Abstract
This paper is devoted to the influence of two types of electronic scavenger additives/compounds, namely, carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) and methyl iodide, which is also called iodomethane (CH3I), on the dielectric strength of transformer mineral oil. The tests are achieved in a sphere-sphere electrodes arrangement under AC voltage according to the IEC 60156 standard. The investigated additive concentrations range from 0 to 600 ppm. The verification of the conformity of the experimental results with normal and Weibull probabilistic distributions as well as the estimation of the breakdown voltage with risk probabilities of 1%, 10%, and 50% are also performed. It is shown that there is an optimum concentration of each type of electronic scavenger compound at which the dielectric strength of the mineral oil is significantly improved (i.e., it reaches a maximum value). This improvement is of 98% with 500 ppm of CH3I and 93% with 200 ppm of CCl4. It is also shown that the breakdown voltage values of all of the investigated samples with and without additives conform to a Weibull distribution but not to a normal distribution. The obtained results are discussed with regard to the possible mechanisms that may be responsible, particularly the two phases of inception and propagation of the streamers.
1. Introduction
The research for additives that can improve the dielectric strength of insulating oils has received the attention of investigators for many decades. Different types of additives have been considered. More specifically, these last three decades, many studies have focused on the addition of nanostructured particles. Thus, it has been observed that several specific nanoparticles such as Fe3O4 significantly enhance the dielectric strength of mineral oils [1,2,3,4,5]. Nevertheless, the results reported in the literature on the influence of aromatic additives on the breakdown voltage of insulating oils are contradictory [6].
Thus, Zaky and Hawley [6] reported that weak concentrations of aromatic additives enhance the breakdown voltage of insulating oils and that there is an optimum concentration of additives that results in a maximum increase of the breakdown strength. Evangelou et al. [7] reported that the breakdown voltage varies with the additive concentration in a complex manner. The characteristics obtained for a very wide range of additive concentrations indicated that there could be more than one optimum concentration.
Contrary to Zaky and Hawley [6], Mathes and Rouse [8] reported that the addition of a small concentration of poly-aromatic compounds significantly reduces the dielectric strength of naphthenic oil in a point-to-sphere electrode arrangement under impulse voltage. This reduction in the breakdown voltage has been attributed to the streamer development and especially to the increase in the velocity of the streamers’ propagation: the faster the streamer, the lower the dielectric strength. Since these poly-aromatic compounds have both low ionization potentials (Vi) [9] and large electronic-trapping sections (Ee) [10], it is difficult to distinguish which property of these additives is responsible for the streamer development.
Thus, in their pioneering work, Devins et al. investigated the influence of each of the additives’ properties separately (electronic scavenger and low ionization potential) and highlighted the importance of electronic processes in the streamer propagation phenomena [11]. They observed that: (1) the addition of electronic scavengers such as sulfur hexafluoride (SF6: Vi = 15.9 eV and Ee = +1.5 eV) or ethyl chloride (C2H5Cl: Vi = 10.97 eV and Ee = 1.4 eV) to naphthenic oil (Marcol 70) or to 2,2,4-trimethyl-pentane renders the negative streamers more filamentary and increases their velocities. With 0.05 mol/L of SF6 or C2H5Cl, the streamer velocity can reach five times its initial value. There is no detectable effect on the positive streamers in these liquids. They also observed that: (2) the addition of a low ionization potential compound such as N,N-dimethyl-aniline; an organic chemical compound and it is substituted derivative of aniline;(DMA: Vi = 7.14 eV and Ee = −2.1 eV) does not change the negative streamer velocity, whereas it increases (two- to three-fold) compared to that of the positive streamers in naphthenic oil and 2,2,4-trimethyl-pentane. In both cases, there is a concentration (about 0.05 mol/L) above which a saturation is observed [11,12]. Chadband et al. [13] confirmed this result in n-hexane. In contrast, Hebner et al. [14] reported that with 0.1 mol/L of DMA, the positive streamer in n-hexane changes from a filamentary structure to a more or less hemispherical shape and that its velocity reduces slightly.
In order to confirm and to extend the above results, Beroual et al. [15,16] considered compounds having either a high electronic affinity or a very low ionization potential. They observed that: (1) the addition of small concentrations of an electronic scavenger such as carbon tetrachloride (CCl4: Vi = 11.47 eV and Ee = +2.1 eV in the gas phase [10]) to cyclohexane increases the negative streamer velocities: 0.04 mol/L of CCl4 increases the velocity by a factor of 10 and the streamer becomes filamentary. Above 0.04 mol/L, the increase in the velocity is not as significant. They also observed that: (2) the addition of a low ionization potential compound (0.05 mol/L) such as tetramethyl-para-diphenylamine (TPMD) (TMPD: Vi = 6.7 eV [17]) to cyclohexane leads to a moderate increase in the negative streamer velocity (by a factor lower than two) and its shape remains practically unmodified. The velocity of the positive streamer is, in the same conditions, multiplied by a factor of three and the streamer becomes still more filamentary.
A similar effect was observed with DMA [16,18], thus confirming the results reported by Devins et al. [11]. There is also a concentration (about 0.06 mol/L) at which saturation is reached. The influence of the electronic scavenger and low ionization potential compounds is comparable in other liquids such as phenylxylylethane (PXE) and mono-dibenzyltoluene (M/DBT) [19]. Note that the influence of both the electronic scavengers and the low ionization potential compounds on the fast negative streamers is absolutely the same for their positive polarity correlates.
The theory according to which the negative streamers are bush-like and the positive streamers are fast and filamentary is not true. The negative streamers can also be filamentary and fast, as reported in References [16,20,21].
From the above, it appears that the addition of electronic scavenger compounds to dielectric liquids accelerates the streamer propagation and thus reduces the dielectric strength. This acceleration is more significant for slow (bush-like) negative streamers.
More recently, several investigators have shown that the addition of given amounts of specific electronic scavenger compounds increases the inception threshold voltage of the streamers, resulting in an increase in the dielectric strength. Ingebrigtsen et al. [22] observed that in a point-plane electrode arrangement, the 1-methylnaphthalene additive increases the initiation threshold voltage of the point anode streamers in cyclohexane. By adding carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) or Iodobenzene (C6H5I) to mineral oil and tetra-ester oil, Beroual and Aka [23] observed an increase in the inception threshold voltage of the streamers. According to Beroual [24,25], if the inception threshold voltage is higher, the streamer will be more energetic and move faster. Thus, the question that is posed is whether the addition of electronic scavenger compounds: (1) accelerates the streamers, resulting in the decrease of the dielectric strength of the liquid or (2) increases the inception threshold voltage of the streamers and thence leads to an increase in the dielectric strength of the liquid.
The goal of this paper is to investigate the effect of two types of electronic scavenger compounds, namely, carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) and methyl iodide, which is also called iodomethane (CH3I), on the dielectric strength of transformer mineral oil. An analysis of the conformity of the experimental results with Weibull and normal distributions is also performed. Our aim is also to clear up the different contradictory results reported in the literature.
2. Materials and Procedure
The characteristic parameters of the basic mineral oil used are given in Table 1. Note that the mineral oil we used is somewhat aged and that the water content was 39 ppm. Two types of electronic scavenger additives/compounds, namely, carbon tetrachloride (CCl4: Vi = 11.47 eV and Ee = +2.1 eV in the gas phase [3]) and methyl iodide, which is also called iodomethane (CH3I: Vi = 9.54 eV) were used. These were provided by Nexgen Chemical, India and BDH Chemicals Ltd. Poole, England, respectively.

Table 1.
Physicochemical properties of the mineral oil.
Mineral oil-based electronic scavenger samples were prepared by adding the scavenger in concentrations ranging from 200 to 600 ppm by micro-pipit into 500 mL of dry oil. The liquids were mixed with the aid of a magnetic stirring process at ambient temperature and at a speed of 1100 rpm for about 15 min. Then, the electronic scavenger samples were placed in the ultrasonic homogenizer for 30 min to obtain a homogeneous dispersion fluid. Then, the samples were kept under a vacuum of 0.16 MPa for 24 h to eliminate humidity and internal bubbles.
The dielectric breakdown (BDV) measurements were performed with a Foster Oil Test 90 type with a test cell of 500 mL according to the IEC 60156 standard [26]. The electrode arrangement consisted of two brass hemispheres 12.5 mm in diameter and an electrode gap of 2.50 ± 0.05 mm. An alternating voltage ramp rate of 2 ± 0.2 kV/s was applied continuously from zero to breakdown. The breakdown voltage is the average of 30 successive measurements and the time delay between the successive measurements was 2 min. For the Weibull distribution, we performed another series of measurements. It is to have a power of 2 (24 = 16) and to deduce the slope of Weibull plots. Sixteen is a reasonable number for a Weibull analysis.
