Validated Analytical Model of 8/6 and 10/8 Switched Reluctance Motors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Vast customization of model elements which is essential to test different scenarios;
- Optimization algorithm;
- Model can be used in order to witness physical phenomena in 3D environment;
- Accurate calculations;
- Validated by an experiment.
2. State of the Art
3. Analytical Method for Calculating the Torque of the SRM Applied in the Model
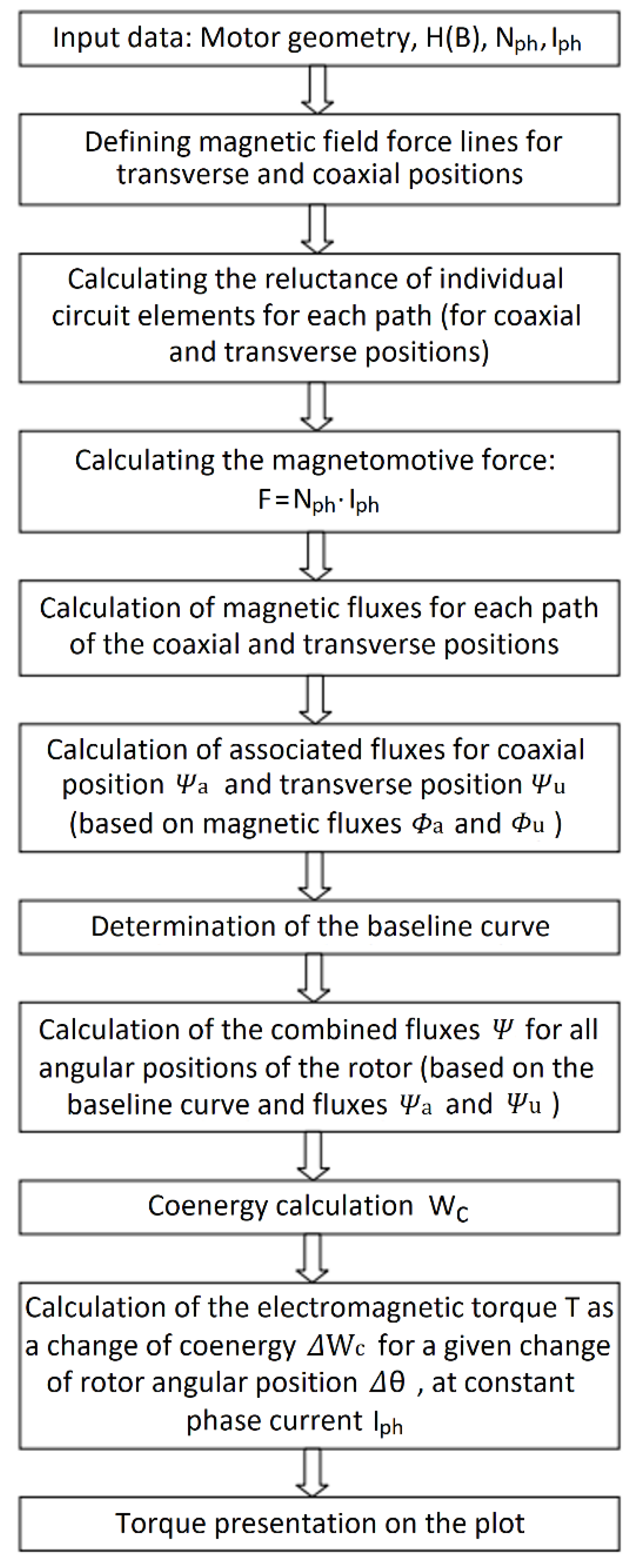
3.1. Detailed Description of the Method
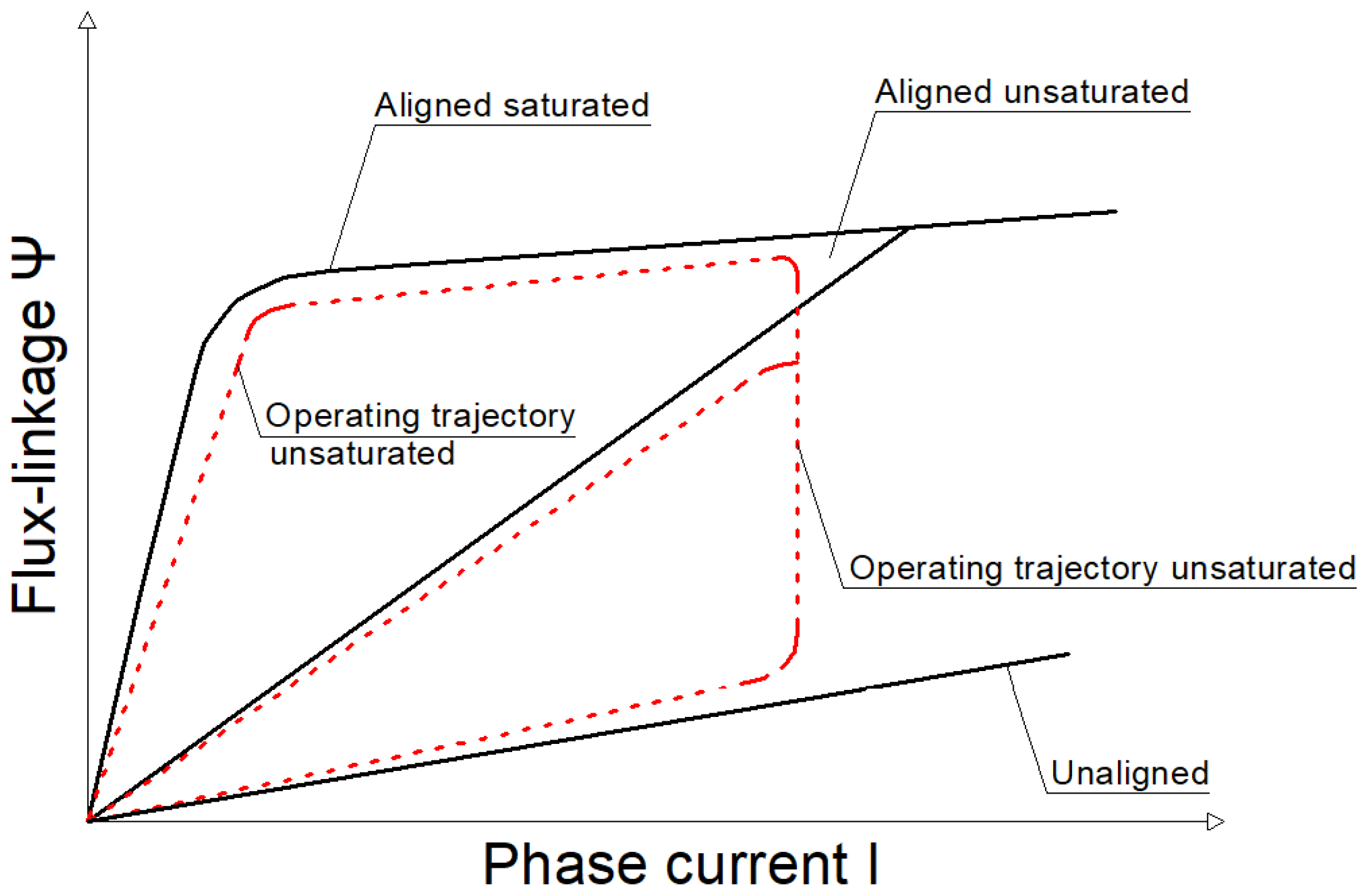
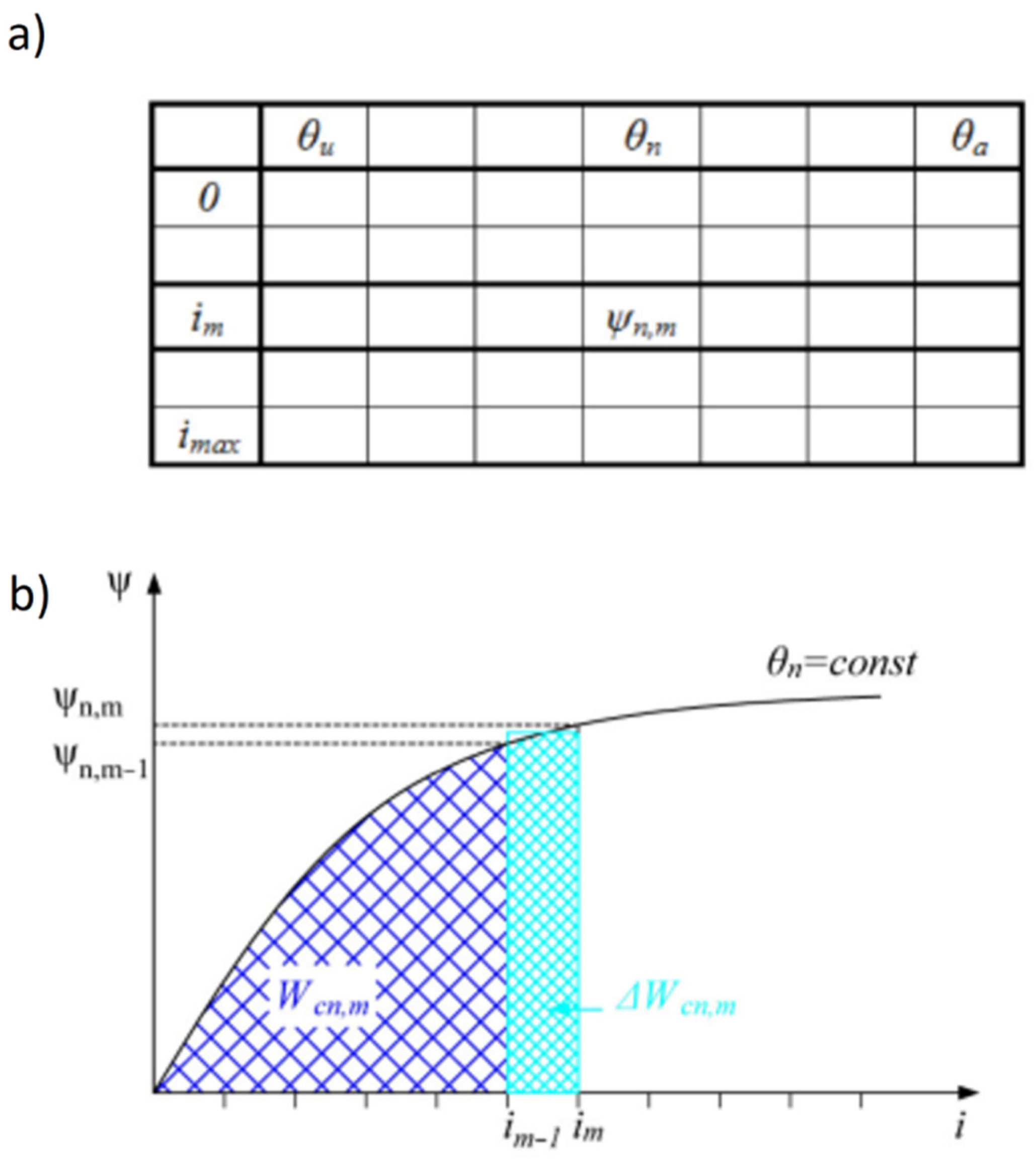
3.2. Conversion of Electro Mechanical Energy
3.3. Calculations of the Static Torque Characteristics
3.4. Structure of the Analytical Model
3.5. Analytical Model Assumptions
- The model will describe the operation of switchable reluctance motors with parallel faces to the stator and rotor poles. This assumption was made due to the much greater popularity of the design of straight-pole motors than of trapezoidal pole-shaped motors;
- The magnetic flux disburdening effect, described in more detail in publication [25], was omitted;
- When calculating the associated fluxes for track 2 in the coaxial position and for all seven tracks in the transverse position, it was assumed that the sum of the reluctances of the individual magnetic guide elements and the air gap is equal to the air gap reluctance. In electric motors, the air gap is the main source of magnetic resistance and preferably should be as low as possible. In the case of switched reluctance motors, the air gap changes its geometry (mainly length) depending on the angular position of the rotor. The maximum length is achieved for the transverse position and the resistance of the slit in this position to the flowing magnetic flux is so great that the reluctances of the individual elements of the magnet guide are negligibly small;
- The entire flux is enclosed in the magnetic circuit, i.e., there is no flux bypass effect at the ends of the stator and rotor package;
- The field force lines in the stator and rotor poles are parallel to the poles;
- The windings are treated as rectangular blocks and the space between the poles of the stator is only partially filled with the windings;
- The field force lines in the stator and rotor yokes are concentric;
- The field force lines in the air-gap consist of concentric arcs and rectilinear segments;
- The magnetic conductivity of the shaft is ignored;
- In order to calculate associated fluxes for all rotor positions only one standard curve was used.
