Voltage-Gain Design and Efficiency Optimization of Series/Series-Parallel Inductive Power Transfer System Considering Misalignment Issue
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Design of Variable Voltage-Gains
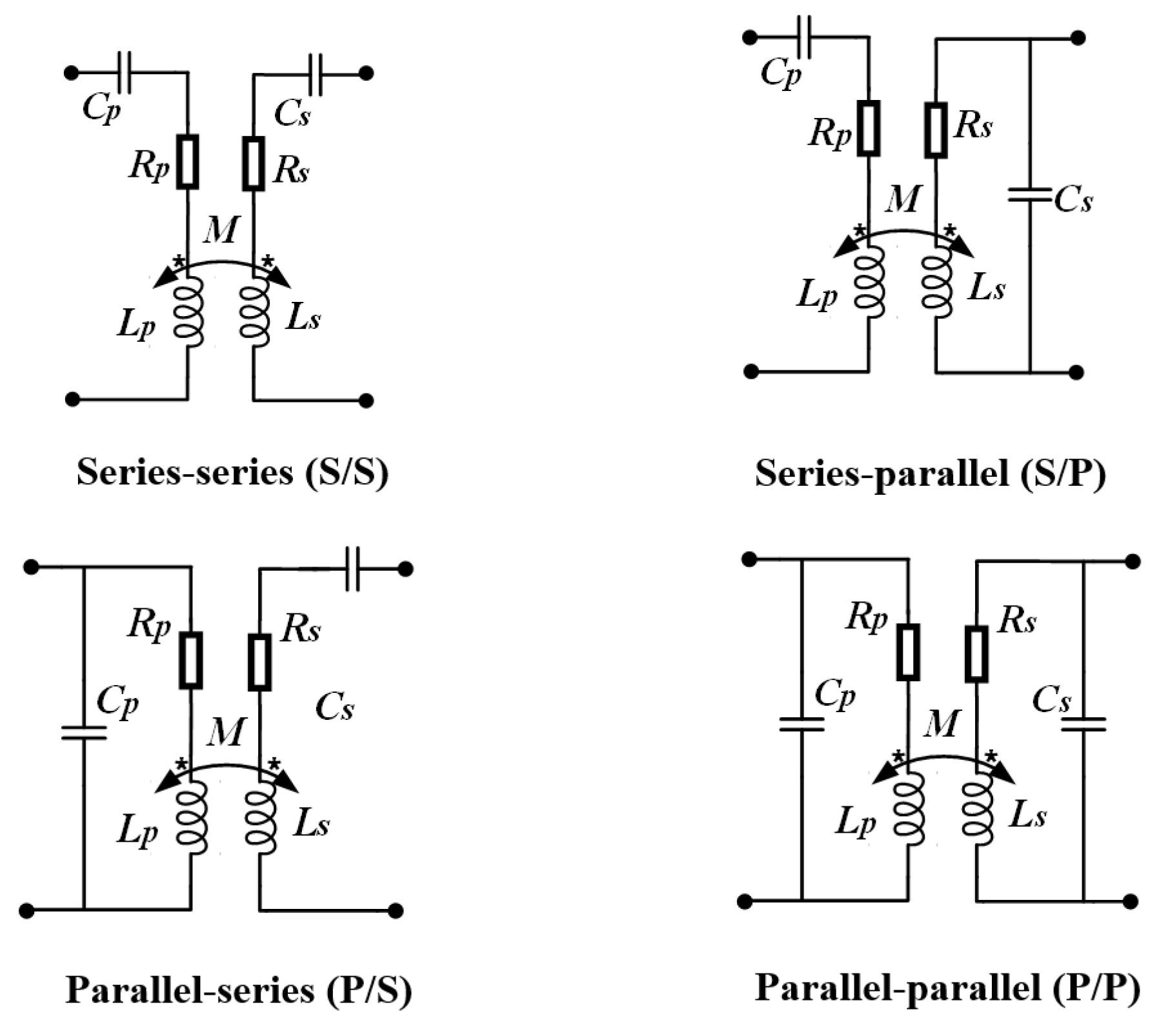
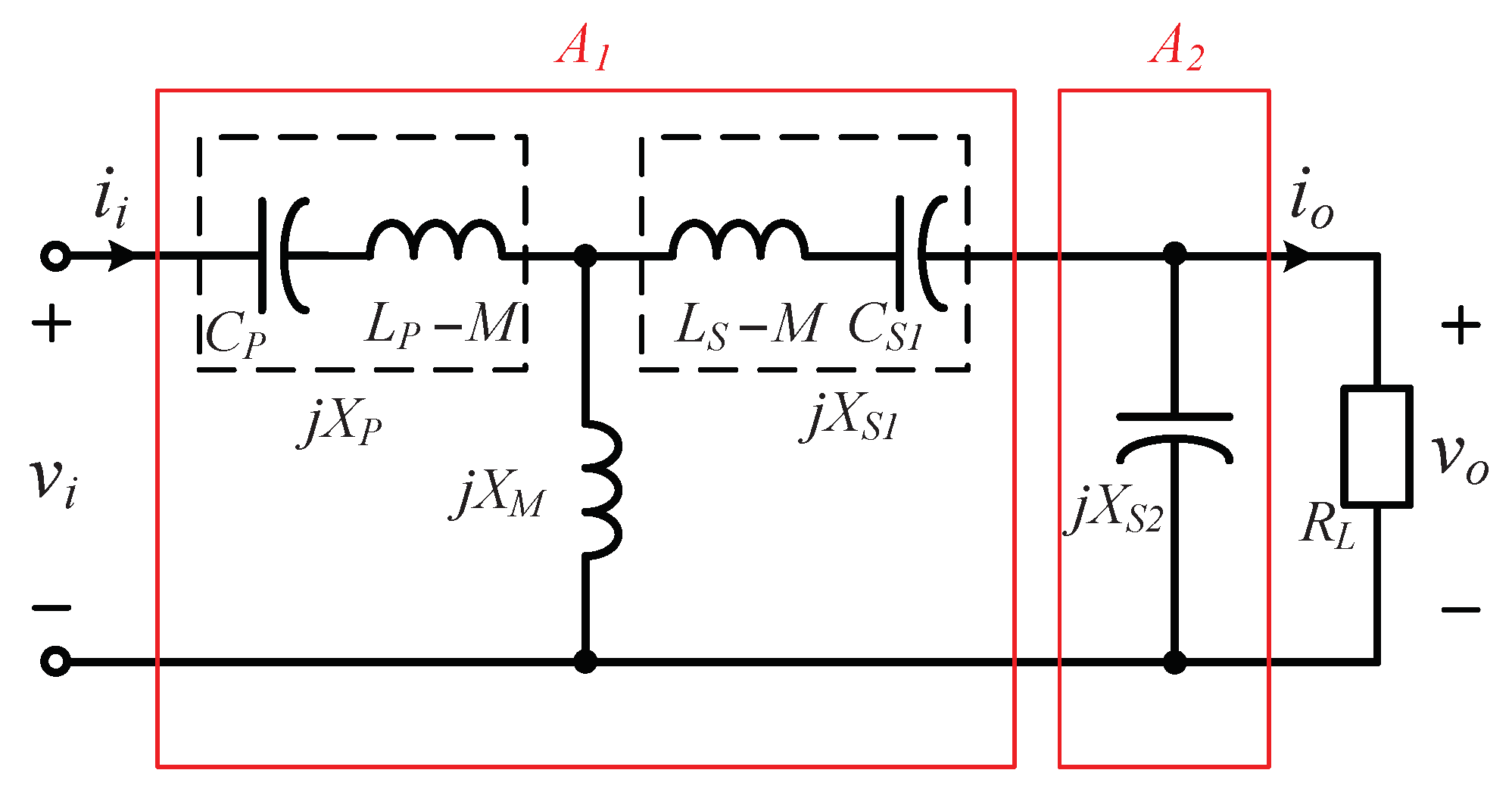
2.1. Fundamental Circuit and Two-Port Network Analysis
2.2. Load-Independent Voltage-Gain with Zero Phase Angle
3. Design Considerations
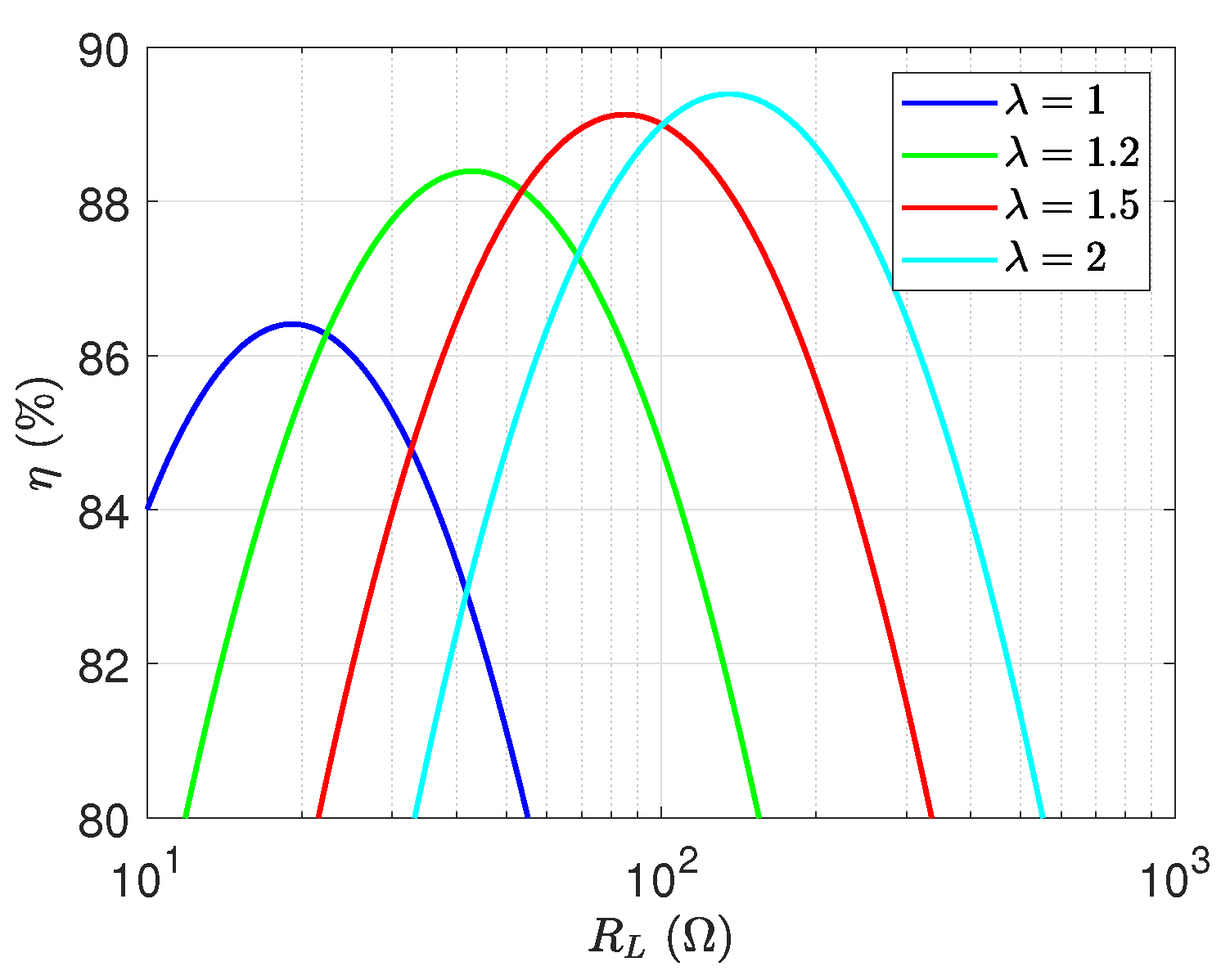
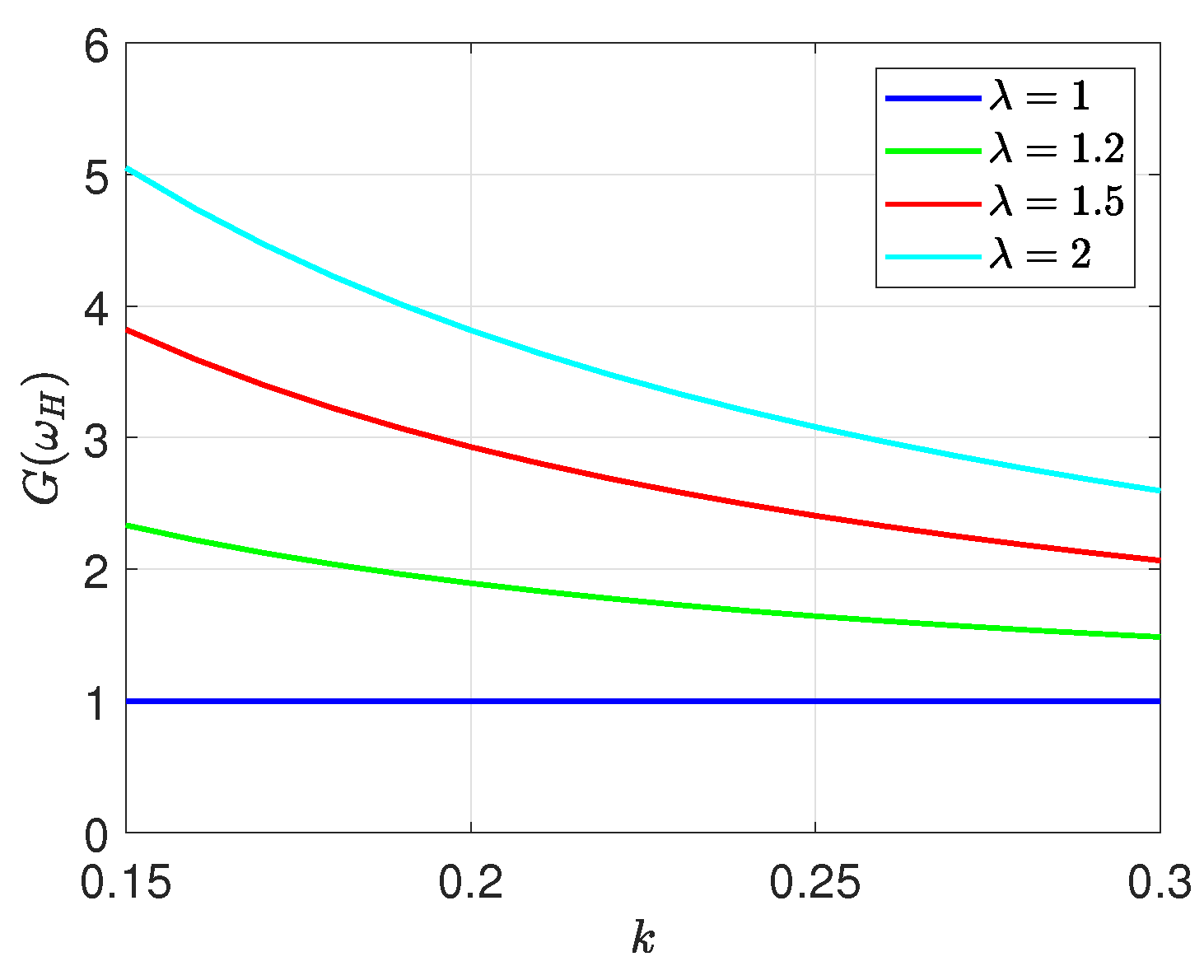
3.1. Efficiency Optimization
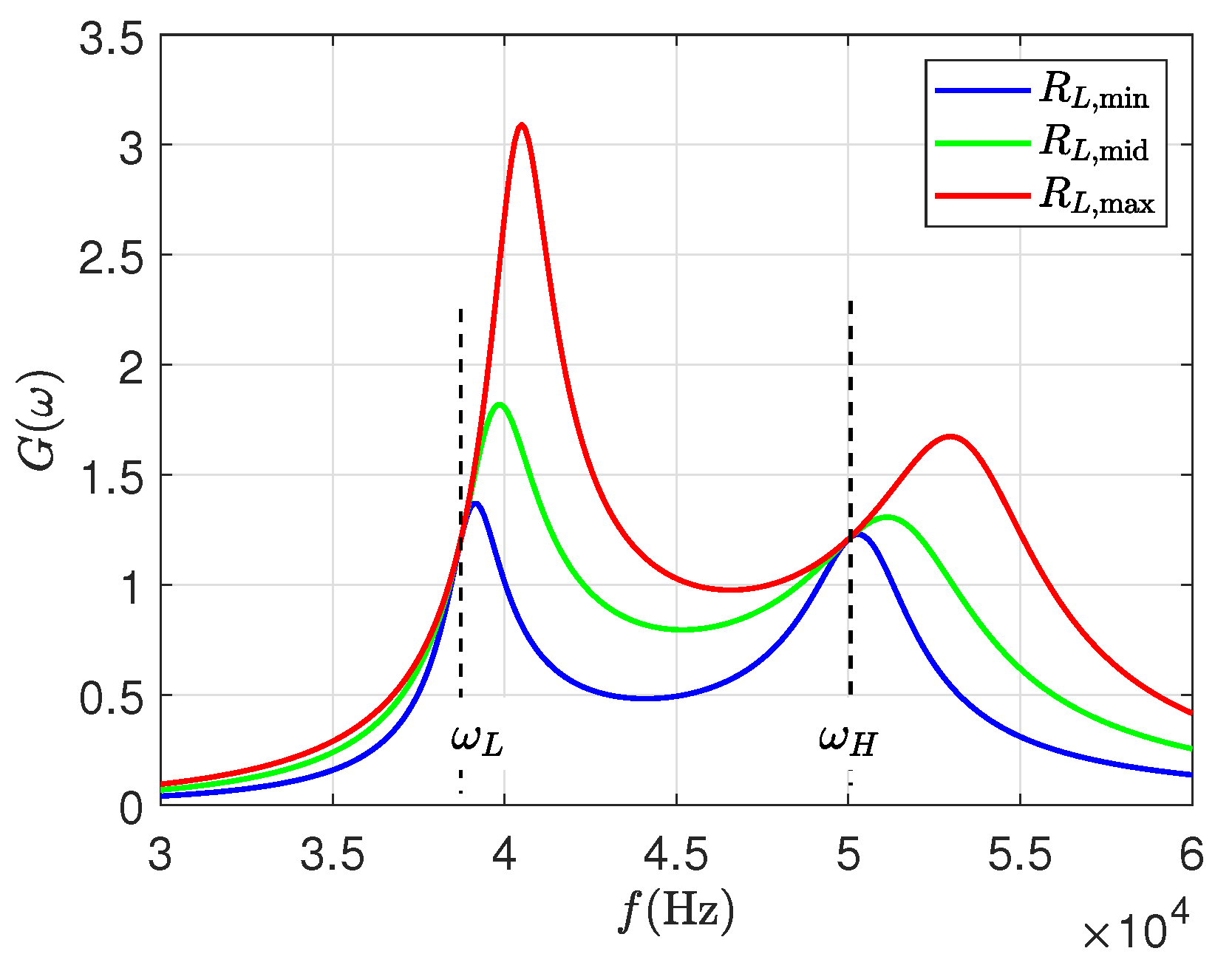
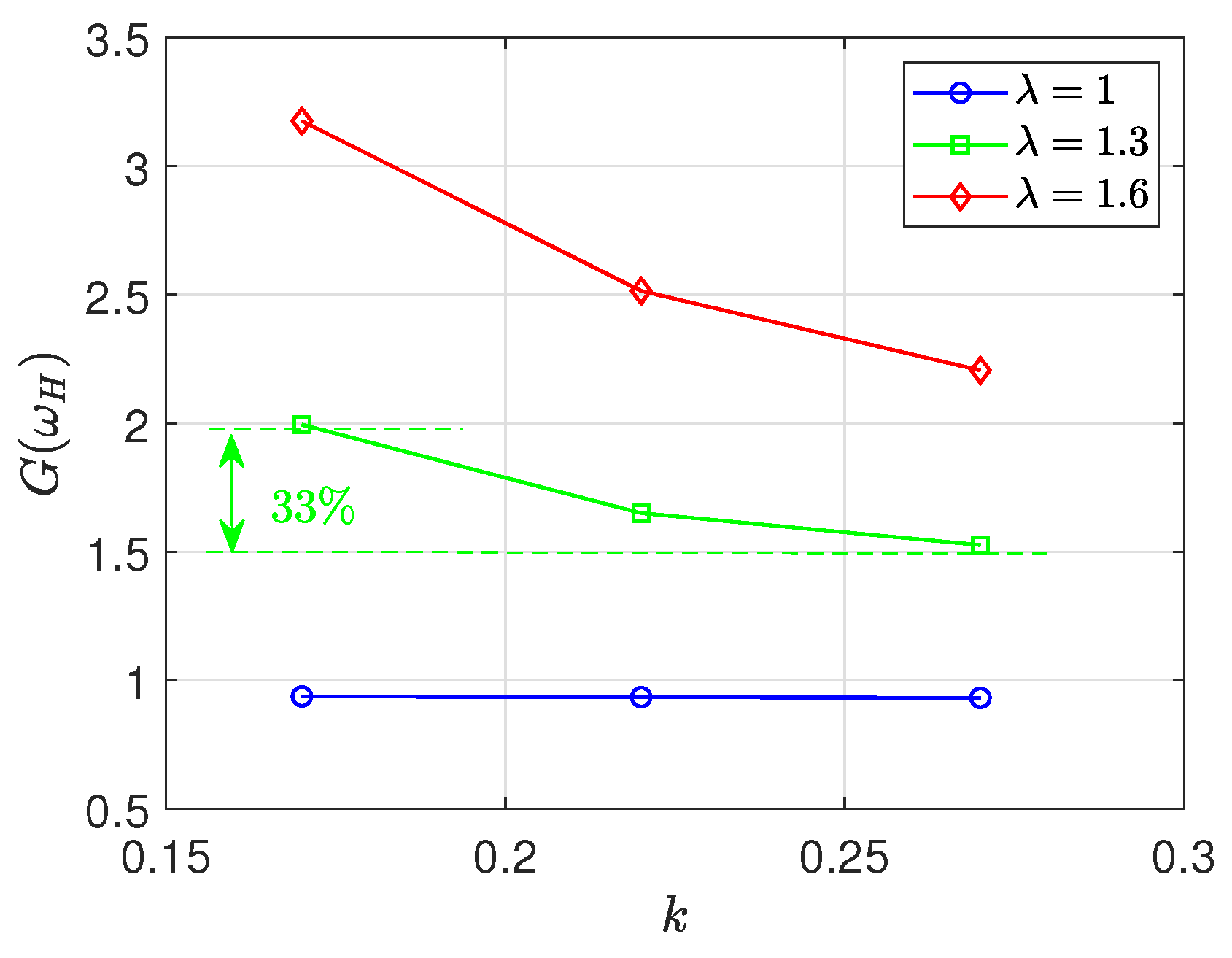
3.2. Constraints Due to Misalignment Issues
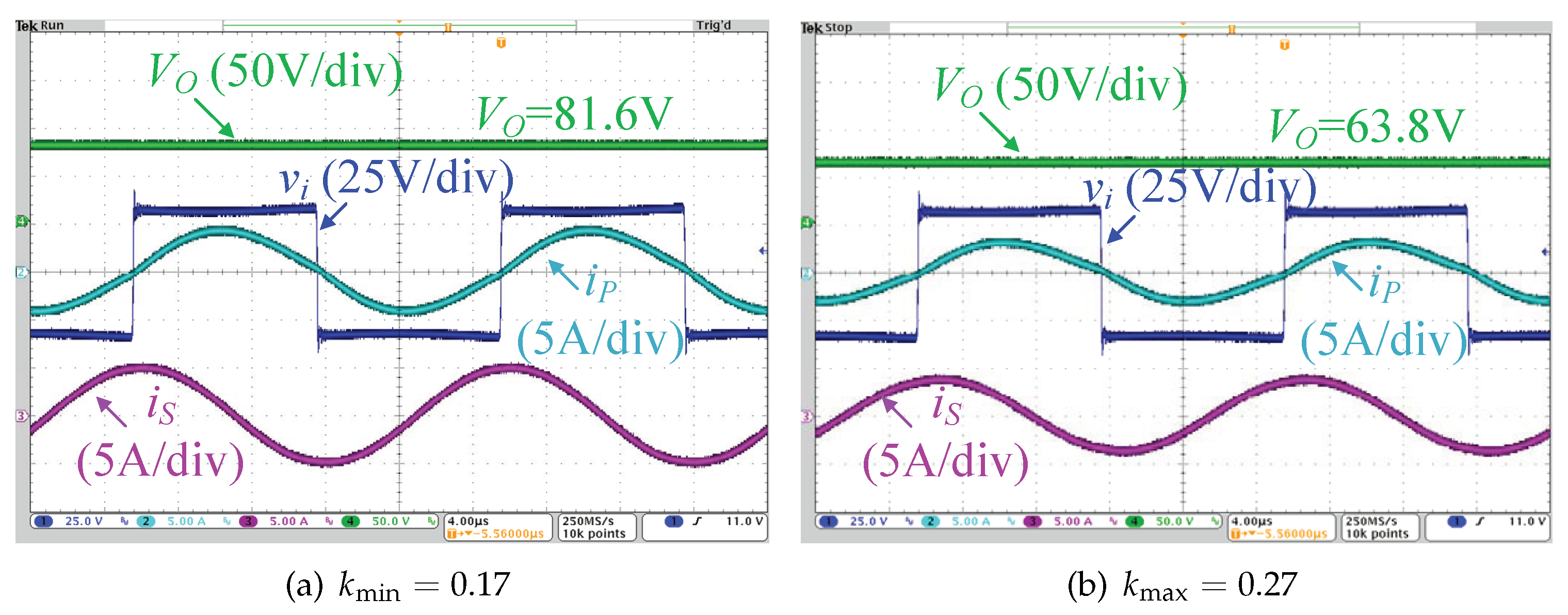
4. Experimental Verification
4.1. Experimental Setup
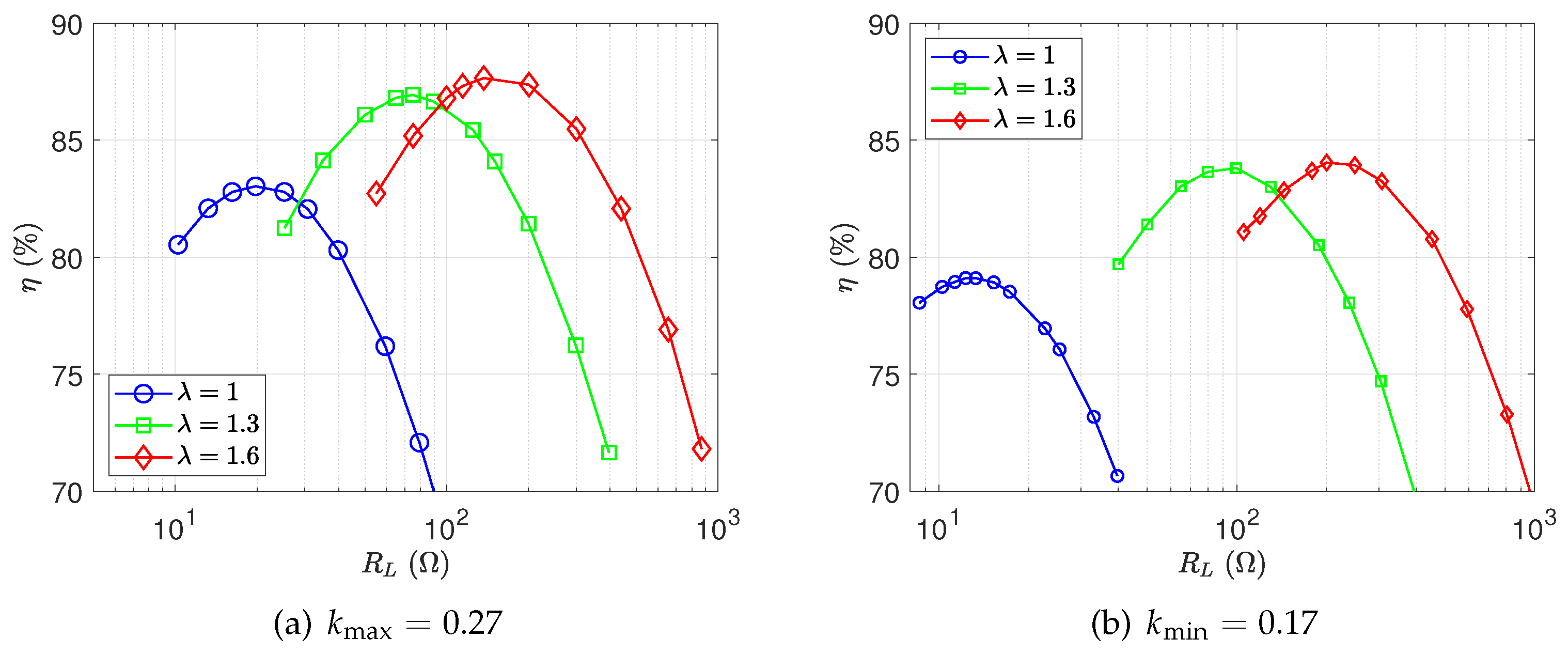
4.2. Experimental Results Analysis
5. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, M.