3. Experimental Results
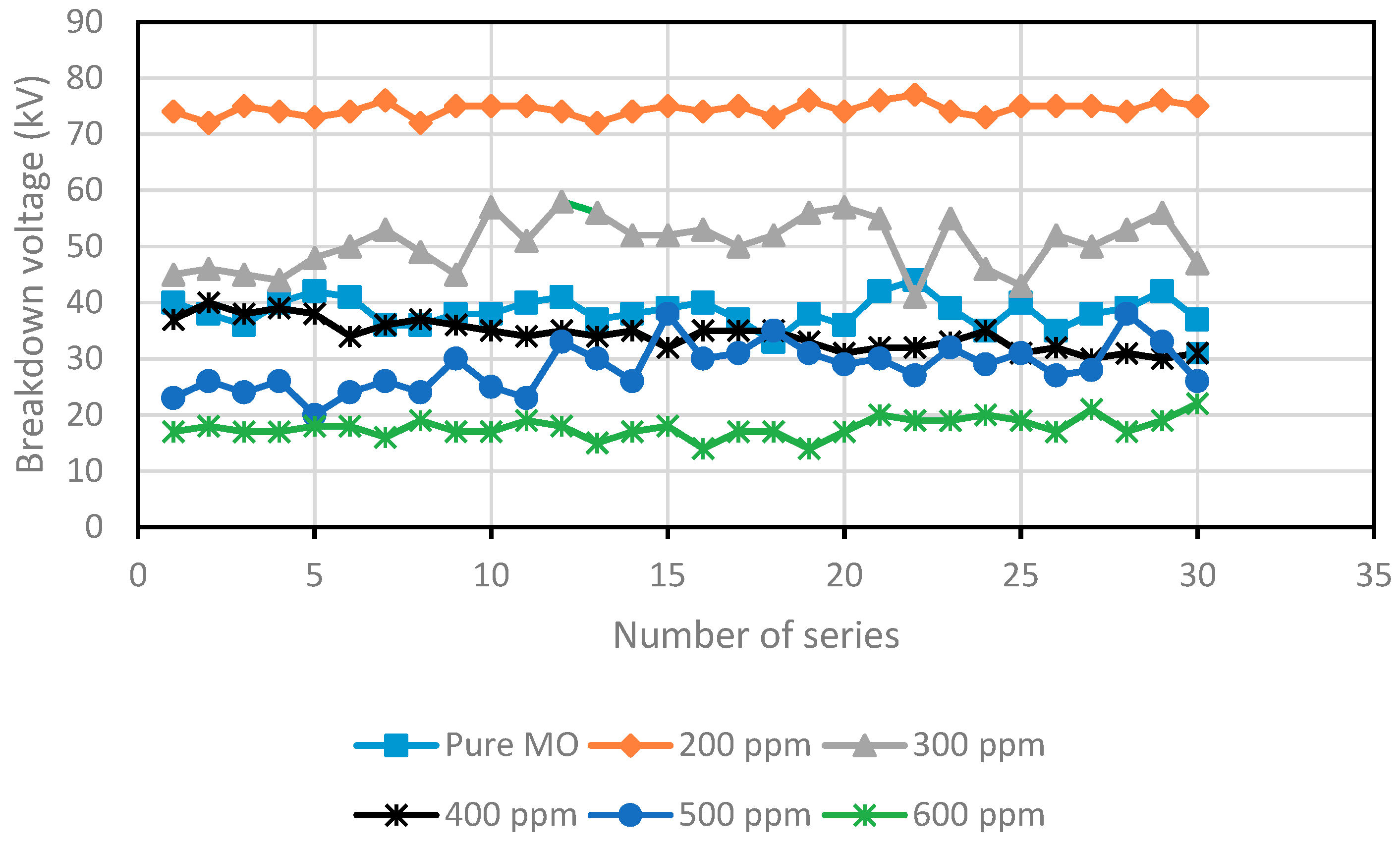
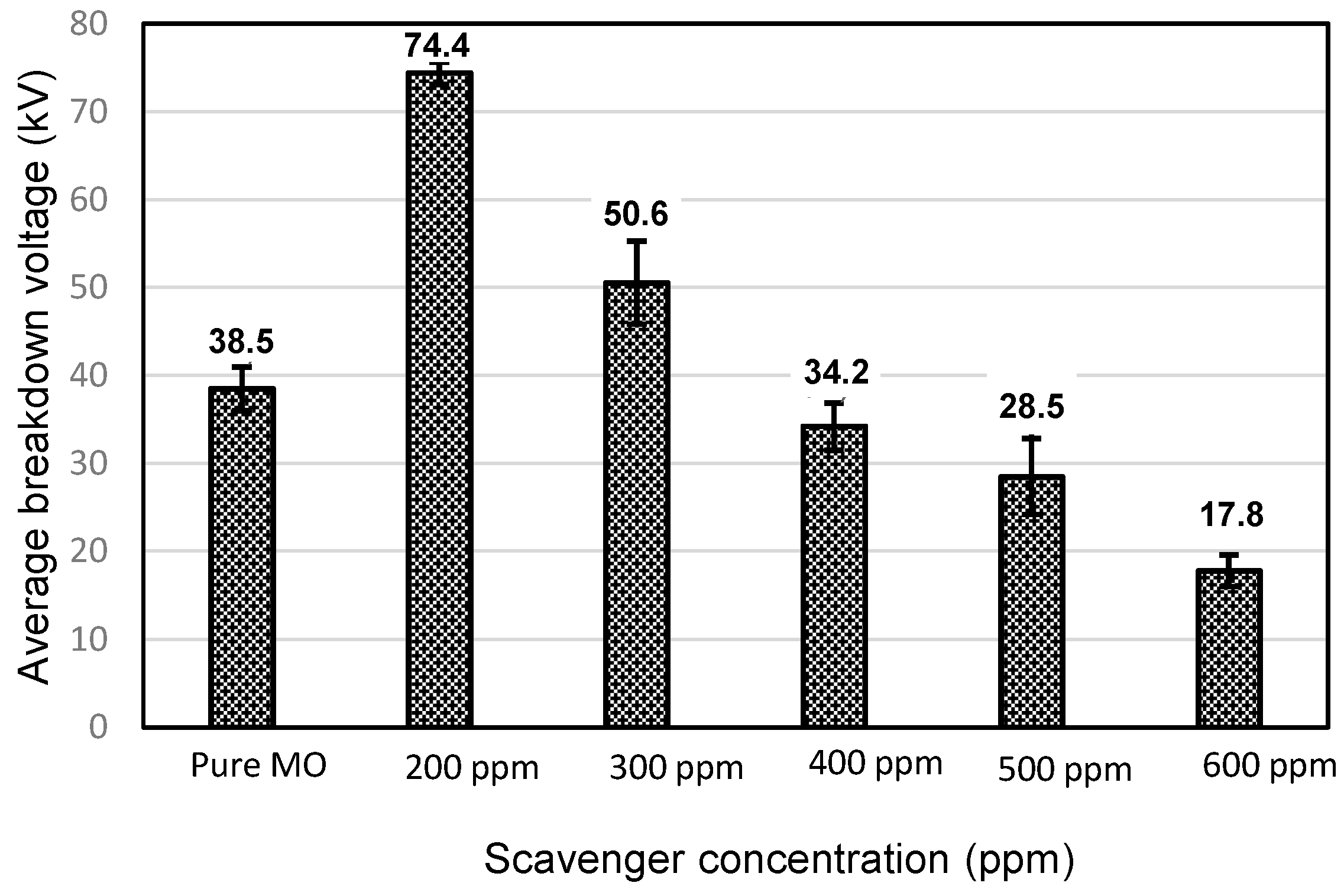
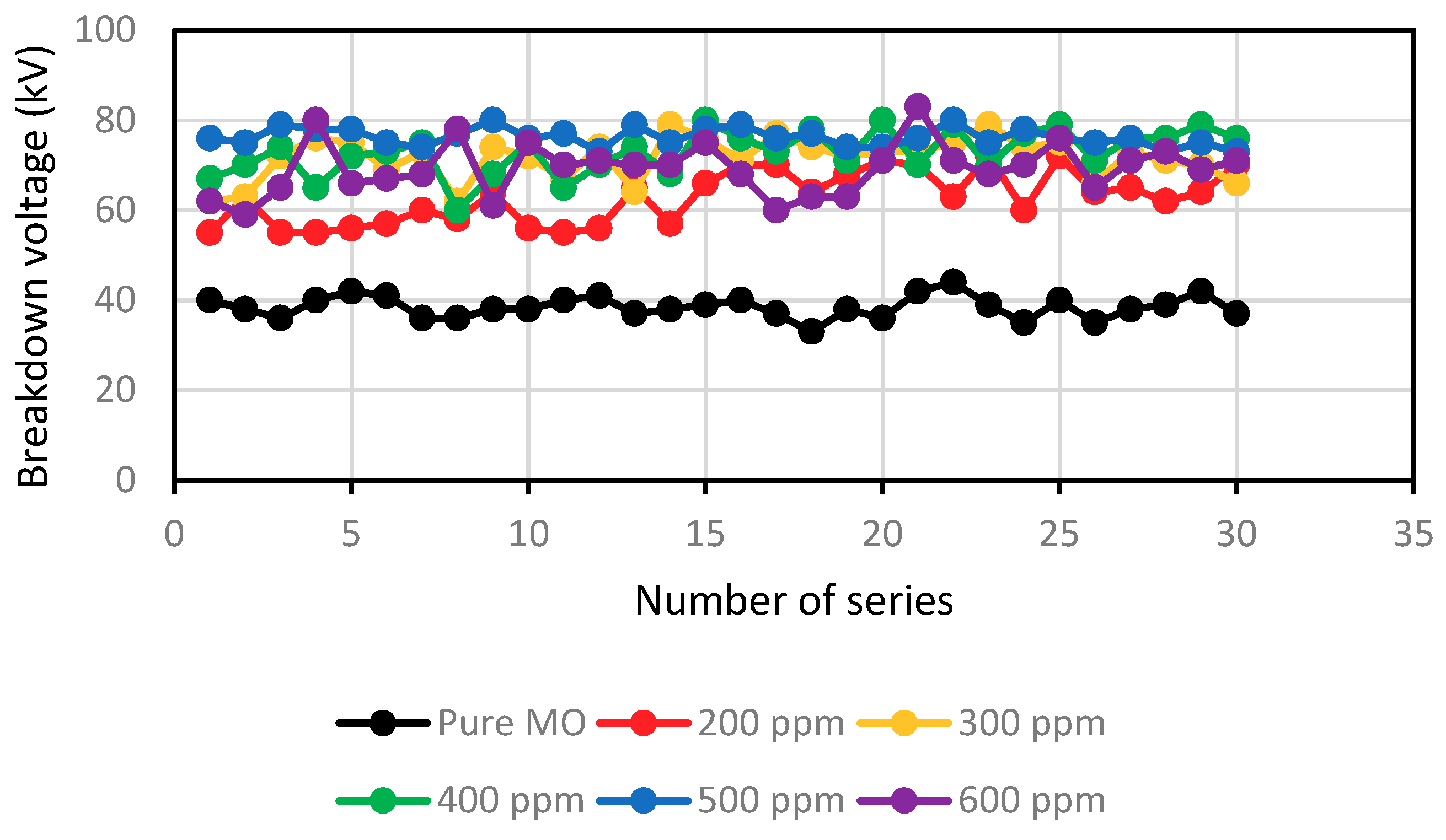
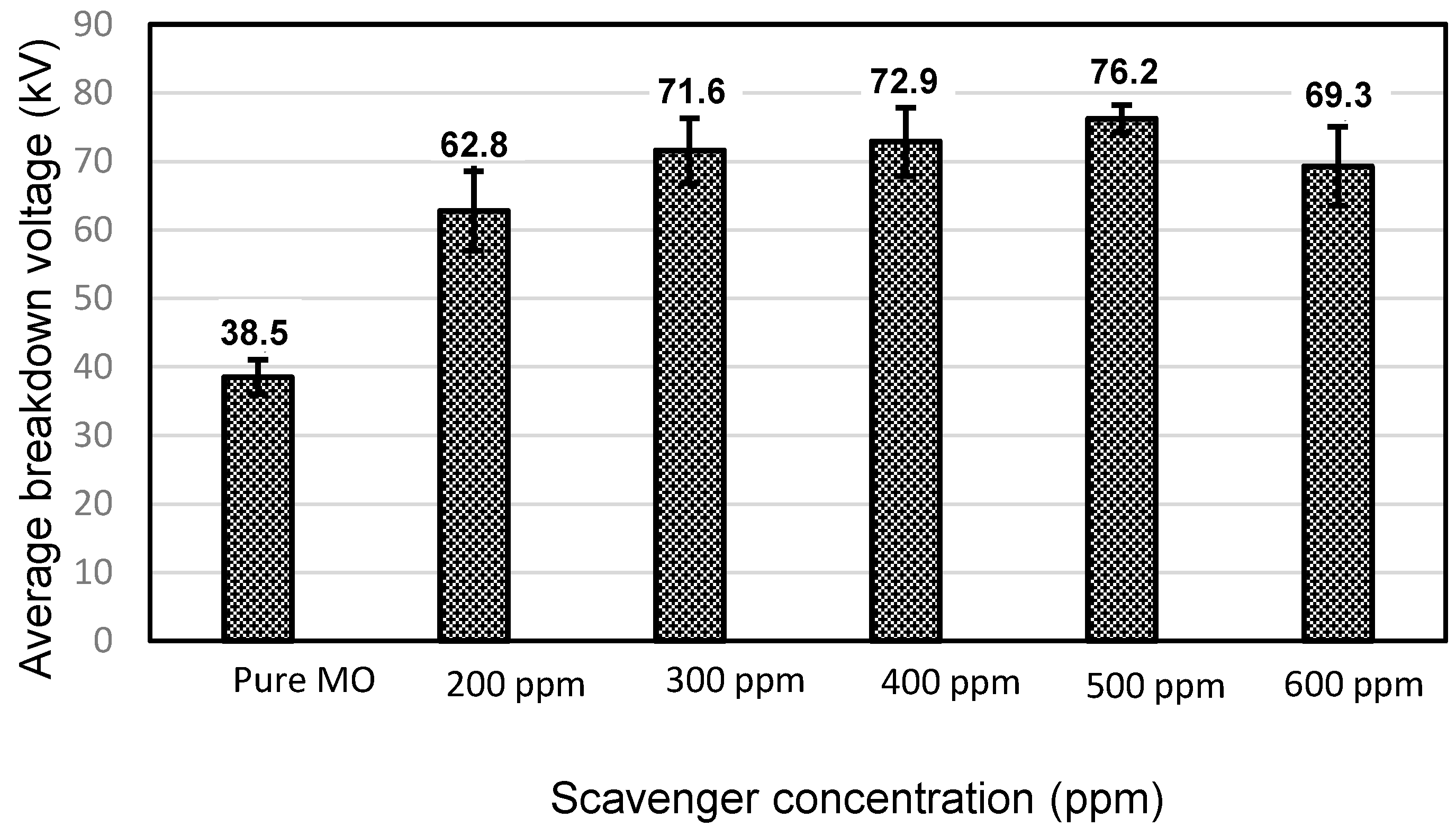
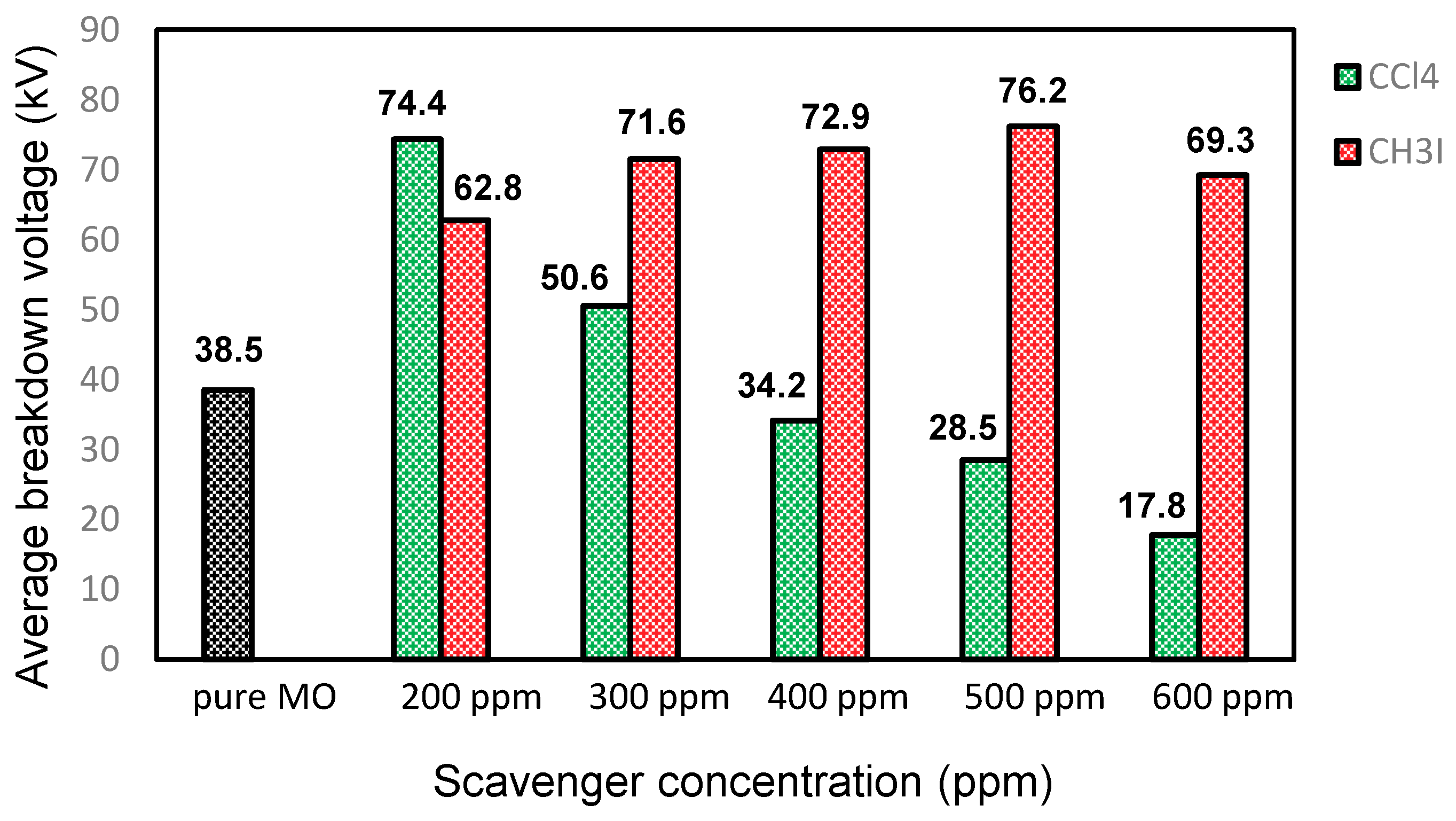
Figure 1 and Figure 2 depict the variation in the breakdown voltage (UBDV) of the mineral oil when adding CCl4 and Figure 3 and Figure 4 depict that of the mineral oil when adding CH3I. We observe that the addition of 200 ppm of CCl4 increases the BDV of the mineral oil by 93%, while with the addition of 300 ppm; there is only a 31% improvement. Beyond this amount of CCl4, the BDV decreases to reach 17.8 kV for a concentration of 600 ppm, i.e., a BDV reduction of 54%. While adding the CH3I, the BDV of the mineral oil increases with the amount of CH3I up to 500 ppm. There is a 98% improvement at this concentration. Beyond this concentration, the BDV decreases, but remains higher than