Microbial Structure and Energy Generation in Microbial Fuel Cells Powered with Waste Anaerobic Digestate
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reactor Set-Up
2.2. Medium and Operation
2.3. Chemical Analyses
2.4. Microbial Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
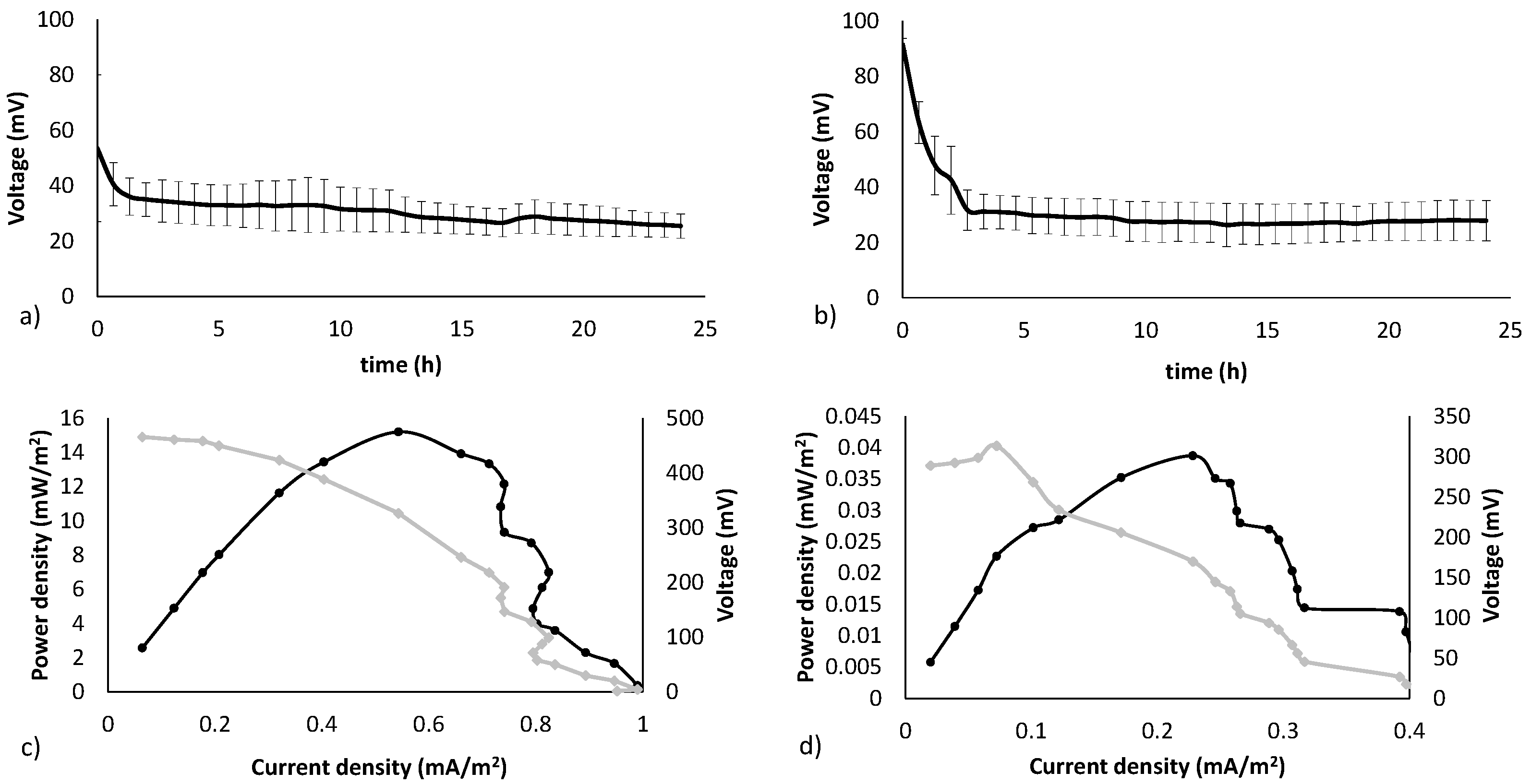
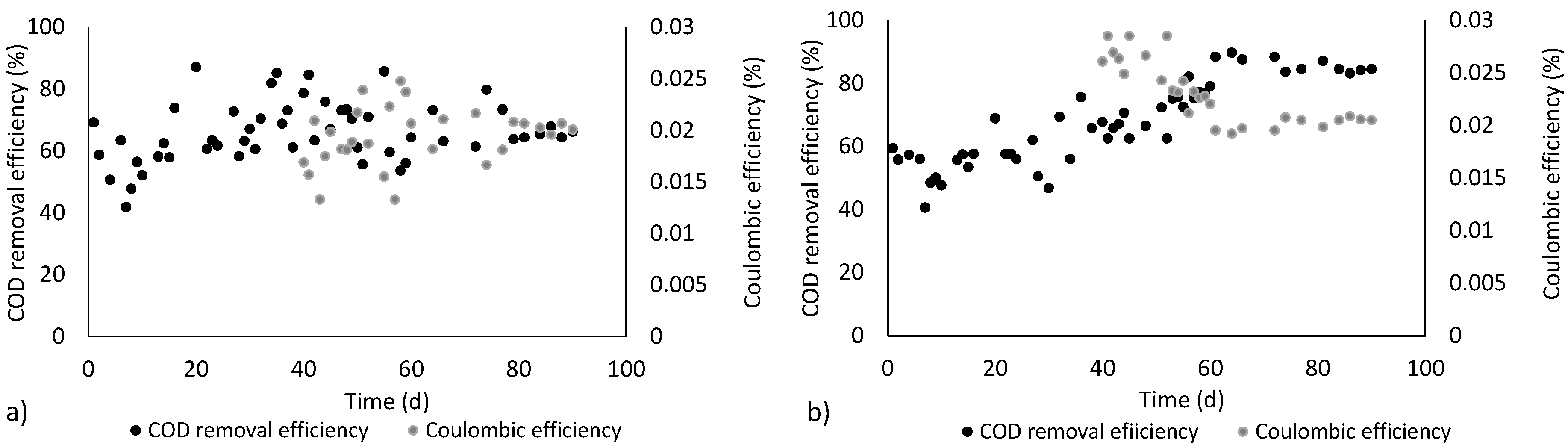
3.1. Electricity Generation
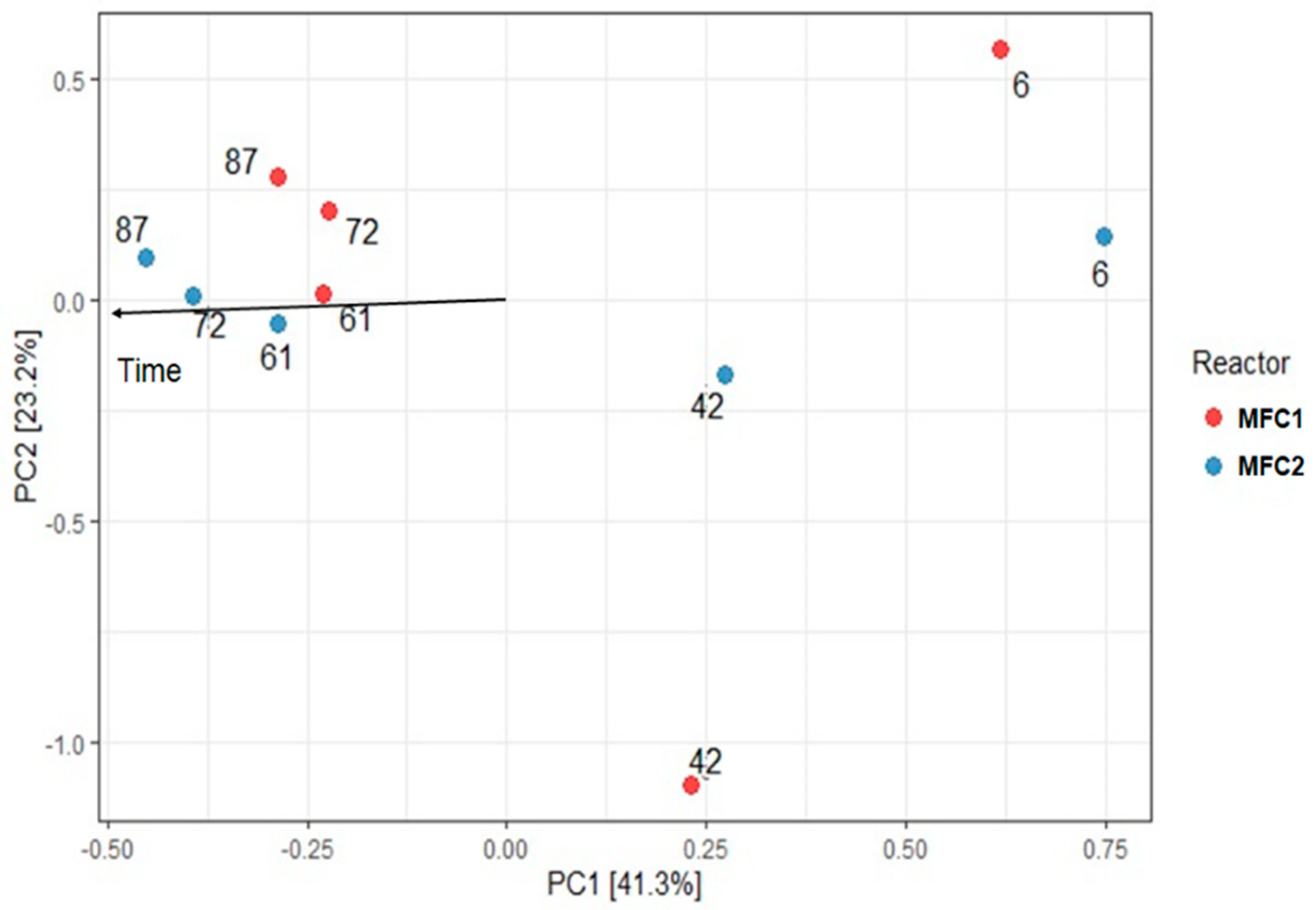
3.2. Microbial Community
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Logan, B.E.; Hamelers, B.; Rozendal, R.; Schröder, U.; Keller, J.; Freguia, S.; Aelterman, P.; Verstraete, W.; Rabaey, K. Microbial fuel cells: Methodology and technology. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 5181–5192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Singh, L.; Zularisam, A.W.; Hai, F.I. Microbial fuel cell is emerging as a versatile technology: A review on its possible applications, challenges and strategies to improve the performances. Int. J. Energy Res. 2018, 42, 369–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.C.; Kharkwal, S.; Chew, K.K.W.; Alwi, R.; Mak, S.F.W.; Ng, H.Y. Enhancing the robustness of microbial fuel cell sensor for continuous copper(II) detection against organic strength fluctuations by acetate and glucose addition. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 259, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christwardana, M.; Frattini, D.; Accardo, G.; Yoon, S.P.; Kwon, Y. Optimization of glucose concentration and glucose/yeast ratio in yeast microbial fuel cell using response surface methodology approach. J. Power Sources 2018, 402, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo, S.; Cañizares, P.; Rodrigo, M.A.; Fernandez-Morales, F.J. Driving force behind electrochemical