Energy Disaggregation Using Two-Stage Fusion of Binary Device Detectors
Abstract
1. Introduction
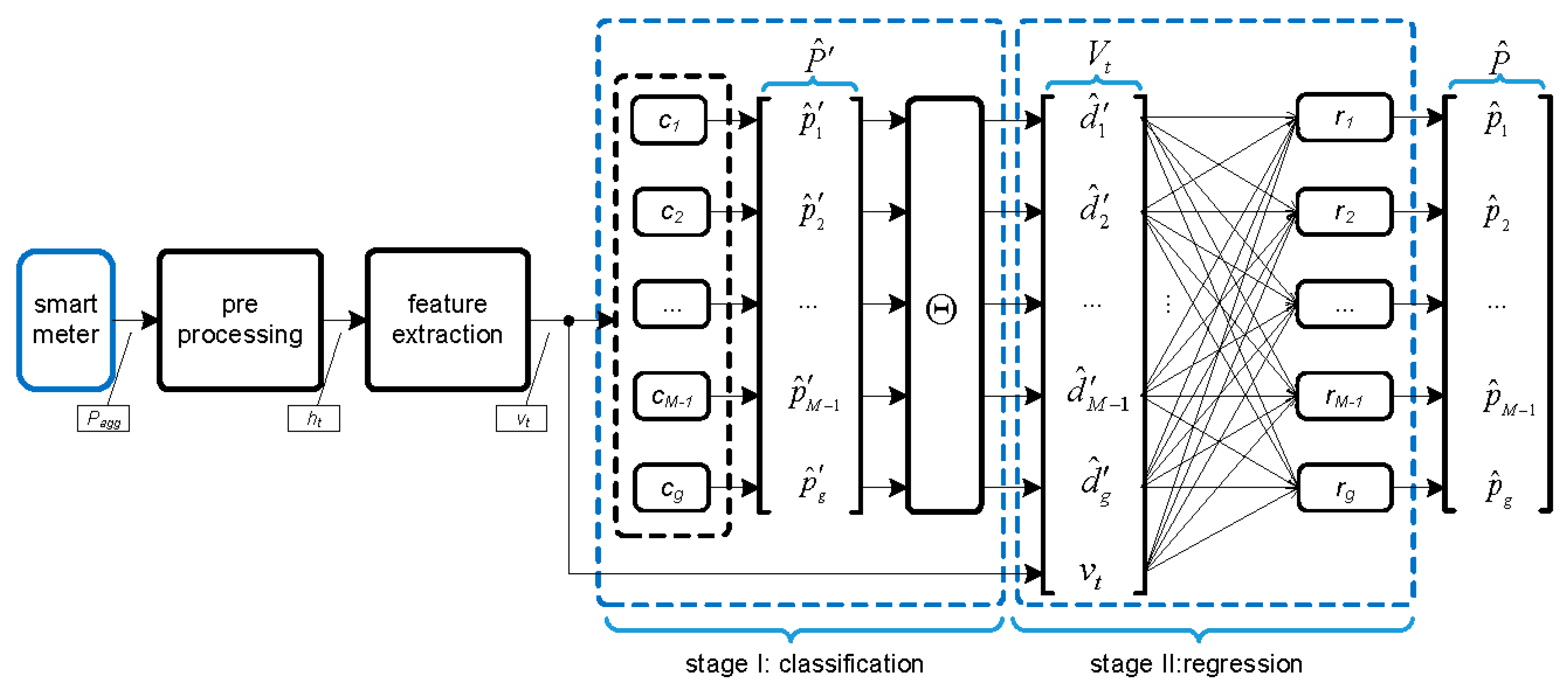
2. Two-Stage Fusion Methodology
3. Experimental Set-up
3.1. Evaluation Data
3.2. Prameterization and Feature Selection
4. Experimental Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eurostat. Energy Statistics—An Overview. 2018. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php?title=Energy_statistics_-_an_overview#Final_energy_consumption (accessed on 27 March 2018).
