Min-Max Regret-Based Approach for Sizing and Placement of DGs in Distribution System under a 24 h Load Horizon
Abstract
:1. Introduction
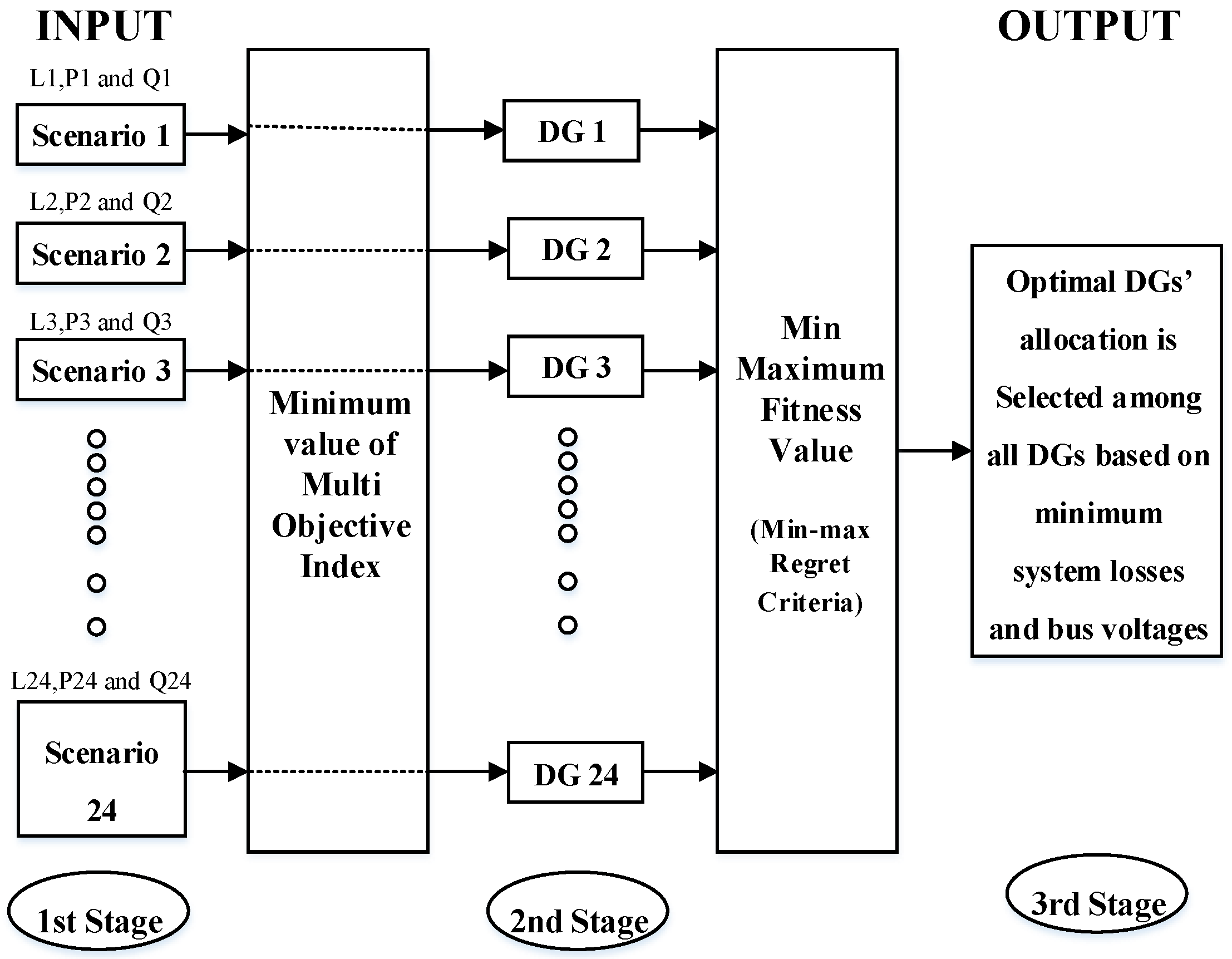
- The min-max regret criteria are analyzed and implemented for calculating the single robust optimal allocation of DGs among all optimal DG allocations of 24 scenarios. However, this technique is used for the first time in these types of problems.
- The problem is formulated in scenarios such as each scenario representing a particular hour’s load and generation.
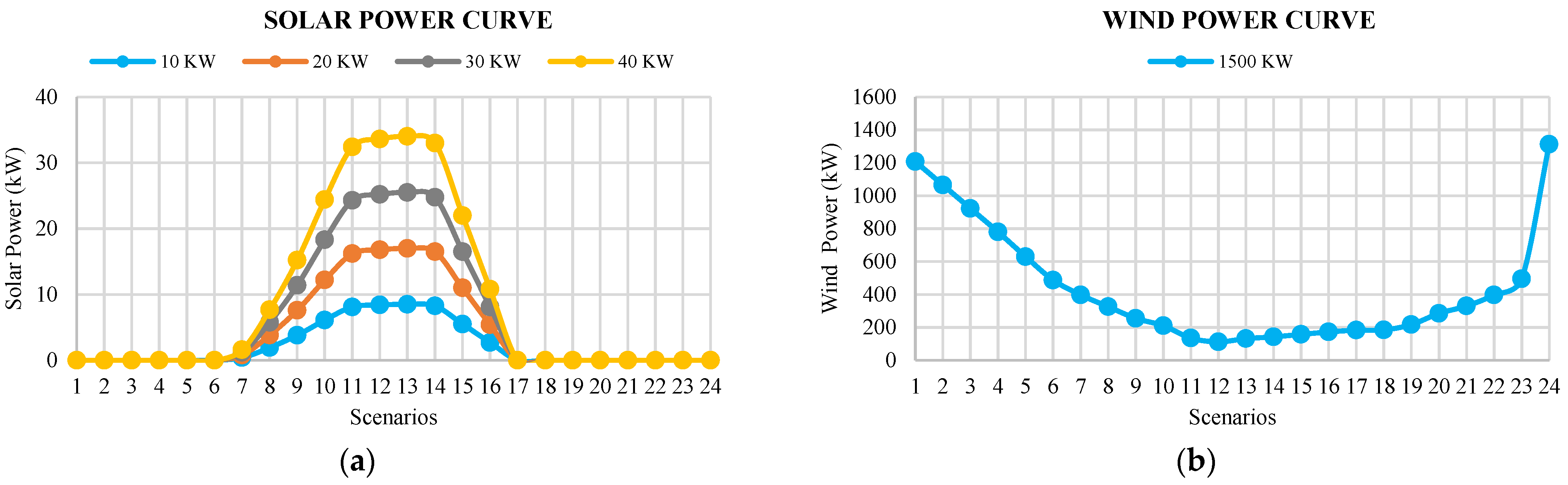
- The methodology is implemented under the 24 h load horizon and renewable generation pattern of wind and solar DGs.
- The battle royale optimization (BRO) algorithm is considered for the first time for DG placement in the current study, to the best of the author’s knowledge, and its optimization performance is also investigated.
- The optimal allocation of DGs is obtained for each particular scenario at minimized MO.
- Active power losses, reactive power losses, and bus voltage profiles are analyzed and discussed for each specific scenario.
- Energy losses of the whole day are calculated and discussed.
- The results are compared with the APSO and GA algorithm at an individual as well as combined objective value.
2. Problem Formulation
2.1. Load Flow Analysis
2.2. Objective Function
2.2.1. Multi Objective Index
Active Power Loss Index
Reactive Power Loss Index
Voltage Deviation Index
2.2.2. Constrains
Limitations of DGs Capacity
Power Balance
3. Optimization Algorithms
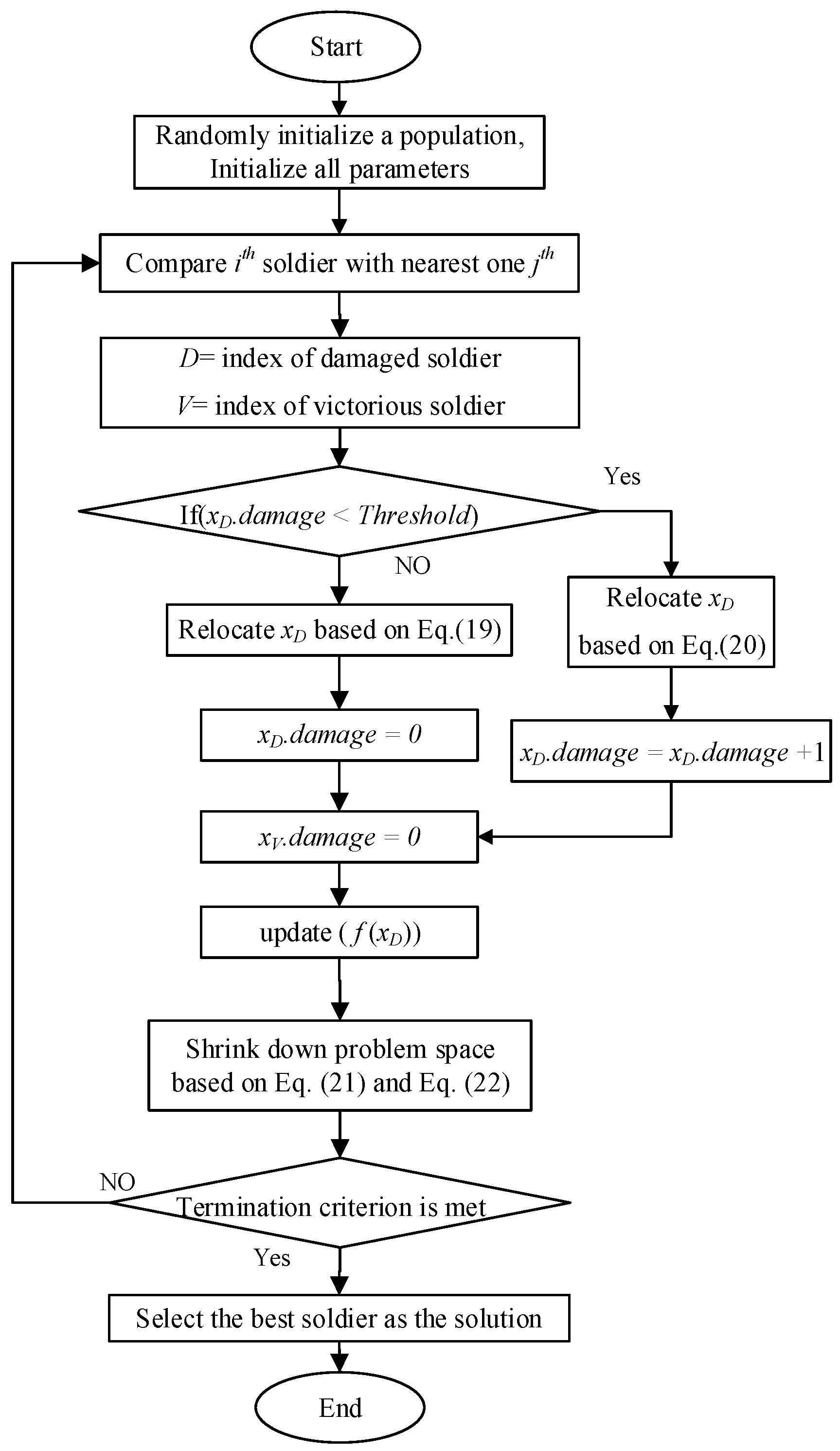
3.1. Battle Royale Optimization Algorithm
- The population of soldiers is replaced with DGs’ locations and sizes.
- The threshold selected in the current paper is 3, and a specific value is used to avoid premature convergence and to attain improved results [29].
- The upper and lower bounds are replaced with the upper and lower limits of DGs’ location and size.
