Abstract
Rapid increases in energy demand and international drive to reduce carbon emissions from fossil fuels have led many oil-rich countries to diversify their energy portfolio and resources. Libya is one of these countries, and it has recently become interested in utilizing its renewable-energy resources in order to reduce financial and energy dependency on oil reserves. This paper introduces an original multicriteria decision-making Pairwise-CODAS model in which the modification of the CODAS method was made using Linguistic Neutrosophic Numbers (LNN). The paper also suggests a new LNN Pairwise (LNN PW) model for determining the weight coefficients of the criteria developed by the authors. By integrating these models with linguistic neutrosophic numbers, it was shown that it is possible to a significant extent to eliminate subjective qualitative assessments and assumptions by decision makers in complex decision-making conditions. The LNN PW-CODAS model was tested and validated in a case study of the selection of optimal Power-Generation Technology (PGT) in Libya. Testing of the model showed that the proposed model based on linguistic neutrosophic numbers provides objective expert evaluation by eliminating subjective assessments when determining the numerical values of criteria. A sensitivity analysis of the LNN PW-CODAS model, carried out through 68 scenarios of changes in the weight coefficients, showed a high degree of stability of the solutions obtained in the ranking of the alternatives. The results were validated by comparison with LNN extensions of four multicriteria decision-making models.
1. Introduction
Nowadays, the demands for new natural resources and energy are significantly increasing. Consequently, the world has become increasingly aware about climate change and its impact. Green solutions and environmental protection are becoming common issues of the twenty-first century [1]. Fossil fuels are the main cause of environmental issues. Many challenges and problems arise while making energy policy because of the concerns of a number of stakeholders [2]. In recent years, many developed countries included environmental issues and reduced reliance on fossil fuels. The E.U. Energy and Climate package was adopted in 2008, which is intended to gradually adapt Europe into a low-carbon economy [3]. For instance, the share of wind energy in Germany accounts for 8.7% of total energy [4]. On the other hand, even with their potential for solar and wind energy, steps are still small in developing countries. Only about 5% of the rural population use electricity in Mozambique and Tanzania, countries with plentiful renewable resources [5]. Implementation of renewable-energy technologies often failed in African countries, or the technologies became unsustainable in the long run [6]. There are several barriers, such as public resistance and lack of skilled manpower, to perform required maintenance and operation [7]. The relationship between society and renewable-energy technologies is one of the critical factors of success that needs to be satisfied if sustainable-energy development is to be achieved [8]. Moreover, dust is a big problem in some countries for the wider application of solar energy. In terms of installed capacity up until 2008, African countries had just 0.005% of the global estimation of 93,900 MW of installed wind-energy projects [9]. Around 90% of Malaysian electricity generation depends on fossil fuels [10]. Since 2015, investments in developing countries in renewable energy had started to surpass those in developed countries [11]. There is a need for a balanced approach, and it is very crucial to evaluate alternative technologies to make the right decisions.
A key challenge for integrating up to 100% renewable energy into the grid is electrical-energy storage. Steps have been taken to support energy-storage technologies, with a focus on battery- and hydrogen-storage technologies, through policy and regulatory change. This is mainly to integrate increasing amounts of intermittent renewable energy that would be required to meet high renewable-energy targets [12]. Yu et al. propose a general evaluation method for performance by comparing six different approaches for promoting wind-power integration [13]. Complex metal hydrides may be used to store hydrogen in a solid state, act as novel battery materials, or store solar heat in a more efficient manner compared to traditional materials used for heat storage [14].
Libya is located in the middle of North Africa between Egypt and Tunisia, and has a coastline along the Mediterranean Sea that extends for about 1900 km. The majority of the population (6.4 million) live in the urban areas along the coast. The area of the desert is about 95% of the total area of the country, which is approximately 1.76 million km2. The most prominent natural resources are petroleum and natural gas, which are the main driving factor of the Libyan economy. Furthermore, Libya is considered a country rich in renewable energy resources such as solar and wind energy. Consequently, there is an urgent need for comprehensive energy strategies in renewable-energy technology [15]. Mohamed et al. [16,17] reported that by the end of the year 2020, the projected demand for electrical power would be more than two and half. Renewable energy could be the effective solution for the increased energy demand. Wind-energy plants could meet part of this demand, since wind potential is reasonable in many remote and isolated areas around the country. Many studies have been conducted in the field of renewable energy in Libya. However, these studies dealt only with a single alternative to generating power [18]. According to Mardani et al. [19] there has been no research and no application of decision-making approaches with regard to energy-management problems in Libya until now.
This paper has several objectives. The first objective is to improve the methodology for treating uncertainties in the field of the Multicriteria Decision-Making (MCDM) group, and the methodology for choosing the optimal Power-Generation Technology (PGT) through a new approach in the uncertainty treatment based on Linguistic Neutrosophic Numbers (LNN). The second goal of the paper is to prioritize the criteria and form a model that would enable an objective, scientifically based approach to the selection of optimal PGT. The third objective of this paper is to bridge the gap that exists in the methodology for the evaluation of PGT through a new approach to the treatment of uncertainty that is based on LNN.
One of the contributions of this paper is an original MCDM model in which modifications of the COmbinative Distance-based ASsessment (CODAS) method was carried out using LNN. Another contribution of the paper is an original LNN Pairwise (LNN PW) model for determining the weight coefficients of the criteria that have been developed by the authors, which contribute to the improvement of MCDM techniques. The third contribution of the paper is to improve the methodology for selecting optimal PGT by means of a new approach to the treatment of uncertainty based on LNN. This practical contribution is reflected in the possibility of applying the proposed criteria and models in the preparation of documents for the selection of optimal PGT.
The rest of the paper is organized in the following way. The third section presents the algorithm for the hybrid LNN PW-CODAS model, which is later tested in the fourth section through the real case study of selecting optimal PGT in Libya. The fifth section includes a discussion of the results for the LNN PW-CODAS model. This discussion is in the form of sensitivity analysis and comparison of the results with LNN extensions of the Technique for Order of Preference by Similarity to Ideal Solution (TOPSIS), VIseKriterijumska Optimizacija I Kompromisno Resenje (VIKOR), Multiattributive Border Approximation Area Comparison (MABAC), and Multiattributive Ideal-Real Comparative Analysis (MAIRCA) models. Finally, the sixth section presents concluding considerations with a special emphasis on directions for future research.
2. Research Background
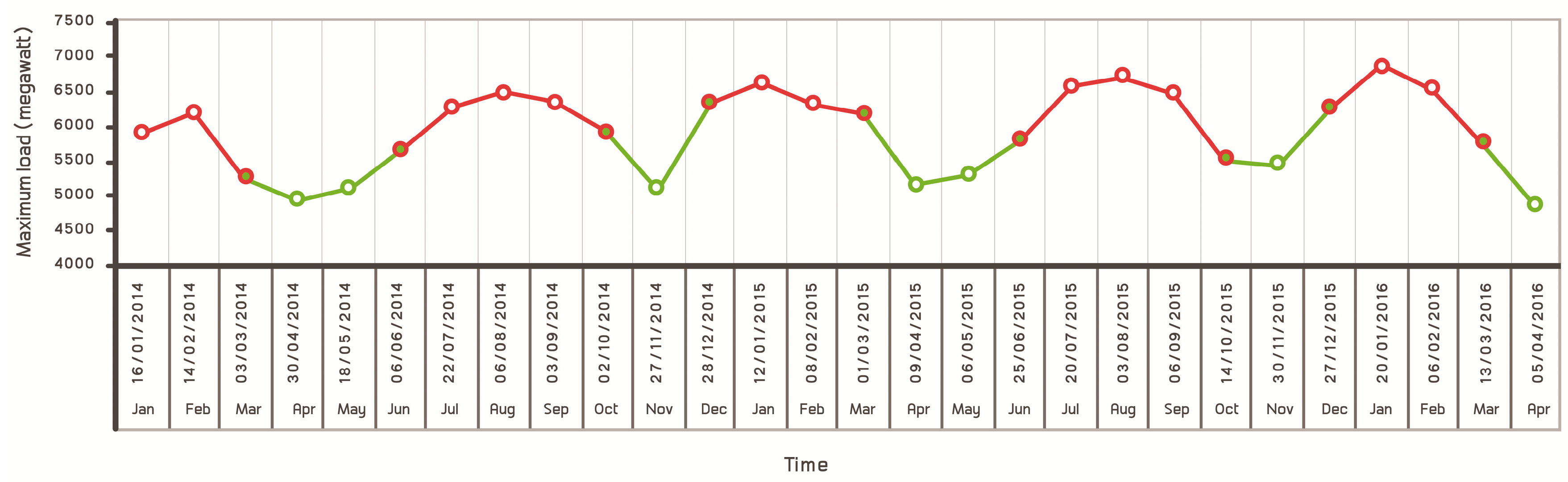
Electricity demand in Libya has risen dramatically in the past fifteen years due to a population growth of about 1 million. Libya is one of the largest countries in North Africa relative electricity consumption. Peak demand was more than 7000 MW over the past four years. The national electricity grid consists of a high-, medium-, and low-voltage network of about 31,500 km [20]. The distribution of citizens in small widely distributed villages makes the connection of these areas an impractical solution. These areas rely on off-grid diesel generators to fulfill their power needs. In general, there are 200 scattered nearby villages with populations ranging between 25 and 500 inhabitancies, and far from the grid by no less than 25 km. That makes electricity-network distribution relatively expensive [21]. According to statistics of the General Electricity Company of Libya (GECOL), energy demand had significant growth between 2003 and 2012 recorded [22], and that increase in energy demand in the household sector in Libya stresses decision makers to have a clear strategy to reduce carbon emissions and energy use by improving occupants’ behavior as well as utilizing other sustainable measures [23]. As shown in Figure 1, the actual demand between January 2014 and April 2016 varied and reached up to 7000 MW. The 2011 civil war led to the destruction of some transmission lines and substations. This led to a decrease in power stations’ generation ability to 5050 MW, which caused a gap of more than 1950 MW between supply and demand, resulting in many blackouts during 2015, 2016, and 2017. For instance, the western region was plunged into a total blackout in June 2017 for many days. A blackout also hit western and southern Libya in January 2017.