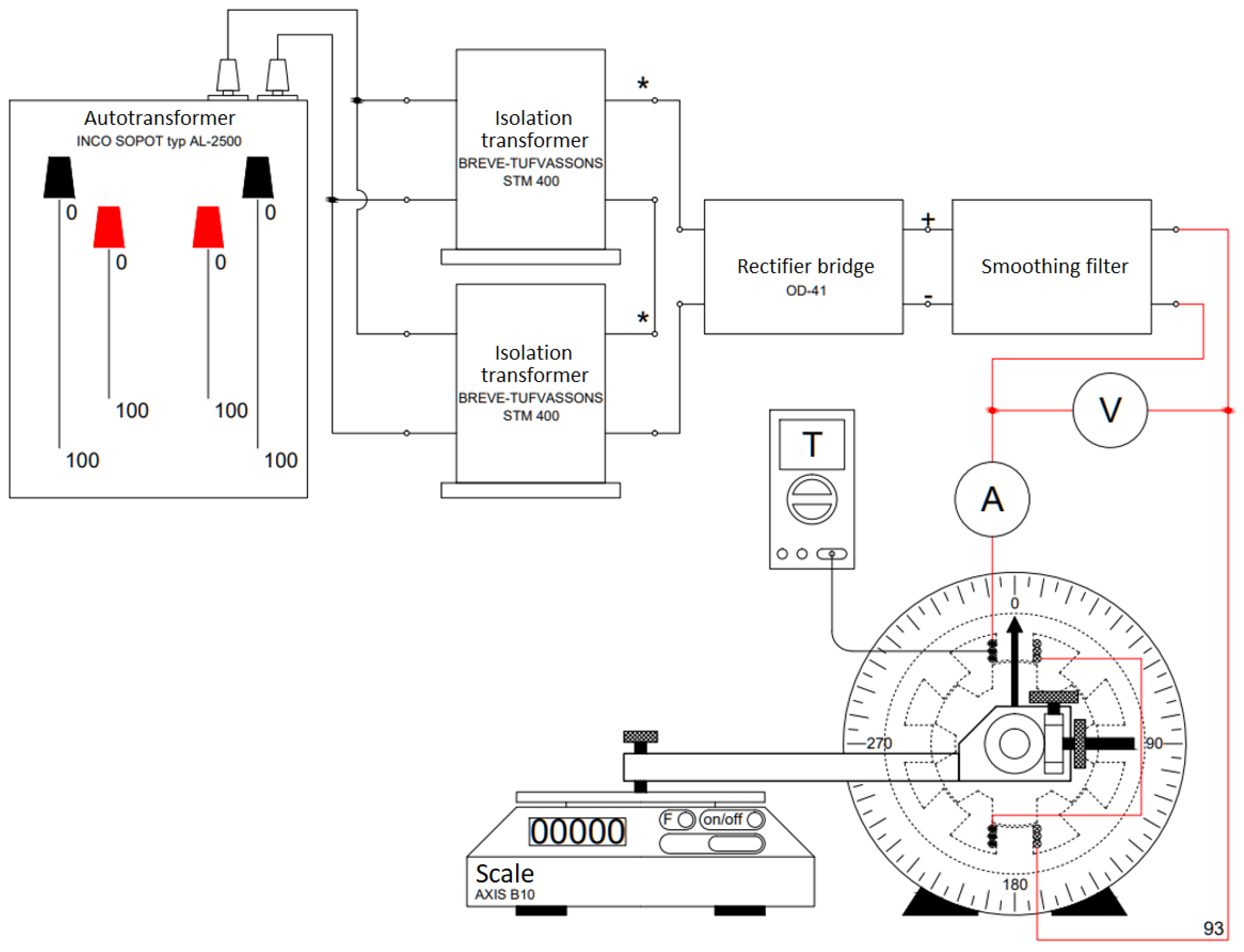
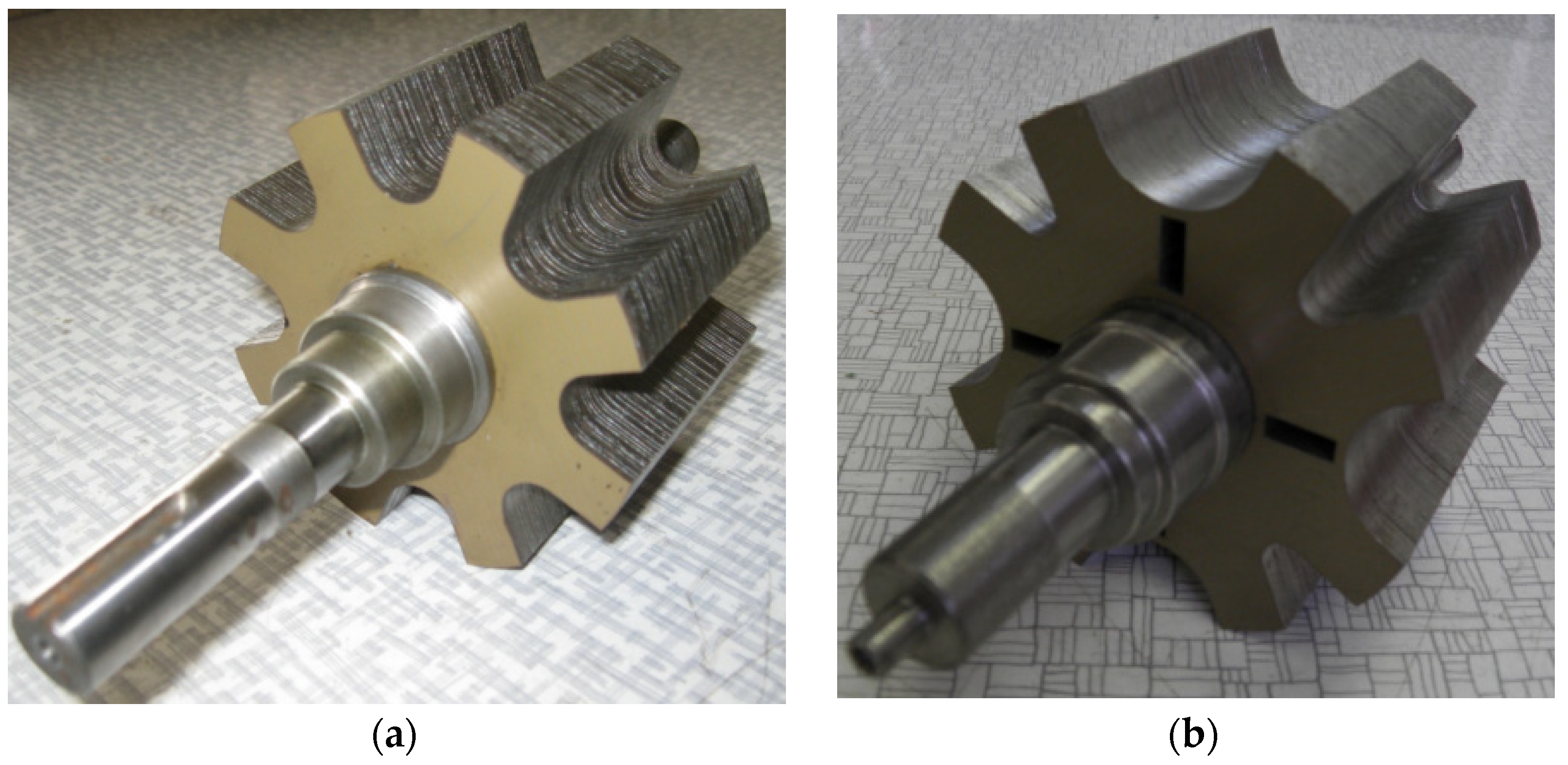
4. Laboratory Measurements of Modeled 8/6 and 10/8 Motors
- SRM 8/6 with symmetrical straight poles rotor;
- SRM 8/6 with symmetrical oblique poles rotor;
- SRM 10/8 with symmetrical straight poles rotor;
- SRM 10/8 with an asymmetrical straight poles rotor.
