Abstract
A huge amount of industrial waste will be generated during the industrialization process and their harmless disposal has always been a headache for reducing carbon emissions. In this study, the combustion behaviors and thermal kinetics of four typical industrial polymeric wastes including rubber, leather, plastic and cloth, were systematically studied by using a Thermogravimetric Analysis. The gas emission and structural evolution was comprehensively analyzed using TG-FTIR, 2D-PCIS, ICP and TEM. The results show that the combustibility of leather and cloth are better than the other two samples, while the rubber and plastic have a wider combustion temperature range for higher content of C-H bonds and, the intermediate oxidation process and the stubborn cracking process of C=C bonds. The surface reaction was considered to be the main reaction of rubber and plastic (pre-exponential factor less than 10−9), while both leather and cloth went through a complex procedure during multiple decomposition. The volatiles products are gases (e.g., CO2, CH4) and small molecules (e.g., H2O). The high levels of basic metals in the industrial waste causes serious slagging and fouling tendency (fouling index higher than 4.0), which have a serious adverse influence on the operation of a waste incineration plant.
1. Introduction
Solid waste is increasing in large quantities with the growth of the population, the rapid development of society and the alteration of people’ s consumption habits [1]. In these solid wastes, waste polymeric materials account for a large proportion. On the one hand, the rapid development of petrochemical industry produces a large number of synthetic resins, especially thermoplastic polymers used in plastics, fibers and other aspects, resulting in the gradual increase in artificial waste polymer materials [2,3]. On the other hand, the improvement of people’s living standard makes the explosion in the application of natural polymer materials such as silk, cotton, wool, and leather, etc., resulting in a gradual increase in derived polymeric solid waste [4]. However, the harmless disposal of such increasing polymeric wastes is relatively backward, so that the pollution caused by garbage has become a prominent problem in the environmental field [3]. Furthermore, the organic solid waste contains a large number of recyclable components. If the components can be rationally utilized, it can not only realize the high-value recycling and utilization of the wastes, but also reduce carbon emissions, which is of great significance to the sustainable development of human society and economy. Hence, the high-value reutilization of abandoned polymeric wastes have aroused global attention.
Polymeric waste disposal should achieve the ultimate goal of its reduction, harmlessness and resource-orientation. The common treatment methods of polymeric waste include sanitary landfill [5], incineration [6] and aerobic composting [7], while new recycling methods such as pyrolysis [8,9,10] and biological treatment technology [11] have gradually emerged. Among them, the proportion of landfill decreased in recent years because of the large occupation of area and low effect of minimization; the strict requirement of garbage sorting is the premise of composting treatment, which subsequently causes serious pollution. Incineration disposal gradually occupied a large proportion and rapidly develops on account of its obvious reduction effect, high degree of harmlessness and preferable resources utilization [12]. This approach has an outstanding performance on volume reduction because incineration converts waste into gas phase products, water, and a little ash slag. The harmful substances can also be better controlled by high temperature treatment so as to achieve the effect of harmlessness in this process, which releases large heat energy to achieve resource utilization. With the intensification of the energy crisis, waste incineration technology has been rapidly developing in recent years. However, the operation effect of boilers has not reached anticipative efficiency for the complex composition, high moisture, and low calorific value of municipal solid waste.
Oxygen-enriched combustion improves the temperature in the furnace, contributes to the full combustion of fuel, effectively inhibiting the pollutants such as dioxin, and solves the problem of combustion difficulties caused by low oxygen content in some special circumstances (e.g., plateau area) [13]. The combustion status of the polymeric waste also depends on its differentiated components [14], so it is very necessary to respectively study the combustion characteristics of typical components. The combustion characteristic and thermal kinetic parameters proved to be an important factor for the design and optimization of suitable combustion systems for polymer waste [15]. The thermogravimetric (TG) characteristics and kinetics of municipal solid waste (MSW) in a conventional air atmosphere have been studied extensively [16,17,18]. Moreover, thermogravimetric analyzer (TGA) has been used to evaluate the oxygen rich incineration behaviors of MSW, but the research mainly focused on CO2/O2 atmosphere [19,20,21]. Some studies [3,22] have focused on the co-combustion characteristics of high moisture content MSW and high sulfur lignite in laboratory scale fluidized beds, analyzing the effects of excess air coefficient, secondary air rate, MSW co-firing rate and water content on gas emission characteristics.
