Abstract
This study explores the possibility of enhancing both mechanical and breakdown properties of insulating presspaper by the introduction of an organic nano additive. Four different concentrations of nanofibrillated cellulose (NFC) were taken into account: 0.5 wt %, 2.5 wt %, 5 wt %, and 10 wt %. Presspaper containing no NFC was also prepared as a reference. Obtained samples were characterized by scanning electron microscope (SEM), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), and X-ray diffraction (XRD). Mechanical properties and breakdown behaviors were measured. Results show that the addition of 10 wt % NFC to softwood fibers can achieve the best performance. Tensile strength of reference presspaper is 109 MPa, whereas that of presspaper modified by 10 wt % NFC is 136 MPa, resulting in a 25% increase. The improved tensile strength can be attributed to the increased density and inter fiber bond strength. More importantly, presspaper reinforced by 10 wt % NFC can also achieve enhanced AC and DC breakdown strengths, which are 19% and 21% higher than those of the reference presspaper. It is concluded that NFC is likely to be a promising nano additive for cellulose insulation.
1. Introduction
Cellulose presspaper and pressboard, together with mineral oil, have been widely used in power transformers for many years due to their low cost and good insulating performances [1,2,3]. With the construction of ultra-high voltage direct current (UHVDC) power transmission, insulation failures in convert transformer have become a severe problem [4,5,6,7]. Enhancing electrical properties of cellulose insulation is therefore of great significance. However, only a few studies deal with the modifications of presspaper despite of the extensive research on mineral oil and other polymers [8,9].
Early studies mainly focus on improving thermal properties of presspaper, reducing its hygroscopicity, and decreasing its relative permittivity [10,11]. Mechanical and electrical strengths are seldom taken into account. Nanotechnology provides a new approach for the modifications of insulating materials. Recently, nanodielectrics have become of high interest [12,13]. Liao et al. performed a series of studies on the insulating performances of nanomodified paper [14,15,16]. They examined the effects of nanometric hollow SiO2, nano-TiO2, and nano-montmorillonite, and found the improvement in AC breakdown strength of oil impregnated paper with an appropriate concentration of nano additives. However, mechanical properties, which played a crucial role in determining the lifetime of insulating paper, normally decreased [17]. In addition, preparation process for the aforementioned nanomodified paper was usually complex due to the incompatibility between inorganic nanoparticles and organic cellulose fibers [8,18]. Therefore, an organic nano additive may be a good substitute, especially when it originates from cellulose fiber and thus will be much less likely to act as impurities.
Nanofibrillated cellulose (NFC) seems to be a promising organic additive. It is a thread-like cellulosic nano-material with a width less than 100 nm and a length of 0.5 μm to 2 μm [19,20,21]. NFC is usually obtained from ordinary softwood fibers by mechanical disintegration [20]. For softwood fibers, they typically have a width of more than 20 μm and a length of several millimeters. Although some chemical treatments may be used prior to the disintegration, NFC still has chemical components and structure similar to cellulose fiber, resulting in a good compatibility. Hollertz et al. compared mechanical strength and dielectric response of kraft paper and nanopaper made from NFC [8]. They found that nanopaper had an improved tensile strength, relative permittivity, and dielectric loss due to the higher density. A lot of studies have investigated the reinforcement of tensile strength of ordinary paper, such as writing paper and newspaper, by introduction of NFC [21,22,23,24,25]. However, electrical properties, especially breakdown behaviors, of insulating presspaper modified by NFC have been rarely reported. The effect of NFC concentration on electrical performances is still unknown.
This study aims to evaluate the electrical properties and tensile strength of NFC modified insulating presspaper to determine whether or not the organic nano additive could be a desirable nano filler. Four different concentrations of NFC were taken into account, namely 0.5 wt %, 2.5 wt %, 5 wt %, and 10 wt %. Presspaper containing no NFC was also prepared as a reference. Surface morphology of the prepared samples was analyzed by scanning electron microscope (SEM, FEI Quanta 450 FEG, FEI Company, Hillsboro, OR, USA). Chemical structures and crystallinities of the obtained samples were characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR, Bruker vertex 70v, Bruker Optics, Billerica, MA, USA) and X-ray diffraction (XRD, Rigaku RINT 2000, Rigaku Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan). Mechanical properties, electrical behaviors and thermal properties of the reference and nanomodified presspaper samples were measured and discussed.
2. Experimental
2.1. Preparation of Samples
NFC was provided by Tianjin University of Science and Technology (Tianjin, China) with a width of 10–20 nm and a length of 0.8–2 μm. Surface charge density of NFC was 0.69 meq/g. It was determined by polyelectrolyte titration with poly-DADMAC. The unbleached sulphate softwood pulp with electrical grade was supplied by Canfor Corporation (Vancouver, BC, Canada). Degree of polymerization (DP) value of the softwood pulp was 1730.
Preparation of reference presspaper without NFC: First, about 60 g of dry pulp sheet was soaked in 2 L pure water (electrical conductivity of about 3 μS/cm) for 12 h. Then, the soaked wet pulp was dispersed and refined by a Valley beater to a Schopper-Riegler (SR) number of about 37. After that, 12 L of pulp suspension with a concentration of 0.5 wt % was transferred to a sheet former to make handsheet. Finally, the wet handsheet was hot-pressed at 115 °C and 450 N/cm2 for 10 min to achieve a dry state with a relatively high density.
For the preparation of presspaper modified by nanofibrillated cellulose: Prior to the sheet forming process, 0.5 wt % NFC suspension was ultrasonically dispersed for 5 min and then added to the 0.5 wt % wood fiber slurry to form a composition with a proper content of NFC. Next, the mixture was stirred for 5 min. Subsequent procedures were the same as the preparation of reference sample. Obtained presspaper samples in this study had a thickness of about 400 μm. Densities of the reference presspaper and presspaper modified by 10 wt % NFC were 0.95 g/cm3 and 0.99 g/cm3, respectively. The measurements were conducted according to the IEC standard 60641-2.
2.2. SEM, FTIR, and XRD
FEI Quanta 450 FEG (FEI Company, Hillsboro, OR, USA) scanning electron microscope was used to observe the surface morphologies of reference presspaper and presspaper modified by NFC at a magnification of 1000×. Prior to the tests, presspaper samples were sputter-coated with gold for 90 s. FTIR spectra of prepared presspaper were recorded via a Bruker vertex 70v (Bruker Optics, Billerica, MA, USA) in reflection mode. Measurement range was from 4000 cm−1 to 600 cm−1, and the resolution was 2 cm−1. XRD analyses were performed using a Rigaku RINT 2000 (Rigaku Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) wide angle goniometer with the continuous scanning mode. The copper K-alpha X-ray source was used to record the diffraction profiles. 2θ ranged from 10° to 50°. Resolution of the measurement was 0.02°.
2.3. Tensile Strength
Tensile tests were performed on a Zwick Z005 (Zwick/Roell, Ulm, Germany) universal testing machine according to the ISO 1924-3. A 2500 N load cell was used. The constant rate of elongation method was adopted. The separation speed of the upper clamp and the lower clamp was 100 mm/min. Initial distance between the two clamps was 100 mm. The width and length of the strip shape test samples were 15 mm and 150 mm, respectively. For each kind of presspaper, five samples were tested. Figure 1 shows the images of the testing machine and the presspaper sample under testing.
Figure 1.
Images of (a) universal testing machine and (b) clamps and presspaper sample under testing.
2.4. DC Volume Resistivity and Dielectric Response
DC volume resistivity was measured according to IEC standard 60093. The three electrodes method was used to avoid the influence of surface current. A Keithley 6517A electrometer (Keithley, Cleveland, OH, USA) was adopted to supply DC voltage and detect the corresponding polarization current. Detailed diagram of the setup could be found in Huang et al. [26]. The measurements were conducted at room temperature. The applied electric field was 1 kV/mm. Prior to the tests, presspaper samples were thermally treated at 105 °C for 12 h to remove moisture.
Dielectric responses of presspaper samples were measured by the Novocontrol broadband dielectric spectrometer. Two identical round copper electrodes with a diameter of 20 mm were used. Test sample having a diameter of about 25 mm was placed between the electrodes. Magnitude of the applied sinusoidal voltage was 1 V. The test frequency was set to 50 Hz.
2.5. Breakdown Behavior
AC and DC breakdown tests were conducted according to IEC standard 60243. Equal diameter electrodes made of stainless steel were used. Diameter of the electrodes was 25 mm. Electrode arrangement for the breakdown tests was the same as that in reference [15]. The rate of voltage rise was 500 V/s. Measurements were performed at room temperature in the air. Size of the presspaper samples was 50 mm × 50 mm. For each kind of presspaper, ten samples were measured.