- Elma, O.; Selamogullar, U.S. A survey of a residential load profile for demand side management systems. In Proceedings of the 5th IEEE International Conference on Smart Energy Grid Engineering (SEGE), Oshawa, ON, Canada, 14–17 August 2017; pp. 85–89. [Google Scholar]
- Mostafavi, S.; Cox, R.W. An unsupervised approach in learning load patterns for non-intrusive load monitoring. In Proceedings of the IEEE 14th International Conference on Networking, Sensing and Control (ICNSC 2017), Calabria, Italy, 16–18 May 2017; pp. 631–636. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Lombard, L.; Ortiz, J.; Pout, C. A review on buildings energy consumption information. Energy Build. 2008, 40, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamouris, M.; Papanikolaou, N.; Livada, I.; Koronakis, I.; Georgakis, C.; Argiriou, A. On the impact of urban climate on the energy consumption of buildings. Sol. Energy 2001, 70, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Cheng, C.-C. Energy savings by energy management systems: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 56, 760–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katipamula, S.; Brambley, M. Review article: Methods for fault detection, diagnostics, and prognostics for building systems—A review, Part II. HVAC&R Res. 2005, 11, 169–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeifman, M.; Roth, K. Viterbi algorithm with sparse transitions (VAST) for nonintrusive load monitoring. In Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Computational Intelligence Applications in Smart Grid, Paris, France, 11–15 April 2011; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ogwumike, C.; Short, M.; Denai, M. Near-optimal scheduling of residential smart home appliances using heuristic approach. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT), Seville, Spain, 17–19 March 2015; pp. 3128–3133. [Google Scholar]
- Indragandhi, V.; Logesh, R.; Subramaniyaswamy, V.; Varadarajan, V.; Siarry, P.; Uden, L. Multi-objective optimization and energy management in renewable based AC/DC microgrid. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2018, 70, 179–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papagiannakopoulou, E.I.; Koukovini, M.N.; Lioudakis, G.V.; Garcia-Alfaro, J.; Kaklamani, D.I.; Venieris, I.S.; Cuppens, F.; Cuppens-Boulahia, N. A privacy-aware access control model for distributed network monitoring. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2013, 39, 2263–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, S.; McDaniel, P.; Aiello, W. Protecting consumer privacy from electric load monitoring. In Proceedings of the 18th ACM conference on Computer and Communications Security, Chicago, IL, USA, 17–21 October 2011; p. 87. [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan, K.; Banks, N.; Preston, I.; Russo, R. The British public’s perception of the UK smart metering initiative: Threats and opportunities. Energy Policy 2016, 91, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrablecová, P.; Bou Ezzeddine, A.; Rozinajová, V.; Šárik, S.; Sangaiah, A.K. Smart grid load forecasting using online support vector regression. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2018, 65, 102–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froehlich, J.; Larson, E.; Gupta, S.; Cohn, G.; Reynolds, M.; Patel, S. Disaggregated end-use energy sensing for the smart grid. IEEE Pervasive Comput. 2011, 10, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Kara, E.C.; Giri, S.; Berges, M. A feasibility study of automated plug-load identification from high-frequency measurements. In Proceedings of the IEEE Global Conference on Signal and Information Processing (GlobalSIP), Piscataway, NJ, USA, 14–16 December 2015; pp. 220–224. [Google Scholar]
- Koutitas, G.C.; Tassiulas, L. Low cost disaggregation of smart meter sensor data. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 1665–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arghandeh, R.; Zhou, Y. (Eds.) Big Data Application in Power Systems; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; ISBN 9780128119686. [Google Scholar]