In this study, the four typical industrial polymeric wastes including waste rubber, waste leather, waste plastic and waste cloth were selected as the raw material. Based on the evaluation of its inherent properties, the combustion characteristics were comprehensively investigated. The combustion parameters and combustion kinetics under different heating rates were systematically and comparatively studied. The gas emission and solid phase evolution was analyzed by the TG-FTIR and 2D-PCIS process. The generated residual ash was as well-characterized by using ICP and TEM. Based on this, the incineration characteristics of four typical polymeric wastes as fuels were obtained, which will provide a directional database for recycling and resource recovery of organic solid waste.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
The four polymeric wastes were obtained from Everbright Environmental Protection Technology Equipment Co., Ltd., Changzhou, Jiangsu province, China. The industrial wastes were dried naturally over 24 h, and then were ground into powder by crusher and sieve for further experiments.
2.2. Proximate Analysis
The polymeric wastes were analyzed for moisture, volatile matter, fixed carbon and ash contents. Moisture was tested at 105 ± 5 °C using a drying oven (DZF-6050, HF-Kejing, Hefei, China) and the contents of volatile matter and ash were determined in a muffle furnace (KSL-1100X, HF-kejing, China) in accordance with the Chinese standard method (GB/T 28731-2012). The fixed carbon was calculated according to Equation (1).
2.3. Ultimate Analysis
The elemental components of waste samples, including carbon, nitrogen, hydrogen, sulfur and chlorine, were analyzed using an Elemental Analyzer Vario MACRO cube (Elementar, Langenselbold, Germany) according to the standard method of ASTM D1762-84. The content of oxygen was calculated by the subtraction method. The lower heating value (LHV) and higher heating value (HHV) were estimated with modified formula [23] such as Equations (2) and (3).
2.4. Combustion Behavior Characteristics
2.4.1. Combustion Process
The combustion process of the polymeric wastes was carried out on a TA-Q500 thermogravimetric analyzer (TA Instruments, New Castle, DE, USA). Five experiments were conducted to obtain the data of solid mass loss in the air atmosphere (40 mL/min) from 50 °C to 800 °C, at the heating rate of 10, 20, 30, 40 and 50 °C/min, respectively. The weight of the sample was about 5 mg in each group experiment.
2.4.2. Determination of Combustion Indexes
The TG and DTG (derivative thermogravimetric) curves were utilized to obtain the combustion parameters such as ignition temperature (Ti), burnout temperature (Tb) and maximum peak temperature (Tp) [24]. Ti and Tb were determined by the tangent method according to the previous report [25,26]. Tp were identified by using a DTG curve, and it presented the maximum rate of mass loss of the sample [27]. To evaluate the combustion performance of the four solid wastes, combustion indexes, including the ignition index (Di, wt.%·min−3), burnout index (Db, wt.%·min−4), flammability index (Ci, wt.%·min−1·°C−2), comprehensive combustion index (Si, wt.%2·min−2·°C−3) and the intensity index of combustion process (Hf) were determined according to well-established equations [28,29,30] such as Equations (4)–(8).
2.4.3. Kinetic Theory
The feedstock conversion rate was defined as Equation (9), where m0 and m∞ were the residual mass initial and after combustion, respectively, and mT was the mass at the temperature of T. For a given conversion rate of α, the reaction rate was only related with T. Under the fixed heating rate of β, the reaction rate of the solid wastes combustion can be defined as Equation (10).
The four non-isothermal model methods, including DAEM, FWO, Kissinger and Starink, were used for thermal kinetic analyses. The DAEM method is considered to be an effective and accurate method to simulate a complex combustion process [31,32]. By avoiding the errors and deficiencies of traditional analytical methods, FWO method can more accurately estimate the reaction rate and mechanism of solid waste the combustion as a function of heating rate, final temperature, and mass of combustion products [33,34]. The Kissinger method assumes that the maximum reaction rate of the DTG curve occurs at peak temperature, avoiding the selection of the conversion function and thus estimating the maximum weight loss rate [35]. The Starink method is a recently developed equal-transformation method that derives Ea from the slope of a best-fitting linear regression model of ln(β/T1.92) and 1/T [36]. These methods were expressed below where slopes are used to estimate activation energy (Ea):
Take DEAM model as an example, ln(β/T2) has a linear relationship with −1/RT under certain α. In this study, the correlation between Ea and α was investigated under conversion rates from 0.05 to 0.95. The four dynamic parameters including the pre-exponential factor (A), enthalpy change (ΔH), Gibbs free energy (ΔG), and entropy (ΔS) were used to calculate Ea as Equations (15)–(18).
where KB, h and Tp attached in the Nomenclature section.
