Design and Evaluation of a Surfactant–Mixed Metal Hydroxide-Based Drilling Fluid for Maintaining Wellbore Stability in Coal Measure Strata
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methodology
2.2.1. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.2.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
2.2.3. Zeta Potential Test
2.2.4. Contact Angle and Surface Tension
2.2.5. Pressure Transmission Test
2.2.6. Low Temperature Nitrogen Adsorption Test
2.2.7. Performance Evaluation of Water-Based Drilling Fluid
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Surface Electrical Property Analysis
3.2. Effect of Surfactants on Wettability of Rock Samples
3.3. Pressure Transmission Test
3.4. Pore Structure Comparison Before and After Treatment with 1# Compound Surfactants and MMH-2
3.5. Water-Based Drilling Fluid Performance Test
3.6. Biotoxicity Evaluation
3.7. Potential for Field Application
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- When the zeta potential was measured as a function of pH, the results show that the zeta potential of the Longtan coal decreases with increasing pH, the isoelectric point of the Longtan coal is around 7, and the cationic surfactant CS-5 could increase the zeta potential of the Longtan coal up to + 41.25 mV.
- (2)
- According to the contact angle results, a cationic surfactant CS-3 could effectively increase the contact angle of shale up to 98.5°. Furthermore, a set of cationic compound surfactants (0.001 wt% CS-4 + 0.001 wt% CS-1 + 0.001 wt% CS-3) was optimized, which could increase the contact angle of the Longmaxi shale and the Longtan coal up 89° and 86°, respectively.
- (3)
- The dominant adsorption mechanism between the cationic surfactant and the Longmaxi shale is via hydrogen bonds, while that of the Longtan coal was physical adsorption (via electrostatic forces).
- (4)
- Pressure transmission test results show that MMH and the 1# optimized compound surfactants can effectively retard the transmission of pore fluid pressure and decrease the permeability of the core samples, thus increasing wellbore stability.
- (5)
- A set of environmentally friendly water-based drilling fluid systems was proposed (4 wt% sodium bentonite +1.5 wt% sodium carboxymethyl cellulose +2 wt% lignite resin +5 wt% potassium chloride +3 wt% MMH-1 + 0.001 wt% CS-4 + 0.001 wt% CS-1 + 0.001 wt% CS-3). Based on the liner expansion results, the proposed drilling fluid system showed a great inhibitive property. Furthermore, the permeability results confirm its low-damage characteristic to CMG reservoirs.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shao, L.Y.; Yang, Z.Y.; Shang, X.X.; Xiao, Z.H.; Wang, S.; Zhang, W.L.; Lu, J. Lithofacies palaeogeography of the Carboniferous and Permian in the Qinshui Basin, Shanxi Province, China. J. Palaeogeogr. 