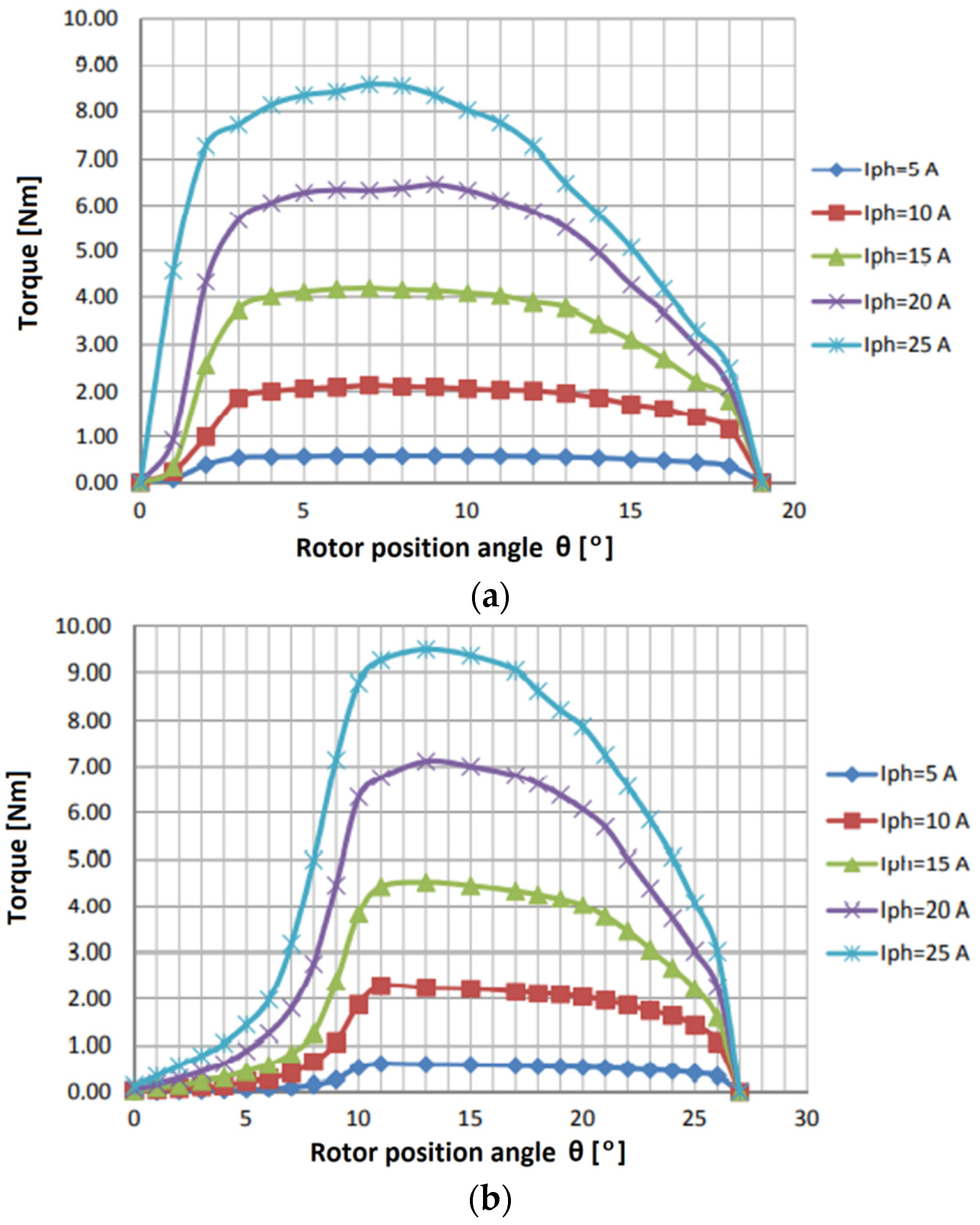
4.1. Measurement Results of the Static Torque Produced by the SRM 8/6 Motor with a Symmetrical Straight Poles and Oblique Poles Rotor
4.2. Measurement Results of the Static Torque Produced by the SRM 10/8 Motor with a Symmetrical and Asymmetrical Straight Poles
5. Analytical Model Calculations and FEM Simulation Results
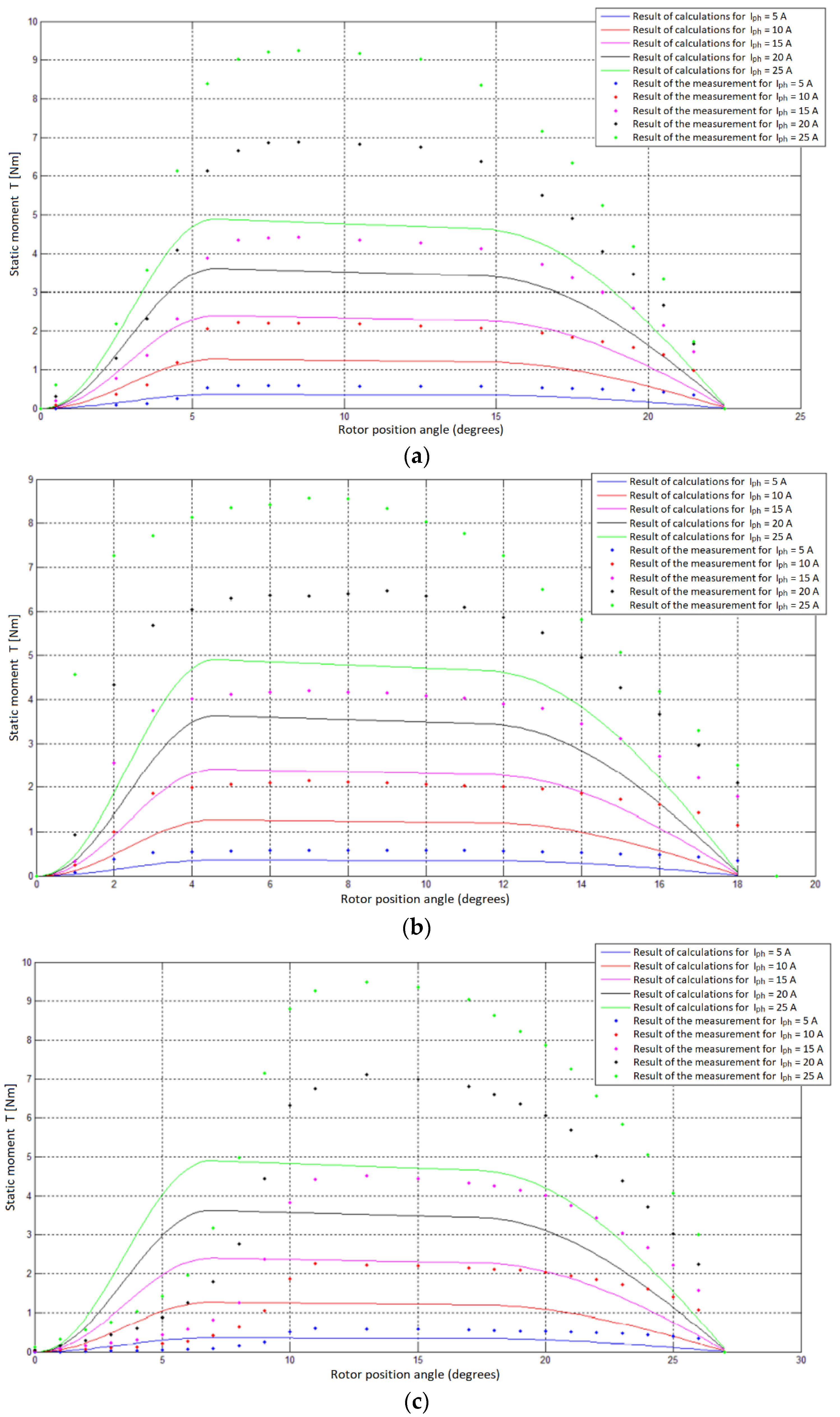
5.1. Juxtaposition of Laboratory Measurements and the Results of Calculations Obtained with the Use of the Developed Analytical Model
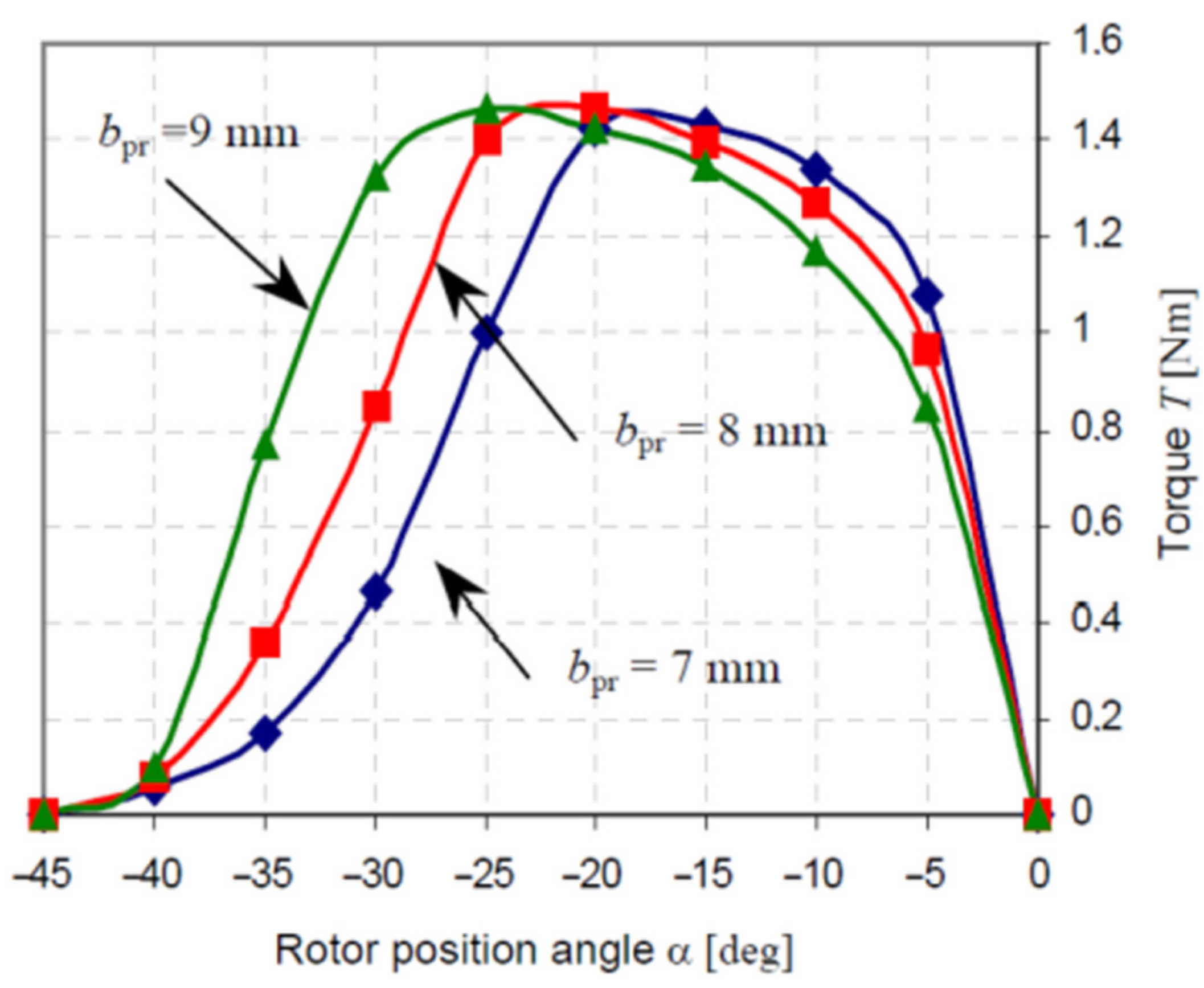
5.2. Impact of Rotor Pole Width Parameter
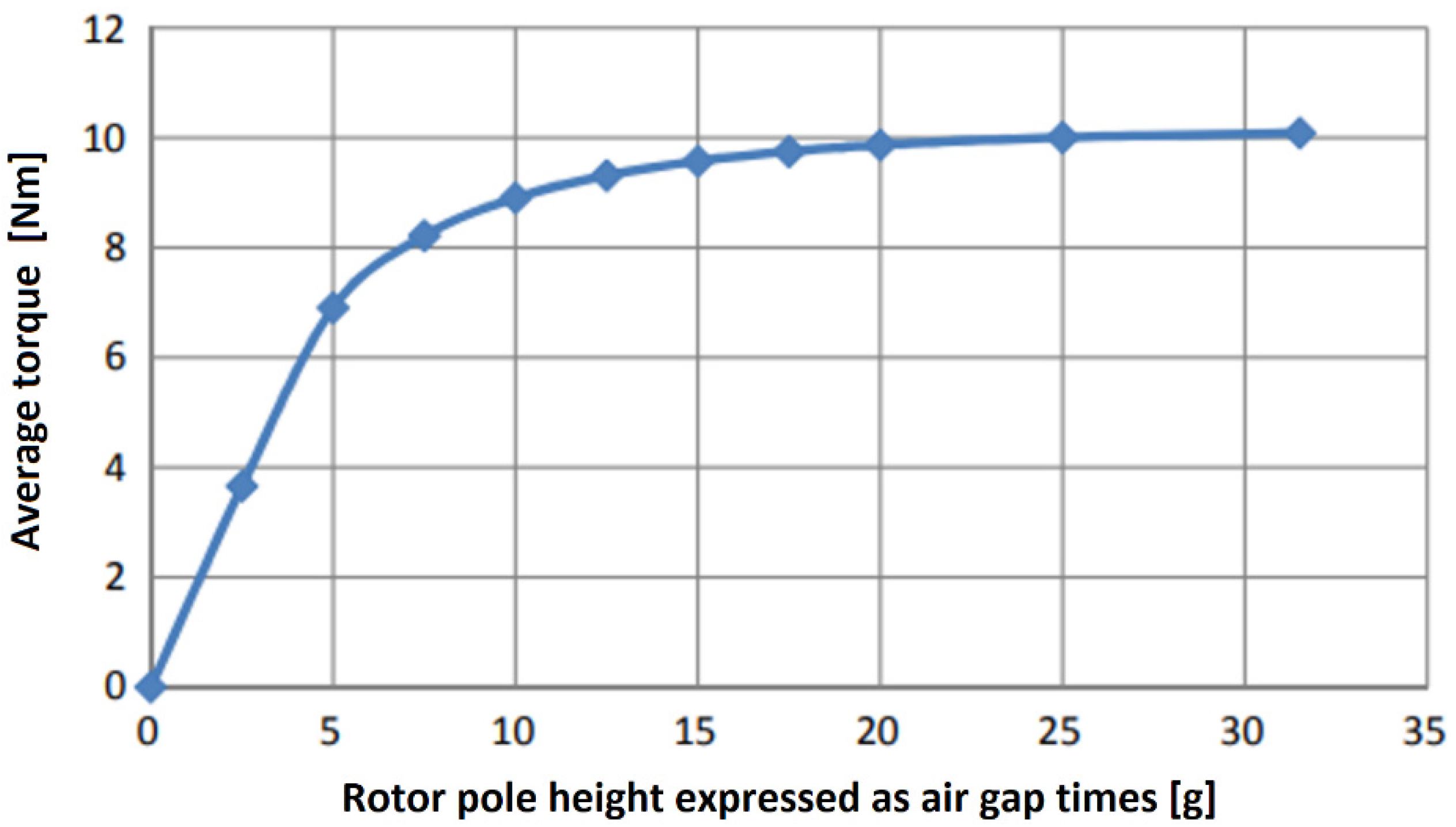
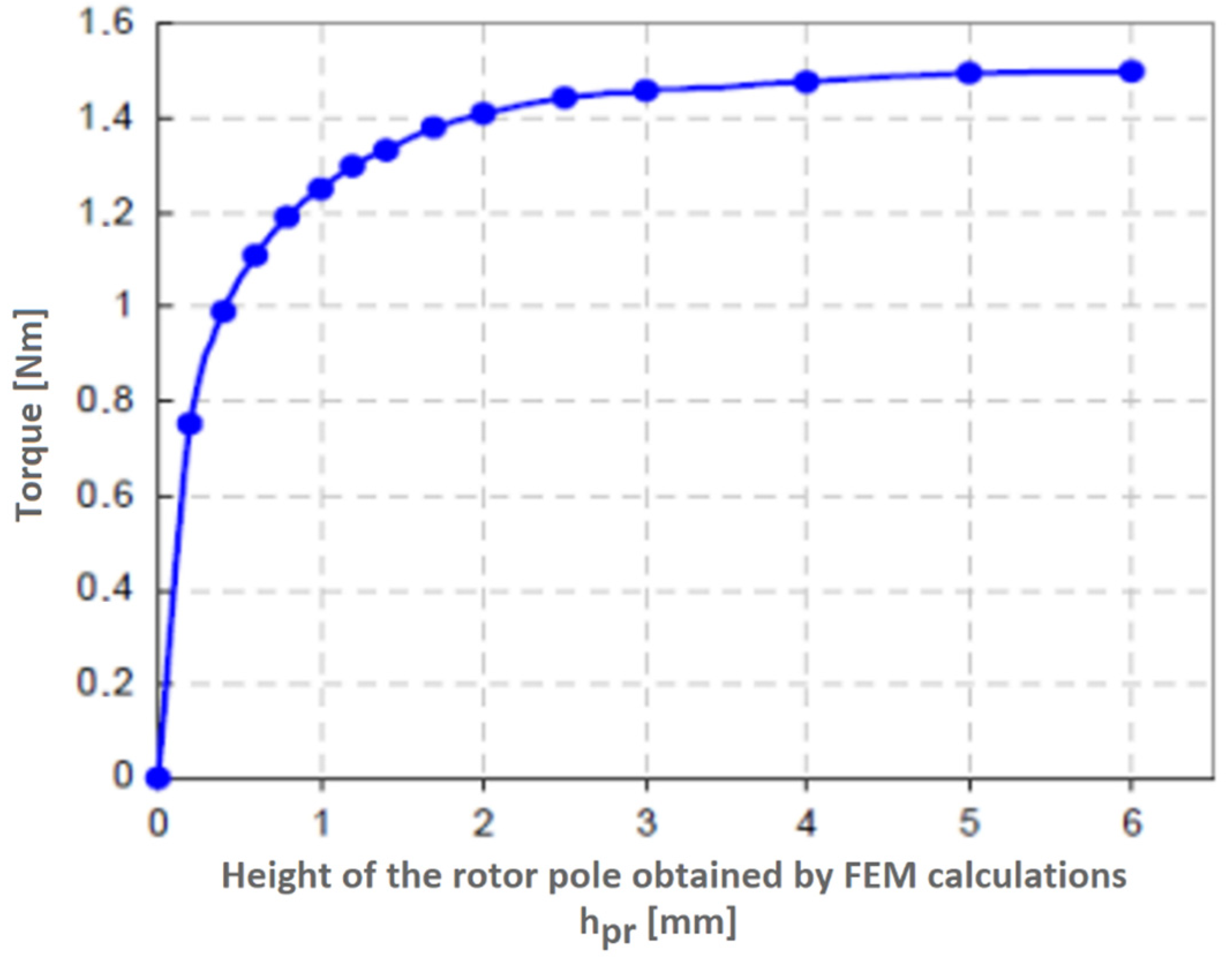
5.3. Impact of Rotor Pole Height Parameter
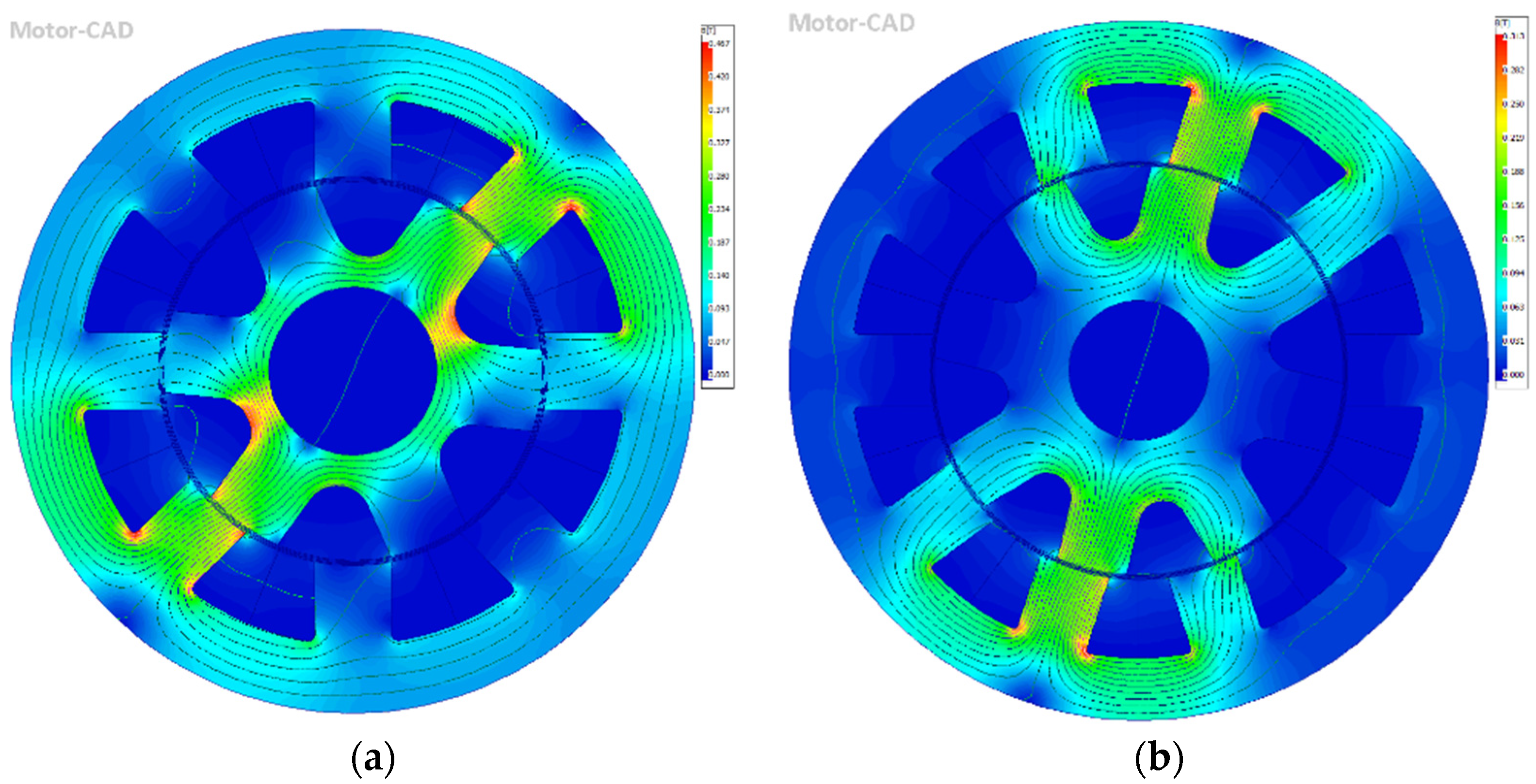
5.4. FEM Model Results
6. Conclusions and Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tong, J.; Zou, Y. Design of a fuse-time testing system on STM32. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Computer Sciences and Applications, Wuhan, China, 17–19 October 2013; pp. 406–409. [Google Scholar]
- Makwana, J.A.; Pramod, A.; Srivastava, S.P. Auto-mation and Signal. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Energy, Bhubaneswar, India, 28–30 December 2011; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Hongbo, M.; Hongmei, L.; Liwen, L.; Mingna, M.; Zhiwei, C. SRM Design Based on the Sequence Sub-space Multi-Objective Optimization. In Proceedings of the 2018 21st International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Jeju, Korea, 7–10 October 2018; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Hadke, V.V.; Thakre, M.P. Integrated Multilevel Converter Topology for Speed Control of SRM Drive in Plug in-Hybrid Electric Vehicle. In Proceedings of the 2019 3rd International Conference on Trends in Electronics and Informatics (ICOEI), Tirunelveli, India, 23–25 April 2019; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Nayak, A.R.; Babu, E.; Kumaravel, S. Performance Analysis of Grid Powered Asymmetrical Bridge Converter Driven SRM. In Proceedings of the 2018 15th IEEE India Council International Conference (INDICON), Coimbatore, India, 16–18 December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lotiya, J. Thermal analysis and optimization of temperature rise in busbar joints configuration by FEM. In Proceedings of the 2014 6th IEEE Power India International Conference (PIICON), Delhi, India, 5–7 December 2014; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Yaman, G. A thermal analysis for a switchgear system. J. Balikesir Univ. Inst. Sci. Technol. 2019, 21, 72–80. [Google Scholar]