2.6. Thermal Properties
Thermal stabilities of obtained samples were evaluated by thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). TGA was conducted on a TGA Q5000 analyzer (TA Instruments; New Castle, DE, USA) under nitrogen flow. The test temperature ranged from room temperature to 800 °C. The heating rate was 10 °C/min.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphology Property and Pore Size Distribution
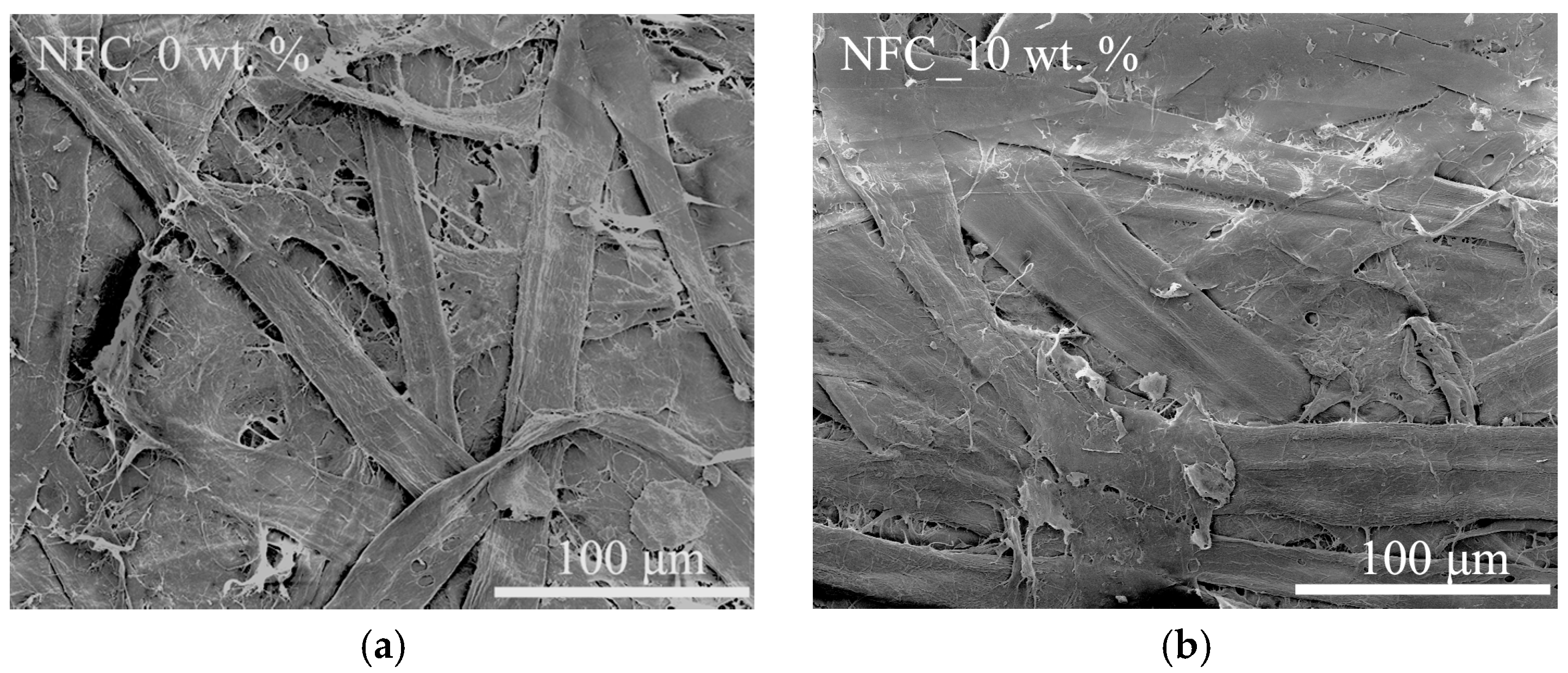
SEM micrographs of reference presspaper and nanomodified presspaper are shown in Figure 2. It can be seen that surface of modified presspaper is smoother than that of the reference presspaper. After pulp refining, external fibrillation is obviously observed in Figure 2a. This makes fiber surface become rough. In contrast, the introduced NFC with nano sized width and micro sized length can be adsorbed to fiber surfaces and act as a coating material, which therefore improves the smoothness of fiber surface [21]. Besides that, fewer and smaller air voids are observed in presspaper containing NFC, which is consistent with the higher density of NFC modified presspaper. The reason is that NFC can contribute to bridge adjacent fibers and fill the micron-sized pores formed by softwood fibers [22].
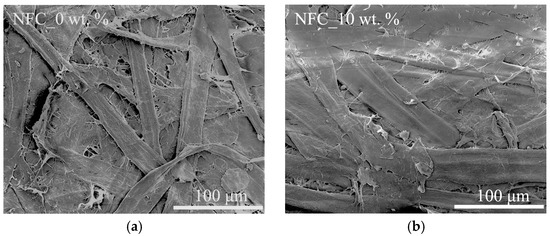
Figure 2.
Scanning electron microscope (SEM) images of (a) reference presspaper without nanofibrillated cellulose (NFC); and (b) presspaper modified by 10 wt % NFC.
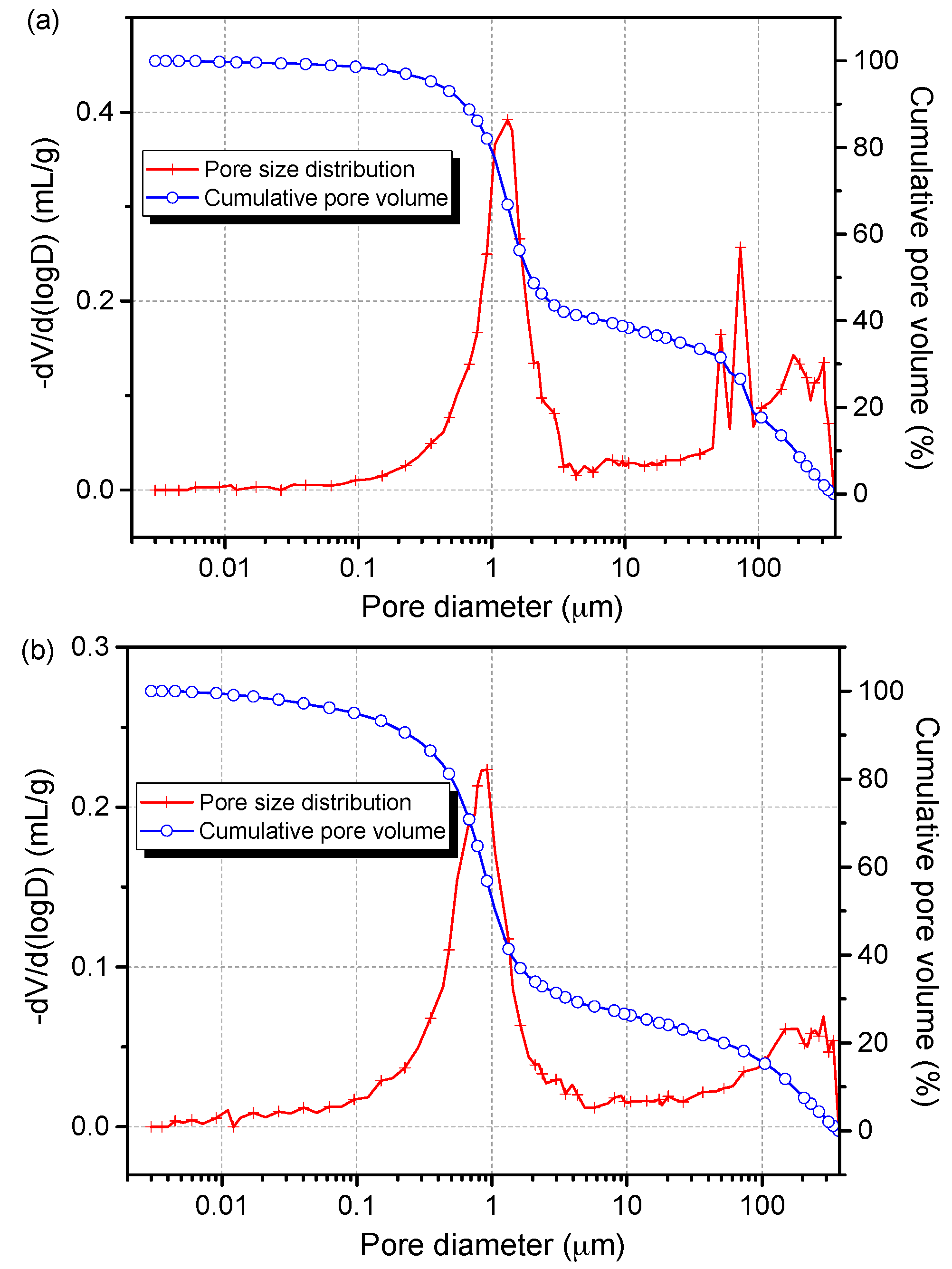
To further determine the pore size distributions of reference presspaper and NFC modified presspaper, the mercury intrusion method was used. The AutoPore IV 9500 (Micromeritics, Norcross, GA, USA) was utilized. Advancing contact angle and receding contact angle of mercury were both set to 130°. Surface tension of mercury was defined as 0.485 N/m. The maximum pressure was 414 MPa. Pores in the range of 3 nm to 380 μm could be determined. Before the test, presspaper samples were dried at 105 °C for 12 h. Figure 3 presents the pore size distributions of reference presspaper and NFC modified presspaper. For reference presspaper, air voids with diameter higher than 50 μm are ascribed to the interspaces between different small pieces of test samples [27]. The cumulative pore volume results also support this. Average pore diameter of reference presspaper is 2 μm. For NFC modified presspaper, a shift towards smaller diameter is observed in pore size distribution curve, indicating that the air voids in nanomodified presspaper are smaller than those in reference presspaper. Average pore diameter of presspaper containing 10 wt % NFC is 1 μm. Porosities of reference presspaper and presspaper modified by 10 wt % NFC are 32.5% and 22.6%, respectively. It is concluded that the addition of NFC to presspaper can decrease pore size and porosity.
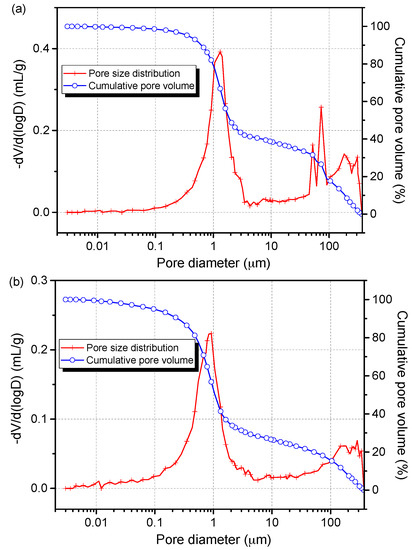
Figure 3.
Pore size distributions and cumulative pore volume curves determined by mercury intrusion method for (a) reference presspaper and (b) presspaper modified by 10 wt % NFC.