2.5. Volatile Analysis
The measurement of volatile products was carried out using a Thermo Gravimetric Analyzer of Jupiter STA 449 F3, in conjunction with a Fourier Transformation Infrared Spectrometer of Thermo TENSOR 27. The experiments were carried out at the heating rate of 20 °C/min within the temperature range from 50 to 950 °C. High purity nitrogen (99.9999%) was used as carrier gas (20 mL/min), and air was used as gasifying agent (40 mL/min) during the overall process. The sample weight was less than 10 mg. The combustion volatiles were quickly swept into the FTIR test cavity. In addition, the FTIR test cavity and transfer tube were preheated to 150 °C prior to each measurement. The spectral scanning range is 4000–667 cm−1 and the resolution were set at 4 cm−1.
2.6. Residual Phase Evolution and ASH Analysis
In the combustion process for the polymeric wastes, the residues obtained at different temperatures were observed through the analysis of FTIR, to understand the chemical composition evolution of the reactants. The functional groups in the residual phase were analyzed using on a Nicolet Nexus 380 FTIR spectrometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). The waste sample were mixed with a certain amount of potassium bromide in a mass ratio of 1:50, and then ground to a fine powder before the test. In each run, a 90 mg of the milled mixed sample was pressed and then loaded onto the infrared testing pool. Each spectrum was scanned cumulatively between 4000 and 600 cm−1 with a resolution of 4 cm−1. For mechanistic assessments, the one-dimensional FTIR spectra were further transformed into two-dimensional correlation spectrum by two-dimensional perturbation correlation infrared spectroscopy (2D-PCIS) method, according to the approach proposed by Noda et al. [37,38] The detailed calculation method was reported in previous literatures [39,40].
The content of inorganic metal salt ions in ash of different samples after combustion was detected by Inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy (PE Avio500 ICP-spectrometer) according to the general method of JY/T 0567-2020. The morphology of final ash was characterized by Transmission Electron Microscope (JEOL JEM-2010 FEG). The particle size of ash after the combustion of the waste plastics and waste cloth at 550 °C and 900 °C, were statistically analyzed. The stacking density of final ash was measured according to the Chinese standard method.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Ultimate and Proximate Analysis
This study analyzes the main organic elements of solid waste, which are the basic parameters for evaluating chemical properties, as shown in Table 1. Among them, carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and sulfur (S) are the combustible elements, while nitrogen (N), oxygen (O), and chlorine (Cl) are non-combustible elements. It can be found that carbon is the main component of the four industrial wastes, among which the C content of waste leather is the highest (62.01 wt.%), followed by waste rubber (52.19 wt.%), and the content of waste plastics and waste cloth is about 40 wt.%. This means that the waste leather will release more heat during combustion, as the carbon will emit more than 32 MJ/kg of heat under complete burning condition. As a secondary combustible element, the H content of all tested samples was lower than 7.0 wt.%, among which, the content of waste rubber and waste plastic was higher at 5.83 wt.% and 6.85 wt.%, respectively. Among the four samples, only the waste plastics contained very little sulfur, which meant that the incineration process produced less harmful emissions such as SOx. The low nitrogen content (<1.0 wt.%) also indicates that all solid waste incineration produces less harmful nitrogen gases (e.g., NOX). The oxygen element of the four wastes is about 30 wt.%, which contributes to the complete combustion of raw materials. As an important combustion-supporting element, oxygen atoms escape in the form of free state and small molecule oxides during combustion. The oxygen content of the four organic wastes is lower than that of lignocellulosic biomass (generally higher than 40 wt.%) [41,42,43], which may limit their combustion efficiency. Table 1 also shows the proximate analysis of the industrial waste samples. It is obvious that the physicochemical characteristics of such solid wastes show great differences, due to their diverse approaches of recycling, storage and transportation. For example, waste rubber and waste plastic have higher moisture content, which results in lower volatile content in both samples. The volatile contents of the other two samples (waste leather and waste cloth) were oppositely higher at 85.8 wt.% and 82.4 wt.%, respectively. Both of them have relatively higher fixed carbon content (9.45 and 8.52 wt.%, respectively). The wastes rubber has the highest ash content of 7.10 wt.%, while the ash contents of other wastes are all lower than 5.0 wt.%. According to the ultimate analysis results, the LHV and HHV of industrial waste were calculated. It was found that waste leather had the highest high heating value of 21.0 MJ/kg, followed by waste rubber and waste plastics, and the calorific value of waste cloth was lower, which was related to the elemental composition and moisture content of industrial waste. Statistically, rubber and leather appear to be more conducive to incineration for power generation due to their relatively higher heating value.

