cotton fabrics. J. Ind. Text. 2021, 51, 3149S–3175S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goda, E.S.; Abu Elella, M.H.; Hong, S.E.; Pandit, B.; Yoon, K.R.; Gamal, H. Smart flame retardant coating containing carboxymethyl chitosan nanoparticles decorated graphene for obtaining multifunctional textiles. Cellulose 2021, 28, 5087–5105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouadil, B.; Amadine, O.; Essamlali, Y.; Cherkaoui, O.; Zahouily, M. A new route for the preparation of hydrophobic and antibacterial textiles fabrics using Ag-loaded graphene nanocomposite. Coll. Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 579, 123713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Park, C.H. Conductivity, superhydrophobicity and mechanical properties of cotton fabric treated with polypyrrole by in-situ polymerization using the binary oxidants ammonium Peroxodisulfate and ferric chloride. Text. Res. J. 2018, 89, 2376–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.L.; El-Naggar, M.E.; Hassabo, A.G. Preparation of hybrid nanoparticles to enhance the electrical conductivity and performance properties of cotton fabrics. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 12, 542–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marolleau, A.; Salaun, F.; Dupont, D.; Gidik, H.; Ducept, S. Influence of textile properties on thermal comfort. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, Busan, Korea, 25–27 August 2017; p. 182007. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.; Chen, Y.; He, H. Preparation and investigation of moisture transfer and electromagnetic shielding properties of double-layer electromagnetic shielding fabrics. J. Ind. Text. 2020, 49, 1357–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noman, M.T.; Petru, M.; Louda, P.; Kejzlar, P. Woven textiles coated with zinc oxide nanoparticles and their thermophysiological comfort properties. J. Nat. Fibers 2021, 19, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Shen, M.; Guo, X.; Jin, X.; Cao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, J. Ti3C2Tx MXene-decorated nanoporous polyethylene textile for passive and active personal precision heating. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 11396–11405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Li, J.; Li, M.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, G.; Li, Y.; Hou, C.; Wang, H. MXene-coated air-permeable pressure-sensing fabric for smart wear. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 46446–46454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supuren, G.; Oglakcioglu, N.; Ozdil, N.; Marmarali, A. Moisture management and thermal absorptivity properties of double-face knitted fabrics. Text. Res. J. 2011, 81, 1320–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Hu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Nie, W.; Wang, P.; Li, C. Roll-to-roll layer-by-layer assembly bark-shaped carbon nanotube/Ti3C2Tx MXene textiles for wearable electronics. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2021, 602, 680–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biermaier, C.; Bechtold, T.; Pham, T. Towards the Functional Ageing of Electrically Conductive and Sensing Textiles: A Review. Sensors 2021, 21, 5944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaman, S.U.; Tao, X.; Cochrane, C.; Koncar, V. Understanding the washing damage to textile ECG dry skin electrodes, embroidered and fabric-based; set up of equivalent laboratory tests. Sensors 2020, 20, 1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rotzler, S.; Krshiwoblozki, M.v.; Schneider-Ramelow, M. Washability of e-textiles: Current testing practices and the need for standardization. Text. Res. J. 2021, 91, 0040517521996727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotzler, S.; Schneider-Ramelow, M. Washability of e-textiles: Failure modes and influences on washing reliability. Textiles 2021, 1, 37–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.C.; Liu, W.; Lo, C.; Chen, C.-C. Laundering reliability of electrically conductive fabrics for e-textile applications. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 69th electronic components and technology conference (ECTC), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 28–31 May 2019; pp. 1826–1832. [Google Scholar]