- Kolimas, Ł.; Łapczyński, S.; Szulborski, M.; Świetlik, M. Low voltage modular circuit breakers: FEM employment for modeling of arc chambers. Bull. Pol. Acad. Sci. Tech. Sci. 2020, 68, 61–70. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, B.; Song, Z.; Fu, P.; Jiang, L.; Wang, M.; Dong, L. Prediction of Temperature Rise in Water-Cooling DC Busbar Through Coupled Force and Natural Convection Thermal-Fluid Analysis. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2016, 44, 3346–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, M.K.; Thompson, J.M. ANSYS Mechanical APDL for Finite Element Analysis; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2017; ISBN 978-0-12-812981-4. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, J.; Deng, Y. Initial Rotor Position Estimation and Sensorless Control of SRM Based on Coordinate Transformation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2015, 64, 1004–1018. [Google Scholar]
- Masi, A.; Danisi, A.; Losito, R.; Perriard, R. Characterization of magnetic immunity of an ironless inductive position sensor. IEEE Sens. J. 2013, 13, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieńkowski, K.; Szulborski, M.; Łapczyński, S.; Kolimas, Ł.; Cichecki, H. Parameterized 2D Field Model of a Switchable Reluctance Motor. Electricity 2021, 2, 590–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yongdae, K.; Choi, H.Y.; Lee, Y.C.H. Design and preliminary evaluation of high-temperature position sensors for aerospace applications. IEEE Sens. J. 2014, 14, 4018–4025. [Google Scholar]
- Khoshnoud, F.; Silva, C.W. Recent advances in MEMS sensor technology mechanical applications. IEEE Instrum. Meas. Mag. 2012, 15, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, C.B.; Fielke, J.M. Recent developments in strored grain sensors, monitoring and management technology. IEEE Instrum. Meas. Mag. 2017, 20, 32–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaney, M.J.; Eren, L. Detecting motor bearing faults. IEEE Instrum. Meas. Mag. 2004, 4, 30–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, P.; Ding, F.; Li, Q. Novel High-Response Electromagnetic Actuator for Electronic Engraving System. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2006, 42, 460–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, Y.; Honda, T.; Kasamura, K.; Nakashima, Y.; Nakano, K.; Kondo, K.; Higaki, H. Bio-inspired shaft seal in coolant pump for electric vehicles. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Renewable Energy Research and Applications (ICRERA), Birmingham, UK, 20–23 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, T.J.E.; Glinka, M.; McGilp, M.; Cossar, C.; Gallegos-Lopez, G.; Ionel, D.; Olaru, M. Ultra-fast model of the switched reluctance motor. In Proceedings of the Thirty-Third IAS Annual Meeting on Industry Applications Conference, St. Louis, MO, USA, 12–15 October 1998; pp. 319–326. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, R.E.; Jewell, G.W.; Forrest, S.J.; Rens, J.; Maerky, J. Design Features for Enhancing the Performance of Electromagnetic Valve Actuation Systems. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2005, 41, 692–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Ding, F.; Wang, C. Novel bidirectional linear actuator for electrohydraulic valves. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2005, 41, 2199–2201. [Google Scholar]