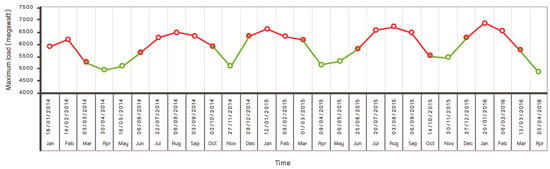
Figure 1.
Electricity demand between 2014 and 2016.
The GECOL increased the dependence on natural gas in order to reduce CO2 emissions; however, they still had difficulties in meeting their demand. Commercial and Public Services accounted for 40% of electricity load in Libya, while the residential sector amounted to 27% and the industry sector to 20% [17].
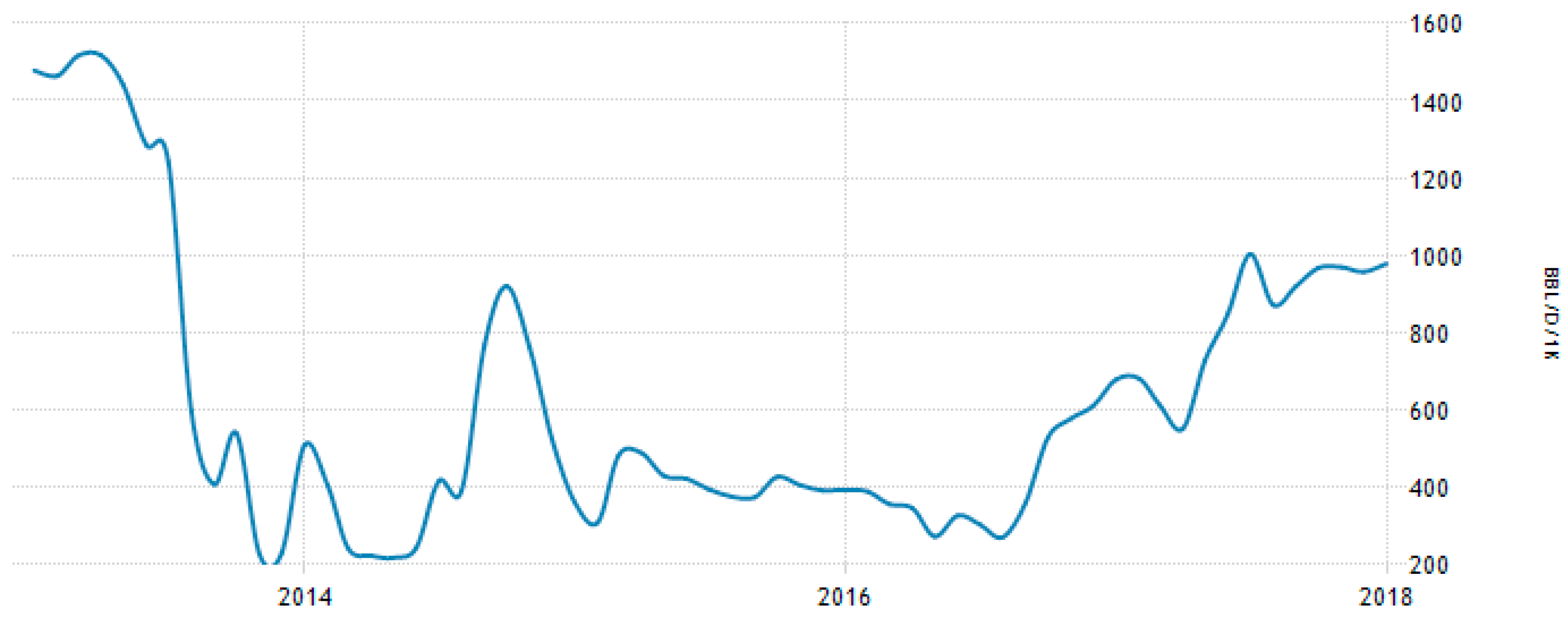
Libya has a variety of energy sources, but the country completely depends on fuel oil and natural gas for generating its growing demands for electricity. Renewable-energy sources are not utilized in significant amounts, and only 5 MW solar energy, separated into several small photovoltaic (PV) projects, have been installed [22]. Crude-oil production during the last five years is shown in Figure 2. Oil production was suspended because of the war and instability that has existed since February 2011.
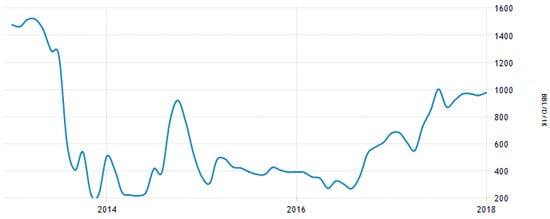
Figure 2.
Libyan crude-oil production from 2012 to 2017 [24].
Libya has had total proven oil reserves of 47.1 billion barrels as reported in January 2012, the largest endowment in Africa, and among the ten largest worldwide [25]. As a result of economic development, demand on energy is expected to increase in the near future. Consequently, this will lead to more consumption of oil and gas, which will cause a reduction in the national economic revenue and more carbon dioxide emissions [26].
Libya has great potential for solar energy. In the coastal regions of the country, the daily average of solar radiation on a horizontal plane is up to 7.1 kWh/m2/day, while radiation is 8.1 kWh/m2/day in the southern region [27]. There is an average sunshine duration of about 3400 h per year. Covering only 1% of Libyan land with 15% efficient solar cells would produce 20 million TJ per year [28]. This is equivalent to a layer of 25 cm of crude oil per year on the land surface.
Libya’s potential for biomass is limited. Biomass-energy sources are small and can only be used on an individual level as an energy source. In the current situation of the country, it is not suitable to produce energy. By reviewing studies regarding municipal solid waste in Libya, it can be noticed that the vast majority of them focused on the classification of solid-waste management rather than utilizing the waste in power generation [29,30].
With regards to wind energy, the average wind speed at a 40 m height is in the range of 6–7.5 m/s. One of several suitable locations along the Libyan coast is at the city of Dernah, where average wind speed is around 7.5 m/s [31]. However, Libya is exposed to dry and hot winds that blow several times during the year [15].
3. MCDM Approaches to Energy Policy
Energy planning is a field that is quite suitable for the use of MCDM [32]. Different multicriteria decision-making methods and techniques have been used to improve the quality of decisions about energy policy. Among these methods is the Analytical Network Process (ANP), Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP) [33,34,35,36], ELimination Et Choix Traduisant la REalité (ELECTRE) [37,38,39,40], PROMETHEE for Sustainability Assessment (PROSA) method [41], and New Easy Approach To Fuzzy Preference Ranking Organization METHod for Enrichment Evaluation (NEAT F-PROMETHEE) [42]. As decision complexity increases, it becomes more difficult for decision makers to identify an alternative that maximizes all decision criteria [43]. AHP is a common multicriteria decision-making method that was developed by Saaty [44,45] to provide a flexible and easily understood way of analyzing complex problems. The AHP method has been used more than any other MCDM method [46]. However, the drawback of this method is that it is still insufficient to explain uncertain conditions, particularly in the pairwise comparison stage. Most human judgments could not be represented as exact numbers because some of the evaluation criteria are subjective and qualitative in nature. Therefore, it is very difficult for the decision maker to express preferences using exact numerical values and to provide exact pairwise comparison judgments [47]. To tackle these problems, AHP has been integrated with other methods, including ANN [48], fuzzy-set theory [49,50,51,52,53,54], Grey Relational Analysis [55,56], and a combination of different methods [42,57]. Stein proposed MCDM using AHP to rank electric power plants using different energy resources. The results indicate that wind, solar, hydro, and geothermal power provide significantly more overall benefits than other technologies [58].