performance of microbial fuel cells fed with different substrates. Chemosphere 2018, 207, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foudhaili, T.; Rakotonimaro, T.V.; Neculita, C.M.; Coudert, L.; Lefebvre, O. Comparative efficiency of microbial fuel cells and electrocoagulation for the treatment of iron-rich acid mine drainage. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, X.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Y. Electric energy production from food waste: Microbial fuel cells versus anaerobic digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 255, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.H.A.; el Nasser, A.; Zohri, A.; Kassim, R.M.F. Electricity generation from sugarcane molasses using microbial fuel cell technologies. Energy 2019, 178, 538–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepè Sciarria, T.; Arioli, S.; Gargari, G.; Mora, D.; Adani, F. Monitoring microbial communities’ dynamics during the start-up of microbial fuel cells by high-throughput screening techniques. Biotechnol. Rep. 2019, 21, e00310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freguia, S.; Teh, E.H.; Boon, N.; Leung, K.M.; Keller, J.; Rabaey, K. Microbial fuel cells operating on mixed fatty acids. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 1233–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-Y.; Cheng, C.-Y.; Chen, C.-K.; Hsieh, M.-C.; Lin, S.-T.; Ho, K.-Y.; Li, J.-W.; Lin, C.-P.; Chung, Y.-C. Hexavalent chromium removal and bioelectricity generation by Ochrobactrum sp. YC211 under different oxygen conditions. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2016, 51, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, K.J.; Choi, M.J.