- Kisannagar, R.R.; Singh, M.; Gupta, D. Multifunctional, Wash Durable and Re-usable Conductive Textiles for Wearable Electro/Physiological Monitoring. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2021, 306, 2000804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petz, P.; Eibensteiner, F.; Langer, J. Reliability of Conductive Textile Sensors Exposed to Ageing and Prolonged Use. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Flexible and Printable Sensors and Systems (FLEPS), Boston, MA, USA, 9–12 July 2022; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; He, J.; Ma, L.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, L.; Xiong, S.; Li, K.; Qu, M. Multifunctional conductive cellulose fabric with flexibility, superamphiphobicity and flame-retardancy for all-weather wearable smart electronic textiles and high-temperature warning device. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 390, 124508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makowski, T.; Svyntkivska, M.; Piorkowska, E.; Mizerska, U.; Fortuniak, W.; Kowalczyk, D.; Brzezinski, S.; Kregiel, D. Antibacterial Electroconductive Composite Coating of Cotton Fabric. Materials 2022, 15, 1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Pang, Z.; Zheng, C.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, H.; Wei, Q. Cotton fabric finished by PANI/TiO2 with multifunctions of conductivity, anti-ultraviolet and photocatalysis activity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 470, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Tian, M.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Qu, L.; Zhu, S. Washable, durable and flame retardant conductive textiles based on reduced graphene oxide modification. Cellulose 2019, 27, 1763–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, S.N.I.; Zainal Ariffin, Z.; Zakaria, A.; Safian, M.F.; Halim, M.I.A.; Ramli, R.; Sofian, Z.M.; Zulkifli, M.F.; Aizamddin, M.F.; Mahat, M.M. Electrically conductive fabric coated with polyaniline: Physicochemical characterisation and antibacterial assessment. Emerg. Mat. 2020, 3, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Hady, M.M.; Farouk, A.; Sharaf, S. Multiwalled-Carbon-Nanotubes (MWCNTs)–GPTMS/Tannic-Acid-Nanocomposite-Coated Cotton Fabric for Sustainable Antibacterial Properties and Electrical Conductivity. Coatings 2022, 12, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wu, M.; Wu, Q.; Liu, J.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J. Conductive, superhydrophobic, and microwave-absorbing cotton fabric by dip-coating of aqueous silk nanofibers stabilized MWCNTs and octadecanoyl chain bonding. Cellulose 2022, 29, 4687–4701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojstršek, A.; Fakin, D. Layered compact textiles applied in fixed-bed column as filters for dye-rich textile wastewaters treatment—A case study. Des. Wat. Treat. 2013, 51, 3060–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojstršek, A.; Kleinschek, K.S.; Fakin, D. Characterization of nano-sized TiO2 suspensions for functional modification of polyester fabric. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 226, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, G.M.N.; Ali, A.; Collie, S. Textile sensors for wearable applications: A comprehensive review. Cellulose 2020, 27, 6103–6131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, A.R. Challenges for eco-design of emerging technologies: The case of electronic textiles. Mat. Des. 2013, 51, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagadeshvaran, P.; Panwar, K.; Ramakrishnan, I.; Bose, S. Smart textiles coated with functional particles derived from sustainable sources that can block both UV and EM. Prog. Org. Coat. 2021, 159, 106404. [Google Scholar]
