Pore-Filled Anion-Exchange Membranes with Double Cross-Linking Structure for Fuel Cells and Redox Flow Batteries
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Membrane Preparation
2.2. Membrane Characterizations
2.3. MEA Performance Tests (ADLFC)
2.4. Charge-Discharge Tests (VRFB)
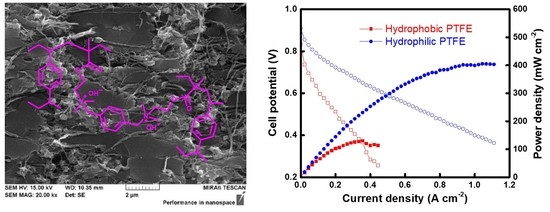
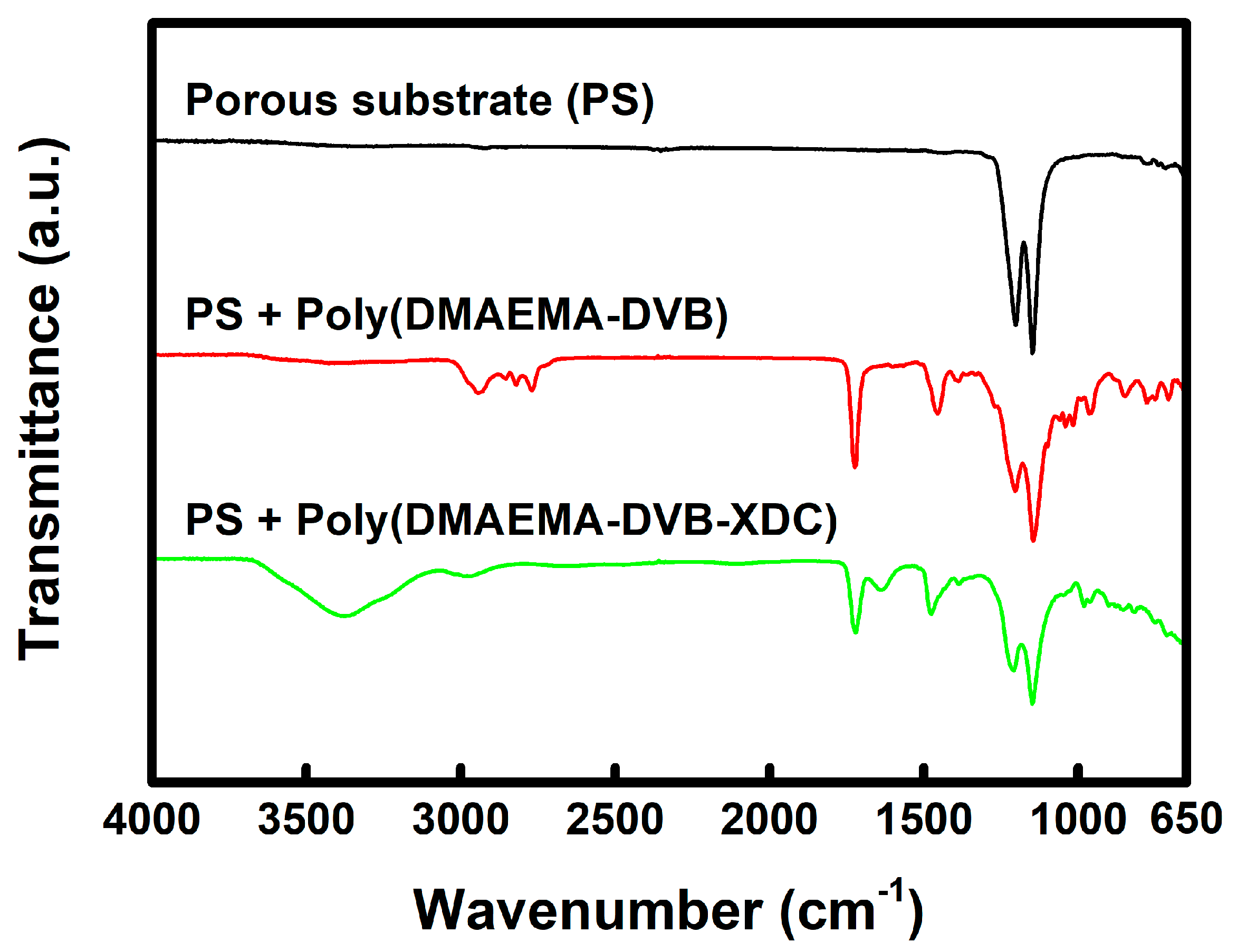
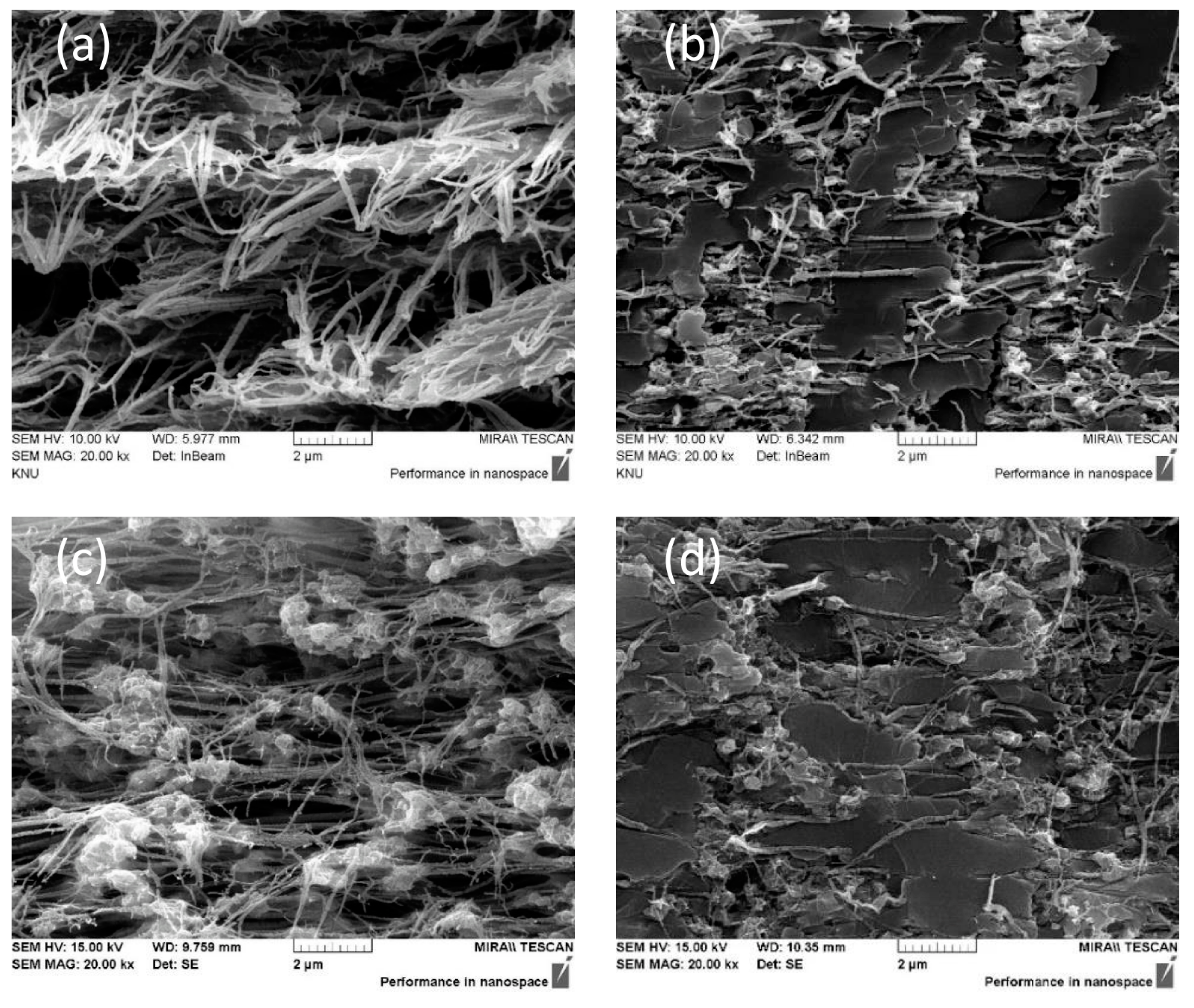
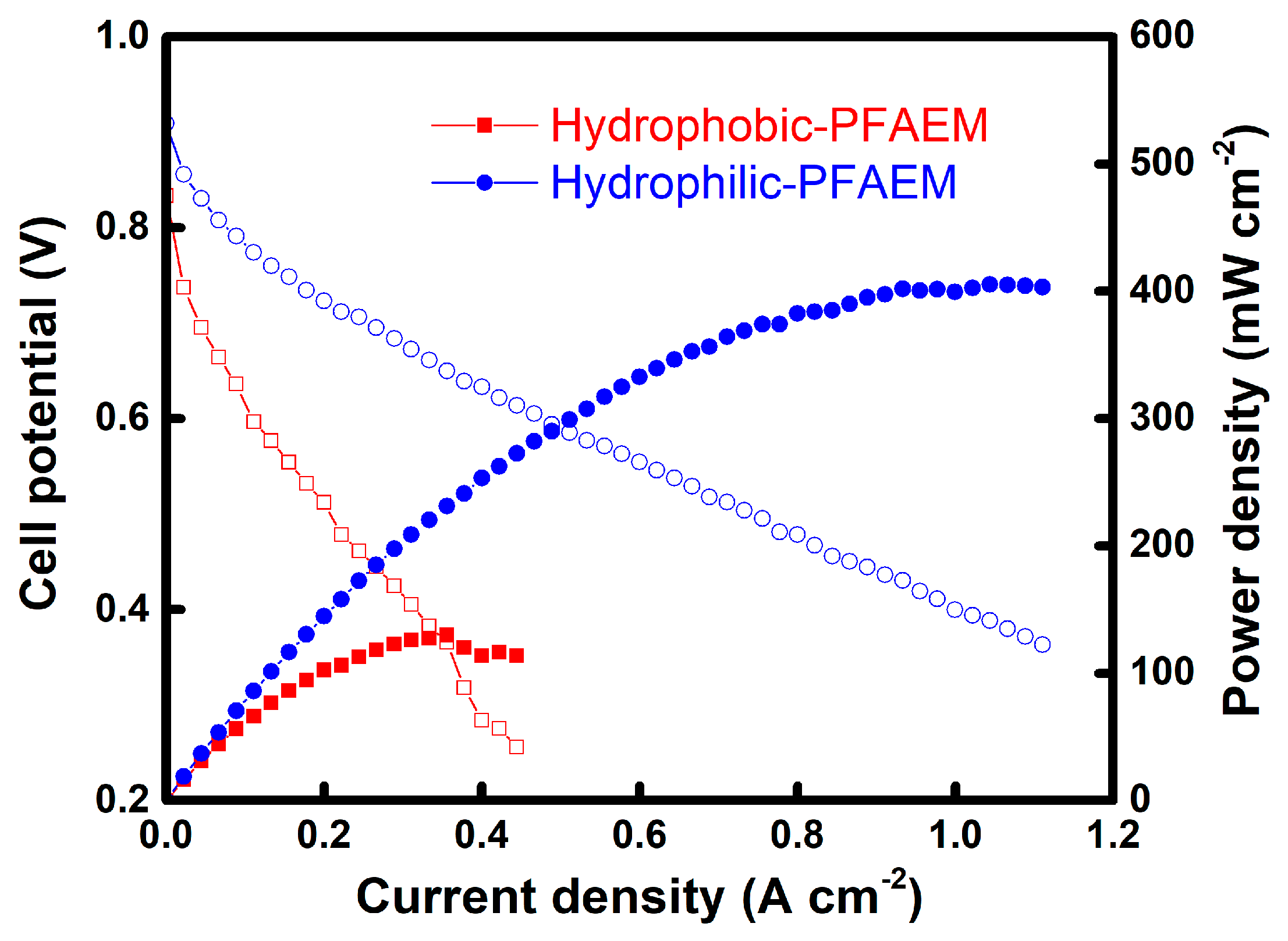
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tanaka, Y. Ion-exchange membrane electrodialysis for saline water desalination and its application to seawater concentration. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 7494–7503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsa, N.; Moheb, A.; Mehrabani-Zeinabad, A.; Masigol, M.A. Recovery of lithium ions from sodium-contaminated lithium bromide solution by using electrodialysis process. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2015, 98, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benvenuti, T.; Krapf, R.S.; Rodrigues, M.A.S.; Bernardes, A.M.; Zoppas-Ferreira, J. Recovery of nickel and water from nickel electroplating wastewater by electrodialysis. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 129, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, F.; Zhang, G.; Tong, J.; Xu, T.; Wu, Y. Anion exchange membranes used in diffusion dialysis for acid recovery from erosive and organic solutions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 122, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-H.; Park, J.-H.; Seo, S.-J.; Park, J.-S.; Jung, S.; Kang, Y.S.; Choi, J.-H.; Kang, M.-S. Development of thin anion-exchange pore-filled membranes for high diffusion dialysis performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 447, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palakkal, V.M.; Rubio, J.E.; Lin, Y.J.; Arges, C.G. Low-resistant ion-exchange membranes for energy efficient membrane capacitive deionization. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 13778–13786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-H.; Choi, Y.-E.; Park, J.-S.; Kang, M.-S. Capacitive deionization employing pore-filled cation-exchange membranes for energy-efficient removal of multivalent cations. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 295, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legrand, L.; Shu, Q.; Tedesco, M.; Dykstra, J.E.; Hamelers, H.V.M. Role of ion exchange membranes and capacitive electrodes in membrane capacitive deionization (MCDI) for CO2 capture. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 564, 478–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Lyu, M.; Wang, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, J. Synthesis and performance of novel anion exchange membranes based on imidazolium ionic liquids for alkaline fuel cell applications. J. Power Sources 2015, 284, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraytsberg, A.; Ein-Eli, Y. Review of advanced materials for proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Energy Fuels 2014, 28, 7303–7330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-H.; Park, J.-S.; Choun, M.; Lee, J.; Kang, M.-S. Pore-filled anion-exchange membranes for electrochemical energy conversion applications. J. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 222, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Omasta, T.J.; Peng, X.; Wang, L.; Varoe, J.R.; Pivovar, B.S.; Mustain, W.E. Quantifying and elucidating the effect of CO2 on the thermodynamics, kinetics and charge transport of AEMFCs. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 2806–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Mandal, M.; Peng, X.; Yang-Neyerlin, A.C.; Pivovar, B.S.; Mustain, W.E.; Kohl, P.A. Composite poly(norbornene) anion conducting membranes for achieving durability, water management and high power (3.4 W/cm2) in hydrogen/oxygen alkaline fuel cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, F637–F644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-S.; Kim, H.-K.; Kim, C.-S.; Suh, H.-Y.; Nahm, K.-S.; Choi, Y.-W. Thin pore-filled ion exchange membranes for high power density in reverse electrodialysis: Effects of structure on resistance, stability, and ion selectivity. ChemistrySelect 2017, 2, 1974–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.G.; Zhang, B.; Glabman, S.; Uzal, N.; Dou, X.; Zhang, H.; Wei, X.; Chen, Y. Potential ion exchange membranes and system performance in reverse electrodialysis for power generation: A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 486, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, E.; Wang, G.; Yu, P.; Zhao, Q.; Yao, F. Poly(phenyl sulfone) anion exchange membranes with pyridinium groups for vanadium redox flow battery applications. J. Power Sources 2015, 282, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-H.; Seo, S.