2015, 4, 384–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, T.S.; Gao, W. Reservoir formation characteristics as well as co-exploration and co-mining orientation of Upper Permian coal-bearing gas in Liupanshui Coalfield. J. China Coal Soc. 2018, 43, 1553–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Ge, Y.; Liang, W.; Li, S. Pressure control and fluid effect of progressive drainage of multiple superposed cbm systems. Nat. Gas Ind. 2013, 33, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Wu, J.G.; Shen, J.; Yang, Z.B.; Shen, Y.L.; Zhang, B. Frontier research of geological technology for coal measure gas joint-mining. J. China Coal Soc. 2018, 43, 1504–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estes, B. Technology Focus: Drilling and completion fluids (November 2009). J. Pet. Technol. 2011, 61, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentzis, T.; Deisman, N.; Chalaturnyk, R.J. Effect of drilling fluids on coal permeability: Impact on horizontal wellbore stability. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2009, 78, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.H.; Gu, S.; Wang, F.; Yang, X.Y.; Yue, Y.; Wu, X.M.; Chixotkin, V.F. Decreasing Coalbed Methane Formation Damage Using Microfoamed Drilling Fluid Stabilized by Silica Nanoparticles. J. Nanomater. 2016, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Li, X.; Qiu, Z.; Jia, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, X. Inhibiting the surface hydration of shale formation using preferred surfactant compound of polymine and tweleve alkyl two hydroxyethyl amine oxide for drilling. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2017, 41, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Q.S.; Chen, J.; Zou, L.P.; Jiang, G.Z.; Tian, Z.L.; Yang, H.L. Research on coalbed methane drilling fluid for horizontal well based on coal reservoir protection in qinshui basin. J. China Coal Soc. 2012, 37, 416–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Q.S.; Ma, X.; Chen, J.; Jiang, G.Z. Instability mechanism of borehole and drilling fluid technical countermeasures for coalbed methane horizontal well in qinshui basin. J. Yangtze Univ. 2014, 11, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.H.; Su, G.D.; Li, Z.H.; Peng, R.; Wang, L.; Wei, P.F.; Han, S.X. The wellbore instability control mechanism of fuzzy ball drilling fluids for coal bed methane wells via bonding formation. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2018, 56, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vryzas, Z.; Kelessidis, V.C. Nano-based drilling fluids: A review. Energies 2017, 10, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.C.; Wu, Q.L.; Song, K.L.; De Hoop, C.F.; Lee, S.; Qing, Y.; Wu, Y.Q. Cellulose nanocrystals and polyanionic cellulose as additives in bentonite water-based drilling fluids: Rheological modeling and filtration mechanisms. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A.R.; Aftab, A.; Ibupoto, Z.H.; Zolkifile, N. The novel approach for the enhancement of rheological properties of water-based drilling fluids by using multi-walled carbon nanotube, nanosilica and glass beads. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2016, 139, 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdo, J.; Haneef, M.D. Clay nanoparticles modified drilling fluids for drilling of deep hydrocarbon wells. Appl. Clay Sci. 2013, 86, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, M.M.; Jung, Y.; Lee, J.K.; Phuoc, T.X.; Chyu, M.K. Fluid filtration and rheological properties of nanoparticle additive and intercalated clay hybrid bentonite drilling fluids. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2015, 127, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerogiorgis, D.I.; Clark, C.; Vryzas, Z.; Kelessidis, V.C. Development and parameter estimation for a multivariate Herschel-Bulkley rheological model of a nanoparticle-based smart drilling fluid. In Proceedings of the 12th International Symposium on Process Systems Engineering and 25th European Symposium on Computer Aided Process Engineering, PT C 2015, Copenhagen, Denmark, 31 May–4 June 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilly, S.I.; Vryzas, Z.; Kelessidis, V.C.; Gerogiorgis, D.I. First-principle rheological modelling and parameter estimation for nanoparticle-based smart drilling fluids. In Proceedings of the 26th European Symposium on Computer Aided Process Engineering, PT A 2016, Portoroz, Slovenia, 12–15 June 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, W.; Ren, D.; Liu, D.; Nan, J. Effects of surfactant on the electrical property of ultra-low permeability sandstone reservoir:the Upper Triassic Chang 8 formation in Longdong area of Ordos basin as an example. Geol. Sci. Technol. Inf. 2016, 35, 235–241. [Google Scholar]
- Adibhatla, B.; Mohanty, K.K. Oil recovery from fractured carbonates by surfactant-aided gravity drainage: Laboratory experiments and mechanistic simulations. SPE Res. Evaluation Eng. 2006, 11, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirasaki, G.; Zhang, D.L. Surface chemistry of oil recovery from fractured, oil-wet, carbonate formations. SPE J. 2004, 9, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, T. An essay on the cohesion of fluids. Philos. Trans. Royal Soc. Lond. 1805, 95, 65–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Förch, R.; Schönherr, H.; Jenkin, A.T.A. Surface Design: Applications in Bioscience and Nanotechnology. Mater. Today 2009, 12, 1–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.L.; Wu, X.M. Research on coalbed methane reservior water blocking damage mechanism and anti-water blocing. J. China Coal Soc. 2014, 39, 1107–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Xiong, J.; Liu, X. Effects