- Egarter, D.; Bhuvana, V.P.; Elmenreich, W. PALDi: Online load disaggregation via particle filtering. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2015, 64, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, J.; Knottenbelt, W. Does disaggregated electricity feedback reduce domestic electricity consumption? A systematic review of the literature. In Proceedings of the 3rd International NILM Workshop, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 14–15 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.; Du, L.; Lu, B.; Harley, R.; Habetler, T. A review of identification and monitoring methods for electric loads in commercial and residential buildings. In Proceedings of the IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Expo, Atlanta, GA, USA, 12–16 September 2010; pp. 4527–4533. [Google Scholar]
- Hart, G.W. Nonintrusive appliance load monitoring. Proc. IEEE 1992, 80, 1870–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cominola, A.; Giuliani, M.; Piga, D.; Castelletti, A.; Rizzoli, A.E. A hybrid signature-based iterative disaggregation algorithm for non-intrusive load monitoring. Appl. Energy 2017, 185, 331–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirmer, P.A.; Mporas, I. Energy disaggregation using fractional calculus. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020; pp. 3257–3261. [Google Scholar]
- Gisler, C.; Ridi, A.; Zufferey, D.; Khaled, O.A.; Hennebert, J. Appliance consumption signature database and recognition test protocols. In Proceedings of the 8th International Workshop on Systems, Signal Processing and Their Applications (WoSSPA), Algiers, Algeria, 12–15 May 2013; pp. 336–341. [Google Scholar]
- Bouhouras, A.S.; Gkaidatzis, P.A.; Panagiotou, E.; Poulakis, N.; Christoforidis, G.C. A NILM algorithm with enhanced disaggregation scheme under harmonic current vectors. Energy Build. 2019, 183, 392–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meziane, M.N.; Abed-Meraim, K. Modeling and estimation of transient current signals. In Proceedings of the 23rd European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), Nice, France, 31 August–4 September 2015; pp. 1960–1964. [Google Scholar]
- Bilski, P.; Winiecki, W. The rule-based method for the non-intrusive electrical appliances identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE 8th International Conference on Intelligent Data Acquisition and Advanced Computing Systems: Technology and Applications (IDAACS), Warsaw, Poland, 24–26 September 2015; pp. 220–225. [Google Scholar]
- Sadeghianpourhamami, N.; Ruyssinck, J.; Deschrijver, D.; Dhaene, T.; Develder, C. Comprehensive feature selection for appliance classification in NILM. Energy Build. 2017, 151, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, T.; Javed, F.; Arshad, N. An empirical investigation of V-I trajectory based load signatures for non-intrusive load monitoring. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2014, 5, 870–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-H.; Tsai, M.-S. An advanced home energy management system facilitated by nonintrusive load monitoring with automated multiobjective power scheduling. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2015, 6, 1839–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilski, P.; Winiecki, W. Generalized algorithm for the non-intrusive identification of electrical appliances in the household. In Proceedings of the IEEE 9th International Conference on Intelligent Data Aquisition and Advanced Computing Systems: Technology and Applications (IDAACS), Bucharest, Romania, 21–23 September 2017; pp. 730–735. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.; Kong, S.; Ko, R.; Joo, S.-K. Electrical event identification technique for monitoring home appliance load using load signatures. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics (ICCE), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 10–13 January 2014; pp. 296–297. [Google Scholar]
- Matt Wytock, J.; Kolter, Z. Contextually supervised source separation with application to energy disaggregation. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Eighth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Québec City, QC, Canada, 27–31 July 2014; pp. 486–492. [Google Scholar]