The CODAS method developed by Ghorabaee et al. [59] in 2016 has a number of features that have not been considered in other multicriteria decision-making methods. It has been compared with some existing MCDM methods, and was efficient in dealing with MCDM problems. An integrated model by combining fuzzy-logic theory and the CODAS method has been used to select the best suppliers [60]. An integrated MCDM framework based on AHP and a fuzzy CODAS approach have been applied for solving a maintenance decision problem in a process industry [61]. The CODAS method was used to select the best supplier, and sensitivity analysis was conducted, confirming the stability of the method [62,63]. It was used to select the best location of a desalination plant, as well [64].
4. LNN PW-CODAS Model
The following section (Section 4.1) gives the basic framework of the linguistic neutrosophic concept [65], as well as basic arithmetic operations with LNN. After this, the PW-CODAS multicriteria model based on the concept of LNN is presented in Section 4.2 and Section 4.3.
4.1. Linguistic Neutrosophic Numbers
Due to the ambiguity of human thinking, the judgment of experts and their preferences in complex decision-making conditions are difficult to present in numerical values. A much more convenient and reliable presentation of expert preferences is enabled by the use of linguistic terms, especially when it comes to qualitative attributes that describe certain phenomena. Therefore, modeling expert preferences in decision-making problems using linguistic terms represents an interesting field of research.
Linguistic neutrosophic numbers imply the independent presentation of the degree of truthfulness, uncertainty, and falsehood of an evaluated object using three independent linguistic variables. The concept of an LNN is a combination of single-valued neutrosophic numbers [65,66] and linguistic variables. LNN uses independent linguistic variables to represent the degree of truthfulness, uncertainty, and falsehood, and not, as in the single-valued neutrosophic numbers (SVNN), correct numerical values. LNN is a very interesting concept for study since it enables the presentation of uncertain and inconsistent linguistic information that is present in human reasoning in complex systems. This particularly refers to the reasoning in complex conditions when it is necessary to evaluate individual qualitative attributes using linguistic information and make an appropriate decision. LNNs are also very suitable for presenting linguistic information about the complex attributes of the decision, since LNN simultaneously exploits the benefits of SVNN and linguistic variables.
Definition 1.
Assume thatis a linguistic set with odd cardinality. Ifis defined forand,,andrepresent linguistic expressions representing independently the degrees of truth, uncertainty, and falsehood, then e is called LNN [67,68,69,70].
Definition 2.
If, andare three LNN in S and, then we can define arithmetic operations on LNN [71]:
- (1)
- Combining LNN “+”
- (2)
- Multiplication LNN “×”
- (3)
- Multiplication of LNN by scalar, where
- (4)
- LNN power, where
Definition 3.
Ifis LNN in S, then we can define the score function and the accuracy function according to the following [71]:
Definition 4.
Ifandare two LNN in S, then their relations of comparison can be defined as [72]:
- (1)
- If, then;
- (2)
- If, then;
- (3)
- Ifand, then;
- (4)
- Ifand, then;
- (5)
- Ifand, then.
4.2. PW-LNN Model for Determination of Criteria Weights
In this paper, a new approach for obtaining criteria weights was used when determining the weight coefficients of the evaluation criteria, which includes pairwise comparisons of linguistic neutrosophic numbers. The PW-LNN model is performed through four steps:
Step 1. Formation of expert correspondent matrices of comparison in pairs of criteria (N(l)). This starts from the assumption that the comparison of evaluation criteria in pairs (where n represents the total number of criteria) is performed by m experts. Experts are assigned weight coefficients , and . Comparison of criteria in pairs is based on a predefined set of linguistic variables .
Each expert () performs comparison of the criteria in pairs and, therefore, for each expert we construct the corresponding initial matrix of comparison in the pairs of criteria:
where elements represent linguistic variables from a set , and . The matrix elements (7) that are on the diagonal of the matrix () have the values in which it is . The elements of the matrix (7) above the diagonal are denoted as , while the elements that lie below the diagonal of the matrix are determined by the expression (8)
Linguistic expressions , that is , i , independently, provide information on the degree of truthfulness, uncertainty and falsehood of experts’ preferences when comparing them in pairs of criteria .
Step 2. Formation of the aggregated matrix of comparison in pairs of criteria (N). The final aggregated matrix of comparison in the pairs N is obtained by applying Expressions (10) or (11)
where elements are obtained by applying the LNN Weighted Arithmetic Averaging (LNNWAA) operator:
or using an LNN Weighted Geometric Averaging (LNNWGA) operator
where represent the elements of expert correspondence matrix (7).
Step 3. Determination of the deviation between elements of the aggregated matrix N. If there are small differences between values () and other values within the criterion () then the criterion does not have much impact on the ranking of the alternatives and the low value of weight coefficient . Conversely, if there are significant deviations between the values () and other values of within the criterion () then the criterion has a major impact on the ranking of the alternatives and the high value of the weight coefficient. Finally, if all the values of are identical within the criterion (), then the criterion has no effect on the ranking of the alternatives and has the value of the weight coefficient .In order to define the above deviations in the matrix , the degree of deviation of the element of the matrix N, (), is calculated within the criterion ().
where represents the distance between () and ().
After that, the degree of deviation between all elements within the framework of the observed criterion () is calculated:
Total deviations of all criteria in matrix N are obtained:
Step 4. Calculation of optimal values of weight coefficients of criteria (). Optimal values of weight coefficients are obtained by applying Expression (15):
where () are the optimal values of the weight coefficients of the criteria and .
4.3. LNN CODAS Method
In this section, we propose an LNN extension of the CODAS methodology to deal with an uncertain domain-based MCDM problem. The CODAS method is an efficient and updated decision-making methodology introduced by Keshavarz Ghorabaee et al. [59,60]. The algorithmic steps of the modified LNN CODAS method are presented as follows:
Step 1: Formulation of the initial decision matrix (N). It starts with the assumption that m experts performing an evaluation of a set of alternatives (where b denotes the final number of alternatives) are involved in the decision-making process in relation to the defined set of evaluation criteria (where n represents the total number criteria). Experts are assigned weight coefficients , and . Evaluation of alternatives is based on a predefined set of linguistic variables .
In order to perform the final ranking of the alternative () from the set of alternatives A, each expert () evaluates the alternatives according to the set of criteria . Therefore, for each expert, we construct a correspondent initial matrix of decision-making:
where the basic elements of the matrix () represent linguistic variables from the set , and . Linguistic expressions , that is , and independently present the information about the degree of truthfulness, uncertainty and falsehood in the evaluation of the alternative () according to the defined set of criteria .
Final aggregated decision matrix N is obtained by averaging elements of Matrix (16) using Expression (18).
where elements are obtained using the LNNWGA operator:
where elements represent the elements of expert correspondence matrix (29).
Step 2. Calculation of the elements of the normalized matrix (). Calculation of the elements of a normalized matrix is carried out using Expression (19).
where B and C are sets of benefit and cost type, respectively, and represents the elements of a normalized matrix .
Step 3. Calculation of elements of weighted matrix (G). Weighted matrix elements are obtained by using Expression (20)
Step 4. Determine FR negative-ideal solution. We obtain the LNN negative-ideal solution matrix as follows
where is LNN described as .
Step 5. Calculate the LNN weighted Euclidean () and LNN weighted Hamming () distances of alternatives from the LNN negative-ideal solution. We obtain and as follows.
LNN weighted Euclidean () distances:
where , which we obtain as follows:
LNN weighted Hamming () distances
where we obtain as follows:
where is a linguistic function obtained as .
Step 6. Determine relative assessment matrix (RA). By applying Equation (26) we obtain elements of the relative assessment matrix
e and z is a threshold function that is defined as follows [60]:
Threshold parameter () of this function can be set by a decision maker. In this study, we used for the calculations.
Step 7. Calculate assessment score (ASi) of each alternative. By applying Equation (28), we obtain the assessment score
The alternative with the highest assessment score is the most desirable alternative.
5. Application of the LNN PW-CODAS Model for the Selection of PGT in Libya
A questionnaire was distributed to a group of relevant experts at universities and power stations in Libya. There are four criteria considered in this research: economic, environmental, social, and technical criteria, as shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Criteria for the pairwise (PW) method.
The research involved four experts () with weight coefficients , , and . It should be noted that, in developing countries, some technologies are more appropriate than others. In this research, the following PGTs were considered: Gas-fired-power generation (A1), Geothermal-power generation (A2), Solar-photovoltaic-power generation (A3), Solar-thermal-power generation (A4), Wind-power generation (A5), and oil-fired power generation (A6). The evaluation of the alternatives by criteria was carried out using a set of linguistic variables , where s = {s0—exceedingly low, s1—pretty low, s2—low, s3—slightly low, s4—medium, s5—slightly high, s6—high, s7—pretty high, s8—exceedingly high}.
5.1. Determination of Weight Coefficients of Criteria Using the PW-LNN Model
As previously mentioned, four experts (, , and ) who performed a comparison in pairs of evaluation criteria participated in the research.