of hydration swelling and wettability on propagation mechanism of shale formation crack. Pet. Geol. Exp. 2014, 36, 780–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, J.O.; Schechter, D.S. Wettability Alteration and Spontaneous Imbibition in Unconventional Liquid Reservoirs by Surfactant Additives. SPE Res. Evaluation Eng. 2017, 20, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintero, L. An Overview of Surfactant Applications in Drilling Fluids for the Petroleum Industry. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2002, 23, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunita, P.; Irawan, S.; Kania, D. Optimization of water-based drilling fluid using non-ionic and anionic surfactant additives. Procedia Eng. 2016, 148, 1184–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadizadeh, S.R.; Moslemizadeh, A.; Dezaki, A.S. A novel nonionic surfactant for inhibiting shale hydration. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 118, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.H.; Ye, Y.; Cao, W.J.; Yang, X.Y.; Wu, X.M. Experimental study on the effect of drilling fluid wettability on shale wellbore stability. J. China Coal Soc. 2016, 41, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasralla, R.A.; Nasr-El-Din, H.A. Double-Layer Expansion: Is It a Primary Mechanism of Improved Oil Recovery by Low-Salinity Waterflooding? SPE Res. Evaluation Eng. 2014, 17, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadaka, D.; Radian, A.; Mishael, Y.G. Applying zeta potential measurements to characterize the adsorption on montmorillonite of organic cations as monomers, micelles, or polymers. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 352, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbil, H.Y. Surface Chemistry of Solid and Liquid Interfaces; Blackwell Pub: Oxford, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Su, C.M.; Fu, J.T. Research on the changing tendency of zeta potential of the clay minerals and drilling fluid. Driuing Fluid Complet. Fluid 2002, 19, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.G.; Hou, W.G. Electrical behavior, inhibition, wall stability and reservoir protection. Drill. Fluid Complet. Fluid 2002, 19, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkan, M.; Demirbaş, Ö.; Doğan, M. Electrokinetic properties of kaolinite in mono- and multivalent electrolyte solutions. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2005, 83, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, J.S.; Liu, Y.; Monsterleet, S. Mechanisms of wetting alteration by crude oils. Spe J. 1998, 3, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, J.O.; Schechter, D.S. Application of wettability alteration in the exploitation of unconventional liquid resources. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2016, 43, 832–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, M.; Jones, F.; Barifcani, A.; Iglauer, S. Influence of surface chemistry on interfacial properties of low to high rank coal seams. Fuel 2017, 194, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y. Zeta Potential of the surface of fine coal. J. Fuel Chem. Technol. 1998, 16, 245–252. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Kang, Y.; Yin, Z. Surface electricity and wettability of coal rock under the condition of different chemical environments. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 2014, 43, 864–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.; Yan, J. Characterization and prevention of formation damage for fractured carbonate reservoir formations with low permeability. Pet. Sci. 2008, 5, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Zhong, N.; Jiao, S. Scanning electron microscope observation of pores in mud stone and shale. J. Chin. Electron Microsc. Soc. 2013, 32, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Fu, Y.Q.; Chen, H.F.; Zeng, L.X.; Li, J.S. Rock mechanical characteristics of shale reservoirs. Nat. Gas Ind. 2012, 32, 12–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X. Comparson of biological toxicity assessment methods for drilling fluids. Environ. Prot. Oil Gas Fields 2006, 16, 25–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Min, L.I.; Zhao, Q.; Qin, Y.; Xie, K. Relationship between surface potential and functional groups of coals. J. Chem. Ind. Eng. 2004, 55, 1329–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maršálek, R. The Influence of Surfactants on the Zeta Potential of Coals. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2008, 31, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.M.; Liu, R.S.; Yu, P.Z.; Wang, C.P. Study and application of electropositive drilling fluid system. Oil Drill. Prot. Technol. 2004, 26, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Liu, X.; Guo, Z.; Liu, Y.; Guo, J.; Zhang, S. Wettability modification and restraint of moisture re-adsorption of lignite using cationic gemini surfactant. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 508, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, S.; Li, L.; Qu, J.; Tao, X.; He, H. Exploration on the mechanism of enhancing low-rank coal flotation with cationic surfactant in the presence of oily collector. Fuel 2018, 227, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, Z.; Yang, X.; Peng, Y.; Cai, J. Improving wellbore stability of shale by adjusting its wettability. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2018, 161, 692–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Das, S.; Ellis, B.R. Effect of surfactant adsorption on the wettability alteration of gas-bearing Shales. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2016, 33, 766–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.P.; Chen, S.Y.; Yang, X.Y.; Yu, L. Enhancing wellbore stability of coal measure strata by electricla inhibition and wettability control. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 174, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Oort, E.; Hale, A.; Mody, F.; Roy, S. Transport in shales and the design of improved water-based shale drilling fluids. SPE Drill. Complet. 1996, 11, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, S.; Fan, M.; Guo, J.; Li, B. Decrease in hydrophilicity and moisture readsorption of Manglai lignite using lauryl polyoxyethylene ether: Effects of the HLB and coverage on functional groups and pores. Fuel Process. Technol. 2018, 174, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdo, J.; Haneef, M.D. Nano-enhanced drilling fluids: Pioneering approach to overcome uncompromising drilling problems. J. Energy Resour. Technol. Trans. ASME 2012, 134, 014501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vryzas, Z.; Kelessidis, V.C.; Nalbantian, L.; Zaspalis, V.; Gerogiorgis, D.I.; Wubulikasimu, Y. Effect of temperature on the rheological properties of neat aqueous Wyoming sodium bentonite dispersions. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 136, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

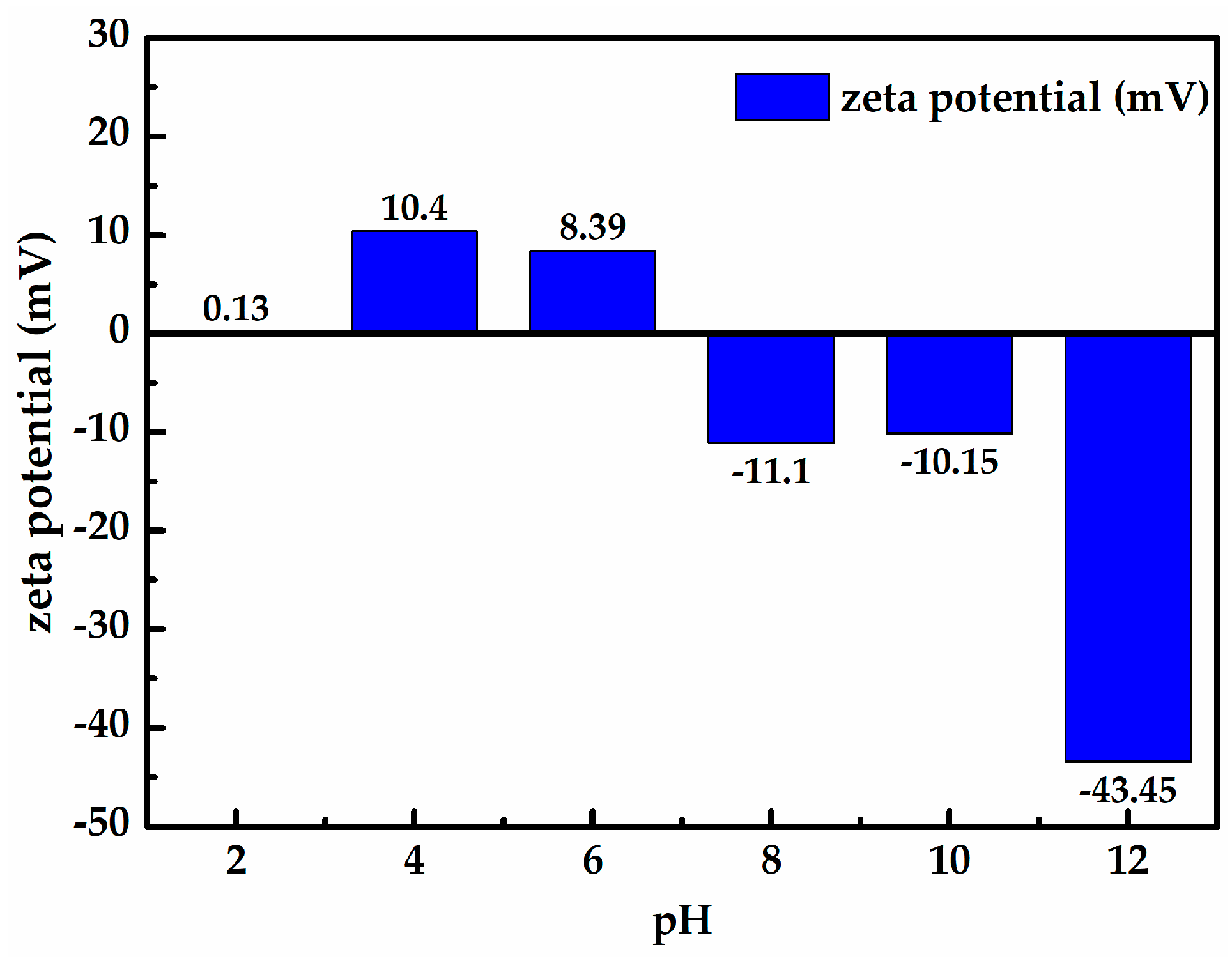




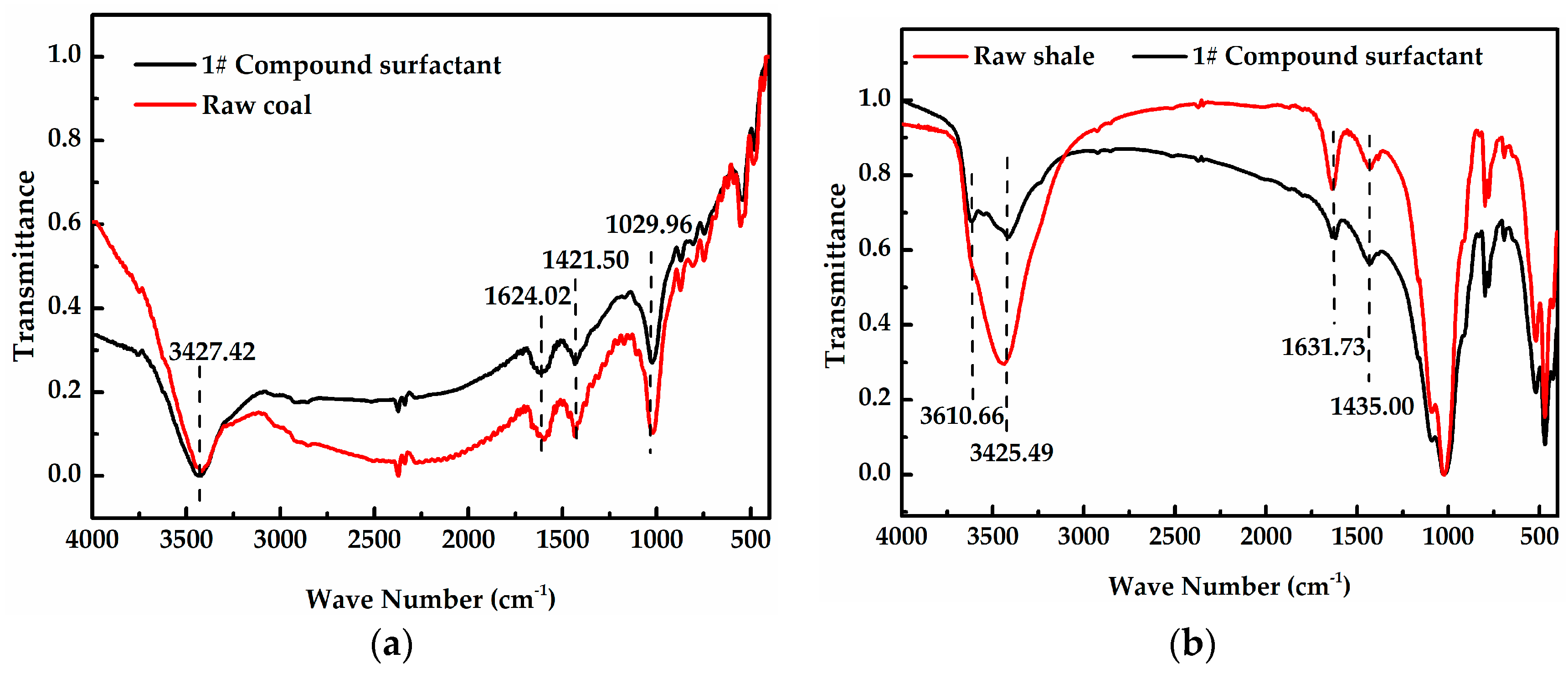

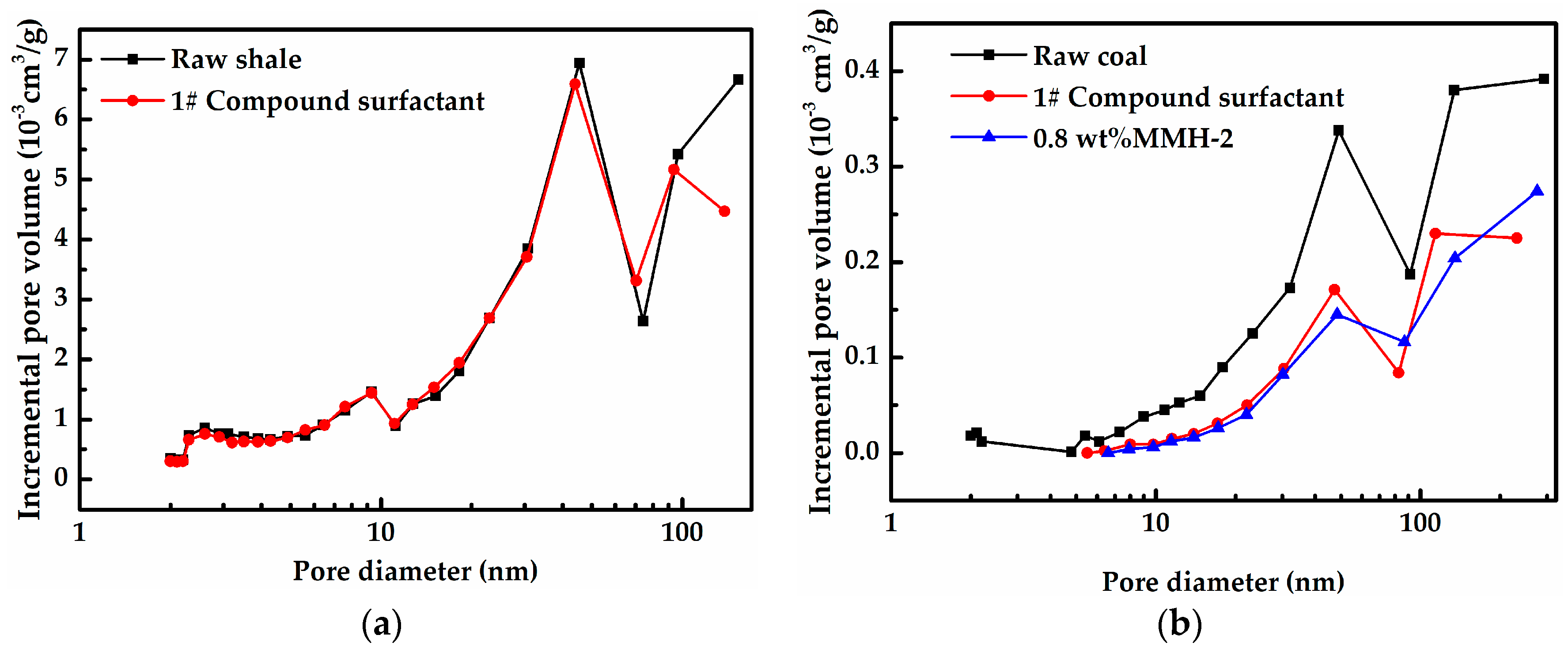


| Minerals | Chlorite | Illite | Calcite | Feldspar | Quartz | Dolomite |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contents (%) | 10 | 10 | 25 | 5 | 47 | 3 |
| Mineral Name | Illite | Kaolinite | Albite | Pyrite | Amorphous |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contents (%) | 22 | 7 | 4.9 | 1.1 | 65 |
| Additive Type | Additive Name | Concentration (wt%) | Lab Unit (per 360 cm3) | Field Unit (per bbl) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| base fluid | fresh water | 87.5 | 315 cm3 | 0.88 bbl |
| clay | sodium bentonite | 4 | 14.4 g | 14.4 lbm |
| fluid loss additive 1 | sodium carboxymethyl cellulose | 1.5 | 5.4 g | 5.4 lbm |
| fluid loss additive 2 | lignite resin | 2 | 7.2 g | 7.2 lbm |
| shale inhibitor | potassium chloride | 5 | 18 g | 18 lbm |
| Dispersions | Zeta Potential (mV) |
|---|---|
| fresh water | −3.63 |
| fresh water + 3%MMH-1 | −21.75 |
| fresh water + 0.8%MMH-2 | 19.75 |
| fresh water + 0.2%AS-1 | −54.05 |
| fresh water + 0.2%CS-5 | 47.25 |
| Formula | Zeta Potential (mV) |
|---|---|
| WBDF | −56.80 |
| WBDF + 3%MMH-1 | −30.40 |
| WBDF + 0.8%MMH-2 | −31.80 |
| Compound Surfactants Combination | CS-3 (%) | CS-1 (%) | CS-4 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1# | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| 2# | 0.001 | 0.005 | 0.005 |
| 3# | 0.001 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| 4# | 0.005 | 0.001 | 0.005 |