- An, Y.; Liu, G.; Wang, P.; Wen, H.; Meng, Z. Magnetic force analysis and experiment of novel permanent magnet axial thrust balance structure in canned motor pump. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2nd International Conference on Advanced Computer Control, Shenyang, China, 27–29 March 2010; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Chang, J. A New Electromagnetic Linear Actuator for Quick Latching. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2007, 43, 1849–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, C.; Tozzi, P.; Hurni, M.; Segesser, Ł.K. No drive line, no seal, no bearing and no wear: Magnetics for impeller suspension and flow assessment in a new VAD. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2004, 3, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Seethaler, R.J. A fully flexible valve actuation system for internal combustion engines. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2011, 16, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdalyan, B.; Dogan, O. Effect of a semi electro-mechanical engine valve on performance and emissions in a single cylinder spark ignited engine. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 2010, 11, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taji, B.; Chan, A.D.C.; Shirmohammadi, S. Effect of Pressure on Skin-Electrode Impedance in Wearable Biomedical Measurement Devices. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2018, 67, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogusz, P.; Korkosz, M. Switched Reluctance Motor—Theoretical Basis; Electric Drives Control Laboratory: Warsaw, Poland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Sheth, N.K.; Rajagopal, K.R. Calculation of the Flux-Linkage Characteristic of a Switched Reluctance Motor by Flux Tube Method. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2005, 41, 4069–4071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairall, W.E.; Berker, B.; Enodi, A. State-of-the-art high-speed switched reluctance machines. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Electric Machines & Drives Conference (IEMDC), Coreur d’Alene, ID, USA, 10–13 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hiller, M. Dynamic Torque Control for Switched Reluctances Drives based on a new Online Machine Model. In Proceedings of the EPE 2005, Dresden, Germany, 11–14 September 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Jun, C.; Zhiquan, D.; Zeyuan, L. Nonlinear Modeling of Switched Reluctance Motor Using Different Methods. In Proceedings of the 2010 Twenty-Fifth Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC), Palm Springs, CA, USA, 21–25 February 2010; pp. 1018–1025. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Xu, Y.; Fu, D.; Zhong, Y. Development of 8/4-pole high speed two-phase SRM used in a griding machine. In Proceedings of the 2015 18th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Pattaya, Thailand, 25–28 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Pittermann, M.; Fort, J.; Diesl, J.; Pavicek, V. Optimal SRM-Control Algorithm to Achieve Maximum Torque and Real Converte Limits. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Mechatronics (ME), Brno, Czech Republic, 5–7 December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Vijayakumar, K.; Karthikeyan, R.; Arumugam, R.; Premsunder, G.; Kannan, S. Coupled Field Finite Element Analysis of Switched Reluctance Motor with Soft Magnetic Compisite Material for Thermal Characterization. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Industrial and Information Systems (ICIIS), Moratuwa, Sri Lanka, 28–31 December 2009; pp. 532–535. [Google Scholar]
- Omekanda, A.M. Robust Torque and Torque-per-Inertia Optimalization of a Switched Reluctance Motor Using the Tauguichi Methods. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Electric Machines and Drives, San Antonio, TX, USA, 15 May 2005; pp. 473–478. [Google Scholar]
- Jingjun, Z.; Haijun, Z.; Ruizhen, G. Fuzzy Compensation Control for Switched Reluctance Motor System Based on Finite Element Model. In Proceedings of the IEEE SoutheastCon 2008, Huntsville, AL, USA, 3–6 April 2008; pp. 480–484. [Google Scholar]
- Wichert, T. Design and Construction Modification of Switched Reluctance Machines. Ph.D. Thesis, Institute of Electrical Machines, Warsaw University of Technology, Warsaw, Poland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Belliwali, S.; Chakravarti, A.; Raju, A.B. Mathematical modelling and simulation of directly coupled PV water pumping system employing Switched Reluctance Motor. In Proceedings of the ISGT2011-India, Kollam, India, 1–3 December 2011; pp. 386–390. [Google Scholar]
- Takeno, M.; Chiba, A.; Hoshi, N.; Ogasawara, S.; Takemoto, M.; Rahman, M.A. Test Results and Torque Improvement of the 50-kW Switched Reluctance Motor Designed for Hybrid Electric Vehicles. IEEE J. Mag. 2012, 48, 1327–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyota, K.; Chiba, A. Design of Switched Reluctance Motor Competitive to 60-kW IPMSM in Third-Generation Hybrid Electric Vehicle. IEEE J. Mag. 2012, 48, 2303–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jong-Han, L.; Eun-Woong, L.; Jun-Ho, K. Design of the single phase SRM for the blower considering self-starting. In Proceedings of the 2005 International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems, Nanjing, China, 27–29 September 2005; pp. 667–670. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.W.; Chou, K.F.; Yeh, M.J.; Wang, C.C.; Yu, S.L.; Yang, C.C.; Chang, Y.C.; Liaw, C.M. Design and control of a switched-reluctance motor-driven cooling fan. IET J. Mag. 2012, 5, 1813–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najmi, N.; Siadatan, A.; Afjei, E. Analysis of 8/6 two-layer switched reluctance motor with rotor shifting technique for servo applications. In Proceedings of the 2012 3rd Power Electronics and Drive Systems Technology (PEDSTC), Tehran, Iran, 15–16 February 2012; pp. 273–277. [Google Scholar]