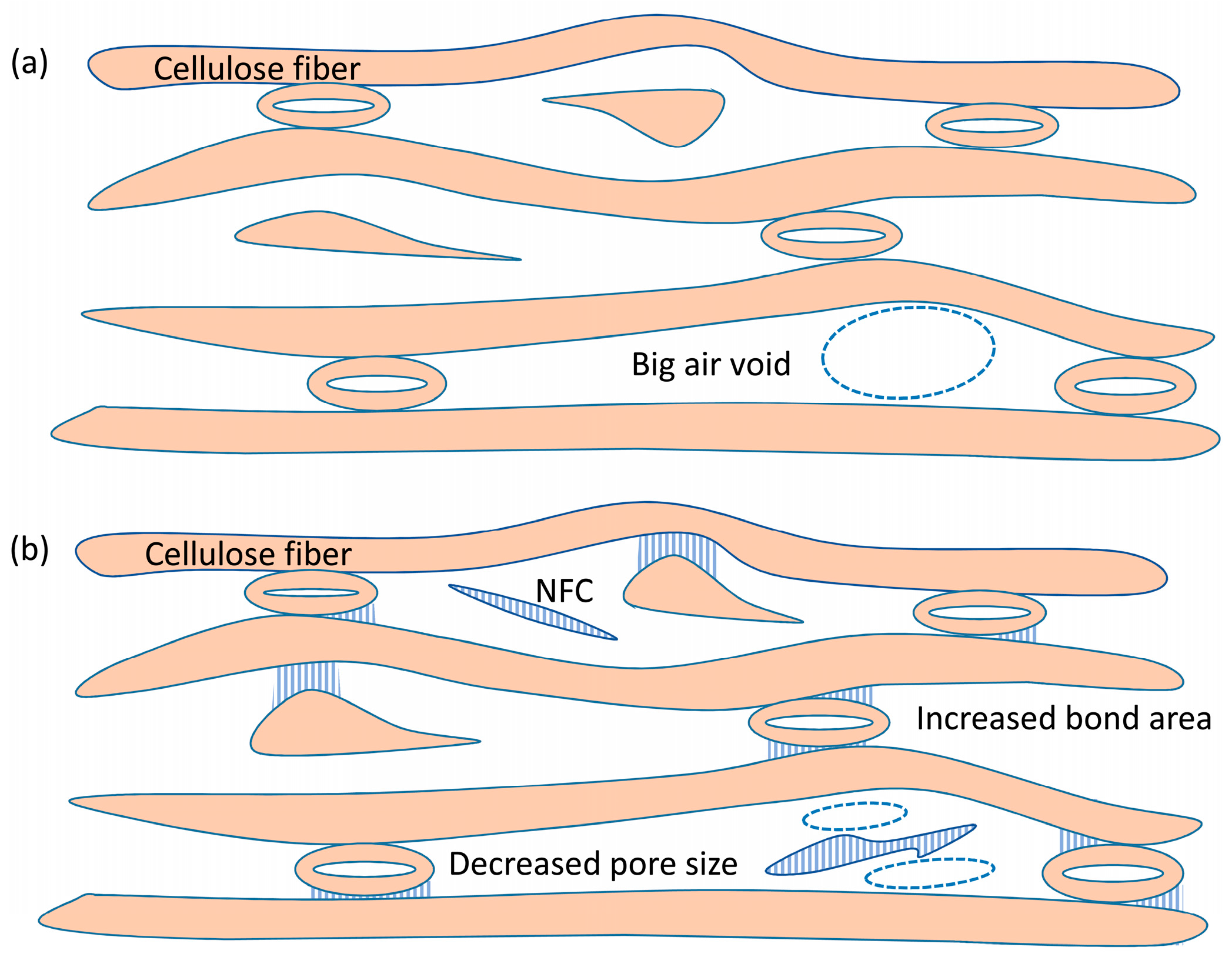
On the basis of the SEM results shown in Figure 2 and the pore size distributions presented in Figure 3, we therefore conclude that introduction of NFC can increase the relative bond area and decrease the size of air voids inside presspaper. These variations in presspaper structure due to the introduction of NFC are schematically shown in Figure 4. The increased relative bond area is good for the mechanical performance, and the decreased pore size can contribute to the electrical breakdown strength.
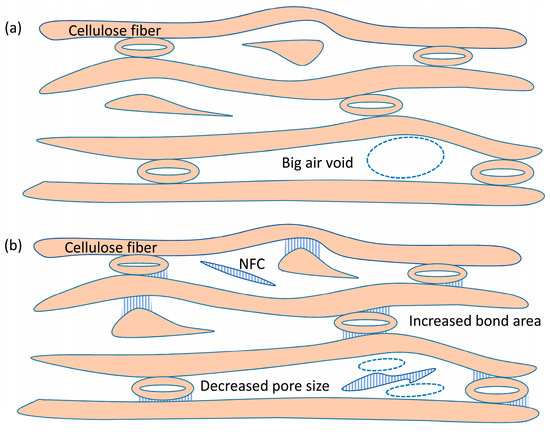
Figure 4.
Schematic representation of the cross section structures of (a) reference presspaper without NFC; and (b) presspaper modified by NFC. The introduction of NFC can increase inter fibre bond area and decrease pore size.
3.2. FTIR and XRD
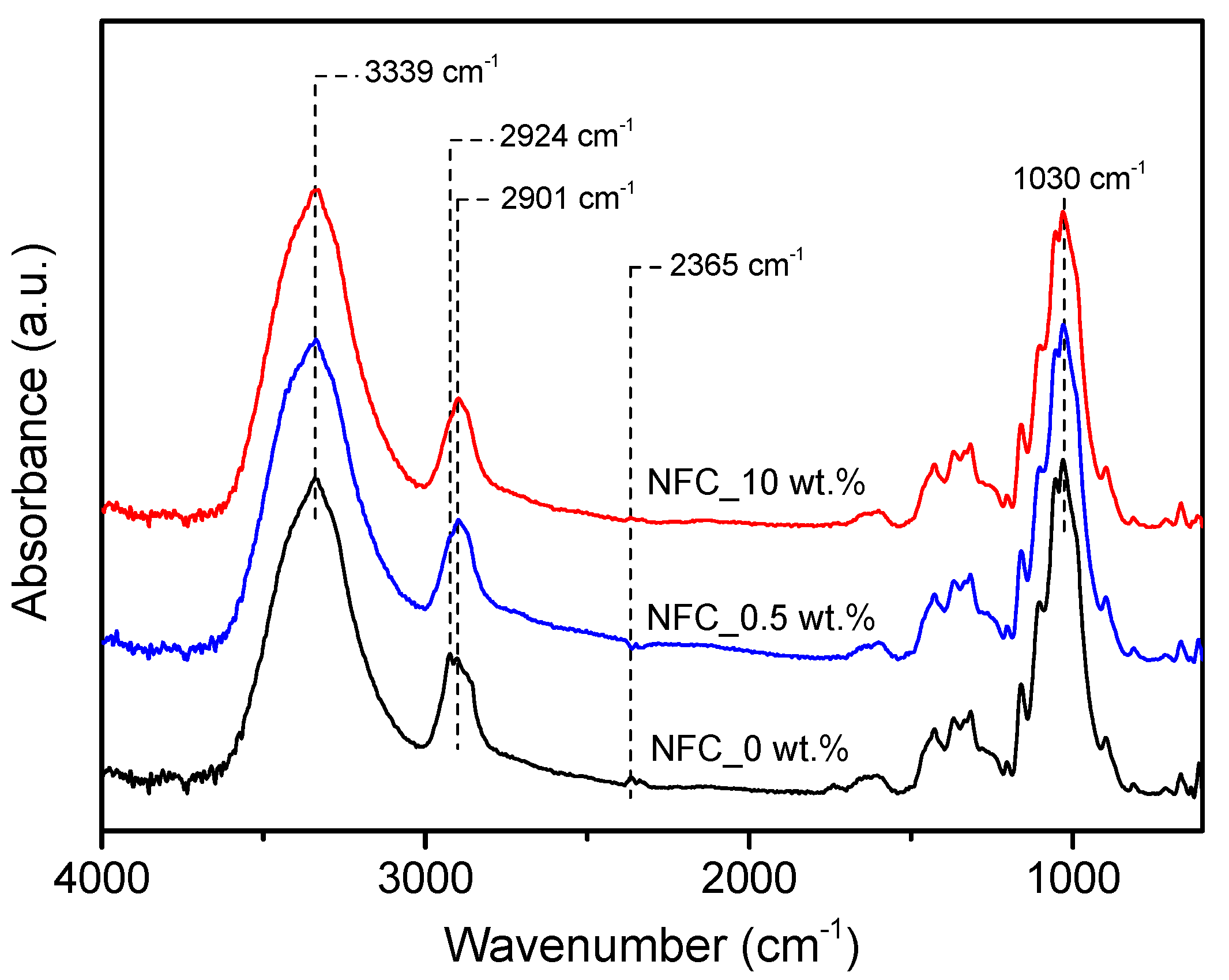
Figure 5 shows the FTIR spectra of reference presspaper and NFC modified presspaper. Similar functional groups are observed for the samples, indicating that the effect of NFC on chemical structure can be neglected. The most two obvious absorption peaks at 3339 cm−1 and 1030 cm−1 are ascribed to the –OH stretching and C–O stretching, respectively. The absorption band at 2924 cm−1 associating with the asymmetric stretching of –CH2 is only observed in reference presspaper. Variation in the peak at 2365 cm−1 is due to the CO2 in the circumstance.
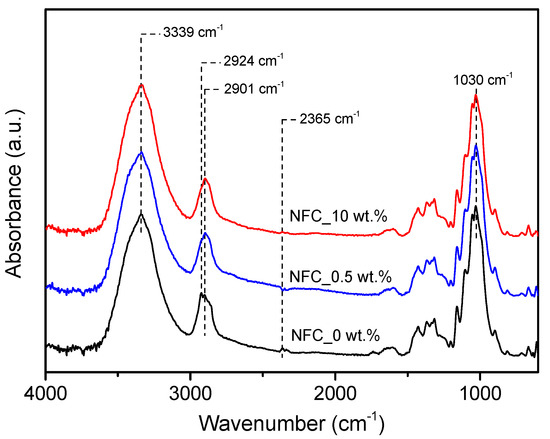
Figure 5.
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) spectra of reference presspaper and NFC modified presspaper.