| 5# | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.01 |
| 6# | 0.005 | 0.01 | 0.001 |
| 7# | 0.01 | 0.001 | 0.01 |
| 8# | 0.01 | 0.005 | 0.001 |
| 9# | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.005 |
| Formula | Contact Angle of the Longmaxi Shale (°) | Contact Angle of the Longtan Coal (°) |
|---|---|---|
| WBDF | 33.5 | 47 |
| WBDF + 3wt% MMH − 1 + 1# compound surfactants | 45.5 | 65 |
| Formula | μa (cP) | μp (cP) | τ0 (lbf/100 sq ft) | FLAPI (mL) | pH | Lubrication Factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WBDF+3wt%MMH-1+1# compound surfactants | 33.5 | 21 | 23.94 | 7 | 10.39 | 0.18 |
| WBDF+0.8wt%MMH-2+1# compound surfactants | 38.5 | 22 | 31.6 | 10.5 | 8.38 | 0.17 |
| Formula | k0 (mD) | k1 (mD) | Permeability Reduction Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| WBDF | 1.25 | 1.08 | 13.6 |
| WBDF + 3 wt% MMH-1 + 1#compound surfactants | 0.60 | 0.54 | 10 |
| Formula | μa (cP) | μp (cP) | τ0 (lbf/100 sq ft) | FLAPI (mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WBDF + 3 wt% MMH-1 + 1# compound surfactants | 33.50 | 21.00 | 23.94 | 7.0 |
| WBDF + 3 wt% MMH-1 + 1# compound surfactants + 3wt %NaCl | 26.50 | 21.00 | 11.50 | 6.0 |
| WBDF + 3 wt% MMH-1 + 1# compound surfactant + 1wt% CaCl2 | 28.00 | 21.00 | 13.40 | 6.0 |
| WBDF + 3 wt% MMH-1 + 1# compound surfactants + 5 wt% attapulgite | 31.00 | 22.00 | 17.24 | 9.5 |
| Level | Poisonous | High Toxicity | Moderate Toxicity | Slight Toxicity | Actually Non-Toxic | Emission Standard |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LC50 (ppm) | <1 | 1~102 | 102~103 | 103~104 | >104 | >3 × 104 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, S.; Shi, Y.; Yang, X.; Xie, K.; Cai, J. Design and Evaluation of a Surfactant–Mixed Metal Hydroxide-Based Drilling Fluid for Maintaining Wellbore Stability in Coal Measure Strata. Energies 2019, 12, 1862. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12101862
Chen S, Shi Y, Yang X, Xie K, Cai J. Design and Evaluation of a Surfactant–Mixed Metal Hydroxide-Based Drilling Fluid for Maintaining Wellbore Stability in Coal Measure Strata. Energies. 2019; 12(10):1862. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12101862
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Shuya, Yanping Shi, Xianyu Yang, Kunzhi Xie, and Jihua Cai. 2019. "Design and Evaluation of a Surfactant–Mixed Metal Hydroxide-Based Drilling Fluid for Maintaining Wellbore Stability in Coal Measure Strata" Energies 12, no. 10: 1862. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12101862
APA StyleChen, S., Shi, Y., Yang, X., Xie, K., & Cai, J. (2019). Design and Evaluation of a Surfactant–Mixed Metal Hydroxide-Based Drilling Fluid for Maintaining Wellbore Stability in Coal Measure Strata. Energies, 12(10), 1862. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12101862