● Step 1:
In the first step, each expert performed a comparison in pairs of four criteria (C1–C4) and eighteen subcriteria. Thus, for each expert, five correspondence matrices (one for the criteria and four for each subcriterion group) were formed (Table 2). Comparison in pairs of criteria/subcriteria was performed using a predefined set of linguistic variables .

Table 2.
Expert comparison in the pairs of criteria/subcriteria.
● Step 2:
In this step, the aggregation of the expert correspondence matrices (Table 2) was performed in the final aggregated matrix of the comparison in the pairs.
Aggregation of expert matrices of comparison of criteria/subcriteria in the pairs was accomplished by using LNNWGA (Expression (11)). Aggregation of element of criterion matrix () is obtained
● Step 3:
After determining the aggregated matrices of the criteria/subcriteria, by applying Expressions (12)–(14) the deviations between the elements within the observed aggregated matrix are calculated. Thus, for criteria (C1–C4), the deviations given in Table 3 were obtained.

Table 3.
Deviations between the criteria in matrix .
Using Expression (15), we obtain the weight coefficients of criteria C1–C4.
In a similar way, the weight coefficients of the subcriterion are obtained. Global and local values of the weight coefficients of the criteria/subcriteria are shown in Table 4.

Table 4.
Weight coefficients of criteria/subcriteria.
Global values of the weight coefficients of the subcriterion were obtained by multiplying the local values of the weight coefficient of the criteria with the values of the weight coefficients of the correspondent subcriterion. So, for example, the values of the weight coefficients of the C11–C14 subcriterion group are obtained by multiplying the local value of the weight coefficient of the C1 criteria with each of the local values of the C11–C14 weight coefficients.
5.2. Evaluation of PGT—Application of LNN CODAS Model
After determining the global values of the weight coefficients of the criteria, the evaluation of the alternatives using the LNN CODAS model was carried out. The four experts carried out the evaluation of PGTs marked A1 to A6. As with the PW model, the experts evaluated alternatives by assigning a certain value from a set of linguistic variables , where {s0—exceedingly low, s1—pretty low, s2—low, s3—slightly low, s4—medium, s5—slightly high, s6—high, s7—pretty high, s8—exceedingly high}.
Steps 1 and 2: In order to form an initial decision matrix, the first step included the formation of expert correspondent matrices in which the expert evaluations of alternatives were shown in accordance with the criteria. Thus, a corresponding initial-decision matrix was constructed for each expert (Table 5).

Table 5.
Expert correspondence matrix.
In order to evaluate the alternatives, the expert correspondence matrices (Table 5) were aggregated into a unique initial-decision matrix (Table 6). Aggregation of expert matrices () was performed using LNNWGA (Expression (18)). Before aggregation using the LNNWGA operator, normalization of the expert correspondence matrices was performed (Expression (19)). Thus, in the C11-A1 position in expert correspondence matrix N(1), normalization of the element was performed as follows:

Table 6.
Aggregated normalized initial matrix of decision-making.
In a similar way, normalization of the remaining criteria in the expert correspondence matrices was performed. Finally, using the LNNWGA operator (Expression (18)) we obtain an aggregated normalized initial decision matrix (Table 6).
The element at position C11-A1 is aggregated using Expression (18)
where (, , and ) represent the weight coefficients of the experts. In the same way, the aggregation of the remaining elements of the aggregated normalized matrix in Table 6 is carried out.
Step 3: Calculation of the elements of the weighted matrix. Elements of the weighted matrix (Table 7) are obtained by multiplying the weight coefficients (Table 4) with the elements of the aggregated normalized matrix (Table 6). Using Expression (20), we obtain the elements of the weighted matrix (Table 7).

Table 7.
Weighted initial matrix of decision-making.
The element at the position C11-A1 was obtained using Expression (20)
where represents the weight coefficient of criterion C11, and represents the element at the position of the C11-A1 aggregated normalized matrix (Table 6).
Step 4: Using Expression (21), we obtain the elements of LNN negative-ideal solution matrix as follows
Step 5: Applying Expressions (23) and (25), LNN-weighted Euclidean () and Hamming () distances of alternatives from the LNN negative-ideal solution, are calculated (Table 8).

Table 8.
LNN-weighted Euclidean and Hamming distances.
The Euclidean and Hamming distances shown in Table 8 are determined on the basis of the distance of the elements of the weighted initial-decision matrix (Table 7) from the negative-ideal values defined in Step 4. Thus, for the element at position C11-A1 (Equations (23) and (25)) we get the following values
Step 6: The values obtained in Table 8 are used to determine the elements of the relative assessment matrix (Table 9).

Table 9.
Relative assessment matrix.
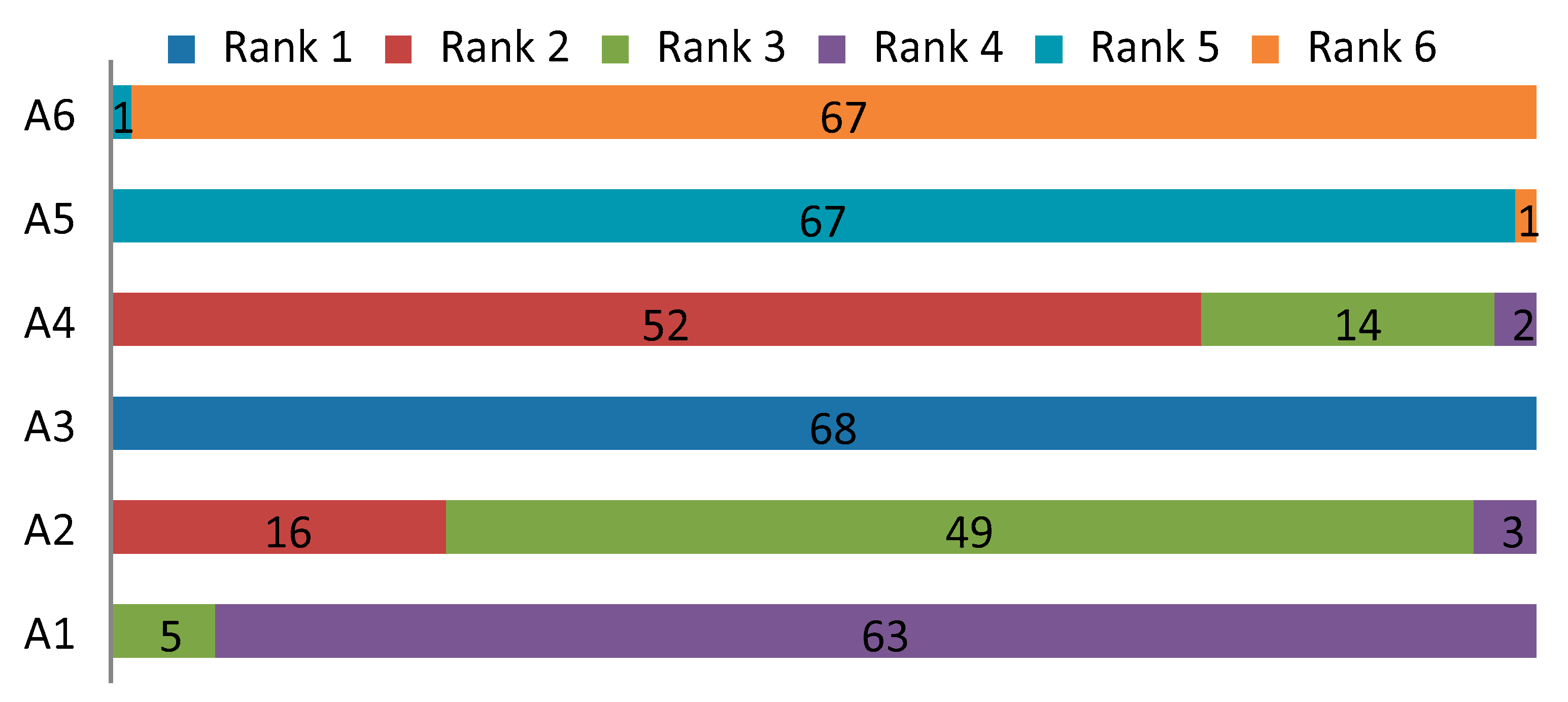
Step 7: By summing the obtained values in the relative assessment matrix (Table 9), we get the assessment score (ASi) for each alternative. An alternative that has the highest ASi value is the most preferred alternative. The value of ASi tells us about the distance of the alternative from the negative-ideal solution. It is desirable that the alternative has as much ASi value as possible, that is, to be as far removed from the negative-ideal solution. ASi values and rank of alternatives are shown in Table 9.
6. Results and Discussion
The results are discussed in two parts. In the first part, a sensitivity analysis of the LNN PW-CODAS model was performed through 68 scenarios. In the second part, a comparison of the obtained results was made with other multicriteria decision-making methods (VKO) for evaluation of the PGT. Since LNN is a new concept applied in the field of VKO, so far from all traditional VKO models, only the LNN-based TOPSIS model is known [73]. Therefore, in order to discuss the results in this paper, extension of MABAC [74], VIKOR [75], and MAIRCA [76] was carried out. A more detailed analysis of the first and second part of the discussion of the results is presented in the following part.