the breakdown voltage of the mineral oil. There is an 80% enhancement at 600 ppm. Thus, there is an optimal concentration of these specific additives at which the dielectric strength of the mineral oil is significantly improved. On the other hand, CH3I appears to be a very effective additive for the improvement of dielectric strengths, as shown in Figure 5.
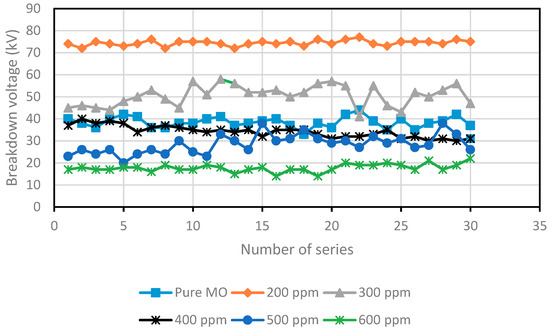
Figure 1.
The breakdown voltage for various concentrations of the mineral oil (MO)/CCl4 scavenger.
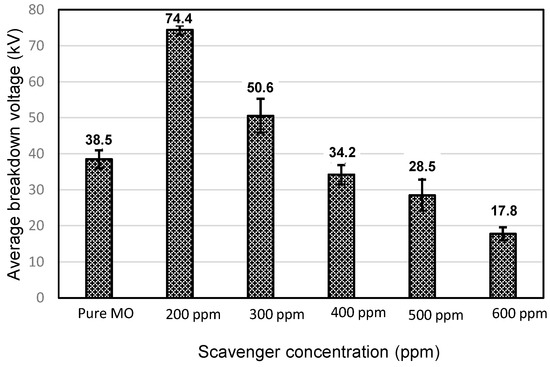
Figure 2.
Comparison between the average AC breakdown voltage of the MO and those of the MO with different CCl4 concentrations.
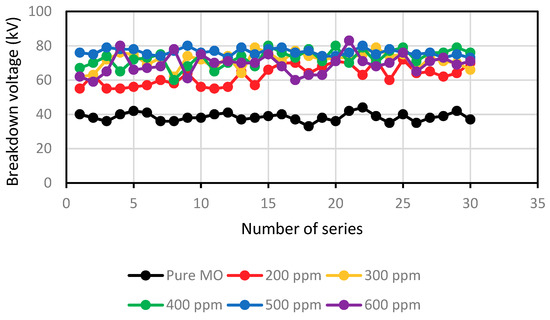
Figure 3.
The breakdown voltage for various concentrations of the MO/CH3I scavenger.
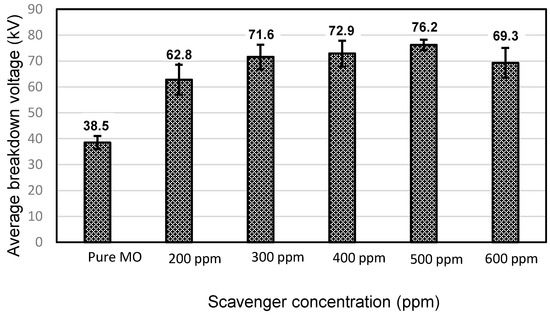
Figure 4.
Comparison between the average AC breakdown voltage of the MO and those of the MO with different CH3I concentrations.