3.2. Accelerated Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm
3.3. Genetic Algorithm
4. Mathematical Modeling of Optimization Problem
4.1. Min-Max Regret Criteria
Handling DG Allocation through Min-Max Regret Criteria
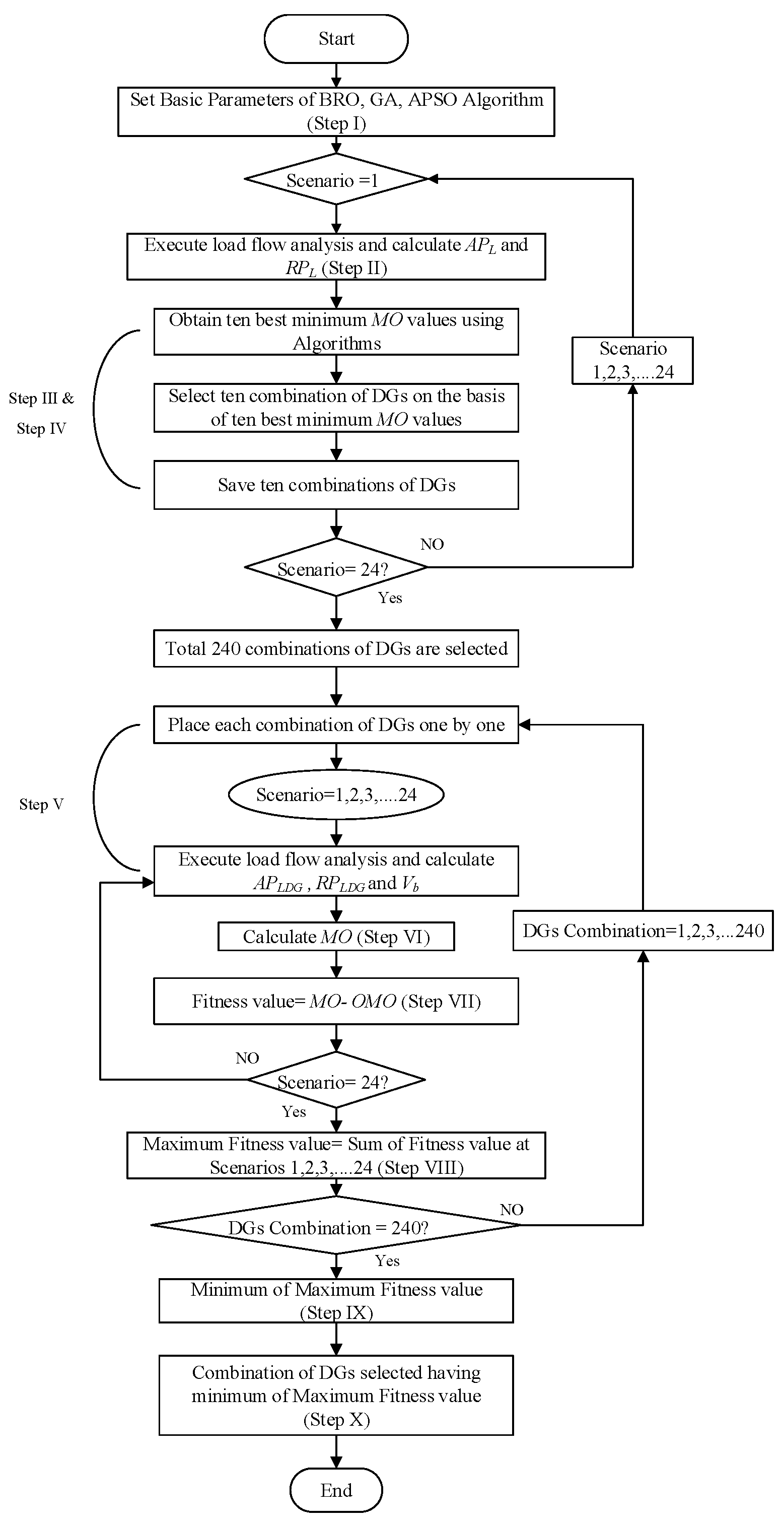
4.2. Modeling of the Optimization Problem
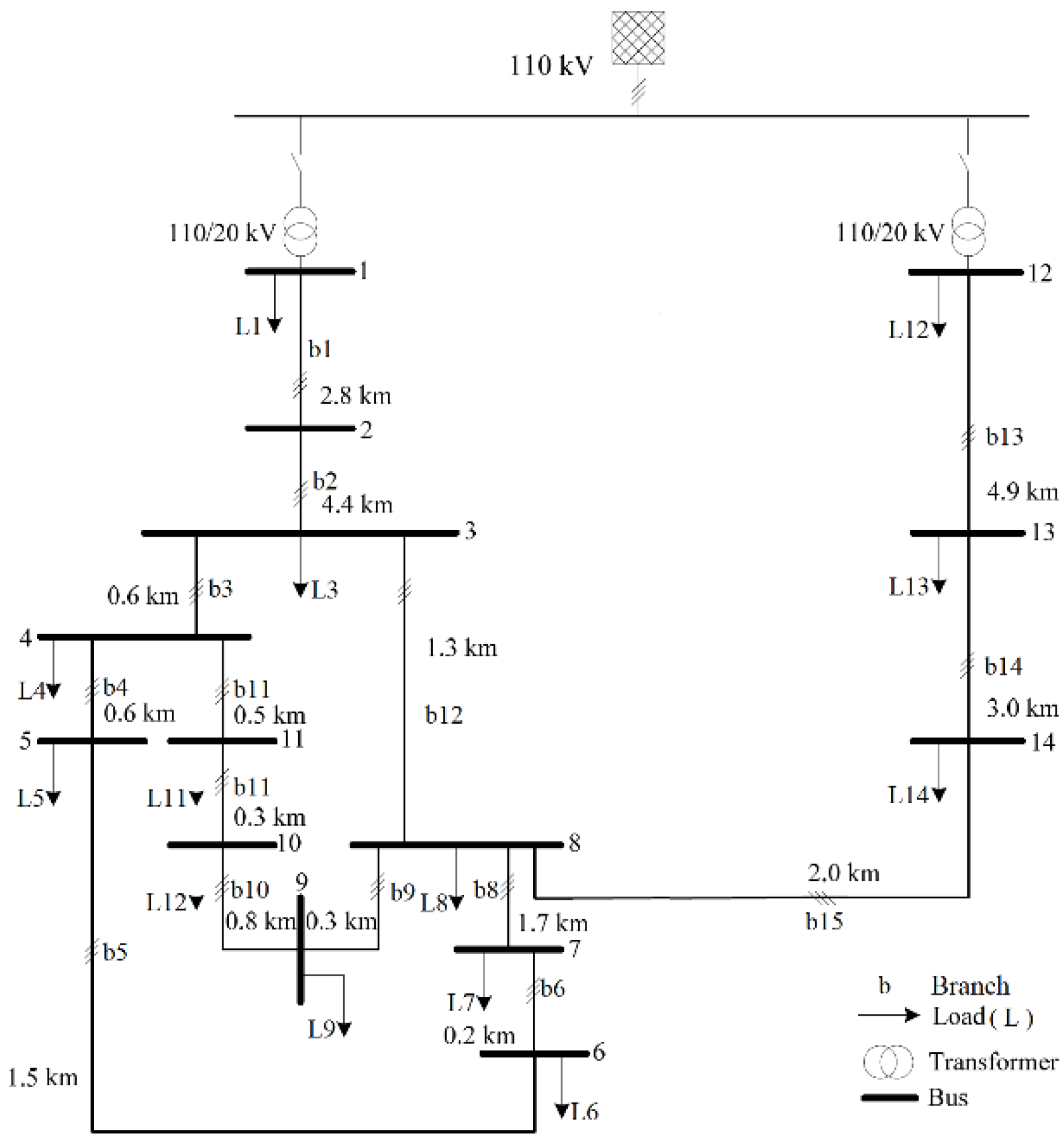
4.3. Test System
4.3.1. CIGRE MV Benchmark Model
4.3.2. Simulation Setup
4.3.3. Input Data Configuration
5. Results
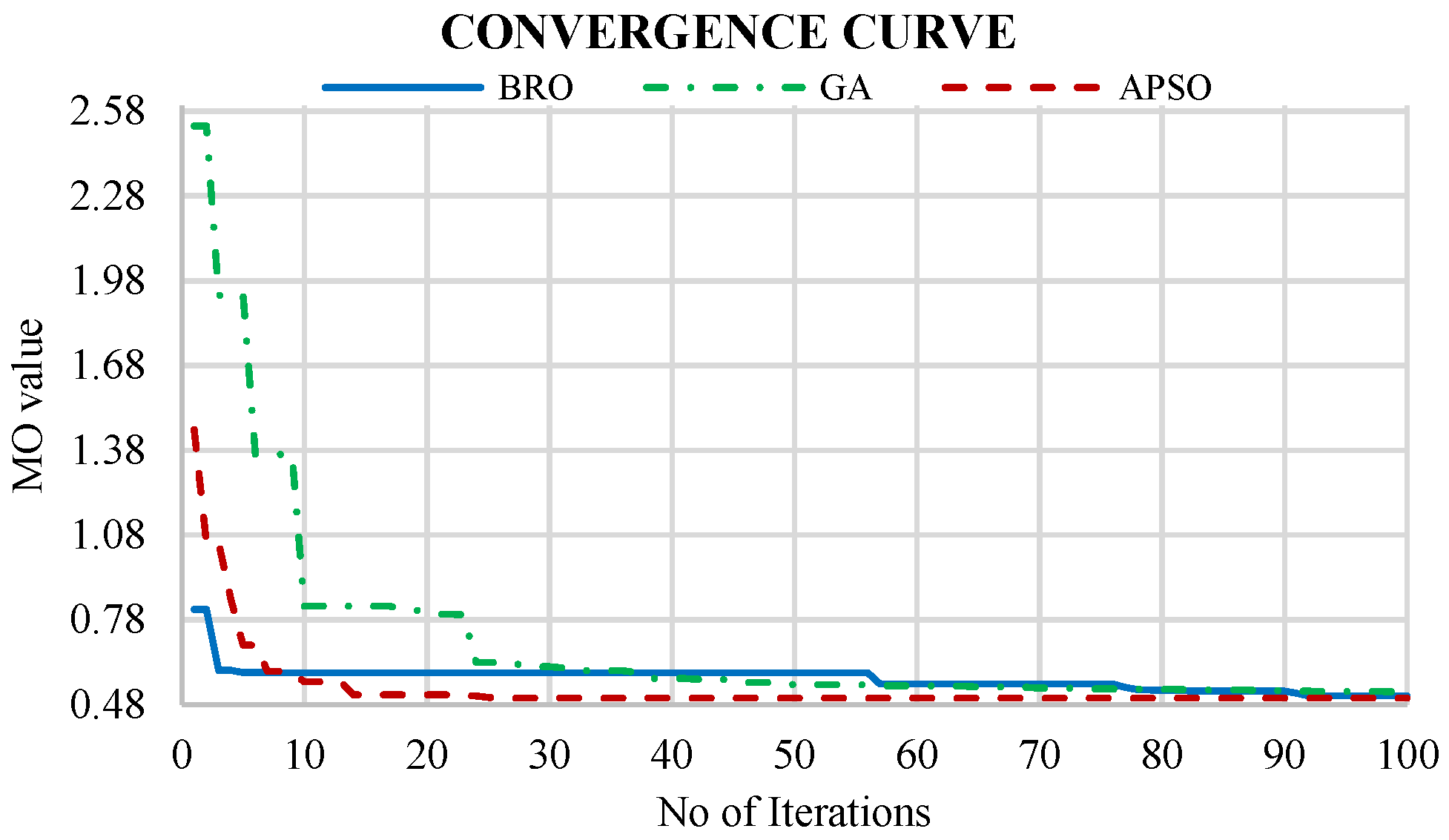
5.1. MO and Fitness Values
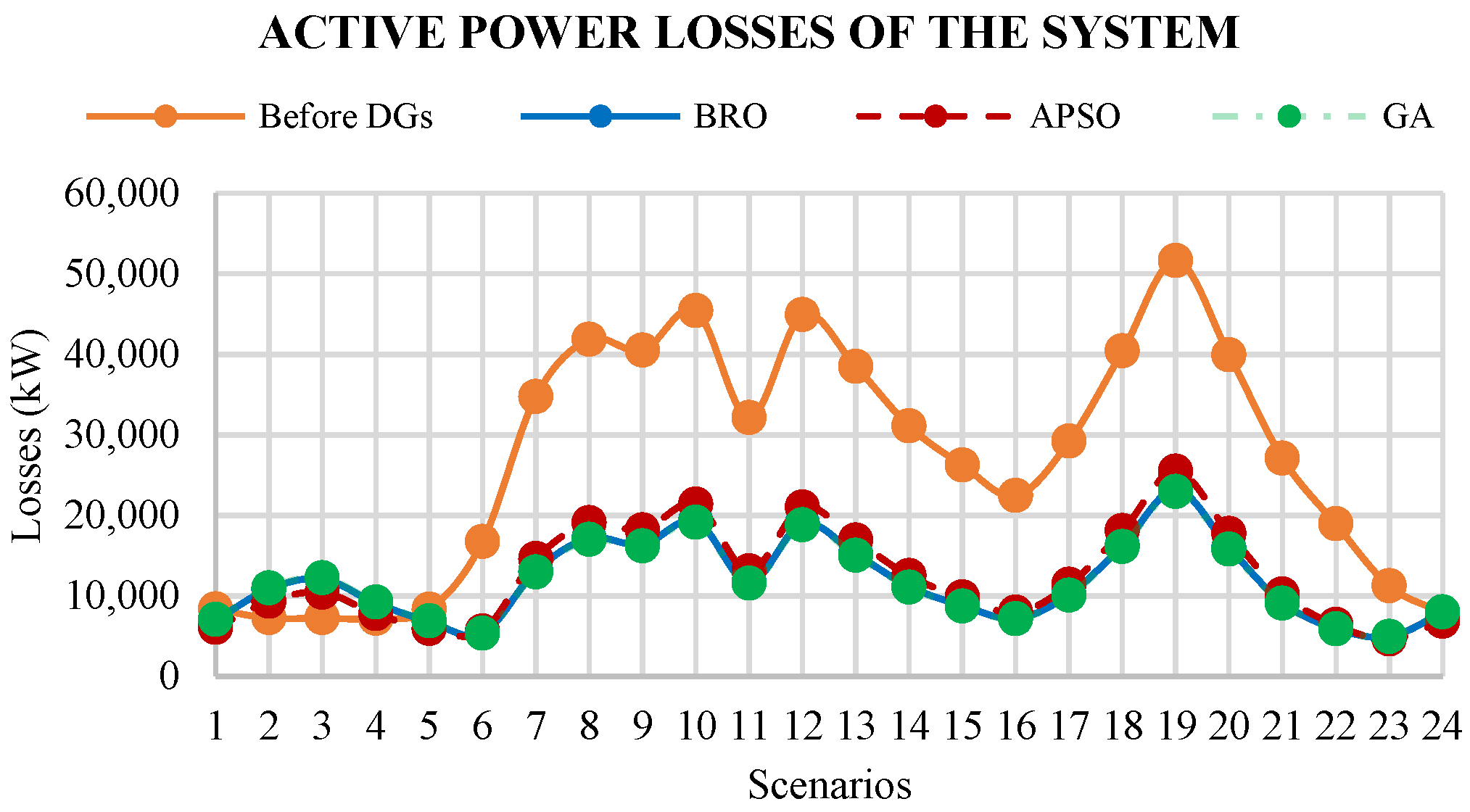
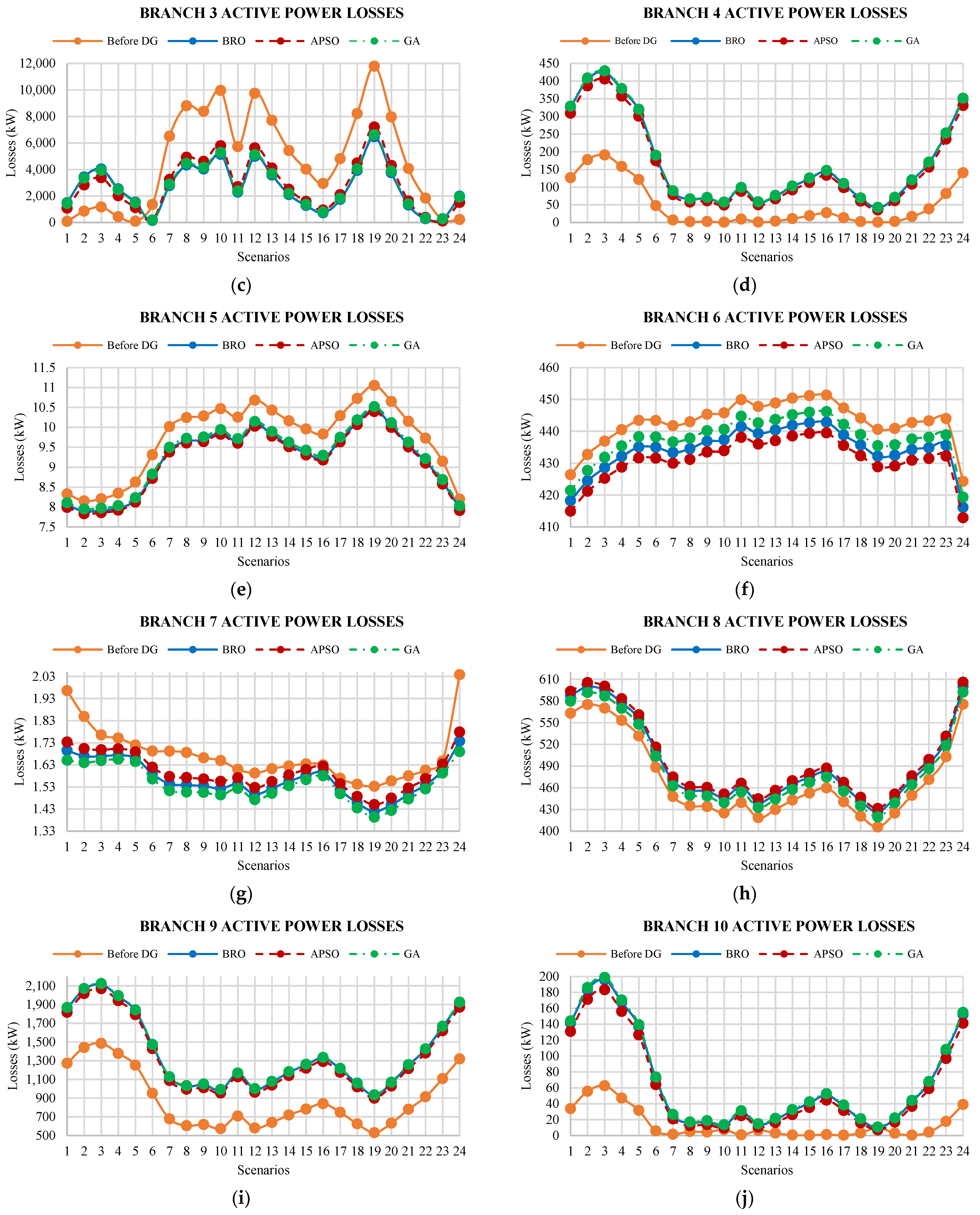
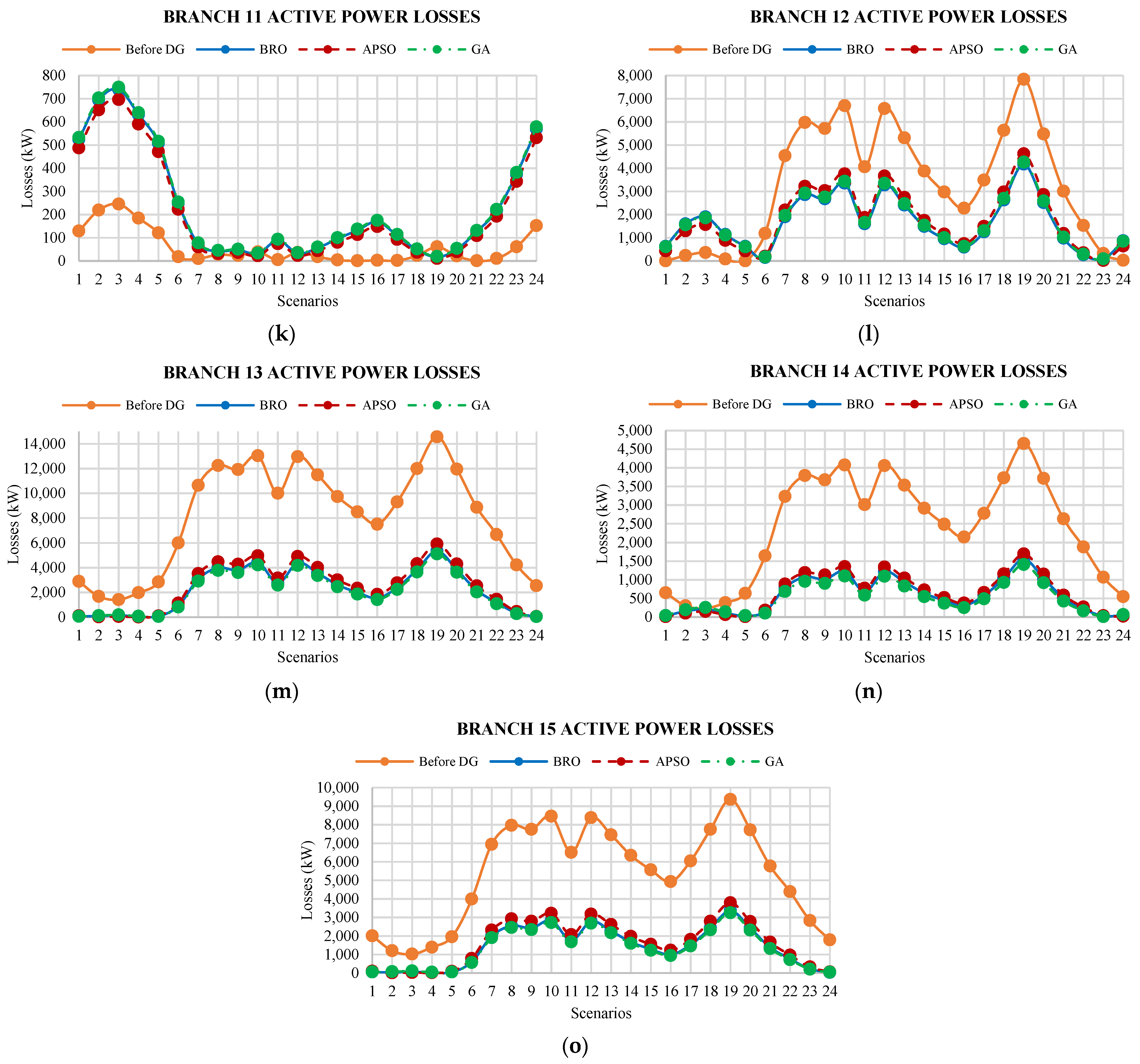
5.2. Active Power Losses
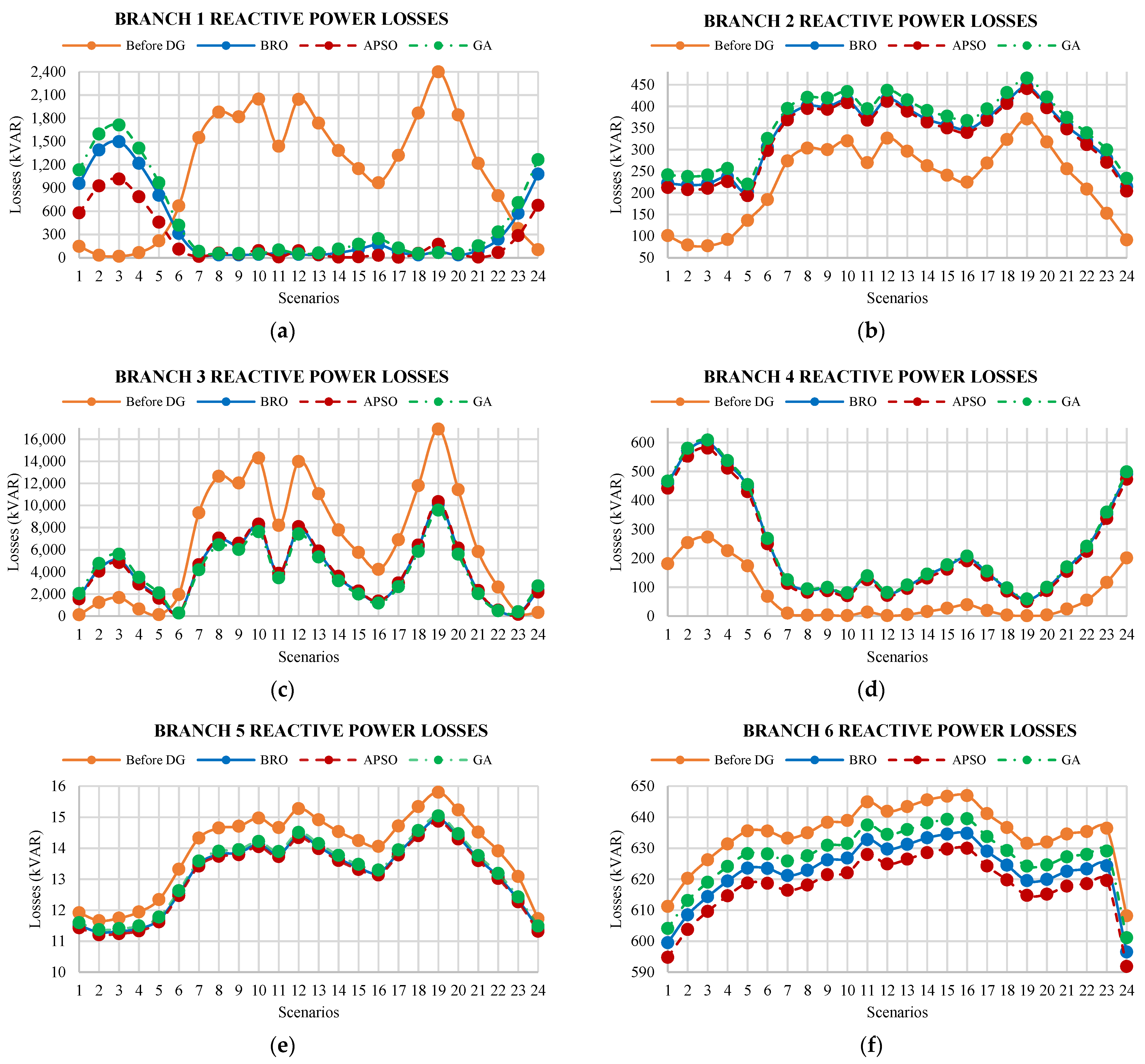
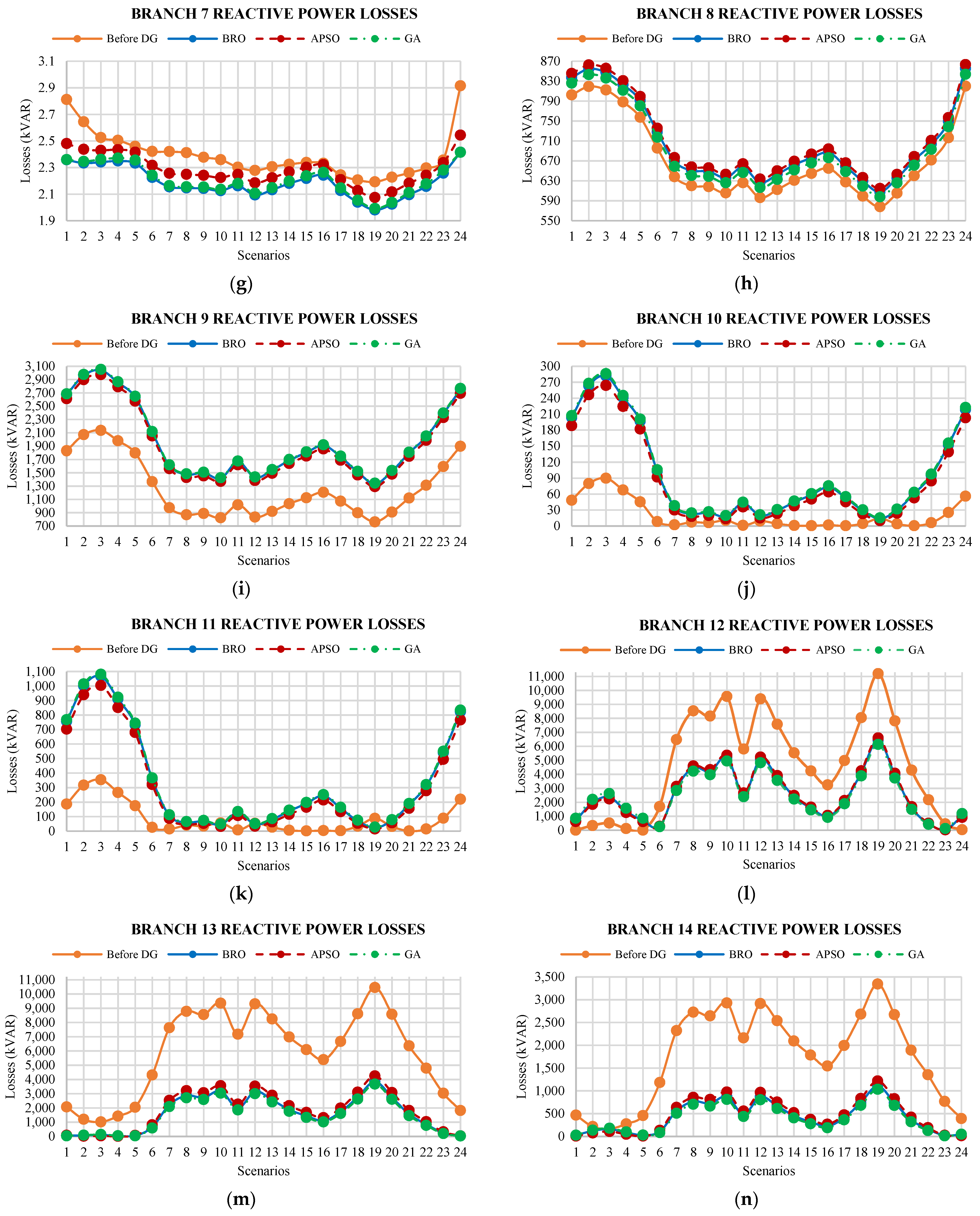
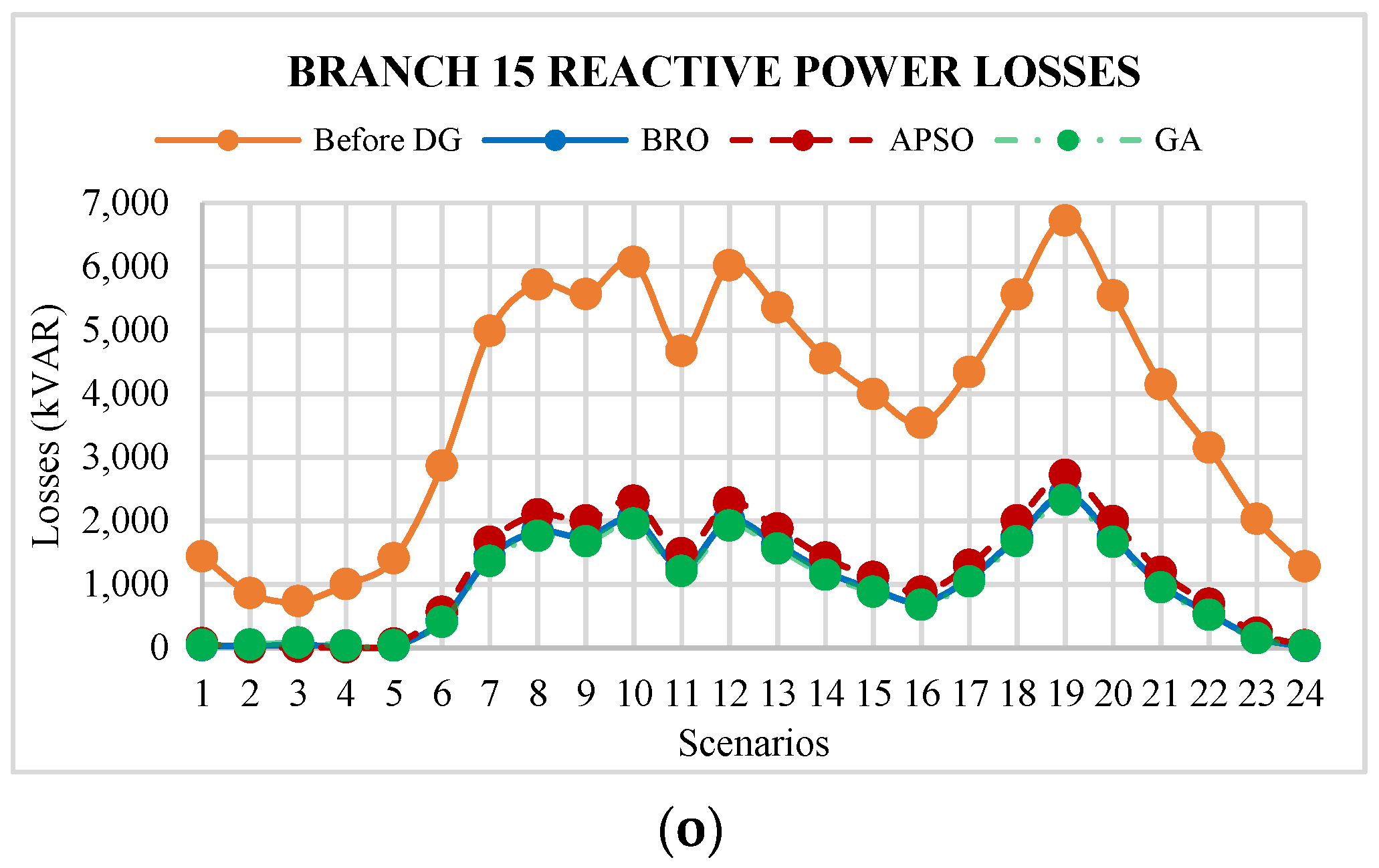
5.3. Reactive Power Losses
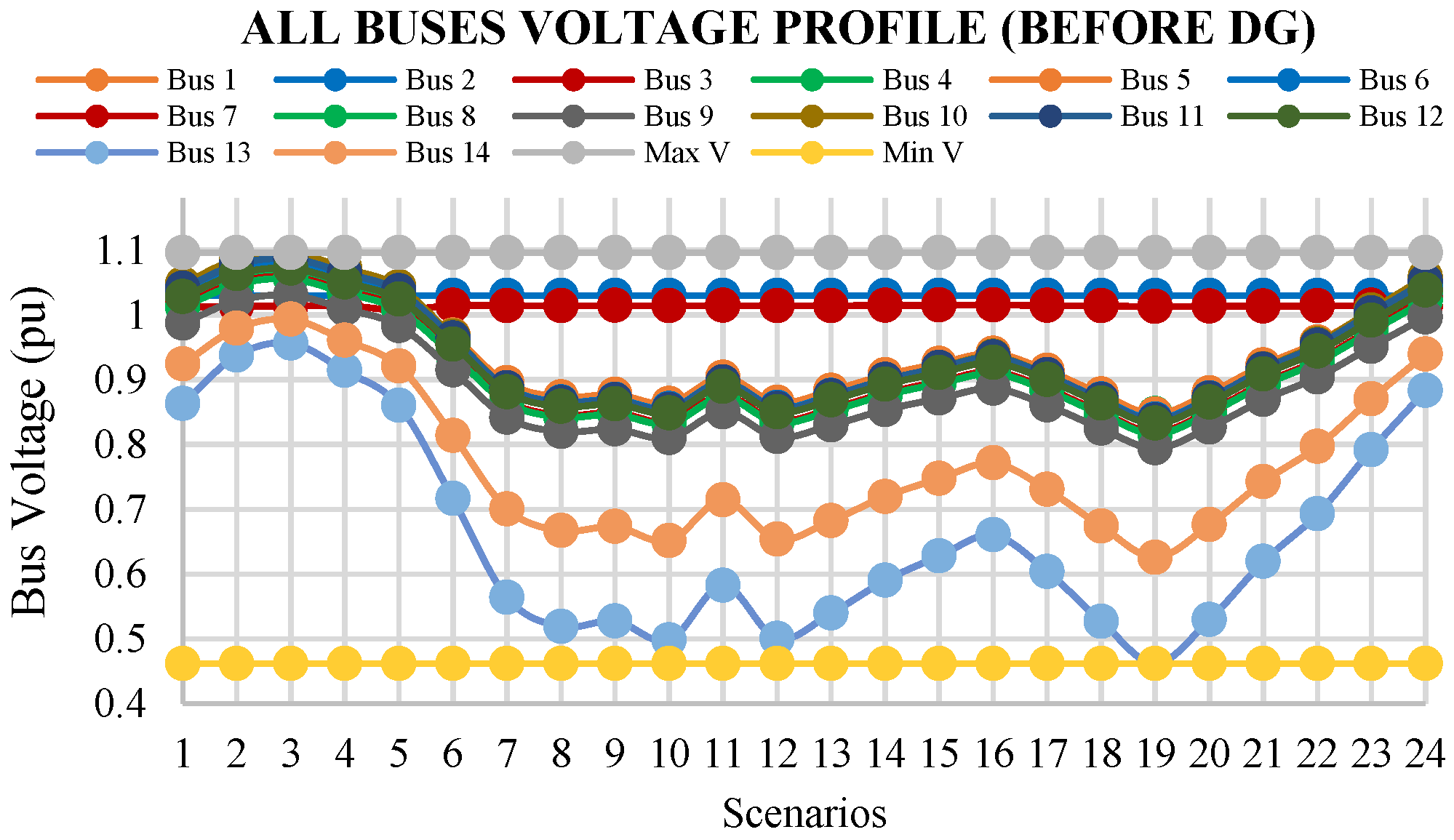
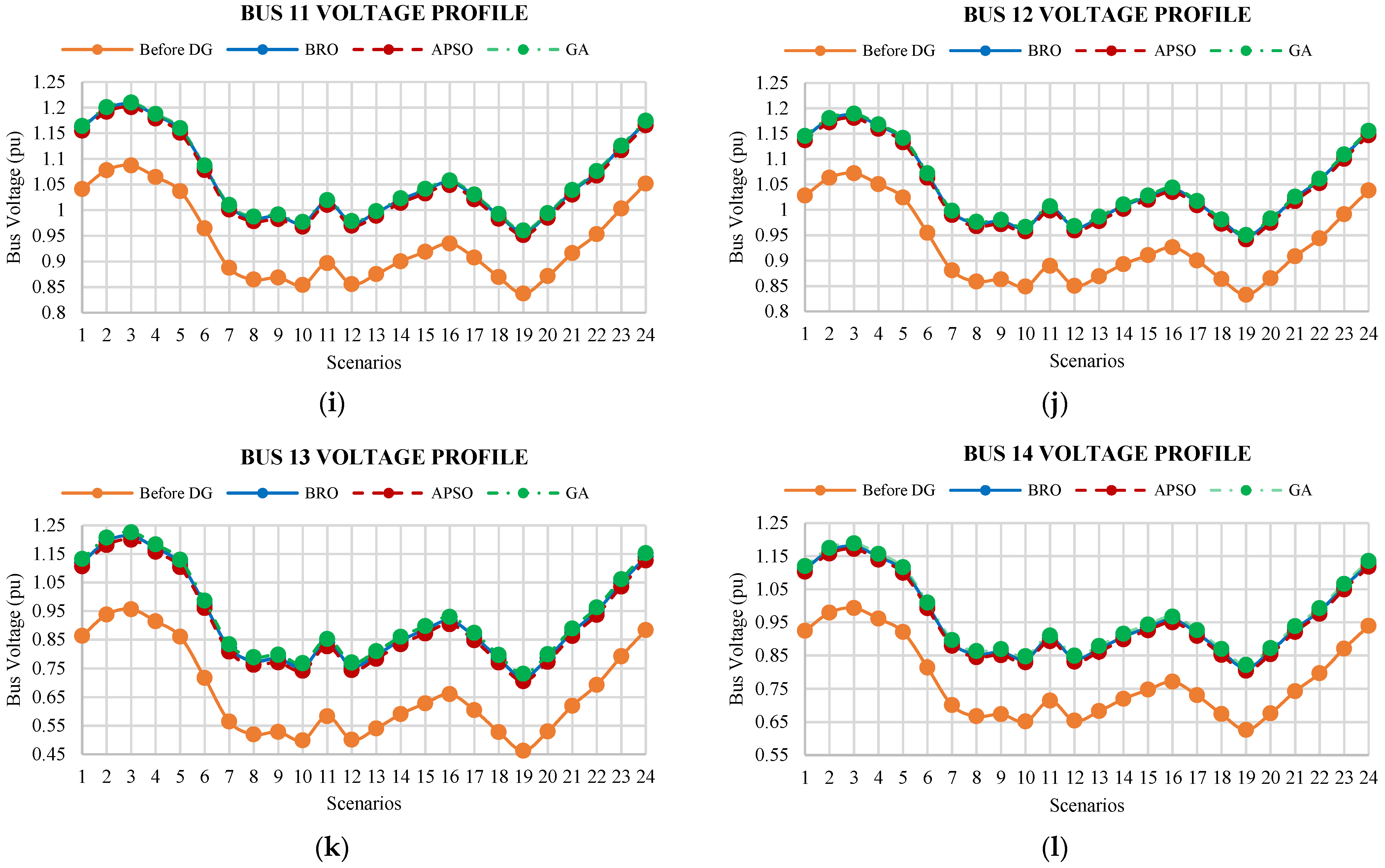
5.4. Bus Voltage Profiles
6. Discussion
6.1. MO and Fitness Values