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, X. An Overview of Regulation Topologies in Resonant Wireless Power Transfer Systems for Consumer Electronics or Bio-Implants. Energies 2018, 11, 1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haerinia, M.; Shadid, R. Wireless Power Transfer Approaches for Medical Implants: A Review. Signals 2020, 1, 209–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Yuan, F.; Yang, G.; Song, K. Coil Positioning for Wireless Power Transfer System of Automatic Guided Vehicle Based on Magnetic Sensing. Sensors 2020, 20, 5304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Yao, P.; Guo, K.; Cao, P.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, H. A Heterogeneous Inductive Power Transfer System for Electric Vehicles with Spontaneous Constant Current and Constant Voltage Output Features. Electronics 2020, 9, 1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; El Baghdadi, M.; Lan, Y.; Benomar, Y.; Van Mierlo, J.; Hegazy, O. Design Methodology, Modeling, and Comparative Study of Wireless Power Transfer Systems for Electric Vehicles. Energies 2018, 11, 1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Wang, Z.; Dai, H. A Critical Review of Wireless Power Transfer via Strongly Coupled Magnetic Resonances. Energies 2014, 7, 4316–4341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wang, C.; Xia, D.; Liu, Y. Design of Magnetic Coupler for Wireless Power Transfer. Energies 2019, 12, 3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Chau, K.T.; Liu, C.; Lee, C.H.T. An Overview of Resonant Circuits for Wireless Power Transfer. Energies 2017, 10, 894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Jing, Y.; Han, H.; Wong, S.C.; Tse, C.K. Higher Order Compensation for Inductive-Power-Transfer Converters with Constant-Voltage or Constant-Current Output Combating Transformer Parameter Constraints. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 394–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, C.-T.; Choi, S.-J. Investigation of Scale Conversion for Inductive Power Transfer in Series-Series Configuration. Electronics 2020, 9, 1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.; Chung, E.; Ha, J.