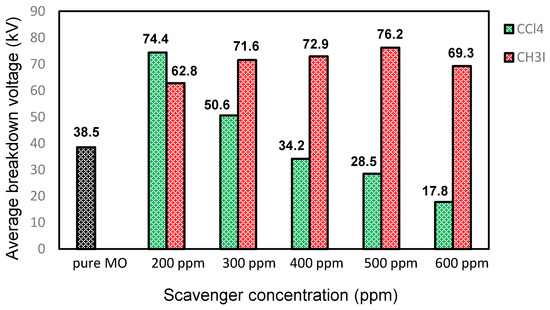
Figure 5.
Comparison between the CCl4 and CH3I additives in the MO.
4. Statistical Analysis of Experimental Data
In this section, we analyze the conformity of the experimental data with two of the main probabilistic functions that are the most frequently used to study the breakdown voltage of dielectric materials, namely, the normal and Weibull distribution laws [27,28,29]. For that purpose, we applied the Shapiro–Wilk [30] and Anderson–Darling [31] tests, respectively, by considering a test level, α, to be significant if it was equal to 5% (α = 0.05) and by using R software [32]. Note that the hypothesis was accepted or rejected depending of the calculated p-value with respect to the value of α. For p-values > α, we accepted the null hypothesis according to which the sample data belongs to a statistical distribution [30,32].