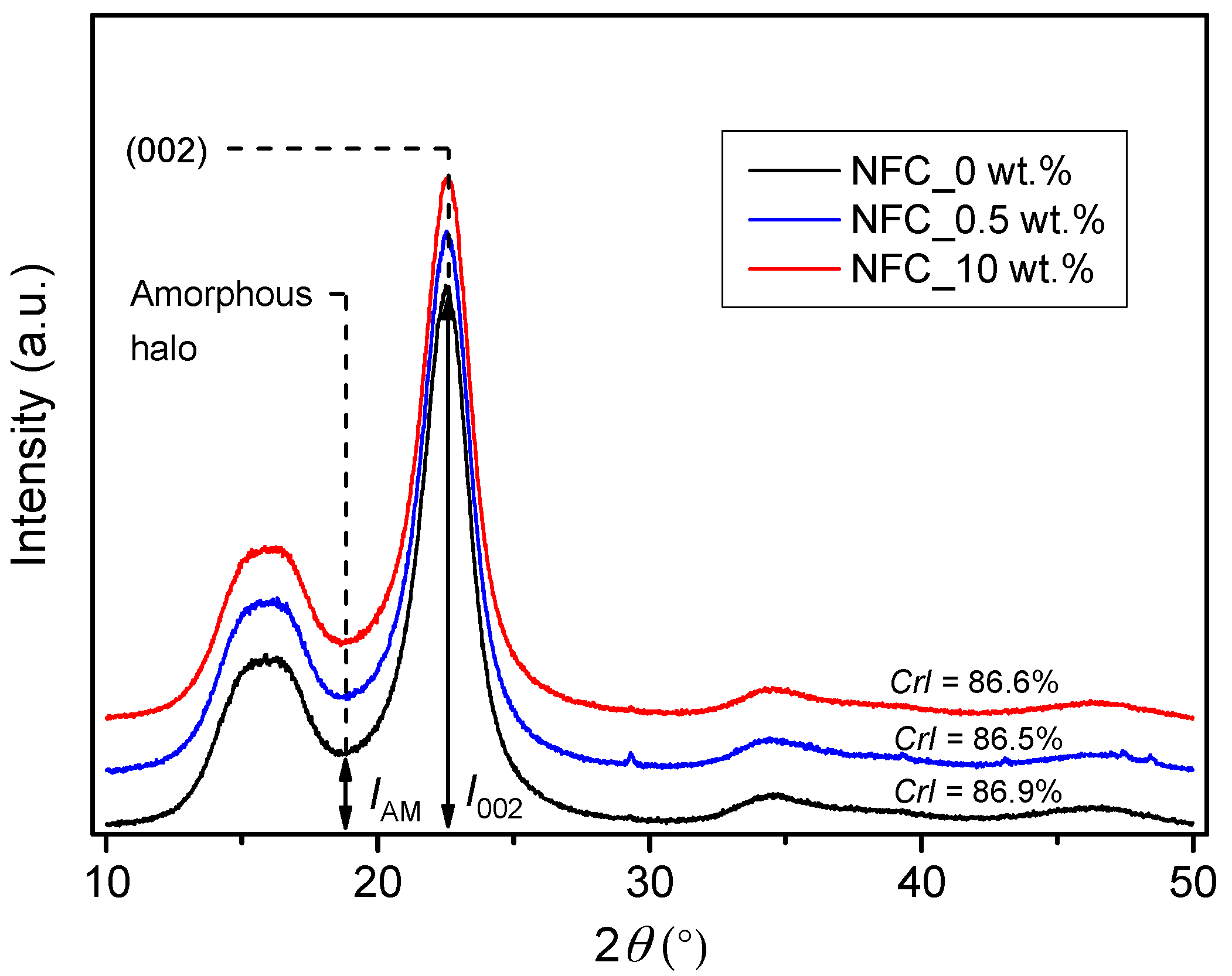
Figure 6 presents the X-ray diffractograms of reference presspaper and NFC modified presspaper. Peak height method developed by Segal et al. [28] is used to calculate crystallinity index (CrI):
where I002 is the intensity of the 002 crystalline peak, and IAM represents the intensity of the amorphous halo. Crystallinity index of reference presspaper is 86.9% and that of presspaper modified by 10 wt % NFC is 86.6%. The reduction in crystallinity is probably due to the breakage of the crystalline region of cellulose during the preparation of NFC. Fatah et al. [29] investigated the crystallinity index of nanofibrillated cellulose obtained from microfibrillated cellulose via a high-pressure homogenizer. They found that crystallinity indexes of nanofibrillated cellulose and microfibrillated cellulose were 42.5% and 80.4%, respectively. In addition, they pointed out that the reduction was associated with the breakdown of hydrogen bond that played a critically important role for the crystal structure of cellulose. Nevertheless, the variation in crystallinity caused by introduction of NFC is quite small. Based on the above results, it is concluded that the influence of NFC on chemical functional groups and crystallinity is really small when NFC concentration is no more than 10 wt %.
CrI = (I002 − IAM)/I002,
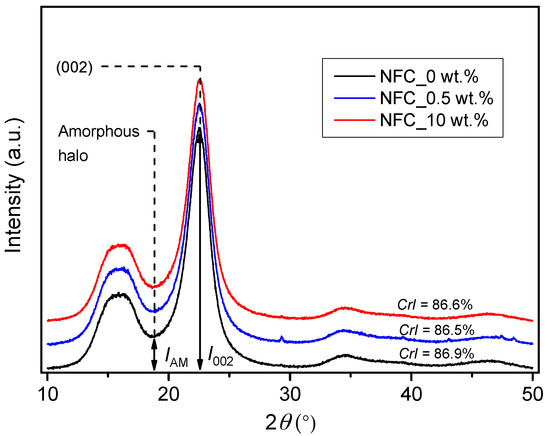
Figure 6.
X-ray diffraction (XRD) results of reference presspaper and NFC modified presspaper.
3.3. Mechanical Strength
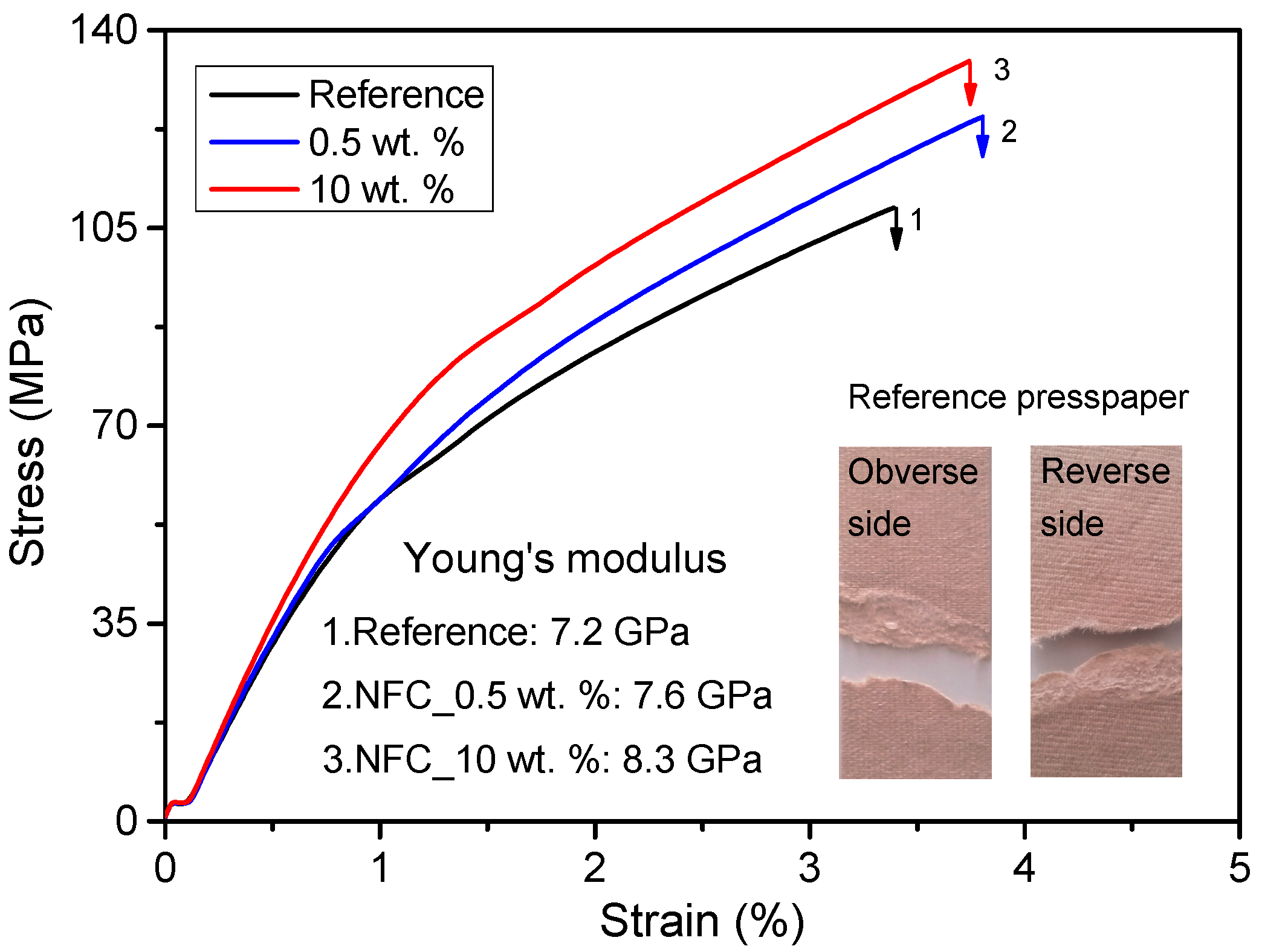
Figure 7 shows the stress-strain behaviors for reference presspaper and NFC modified presspaper. It can be seen that presspaper containing NFC has a higher Young’s modulus when compared with ordinary presspaper that made from softwood fibers only. The introduction of 10 wt % NFC can achieve a Young’s modulus of 8.3 GPa, which is about 15% higher than the reference presspaper. Although an addition of 0.5 wt % NFC can also improve the Young’s modulus of prepared sample, the addition of 10 wt % NFC results in a better performance. The reason for the enhancement of Young’s modulus is probably attributed to the improved interfiber stress transfer efficiency [22]. Presspaper can be regarded as a network of fibers with certain lengths. When external stress is applied, the stress has to be transferred from one fiber to its adjacent fibers. Young’s modulus of presspaper is determined by the Young’s modulus of component fiber and the efficiency of stress transfer between different fibers. Long fibers and large relative bonded areas are beneficial for the stress transfer [26]. As shown in Figure 4, NFC can contribute to the bonding of neighboring fibers. Therefore, the load transfer will be more effective, leading to a higher Young’s modulus of the NFC modified presspaper.