- Pathak, N.; Roy, N.; Biswas, A. Iterative signal separation assisted energy disaggregation. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Green and Sustainable Computing Conference, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 14–16 December 2015; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Semwal, S.; Joshi, D.; Prasad, R.S.; Raveendhra, D. The practicability of ICA in home appliances load profile separation using current signature: A preliminary study. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Power, Energy and Control (ICPEC 2013), Dindigul, India, 6–8 February 2013; pp. 756–759. [Google Scholar]
- Figueiredo, M.; Ribeiro, B.; de Almeida, A. Electrical signal source separation via nonnegative tensor factorization using on site measurements in a smart home. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2014, 63, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piga, D.; Cominola, A.; Giuliani, M.; Castelletti, A.; Rizzoli, A.E. Sparse optimization for automated energy end use disaggregation. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2016, 24, 1044–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makonin, S.; Popowich, F.; Bartram, L.; Gill, B.; Bajic, I.V. AMPds: A public dataset for load disaggregation and eco-feedback research. In Proceedings of the IEEE Electrical Power & Energy Conference, Halifax, NS, Canada, 21–23 August 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, D.; Stankovic, L.; Stankovic, V.; Lulic, S.; Sladojevic, S. Transferability of neural network approaches for low-rate energy disaggregation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Hove, UK, 12–17 May 2019; pp. 8330–8334. [Google Scholar]
- Barsim, K.S.; Yang, B. On the Feasibility of Generic Deep Disaggregation for Single-Load Extraction. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.02139 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Han, X.; Liang, K.X. Event-based non-intrusive load identification algorithm for residential loads combined with underdetermined decomposition and characteristic filtering. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2019, 13, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çavdar, İ.; Faryad, V. New design of a supervised energy disaggregation model based on the deep neural network for a smart grid. Energies 2019, 12, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Chai, Y. An empirical study on energy disaggregation via deep learning. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Industrial Engineering (AIIE 2016), Beijing, China, 19 September–20 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Mauch, L.; Yang, B. A new approach for supervised power disaggregation by using a deep recurrent LSTM network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Global Conference on Signal and Information Processing (GlobalSIP), Orlando, FL, USA, 14–16 December 2015; pp. 63–67. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, F.C.C.; Creayla, C.M.C.; Macabebe, E.Q.B. Development of an intelligent system for smart home energy disaggregation using stacked denoising autoencoders. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2017, 105, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Oechtering, T.J.; Skoglund, M. Privacy-preserving energy flow control in smart grids. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Shanghai, China, 20–25 March 2016; pp. 2194–2198. [Google Scholar]
- Chin, J.-X.; De Rubira, T.; Hug, G. Privacy-protecting energy management unit through model-distribution predictive control. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2017, 8, 3084–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirmer, P.A.; Mporas, I. Energy disaggregation from low sampling frequency measurements using multi-layer zero crossing rate. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020; pp. 3777–3781. [Google Scholar]