-I. Cost-Effective High-Performance Digital Control Method in Series-Series Compensated Wireless Power Transfer System. Electronics 2020, 9, 1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.S.; Covic, G.A.; Stielau, O.H. Power Transfer Capability and Bifurcation Phenomena of Loosely Coupled Inductive Power Transfer Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2004, 51, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wong, S.C.; Tse, C.K.; Chen, Q. Analysis and Comparison of Secondary Series- and Parallel-Compensated Inductive Power Transfer Systems Operating for Optimal Efficiency and Load-Independent Voltage-Transfer Ratio. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 2979–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wong, S.C.; Tse, C.K.; Chen, Q. Load-Independent Duality of Current and Voltage Outputs of a Series- or Parallel-Compensated Inductive Power Transfer Converter with Optimized Efficiency. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2015, 3, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hu, J.; Li, X.; Chen, F.; Xu, Q.; Mai, R.; He, Z. Analysis, Design, and Experimental Verification of a Mixed High-Order Compensations-Based WPT System with Constant Current Outputs for Driving Multistring LEDs. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Chu, H.; Huang, Z.; Wong, S.C.; Tse, C.K.; Mi, C.C.; Chen, X. Wide Design Range of Constant Output Current Using Double-Sided LC Compensation Circuits for Inductive-Power-Transfer Applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 2364–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, V.; Tran, D.; Choi, W. Implementation of the Constant Current and Constant Voltage Charge of Inductive Power Transfer Systems with the Double-Sided LCC Compensation Topology for Electric Vehicle Battery Charge Applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 7398–7410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.M.; Mekhilef, S.; Bassi, H.; Rawa, M.J.H. Analysis of LC-LC2 Compensated Inductive Power Transfer for High Efficiency and Load Independent Voltage Gain. Energies 2018, 11, 