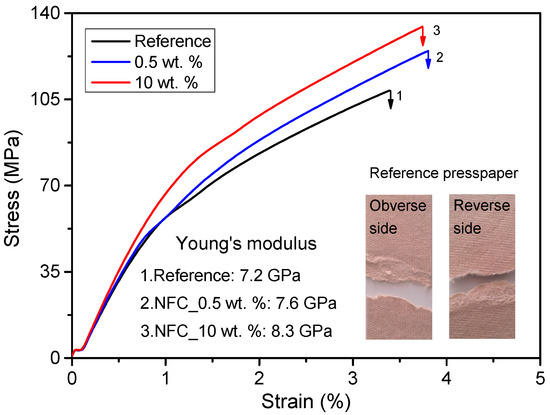
Figure 7.
Tensile stress-strain curves of reference presspaper and NFC modified presspaper.
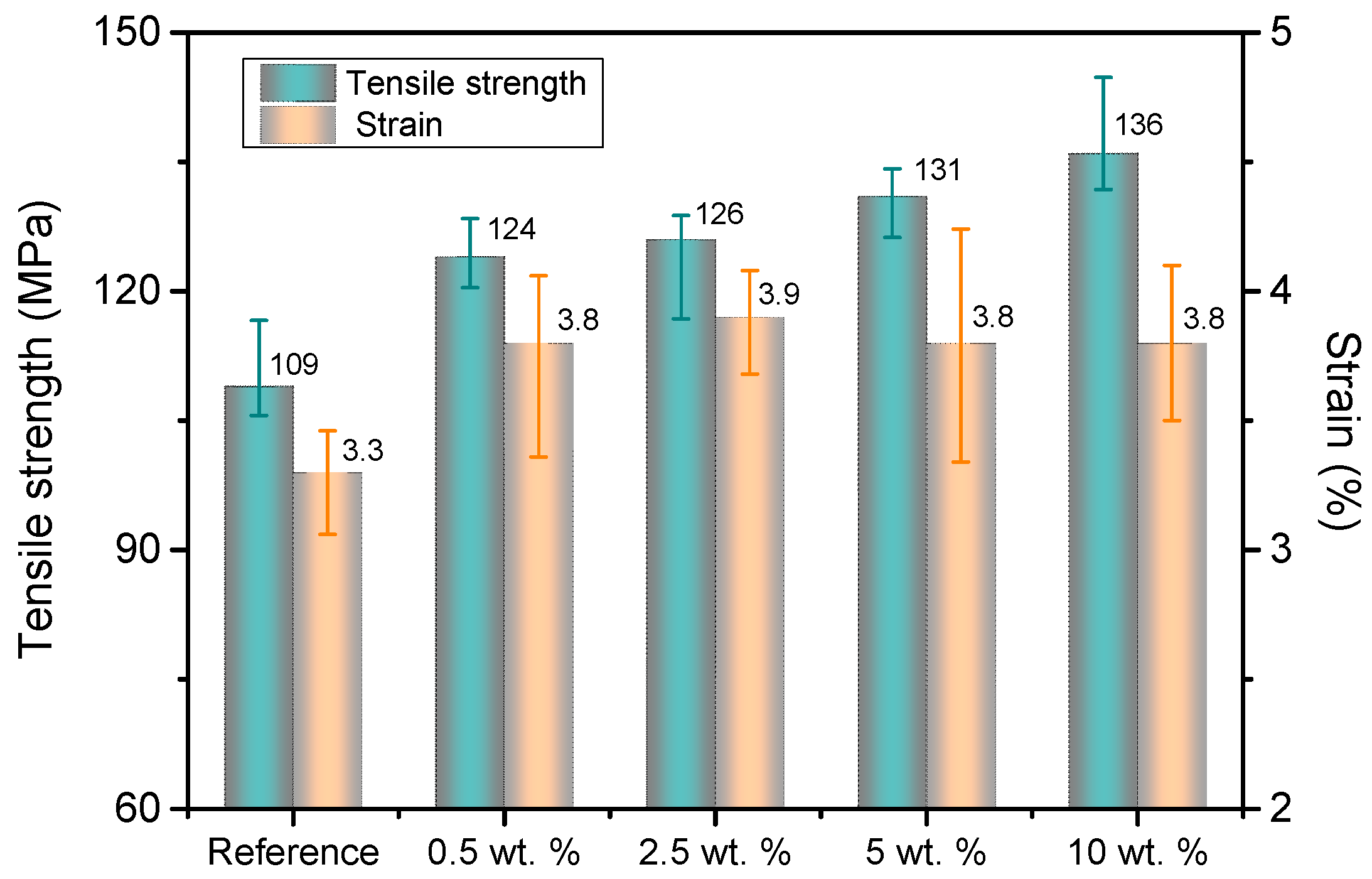
Mechanical strength and strain results of the obtained presspaper samples are presented in Figure 8. It can be seen that the addition of NFC to softwood fibers can significantly improve mechanical performance. Presspaper modified by 10 wt % NFC can achieve a better performance than presspaper reinforced by other contents of NFC. Tensile strength of reference presspaper is 109 MPa, whereas that of presspaper modified by 10 wt % NFC is as high as 136 MPa, resulting in a 25% increase. Before further discuss the reason for the improvement, density is firstly taken into account. Density of reference presspaper is 0.95 g/cm3. That of presspaper containing 10 wt % NFC is 0.99 g/cm3. Specific strength, namely the strength-to-weight ratio, of unmodified presspaper is 115 MPa·g−1·cm3, that of presspaper modified by 10 wt % NFC is 137 MPa·g−1·cm3. The latter is still higher than the former. Consequently, higher density is not the only reason for the increase of tensile strength. According to Page’s equation [30,31],
where T is the tensile strength of presspaper; F and B describe the strengths of individual fibers and interfiber bonds. Because of the lower strength of interfiber bond when compared to the strength of individual fiber, some softwood fibers are pulled out and remain undamaged during the tensile test (see the fractured surfaces of reference presspaper in Figure 7). On the basis of the results in Figure 2 and Figure 4, it is suggested that the introduction of NFC can increase relative bond area. Therefore, inter fiber bond strength increases and results in the enhancement of tensile strength of nanomodified presspaper [21,22]. On the basis of the above discussion, we conclude that the improvement of tensile strength of presspaper is due to the increased density and relative bond area. Strain of modified presspaper also increases.
1/T = 1/F + 1/B,
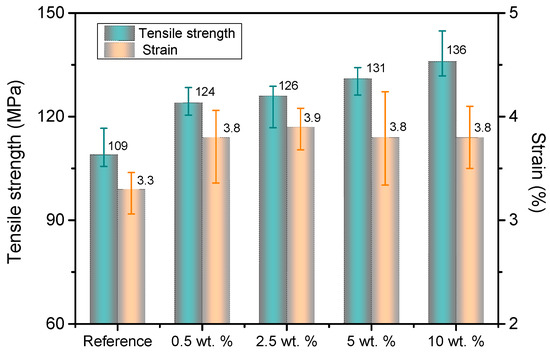
Figure 8.
Tensile stress and strain results of reference presspaper and NFC modified presspaper.
3.4. Volume Resistivity and Dielectric Response
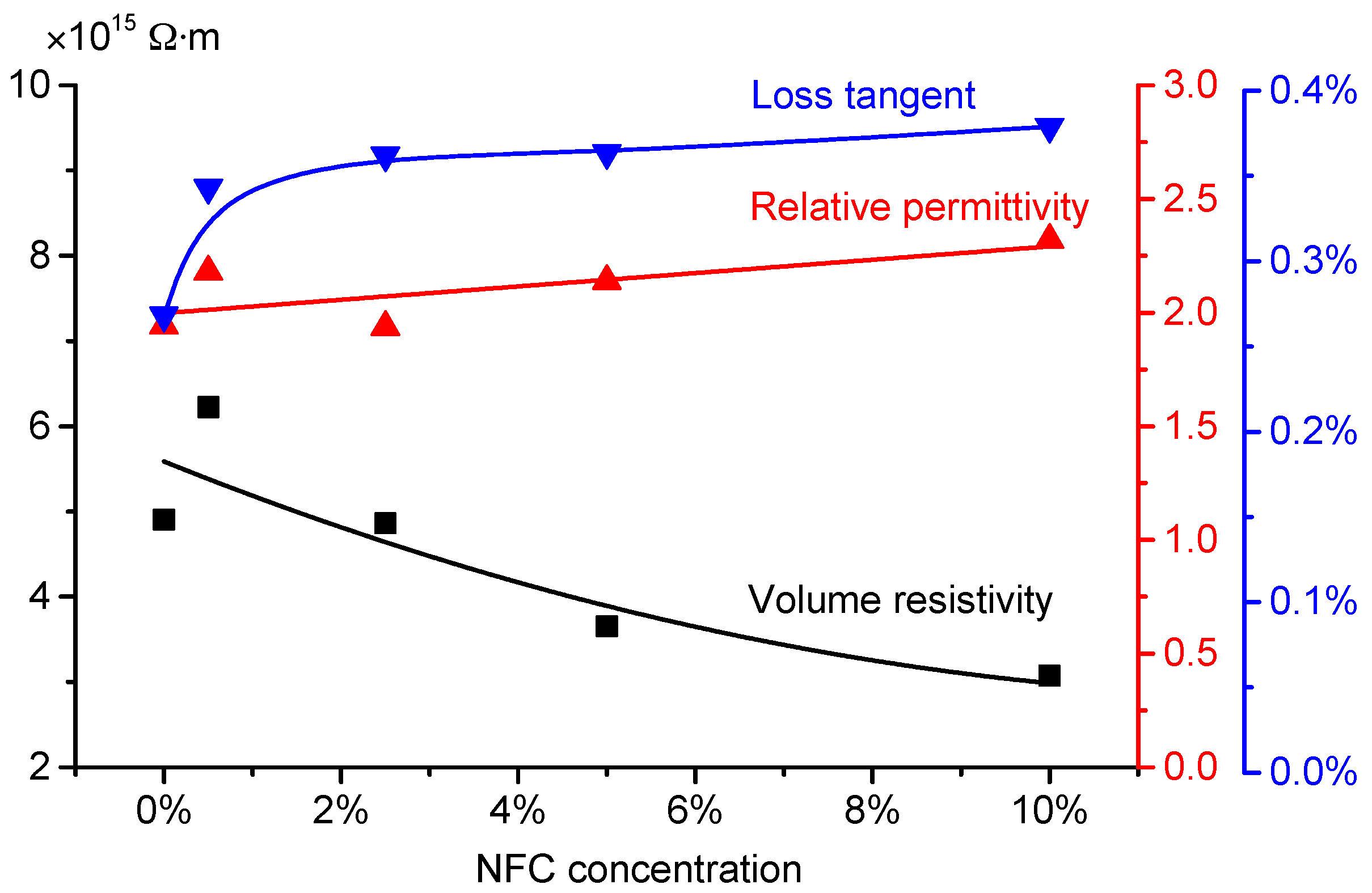
Variation of DC volume resistivity is shown in Figure 9. With the increase of NFC content, DC volume resistivity of nanomodified presspaper tends to decrease. For the reference sample, the value is 4.9 × 1015 Ω·m. For modified presspaper containing 10 wt % NFC, the value decreases to 3.1 × 1015 Ω·m. Because air normally has a lower electrical conductivity than cellulose fibers, ionic charge carriers therefore tend to move along fibers. Due to the increased relative bond area, the carriers in nanomodified presspaper can obtain a higher mobility. As a result, NFC modified presspaper tends to have a relatively lower resistivity. Considering that volume resistivities of reference presspaper and NFC modified presspaper are of the same order of magnitude, the effect of NFC on volume resistivity is not very significant.