Table 1.
The ultimate and proximate analysis of individual polymeric wastes.
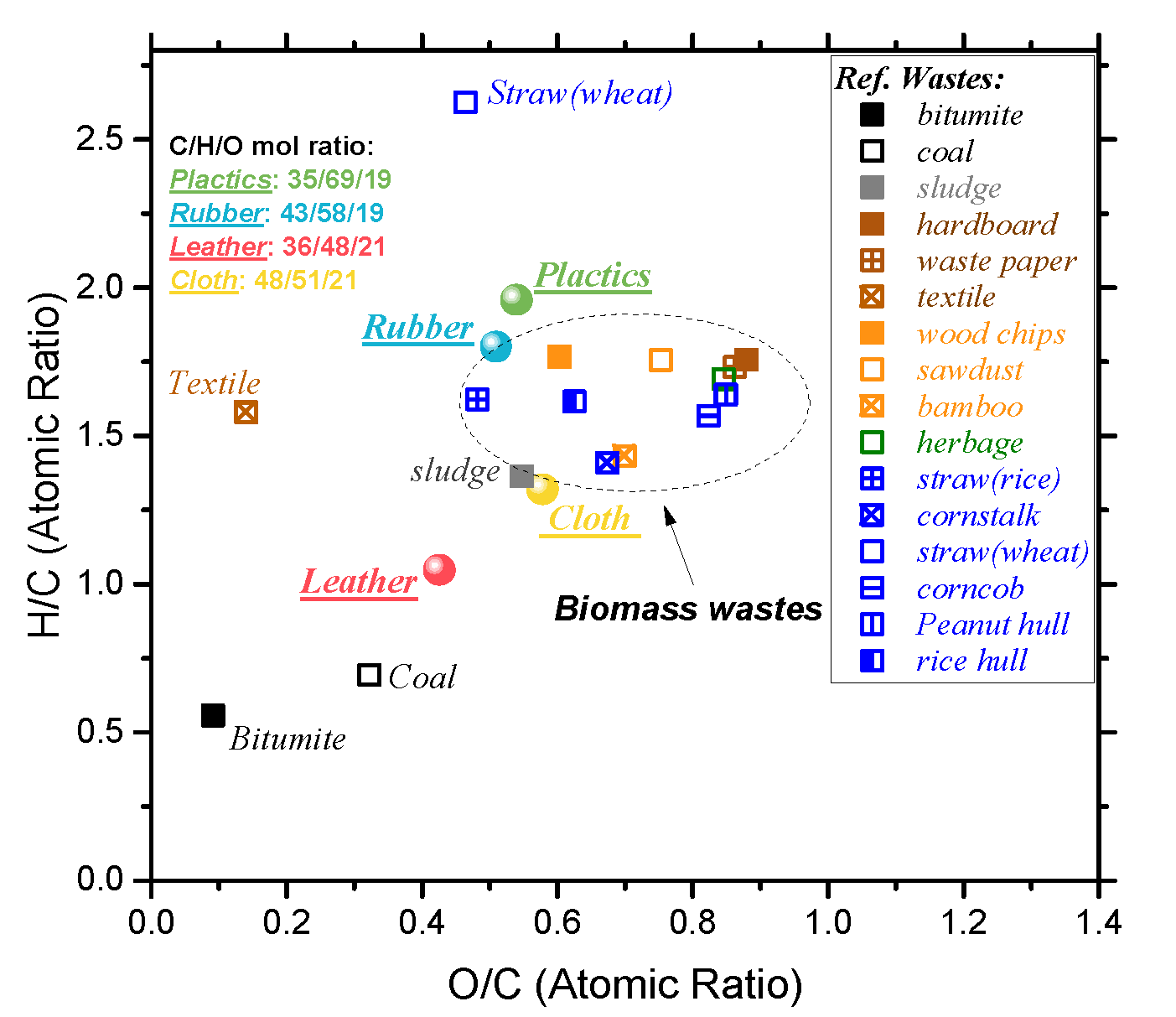
Figure 1 shows the Van Krevelen plot of four waste and some combustible organic materials, such as solid waste biomass and fossil fuels, etc. It can be seen that the hydrogen and oxygen contents of rubber and cloth are close to that of typical biomass. The hydrogen content of waste plastics is slightly higher than that of biomass. The O/C and H/C ratio of waste leather is lower than that of biomass, but close to that of coal, indicating that the carbonization degree of waste leather is between that of biomass and coal. According to the previous research [44,45], its position in the V-K diagram is similar to that of low-rank coal, such as peat and lignite. Since the dissociation energy of the C-C bond is generally higher than that of the C-H bond (or C-O bond), the lower the O/C ratio (or H/C ratio), the higher the energy density of the fuel. Based on this, it can be inferred that the waste leather will release higher energy than the other three solid wastes when completely burned.
