Effect of Biodiesel Blends on the Transient Performance of Compression Ignition Engines
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. CI Engine and Test Bed Facilities
2.1. Details of Biodiesel and Petro Diesel Fuels Used in the Investigation
2.2. Calibration of Instruments
3. Results and Discussion
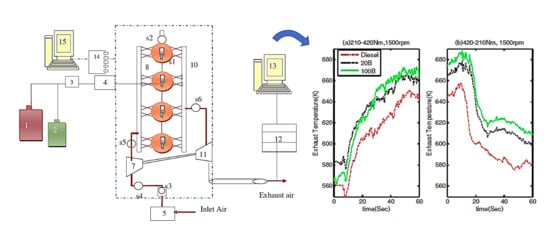
3.1. Performance Characteristics during Transient Operation
3.1.1. Fuel Consumption Rate
3.1.2. Exhaust Gas Temperature
3.1.3. In-Cylinder Pressure
3.2. Emission Characteristics of CI Engine during Transient Operation
3.2.1. Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Emission
3.2.2. NOx Emission
3.2.3. Carbon Monoxide (CO) Emission
3.2.4. Total Hydrocarbon (THC) Emissions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Patel, A.; Arora, N.; Sartaj, K.; Pruthi, V.; Pruthi, P.A. Sustainable biodiesel production from oleaginous yeasts utilizing hydrolysates of various non-edible lignocellulosic biomasses. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 62, 836–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Khoa, N.; Tuan, L. The Correlation of Biodiesel Blends with the Common Rail Diesel Engine’s Performance and Emission Characteristics. Energies 2021, 14, 2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alptekin, E.; Canakci, M. Determination of the density and the viscosities of biodiesel–diesel fuel blends. Renew. Energy 2008, 33, 2623–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tate, R.; Watts, K.; Allen, C.; Wilkie, K. The viscosities of three biodiesel fuels at temperatures up to 300 °C. Fuel 2006, 85, 1010–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tate, R.; Watts, K.; Allen, C.; Wilkie, K. The densities of three biodiesel fuels at temperatures up to 300 °C. Fuel 2006, 85, 1004–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, B.; Bagby, M.O. Heats of combustion of fatty esters and triglycerides. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1989, 66, 1601–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamane, K.; Ueta, A.; Shimamaoto, Y. Influence of physical and chemical properties of biodiesel fuels on injection, combustion and exhaust emission characteristics in a direct injection compression ignition engine. Int. Res. J. 2001, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumus, M. A comprehensive experimental investigation of combustion and heat release characteristics of a biodiesel (hazelnut kernel oil methyl ester) fueled direct injection compression ignition engine. Fuel 2010, 89, 2802–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjumea, P.; Agudelo, J.; Agudelo, A. Effect of altitude and palm oil biodiesel fuelling on the performance and combustion characteristics of a HSDI diesel engine. Fuel 2009, 88, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Deng, J.; Li, C.; Dang, F.; Liao, Z.; Wu, Z.; Li, L. Experimental study of the spray characteristics of biodiesel based on inedible oil. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 616–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kegl, B.; Hribernik, A. Experimental Analysis of Injection Characteristics Using Biodiesel Fuel. Energy Fuels 2006, 20, 2239–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannikov, M.G.; Tyrlovoy, S.I.; Vasilev, I.P.; Chattha, J.A. Investigation of the Characteristics of the Fuel Injection Pump of a Diesel Engine Fuelled with Viscous Vegetable Oil-Diesel Oil Blends. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng. 2006, 220, 787–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soudagar, M.E.M.; Mujtaba, M.; RezaSafaeibcd, M.; Afzale, A.; V, D.R.; Ahmeda, W.; Banapurmath, N.; Hossainh, N.; Bashiri, S.; AnjumBadruddinjk, I.; et al. Effect of Sr@ZnO nanoparticles and Ricinus communis biodiesel-diesel fuel blends on modified CRDI diesel engine characteristics. Energy 2021, 215, 119094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.; Soudagar, M.E.M.; Kumar, R.H.; Safaei, M.R.; Farooq, M.; Khidmatgar, A.; Banapurmath, N.R.; Farade, R.A.; Abbas, M.M.; Afzal, A.; et al. Effect of Nano-Graphene Oxide and n-Butanol Fuel Additives Blended with Diesel—Nigella sativa Biodiesel Fuel Emulsion on Diesel Engine Characteristics. Symmetry 2020, 12, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szybist, J.; Song, J.; Alam, M.; Boehman, A.L. Biodiesel combustion, emissions and emission control. Fuel Process. Technol. 2007, 88, 679–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, A.; Hanna, M.A. In-Cylinder Pressure Characteristics of a D.I. Heavy Duty Diesel Engine on Biodiesel Fuel. SAE 1997, 971683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monyem, A.; Van Gerpen, J.H. The effect of biodiesel oxidation on engine performance and emissions. Biomass-Bioenergy 2001, 20, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martyr, A.J.; Plint, M.A. Engine Testing: Theory and Practice, 3rd ed.; A Butterworth-Heinemann Title: Oxford, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Abu-Qudais, M. Exhaust gas temperature for knock detection and control in spark ignition engine. Energy Convers. Manag. 1996, 37, 1383–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morey, F.; Seers, P. Comparison of cycle-by-cycle variation of measured exhaust-gas temperature and in-cylinder pressure measurements. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2010, 30, 487–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hountalas, D.T.; Mavropoulos, G.; Zannis, T.C.; Mamalis, S.D. Use of Water Emulsion and Intake Water Injection as NOx Reduction Techniques for Heavy Duty Diesel Engines. In SAE Technical Paper Series; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Shemmeri, T.; Oberweis, S. Correlation of the NOx emission and exhaust gas temperature for biodiesel. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2011, 31, 1682–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Zaid, M. Performance of single cylinder, direct injection Diesel engine using water fuel emulsions. Energy Convers. Manag. 2004, 45, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-Y.; Lin, H.-A. Diesel engine performance and emission characteristics of biodiesel produced by the peroxidation process. Fuel 2006, 85, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-Y.; Wang, K.-H. Diesel engine performance and emission characteristics using three-phase emulsions as fuel. Fuel 2004, 83, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadhas, A.; Muraleedharan, C.; Jayaraj, S. Performance and emission evaluation of a diesel engine fueled with methyl esters of rubber seed oil. Renew. Energy 2005, 30, 1789–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carraretto, C.; Macor, A.; Mirandola, A.; Stoppato, A.; Tonon, S. Biodiesel as alternative fuel: Experimental analysis and energetic evaluations. Energy 2004, 29, 2195–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raheman, H.; Phadatare, A. Diesel engine emissions and performance from blends of karanja methyl ester and diesel. Biomass-Bioenergy 2004, 27, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Chen, G.; Wang, Y. Biodiesel production from waste cooking oil via alkali catalyst and its engine test. Fuel Process. Technol. 2008, 89, 851–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labeckas, G.; Slavinskas, S. The effect of rapeseed oil methyl ester on direct injection Diesel engine performance and exhaust emissions. Energy Convers. Manag. 2006, 47, 1954–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, D.; Geng, L.; Chen, H.; Bian, Y.; Liu, J.; Ren, X. Combustion and performance evaluation of a diesel engine fueled with biodiesel produced from soybean crude oil. Renew. Energy 2009, 34, 2706–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapuerta, M.; Armas, O.; Fernández, J.R. Effect of biodiesel fuels on diesel engine emissions. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2008, 34, 198–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesfa, B.; Mishra, R.; Gu, F.; Powles, N. Prediction models for density and viscosity of biodiesel and their effects on fuel supply system in CI engines. Renew. Energy 2010, 35, 2752–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tesfa, B.; Mishra, R.; Gu, F.; Ball, A. Water injection effects on the performance and emission characteristics of a CI engine operating with biodiesel. Renew. Energy 2012, 37, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tesfa, C.B.; Mishra, R.; Zhang, C.; Gu, F.; Ball, A.D. Commbustion and performance characteristics of CI (compression ignition) engine running with biodiesel. Energy 2013, 51, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tesfa, B.; Gu, F.; Mishra, R.; Ball, A. LHV predication models and LHV effect on the performance of CI engine running with biodiesel blends. Energy Convers. Manag. 2013, 71, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






















| Engine Type | Turbo Charged Diesel Engine |
|---|---|
| Number of cylinders | 4 |
| Bore | 103 mm |
| Stroke | 132 mm |
| Diameter of inlet valve | 36.5 mm |
| Diameter of exhaust valve | 33.2 mm |
| Compression ratio | 18.3 |
| Number of valves | 16 |
| Method of injection | Direct injection |
| Engine displacement | 4.399 litre |
| Cooling system | Water |
| Recommended speed | 850 rpm |
| Max power | 74.2 kW@ 2200 rpm |
| Emission Type | Analyser Type | Measuring Range | Uncertainty |
|---|---|---|---|
| CO | non-dispersive infrared (NDIR) | 0–2000 ppm | ±2% |
| CO2 | non-dispersive infrared (NDIR) | 0–100% | ±2% |
| NOx | heated chemiluminescent detector (HCLD) | 0–5000 ppm | ±2% |
| THC | heated flame ionisation detector (HFID) | 0–100 ppm | ±1% |
| O2 | paramagnetic detector | 0–25% | ±1% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tesfa, B.C.; Mishra, R.; Aliyu, A.M. Effect of Biodiesel Blends on the Transient Performance of Compression Ignition Engines. Energies 2021, 14, 5416. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14175416
Tesfa BC, Mishra R, Aliyu AM. Effect of Biodiesel Blends on the Transient Performance of Compression Ignition Engines. Energies. 2021; 14(17):5416. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14175416
Chicago/Turabian StyleTesfa, Belachew Cekene, Rakesh Mishra, and Aliyu M. Aliyu. 2021. "Effect of Biodiesel Blends on the Transient Performance of Compression Ignition Engines" Energies 14, no. 17: 5416. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14175416
APA StyleTesfa, B. C., Mishra, R., & Aliyu, A. M. (2021). Effect of Biodiesel Blends on the Transient Performance of Compression Ignition Engines. Energies, 14(17), 5416. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14175416