4.1. Weibull Probability of the AC Breakdown Voltage of the Investigated Samples
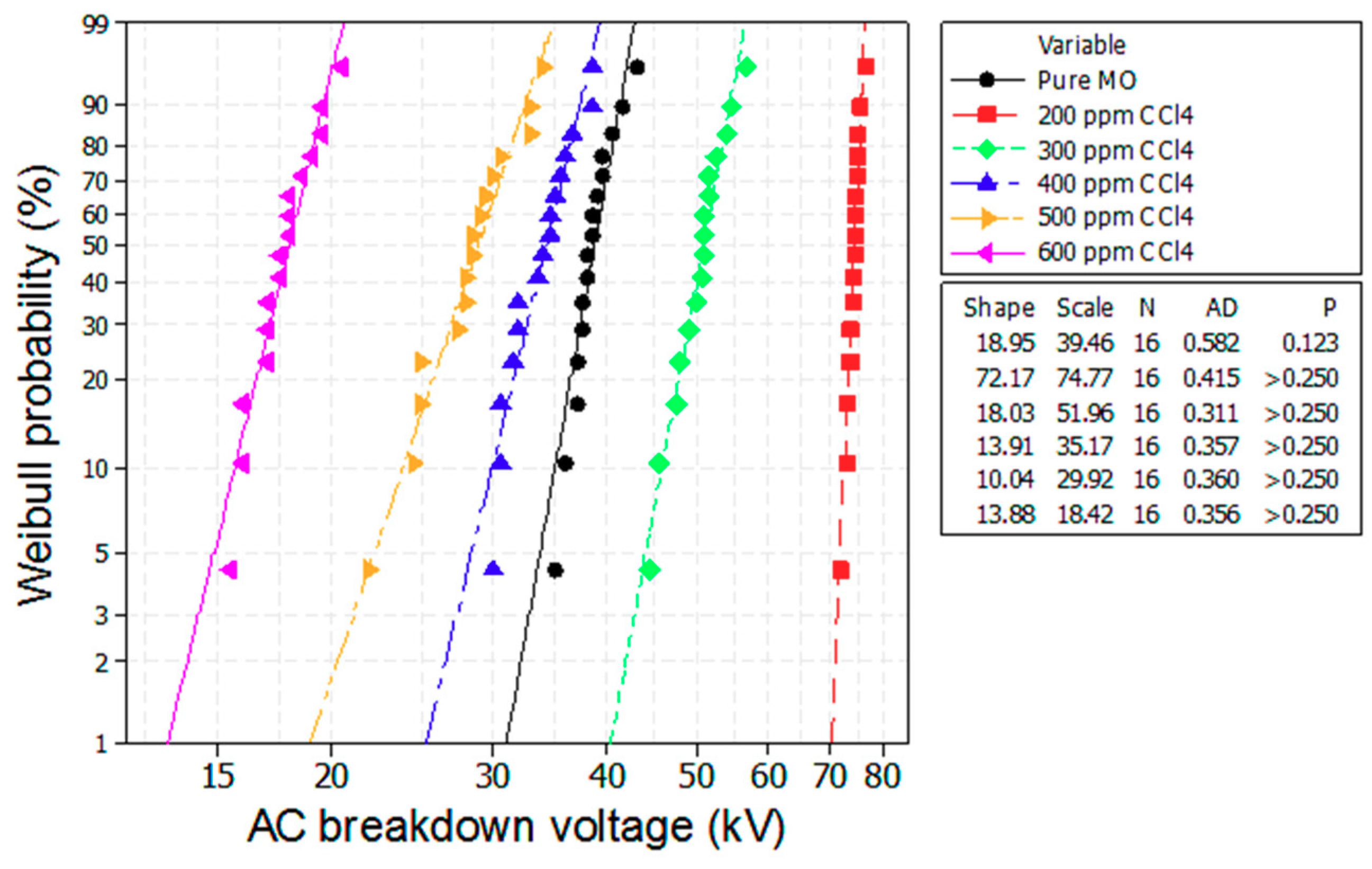
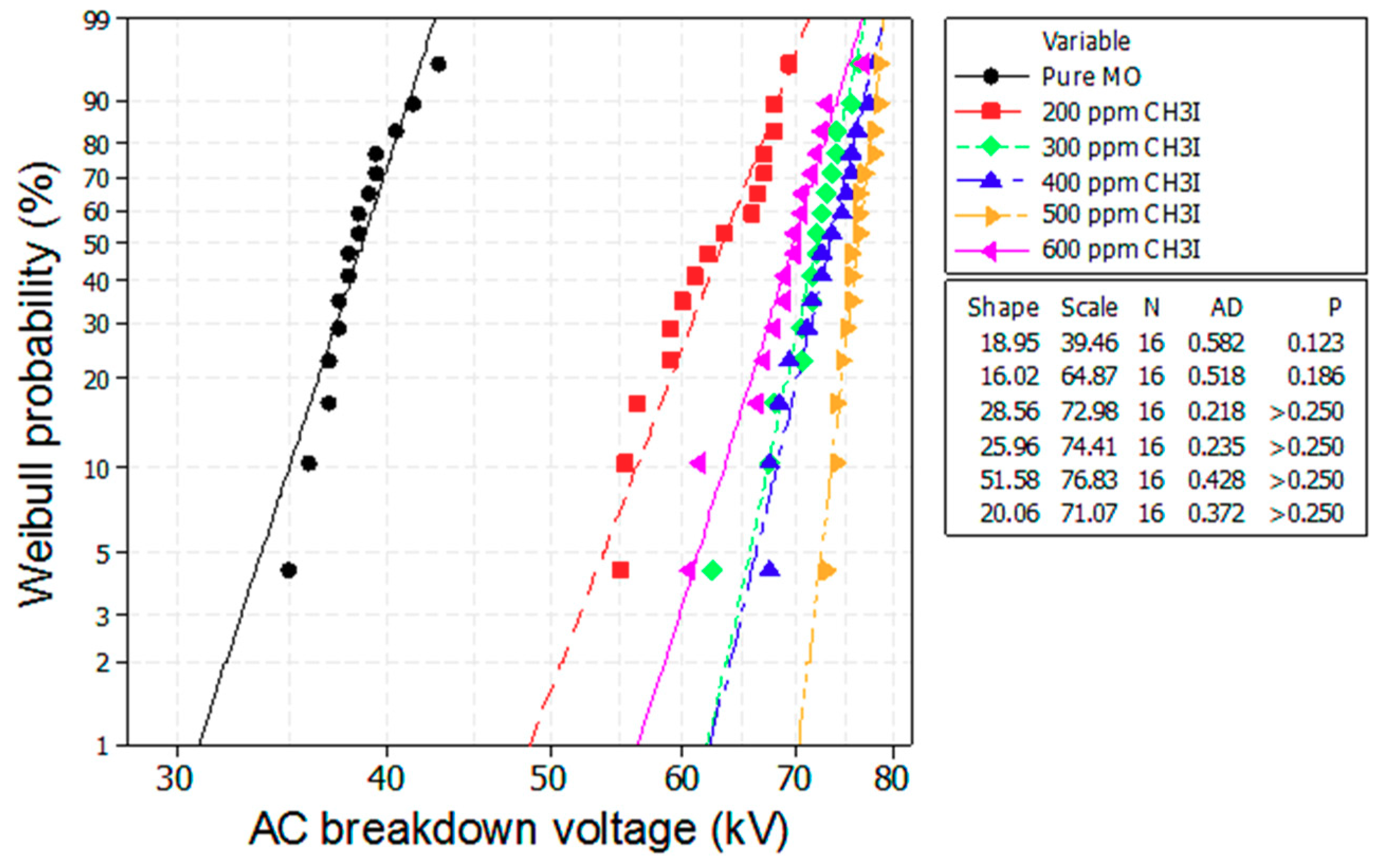
Figure 6 and Figure 7 depict the Weibull plots of the AC breakdown voltages of the mineral oil with different concentrations of CCl4 and CH3I. We observe that the experimental data from all of the investigated samples conforms to a Weibull distribution function, as shown in Table 2.
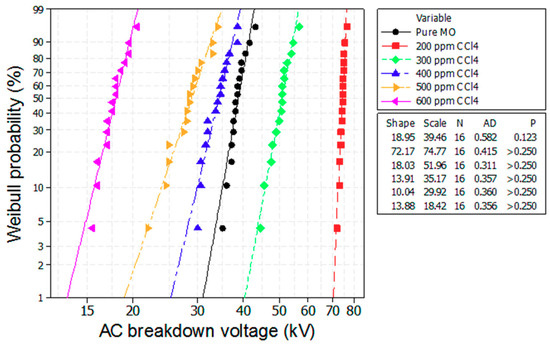
Figure 6.
Weibull plot of the breakdown voltage of the mineral oil with various scavenger additives of CCl4.
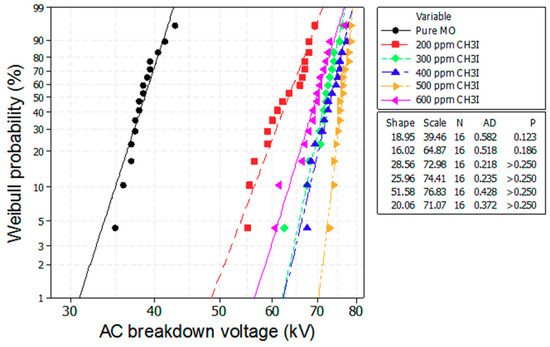
Figure 7.
Weibull plot of the breakdown voltage of the mineral oil with various concentrations of the CH3I scavenger additive.

Table 2.
The p-value of the mineral oil with various concentrations of CCl4 and CH3I scavenger additives.
Where the shape parameter is equal to the slope of the line in a probability plot, it affects the shape of the curve. The scale parameter is related to the scattering of the data and indicates the degree of failure. The Anderson–Darling (AD) value is the Anderson–Darling measure of the area between the fitted line and the empirical distribution function, which is based on the data points. N is the number of breakdown voltage data points. The p-value is a probability that measures the evidence against the null hypothesis.