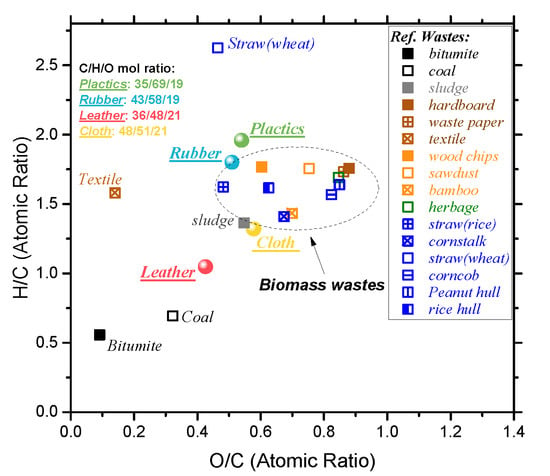
Figure 1.
Van Krevelen plot of four polymeric wastes and the other compared fuels.
3.2. Combustion Behaviors of the Polymeric Wastes
3.2.1. General
Thermogravimetric characteristics are an effective method to evaluate the incineration characteristics of industrial waste. The TG-DTG curves obtained from the investigation of the combustion process of four kinds of polymeric wastes are shown in Figure S1 in the supplementary materials. It can be found that the thermogravimetric status of the industrial wastes presents a non-single interval change in the whole temperature-rise range. The combustion process of all the waste samples generally has 2–3 weight loss intervals. Except for waste rubber, there is an initial weight-loss stage before the main weight-loss stage (rapid combustion stage) of the other three solid wastes. Such a stage can be regarded as the initial pyrolysis process before combustion, accompanied by the generation of free radicals [46,47]. This initial stage of waste plastics is between 150 and 250 °C, while that of leather and cloth is between 300 and 400 °C. In the major weight-loss stage, only waste rubber has two main weight-loss peaks, and the other three samples only have one main weight-loss peak. Compared with the waste leather and cloth, of which the main weight-loss range is between 350 and 520 °C, the main weight-loss range of rubber and plastic is wider with a relatively lower initial weight-loss temperature. For example, the main weight-loss stage during the combustion process of waste rubber is between 200 and 600 °C, and the conversion rate in this stage is exceed 80%. Since natural rubber (NR) is easy to degrade and burn at lower temperatures (300–400 °C), while synthetic rubber (such as polybutadiene rubber (PBR), styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR), etc.) is easy to thermo-decompose at higher temperatures (400–500 °C) [48], the main component of waste rubber in this study may be natural rubber. The temperature range of main weight-loss stage during waste plastics combustion is similar to that of waste rubber, but there is only one weight-loss peak between 200 and 500 °C. Beyond the main weight-loss stage, there is a secondary weight-loss stage at around 500–800 °C for all four solid wastes. Such phenomenon is likely caused by the re-combustion of carbon black and a small amount of organic minerals [48,49]. During the combustion process, the hysteresis effect of heat transfer can be obviously found. An obvious manifestation is that with the heating rate increase, both weight-loss peaks of the main stage and the secondary stage shift to the higher temperature region and the corresponding maximum weight-loss rate also increases. In addition, the increase in heating rate also leads to a higher of weight-loss rate, due to a greater instantaneous temperature difference during heat transfer [50]. In order to more accurately evaluate the combustion behaviors of various industrial wastes, the basic combustion parameters are accurately obtained from the curves, including mass, temperature and weight loss rate corresponding to the combustion stages, as listed in Table S1.