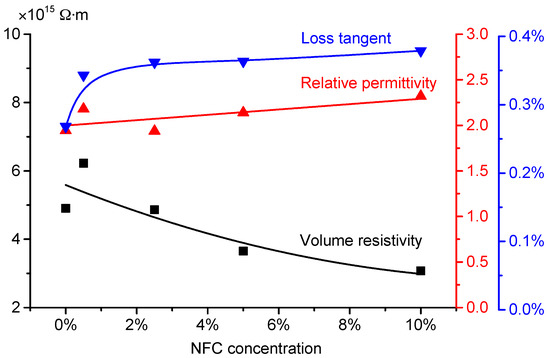
Figure 9.
Volume resistivity and dielectric response (at 50 Hz) results of reference presspaper and NFC modified presspaper.
Figure 9 also presents the dielectric responses of prepared presspaper. The results were measured at 50 Hz. With the increase of NFC content, loss tangent value first increases obviously, then varies slightly. The difference between the highest and the lowest values is less than 0.1%. The increased dielectric loss is partly due to the decreased DC volume resistivity. Relative permittivity of presspaper containing NFC tends to be higher than that of reference presspaper. One of the reasons is that NFC modified presspaper has a higher density. According to [32],
where εeff represents the relative permittivity of presspaper; εf is the permittivity value of cellulose fiber; εa is the permittivity value of air; θf is the volume ratio of cellulose fiber to the whole composite. At 50 Hz, εf is assumed to be 6.5, and εa is regarded as 1 [32]. Because θf is proportional to density, a higher density will result in a higher θf, and therefore increase the relative permittivity of presspaper sample. Another reason for the enhanced relative permittivity of presspaper containing NFC is probably associated with the increased dipoles. NFC has a larger surface to volume ratio than softwood fiber, which means that NFC can provide more –OH groups to form hydrogen bonds with adjacent fibers. As a result, the number of the formed dipoles increases. The relatively low volume resistivity and high dielectric constant of nanomodified presspaper indicate that the corresponding oil impregnated NFC modified presspaper insulation will be more suitable for applications under DC voltage.
1/εeff = θf/εf + (1 − θf)/εa,
3.5. Breakdown Behavior
Figure 10 and Figure 11 describe the AC and DC breakdown strengths of reference presspaper and nanomodified presspaper. The Weibull statistics were performed according to IEC 62539. After sorting the breakdown strengths from the smallest to the largest, probability F(i,n) for the ith breakdown field from the total n tests is,
F(i,n) = (i − 0.44)/(n + 0.25) × 100%.
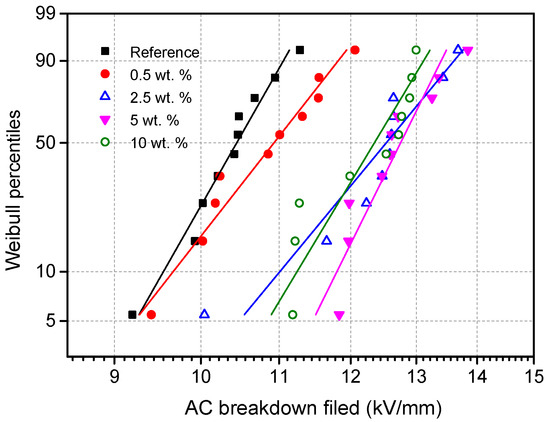
Figure 10.
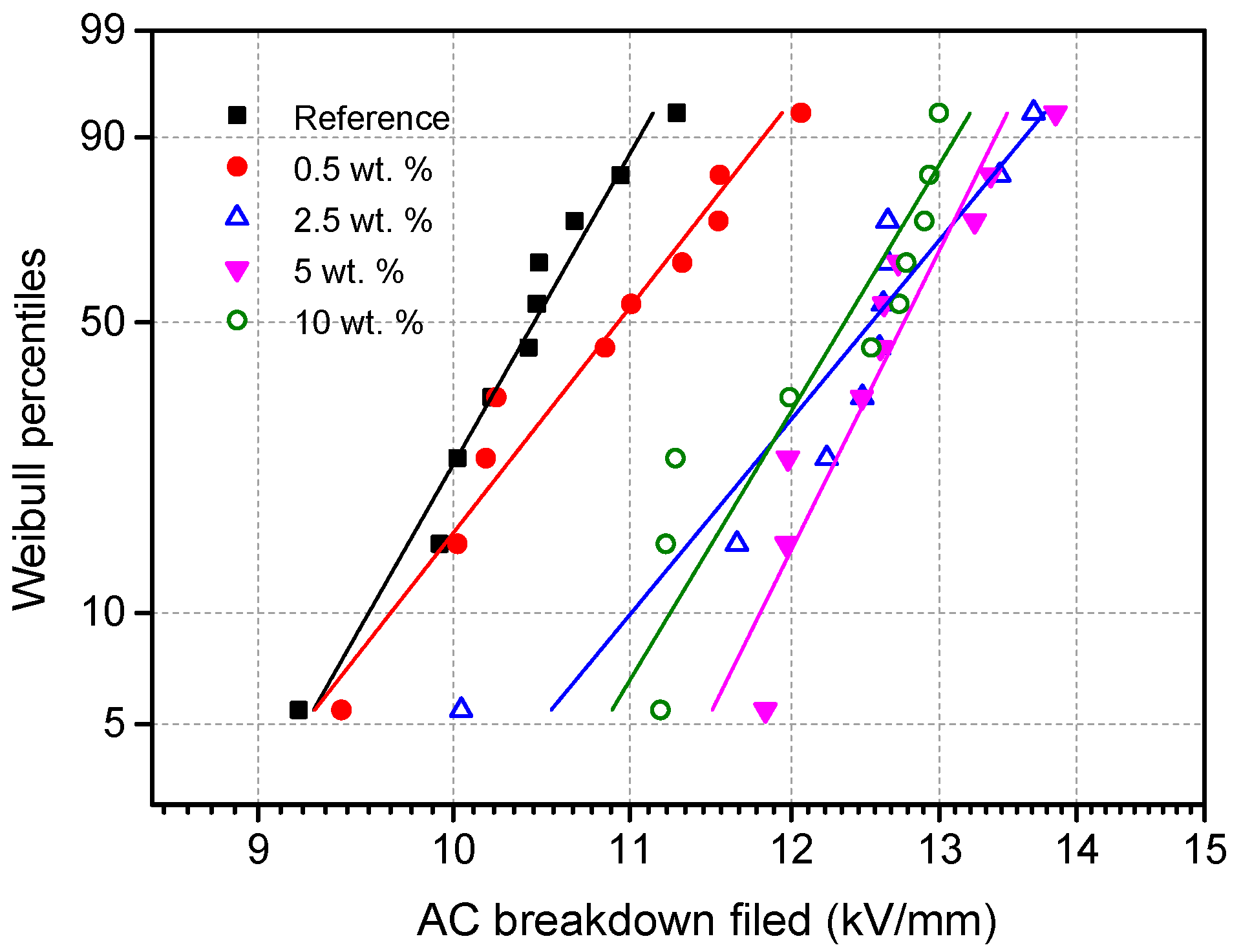
Weibull plots for AC breakdown fields of reference presspaper and NFC modified presspaper.
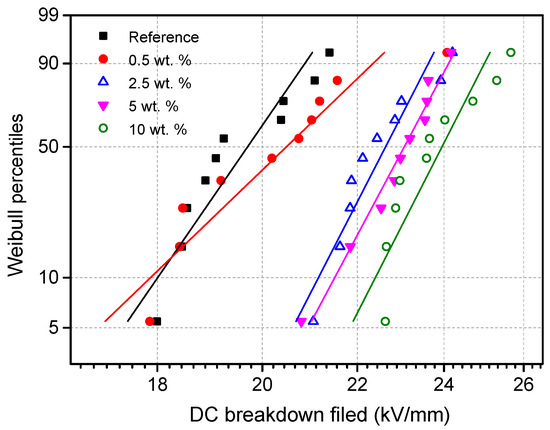
Figure 11.