-J.; Lee, M.-J.; Park, J.-S.; Moon, S.-H.; Kang, Y.S.; Choi, Y.-W.; Kang, M.-S. Pore-filled anion-exchange membranes for non-aqueous redox flow batteries with dual-metal-complex redox shuttles. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 454, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.-B.; Kim, D.-H.; Kang, M.-S. Thin reinforced poly(2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene oxide)-based anion-exchange membranes with high mechanical and chemical stabilities. Chem. Lett. 2019, 48, 1500–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Xiao, M.; Song, S.; Han, D.; Hickner, M.A.; Meng, Y. Amphoteric ion exchange membrane synthesized by direct polymerization for vanadium redox flow battery application. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2014, 39, 16123–16131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peighambardoust, S.J.; Rowshanzamir, S.; Amjadi, M. Review of the proton exchange membranes for fuel cell applications. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2010, 35, 9349–9384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirubakaran, A.; Jain, S.; Nema, R.K. A review on fuel cell technologies and power electronic interface. Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 2009, 13, 2430–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.; Hong, S.; Kim, D.-H.; Kang, M.-S.; Park, J.-S.; Uhm, S.; Lee, J. Optimistic performance of carbon-free hydrazine fuel cells based on controlled electrode structure and water management. J. Energy Chem. 2020, 51, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouzgou, A.; Podias, A.; Tsiakaras, P. PEMFCs and AEMFCs directly fed with ethanol: A current status comparative review. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2013, 43, 119–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benipal, N.; Qi, J.; Gentile, J.C.; Li, W. Direct glycerol fuel cell with polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) thin film separator. Renew. Energy 2017, 105, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartrom, A.M.; Haan, J.L. The direct formate fuel cell with an