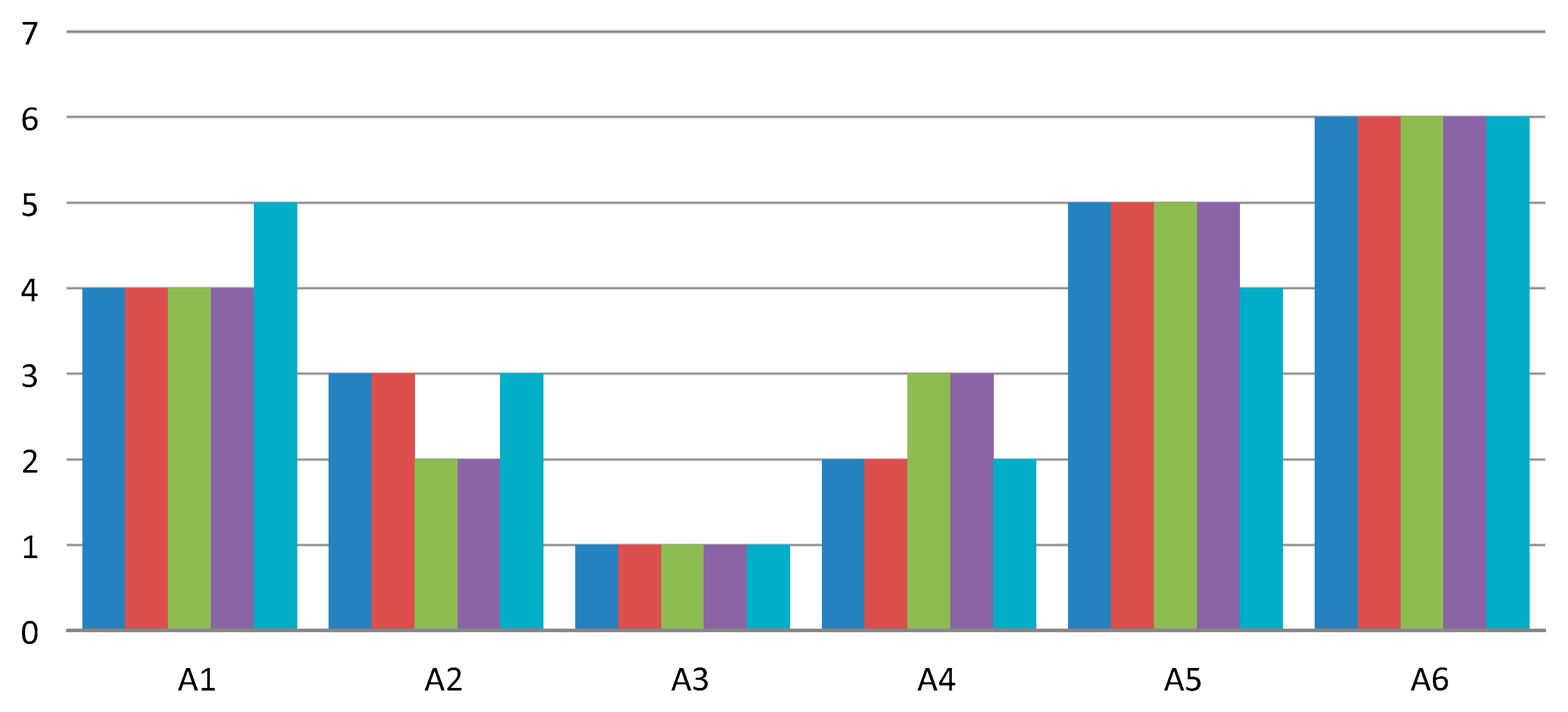
Changes in weight coefficients can significantly affect the ranking of alternatives, and hence analysis of weight-coefficient changes is one of the important steps for validating the results of the decision-making model. In this paper, the sensitivity analysis of ranking alternatives in relation to changes in the weight coefficients of criteria through 68 scenarios was made, divided into four groups. The first group of scenarios consisted of the first 17 scenarios, marked with S1–S17. In each scenario, one criterion was favored, and its value was increased by 1.45, while the values of the remaining criteria were reduced by 0.35. In the second group of scenarios, labeled S18–S34, the same procedure was repeated, where in each scenario, the value of the favorable criterion was increased by 1.65, while the remaining values were reduced by 0.35. In the third and fourth group of scenarios (scenarios S35–S51 and S52–S68), the value of the favorable criterion was increased by 1.85 and 2.05, respectively, while the remaining values, as in the previous two groups of scenarios, were reduced by 0.35. Changes in the ranking of alternatives in 68 scenarios are shown in Figure 3.
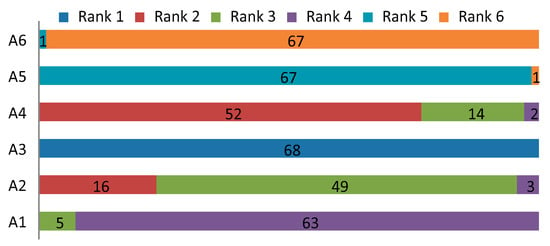
Figure 3.
An analysis of the change in the ranking of alternatives through 68 scenarios.
Changes in weight coefficients through 68 scenarios show that assigning different weight to the criteria leads to a change in the ranks of individual alternatives, which confirms that the model is sensitive to changes in weight coefficients. By comparing the first-ranked alternatives (A3 and A4) through scenarios with initial ranks from Table 9, we can notice that the starting rank is confirmed. Alternative A3 remained first-ranked through all scenarios, while the A4 alternative is second-ranked in 54 scenarios, in 14 scenarios it is third-ranked, and in two scenarios it is fourth. It is similar with other alternatives, so alternatives A5 and A6 through 67 scenarios (98.53%) kept their rankings, while the A1 alternative in 92.64% of the scenarios remained fourth in the ranking. Minor variations in the rankings occurred with alternative A2, which was initially the third-ranked alternative. Alternative A1 kept its initial rank in 72.06%, while in the remaining scenarios it was second-ranked (16 scenarios) and fourth-ranked (three scenarios).
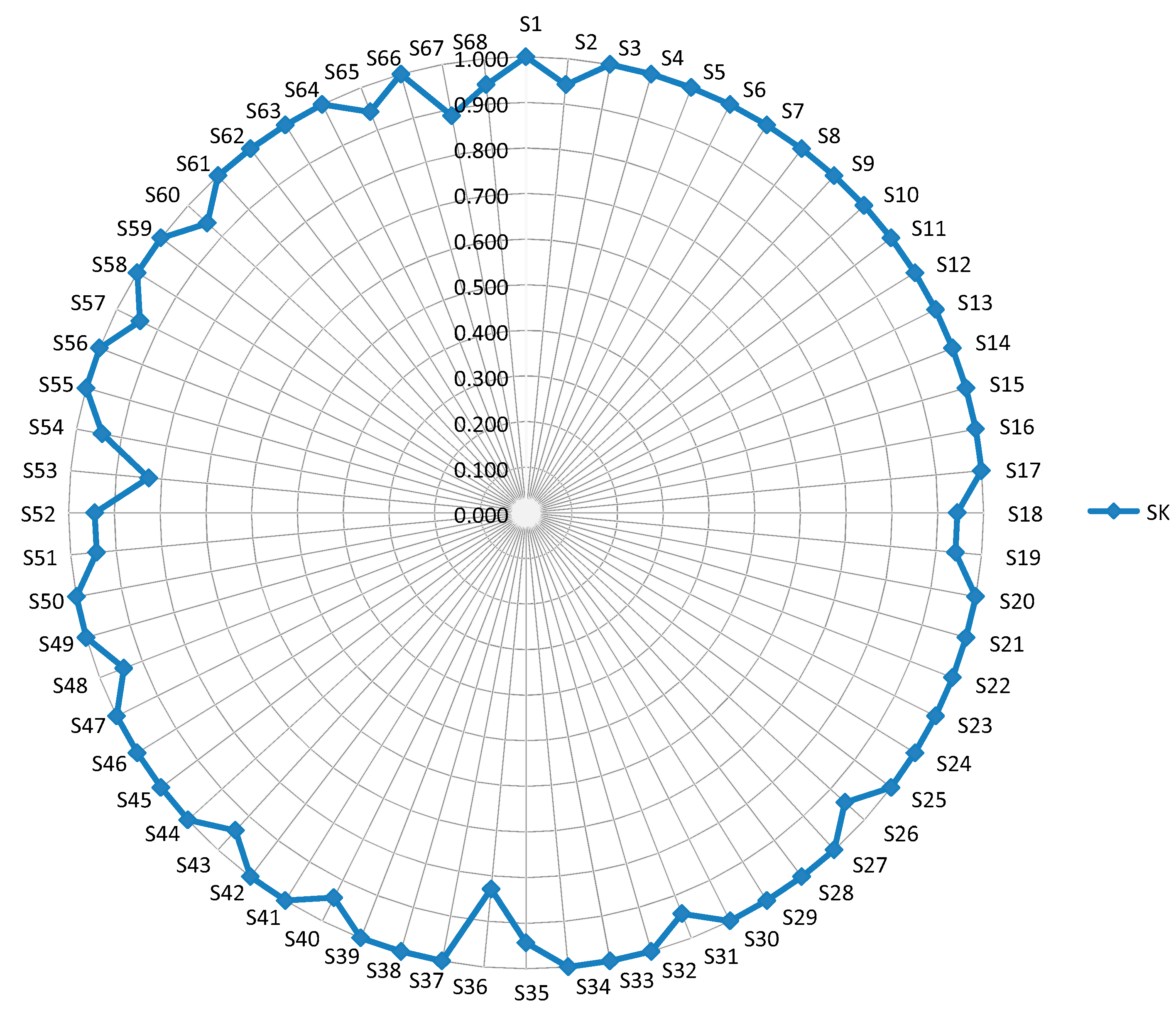
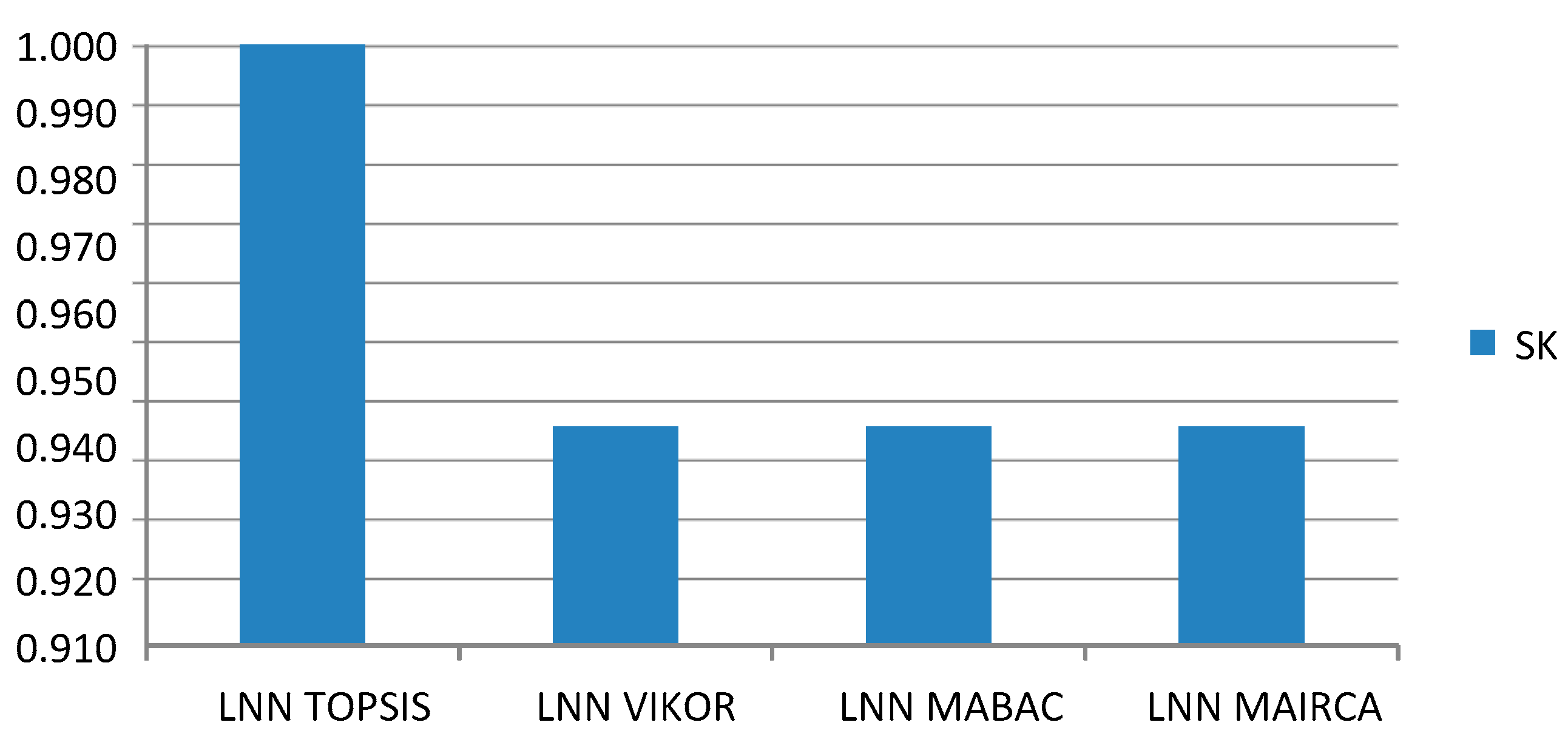
Based on the presented analysis, we can conclude that changes in rankings through the scenarios were not dramatic, which is also confirmed by the values of Spearman’s coefficient (SK), as one of the reliable criteria for the correlation of ranking [77] (Figure 4).
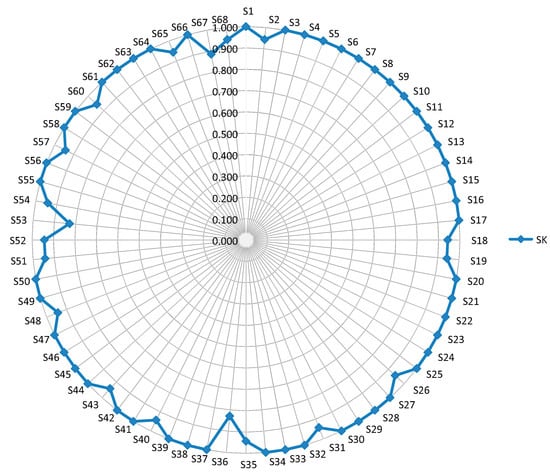