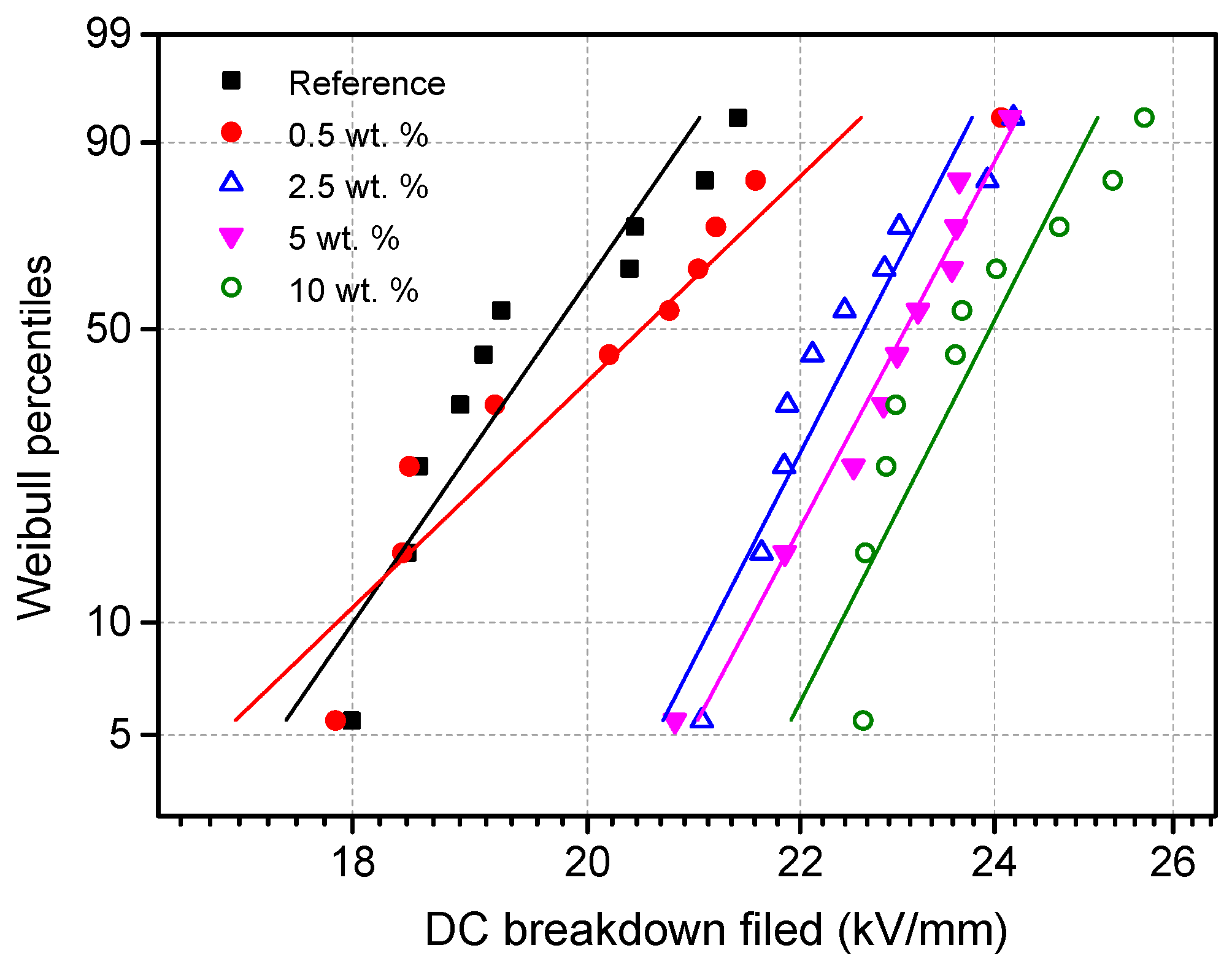
Weibull plots for DC breakdown fields of reference presspaper and NFC modified presspaper.
It can be seen that both AC and DC breakdown behaviors are improved with the introduction of NFC. With the increase of NFC concentration, breakdown strength first increases obviously, then a slowdown in the rate of the increase is observed. For AC tests, breakdown strength of nanomodified presspaper varies slightly when NFC content is higher than 2.5 wt %. For DC tests, further NFC addition above 2.5% can continue improving the breakdown properties.
Table 1 lists the results of scale parameters and their 90% confidence intervals derived from the Weibull distributions shown in Figure 10 and Figure 11. Scale parameter equals to the breakdown strength corresponding to the 63.2% probability of the failure. As only ten tests were conducted for each kind of sample, the White method recommended by the IEC guide was adopted for parameter estimation. For AC breakdown strength, scale parameter of reference presspaper is 10.6 kV/mm. That of presspaper modified by 10 wt % NFC is 12.6 kV/mm. For DC breakdown performance, scale parameter of unmodified presspaper is 20.1 kV/mm, that of 10 wt % NFC reinforced presspaper is 24.3 kV/mm. Increases in AC breakdown field and DC breakdown strength by adding 10 wt % NFC to softwood fibers can reach 19% and 21%, respectively.

Table 1.
Scale parameters and their confidence intervals for the Weibull distributions.
As a porous material, breakdown of presspaper is mainly due to the internal partial discharges [33]. Sikorski et al. [34] observed an electrical breakdown of oil-paper insulation due to the high-energy internal discharges with magnitude higher than 15 nC. Because cellulose has a higher breakdown strength than air, decreasing the number of air voids inside presspaper (by increasing the density of presspaper) is one way to improve breakdown performance [35,36]. According to Paschen’s law, smaller air voids tend to have a higher breakdown strength [33]. Therefore, decreasing the average pore diameter will be beneficial for the dielectric strength. Kaplan et al. [37] discussed the influence of pore size on breakdown strength of paper. They found that breakdown strength of paper can be enhanced if the average pore size decreased. Based on the density results and SEM micrographs, the improved breakdown performance of NFC modified presspaper is mainly due to the increased density and decreased pore size.
3.6. Thermal Properites
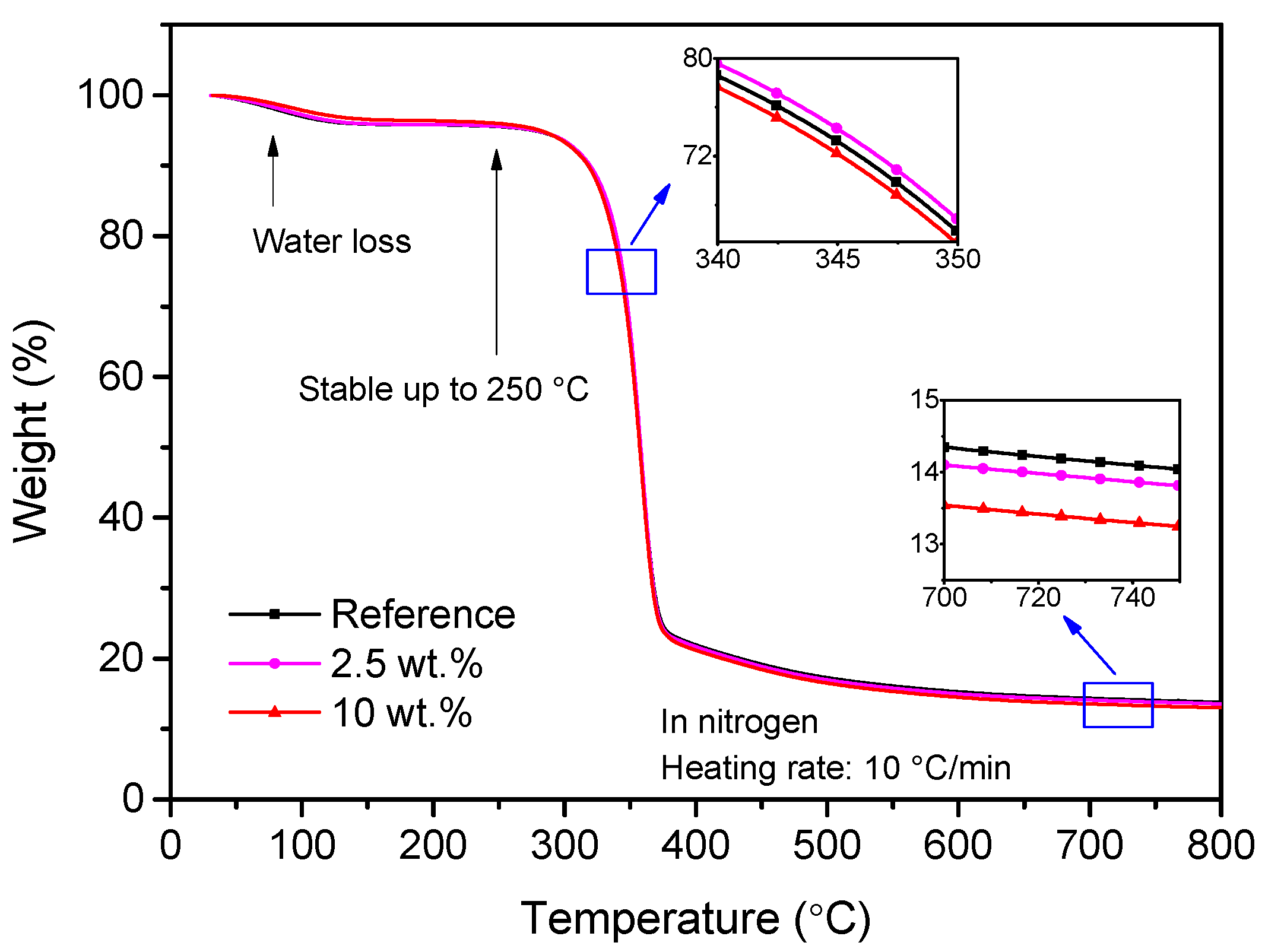
The thermogravimetric curves for reference presspaper and modified presspaper containing NFC are shown in Figure 12. It can be seen that the TGA curves are very similar, which indicates that the introduction of NFC has negligible effect on thermal properties of presspaper. With the increase of temperature, water is firstly removed, resulting in a mass loss of about 4%. Presspaper modified by 10 wt % NFC has a relatively smaller moisture content. Then presspaper samples maintain stable until 250 °C. After that, the further increase of temperature will cause thermal decomposition. All the three samples exhibit a very similar thermal endurance. For a given weight loss, the difference in temperature is less than 5 °C. This is partly due to the similar chemical functional groups and crystallinity indexes of reference presspaper and NFC modified presspaper [26], see Figure 5 and Figure 6. Residue of tested samples is about 14%. Presspaper modified by 10 wt % NFC has a slightly lower residue than reference presspaper. It is concluded that thermal stability of nanomodified presspaper containing NFC is as good as that of ordinary unmodified presspaper.