alkaline anion exchange membrane. J. Power Sources 2012, 214, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Tang, Z.K.; Zhao, T.S. A high-performance alkaline exchange membrane direct formate fuel cell. Appl. Energy 2014, 115, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merle, G.; Wessling, M.; Nijmeijer, K. Anion exchange membranes for alkaline fuel cells: A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 377, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.F.; An, L.; Zhao, T.S.; Tang, Z.K. Advances and challenges in alkaline anion exchange membrane fuel cells. Prog. Energy Combust. 2018, 66, 141–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henkensmeier, D.; Najibah, M.; Harms, C.; Žitka, J.; Hnát, J.; Bouzek, K. Overview: State-of-the art commercial membranes for anion exchange membrane water electrolysis. J. Electrochem. Energy Conv. Stor. 2020, 18, 024001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsehaye, M.T.; Alloin, F.; Iojoiu, C. Prospects for anion-exchange membranes in alkali metal-air batteries. Energies 2019, 12, 4702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulaganathan, M.; Aravindan, V.; Yan, Q.; Madhavi, S.; Skyllas-Kazacos, M.; Lim, T.M. Recent advancements in all-vanadium redox flow batteries. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 3, 1500309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, D.; Zhang, S.; Yin, C.; Zhang, B.; Jian, X. Effect of amination agent on the properties of quaternized poly(phthalazinone ether sulfone) anion exchange membrane for vanadium redox flow battery application. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 354, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Zhao, T.S.; Wei, L.; Zeng, Y.K.; Zhang, Z.H. Highly stable pyridinium-functionalized cross-linked anion exchange membranes for all vanadium redox flow batteries. J. Power Sources 2016, 331, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yin, C.; Xing, D.; Yang, D.; Jian, X. Preparation of chloromethylated/quaternized poly(phthalazinone ether ketone) anion exchange membrane materials for vanadium redox flow battery applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 363, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Ryu, S.; Maurya, S.; Lee, J.-Y.; Sung, K.-W.; Lee, J.-S.; Moon, S.