- Ridi, A.; Gisler, C.; Hennebert, J. A survey on intrusive load monitoring for appliance recognition. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Stockholm, Sweden, 24–28 August 2014; pp. 3702–3707. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, H.-H.; Lian, K.-L.; Su, Y.-C.; Lee, W.-J. Power-spectrum-based wavelet transform for nonintrusive demand monitoring and load identification. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2014, 50, 2081–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Lu, S. Load profile disaggregation by Blind source separation: A wavelets-assisted independent component analysis approach. In Proceedings of the IEEE PES General Meeting: Conference & Exposition, National Harbor, MD, USA, 27–31 July 2014; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Schirmer, P.A.; Mporas, I. Integration of temporal contextual information for robust energy disaggregation. In Proceedings of the IEEE 38th International Performance Computing and Communications Conference (IPCCC), London, UK, 29–31 October 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Harell, A.; Makonin, S.; Bajić, I.V. Wavenilm: A Causal Neural Network for Power Disaggregation from the Complex Power Signal. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Brighton, UK, 12–17 May 2019; pp. 8335–8339. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, M.J.; Willsky, A.S. Bayesian nonparametric hidden semi-Markov models. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2013, 14, 673–701. [Google Scholar]
- Makonin, S. Investigating the switch continuity principle assumed in Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring (NILM). In Proceedings of the IEEE Canadian Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering (CCECE), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 14–18 May 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Yang, W. An iterative load disaggregation approach based on appliance consumption pattern. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabaei, S.M.; Dick, S.; Xu, W. Toward non-intrusive load monitoring via multi-label classification. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2017, 8, 26–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckel, C.; Kleiminger, W.; Cicchetti, R.; Staake, T.; Santini, S. The ECO data set and the performance of non-intrusive load monitoring algorithms. In Proceedings of the 1st ACM Conference on Embedded Systems for Energy-Efficient Buildings, Memphis, TN, USA, 4–6 November 2014; pp. 80–89. [Google Scholar]
- Kolter, J.Z.; Johnson, M.J. REDD: A Public Data Set for Energy Disaggregation Research; Massachusetts Institute of Technology: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Batra, N.; Gulati, M.; Singh, A.; Srivastava, M.B. It’s different. In Proceedings of the 5th ACM Workshop on Embedded Systems for Energy-Efficient Buildings, Rome, Italy, 14–15 November 2013; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Andrean, V.; Zhao, X.-H.; Teshome, D.F.; Huang, T.-D.; Lian, K.-L. A hybrid method of cascade-filtering and committee decision mechanism for non-intrusive load monitoring. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 41212–41223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, J.; Batra, N.; Parson, O.; Dutta, H.; Knottenbelt, W.; Rogers, A.; Singh, A.; Srivastava, M. NILMTK v0.2: A non-intrusive load monitoring toolkit for large scale data sets. In Proceedings of the 1st ACM Conference on Embedded Systems for Energy-Efficient Buildings, Memphis, TN, USA, 4–6 November 2014; pp. 182–183. [Google Scholar]
- van Cutsem, O.; Lilis, G.; Kayal, M. Automatic multi-state load profile identification with application to energy disaggregation. In Proceedings of the 22nd IEEE International Conference on Emerging Technologies and Factory Automation, Limassol, Cyprus, 12–15 September 2017; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Zoha, A.; Gluhak, A.; Imran, M.A.; Rajasegarar, S. Non-intrusive load monitoring approaches for disaggregated energy sensing: A survey. Sensors (Basel) 2012, 12, 16838–16866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, S.R.; Leeb, S.B.; Norford, L.K.; Cox, R.W. Nonintrusive load monitoring and diagnostics in power systems. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2008, 57, 1445–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirmer, P.A.; Mporas, I.; Paraskevas, M. Energy disaggregation using elastic matching algorithms. Entropy 2020, 22, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirmer, P.A.; Mporas, I. Improving energy disaggregation performance using appliance-driven sampling rates. In Proceedings of the 27th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), La Coruña, Spain, 2–6 September 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, L.; Nunes, N. Performance evaluation in non-intrusive load monitoring: Datasets, metrics, and tools—A review. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2018, 8, e1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kononenko, I.; Robnik-Sikonja, M.; Robnik, M.; Pompe, U. ReliefF for Estimation and Discretization of Attributes in Classification, Regression, and ILP Problems; Artificial Intelligence: Methodology, Systems, Applications; 1996; pp. 31–40. Available online: http://lkm.fri.uni-lj.si/rmarko/papers/kononenko96-aimsa.pdf (accessed on 22 April 2020).
- Schirmer, P.A.; Mporas, I. Statistical and electrical features evaluation for electrical appliances energy disaggregation. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirmer, P.A.; Mporas, I.; Paraskevas, M. Evaluation of regression algorithms and features on the energy disaggregation task. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Information, Intelligence, Systems and Applications (IISA), Patras, Greece, 15–17 July 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Basu, K.; Debusschere, V.; Bacha, S.; Maulik, U.; Bondyopadhyay, S. Nonintrusive load monitoring: A temporal multilabel classification approach. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2015, 11, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Lin, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, P.; Zhou, Y.; Liang, X. Towards energy-awareness smart building: Discover the fingerprint of your electrical appliances. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2017, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makonin, S.; Popowich, F.; Bajic, I.V.; Gill, B.; Bartram, L. Exploiting HMM sparsity to perform online real-time nonintrusive load monitoring. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2016, 7, 2575–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welikala, S.; Dinesh, C.; Ekanayake, M.P.B.; Godaliyadda, R.I.; Ekanayake, J. Incorporating appliance usage patterns for non-intrusive load monitoring and load forecasting. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2019, 10, 448–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, J.; Knottenbelt, W. The UK-DALE dataset, domestic appliance-level electricity demand and whole-house demand from five UK homes. Sci. Data 2015, 2, 150007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaselimi, M.; Doulamis, N.; Doulamis, A.; Voulodimos, A.; Protopapadakis, E. Bayesian-optimized bidirectional LSTM regression model for non-intrusive load monitoring. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Hove, UK, 12–17 May 2019; pp. 2747–2751. [Google Scholar]
- Elhamifar, E.; Sastry, S. Energy disaggregation via learning ‘powerlets’ and sparse coding. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Ninth AAAI Conference on Artificial, Austin, TX, USA, 25–30 January 2015; pp. 629–635. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.; Majumdar, A. Deep sparse coding for non-intrusive load monitoring. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2017, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolter, J.Z.; Batra, S.; Ng, A.Y. Energy disaggregation via discriminative sparse coding. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Kyoto, Japan, 16–21 October 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Stankovic, V.; Liao, J.; Stankovic, L. A graph-based signal processing approach for low-rate energy disaggregation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Computational Intelligence for Engineering Solutions (CIES), Orlando, FL, USA, 9–12 December 2014; pp. 81–87. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, W.; Dong, Z.Y.; Ma, J.; Hill, D.J.; Zhao, J.; Luo, F. An extensible approach for non-intrusive load disaggregation with smart meter data. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2018, 9, 3362–3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Dataset | #App | Ts | T | App. Type | Appliances |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ECO-1 | 7(6) | 1s | 7d | One/Multi-State | (1) fridge, (2) dryer, (3) coffee machine, (4) kettle, (5) washing machine, (6) PC, (7) freezer |
