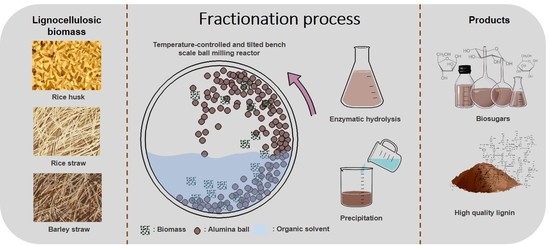
Extraction Behaviors of Lignin and Hemicellulose-Derived Sugars During Organosolv Fractionation of Agricultural Residues Using a Bench-Scale Ball Milling Reactor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Experimental Setup and Operation
2.3. Characterization of Organosolv-Separated Lignin
2.4. Solid and Liquid Composition Analysis of Untreated and Pretreated Samples
2.5. Enzymatic Digestibility Test
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Compositions of Raw Agricultural Residues Used in This Study
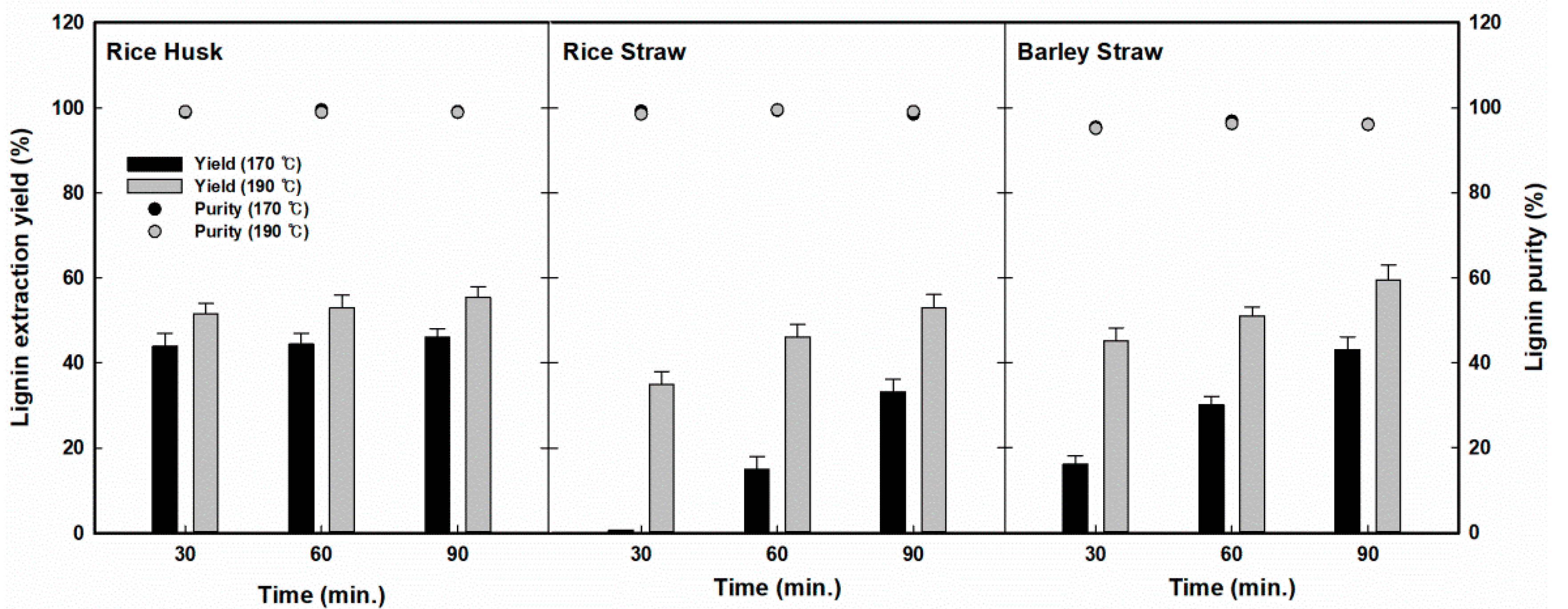
3.2. Lignin Extraction Yields and Purities for Various Fractionation Conditions
3.3. Compositional Changes in Solid Residues after Fractionation
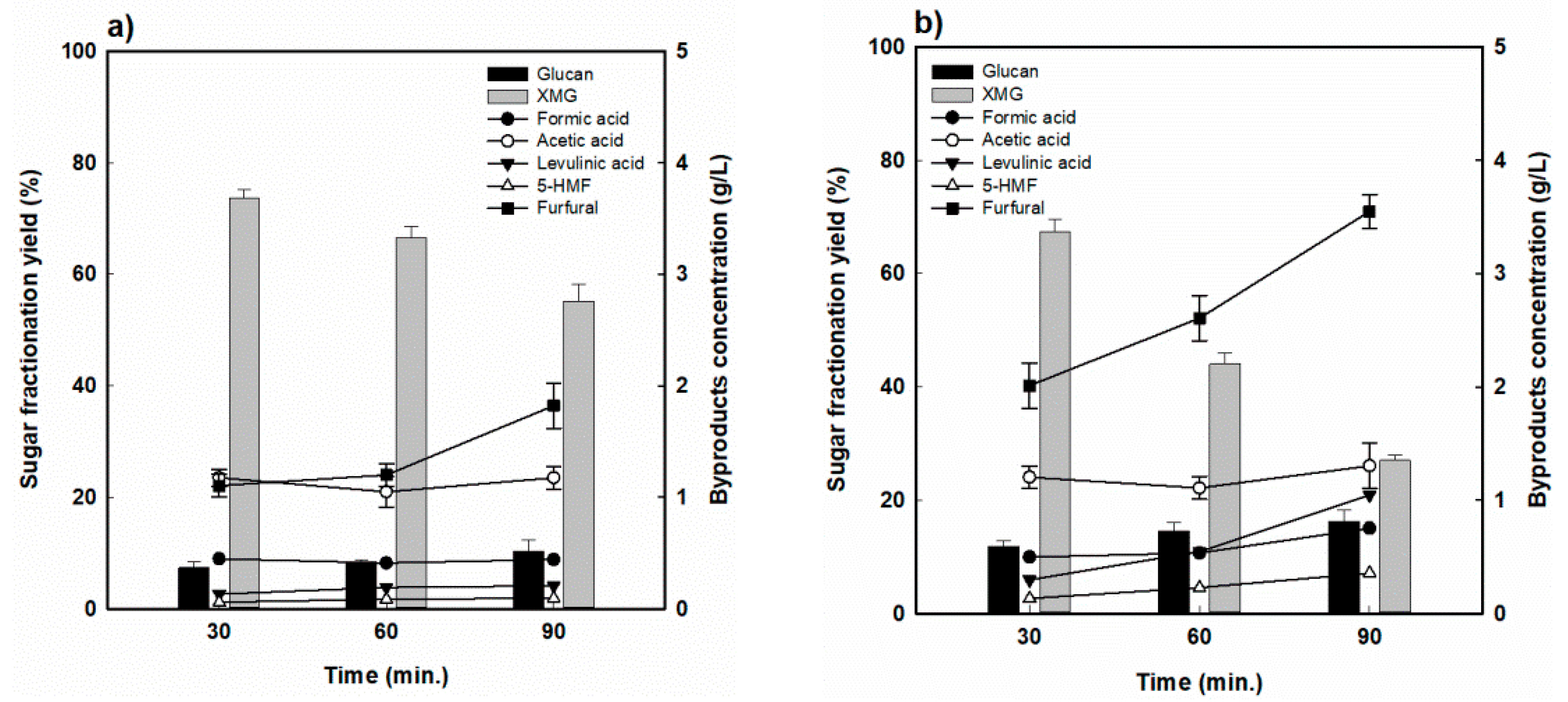
3.4. Sugar Recovery and Decomposition Behavior in the Fractionated Hydrolysate