6.2. Active Power Losses
- The average active power loss arising in the existing system is 26,617.93 kW in all scenarios, which is reduced to 11,743 kW, 12,502.73 kW, and 11,794.14 kW using GA, APSO, and BRO algorithms, respectively.
- The existing active power loss from scenarios 2 to 4 are lesser than the losses calculated after the placement of DGs. Hence, the results described above signify that the proposed method, when applied to allocating DGs in the system, helps to reduce the overall total active and reactive power losses in the system for all the considered scenarios. Therefore, the planned DGs deliver the same active power for a whole day. However, the power demand for scenarios 2 to 4 is less than the generated power, and this causes an increase in active power losses.
- The total active power losses for all scenarios are considered as active energy losses of 24 h. After the placement of DGs optimally, the active energy losses are calculated as 300,065.4 kWh, 281,838 kWh, and 283,059.7 kWh for APSO, GA, and BRO, respectively. Hence, it shows that 53.03%, 55.88%, and 55.69% of reduction in active energy loss has been seen in the system compared to the actual energy loss before the placement of DGs.
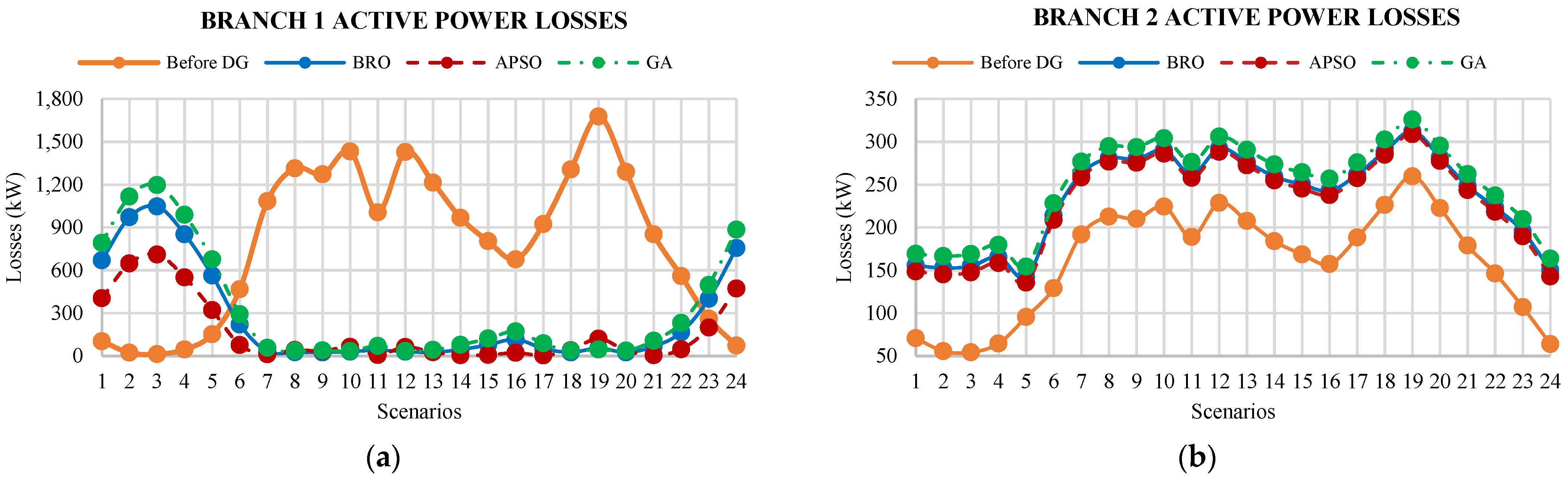
- Figure 11 shows that the active power losses are lower for most branches’ initial and final scenarios. These scenarios incorporate off-peak hours, including late-night hours in which the load requirement is lower than the peak hours during the daytime. Therefore, the system losses are lower during the late-night period.
- The maximum loss occurs in the 19th scenario for most of the branches. The actual peak active power loss of 14,569.43 kW occurs among all branches of the system. This loss is minimized to 6619.197 kW, 7199.756 kW, and 6465.435 kW by the optimal allocation of DGs using the GA, APSO, and BRO cases, respectively.
- The actual minimum loss of 0.346432 kW occurred among all branches of the system is further increased up to 1.392466 kW, 1.45 kW, and 1.384796 kW while placing DGs using the GA, APSO, and BRO algorithms, respectively.
6.3. Reactive Power Losses
- The actual average reactive power loss for all scenarios is 26,805.49 kvar. This loss is minimized to 14,412.65 kvar, 13,813.92 kvar, and 13,999.75 kvar after the placement of DGs using APSO, BRO, and GA. It shows that BRO has a better performance in the case of reactive power loss minimization.
- The present system’s reactive power losses from scenarios 1 to 5 are less than the existing system before the placement of DGs. The proposed method is applied to allocate the optimal size and location of DGs while reducing the system’s overall total reactive power losses for all considered scenarios. Therefore, the planned DGs deliver the same power for a whole day. However, the power demand from scenarios 1 to 5 is less than the generated power which has caused the increase in loss.