2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hu, J.; Li, X.; Cheng, K.E. A Flexible Load-Independent Multi-Output Wireless Power Transfer System Based on Cascaded Double T-Resonant Circuits: Analysis, Design and Experimental Verification. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2019, 66, 2803–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Chen, Q.; Wong, S.C.; Tse, C.K.; Ruan, X. Analysis and Control of Series/Series-Parallel Compensated Resonant Converter for Contactless Power Transfer. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2015, 3, 124–136. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, J.; Chen, Q.; Ren, X.; Ruan, X.; Wong, S.C.; Tse, C.K. Precise Characteristics Analysis of Series/Series-Parallel Compensated Contactless Resonant Converterr. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2015, 3, 101–110. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Lu, K.; Xu, D. Analysis and Design of an S/SP Compensated IPT System to Minimize Output Voltage Fluctuation Versus Coupling Coefficient and Load Variation. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2018, 67, 9262–9272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameters | Symbols | Values |
|---|---|---|
| Input voltage | 35 V | |
| Switching frequency | f | 50 kHz |
| MOSFETs | IPP65R045 | |
| Diode | MBR20200 | |
| Dead Time | 200 ns | |
| Self inductance | , | 117 H, 174 H |
| Coupling coefficient | k | 0.17, 0.22, 0.27 |
| Coil resistances | , | 0.4 , 0.6 |
| Unit (nf) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 110 | 74 | 270 | |
| 98 | 95 | 150 | |
| 94 | 142 | 99 |
| Parameters | Symbols | Values |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | Litz Wire | AWG38 |
| Turns | 30, 46 | |
| Outer Diameter | , | 300 mm, 500 mm |
| Inner Diameter | , | 35 mm, 35 mm |
| Radius | , | 0.5 mm, 0.75 mm |
| Unit (V) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 32.81 | 69.825 | 111.16 | |
| 32.7 | 57.75 | 88.03 | |
| 33.62 | 53.41 | 77.21 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, L.; Zong, M.; Li, C. Voltage-Gain Design and Efficiency Optimization of Series/Series-Parallel Inductive Power Transfer System Considering Misalignment Issue. Energies 2021, 14, 2999. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14112999
Yang L, Zong M, Li C. Voltage-Gain Design and Efficiency Optimization of Series/Series-Parallel Inductive Power Transfer System Considering Misalignment Issue. Energies. 2021; 14(11):2999. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14112999
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Libin, Ming Zong, and Chunlai Li. 2021. "Voltage-Gain Design and Efficiency Optimization of Series/Series-Parallel Inductive Power Transfer System Considering Misalignment Issue" Energies 14, no. 11: 2999. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14112999
APA StyleYang, L., Zong, M., & Li, C. (2021). Voltage-Gain Design and Efficiency Optimization of Series/Series-Parallel Inductive Power Transfer System Considering Misalignment Issue. Energies, 14(11), 2999. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14112999