Figure 4.
Values of Spearman’s coefficient through 68 scenarios.
Values of SK correlation of ranges through scenarios were obtained by comparing the initial rank of the LNN PW-CODAS model (Table 9) with ranks obtained through the scenarios. From Figure 4, we can see that there are no significant deviations in ranking through the 68 scenarios. In all scenarios, the values of SK did not fall below 0.829. The average SK value for all scenarios was 0.980, which shows that rank correlation was very high through the scenarios. Since all SK values were significantly higher than 0.8, we can conclude that there was very high correlation (closeness) of rankings, and that the proposed rank is confirmed and credible [77].
In the following part, the validation of the LNN PW-CODAS model was performed by comparing the results with LNN TOPSIS [73], LNN MABAC (proposed), LNN VIKOR (proposed), and LNN MAIRCA (proposed) models. A comparison of the ranking of alternatives according to LNN VKO models is shown in Figure 5.
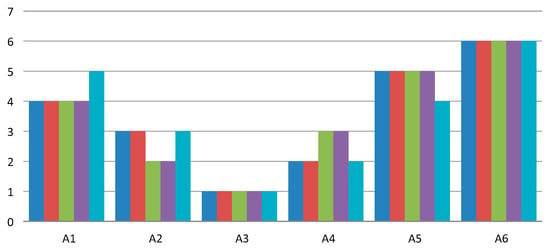
Figure 5.
Comparison of ranking of alternatives according to methods.
Spearman’s coefficient of rank correlation was used to determine the relation between results obtained by different approaches. The results of the ranking comparison show extremely high correlation between the applied models. Correlation between the LNN PW-CODAS and LNN TOPSIS model is 1.00, while the correlation between LNN PW-CODAS and the remaining models is 0.943 (Figure 6).
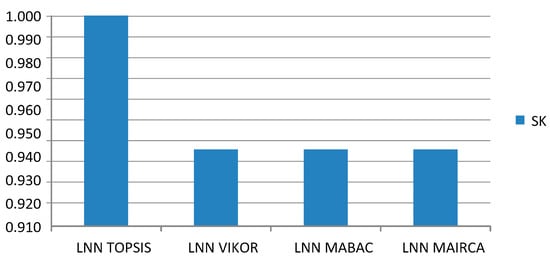
Figure 6.
Values of the Spearman coefficient for VKO models.
Mean value of SK through all scenarios was 0.956, which shows extremely high correlation. Since all values of SK were significantly higher than 0.8, we can conclude that there is a very high correlation (closeness) of ranks, and that the proposed rank is confirmed and credible.
Based on the presented analysis, in addition to the confirmation of ranking credibility, we can conclude that the LNN-based approach successfully exploits the uncertainties that arise in the group decision-making process. By examining the four main criteria and 17 subcriteria, this study helps firm managers in understanding the PGT and offers the following benefits: The first benefit of this study is developing criteria and subcriteria selection based on a comprehensive literature review. The second benefit is not only in selecting the best PGT, but also analysis of technology that did not meet the defined criteria. The methodology’s flexibility in selection and weighing of performance measures to be used is also valuable. This flexibility would allow management to perform sensitivity analysis at multiple levels and thus obtain more robust and relevant solutions.