3.2.2. Ignition and Burnout Characteristics
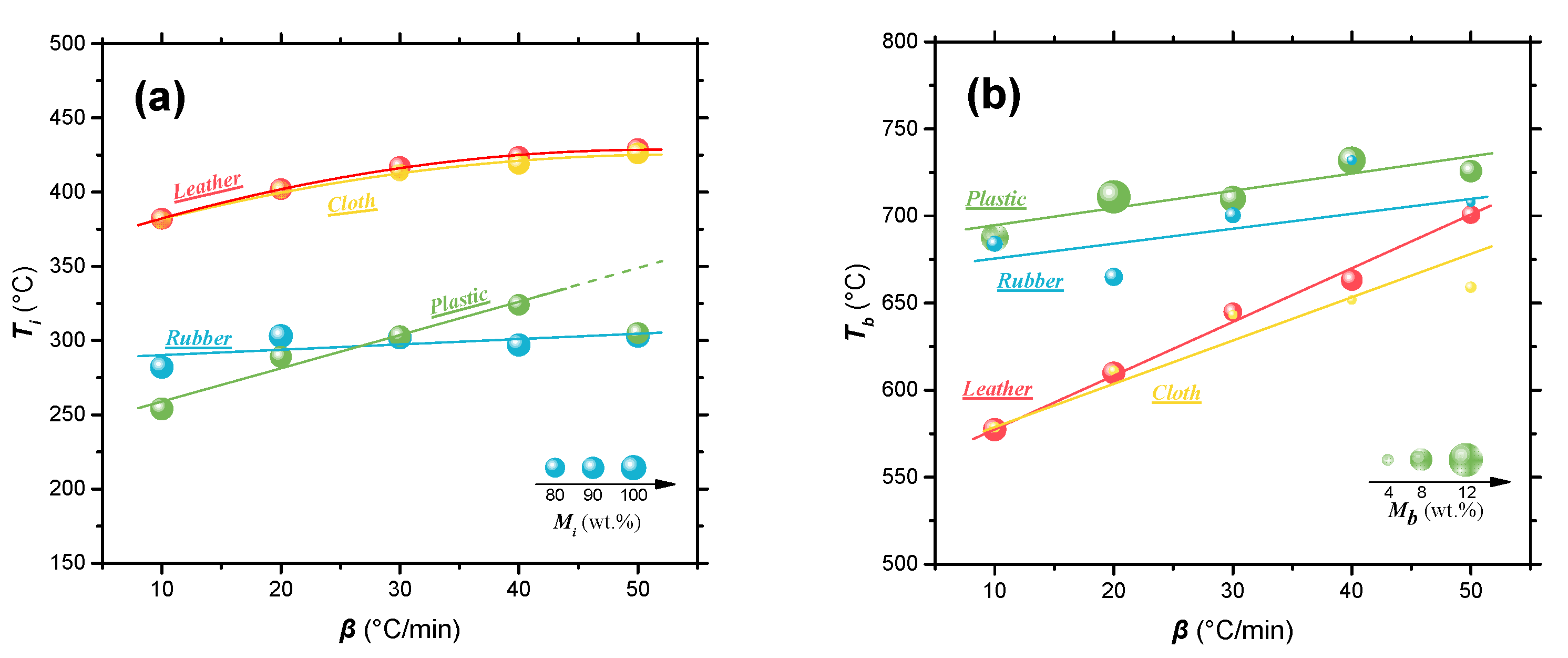
Figure 2 shows the temperature and residual mass corresponding to ignition and burnout of four solid wastes in the combustion process at different heating rates. As shown in Figure 2a, when the heating rate was fixed at 10 °C/min, the ignition temperature (Ti) of waste rubber and plastic was relatively low (<300 °C), while the ignition temperature of leather and cloth was over 380 °C. This higher ignition temperature means that the sample underwent a longer initial pyrolysis stage, which corresponds to a larger mass loss, before starting conflagration. For instance, the mass loss at ignition temperature of waste leather and cloth is about 15 wt.%, while that mass loss of waste rubber and plastic is less than 9 wt.%. An obvious trend is that the ignition temperatures of the four solid wastes all increased with heating rate, but the change in mass loss during the initial pyrolysis stage (i.e., mass loss corresponding to the Ti) was not an obvious change. Figure 2b shows a large difference of the burnout temperatures (Tb) of the four solid wastes. Compare with the waste leather and cloth, the waste rubber and plastic have a higher burnout temperature. In addition, it also shows that the burnout temperature of solid waste tends to increase with the heating rate. Taking waste leather (owning the biggest Tb increase) as an example, when the heating rate increases from 10 °C/min to 50 °C/min, the burnout temperature increases by 124 °C. After combustion, mass residue inevitably exists due to a series of reasons such as inadequate combustion and non-combustible components (e.g., inorganic salts, etc.) [51]. The final sample weight (Mf) of waste plastics after combustion is the highest in the four wastes (more than 10% below 20 °C/min). Then with the increasing heating rate, the Mf of waste plastic (or rubber) was reduced, indicating that slow heating rate would lead to inadequate combustion. On the contrary, the Mf of waste leather and cloth samples after combustion were basically stable at 5–6% and 2–3%, respectively. This indicates that waste leather and cloth can be completely burned out at a lower heating rate, thus, saving energy consumption to a certain extent.