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, K.Y.; Kim, I.S. Effect of different substrates on the performance, bacterial diversity, and bacterial viability in microbial fuel cells. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 3518–3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freguia, S.; Rabaey, K.; Yuan, Z.; Keller, J. Syntrophic processes drive the conversion of glucose in microbial fuel cell anodes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 7937–7943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costerton, J.W. Control of all Biofilm Strategies and Behaviours. In The Biofilm Primer; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 85–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.B.; Zhong, W.H.; Han, C.; Deng, H. Characterization of electricity generated by soil in microbial fuel cells and the isolation of soil source exoelectrogenic bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondaveeti, S.; Lee, S.H.; Park, H.D.; Min, B. Specific enrichment of different Geobacter sp. in anode biofilm by varying interspatial distance of electrodes in air-cathode microbial fuel cell (MFC). Electrochim. Acta 2020, 331, 135388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almatouq, A.; Babatunde, A.O.; Khajah, M.; Webster, G.; Alfodari, M. Microbial community structure of anode electrodes in microbial fuel cells and microbial electrolysis cells. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 34, 101140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asefi, B.; Li, S.L.; Moreno, H.A.; Sanchez-Torres, V.; Hu, A.; Li, J.; Yu, C.P. Characterization of electricity production and microbial community of food waste-fed microbial fuel cells. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 125, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peixoto, L.; Rodrigues, A.L.; Martins, G.; Nicolau, A.; Brito, A.B.; Silva, M. Flat microbial fuel cell in small and deconcentrated applications: Performance and optimization. Environ. Technol. 2013, 34, 1947–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Patil, S.A.; Brown, R.K.; Schröder, U. Strategies for optimizing the power output of microbial fuel cells: Transitioning from fundamental studies to practical implementation. Appl. Energy 2019, 233–234, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanas, V.; Ahn, Y.; Logan, B.E. Effects of carbon brush anode size and loading on microbial fuel cell performance in batch and continuous mode. J. Power Sources 2014, 247, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, R.; Evans, P.J.; Logan, B.E. Impact of flow recirculation and anode dimensions on performance of a large scale microbial fuel cell. J. Power Sources 2019, 412, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Świątczak, P.; Cydzik-Kwiatkowska, A. Performance and microbial characteristics of biomass in a full-scale aerobic granular sludge wastewater treatment plant. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 1655–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 18th ed.; American Public Health Association (APHA), American Water Works Association (AWWA), Water Pollution Control Federation (WPCF): Washington, DC, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, V.J.; Logan, B.E. Analysis of polarization methods for elimination of power overshoot in microbial fuel cells. Electrochem. Commun. 2011, 13, 54–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Development Core Team. A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- RStudio Team RStudio: Integrated Development for R, Computer Software v0.98.1074; RStudio, Inc.: Boston, MA, USA, 2015.