| ECO-2 | 12(9) | 1s | 7d | One/Multi-State | (1) tablet, (2) dishwasher, (3) air exhaust, (4) fridge, (5) entertainment, (6) freezer, (7) kettle, (8) lamp, (9) laptop, (10) Stove, (11) TV, (12) Stereo |
| ECO-4 | 8(8) | 1s | 7d | One/Multi-State/Nonlinear | (1) fridge, (2) kitchen appliances, (3) lamp, (4) stereo/laptop, (5) freezer, (6) tablet, (7) entertainment, (8) microwave |
| ECO-5 | 8(6) | 1s | 7d | One/Multi-State/Nonlinear | (1) tablet, (2) coffee machine, (3) kettle, (4) microwave, (5) fridge, (6) entertainment, (7) PC, router/printer, (8) fountain |
| ECO-6 | 7(6) | 1s | 7d | One/Multi-State/Nonlinear | (1) lamp, (2) laptop/printer, (3) routers, (4) coffee machine, (5) entertainment, (6) fridge, (7) kettle |
| REDD-1 | 18(17) | 3s | All | One/Multi-State/Continuous | (1) oven, (2) oven, (3) refrigerator, (4) dishwasher, (5) kitchen-outlets, (6) kitchen-outlets, (7) lighting, (8) washer-dryer, (9) microwave, (10) bathroom, (11) electric- heat, (12) stove, (13) kitchen-outlets, (14) kitchen-outlets, (15) lighting, (16) lighting, (17) Washer-dryer, (18) Washer-dryer |
| REDD-2 | 9(10) | 3s | All | One/Multi-State | (1) kitchen-outlets, (2) lighting, (3) stove, (4) microwave, (5) washer-dryer, (6) kitchen-outlets, (7) refrigerator, (8) dishwasher, (9) disposal |
| REDD-3 | 20(18) | 3s | All | One/Multi-State/Nonlinear | (1) outlets-unknown, (2) outlets-unknown, (3) lighting, (4) electronics, (5) refrigerator, (6) disposal, (7) dishwasher, (8) furnace, (9) lighting, (10) outlets-unknown, (11) washer-dryer, (12) washer-dryer, (13) lighting, (14) microwave, (15) lighting, (16) smoke-alarms, (17) lighting, (18) bathroom, (19) kitchen-outlets, (20) kitchen-outlets |
| REDD-4 | 18(16) | 3s | All | One/Multi-State/Nonlinear | (1) lighting, (2) furnace, (3) kitchen-outlets, (4) outlets-unknown, (5) washer-dryer, (6) stove, (7) air-conditioning, (8) air-conditioning, (9) miscellaneous, (10) smoke-alarms, (11) lighting, (12) kitchen-outlets, (13) dishwasher, (14) bathroom, (15) bathroom, (16) lighting, (17) lighting, (18) air-conditioning |
| REDD-6 | 15(14) | 3s | All | One/Multi-State/Nonlinear | (1) kitchen-outlets, (2) washer-dryer, (3) stove, (4) electronics, (5) bathroom, (6) refrigerator, (7) dishwasher, (8) outlets-unknown, (9) outlets-unknown, (10) electric- heat, (11) kitchen-outlets, (12) lighting, (13) air-conditioning, (14) air-conditioning, (15) air-conditioning |
| iAWE | 10(9) | 1s | 7d | One/Multi-State/Nonlinear/Continuous | (1) fridge, (2) air-condition, (3) air-conditioning, (4) washing machine, (5) laptop, (6) iron, (7) kitchen, (8) TV, (9) waterfilter, (10) watermotor |
| Deep Neural Network (DNN) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nodes/Layers | 4 | 8 | 16 | 32 | 64 | 128 |
| 1 | 80.4 | 87.5 | 87.9 | 83.7 | 86.4 | 81.7 |
| 2 | 70.1 | 86.4 | 86.9 | 87.5 | 82.7 | 83.6 |
| 3 | 80.4 | 86.7 | 87.9 | 88.7 | 88.4 | 84.2 |
| 4 | 75.4 | 87.9 | 87 | 87.2 | 85.3 | 83.7 |
| Random Forest (RF) | ||||||
| Trees | 8 | 16 | 32 | 64 | 128 | 256 |
| 85.5 | 85.3 | 85.5 | 85.4 | 85.4 | 85.4 | |
| K-Nearest-Neighbours (KNN) | ||||||
| K | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| 82.2 | 82.7 | 82.7 | 83.1 | 83.3 | 82.4 | |
| Support Vector Machine (SVM) | ||||||
| Kernel | Linear | Gaussian | Rbf | Pol-2 | Pol-3 | Pol-4 |
| 55.0 | 72.3 | 76.3 | 59.2 | 63.6 | 67.8 | |
| Dataset | DNN | RF | KNN | SVM | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | II | I | II | I | II | I | II | |
| ECO-1 | 74.5 | 76.2 | 78.4 | 79.4 | 76.0 | 77.7 | 67.0 | 67.0 |