- Yazıcı, P.; Alkhateab, B.; Sezer, E.; Koçak, D.; Ustamehmetoğlu, B. Synthesize and characterization of sustainable natural fibers/conductive polymer composites. J. Ind. Text. 2022, 2022, 15280837221098198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncu-Berk, G. Smart textiles and clothing: An opportunity or a threat for sustainability. In Proceedings of the Textile Intersections, London, UK, 12–14 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Köhler, A.R.; Hilty, L.M.; Bakker, C. Prospective Impacts of Electronic Textiles on Recycling and Disposal. J. Ind. Ecol. 2011, 15, 496–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, J. Can Design for Disassembly Principles Inform Policy for E-Textiles Waste? In Proceedings of the E-Textiles, Virtual Event, Manchester, UK, 3–4 November 2021. [Google Scholar]
- McLaren, A.; Hardy, D.; Hughes-Riley, T. Electronic textiles and product lifetimes: Exploring design strategies for product longevity. In PLATE: Product lifetimes and the Environment; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 473–476. [Google Scholar]
- Schischke, K.; Nissen, N.F.; Schneider-Ramelow, M. Flexible, stretchable, conformal electronics, and smart textiles: Environmental life cycle considerations for emerging applications. MRS Commun. 2020, 10, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.R.; Islam, T.; Repon, M.R.; Hoque, M.E. Carbon-based polymer nanocomposites for electronic textiles (e-textiles). In Advanced Polymer Nanocomposites; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 443–482. [Google Scholar]
- Veske, P.; Ilén, E. Review of the end-of-life solutions in electronics-based smart textiles. J. Text. Inst. 2020, 112, 1500–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rădulescu, I.R.; Surdu, L.; Visileanu, E.; Mitu, B.; Morari, C. Life Cycle Assessment of Flexible Electromagnetic Shields. In Recent Topics in Electromagnetic Compatibility; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wójcik-Augustyniak, M.; Szajczyk, M.; Ojstršek, A.; Leber, M. Life Cycle Assessment of Metallised Textiles. The Case Study of Maturolife Project. Zesz. Nauk. Uniw. Przyr.-Humanist. W Siedlcach. 2020, 50, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, H.; Zaidi, S.J. Sustainable Use of Nanomaterials in Textiles and Their Environmental Impact. Materials 2020, 13, 5134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, A.; van der Velden, N.M.; Persson, N.-K.; Hamedi, M.M.; Müller, C. Electrically conducting fibres for e-textiles: An open playground for conjugated polymers and carbon nanomaterials. Mater. Sci. Eng R Rep. 2018, 126, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Velden, N.M.; Kuusk, K.; Köhler, A.R. Life cycle assessment and eco-design of smart textiles: The importance of material selection demonstrated through e-textile product redesign. Mater. Des. 2015, 84, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacruz, A.; Salvador, M.; Blanco, M.; Vidal, K.; Goitandia, A.M.; Martinkova, L.; Kyselka, M.; de Ilarduya, A.M. Biobased Waterborne Polyurethane-Urea/SWCNT Nanocomposites for Hydrophobic and Electrically Conductive Textile Coatings. Polymers 2021, 13, 1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Key Words | Projects | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| FP6 | FP7 | H2020 | |
| “electronic textile” | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| “e-textile” | 2680 | 6214 | 9702 |
| “conductive textile” | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| “smart textile” | 3 | 14 | 21 |
| “electronic” AND “textile” | 7 | 24 | 98 |
| “conductive” AND “textile” | 8 | 16 | 56 |
| Textile | Conductive Layer | Electrical Resistance | Electrical Conductivity | Application | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| aramid fabric | PEDOT:PSS PANI:CSA 1 | 0.61 mS/cm 1.8 · 10−4 mS/cm | radar absorbing structure | [26] | |
| cotton fabric | PEDOT:PSS | 51–82.7 S/cm | EMI shielding | [27] | |
| cotton, rayon and polyester | PANI | 14.7 ± 4.8 kΩ/cm | gas sensors for real-time monitoring of ammonia gas | [28] | |
| polyamide/lycra knitted fabric | PEDOT:PSS | 1.7 Ω/sq | 14 S/cm | wearable e-textiles | [24] |
| silk yarn | PEDOT:PSS | 70 S/cm | touch sensor device | [29] | |
| cotton, wool, silk and polyester | PPy | ˂10 Ω/sq | wearable heater | [30] | |
| polyester fabric | PEDOT:PSS | 1.5 S/cm | energy harvesting | [31] |