4.2. Histogram and Normal Distribution of the AC Breakdown Voltage of the Investigated Samples
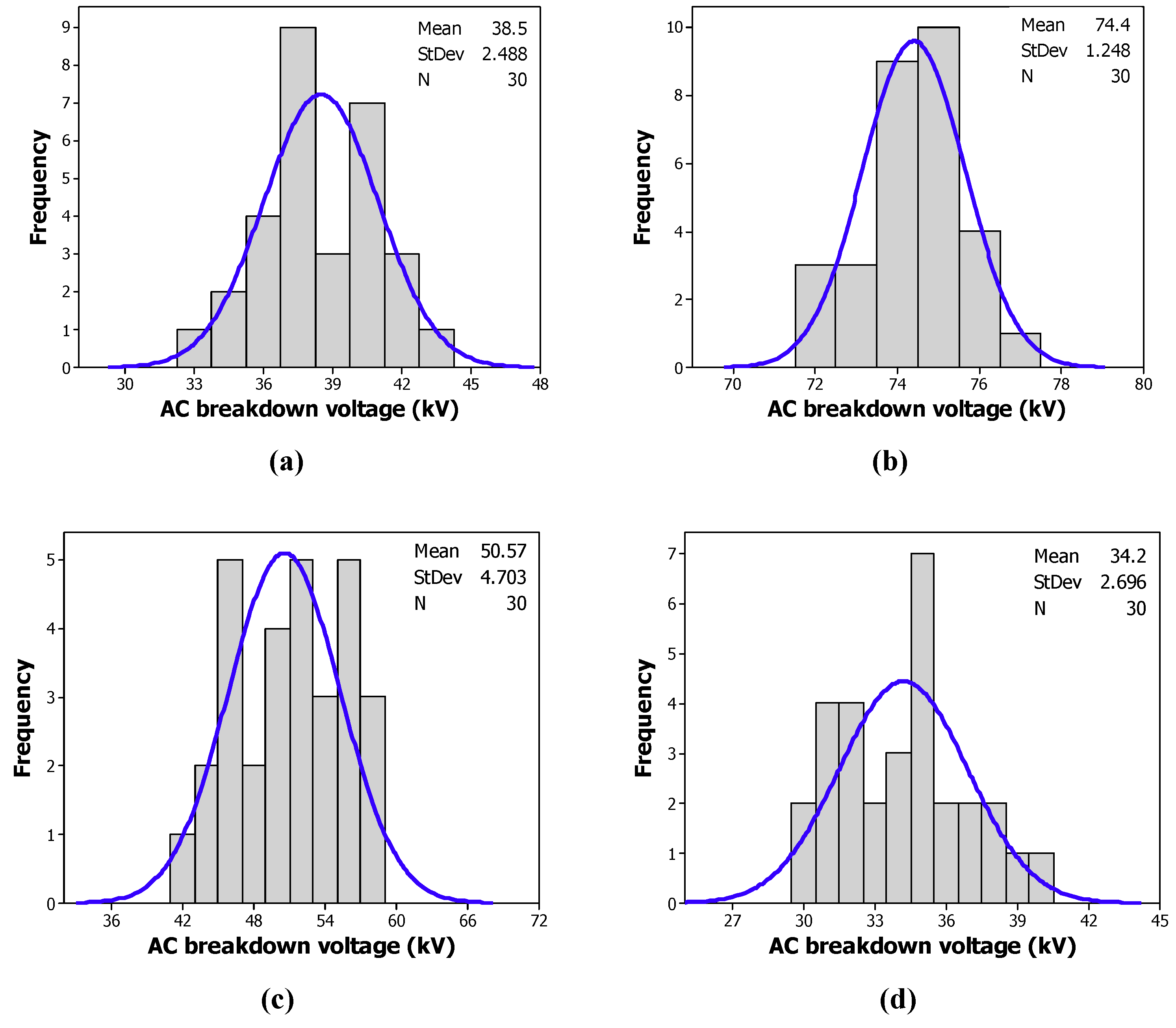
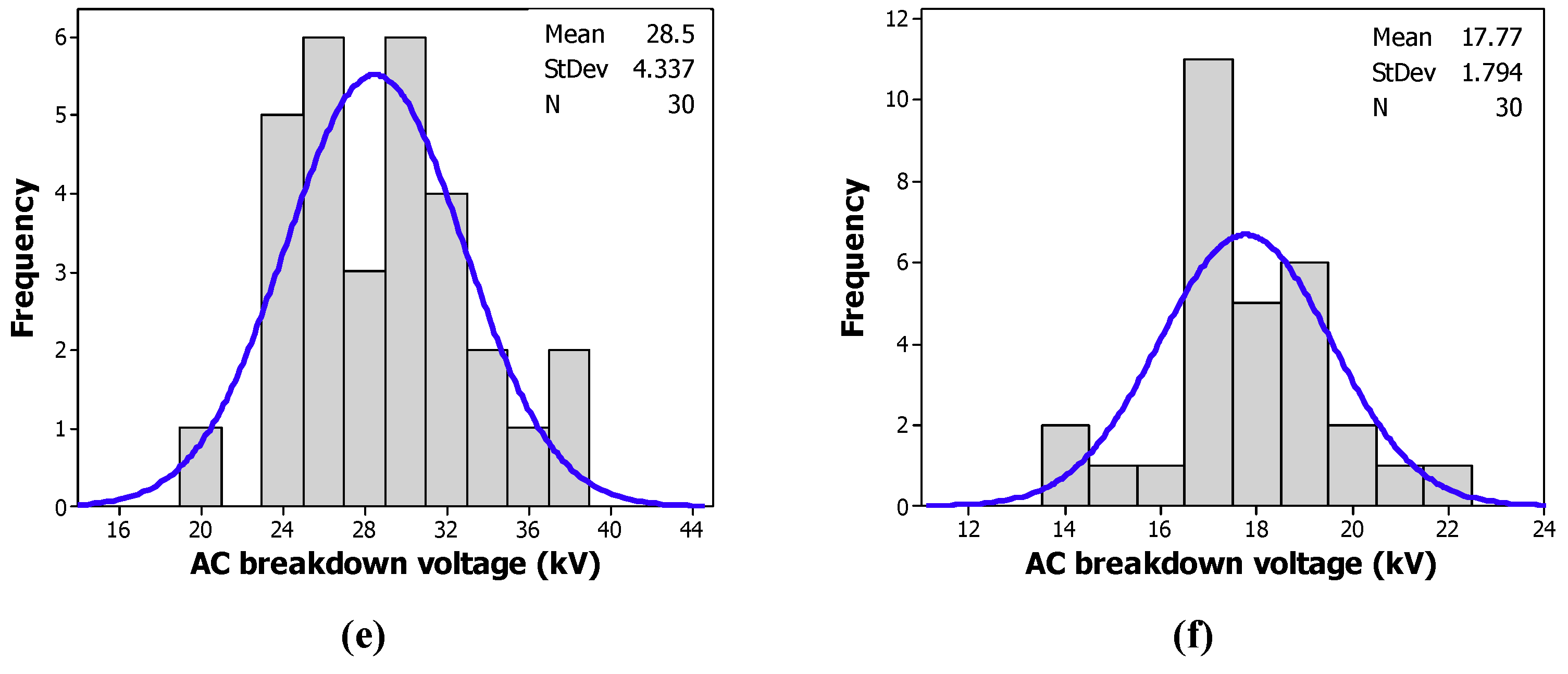
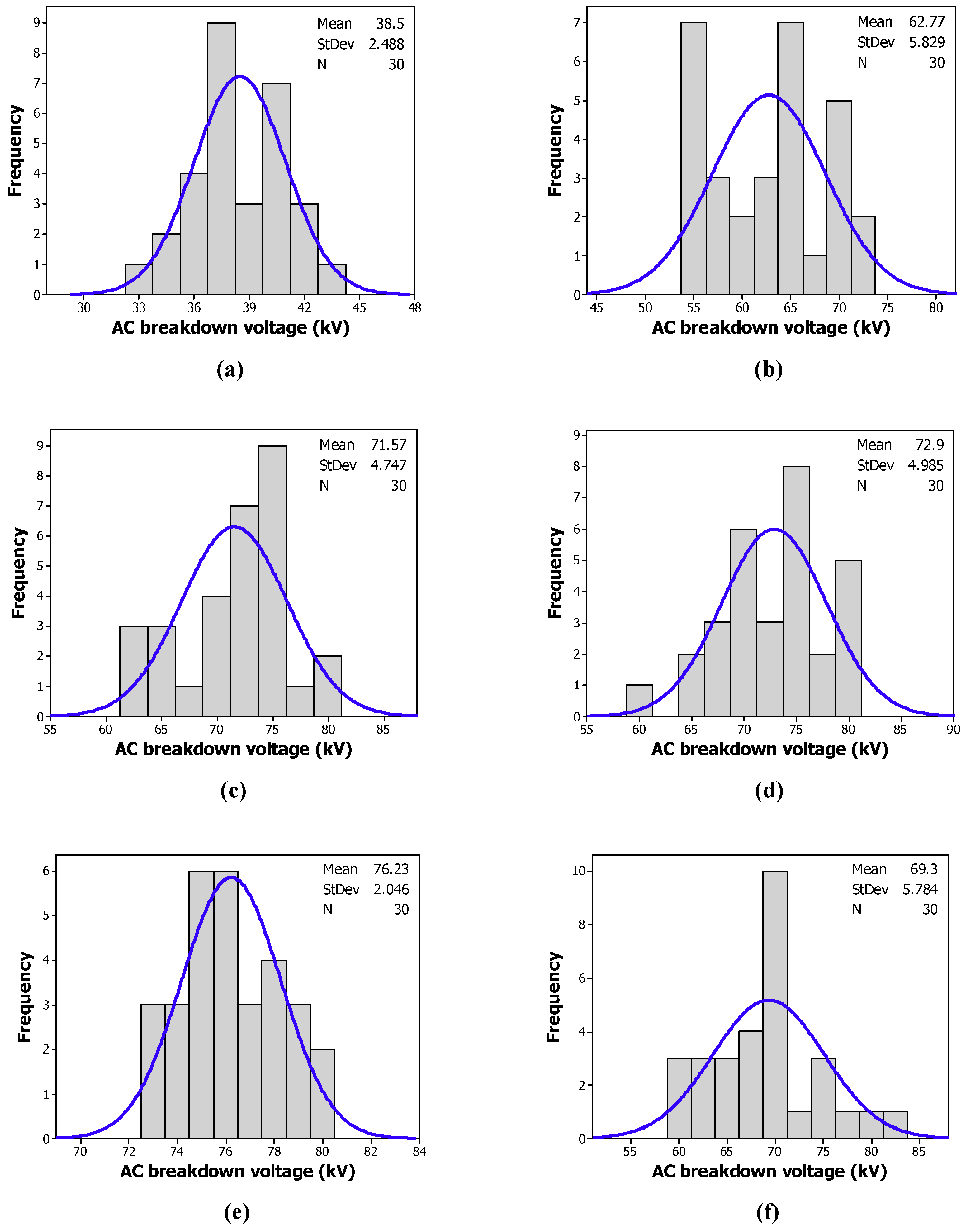
Figure 8 and Figure 9 give the histograms of the distribution of the breakdown voltages of the tested samples with CCl4 and CH3I, respectively. The blue lines refer to normal distribution of the tested sample measurements. Contrary to a Weibull distribution, we observe some anomalies, as depicted in Table 3. The experimental data does not obey a normal distribution.
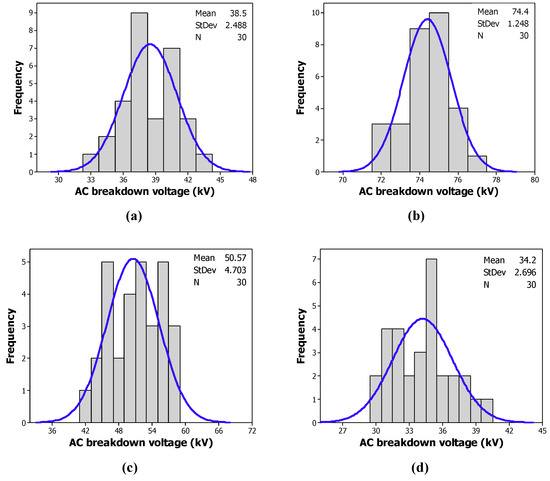
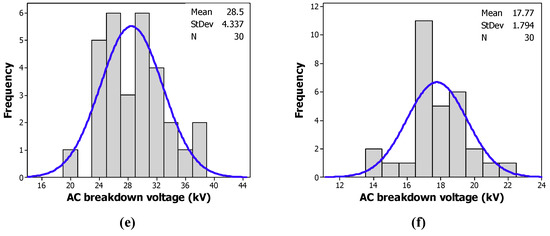
Figure 8.
Frequency of the breakdown voltage of: (a) the MO; (b) the MO/CCl4 (200 ppm); (c) the MO/CCl4 (300 ppm); (d) the MO/CCl4 (400 ppm); (e) the MO/CCl4 (500 ppm); (f) the MO/CCl4 (600 ppm).
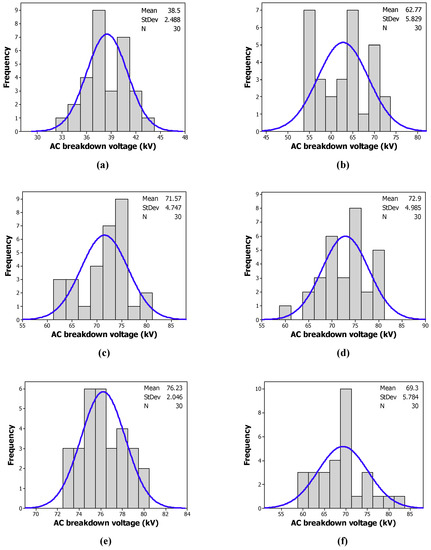
Figure 9.
Frequency of the breakdown voltage of: (a) the MO; (b) the MO/CH3I (200 ppm); (c) the MO/CH3I (300 ppm); (d) the MO/CH3I (400 ppm); (e) the MO/CH3I (500 ppm); (f) the MO/CH3I (600 ppm).

Table 3.
The p-value of the mineral oil with various concentrations of the CCl4 and CH3I electronic scavenger additives.
4.3. Estimation of the the Main Breakdown Voltage Probabilities
Table 4 gives the AC breakdown voltage probabilities at 1%, 10%, and 50% of the Weibull distribution for the investigated samples. In addition, it shows the incremental percentage of the mineral oil with various concentrations of electronic scavenger additives. The breakdown voltage at a cumulative probability of 50% is an indication of the median value. The breakdown voltage at a cumulative probability of 1% gives an indication about the reliability of the oil. This is fundamental for determining the nominal voltage for the equipment design (i.e., the safety coefficient).

Table 4.
The AC breakdown voltage at different breakdown probabilities for the mineral oil with CCl4 and CH3I electronic scavenger additives at various concentrations in the mineral oil.