The result of this study helps managers establish the systematic approach to select the best PGT within the set of criteria and analyze the most appropriate alternate PGT. This tool would be acceptable to managers who have to deal with greater magnitudes of uncertainties and imprecision in evaluation of the best PGT.
7. Conclusions
Taking into account the uncertainties present in the decision-making process is a precondition for objective decision making. This paper presents a novel approach for treating uncertainty based on the application of LNN. An LNN-based approach is the integration of linguistic variables in neutrosophic decision theory. The LNN approach takes into account the uncertainties in evaluations made by decision makers since, for each rating of a decision maker, only the linguistic variables from a predefined set of variables are used. This eliminates subjective estimates when determining the numerical values of the attributes.
The LNN approach was applied in a case study to select optimal PGT in Libya. In the PW-CODAS multicriteria model, the original modification of the CODAS method was performed using LNN. In addition to the above modification, the paper presents the original PW model for determining the weight coefficients of the criteria. Finally, model validation was performed by comparing results with existing LNN-based MCDM models. Discussion of the results and validation showed significant stability of the results and pointed to the significant possibilities of applying the presented LNN PW-CODAS model.
Since this is a new model that has not been considered in the literature so far, the direction of future research should focus on the application of LNN in other traditional MCDM models for determining the weight coefficients of the criteria (e.g., Best–Worst method, DEMATEL method, etc.). Further integration of LNN approaches into traditional VKO models would allow taking into account the subjectivity present in the decision-making process.
The research provides guidance for energy-policy makers to reach their decision in a more structured and strategic way. The results support GECOL plans to develop Libya’s renewable-energy capacity. The model could be applied in other countries and could be generalized for other applications. However, the importance weights may vary among different countries. For instance, public acceptance or investment costs are expected to vary among different regions according to the culture and costs related to the technology. Through this paper, detailed presentation, development, and validation of the LNN PW-CODAS model was carried out. Given the promising results, future work could include developing a software solution for real-world applications. Authors believe that further research in the future should be directed towards the development of a software model based on the LNN PW-CODAS model. A software application would be very useful for managerial uses.
Author Contributions
This research was carried out in collaboration between all authors. I.B. and S.K. designed this research and collected data. D.P. and R.O. performed the simulation of the multi-criteria and the methodology. The discussions and analysis were carried out by all authors. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kravanja, Z.; Čuček, L. Multi-objective optimisation for generating sustainable solutions considering total effects on the environment. Appl. Energy 2013, 101, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Paatero, J.V.; Lahdelma, R.; Wahid, M.A. Multicriteria-based decision aiding technique for assessing energy policy elements-demonstration to a case in Bangladesh. Appl. Energy 2016, 164, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baležentis, T.; Streimikiene, D. Multi-criteria ranking of energy generation scenarios with Monte Carlo simulation. Appl. Energy 2017, 185, 862–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höfer, T.; Sunak, Y.; Siddique, H.; Madlener, R. Wind farm siting using a spatial Analytic Hierarchy Process approach: A case study of the Städteregion Aachen. Appl. Energy 2016, 163, 222–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlborg, H.; Hammar, L. Drivers and barriers to rural electrification in Tanzania and Mozambique–Grid-extension, off-grid, and renewable energy technologies. Renew. Energy 2014, 61, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, M.-L.; Steyn, H.; Brent, A. Selection of renewable energy technologies for Africa: Eight case studies in Rwanda, Tanzania and Malawi. Renew. Energy 2011, 36, 2845–2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiciudean, G.; Harun, R.; Arion, F.; Chiciudean, D.; Oroian, C.; Muresan, I. A Critical Approach on Sustainable Renewable Energy Sources in Rural Area: Evidence from North-West Region of Romania. Energies 2018, 11, 2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brent, A.C.; Kruger, W.J. Systems analyses and the sustainable transfer of renewable energy technologies: A focus on remote areas of Africa. Renew. Energy 2009, 34, 1774–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aïssa, M.S.B.; Jebli, M.B.; Youssef, S.B. Output, renewable energy consumption and trade in Africa. Energy Policy 2014, 66, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Tahar, R.M. Selection of renewable energy sources for sustainable development of electricity generation system using analytic hierarchy process: A case of Malaysia. Renew. Energy 2014, 63, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Xie, N.; Fang, D.; Zhang, X. The role of renewable energy consumption and commercial services trade in carbon dioxide reduction: Evidence from 25 developing countries. Appl. Energy 2018, 211, 1229–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.; Shabani, B. A Critical Study of Stationary Energy Storage Policies in Australia in an International Context: The Role of Hydrogen and Battery Technologies. Energies 2016, 9, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Chen, H.; Chen, L. Comparative Study of Electric Energy Storages and Thermal Energy Auxiliaries for Improving Wind Power Integration in the Cogeneration System. Energies 2018, 11, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møller, K.T.; Sheppard, D.; Ravnsbæk, D.B.; Buckley, C.E.; Akiba, E.; Li, H.-W.; Jensen, T.R. Complex metal hydrides for hydrogen, thermal and electrochemical energy storage. Energies 2017, 10, 1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abohedma, M.B.; Alshebani, M.M. Wind load characteristics in Libya. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2010, 4, 88–91. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, A.M.; Al-Habaibeh, A.; Abdo, H.; Abdunnabi, M.J.R. The significance of utilizing renewable energy options into the Libyan Energy Mix. Energy Res. J. 2013, 4, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.M.; Al-Habaibeh, A.; Abdo, H. An investigation into the current utilisation and prospective of renewable energy resources and technologies in Libya. Renew. Energy 2013, 50, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljamel, S.A.; Badi, I.A.; Shetwan, A.G. Using Analytical Hierarchy Process to Select the Best Power Generation Technology in Libya. Int. J. Eng. Inf. Technol. 2017, 3, 159–163. [Google Scholar]
- Mardani, A.; Zavadskas, E.K.; Khalifah, Z.; Zakuan, N.; Jusoh, A.; Nor, K.M.; Khoshnoudi, M. A review of multi-criteria decision-making applications to solve energy management problems: Two decades from 1995 to 2015. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 71, 216–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, I.S.; Kreama, N.; Khalat, M.; Matouq, M. Three years performance of thirty stand alone PV systems used to electrify an isolated village in Libya. In Proceedings of the 22th European Photovoltaic Solar Energy Conference, Milan, Italy, 3–7 September 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Saleh, I.M. Prospects of renewable energy in Libya. In Proceedings of the Solar Physics and Solar Eclipses (SPSE 2006), Waw an Namos, Libya, 27–29 March 2006; pp. 153–161. [Google Scholar]
- GECOL. Current Status of the Libyan Power System and Its Future Plans; GECOL: Tripoli, Libya, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, A.M.; Al-Habaibeh, A.; Abdo, H.; Elabar, S. Towards exporting renewable energy from MENA region to Europe: An investigation into domestic energy use and householders’ energy behaviour in Libya. Appl. Energy 2015, 146, 247–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Economics, T.; Libya Crude Oil Production. Trading Economics: 2018. Available online: https://tradingeconomics.com/libya/crude-oil-production (accessed on 20 March 2018).