| Textile | Conductive Layer | Electrical Resistance | Electrical Conductivity | Application | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cotton fabric | rGO | 13.8 ± 2.7 Ω/sq | 580.1 ± 4.3 S/m | electrochemical energy storage, EMI shielding, electrothermal and human motion detection | [45] |
| nylon and cotton | GO | 350 Ω/sq 1 kΩ/sq | temperature, humidity, and heart rate sensors | [38] | |
| polyurethane yarn | rGO | strain sensing | [44] | ||
| nylon 6 filaments | G | 6.43 S/m | strain sensing | [39] | |
| knitted para-aramid fabric | G | 7.5 × 104 Ω/sq | wearable heater | [22] | |
| knitted wool fabric | rGO | strain sensing | [43] | ||
| spandex yarn | G | up to 100 S/m | health monitor sensing | [40] | |
| cotton fabric | SWCNT | 555 Ω/sq | wearable electronics and heater | [46] | |
| nylon spandex fabric | MWCNT and rGO | strain sensing | [36] | ||
| cotton fabric | MWCNT G | 33.2 Ω/sq 29.8 Ω/sq | strain sensing and wearable heater | [42] | |
| polyamide fabric | SWCNT | up to 7.4 × 102 S/m | EMI shielding and wearable heater | [6] |
| Textile | Conductive Layer | Mechanical Property | Standard | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cotton fabric | Co, Cu, Mn or PANI | Tensile strength | ASTM D 5034 | [98] |
| Elongation at break | ||||
| Knitted wool fabric | rGO | Tensile strength | - | [43] |
| Cotton/polyester fabric | O-carboxymethyl chitosan-graphene nanosheet/PPy-Ag | Tensile stress | - | [99] |
| Elongation at break | ||||
| Polyester fabric | rGO/PPy | Tensile properties | ASTM D 5035 | [91] |
| Bending rigidity | ASTM D 1388-96 | |||
| Polyester fabric | G, GO, G/Ag | Tensile strength | - | [100] |
| Elongation at break | ||||
| Cotton fabric | PPy | Tensile strength | ASTM D 5035 | [101] |
| Stiffness | ISO 4606: 2013 | |||
| Cotton fabric | PPy | Tensile strength | ASTM D 1682-2004 | [102] |
| Elongation at break |
| Textile | Coating Layer | Functional Features | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cellulose fabric | Ag/PANI/AEGDP 1 Ag/PANI/PFOTS 2 | flame retardancy, super amphiphobicity and self-cleaning | [117] |
| Cotton yarn | CNT/PPy | antibacterial | [73] |
| Polyester fabric | rGO/PPy | antibacterial, UV-protective and thermal stability | [91] |
| Cotton fabric | rGO/Ag | antibacterial | [118] |
| Cotton fabric | PANI/TiO2 | UV-protective, photocatalytic activity and thermal stability | [119] |
| Cotton fabric | Ppy/TiO2/APTEOS 3 | UV-protective and antibacterial | [102] |
| Cotton/polyester fabric | O-GRP 4/PPy-Ag | antibacterial and flame retardancy | [99] |
| Cotton/polyester fabric | rGO/PFR 5 | flame retardancy and thermal stability | [120] |
| Polyester fabric | G, GO, G/Ag | antibacterial, hydrophobic and thermal stability | [100] |
| Cotton and polyester fabrics | PANI | antibacterial | [121] |
| Cotton fabric | PPy/DTMS 6 | superhydrophobic and self-cleaning | [101] |
| Cotton fabric | MWCNTs–GPTMS 7/tannic acid | antibacterial and UV-protective | [122] |
| Pristine fabric | PDA 8/MXene/PDMS | superhydrophobic | [95] |
| Cotton fabric | MWCNTs/stearoyl chloride | superhydrophobic and thermal stability | [123] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ojstršek, A.; Jug, L.; Plohl, O. A Review of Electro Conductive Textiles Utilizing the Dip-Coating Technique: Their Functionality, Durability and Sustainability. Polymers 2022, 14, 4713. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14214713
Ojstršek A, Jug L, Plohl O. A Review of Electro Conductive Textiles Utilizing the Dip-Coating Technique: Their Functionality, Durability and Sustainability. Polymers. 2022; 14(21):4713. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14214713
Chicago/Turabian StyleOjstršek, Alenka, Laura Jug, and Olivija Plohl. 2022. "A Review of Electro Conductive Textiles Utilizing the Dip-Coating Technique: Their Functionality, Durability and Sustainability" Polymers 14, no. 21: 4713. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14214713
APA StyleOjstršek, A., Jug, L., & Plohl, O. (2022). A Review of Electro Conductive Textiles Utilizing the Dip-Coating Technique: Their Functionality, Durability and Sustainability. Polymers, 14(21), 4713. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14214713