-H. Fabrication of a composite anion exchange membrane with aligned ion channels for a high-performance non-aqueous vanadium redox flow battery. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 5010–5025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Miyata, F.; Nakao, S. Pore-filling type polymer electrolyte membranes for a direct methanol fuel cell. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 214, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, D.S.; Sherazia, T.A.; Sohn, J.Y.; Noh, Y.C.; Park, C.H.; Guiver, M.D.; Lee, Y.M. Anisotropic radio-chemically pore-filled anion exchange membranes for solid alkaline fuel cell (SAFC). J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 495, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yu, H.; Xie, F.; Liu, Y.; Shao, Z.; Yi, B. High durability and hydroxide ion conducting pore-filled anion exchange membranes for alkaline fuel cell applications. J. Power Sources 2014, 269, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Choi, Y.-W.; Choi, J.; Jeong, N.; Kim, H.; Nam, J.-Y.; Jeong, H. R2R Fabrication of pore-filling cation-exchange membranes via one-time impregnation and their application in reverse electrodialysis. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 12200–12213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palatý, Z.; Bendová, H. Numerical error analysis of mass transfer measurements in batch dialyzer. Desalin. Water Treat. 2011, 26, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Tighe, T.B.; Schwenzer, B.; Yan, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Yang, Z.; Hickner, M.A. Chemical and mechanical degradation of sulfonated poly(sulfone) membranes in vanadium redox flow batteries. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2011, 41, 1201–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Wang, Y.; Ma, J.; Qiu, J.; Peng, J.; Li, J.; Zhai, M. A novel amphoteric ion exchange membrane synthesized by radiation-induced grafting α-methylstyrene and N,N-dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate for vanadium redox flow battery application. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 407–408, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Specification Sheet for Hydrophilic PTFE Membrane Filters. Available online: http://advantecmfs.com/filtration/membranes/mb_ptfephil.php (accessed on 11 September 2020).