- The total reactive power losses for all scenarios are considered as reactive energy losses of 24 h. After the placement of DGs, reactive energy losses are at 345,903.6 kvarh, 335,994.1 kvarh, and 331,534.010 kvarh using APSO, GA, and BRO, respectively.
- The actual peak loss of 16,907.7 kvar that arises at branches is minimized to 9493.322 kvar, 10,325.97 kvar, and 9272.794 kvar using GA, APSO, and BRO.
- The actual minimum loss of 0.498524 kvar at branches is increased up to 1.98112 kvar, 2.074574 kvar, and 1.992093 kvar by using GA, APSO, and BRO.
- Figure 13 shows that reactive power losses for initial and last scenarios are lower. These scenarios represent late-night hours, and their load requirement is lower compared to daytime hours. Accordingly, the system losses are lower during the late-night period.
- The maximum reactive power loss arises for the 19th scenario at most branches. The maximum average reactive power loss occurs at branch 3. This loss is best minimized to 3811 kvar using BRO.
- The average reactive power losses across branches 3, 5, 7, 12, and 13 are also best minimized using BRO.
- The average reactive power losses across branches 1, 2, 4, 6, 9, 10, and 11 are best minimized using APSO.
- The GA attains a better reactive power losses minimization for branches 8, 14, and 15.
- For busses 2, 4, 8, 9, 10, and 11, the average reactive power losses are increased after the placement of DGs.
6.4. Bus Voltage Profiles
- The maximum voltage before the allocation of DGs is 1.0958 pu, which was enhanced up to 1.225032 pu, 1.215942 pu, and 1.226702 pu by using the BRO, APSO, and GA.
- Figure 15 shows that the proposed method improves bus voltage profiles for all scenarios. The proposed BRO algorithm attains better performance in terms of voltage profile improvement as compared to the ASPO and GA.
- The average minimum voltage before the placement of DGs is 0.6654 pu at bus 13, which is improved to 0.9358 pu, 0.9088 pu, and 0.9293 pu by using the GA, APSO, and BRO.
6.5. Main Findings and Comparison of Algorithms
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Scenarios | Bus 1 L1 | Bus 2 L2 | Bus 3 L3 | Bus 4 L4 | Bus 5 L5 | Bus 6 L6 | Bus 7 L7 | Bus 8 L8 | Bus 9 L9 | Bus 10 L10 | Bus 11 L11 | Bus 12 L12 | Bus 13 L13 | Bus 14 L14 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5477.40 | 0.00 | 146.86 | 110.61 | 186.42 | 140.44 | 25.82 | 150.38 | 193.64 | 144.75 | 84.51 | 5535.11 | 11.48 | 165.32 |
| 2 | 5979.11 | 0.00 | 154.41 | 126.80 | 213.70 | 160.99 | 24.86 | 172.39 | 186.47 | 161.72 | 96.88 | 6034.69 | 11.05 | 169.00 |
| 3 | 4072.67 | 0.00 | 111.79 | 79.59 | 134.13 | 101.05 | 20.66 | 108.20 | 154.91 | 105.99 | 60.81 | 4118.84 | 9.18 | 127.96 |
| 4 | 3595.82 | 0.00 | 90.93 | 78.24 | 131.86 | 99.33 | 13.87 | 106.37 | 103.99 | 98.47 | 59.78 | 3626.81 | 6.16 | 97.88 |
| 5 | 4597.97 | 0.00 | 134.90 | 80.93 | 136.41 | 102.76 | 28.21 | 110.03 | 211.57 | 114.19 | 61.84 | 4661.03 | 12.54 | 161.34 |
| 6 | 5909.31 | 0.00 | 173.52 | 103.87 | 175.06 | 131.88 | 36.34 | 141.21 | 272.53 | 146.67 | 79.36 | 5990.53 | 16.15 | 207.65 |
| 7 | 9490.97 | 0.00 | 265.10 | 180.75 | 304.64 | 229.50 | 50.72 | 245.74 | 380.40 | 244.12 | 138.10 | 9604.35 | 22.54 | 307.12 |
| 8 | 13,296.34 | 0.00 | 365.78 | 258.99 | 436.50 | 328.83 | 67.89 | 352.11 | 509.20 | 345.53 | 197.88 | 13,448.10 | 30.18 | 419.34 |
| 9 | 14,403.68 | 0.00 | 401.49 | 275.18 | 463.78 | 349.38 | 76.50 | 374.12 | 573.75 | 371.00 | 210.25 | 14,574.68 | 34.00 | 464.45 |
| 10 | 14,187.40 | 0.00 | 395.38 | 271.13 | 456.96 | 344.24 | 75.31 | 368.62 | 564.79 | 365.49 | 207.16 | 14,355.73 | 33.47 | 457.32 |
| 11 | 14,935.67 | 0.00 | 410.45 | 291.36 | 491.06 | 369.93 | 76.02 | 396.12 | 570.16 | 388.40 | 222.62 | 15,105.60 | 33.79 | 470.20 |
| 12 | 12,840.91 | 0.00 | 344.61 | 258.99 | 436.50 | 328.83 | 60.70 | 352.11 | 455.27 | 339.14 | 197.88 | 12,976.60 | 26.98 | 388.18 |
| 13 | 14,914.63 | 0.00 | 387.12 | 314.30 | 529.71 | 399.05 | 63.11 | 427.30 | 473.34 | 402.18 | 240.14 | 15,055.71 | 28.05 | 425.34 |
| 14 | 13,909.77 | 0.00 | 373.27 | 280.57 | 472.88 | 356.23 | 65.74 | 381.45 | 493.07 | 367.38 | 214.37 | 14,056.73 | 29.22 | 420.44 |
| 15 | 12,629.51 | 0.00 | 349.24 | 244.15 | 411.49 | 309.99 | 65.50 | 331.94 | 491.27 | 327.07 | 186.54 | 12,775.93 | 29.11 | 401.81 |
| 16 | 11,659.24 | 0.00 | 333.05 | 214.48 | 361.48 | 272.31 | 66.46 | 291.59 | 498.45 | 295.24 | 163.87 | 11,807.79 | 29.54 | 391.61 |
| 17 | 10,841.01 | 0.00 | 309.47 | 199.64 | 336.47 | 253.47 | 61.68 | 271.42 | 462.59 | 274.65 | 152.53 | 10,978.88 | 27.41 | 363.73 |
| 18 | 12,347.42 | 0.00 | 303.26 | 277.88 | 468.33 | 352.81 | 42.55 | 377.79 | 319.15 | 343.80 | 212.31 | 12,442.54 | 18.91 | 318.65 |
| 19 | 14,323.99 | 0.00 | 332.06 | 342.62 | 577.45 | 435.02 | 38.25 | 465.81 | 286.88 | 411.27 | 261.78 | 14,409.49 | 17.00 | 331.29 |
| 20 | 16,001.41 | 0.00 | 357.46 | 396.58 | 668.39 | 503.52 | 35.14 | 539.17 | 263.57 | 467.92 | 303.00 | 16,079.96 | 15.62 | 343.89 |
| 21 | 14,305.18 | 0.00 | 320.67 | 353.41 | 595.64 | 448.72 | 32.03 | 480.48 | 240.26 | 417.63 | 270.02 | 14,376.79 | 14.24 | 309.57 |
| 22 | 12,028.67 | 0.00 | 275.30 | 291.36 | 491.06 | 369.93 | 30.12 | 396.12 | 225.91 | 347.60 | 222.62 | 12,096.00 | 13.39 | 271.30 |
| 23 | 10,175.30 | 0.00 | 236.45 | 242.80 | 409.22 | 308.28 | 27.49 | 330.10 | 206.19 | 291.79 | 185.51 | 10,236.75 | 12.22 | 236.44 |
| 24 | 7669.13 | 0.00 | 188.29 | 172.66 | 291.00 | 219.22 | 26.39 | 234.74 | 197.94 | 213.58 | 131.92 | 7728.12 | 11.73 | 197.79 |
| Scenarios | Bus 1 L1 | Bus 2 L2 | Bus 3 L3 | Bus 4 L4 | Bus 5 L5 | Bus 6 L6 | Bus 7 L7 | Bus 8 L8 | Bus 9 L9 | Bus 10 L10 | Bus 11 L11 | Bus 12 L12 | Bus 13 L13 | Bus 14 L14 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5180.28 | 0.00 | 124.96 | 66.23 | 111.62 | 84.08 | 28.04 | 90.04 | 210.27 | 97.84 | 50.60 | 5233.01 | 12.46 | 153.49 |
| 2 | 5664.39 | 0.00 | 128.11 | 75.92 | 127.95 | 96.39 | 27.00 | 103.21 | 202.48 | 107.59 | 58.00 | 5715.17 | 12.00 | 153.67 |
| 3 | 3847.52 | 0.00 | 96.56 | 47.65 | 80.31 | 60.50 | 22.43 | 64.78 | 168.22 | 72.41 | 36.41 | 3889.71 | 9.97 | 120.21 |
| 4 | 3409.69 | 0.00 | 74.33 | 46.84 | 78.95 | 59.47 | 15.06 | 63.68 | 112.92 | 64.96 | 35.79 | 3438.01 | 6.69 | 87.88 |
| 5 | 4329.62 | 0.00 | 121.23 | 48.46 | 81.67 | 61.52 | 30.63 | 65.88 | 229.74 | 80.59 | 37.02 | 4387.24 | 13.61 | 156.15 |
| 6 | 6974.13 | 0.00 | 156.01 | 62.19 | 104.81 | 78.96 | 39.46 | 84.55 | 295.94 | 103.55 | 47.51 | 5638.40 | 17.54 | 201.03 |
| 7 | 8958.81 | 0.00 | 231.48 | 108.22 | 182.40 | 137.40 | 55.08 | 147.13 | 413.07 | 168.12 | 82.69 | 9062.39 | 24.48 | 290.95 |
| 8 | 12,559.96 | 0.00 | 316.39 | 155.06 | 261.34 | 196.88 | 73.73 | 210.82 | 552.94 | 236.28 | 118.48 | 12,698.62 | 32.77 | 394.39 |
| 9 | 13,597.42 | 0.00 | 350.11 | 164.75 | 277.68 | 209.18 | 83.07 | 223.99 | 623.03 | 255.26 | 125.88 | 13,753.66 | 36.92 | 439.57 |
| 10 | 13,393.39 | 0.00 | 344.74 | 162.33 | 273.59 | 206.11 | 81.77 | 220.70 | 613.29 | 251.43 | 124.03 | 13,547.19 | 36.34 | 432.78 |
| 11 | 14,109.20 | 0.00 | 354.79 | 174.45 | 294.01 | 221.49 | 82.55 | 237.17 | 619.13 | 265.46 | 133.28 | 14,264.46 | 36.69 | 442.00 |
| 12 | 12,143.84 | 0.00 | 293.40 | 155.06 | 261.34 | 196.88 | 65.92 | 210.82 | 494.37 | 229.34 | 118.48 | 12,267.81 | 29.30 | 360.55 |
| 13 | 14,126.40 | 0.00 | 322.31 | 188.18 | 317.15 | 238.92 | 68.53 | 255.83 | 514.00 | 268.12 | 143.77 | 14,255.29 | 30.46 | 387.89 |
| 14 | 13,154.72 | 0.00 | 317.78 | 167.98 | 283.12 | 213.28 | 71.39 | 228.38 | 535.41 | 248.43 | 128.35 | 13,288.99 | 31.73 | 390.51 |
| 15 | 11,927.13 | 0.00 | 303.06 | 146.18 | 246.37 | 185.60 | 71.13 | 198.74 | 533.47 | 224.19 | 111.69 | 12,060.91 | 31.61 | 378.85 |
| 16 | 10,993.47 | 0.00 | 294.73 | 128.41 | 216.42 | 163.04 | 72.17 | 174.58 | 541.25 | 205.55 | 98.11 | 11,129.21 | 32.07 | 374.77 |
| 17 | 10,222.30 | 0.00 | 273.76 | 119.53 | 201.45 | 151.76 | 66.98 | 162.50 | 502.31 | 191.15 | 91.32 | 10,348.27 | 29.77 | 347.98 |
| 18 | 11,722.94 | 0.00 | 242.61 | 166.37 | 280.40 | 211.23 | 46.21 | 226.19 | 346.56 | 224.27 | 127.11 | 11,809.84 | 20.54 | 280.61 |
| 19 | 13,631.72 | 0.00 | 253.68 | 205.14 | 345.73 | 260.45 | 41.54 | 278.89 | 311.51 | 262.80 | 156.73 | 13,709.84 | 18.46 | 279.10 |
| 20 | 15,250.04 | 0.00 | 264.43 | 237.44 | 400.18 | 301.47 | 38.16 | 322.81 | 286.20 | 295.37 | 181.42 | 15,321.82 | 16.96 | 280.08 |
| 21 | 13,631.68 | 0.00 | 237.94 | 211.60 | 356.62 | 268.66 | 34.79 | 287.68 | 260.89 | 263.91 | 161.67 | 13,697.10 | 15.46 | 252.97 |
| 22 | 11,453.12 | 0.00 | 208.03 | 174.45 | 294.01 | 221.49 | 32.71 | 237.17 | 245.32 | 221.16 | 133.28 | 11,514.64 | 14.54 | 226.02 |
| 23 | 9682.61 | 0.00 | 181.00 | 145.37 | 245.01 | 184.57 | 29.85 | 197.64 | 223.90 | 186.61 | 111.07 | 9738.75 | 13.27 | 199.60 |
| 24 | 7281.36 | 0.00 | 150.59 | 103.38 | 174.23 | 131.25 | 28.66 | 140.54 | 214.94 | 139.30 | 78.98 | 7335.26 | 12.74 | 174.14 |
References