We observe that the UBDV (1%) is also optimum at 200 ppm of CCl4, with an improvement of 126%, and that it is optimum at 500 ppm of CH3I with an improvement of 126% as well with respect to the UBDV (1%) of the mineral oil. The improvement with respect to the AC average breakdown voltage of the mineral oil (UBDV = 38.5 kV) is 82%. These interesting results can be very useful when designing high-voltage oil-filled apparatus.
5. Discussion
It appears from the above results that electronic scavenger additives enable the improvement of the dielectric strength of mineral oil and that for each type of additive, there is an optimal concentration allowing to the achievement of the optimum breakdown voltage value. Beyond this concentration, the effect of the electronic scavenger additives drops. It is also possible to have different optimum concentrations. This somewhat confirms the idea reported by Evangelou et al. [7].
As indicated in Section 1, many investigators attributed the reduction or the enhancement of the dielectric strength to the streamer development. What is the underlying mechanism?
To explain the influence of the additives on the streamer propagation, Devins et al. [11] proposed a model in which they assume that field ionization occurs in the liquid. They use Zener’s theory of tunneling in solids to calculate the concentration of the positive and negative carriers contained in a cylindrical conducting channel. According to this model, the positive streamer velocity is constant. Concerning the negative streamers, the propagation occurs in two stages: an electron injection and trapping followed by ionization within the liquid. This produces a plasma similar to that produced with positive polarity. The negative streamer velocity is determined by the time spent in one or the other stage, i.e., the injection or the trapping.
Even if this model is questionable, because some assumptions need to be justified [15], it is supported by two interesting facts. The first is that the addition of electron scavengers reduces the trapping distance and the time (t1) spent in the first step and thus increases the negative velocity. The second fact is that the addition of low ionization potential additives increases the rate of ionization and reduces the time (t2) spent in the second step, and thus still increases the velocity. The velocity computed according to this model is constant. This is not true. The propagation of the streamers is done in jumps.