- World Energy Council. World Energy Resources; World Energy Council: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Khalil, A.; Asheibe, A. The chances and challenges for renewable energy in Libya. In Proceedings of the 4th Renewable Energy Conference, Palermo, Italy, 22–25 November 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Rajab, Z.; Zuhier, M.; Khalil, A.; El-Faitouri, A.S. Techno-economic feasibility study of Solar Water Heating system in Libya. In Proceedings of the 2017 8th International Renewable Energy Congress (IREC), Amman, Jordan, 21–23 March 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Eljrushi, G.S.; Zubia, J. Photovoltaic power plant for the southern region of Libya. Appl. Energy 1995, 52, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelnaser, O.; Alsadey, S.; Gavrilescu, M. Municipal solid waste management in Bani Walid City, Libya: Practices and challenges. J. Environ. Manag. Tour. 2011, 2, 228–237. [Google Scholar]
- Hamad, T.A.; Agll, A.A.; Hamad, Y.M.; Sheffield, J.W. Solid waste as renewable source of energy: Current and future possibility in Libya. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2014, 4, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahwide, F.; Spena, A.; El-Kafrawy, A. Estimation of electricity generation in libya using processing technology of wind available data: The case study in derna. APCBEE Procedia 2013, 5, 451–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Løken, E. Use of multicriteria decision analysis methods for energy planning problems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2007, 11, 1584–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrović, I.; Kankaraš, M. DEMATEL-AHP multi-criteria decision making model for the selection and evaluation of criteria for selecting an aircraft for the protection of air traffic. Decis. Mak. Appl. Manag. Eng. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Aiwu, G.; Lukovac, V.; Vukic, M. A multicriteria model for the selection of the transport service provider: A single valued neutrosophic DEMATEL multicriteria model. Decis. Mak. Appl. Manag. Eng. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesković, S.; Stević, Ž.; Stojić, G.; Vasiljević, M.; Milinković, S. Evaluation of the railway management model by using a new integrated model DELPHI-SWARA-MABAC. Decis. Mak. Appl. Manag. Eng. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milosavljević, M.; Bursać, M.; Tričković, G. Selection of the railroad container terminal in Serbia based on multi criteria decision-making methods. Decis. Mak. Appl. Manag. Eng 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahraman, C.; Kaya, İ. A fuzzy multicriteria methodology for selection among energy alternatives. Expert Syst. Appl. 2010, 37, 6270–6281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şengül, Ü.; Eren, M.; Shiraz, S.E.; Gezder, V.; Şengül, A.B. Fuzzy TOPSIS method for ranking renewable energy supply systems in Turkey. Renew. Energy 2015, 75, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prebeg, P.; Gasparovic, G.; Krajacic, G.; Duic, N. Long-term energy planning of Croatian power system using multi-objective optimization with focus on renewable energy and integration of electric vehicles. Appl. Energy 2016, 184, 1493–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallaro, F. Fuzzy TOPSIS approach for assessing thermal-energy storage in concentrated solar power (CSP) systems. Appl. Energy 2010, 87, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziemba, P.; Wątróbski, J.; Zioło, M.; Karczmarczyk, A. Using the PROSA method in offshore wind farm location problems. Energies 2017, 10, 1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziemba, P. NEAT F-PROMETHEE—A New Fuzzy Multiple Criteria Decision Making Method Based on the Adjustment of Mapping Trapezoidal Fuzzy Numbers. Expert Syst. Appl. 2018, 110, 363–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, T.; Kahraman, C. Multicriteria renewable energy planning using an integrated fuzzy VIKOR and AHP methodology: The case of Istanbul. Energy 2010, 35, 2517–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T.L. How to make a decision: The analytic hierarchy process. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1990, 48, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T.L. Applications of analytical hierarchies. Math. Comput. Simul. 1979, 21, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.; Liu, J.N.; Ngai, E.W. Application of decision-making techniques in supplier selection: A systematic review of literature. Expert Syst. Appl. 2013, 40, 3872–3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhametzyanov, I.; Pamucar, D. A sensitivity analysis in MCDM problems: A statistical approach. Decis. Mak. Appl. Manag. Eng. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, R.J.; Chi, S.-C.; Kao, S.-S. A decision support system for selecting convenience store location through integration of fuzzy AHP and artificial neural network. Comput. Ind. 2002, 47, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, V.; Sangaiah, A.K.; Sakhuja, S.; Thoduka, N.; Aggarwal, R. Supplier selection using fuzzy AHP and TOPSIS: A case study in the Indian automotive industry. Neural Comput. Appl. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, S.; Awasthi, A. Sustainable global supplier selection extended towards sustainability risks from (1 + n) th tier suppliers using fuzzy AHP based approach. IFAC-Pap. 2015, 48, 966–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stević, Ž.; Tanackov, I.; Vasiljević, M.; Novarlić, B.; Stojić, G. An integrated fuzzy AHP and TOPSIS model for supplier evaluation. Serbian J. Manag. 2016, 11, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Božanić, D.; Pamučar, D.; Bojanić, D. Modification of the analytic hierarchy process (AHP) method using Fuzzy logic: Fuzzy AHP approach as a support to the decision making process concerning engagement of the Group for additional hindering. Serbian J. Manag. 2015, 10, 151–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasiljević, M.; Stević, Ž.; Ćosić, I.; Mirčetić, D. Combined FUZZY AHP and TOPSIS method for solving location problem. Horizons 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadic, D.; Gumus, A.T.; Arsovski, S.; Aleksic, A.; Stefanovic, M. An evaluation of quality goals by using fuzzy AHP and fuzzy TOPSIS methodology. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2013, 25, 547–556. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, W.Y.; Huang, C.-C.; Lin, Y.-C.; Chang, T.H.; Shih, M.H. The multi-objective label correcting algorithm for supply chain modeling. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2013, 142, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bali, O.; Kose, E.; Gumus, S. Green supplier selection based on IFS and GRA. Grey Syst. Theory Appl. 2013, 3, 158–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamučar, D.S.; Božanić, D.I.; Kurtov, D.V. Fuzzification of the Saaty’s scale and a presentation of the hybrid fuzzy AHP-TOPSIS model: An example of the selection of a brigade artillery group firing position in a defensive operation. Vojn. Glas. 2016, 64, 966–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, E.W. A comprehensive multi-criteria model to rank electric energy production technologies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 22, 640–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshavarz Ghorabaee, M.; Zavadskas, E.K.; Turskis, Z.; Antucheviciene, J. A new Combinative Distance-based ASsessment (CODAS) method for multi-criteria decision-making. Econ. Comput. Econ. Cybern. Stud. Res. 2016, 50, 25–44. [Google Scholar]
- Ghorabaee, M.K.; Amiri, M.; Zavadskas, E.K.; Hooshmand, R.; Antuchevičienė, J. Fuzzy extension of the CODAS method for multi-criteria market segment evaluation. J. Bus. Econ. Manag. 2017, 18, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchal, D.; Chatterjee, P.; Shukla, R.K.; Choudhury, T.; Tamosaitiene, J. Integrated FUZZY AHP-CODAS framework for maintenance decision in UREA fertilizer industry. Econ. Comput. Econ. Cybern. Stud. Res. 2017, 51, 179–196. [Google Scholar]
- Badi, I.A.; Abdulshahed, A.M.; Shetwan, A.G. A case study of supplier selection for steelmaking company in Libya by using Combinative Distance-based ASsessemnt (CODAS) model. Decis. Mak. Appl. Manag. Eng. 2018, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badi, I.A.; Abdulshahed, A.M.; Shetwan, A.G. Supplier selection using COmbinative Distance-based ASsessment (CODAS) method for multi-criteria decision-making. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Management, Engineering and Environment ICMNEE, Belgrade, Serbia, 28–29 September 2017; pp. 27–37. [Google Scholar]
- Badi, I.; Ballem, M.A.; Shetwan, A.G. Site selection of desalination plant in LIBYA by using COmbinative Distance-based ASsessment (CODAS) METHOD. Int. J. Qual. Res. 2018, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazimieras Zavadskas, E.; Baušys, R.; Lazauskas, M. Sustainable assessment of alternative sites for the construction of a waste incineration plant by applying WASPAS method with single-valued neutrosophic set. Sustainability 2015, 7, 15923–15936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, P.; Pramanik, S.; Giri, B.C. TOPSIS method for multi-attribute group decision-making under single-valued neutrosophic environment. Neural Comput. Appl. 2016, 27, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smarandache, F. A Unifying Field in Logics: Neutrosophic Logic. Neutrosophy, Neutrosophic Set, Neutrosophic Probability and Statistics, ProQuest Info and Learning; American Research Press: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2007; 156p. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, P.; Cheng, P.-F.; Zhang, H.-Y.; Wang, J.-Q. Interval-Valued Neutrosophic Bonferroni Mean Operators and the Application in the Selection of Renewable Energy. New Trends Neutrosophic Theory Appl. 2018, 12–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanujkic, D.; Smarandache, F.; Zavadskas, E.K.; Karabasevic, D. An Approach to Measuring the Website Quality Based on Neutrosophic Sets; Quai du Batelage: Brussells, Belgium, 2018; Volume II. [Google Scholar]
- Şahin, M.; Kargın, A.; Smarandache, F. Generalized Single Valued Triangular Neutrosophic Numbers and Aggregation Operators for Application to Multi-attribute Group Decision Making; Quai du Batelage: Brussells, Belgium, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Ye, J. Multiple attribute group decision-making method based on linguistic neutrosophic numbers. Symmetry 2017, 9, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şahin, M.; Uluçay, V.; Acıoglu, H. Some Weighted Arithmetic Operators and Geometric Operators with SVNSs and Their Application to Multi-Criteria Decision Making Problems; Infinite Study; Quai du Batelage: Brussells, Belgium, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, W.; Zhao, G.; Wu, H. Evaluating investment risks of metallic mines using an extended TOPSIS method with linguistic neutrosophic numbers. Symmetry 2017, 9, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamučar, D.; Ćirović, G. The selection of transport and handling resources in logistics centers using Multi-Attributive Border Approximation area Comparison (MABAC). Expert Syst. Appl. 2015, 42, 3016–3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opricovic, S.; Tzeng, G.-H. Compromise solution by MCDM methods: A comparative analysis of VIKOR and TOPSIS. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2004, 156, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamučar, D.; Mihajlović, M.; Obradović, R.; Atanasković, P. Novel approach to group multi-criteria decision making based on interval rough numbers: Hybrid DEMATEL-ANP-MAIRCA model. Expert Syst. Appl. 2017, 88, 58–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stević, Ž.; Pamučar, D.; Vasiljević, M.; Stojić, G.; Korica, S. Novel Integrated Multi-Criteria Model for Supplier Selection: Case Study Construction Company. Symmetry 2017, 9, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).