- Farukh, A.; Yingyun, S.; Rehman, U. Electric Propulsion Unit Powered by Switch Reluctance Machine SRM. In Proceedings of the 2015 Seventh International Conference on Computational Intelligence Modeling and Simulation (CIMSim), Kuatanton, Malayna, 27–29 July 2015. [Google Scholar]










| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 160 | 160 | 120 | 120 | 120 | |
| 8 | 8 | 10 | 10 | 10 | |
| 6 | 6 | 8 | 8 | 8 | |
| l [m] | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 |
| [m] | 0.014 | 0.014 | 0.014 | 0.014 | 0.014 |
| [m] | 0.016 | 0.01325 | 0.0138 | 0.0138 | 0.0138 |
| D [m] | 0.074 | 0.074 | 0.0956 | 0.0956 | 0.0956 |
| [m] | 0.1305 | 0.1305 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.16 |
| [m] | 0.032 | 0.032 | 0.032 | 0.032 | 0.032 |
| [m] | 0.0732 | 0.0732 | 0.0948 | 0.0948 | 0.0948 |
| [m] | 0.0126 | 0.0126 | 0.0165 | 0.0154 | 0.0154 |
| [m] | 0.008 | 0.008 | 0.0149 | 0.016 | 0.016 |
| [m] | 0.01325 | 0.01325 | 0.0184 | 0.0184 | 0.0184 |
| [m] | 0.015 | 0.015 | 0.0092 | 0.0092 | 0.0092 |
| Air Gap Multiplication | T [Nm] | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 2.5 | 3.65 |
| 2 | 5 | 6.90 |
| 3 | 7.5 | 8.21 |
| 4 | 10 | 8.90 |
| 5 | 12.5 | 9.31 |
| 6 | 15 | 9.57 |
| 7 | 17.5 | 9.74 |
| 8 | 20 | 9.86 |
| 10 | 25 | 10.00 |
| 12.6 | 31.5 | 10.08 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bieńkowski, K.; Łapczyński, S.; Szulborski, M.; Kozarek, Ł.; Gołota, K.; Cichecki, H.; Kolimas, Ł.; Żelaziński, T.; Smolarczyk, A.; Babiński, A.; et al. Validated Analytical Model of 8/6 and 10/8 Switched Reluctance Motors. Energies 2022, 15, 630. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15020630
Bieńkowski K, Łapczyński S, Szulborski M, Kozarek Ł, Gołota K, Cichecki H, Kolimas Ł, Żelaziński T, Smolarczyk A, Babiński A, et al. Validated Analytical Model of 8/6 and 10/8 Switched Reluctance Motors. Energies. 2022; 15(2):630. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15020630
Chicago/Turabian StyleBieńkowski, Krzysztof, Sebastian Łapczyński, Michał Szulborski, Łukasz Kozarek, Karol Gołota, Hubert Cichecki, Łukasz Kolimas, Tomasz Żelaziński, Adam Smolarczyk, Adam Babiński, and et al. 2022. "Validated Analytical Model of 8/6 and 10/8 Switched Reluctance Motors" Energies 15, no. 2: 630. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15020630
APA StyleBieńkowski, K., Łapczyński, S., Szulborski, M., Kozarek, Ł., Gołota, K., Cichecki, H., Kolimas, Ł., Żelaziński, T., Smolarczyk, A., Babiński, A., & Owsiński, M. (2022). Validated Analytical Model of 8/6 and 10/8 Switched Reluctance Motors. Energies, 15(2), 630. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15020630