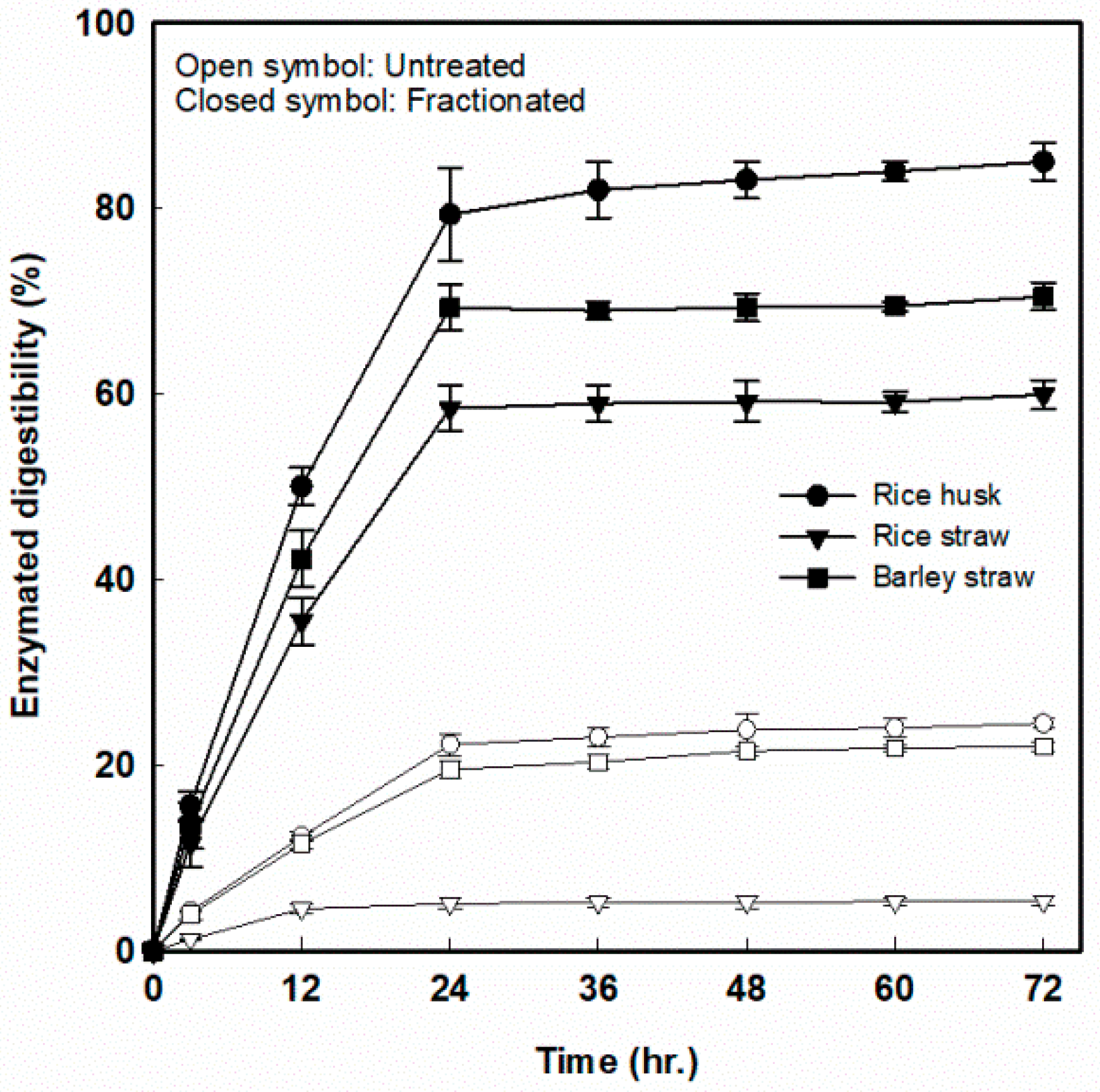
3.5. Enzymatic Digestibility of Fractionated Solid Residues
3.6. Chemical Characteristics of Extracted Lignin from RS, RH, and BS
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barakat, A.; Vries, H.; Rouau, X. Dry fractionation process as an important step in current and future lignocellulose biorefineries: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 134, 362–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherubini, F. The biorefinery concept: Using biomass instead of oil for producing energy and chemicals. Energy Convers. Manag. 2010, 51, 1412–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsakas, L.; Gao, Q.; Jansson, S.; Rova, U.; Christakopoulos, P. Green conversion of municipal solid wastes into fuels and chemicals. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 26, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsimpouras, C.; Zacharopoulou, M.; Matsakas, L.; Rova, U.; Christakopoulos, P.; Topakas, E. Sequential high gravity ethanol fermentation and anaerobic digestion of steam explosion and organosolv pretreated corn stover. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 244, 1129–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momayez, F.; Karimi, K.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Energy recovery from industrial crop wastes by dry anaerobic digestion: A review. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 129, 673–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statista. Available online: http://www.statista.com/statistics/255937/leading-rice-producers-worldwide/ (accessed on 16 October 2019).