- Gopi, K.H.; Bhat, S.D. Anion exchange membrane from polyvinyl alcohol functionalized with quaternary ammonium groups via alkyl spacers. Ionics 2018, 24, 1097–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Miao, L.; Bai, Y.; Lü, C. Facile construction of crosslinked anion exchange membranes based on fluorenyl-containing polysulfone via click chemistry. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 4403–4413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Substrate | Thickness (μm) | Pore Size (μm) | Porosity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrophobic PTFE (T020A142C) | 80 | 0.2 | 74 |
| Hydrophilic PTFE (H020A142C) | 35 | 0.2 | 71 |
| Membranes | Thickness (μm) | Contact Angle (Degree) | WU (%) | IEC (meq./g) | σ 1 (S/cm) | EAR 2 (Ω cm2) | t−3 (-) | t− 4 (-) | WL 5 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AMX (Astom Corp.) | 135 | 44.8 | 21.1 | 1.40 | 0.015 | 0.93 | 0.975 | 0.853 | 10.2 |
| Hydrophobic-PFAEM | 82 | 93.2 | 13.2 | 1.46 | 0.010 | 0.84 | 0.984 | 0.926 | 0.32 |
| Hydrophilic-PFAEM | 40 | 70.7 | 21.1 | 1.42 | 0.019 | 0.21 | 0.990 | 0.954 | 0.45 |
| Membranes | Diffusion Coefficient (×109, cm2 s−1) |
|---|---|
| Hydrophobic-PFAEM | 5.75 |
| Hydrophilic- PFAEM | 6.99 |
| Membranes | CE (%) | VE (%) | EE (%) | KA (×106, m s−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AMX (Astom Corp.) | 93.6 | 87.7 | 82.1 | 2.16 |
| Hydrophobic-PFAEM | 97.2 | 89.4 | 86.9 | 2.63 |
| Hydrophilic-PFAEM | 90.9 | 91.3 | 83.0 | 7.69 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, D.-H.; Kang, M.-S. Pore-Filled Anion-Exchange Membranes with Double Cross-Linking Structure for Fuel Cells and Redox Flow Batteries. Energies 2020, 13, 4761. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13184761
Kim D-H, Kang M-S. Pore-Filled Anion-Exchange Membranes with Double Cross-Linking Structure for Fuel Cells and Redox Flow Batteries. Energies. 2020; 13(18):4761. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13184761
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Do-Hyeong, and Moon-Sung Kang. 2020. "Pore-Filled Anion-Exchange Membranes with Double Cross-Linking Structure for Fuel Cells and Redox Flow Batteries" Energies 13, no. 18: 4761. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13184761
APA StyleKim, D.-H., & Kang, M.-S. (2020). Pore-Filled Anion-Exchange Membranes with Double Cross-Linking Structure for Fuel Cells and Redox Flow Batteries. Energies, 13(18), 4761. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13184761