Construction of Biodigesters to Optimize the Production of Biogas from Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Food Waste and Sewage
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Description: Food Waste, Sewage and Anaerobic Sludge (Inoculum)
2.2. Ideal Dry Weight Determination (DW) for Use in Biodigesters
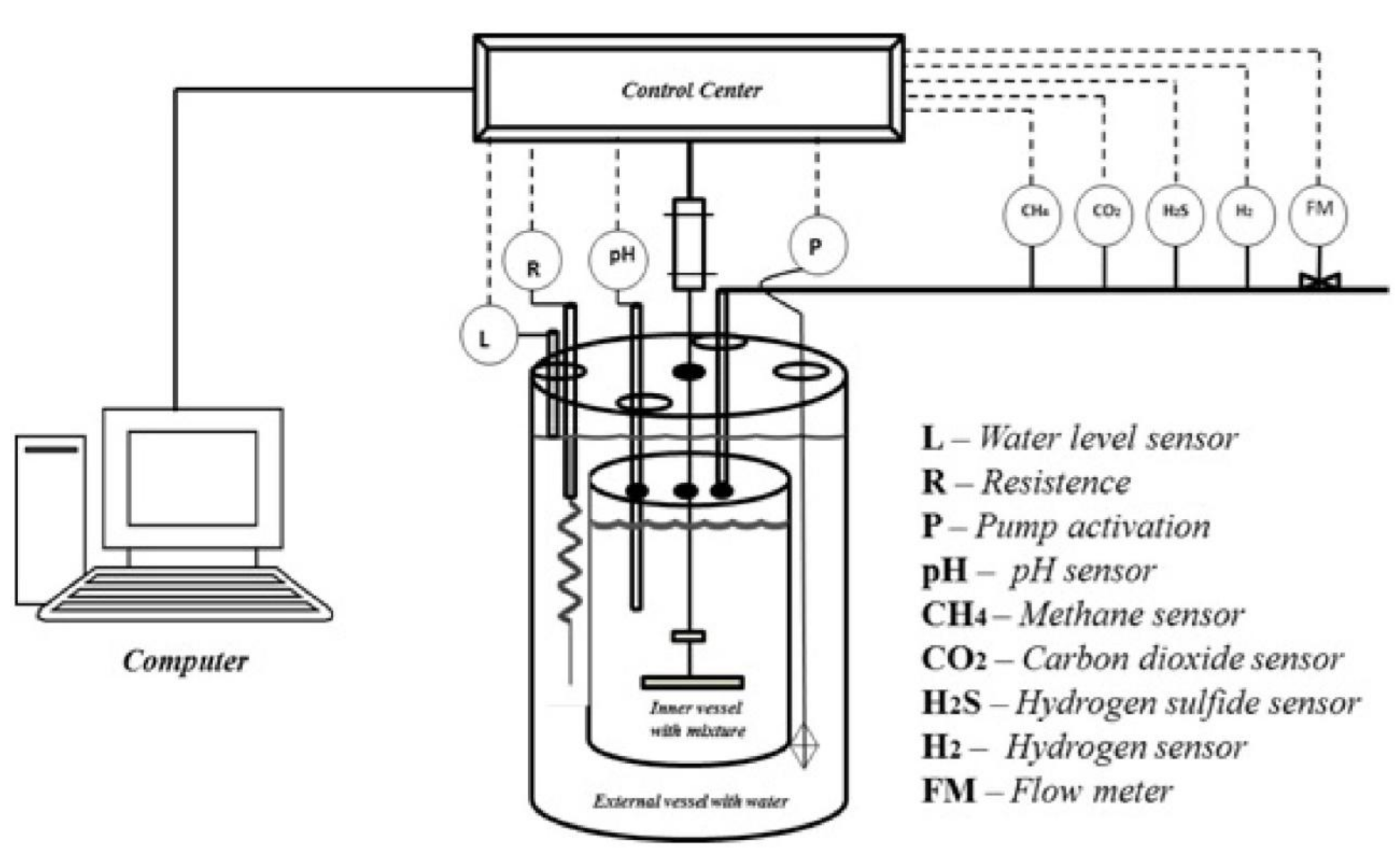
2.3. Development and Construction of Anaerobic Biodigesters for Biogas Production
2.3.1. Software Development for Control and Monitoring
2.3.2. Analysis and Calibration of Sensors in Biogas Produced Compounds
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Description of Food Waste Used before Blending
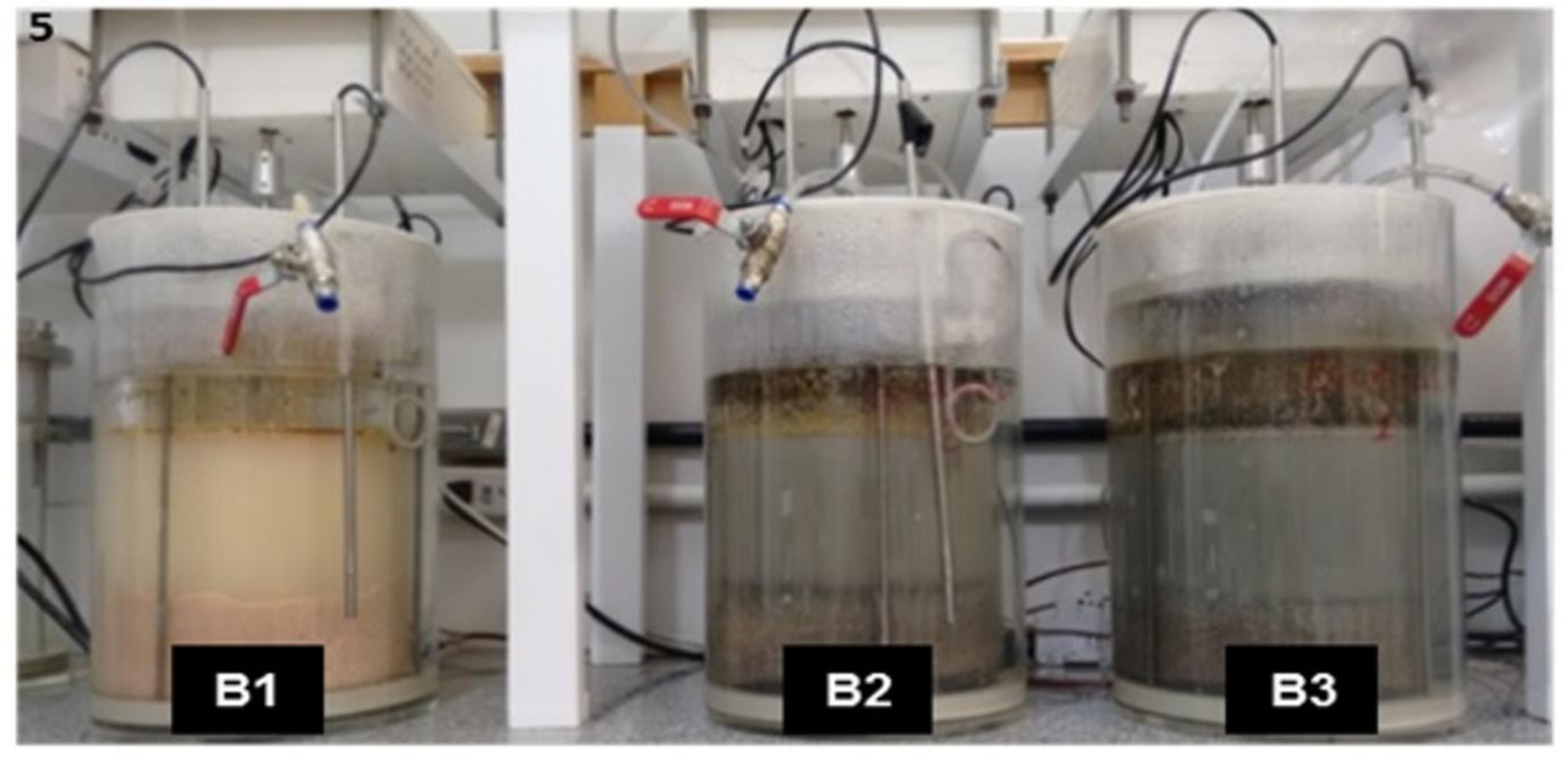
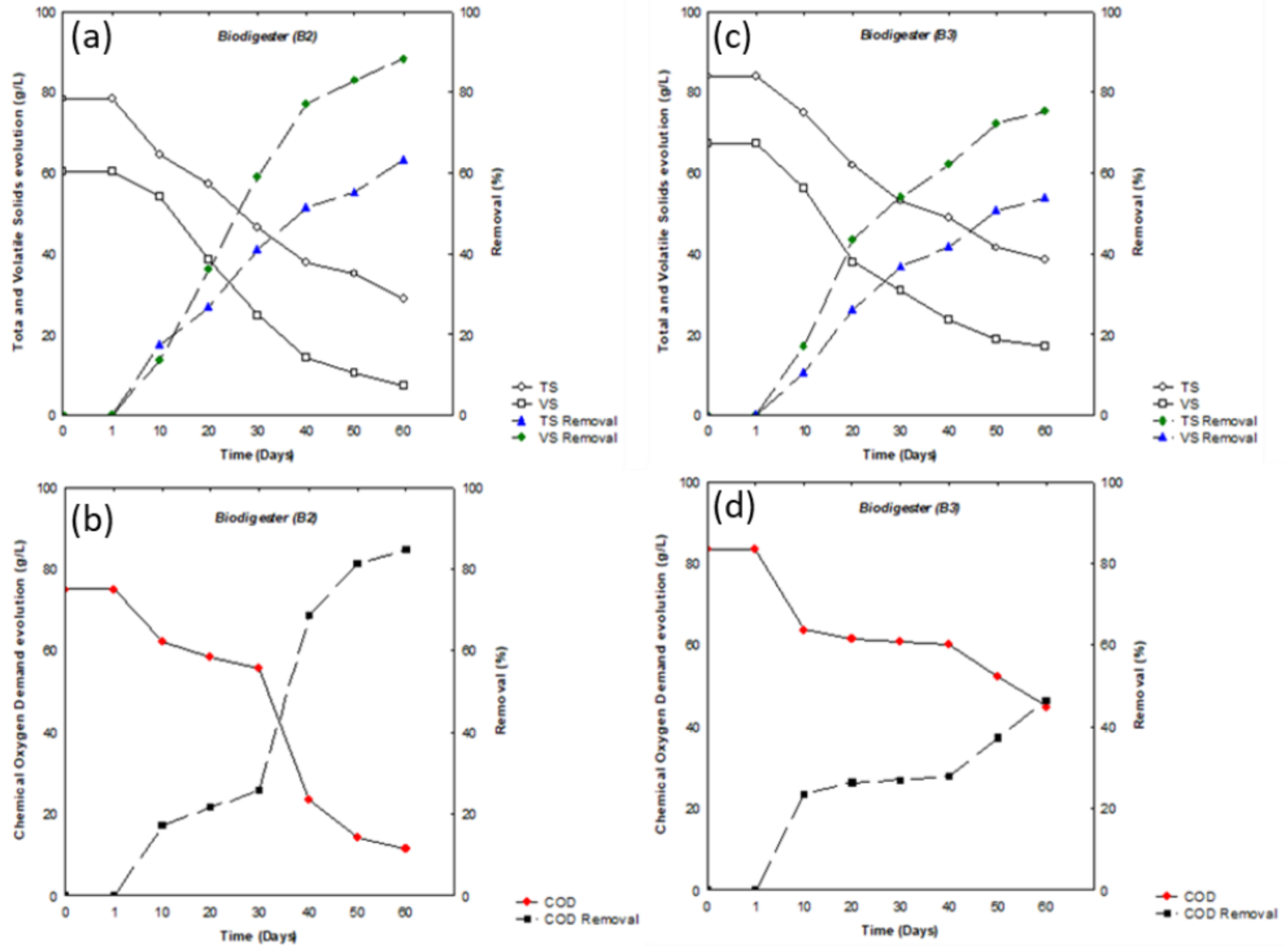
3.2. Biodigesters Construction and Efficiency of Food Waste and Sewage Co-Digestion