In recent work, a new model perfectly describing this step propagation and the influence of additives was proposed [24,25]. This model, based on considerations related to energy, allows us to explain the pre-breakdown processes and to evaluate the propagation velocity of the streamer. According to this model, the electronic scavenger additives increase the current pulse frequency and reduce the time duration between consecutive discharges, and then increase the electrical charge that assists the streamer in its propagation. This results in an increase in the average propagation velocity of the streamer. The streamer becomes more energetic, then more filamentary, and thence rapid [24,25]. Thus, if the streamer is more rapid, the time to breakdown will be shorter. However, this does not necessarily mean that the dielectric strength (breakdown voltage) of the liquid will be low/reduced. As reported by Beroual [23] and Beroual et al. [25], electronic scavenger additives act on the initiation of the streamers by increasing their threshold voltage. This means that if the voltage is high, then the initiated streamer will be more energetic and become faster. As long as the amount of additive has not reached the saturation threshold, all of the injected charges are captured. Beyond this saturation threshold, the electronic scavenger additive accelerates the streamers, resulting in the drop of the dielectric strength of the oil.
6. Conclusions
This work shows that the dielectric strength of liquids can be improved by adding a certain concentration of an electronic scavenger compound. Electronic scavenger additives act on the initiation of streamers by reducing the injected charge carriers. This results in an increase in the threshold voltages of the streamers and thence in an increase of the dielectric strength of the oil. The breakdown voltage increases up to a certain optimal concentration of additives. Beyond this optimal amount of additive, which can be considered the saturation level, the electronic scavenger additive accelerates the streamers, resulting in the drop in the dielectric strength of the oil.
Such a result is of great importance for industrial applications and especially for high-voltage oil-filled apparatuses.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, U.K. and A.B.; Methodology and Software, U.K.; Validation, A.B.; Formal Analysis, Investigation, Resources, Data Curation, A.B. and U.K.; Writing-Original Draft Preparation, A.B.; Writing-Review & Editing, A.B. and U.K.; Project Administration and Funding Acquisition, U.K.
Funding
This research was funded by King Saud University grant number ISPP#47.
Acknowledgments
The authors extend their appreciation to the International Scientific Partnership Program (ISPP) at King Saud University for funding this research work through ISPP#47.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Segal, V.; Hjortsberg, A.; Rabinovich, A.; Nattrass, D.; Raj, K. AC (60 Hz) and Impulse Breakdown Strength of a Colloidal Fluid Based on Transformer Oil and Magnetite Nanoparticles. In Proceedings of the Conference Record of the 1998 IEEE International Symposium on Electrical Insulation, Arlington, VA, USA, 7–10 June 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Kopcansky, P.; Tomco, L.; Marton, K.; Koneracka, M.; Timko, M.; Potocova, I. The DC dielectric breakdown strength of magnentic fluids based on transformer oil. J. Magn. Mater. 2005, 289, 415–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari, M.; Rasoulifard, M.H.; Hosseini, H. Dielectric breakdown strength of magnetic nanofluid based on insulation oil after impulse test. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 399, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiq, M.; Li, C.; Ge, Y.; Lv, Y.; Yi, K. Effect of Fe3O4 Nanoparticle Concentrations on Dielectric Property of Transformer Oil. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on High Voltage Engineering and Application (ICHVE), Chengdu, China, 19–22 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, Y.; Rafiq, M.; Li, C.; Shan, B. Study of dielectric breakdown performance of transformer oil based magnetic nanofluids. Energies 2017 10, 1025.
- Zaky, A.A.; Megahed, I.Y.; Evangelou, C. The effect of organic additives on the breakdown and gassing properties of mineral oils. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1976, 9, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelou, C.; Zaky, A.A.; Megahed, I.Y. The effect of organic additives on the breakdown strength of transformer oil. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1973, 6, 60–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathes, K.N.; Rouse, T.O. Influence of Aromatic compounds in oil on Pirelli Gassing and Impulse Surge Breakdown. In Proceedings of the Conference on Electrical Insulation & Dielectric Phenomena-Annual Report, Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 3–6 November 1975; pp. 129–140. [Google Scholar]
- Blaunstein, R.P.; Christophorou, L.G. On Molecular Parameters of Physical, Chemical and Biological Interest. Radiat Res. Rev. 1971, 3, 69–118. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, A.O.; Gangwer, T.E.; Holroyd, R. Chemical Reaction Rates of Quasi Free Electrons in Non-Polar Liquids. J. Phys. Chem. 1975, 79, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devins, J.C.; Rzad, S.J.; Schwabe, R.J. Breakdown and Pre-breakdown Phenomena in Liquids. J. Appl. Phys. 1981, 52, 4531–4545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, S.; Yamada, H. Optical Study of Conduction and Breakdown in Dielectric Liquids. IEEE Trans. Electr. Insul. 1980, 15, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadband, W.G.; Sufian, T.M. Experimental Support for a Model of Positive Streamers Propagation in Liquid Insulation. IEEE Trans. Electr. Insul. 1985, 20, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebner, R.E.; Kelley, E.F.; Forster, E.O.; Fitzpatrick, G.J. Observation of Pre-breakdown and Breakdown Phenomena in Liquid Hydrocarbons Non-uniform Field Conditions. IEEE Trans. Electr. Insul. 1985, 20, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beroual, A.; Tobazéeon, R. Pre-breakdown Phenomena in Liquid Dielectrics. IEEE Trans. Electr. Insul. 1986, 21, 613–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beroual, A.; Tobazeon, R. Propagation et génération des streamers dans les diélectriques liquides. Rev. Phys. Appl. 1987, 22, 1117–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houser, H.; Jarnagin, R.C. Electron Ejection from Triplet State in Fluid Solution. J. Chem. Phys. 1970, 52, 1069–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakao, Y.; Itoh, H.; Hoshino, S.; Sakai, Y.; Tagashira, H. Effects of additives on prebreakdown phenomena in n-hexane. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 1994, 1, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beroual, A. Electronic processes and streamer propagation phenomena in insulating oils. Arch. Electr. Eng. 1995, 4, 579–592. [Google Scholar]
- Beroual, A.; Zahn, M.; Badent, A.; Kist, K.; Schwabe, A.J.; Yamashita, H.; Yamazawa, K.; Danikas, M.; Chadband, W.D.; Torshin, Y. Propagation and structure of streamers in liquid dielectrics. IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag. 1998, 14, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, H.; Sato, T. High-speed Electro-optical Measurement of Pre-breakdown Current in Dielectric Liquids. IEEE Trans. Electr. Insul. 1985, 20, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingebrigtsen, S.; Lundgaard, L.E.; Åstrand, P.-O. Effects of additives on prebreakdown phenomena in liquid cyclohexane: I. Streamer initiation. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2007, 40, 5161–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beroual, A.; Aka-N’Gnui, T. Influence of Additives and Hydrostatic Pressure on Streamers Initiation and Dielectric Strength of Liquids. In Proceedings of the Annual Report Conference on Electrical Insulation and Dielectric Phenomena, Cancun, QR, Mexico, 20–24 October 2002; pp. 248–251. [Google Scholar]
- Beroual, A. Electronic and gaseous processes in the prebreakdown phenomena of dielectric liquids. J. Appl. Phys. 1993, 73, 4528–4533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beroual, A. Pre-Breakdown Mechanisms in Dielectric Liquids and Predicting Models. In Proceedings of the IEEE Electrical Insulation Conference, Montréal, QC, Canada, 19–22 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- IEC TC/SC 10. IEC 60156 Ed. 2, Insulating Liquids-Determination of the Breakdown Voltage at Power Frequency–Test Method; ANSI: Washington, DC, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Makmud, M.Z.H.; Illias, H.A.; Chee, C.Y.; Sarjadi, M.S. Influence of conductive and semi-conductive nanoparticles on the dielectric response of natural ester-based nanofluid Insulation. Energies 2018, 11, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppas, G.D.; Danikas, M.G.; Bakandritsos, A.; Charalampakos, V.P.; Pyrgioti, E.C.; Gonos, I.F. Statistical investigation of ac breakdown voltage of nanofluids compared with mineral and natural ester oil. IET Sci. Meas. Technol. 2016, 10, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, V.-H.; Beroual, A.; Perrier, C. Comparative Study of Statistical Breakdown in Mineral, Synthetic and Natural Ester Oils under AC Voltage. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Dielectric Liquids, Trondheim, Norway, 26–30 June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro, S.S.; Wilk, M.B. An analysis of variance test for normality (complete samples). Biometrika 1965, 52, 591–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, T.W.; Darling, D.A. Asymptotic theory of certain “goodness of fit” criteria based on stochastic processes. Ann. Math. Stat. 1952, 23, 193–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The R Project for Statistical Computing. Available online: www.r-project.org (accessed on 2 July 2018).
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).