- Zohuri, B. Electricity, an Essential Necessity in Our Life. In Application of Compact Heat Exchangers for Combined Cycle Driven Efficiency in Next Generation Nuclear Power Plants; Springer Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 17–35. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.F.N.; Malik, T.N.; Sajjad, I.A. Impact of time varying load models on PV DG planning. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2018, 10, 035501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Mukherjee, V. Optimal placement and sizing of DGs in RDS using chaos embedded SOS algorithm. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2016, 10, 3671–3680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Mandal, K.; Chakraborty, N. Optimal DG placement by multi-objective opposition based chaotic differential evolution for techno-economic analysis. Appl. Soft Comput. 2019, 78, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waqar, A.; Subramaniam, U.; Farzana, K.; Elavarasan, R.M.; Habib, H.U.R.; Zahid, M.; Hossain, E. Analysis of Optimal Deployment of Several DGs in Distribution Networks Using Plant Propagation Algorithm. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 175546–175562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawambwa, S.; Hamisi, N.; Mafole, P.; Kundaeli, H. A cloud model based symbiotic organism search algorithm for DG allocation in radial distribution network. Evol. Intell. 2021, 15, 545–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, W.; Hassan, S.J.U.; Mehdi, A.; Hussain, A.; Adjayeng, G.O.M.; Kim, C.-H. Voltage Profile Enhancement and Loss Minimization Using Optimal Placement and Sizing of Distributed Generation in Reconfigured Network. Machines 2021, 9, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, M.; Waseem, M.; Liaqat, R.; Sajjad, I.A.; Dampage, U.; Salmen, S.H.; Al Obaid, S.; Mohamed, M.A.; Annuk, A. SPSO Based Optimal Integration of DGs in Local Distribution Systems under Extreme Load Growth for Smart Cities. Electronics 2021, 10, 2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nageswari, D.; Kalaiarasi, N.; Geethamahalakshmi, G. Optimal Placement and Sizing of Distributed Generation Using Metaheuristic Algorithm. Comput. Syst. Sci. Eng. 2022, 41, 493–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balu, K.; Mukherjee, V. Optimal siting and sizing of distributed generation in radial distribution system using a novel student psychology-based optimization algorithm. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 15639–15667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, S.K.; Mishra, S.; Abdelaziz, A.Y.; Alghaythi, M.L.; Allehyani, A. Optimal Allocation of Distributed Generators in Active Distribution Networks Using a New Oppositional Hybrid Sine Cosine Muted Differential Evolution Algorithm. Energies 2022, 15, 2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, M.I.; Kazmi, S.A.A.; Alrumayh, O.; Khan, Z.A.; Altamimi, A.; Malik, M.M. A Novel Hybrid Optimization-Based Algorithm for the Single and Multi-Objective Achievement with Optimal DG Allocations in Distribution Networks. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 25669–25687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, D.B.; Lakshminarayana, C. Multiple DG placements in radial distribution system for multi objectives using Whale Optimization Algorithm. Alex. Eng. J. 2018, 57, 2797–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Park, J.-W. Optimal Placement and Sizing of Multiple DGs in a Practical Distribution System by Considering Power Loss. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2013, 49, 2262–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelkader, M.; Elshahed, M.; Osman, Z. An analytical formula for multiple DGs allocations to reduce distribution system losses. Alex. Eng. J. 2019, 58, 1265–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.F.N.; Malik, T.N. Probablistic generation model for optimal allocation of PV DG in distribution system. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2017, 9, 065503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, A. Allocation of distributed generations in radial distribution systems using adaptive PSO and modified GSA multi-objective optimizations. Alex. Eng. J. 2020, 59, 4771–4786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Nadeem, M.F.; Ali, I. Probabilistic generation model for optimal allocation of wind DG in distribution systems with time variable models. Sustain. Energy Grids Netw. 2020, 22, 100358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ammar, E.A.; Farzana, K.; Waqar, A.; Aamir, M.; Saifullah; Haq, A.U.; Zahid, M.; Batool, M. ABC algorithm based optimal sizing and placement of DGs in distribution networks considering multiple objectives. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2020, 12, 697–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, M.-T.; Bruyere, A.; Francois, B. Sensitivity analysis of the CIGRE distribution network benchmark according to the large scale connection of renewable energy generators. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Manchester PowerTech, Manchester, UK, 18–22 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Prabha, D.R.; Jayabarathi, T. Optimal placement and sizing of multiple distributed generating units in distribution networks by invasive weed optimization algorithm. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2016, 7, 683–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bohre, A.K.; Agnihotri, G.; Dubey, M. Optimal sizing and sitting of DG with load models using soft computing techniques in practical distribution system. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2016, 10, 2606–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, N.; Singh, S.; Srivastava, S. PSO based placement of multiple wind DGs and capacitors utilizing probabilistic load flow model. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2014, 19, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onlam, A.; Yodphet, D.; Chatthaworn, R.; Surawanitkun, C.; Siritaratiwat, A.; Khunkitti, P. Power Loss Minimization and Voltage Stability Improvement in Electrical Distribution System via Network Reconfiguration and Distributed Generation Placement Using Novel Adaptive Shuffled Frogs Leaping Algorithm. Energies 2019, 12, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prakash, R.; Lokeshgupta, B.; Sivasubramani, S. Optimal Site and Size of DG with different Load Models using Cuckoo Search Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Power Electronics, Drives and Energy Systems (PEDES), Chennai, India, 18–21 December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Arulraj, R.; Kumarappan, N. Simultaneous Multiple DG and Capacitor Installation Using Dragonfly Algorithm for Loss Reduction and Loadability Improvement in Distribution System. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Power, Energy, Control and Transmission Systems (ICPECTS), Chennai, India, 22–23 February 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Dubey, A. Load flow analysis of power systems. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2016, 7, 79–84. [Google Scholar]
- Teng, J.-H. A modified Gauss–Seidel algorithm of three-phase power flow analysis in distribution networks. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2002, 24, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farshi, T.R. Battle royale optimization algorithm. Neural Comput. Appl. 2020, 33, 1139–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.-S. Engineering Optimization: An Introduction with Metaheuristic Applications; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Mahesh, K.; Nallagownden, P.A.L. Optimal placement and sizing of DG in distribution system using accelerated PSO for power loss minimization. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Energy Conversion, Johor Bahru, Malaysia, 18 February 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Prajna, K.; Sasi Bhushan Rao, G.; Reddy, K.V.V.S. A New Dual Channel Speech Enhancement Approach Based on Accelerated Particle Swarm Optimization (APSO). Int. J. Intell. Syst. Technol. Appl. 2014, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasant, P.; Marmolejo, J.A.; Litvinchev, I.; Aguilar, R.R. Nature-inspired meta-heuristics approaches for charging plug-in hybrid electric vehicle. Wirel. Netw. 2019, 26, 4753–4766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, V.K.; Kumar, B. Genetic algorithm: An overview and its application. Int. J. Adv. Stud. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2014, 3, 21. [Google Scholar]
- Madhusudhan, M.; Kumar, N.; Pradeepa, H. Optimal location and capacity of DG systems in distribution network using genetic algorithm. Int. J. Inf. Technol. 2020, 13, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambora, A.; Gupta, K.; Chopra, K. Genetic Algorithm- A Literature Review. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Machine Learning, Big Data, Cloud and Parallel Computing (COMITCon), Faridabad, India, 14–16 February 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Aissi, H.; Bazgan, C.; Vanderpooten, C. Min–max and min–max regret versions of combinatorial optimization: A survey. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2009, 197, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farrokhseresht, M.; Slootweg, H.; Gibescu, M. Day-ahead bidding strategies of a distribution market operator in a coupled local and central market. Smart Energy 2021, 2, 100021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudion, K.; Orths, A.; Styczynski, Z.A.; Strunz, K. Design of benchmark of medium voltage distribution network for investigation of DG integration. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE Power Engineering Society General Meeting, Montreal, QC, Canada, 18–22 June 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Strunz, K.; Ehsan, A.; Robert, F.; Nikos, H.; Reza, I.; Géza, J. TF C6.04.02: TB 575—Benchmark Systems for Network Integration of Renewable and Distributed Energy Resources; CIGRE: Paris, France, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Ji, Y.; Zhuang, H.; Wu, H. Multi-Objective Dynamic Economic Dispatch of Microgrid Systems Including Vehicle-to-Grid. Energies 2015, 8, 4476–4495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Indices | W |