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CPU | central processing unit |
| DAC | digital-analog converters |
| FID | flame ionization detectors |
| FW | food waste |
| MSW | municipal solid waste |
| PID | proportional–integral–derivative |
| PLC | programmable logic controller |
| S | sewage |
| TCD | thermal conductivity detectors |
| WWTP | wastewater treatment plant |
References
- Carlini, M.; Mosconi, E.M.; Castelluci, S.; Villarini, M.; Colantoni, A. An Economical Evaluation of Anaerobic Digestion Plants Fed with Organic Agro-Industrial Waste. Energies 2017, 10, 1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apetato, M.M.; Nobre, A.M.; Alves, J.C.; Robalo, G.S.; Ferreira, F. Taxa de Resíduos Urbanos: Deficiências e Soluções. In Proceedings of the 6a Conferência Nacional sobre Qualidade do Ambiente, Lisboa, Portugal, 20 October 1999; Editora Plátano: Lisboa, Portugal, 1999; Volume 3, pp. 363–369. [Google Scholar]
- Lindkvist, E.; Johansson, M.T.; Rosenqvist, J. Methodology for Analysing Energy Demand in Biogas Production Plants—A Comparative Study of Two Biogas Plants. Energies 2017, 10, 1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lansing, S.; Botero, R.B.; Martin, J.F. Waste treatment and biogas quality in small-scale agricultural digesters. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 5881–5890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plano Nacional de Resíduos Sólidos. Lei n° 12.305/10. Available online: http://www.mma.gov.br/estruturas/253/_publicacao/253_publicacao02022012041757.pdf (accessed on 30 March 2017).