- Statista. Available online: http://www.statista.com/statistics/271973/world-barley-production-since-2008/ (accessed on 16 October 2019).
- Kim, S.H.; Gregory, J.M. Straw to Grain Ratio Equation for Combine Simulation. J. Biosyst. Eng. 2015, 40, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- John, R.P.; Nampoothiri, K.M.; Pandey, A. Fermentative production of lactic acid from biomass: An overview on process developments and future perspectives. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 74, 524–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragauskas, A.J.; Williams, C.K.; Davison, B.H.; Britovsek, G.; Cairney, J.; Eckert, C.A.; Frederick, W.J.; Hallett, J.P.; Leak, D.J.; Liotta, C.L.; et al. The path forward for biofuels and biomaterials. Science 2006, 311, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hahn-Hägerdal, B.; Galbe, M.; Gorwa-Grauslund, M.F.; Lidén, G.; Zacchi, G. Bio-ethanol–The fuel of tomorrow from the residues of today. Trends Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kai, D.; Tan, M.J.; Chee, P.L.; Chua, Y.K.; Yap, Y.L.; Loh, X.J. Towards lignin-based functional materials in a sustainable world. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 1175–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.; Wang, S.; Price, J.T.; Konduri, M.K.; Fatehi, P. Water soluble kraft lignin–acrylic acid copolymer: Synthesis and characterization. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 4355–4366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achinivu, E.C.; Howard, R.M.; Li, G.; Gracz, H.; Henderson, W.A. Lignin extraction from biomass with protic ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 1114–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishtal, A.G.; Kraslawski, A. Challenges in industrial applications of technical lignins. Bio. Res. 2011, 6, 3547–3568. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.J.; Zhang, Q.G.; Lee, D.J. Kraft lignin biorefinery: A perspective. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 1181–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Løhre, C.; Kleinert, M.; Barth, T. Organosolv extraction of softwood combined with lignin-to-liquid-solvolysis as a semi-continuous percolation reactor. Biomass Bioenergy 2017, 99, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Long, J.; Wang, T.; Shu, R.; Zhang, Q.; Ma, L. Process intensification effect of ball milling on the hydrothermal pretreatment for corn straw enzymolysis. Energy Convers. 2015, 101, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, R.C.A.; Fonseca, B.F.; Santos, H.T.L.; Ferreira, I.S.; Mussatto, S.I.; Roberto, I.C. Alkaline deacetylation as a strategy to improve sugars recovery and ethanol production from rice straw hemicellulose and cellulose. Ind. Crops Prod. 2017, 106, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussatto, S.I. (Ed.) Biomass pretreatment with acids. In Biomass Fractionation Technologies for a Lignocellulosic Feedstock Based Biorefinery; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 169–185. [Google Scholar]
- Barakat, A.; Chuetor, S.; Monlau, F.; Solhy, A.; Rouau, X. Eco-friendly dry chemo-mechanical pretreatments of lignocellulosic biomass: Impact on energy and yield of the enzymatic hydrolysis. Appl. Energy 2014, 113, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaria, M.R.; Hirata, S.; Hassan, M.A. Combined pretreatment using alkaline hydrothermal and ball milling to enhance enzymatic hydrolysis of oil palm mesocarp fiber. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 169, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.M.; Dien, B.S.; Tumbleson, M.E.; Rausch, K.D.; Singh, V. Improvement of sugar yields from corn stover using sequential hot water pretreatment and disk milling. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 216, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, A.; Ren, J.; Wang, W.; Li, H.; Lin, Q.; Yan, Y.; Sun, R.; Liu, G. Production of xylo-sugars from corncob by oxalic acid-assisted ball milling and microwave-induced hydrothermal treatments. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 79, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, H.; Yano, S.; Endo, T.; Sakaki, T.; Sawayama, S. Combining hot-compressed water and ball milling pretreatments to improve the efficiency of the enzymatic hydrolysis of eucalyptus. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2008, 1, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Silva, A.S.; Inoue, H.; Endo, T.; Yano, S.; Bon, E.P.S. Milling pretreatment of sugarcane bagasse and straw for enzymatic hydrolysis and ethanol fermentation. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 7402–7409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Huang, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.; Yan, L.; Chen, J. Ball milling pretreatment of corn stover for enhancing the efficiency of enzymatic hydrolysis. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2010, 162, 1872–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Arato, C.; Gilkes, N.; Gregg, D.; Mabee, W.; Pye, K.; Xiao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Saddler, J. Biorefining of softwoods using ethanol organosolv pulping: Preliminary evaluation of process streams for manufacture of fuel-grade ethanol and co-products. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2005, 90, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Cheng, K.; Liu, D. Organosolv pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass for enzymatic hydrolysis. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 82, 815–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakzeski, J.; Bruijnincx, P.C.A.; Jongerius, A.L.; Weckhuysen, B.M. The catalytic valorization of lignin for the production of renewable chemicals. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 3552–3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torre, M.; Moral, A.; Hernández, M.; Cabeza, E.; Tijero, A. Organosolv lignin for biofuel. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 45, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Um, B.H.; Im, D.J.; Lee, J.H.; Oh, K.K. Combined Ball Milling and Ethanol Organosolv Pretreatment to Improve the Enzymatic Digestibility of Three Types of Herbaceous Biomass. Energies 2018, 11, 2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koo, B.W.; Kim, H.Y.; Park, N.; Lee, S.M.; Yeo, H.; Choi, I.G. Organosolv pretreatment of Liriodendron tulipifera and simultaneous saccharification and fermentation for bioethanol production. Biomass Bioenergy 2011, 35, 1833–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sluiter, A.; Ruiz, R.; Scarlata, C.; Sluiter, J.; Templeton, D. Determination of Extractives in Biomass; NREL/TP-510-42619; National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Golden, CO, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Sluiter, A.; Hames, B.; Ruiz, R.; Scarlata, C.; Sluiter, J.; Templeton, D. Determination of Structural Carbohydrates and Lignin in Biomass; NREL/TP-510-42618; National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Golden, CO, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Selig, M.; Weiss, N.; Ji, Y. Enzymatic Saccharification of Lignocellulosic Biomass; NREL/TP-510-42629; National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Golden, CO, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Carolina, C.M.; Arturo, J.G.; Mahmoud, E.H. A comparison of pretreatment methods for bioethanol production from lignocellulosic materials. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2012, 90, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limayem, A.; Ricke, S.C. Lignocellulosic biomass for bioethanol production: Current perspectives, potential issues and future prospects. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2012, 38, 449–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, V.; Rao, M. Trends in bioconversion of lignocellulose: Biofuels, platform chemicals & biorefinery concept. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2012, 38, 522–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mor, S.; Manchanda, C.K.; Kansal, S.K.; Ravindra, K. Nanosilica extraction from processed agricultural residue using green technology. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 143, 1284–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y. Rice husk silica derived nanomaterials for sustainable applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 80, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kwon, J.H.; Lee, J.W.; Lee, H.S.; Chang, J.H.; Sang, B.I. Preparation of high purity silica originated from rice husks by chemically removing metallic impurities. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 50, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotana, F.; Cavalaglio, G.; Nicolini, A.; Gelosia, M.; Coccia, V.; Petrozzi, A. Lignin as co-product of second generation bioethanol production from ligno-cellulosic biomass. Energy Procedia 2014, 45, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mesa, L.; Gonzalez, E.; Cara, C.; González, M.; Castro, E.; Mussattoc, S.I. The effect of organosolv pretreatment variables on enzymatic hydrolysis of sugarcane bagasse. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 168, 1157–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.Y.; Ryu, H.J.; Oh, K.K. Acid-catalyzed hydrothermal severity on the fractionation of agricultural residues for xylose-rich hydrolyzates. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 132, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yáñez-S, M.; Matsuhiro, B.; Nuñez, C.; Pan, S.; Hubbell, C.A.; Sannigrahi, P.; Ragauskas, A.J. Physicochemical characterization of ethanol organosolv lignin (EOL) from Eucalyptus globulus: Effect of extraction conditions on the molecular structure. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2014, 110, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baucher, M.; Monties, B.; Van Montagu, M.; Boerjan, W. Biosynthesis and genetic engineering of lignin. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 1998, 17, 125–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.C.; Sun, X.F.; Wang, S.Q.; Zhu, W.; Wang, X.Y. Ester and ether linkages between hydroxycinnamic acids and lignins from wheat, rice, rye, and barley starws, maize stems, and fast-growing poplar wood. Ind. Crops Prod. 2002, 15, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClelland, D.J.; Motagamwala, A.H.; Li, Y.; Rover, M.R.; Wittrig, A.M.; Wu, C.; Huber, G.W. Functionality and molecular weight distribution of red oak lignin before and after pyrolysis and hydrogenation. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 1378–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Components | Composition (wt. %) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rice Straw | Rice Husk | Barley Straw | ||
| Carbohydrates | Glucan | 32.9 ± 0.5 | 35.6 ± 0.8 | 41.5 ± 0.8 |
| Xylan | 16.2 ± 0.3 | 13.6 ± 0.4 | 18.1 ± 0.5 | |
| Galactan | 1.5 ± 0.1 | - | 0.7 ± 0.1 | |
| Arabinan | 3.1 ± 0.1 | 1.7 ± 0.0 | 2.6 ± 0.1 | |