- Hill, M.O. Diversity and evenness: A unifying notation and its consequences. Ecology 1973, 54, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, J.-d.-r.; Chang, H.N.; Han, J.-I. Performance of microbial fuel cell with volatile fatty acids from food wastes. Biotechnol. Lett. 2011, 33, 705–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tardy, G.M.; Lóránt, B.; Lóka, M.; Nagy, B.; László, K. Enhancing substrate utilization and power production of a microbial fuel cell with nitrogen-doped carbon aerogel as cathode catalyst. Biotechnol. Lett. 2017, 39, 993–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revelo Romo, D.M.; Hurtado Gutiérrez, N.H.; Ruiz Pazos, J.O.; Pabón Figueroa, L.V.; Ordóñez Ordóñez, L.A. Bacterial diversity in the Cr(VI) reducing biocathode of a Microbial Fuel Cell with salt bridge. Rev. Argent. Microbiol. 2019, 51, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.E.; Logan, B.E. Proton exchange membrane and electrode surface areas as factors that affect power generation in microbial fuel cells. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 70, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandukar, M.; Huber, S.J.; Onodera, T.; Pavlostathis, S.G. Biological chromium(VI) reduction in the cathode of a microbial fuel cell. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 8159–8165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boone, D.R.; Genus, I. Methanobacterium. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology; George, M.G., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 215–218. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.Y.; Chen, T.Y.; Chung, Y.C. A comparison of bioelectricity in microbial fuel cells with aerobic and anaerobic anodes. Environ. Technol. 2014, 35, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiva-Aravena, E.; Leiva, E.; Zamorano, V.; Rojas, C.; Regan, J.M.; Vargas, I.T. Organotrophic acid-tolerant microorganisms enriched from an acid mine drainage affected environment as inoculum for microbial fuel cells. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 678, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jangir, Y.; French, S.; Momper, L.M.; Moser, D.P.; Amend, J.P.; El-Naggar, M.Y. Isolation and characterization of electrochemically active subsurface Delftia and Azonexus species. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heylen, K.; Lebbe, L.; de Vos, P. Acidovorax caeni sp. nov., a denitrifying species with genetically diverse isolates from activated sludge. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2008, 58, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, X.; Xing, D.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, H.; Guo, C.; Ren, N. Adaptation of microbial community of the anode biofilm in microbial fuel cells to temperature. Bioelectrochemistry 2017, 117, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, D.; Zuo, Y.; Cheng, S.; Regan, J.M.; Logan, B.E. Electricity generation by Rhodopseudomonas palustris DX-1. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 4146–4151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Wang, X.; Yang, H.; Guo, L. A comparison of hydrogen production amog three photosynthetic baterial strains. Int. J. Hydrog. 2010, 35, 7194–7199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.F.; Lee, C.M. Enhancement of photohydrogen production using phbC deficient mutant Rhodopseudomonas palustris strain M23. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 5418–5424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Cai, T.; Huang, M.; Chen, D. Comparison of electrochemical performances and microbial community structures of two photosynthetic microbial fuel cells. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2017, 124, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, R.; Simon, J. The hydE gene is essential for the formation of Wolinella succinogenes NiFe-hydrogenase. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2003, 227, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iino, T.; Mori, K.; Uchino, Y.; Nakagawa, T.; Harayama, S.; Suzuki, K.I. Ignavibacterium album gen. nov., sp. nov., a moderately thermophilic anaerobic bacterium isolated from microbial mats at a terrestrial hot spring and proposal of Ignavibacteria classis nov., for a novel lineage at the periphery of green sulfur bacteria. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 1376–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.W.; Li, W.W.; Yu, H.Q. Cathodic catalysts in bioelectrochemical systems for energy recovery from wastewater. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 7718–7745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Liang, P.; Song, X.S.; Wang, Y.H.; Qiu, Y.; Huang, X. Trickling filter in a biocathode microbial fuel cell for efficient wastewater treatment and energy production. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2019, 62, 1703–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rismani-Yazdi, H.; Christy, A.D.; Dehority, B.A.; Morrison, M.; Yu, Z.; Tuovinen, O.H. Electricity generation from cellulose by rumen microorganisms in microbial fuel cells. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2007, 97, 1398–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tracy, B.P.; Jones, S.W.; Fast, A.G.; Indurthi, D.C.; Papoutsakis, E.T. Clostridia: The importance of their exceptional substrate and metabolite diversity for biofuel and biorefinery applications. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2012, 23, 364–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Houari, A.; Ranchou-Peyruse, M.; Ranchou-Peyruse, A.; Dakdaki, A.; Guignard, M.; Idouhammou, L.; Bennisse, R.; Bouterfass, R.; Guyoneaud, R.; Qatibi, A.I. Desulfobulbus oligotrophicus sp. Nov., a sulfate-reducing and propionate-oxidizing bacterium isolated from a municipal anaerobic sewage sludge digester. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, D.E.; Bond, D.R.; Lovley, D.R. Electron Transfer by Desulfobulbus propionicus to Fe(III) and Graphite Electrodes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 1234–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vilas Boas, J.; Oliveira, V.B.; Marcon, L.R.C.; Pinto, D.P.; Simões, M.; Pinto, A.M.F.R. Effect of operating and design parameters on the performance of a microbial fuel cell with Lactobacillus pentosus. Biochem. Eng. J. 2015, 104, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wenzel, J.; Fuentes, L.; Cabezas, A.; Etchebehere, C. Microbial fuel cell coupled to biohydrogen reactor: A feasible technology to increase energy yield from cheese whey. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2017, 40, 807–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, W.; Sun, J.; Sun, S.; Quan, X. Enriching functional microbes with electrode to accelerate the decomposition of complex substrates during anaerobic digestion of municipal sludge. Biochem. Eng. J. 2016, 111, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.S.; Malyan, S.K.; Basu, S.; Bishnoi, N.R. Syntrophic association and performance of Clostridium, Desulfovibrio, Aeromonas and Tetrathiobacter as anodic biocatalysts for bioelectricity generation in dual chamber microbial fuel cell. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 16019–16030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, J.; Vedrenne, F.; Denis, C.; Mottet, A.; Déléris, S.; Steyer, J.P.; Cacho Rivero, J.A. A statistical comparison of protein and carbohydrate characterisation methodology applied on sewage sludge samples. Water Res. 2013, 47, 1751–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lingens, F.; Blecher, R.; Blecher, H. Phenylobacterium immobile gen. nov., sp. nov., a gram-negative bacterium that degrades the herbicide chloridazon. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1985, 35, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kämpfer, P.; Nurmiaho Lassila, E.L.; Ulrych, U.; Busse, H.J.; Weiss, N.; Mikkola, R.; Salkinoja-Salonen, M. Frigoribacterium. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematics of Archaea and Bacteria; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2000; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi, M.; Weiss, N.; Schumann, P.; Yokota, A. Leucobacter komagatae gen. nov., sp. nov., a new aerobic gram-positive, nonsporulating rod with 2,4-diaminobutyric acid in the cell wall. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1996, 46, 967–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quan, X.; Quan, Y.; Tao, K.; Jiang, X. Comparative investigation on microbial community and electricity generation in aerobic and anaerobic enriched MFCs. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 128, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Day | MFC1 | MFC2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Operational Taxonomic Units (OTUs) | Shannon | Reads | OTUs | Shannon | Reads | |
| 6 | 1019 | 3.963 | 38,439 | 1026 | 4.548 | 40,590 |
| 42 | 466 | 2.934 | 43,939 | 673 | 4.044 | 32,622 |
| 61 | 1026 | 4.869 | 57,866 | 1155 | 5.423 | 40,904 |
| 72 | 984 | 4.808 | 40,880 | 1027 | 5.219 | 37,040 |
| 87 | 905 | 4.907 | 41,054 | 823 | 4.906 | 41,304 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nosek, D.; Cydzik-Kwiatkowska, A. Microbial Structure and Energy Generation in Microbial Fuel Cells Powered with Waste Anaerobic Digestate. Energies 2020, 13, 4712. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13184712
Nosek D, Cydzik-Kwiatkowska A. Microbial Structure and Energy Generation in Microbial Fuel Cells Powered with Waste Anaerobic Digestate. Energies. 2020; 13(18):4712. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13184712
Chicago/Turabian StyleNosek, Dawid, and Agnieszka Cydzik-Kwiatkowska. 2020. "Microbial Structure and Energy Generation in Microbial Fuel Cells Powered with Waste Anaerobic Digestate" Energies 13, no. 18: 4712. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13184712
APA StyleNosek, D., & Cydzik-Kwiatkowska, A. (2020). Microbial Structure and Energy Generation in Microbial Fuel Cells Powered with Waste Anaerobic Digestate. Energies, 13(18), 4712. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13184712