|---|---|
| API | 0.5 |
| RPI | 0.25 |
| VD | 0.25 |
| Parameters | BRO | APSO | GA |
|---|---|---|---|
| No. of Iterations | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Population Size | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Size Range of DGs (kW and kvar) | 10~500 | 10~500 | 10~500 |
| Scenarios | APSO | GA | BRO | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DG Locations | DG Sizes | DG Locations | DG Sizes | DG Locations | DG Sizes | |
| 1 | 1, 2, 12 | 171.30, 10, 43.87 | 12, 1, 2 | 51.35, 214.26, 14.73 | 2, 1, 12 | 15.51, 162.58, 40.43 |
| 2 | 1, 12, 2 | 166.89, 24.50, 10 | 12, 1, 2 | 24.37, 205.93, 57.49 | 2, 1, 12 | 14.78, 168.37, 25.66 |
| 3 | 2, 1, 12 | 10, 158.81, 19.60 | 12, 1, 2 | 65.80, 413.49, 50.08 | 2, 1, 12 | 18.66, 174.74, 23.16 |
| 4 | 13, 1, 12 | 10, 166.26, 24.47 | 2, 12, 1 | 10.14, 28.47, 146.75 | 1, 2, 8 | 135.25, 43.98, 11.57 |
| 5 | 1, 12, 8 | 194.65, 41.99, 10 | 2, 1, 12 | 32.49, 173.65, 39.49 | 12, 1, 2 | 40.54, 169.10, 21.74 |
| 6 | 12, 1, 2 | 81.44, 172.96, 10 | 12, 1, 13 | 61.33, 198.32, 26.40 | 12, 8, 1 | 84.15, 12.57, 240.66 |
| 7 | 1, 6, 12 | 200.19, 10, 116.28 | 1, 12, 13 | 235.07, 99.55, 33.70 | 1, 12, 13 | 216.04, 105.89, 24.47 |
| 8 | 1, 2, 12 | 178.15, 10, 129.19 | 12, 2, 1 | 127.44, 55.41, 201.71 | 13, 1, 12 | 16.55, 179.16, 114.01 |
| 9 | 1, 2, 12 | 177.58, 10, 127.21 | 2, 1, 12 | 42.21, 238.37, 136.20 | 2, 1, 12 | 51.20, 202.74, 127.79 |
| 10 | 12, 1, 8 | 131.33, 196.0, 10 | 12, 13, 1 | 126.07, 13.87, 205.31 | 12, 2, 1 | 136.29, 31.52, 207.41 |
| 11 | 12, 6, 1 | 111.92, 10, 199.07 | 13, 12, 1 | 21.92, 97.80, 194.21 | 2, 1, 12 | 21.21, 203.31, 116.99 |
| 12 | 12, 13, 1 | 127.28, 10, 185.68 | 2, 12, 1 | 53.44, 131.12, 203.13 | 1, 12, 2 | 227.45, 136.17, 77.57 |
| 13 | 1, 2, 12 | 178.40, 10, 124.37 | 12, 1, 2 | 126.32, 202.01, 21.50 | 14, 1, 12 | 11.28, 187.81, 113.93 |
| 14 | 13, 1, 12 | 10, 182.84, 106.16 | 12, 2, 1 | 109.70, 35.14, 186.68 | 1, 8, 12 | 186.22, 13.79, 104.92 |
| 15 | 2, 1, 12 | 10, 174.06, 103.36 | 2, 12, 1 | 72.13, 98.57, 204.19 | 1, 2, 12 | 208.96, 96.62, 96.12 |
| 16 | 2, 1, 12 | 10, 172.15, 95.42 | 12, 2, 1 | 84.97, 135.51, 219.17 | 12, 1, 2 | 89.80, 206.86, 60.59 |
| 17 | 1, 2, 12 | 177.77, 109.28, 10 | 1, 2, 12 | 190.36, 33.58, 107.72 | 1, 12, 2 | 184.21, 99.20, 90.54 |
| 18 | 12, 1, 2 | 127.56, 18.48, 10 | 13, 12, 1 | 29.45, 107.84, 214.17 | 13, 1, 12 | 29.10, 249.02, 115.30 |
| 19 | 12, 8, 1 | 139.92, 10, 201.15 | 1, 13, 12 | 243.72, 55.93, 105.24 | 12, 13, 1 | 134.70, 15.65, 208.25 |
| 20 | 8, 12, 1 | 10, 124.32, 201.26 | 2, 1, 12 | 10, 183.09, 126.88 | 1, 2, 12 | 190.74, 49.36, 122.56 |
| 21 | 8, 12, 1 | 10, 10.86, 198.24 | 2, 1, 12 | 10.02, 176.03, 104.47 | 2, 12, 1 | 44.88, 98.21, 152.83 |
| 22 | 2, 12, 1 | 10, 87.56, 177.39 | 1, 2, 12 | 173.30, 10, 87.15 | 8, 1, 12 | 11.12, 207.20, 86.28 |
| 23 | 8, 12, 1 | 10, 59.63, 187.21 | 2, 1, 12 | 36.33, 213.13, 66.79 | 8, 12, 1 | 11.64, 57.52, 180.04 |
| 24 | 8, 12, 1 | 10, 35.87, 187.81 | 12, 1, 2 | 23.07, 89.04, 19.91 | 2, 1, 12 | 54.13, 200.46, 35.66 |
| Algorithms | DG 1 Location | DG 2 Location | DG 3 Location | DG 1 Size (×1000) | DG 2 Size (×1000) | DG 3 Size (×1000) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GA | 1 | 12 | 2 | 181.119 | 62.568 | 10.504 |
| APSO | 1 | 12 | 2 | 208.643 | 70.117 | 33.410 |
| BRO | 1 | 12 | 2 | 200.221 | 69.168 | 29.152 |
| Scenarios | BRO | GA | APSO | Scenarios | BRO | GA | APSO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.5027 | 0.5143 | 0.5027 | 13 | 0.0973 | 0.1006 | 0.1070 |
| 2 | 0.5643 | 0.5643 | 0.5642 | 14 | 0.1207 | 0.1245 | 0.1207 |
| 3 | 0.6560 | 0.5580 | 0.5580 | 15 | 0.1433 | 0.1474 | 0.1567 |
| 4 | 0.5642 | 0.5642 | 0.5642 | 16 | 0.1683 | 0.1682 | 0.6334 |
| 5 | 0.4984 | 0.4869 | 0.7834 | 17 | 0.1416 | 0.1332 | 0.1292 |
| 6 | 0.2326 | 0.2326 | 0.2537 | 18 | 0.0934 | 0.0933 | 0.1027 |
| 7 | 0.1118 | 0.1118 | 0.1083 | 19 | 0.0734 | 0.0734 | 0.0762 |
| 8 | 0.0893 | 0.0924 | 0.0924 | 20 | 0.0953 | 0.0953 | 0.1048 |
| 9 | 0.1015 | 0.0922 | 0.0954 | 21 | 0.1457 | 0.1414 | 0.1456 |
| 10 | 0.0822 | 0.0822 | 0.1991 | 22 | 0.2060 | 0.2116 | 0.2116 |
| 11 | 0.1207 | 0.1170 | 0.1170 | 23 | 0.3659 | 0.3570 | 0.3570 |
| 12 | 0.0920 | 0.0834 | 0.0920 | 24 | 0.5788 | 0.5318 | 0.5318 |
| Algorithm | Before DG | GA | APSO | Proposed BRO |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum Fitness | --- | 6.39 | 6.69 | 6.48 |
| V min (pu) | 0.4622 | 0.7326 | 0.7056 | 0.7261 |
| V max (pu) | 1.0958 | 1.2269 | 1.2159 | 1.2250 |
| P loss (%) Red | 0 | 55.88 | 53.03 | 55.69 |
| Q loss (%) Red | 0 | 47.77 | 46.23 | 48.47 |
| Min Line Losses (P, Q) (kW, kvar) | 0.346432, 0.498524 | 1.392466, 1.992093 | 1.45, 2.074574 | 1.384796, 1.98112 |
| Max Line Losses (P, Q) (kW, kvar) | 14,569.43, 16,907.7 | 6619.197, 9493.322 | 7199.756, 10,325.97 | 6465.435, 9272.794 |
| Average Active Power loss (All Scenarios) | 26,617.93 | 11,743.23 | 12,502.73 | 11,794.14 |
| Average Reactive Power loss (All Scenarios) | 26,805.49 | 13,999.75 | 14,412.65 | 13,813.91 |
| Active Energy loss (All Scenarios) (kWh) | 638,830.3 | 281,838 | 300,065.4 | 283,059.7 |
| Reactive Energy Losses (All Scenarios) (kvarh) | 643,331.89 | 335,994.1 | 345,903.6 | 331,534.010 |
| Algorithms | Branch 1 | Branch 2 | Branch 3 | Branch 4 | Branch 5 | Branch 6 | Branch 7 | Branch 8 | Branch 9 | Branch 10 | Branch 11 | Branch 12 | Branch 13 | Branch 14 | Branch 15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before DG | 789.4 | 159.9 | 4678.5 | 50.1 | 9.7 | 442.7 | 1.7 | 473.2 | 882.7 | 14.4 | 59.0 | 3214.7 | 8124.1 | 2405.8 | 5312.2 |
| GA | 320.1 | 249.1 | 2724.1 | 172.4 | 9.3 | 437.6 | 1.5 | 488.2 | 1381.5 | 68.8 | 239.8 | 1697.0 | 2074.6 | 535.3 | 1343.9 |
| APSO | 163.4 | 230.0 | 2845.2 | 158.8 | 9.1 | 431.0 | 1.6 | 500.7 | 1337.9 | 60.5 | 212.8 | 1792.6 | 2489.7 | 642.7 | 1626.6 |
| Proposed BRO | 263.2 | 235.1 | 2671.2 | 170.2 | 9.2 | 434.3 | 1.5 | 495.6 | 1374.3 | 67.0 | 234.5 | 1661.6 | 2194.6 | 584.0 | 1398.0 |
| Algorithms | Branch 1 | Branch 2 | Branch 3 | Branch 4 | Branch 5 | Branch 6 | Branch 7 | Branch 8 | Branch 9 | Branch 10 | Branch 11 | Branch 12 | Branch 13 | Branch 14 | Branch 15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before DG | 1129.3 | 228.3 | 6709.9 | 71.6 | 13.9 | 634.6 | 2.4 | 674.2 | 1268.8 | 20.7 | 85.1 | 4595.2 | 5829.0 | 1730.1 | 3812.3 |
| GA | 458.0 | 355.6 | 3906.9 | 246.3 | 13.2 | 627.2 | 2.2 | 695.8 | 1985.9 | 99.0 | 345.9 | 2425.8 | 1488.5 | 385.0 | 964.4 |
| APSO | 233.7 | 328.4 | 4080.6 | 226.9 | 13.1 | 617.8 | 2.3 | 713.6 | 1923.2 | 87.0 | 307.1 | 2562.4 | 1786.4 | 462.2 | 1167.3 |
| Proposed BRO | 376.5 | 335.7 | 3831.0 | 243.1 | 13.1 | 622.5 | 2.2 | 706.3 | 1975.5 | 96.4 | 338.2 | 2375.1 | 1574.6 | 420.0 | 1003.3 |
| Algorithms | Bus 1 | Bus 2 | Bus 3 | Bus 4 | Bus 5 | Bus 6 | Bus 7 | Bus 8 | Bus 9 | Bus 10 | Bus 11 | Bus 12 | Bus 13 | Bus 14 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before DG | 1.0300 | 1.0300 | 1.0138 | 0.9365 | 0.9444 | 0.9370 | 0.9168 | 0.9137 | 0.8906 | 0.9403 | 0.9389 | 0.9302 | 0.6654 | 0.7762 |
| GA | 1.0300 | 1.0300 | 1.0797 | 1.0447 | 1.0626 | 1.0554 | 1.0353 | 1.0322 | 1.0088 | 1.0712 | 1.0629 | 1.0488 | 0.9358 | 0.9735 |
| APSO | 1.0300 | 1.0300 | 1.0768 | 1.0359 | 1.0530 | 1.0458 | 1.0259 | 1.0227 | 0.9990 | 1.0605 | 1.0527 | 1.0391 | 0.9088 | 0.9545 |
| Proposed BRO | 1.0300 | 1.0300 | 1.0770 | 1.0434 | 1.0612 | 1.0539 | 1.0340 | 1.0309 | 1.0073 | 1.0696 | 1.0613 | 1.0473 | 0.9293 | 0.9699 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abbas, A.; Qaisar, S.M.; Waqar, A.; Ullah, N.; Al Ahmadi, A.A. Min-Max Regret-Based Approach for Sizing and Placement of DGs in Distribution System under a 24 h Load Horizon. Energies 2022, 15, 3701. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15103701
Abbas A, Qaisar SM, Waqar A, Ullah N, Al Ahmadi AA. Min-Max Regret-Based Approach for Sizing and Placement of DGs in Distribution System under a 24 h Load Horizon. Energies. 2022; 15(10):3701. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15103701
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbbas, Asad, Saeed Mian Qaisar, Asad Waqar, Nasim Ullah, and Ahmad Aziz Al Ahmadi. 2022. "Min-Max Regret-Based Approach for Sizing and Placement of DGs in Distribution System under a 24 h Load Horizon" Energies 15, no. 10: 3701. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15103701
APA StyleAbbas, A., Qaisar, S. M., Waqar, A., Ullah, N., & Al Ahmadi, A. A. (2022). Min-Max Regret-Based Approach for Sizing and Placement of DGs in Distribution System under a 24 h Load Horizon. Energies, 15(10), 3701. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15103701