| Lignins | Acid insoluble lignin | 11.7 ± 0.0 | 22.7 ± 0.0 | 14.9 ± 0.2 |
| Acid soluble lignin | 0.9 ± 0.0 | 0.7 ± 0.2 | 3.7 ± 0.0 | |
| Extractives | Water | 10.9 ± 2.6 | 6.6 ± 0.1 | 11.6 ± 0.8 |
| Ethanol | 3.1 ± 0.3 | 1.2 ± 0.0 | 1.3 ± 0.1 | |
| Ash | 14.1 ± 0.0 | 15.7 ± 0.2 | 7.4 ± 0.1 | |
| Total | 94.4 | 97.8 | 101.8 | |
| Biomass | Reaction Conditions | Carbohydrate and Lignin Contents | S.R. 1 (wt%) | Fractionation Results | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temp. (°C) | Time (min) | Glucan (wt%) | XMG 2 (wt%) | Lignin (wt%) | Glucan Retention (%) | XMG 3 Dissolved (%) | Lignin Dissolved (%) | ||
| Rice Husk | Untreated | - | 35.6 | 13.6 | 22.7 | 100.0 | - | - | - |
| 170 | 30 | 54.0 | 4.6 | 12.3 | 60.7 | 92.3 | 79.7 | 67.0 | |
| 60 | 54.1 | 3.9 | 12.3 | 59.4 | 90.5 | 82.8 | 67.8 | ||
| 90 | 55.4 | 3.3 | 13.0 | 58.6 | 91.3 | 85.8 | 66.4 | ||
| 190 | 30 | 55.6 | 1.9 | 8.7 | 54.9 | 85.9 | 92.4 | 78.9 | |
| 60 | 55.5 | 1.3 | 8.3 | 52.5 | 82.0 | 95.1 | 80.8 | ||
| 90 | 54.1 | 0.7 | 8.2 | 48.5 | 73.8 | 97.4 | 82.4 | ||
| Rice Straw | Untreated | - | 32.9 | 16.2 | 11.7 | 100.0 | - | - | - |
| 170 | 30 | 39.2 | 18.3 | 14.3 | 81.7 | 97.5 | 7.8 | 0.3 | |
| 60 | 40.4 | 16.9 | 13.0 | 75.7 | 93.1 | 20.9 | 15.8 | ||
| 90 | 43.1 | 14.6 | 11.3 | 67.2 | 88.3 | 39.3 | 35.4 | ||
| 190 | 30 | 46.6 | 14.7 | 11.0 | 67.4 | 95.7 | 38.8 | 36.8 | |
| 60 | 49.2 | 12.3 | 9.8 | 61.6 | 92.3 | 53.1 | 48.7 | ||
| 90 | 51.8 | 10.2 | 9.0 | 57.7 | 90.8 | 63.5 | 55.9 | ||
| Barley Straw | Untreated | - | 41.5 | 18.1 | 14.9 | 100.0 | - | - | - |
| 170 | 30 | 51.9 | 18.4 | 16.2 | 75.6 | 94.5 | 23.1 | 17.6 | |
| 60 | 56.6 | 16.9 | 14.7 | 68.3 | 93.1 | 36.3 | 32.7 | ||
| 90 | 61.2 | 15.1 | 13.1 | 60.7 | 89.4 | 49.3 | 46.5 | ||
| 190 | 30 | 61.2 | 14.2 | 13.0 | 62.6 | 92.5 | 50.9 | 45.1 | |
| 60 | 66.0 | 11.8 | 11.9 | 56.4 | 89.7 | 63.2 | 55.0 | ||
| 90 | 70.2 | 9.4 | 10.4 | 51.5 | 87.2 | 73.2 | 63.9 | ||
| Biomass | Lignin Monomers | Molecular Weight | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aliphatic | H Unit 1 | G Unit 2 | S Unit 3 | Phenols | COOH | Mn | Mw | PDI 4 | |
| (mmol/g) | (mmol/g) | (mmol/g) | (mmol/g) | (mmol/g) | (mmol/g) | (g/mol) | (g/mol) | (-) | |
| Rice husk | 0.93 | 0.55 | 1.49 | 0.90 | 2.94 | 0.21 | 1453 | 1771 | 1.22 |
| Rice straw | 1.84 | 0.57 | 0.98 | 0.64 | 2.19 | 0.33 | 1523 | 1756 | 1.15 |
| Barley straw | 1.66 | 0.34 | 0.74 | 0.60 | 1.67 | 0.34 | 1703 | 2110 | 1.24 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, T.H.; Kwak, H.; Kim, T.H.; Oh, K.K. Extraction Behaviors of Lignin and Hemicellulose-Derived Sugars During Organosolv Fractionation of Agricultural Residues Using a Bench-Scale Ball Milling Reactor. Energies 2020, 13, 352. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13020352
Kim TH, Kwak H, Kim TH, Oh KK. Extraction Behaviors of Lignin and Hemicellulose-Derived Sugars During Organosolv Fractionation of Agricultural Residues Using a Bench-Scale Ball Milling Reactor. Energies. 2020; 13(2):352. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13020352
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Tae Hoon, Hyun Kwak, Tae Hyun Kim, and Kyeong Keun Oh. 2020. "Extraction Behaviors of Lignin and Hemicellulose-Derived Sugars During Organosolv Fractionation of Agricultural Residues Using a Bench-Scale Ball Milling Reactor" Energies 13, no. 2: 352. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13020352
APA StyleKim, T. H., Kwak, H., Kim, T. H., & Oh, K. K. (2020). Extraction Behaviors of Lignin and Hemicellulose-Derived Sugars During Organosolv Fractionation of Agricultural Residues Using a Bench-Scale Ball Milling Reactor. Energies, 13(2), 352. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13020352