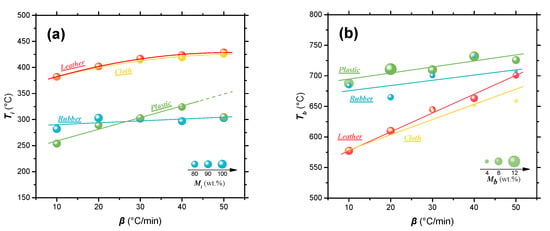
Figure 2.
The ignition temperature (a) and burnout temperature (b) and the corresponding residual mass in the combustion process of four polymeric wastes at different heating rates.
3.2.3. Comprehensive Combustion Characteristic
The burnout index (Db) also represents the combustion characteristics. At the same heating rate, the burnout indexes of the waste samples are ranked as follows: rubber < plastic < cloth < leather. This result is in accordance with that of burnout time (tb), that is, the higher burnout temperature means the longer combustion time, and the slower heat and mass transfer rate leads to the lower burnout efficiency. It is a generally accepted reason that the higher ash content is an important factor leading to the low burnout index. For example, the dry based ash content of waste plastic (8.2 wt.%) and waste rubber (6.3 wt.%) is significantly higher than that of waste cloth and waste leather (both around 4.6%). There are temperature and pressure gradients between the upper and lower parts of ash slag, which increase the resistance of oxygen contact and thermal diffusion. This results in a slower combustion process and a lower exhaust index. In addition, the thickness of the ash layer covering the sample surface during combustion, produces additional resistance to the diffusion of oxygen [52]. For that, the combustion performance can be enhanced by erosion of the ash layer and dust discarding.
The data of ignition and burnout can provide a basis for establishing optimal conditions for combustion [53]. The direct parameters mentioned above cannot be used to quantitatively describe the combustion process. Hence, the above intrinsic parameters were used to calculate quantified characteristics during combustion process. The ignition index (Di) was used to evaluate the difficulty and speed of sample ignition. The larger the value is, the easier the sample is to ignite, and the more intense the reaction is in the initial pyrolysis stage. Table 2 shows the Di of waste rubber is relatively lower than that of the other three solid wastes below 30 °C/min. The ignition index of waste rubber significantly increased when then heating rate exceeded 40 °C/min. The faster rate of heating allows a large amount in heat to be supplied to the combustion system in the initial stages, so that the increase of heating rate has a positive response to the ignition behavior. Another parameter, flammability index (Ci), also reflects the reaction intensity in early stage of combustion and is positively correlated with the burning stability. The greater the Ci value, the better the flammability of samples, the more stable the flame of its combustion. At different heating rates, the four kinds of solid wastes exhibit diverse ignition stability. That is, when the heating rate is fixed at 10 °C/min, the combustibility index of the four materials is not much different (about 0.8); when the heating rate is between 20 and 30 °C/min, the combustion stability and flammability of the four samples are ranked as follows: rubber < cloth < leather < plastics; when the heating rate exceeds 40 °C/min, the combustion stability and flammability of the samples are ranked as follows: cloth < leather < rubber < plastics. Therefore, it is concluded that among the four materials, the combustion stability of waste rubber is greatly affected by heating rate, while waste plastic has the best flammability and combustion stability after ignition. The combustibility of four kinds of solid wastes is closely related to their volatile characteristics. For example, waste rubber has the lowest flammability index and ignition index, which is because its Vad is the lowest among the four samples. In contrast, the excellent flammability of waste plastics may be due to its high volatile content (92.0 wt.% dry based). The ignition temperature does not always coincide with the changes in volatile content. This suggests that ignition temperature is not only affected by volatile content, but also by other factors.

Table 2.
Quantitative comprehensive combustion parameters of four polymeric waste polymers at different heating rate.