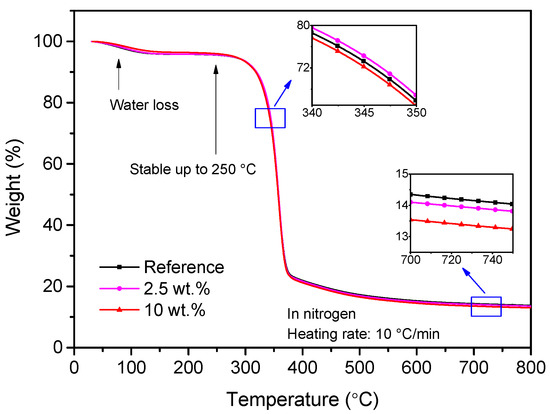
Figure 12.
TGA plots for reference presspaper and nanomodified presspaper containing NFC.
4. Conclusions
This study explored the possibility of improving both mechanical and electrical properties of insulating presspaper by adding an organic nano additive to softwood fibers. Four different concentrations of NFC were taken into account: 0.5 wt %, 2.5 wt %, 5 wt %, and 10 wt %. The major results are as follows:
- (1)
- Presspaper modified by NFC has an increased density and inter fiber bond area. Porosities of reference presspaper and presspaper modified by 10 wt % NFC are 32.5% and 22.6%, respectively. Average pore diameter of reference presspaper is 2 μm. That of presspaper containing 10 wt % NFC is 1 μm. The effect of NFC on chemical functional groups and crystallinity is negligible when NFC content is no more than 10 wt %.
- (2)
- Presspaper modified by 10 wt % NFC has better mechanical and DC breakdown performances than presspaper containing other NFC contents.
- (3)
- Mechanical properties of nanomodified presspaper are improved due to the increased density and inter fiber bond strength. Tensile strength of reference presspaper is 109 MPa, whereas that of presspaper modified by 10 wt % NFC is 136 MPa, resulting in a 25% increase.
- (4)
- Breakdown behaviors of nanomodified presspaper are also enhanced because of the increased density and decreased pore size. Increases in AC and DC breakdown strengths by adding 10 wt % NFC to softwood fibers are 19% and 21%, respectively. The introduction of NFC has negligible effect on thermal stability of presspaper.
- (5)
- NFC has a small effect on volume resistivity and dielectric response. The slightly lower volume resistivity and higher dielectric constant of NFC modified presspaper indicate that the corresponding oil impregnated nanomodified presspaper insulation will be more suitable for applications in DC power equipment.
Acknowledgments
This research was financed by the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program) (2014CB239501) and the Science and Technology Project of China Southern Power Grid (No. KY2014-2-0016).
Author Contributions
Jianwen Huang wrote the manuscript. Jianwen Huang, Longyu Dong, and Zhongliu Zhou jointly designed and performed the experiments. Yuanxiang Zhou and Zengxiang Jun reviewed and edited the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ali, M.; Eley, C.; Emsley, A.M.; Heywood, R.; Xaio, X. Measuring and understanding the ageing of kraft insulating paper in power transformers. IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag. 1996, 12, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Mu, H.; Zhang, G.; Chen, G. A study of oil-impregnated paper insulation aged with thermal-electrical stress: PD characteristics and trap parameters. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2016, 23, 3411–3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollertz, R.; Wagberg, L.; Pitois, C. Effect of composition and morphology on the dielectric response of cellulose-based electrical insulation. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2015, 22, 2339–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Huang, J.; Sha, Y.; Zhang, L.; Jin, F.; Huang, M. Electrical properties of oil-paper affected by water conductivity during paper-making process. High Volt. Eng. 2015, 41, 382–388. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; He, Z.; Bao, L.; Yang, L. Influences of corrosive sulfur on copper wires and oil-paper insulation in transformers. Energies 2011, 4, 1563–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Bao, L. Two factors failure model of oil-paper insulation aging under electrical and thermal multistress. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2014, 9, 957–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, W.; Sha, Y.; Jin, F. Influence of voltage reversal on space charge behavior in oil-paper insulation. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2014, 21, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollertz, R.; Wagberg, L.; Pitois, C. Novel cellulose nanomaterials: Towards usage in electrical insulation. In Proceedings of the IEEE 18th International Conference on Dielectric Liquids (ICDL), Bled, Slovenia, 29 June–3 July 2014; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelmalik, A.A.; Dodd, S.J.; Dissado, L.A.; Chalashkanov, N.M.; Fothergill, J.C. Charge Transport in thermally aged paper impregnated with natural ester oil. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2014, 21, 2318–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baral, A.; Chakravorti, S. Compensating the effect of temperature variation on dielectric response of oil-paper insulation used in power transformers. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2016, 23, 2462–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prevost, T.A.; Oommen, T.V. Cellulose insulation in oil-filled power transformers: Part I—History and development. IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag. 2006, 22, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Imai, T. Advances in nanodielectric materials over the past 50 years. IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag. 2013, 29, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andritsch, T.; Fabiani, D.; Ramirez Vazquez, I. Nanodielectrics-examples of preparation and microstructure. IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag. 2013, 29, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Liao, R. A novel nanomodified cellulose insulation paper for power transformer. J. Nanomater. 2014, 2014, 510864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, R.; Zhang, F.; Yuan, Y.; Yang, L.; Liu, T.; Tang, C. Preparation and electrical properties of insulation paper composed of SiO2 hollow spheres. Energies 2012, 5, 2943–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, R.; Lv, C.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, W.; Tang, C. The insulation properties of oil-impregnated insulation paper reinforced with nano-TiO2. J. Nanomater. 2013, 2013, 373959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oommen, T.V.; Prevost, T.A. Cellulose insulation in oil-filled power transformers: Part II—Maintaining insulation integrity and life. IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag. 2006, 22, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Dong, L.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, R. Enhancement of mechanical and electrical performances of insulating presspaper by introduction of nanocellulose. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 138, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Missoum, K.; Belgacem, M.N.; Bras, J. Nanofibrillated cellulose surface modification: A review. Materials 2013, 6, 1745–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, H.P.S.A.; Davoudpour, Y.; Islam, M.N.; Mustapha, A.; Sudesh, K.; Dungani, R.; Jawaid, M. Production and modification of nanofibrillated cellulose using various mechanical processes: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 99, 649–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boufi, S.; Gonzalez, I.; Delgado-Aguilar, M.; Tarres, Q.; Angels Pelach, M.; Mutje, P. Nanofibrillated cellulose as an additive in papermaking process: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 154, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sehaqui, H.; Allais, M.; Zhou, Q.; Berglund, L.A. Wood cellulose biocomposites with fibrous structures at micro- and nanoscale. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2011, 71, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelina Vallejos, M.; Esteban Felissia, F.; Cristina Area, M.; Vanesa Ehman, N.; Tarres, Q.; Mutje, P. Nanofibrillated cellulose (CNF) from eucalyptus sawdust as a dry strength agent of unrefined eucalyptus handsheets. Carbohyd. Polym. 2016, 139, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, I.; Boufi, S.; Angels Pelach, M.; Alcala, M.; Vilaseca, F.; Mutje, P. Nanofibrillated cellulose as paper additive in eucalyptus pulps. BioResources 2012, 7, 5167–5180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehaqui, H.; Zhou, Q.; Berglund, L.A. Nanofibrillated cellulose for enhancement of strength in high-density paper structures. Nord. Pulp Pap. Res. J. 2013, 28, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, M.; Sha, Y. Study on the suitability of bamboo fiber for manufacturing insulating presspaper. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2016, 23, 3641–3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsolini, P.; Michen, B.; Huch, A.; Tingaut, P.; Caseri, W.R.; Zimmermann, T. Characterization of pores in dense nanopapers and nanofibrillated cellulose membranes: A critical assessment of established methods. ACS Appl. Mater. Interface 2015, 7, 25884–25897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Baker, J.O.; Himmel, M.E.; Parilla, P.A.; Johnson, D.K. Cellulose crystallinity index: Measurement techniques and their impact on interpreting cellulase performance. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2010, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatah, I.Y.A.; Khalil, H.P.S.A.; Hossain, M.S.; Aziz, A.A.; Davoudpour, Y.; Dungani, R.; Bhat, A. Exploration of a chemo-mechanical technique for the isolation of nanofibrillated cellulosic fiber from oil palm empty fruit bunch as a reinforcing agent in composites materials. Polymers 2014, 6, 2611–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, D.H. A theory for tensile strength of paper. Tappi 1969, 52, 674–681. [Google Scholar]
- Hubbe, M.A. Prospects for maintaining strength of paper and paperboard products while using less forest resources: A review. BioResources 2014, 9, 1634–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, V.T. Effects of frequency, temperature, compression, and air pressure on the dielectric properties of a multilayer stack of dry kraft paper. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 1998, 5, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dissado, L.A.; Fothergill, J.C. Electrical Degradation and Breakdown in Polymers; P. Peregrinus: London, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski, W.; Walczak, K.; Przybylek, P. Moisture migration in an oil-paper insulation system in relation to online partial discharge monitoring of power transformers. Energies 2016, 9, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohman, G.T. Cellulose as an insulating material. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1939, 31, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, R. Dramatically enhanced electrical breakdown strength in cellulose nanopaper. AIP Adv. 2016, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, A.M.; Chekunaev, N.I.; Bezhikina, L.V.; Nikolskii, V.G. Composite papers with enhanced electrical strength. Compos. Sci. Technol. 1994, 51, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).