| ECO-2 | 85.5 | 87.5 | 86.3 | 89.3 | 85.4 | 86.4 | 78.5 | 80.5 |
| ECO-4 | 83.8 | 84.6 | 83.8 | 86.9 | 82.1 | 82.2 | 81.5 | 81.5 |
| ECO-5 | 88.3 | 90.3 | 89.2 | 90.2 | 88.1 | 89.1 | 88.4 | 89.4 |
| ECO-6 | 78.4 | 80.1 | 84.6 | 86.1 | 83.7 | 84.2 | 71.9 | 74.6 |
| REDD-1 | 71.3 | 73.1 | 78.0 | 79.0 | 74.9 | 75.3 | 66.3 | 66.3 |
| REDD-2 | 74.9 | 79.0 | 85.3 | 87.3 | 84.4 | 84.4 | 81.1 | 81.1 |
| REDD-3 | 67.6 | 69.6 | 70.6 | 71.7 | 69.2 | 69.9 | 66.3 | 66.3 |
| REDD-4 | 73.9 | 75.3 | 74.5 | 75.1 | 72.6 | 73.5 | 72.5 | 73.3 |
| REDD-6 | 79.9 | 81.3 | 81.6 | 82.7 | 79.3 | 79.5 | 70.8 | 70.8 |
| iAWE | 64.7 | 66.0 | 67.2 | 69.2 | 66.9 | 67.9 | 77.4 | 80.8 |
| Device | Category | ECO-2 | REDD-2 | iAWE | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | II | I | II | I | II | ||
| Air exhaust | one-state | 98.4 | 98.4 | - | - | - | - |
| Fridge | one-state (PS) | 74.7 | 79.2 | 86.1 | 92.3 | 48.3 | 55.6 |
| Entertainment | nonlinear | 83.9 | 91.6 | - | - | - | - |
| Freezer | one-state (PS) | 83.6 | 87.5 | - | - | - | - |
| Lamp/Light | one-state/nonlinear | 55.6 | 55.6 | 71.8 | 78.8 | - | - |
| Laptop | nonlinear | 59.9 | 65.6 | - | 73.7 | 54.3 | 59.0 |
| Stove | multi-state | - | - | 73.5 | - | - | - |
| TV | nonlinear | 84.6 | 94.7 | - | - | 59.0 | 65.5 |
| Stereo | nonlinear | 84.5 | 85.5 | - | 68.1 | - | - |
| Kitchen | - | - | - | 67.8 | 74.1 | - | - |
| Microwave | one-state | - | - | 75.8 | 89.7 | - | - |
| WM | multi-state | - | - | 89.6 | 79.5 | 78.8 | 78.7 |
| DW | multi-state | - | - | 79.1 | 97.5 | - | - |
| Disposal | one-state | - | - | 97.5 | - | - | - |
| Iron | one-state | - | - | - | - | 91.2 | 91.2 |
| Air Condition | continuous (PS) | - | - | - | - | 45.4 | 50.3 |
| Watermotor | continuous | - | - | - | 87.8 | 57.4 | 62.3 |
| Ghost | - | 80.5 | 87.0 | 84.4 | 80.1 | 87.6 | |
| Device | Category | REDD-2 (noisy) | REDD-2 (noiseless) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | II | I | II | ||
| Fridge | one-state | 80.2 | 93.2 | 87.5 | 94.2 |
| Light | nonlinear | 78.7 | 81.5 | 77.9 | 81.6 |
| Dishwasher | multi-state | 87.0 | 88.7 | 93.8 | 94.2 |
| Microwave | one-state | 93.1 | 93.7 | 95.6 | 95.8 |
| Furnace | multi-state | 82.4 | 83.9 | 87.2 | 87.8 |
| Average | - | 90.7 | 93.4 | 93.2 | 95.7 |
| NILM Method | Publication | Year | Dataset | EACC | Fusion (EACC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Powerlets-PED | [79] | 2015 | REDD-1/2/3/4/6 | 72.0 | 79.3 |
| Exact Deep SC | [80] | 2017 | REDD-1/2/3/4/6 | 66.1 | |
| Greedy Deep SC | [80] | 2017 | REDD-1/2/3/4/6 | 62.6 | |
| Discriminate SC | [81] | 2010 | REDD-1/2/3/4/6 | 59.3 | |
| General SC | [81] | 2010 | REDD-1/2/3/4/6 | 56.4 | |
| Temporal ML | [82] | 2011 | REDD-1/2/3/4/6 | 53.3 | |
| Sparse HMM | [75] | 2015 | REDD-2 (5 App.) | 94.8 | 93.4 |
| SIQCP | [83] | 2018 | REDD-2 (5 App.) | 86.4 | |
| F-HDP-HSMM | [55] | 2013 | REDD-2 (5 App.) | 84.8 | |
| F-HDP-HMM | [55] | 2013 | REDD-2 (5 App.) | 70.7 | |
| EM-FHMM | [55] | 2013 | REDD-2 (5 App.) | 50.8 | |
| CNN-RNN | [43] | 2019 | REDD-2 (Fridge) | 87.9 | 92.3 (0.24) |
| CNN* | [40] | 2019 | REDD-2 (Fridge) | 83.5 | |
| LSTM* | [45] | 2015 | REDD-2 (Fridge) | 0.35 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schirmer, P.A.; Mporas, I.; Sheikh-Akbari, A. Energy Disaggregation Using Two-Stage Fusion of Binary Device Detectors. Energies 2020, 13, 2148. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13092148
Schirmer PA, Mporas I, Sheikh-Akbari A. Energy Disaggregation Using Two-Stage Fusion of Binary Device Detectors. Energies. 2020; 13(9):2148. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13092148
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchirmer, Pascal A., Iosif Mporas, and Akbar Sheikh-Akbari. 2020. "Energy Disaggregation Using Two-Stage Fusion of Binary Device Detectors" Energies 13, no. 9: 2148. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13092148
APA StyleSchirmer, P. A., Mporas, I., & Sheikh-Akbari, A. (2020). Energy Disaggregation Using Two-Stage Fusion of Binary Device Detectors. Energies, 13(9), 2148. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13092148