- Li, Y.; Park, S.Y.; Zhu, J. Solid-state anaerobic digestion for methane production from organic waste. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 821–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecchi, F.; Pavan, P.; Alvarez, J.M.; Bassetti, A.; Cozzolino, C. Anaerobic digestion of municipal solid waste: Thermophilic vs. mesophilic performance at high solids. Waste Manag. Res. 1991, 9, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernicaro, C.A.L. Princípios do Tratamento Biológico de águas Residuárias. Reatores Anaeróbios; Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais: Belo Horizonte, Brazil, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Budzianowski, W.M.; Budzianowska, D.A. Economic analysis of biomethane and bioelectricity generation from biogas using different support schemes and plant configurations. Energy 2015, 88, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, T.; Esteves, S.; Dinsdale, R.; Guwy, A. Life cycle assessment of biogas infrastructure options on a regional scale. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 7313–7323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, A.K.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Ban, Q.; Jin, Y. Comparison between Wet and Dry Anaerobic Digestions of Cow Dung under Mesophilic and Thermophilic Conditions. Adv. Water Resour. Prot. 2013, 1, 28–38. [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesh, G.; Elmi, R.A. Economic-environmental analysis of handling biogas from sewage sludge digesters in WWTPs (wastewater treatment plants) for energy recovery: Case study of Bekkelaget WWTP in Oslo (Norway). Energy 2013, 58, 220–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, A.J.; Hobbis, P.J.; Holliman, P.J.; Jones, D.L. Optimization of the Anaerobic Digestion of Agricultural Resources. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 7928–7940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, J.; Perez, M.; Romero, L.I. Kinetics of mesophilic anaerobic digestion of the organic fraction of the municipal solid waste: Influence of initial total solid concentration. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 6322–6328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; OH, S.E. Continuous high-solids anaerobic co-digestion of organic solid wastes under mesophilic conditions. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 1943–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charles, W.; Walker, L.; Cord-Ruwisch, R. Effect of pre-aeration and inoculum on the start-up of batch termophilic anaerobic digestion of municipal solid waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 2329–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mata-Alvarez, J.; Macé, S.; Llabrés, P. Anaerobic Digestion of Organic Solid Wastes. An Overview of Research Achievements and Perspectives. Bioresour. Technol. 2000, 74, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Public Health Association (APHA). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Brazilian Association of Technical Standards. NBR 10007. Sampling of Solid Waste, 2nd ed.; Brazilian Association of Technical Standards: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Guimarães, C.S.; Maia, D.R.S.; Serra, E.G. Control and Monitoring Software Website. GitHub. 2018. Available online: https://github.com/DavidRSMaia/Software-de-Controle-e-Monitoramento (accessed on 22 February 2018).
- Appels, L.; Baeyens, J.; Degrève, J.; Dewil, R. Principles and potential of the anaerobic digestion of waste-activated sludge. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2008, 34, 755–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-W.; Han, S.-K.; Shin, H.-S. The optimisation of food waste addition as a co-substrate in anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge. Waste Manag. Res. 2003, 21, 515–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Parameters | Food Waste | Sewage | Sludge |
|---|---|---|---|
| (Average ± SD) | (Average ± SD) | (Average ± SD) | |
| Moisture % | 75 ± 8.2 | 97 ± 2.1 | 93 ± 4.1 |
| pH | 5.4 ± 0.2 | 6.2 ± 0.6 | 6.5 ± 0.3 |
| TFS (mg/g) | 8.4 ± 4.6 | 0.7 ± 0.2 | 22.4 ± 3.1 |
| TVS (mg/g) | 95.4 ± 34.1 | 0.6 ± 0.2 | 31.6 ± 4.4 |
| TKN (mg/L) | 18.5 ± 3.6 | 42.4 ± 5.4 | 26.5 ± 4.8 |
| TP (mg/L) | 0.05 ± 0.02 | 8.2 ± 0.9 | 15.4 ± 2.3 |
| 60 Days | Organic Matter Removal (%) | Biogas Production (L/day) | Accumulative (L) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TVS | COD | TS | Biogas | Methane | ||
| Biodigester (B2) | 88.3 | 84.7 | 63.3 | 1.1 | 63 | 59.9 |
| Biodigester (B1) | 75.1 | 46.2 | 53.8 | 0.5 | 28 | 23.8 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guimarães, C.D.S.; Maia, D.R.d.S.; Serra, E.G. Construction of Biodigesters to Optimize the Production of Biogas from Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Food Waste and Sewage. Energies 2018, 11, 870. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11040870
Guimarães CDS, Maia DRdS, Serra EG. Construction of Biodigesters to Optimize the Production of Biogas from Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Food Waste and Sewage. Energies. 2018; 11(4):870. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11040870
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuimarães, Claudinei De Souza, David Rodrigues da Silva Maia, and Eduardo Gonçalves Serra. 2018. "Construction of Biodigesters to Optimize the Production of Biogas from Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Food Waste and Sewage" Energies 11, no. 4: 870. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11040870
APA StyleGuimarães, C. D. S., Maia, D. R. d. S., & Serra, E. G. (2018). Construction of Biodigesters to Optimize the Production of Biogas from Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Food Waste and Sewage. Energies, 11(4), 870. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11040870