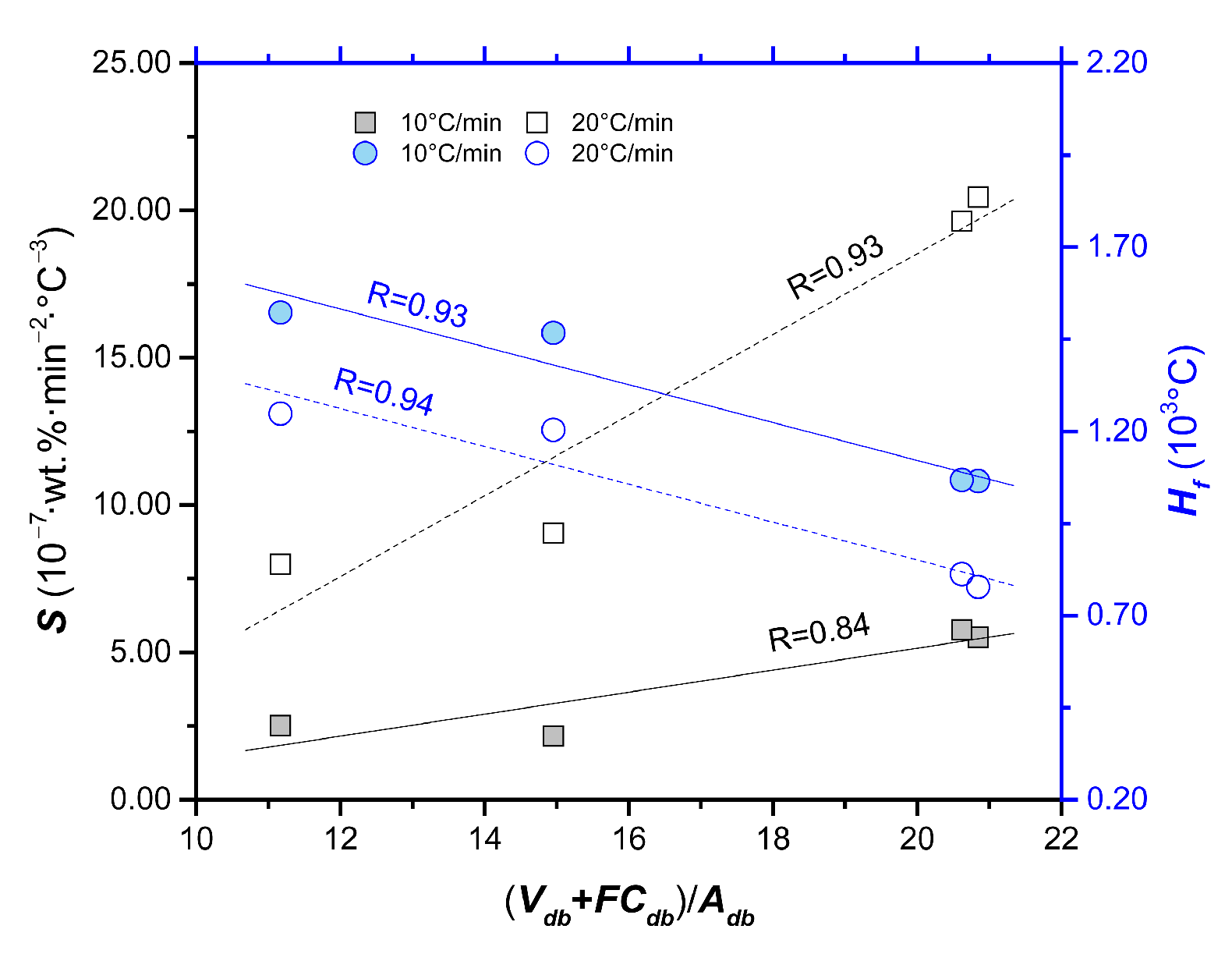
The index Si reflects the ignition, combustion and burnout properties of a sample [54]. The index Hf describes the rate and the intensity of the combustion process. The smaller the Hf value, the better the combustion performance. From Table 2, it can be found that the Si of waste leather and waste cloth are greater than that of waste rubber and waste plastic, indicating that the combustion performance of leather and cloth is superior to that of rubber and plastic. This result is in accordance with the results of Di and Df and such consistency also applies to the value of Hf. Figure 3 shows the relationship between comprehensive indexes (Si and Hf) and composition of the polymeric wastes. (Vad + FCad)/Aad is moderately positively correlated with Si (r = 0.91 and 0.96), and moderate negative correlation with comprehensive index Hf (correlation coefficient, r = −0.97 and −0.96). These indicate that high content of ash can inhibit the combustion of solid waste, resulting in the decline of combustion performance. The previous study [55] indicated that volatile matter plays an important role in combustion process, that is, the rapid ignition can increase particle temperature and ignite the fixed carbon in advance. This is in accordance with the volatile content of each sample difference in the proximate analysis section. In conclusion, the combustion properties (Di, Db, Ci, Si and Hf) of the polymeric wastes have the following order: rubber < plastic < cloth < leather.
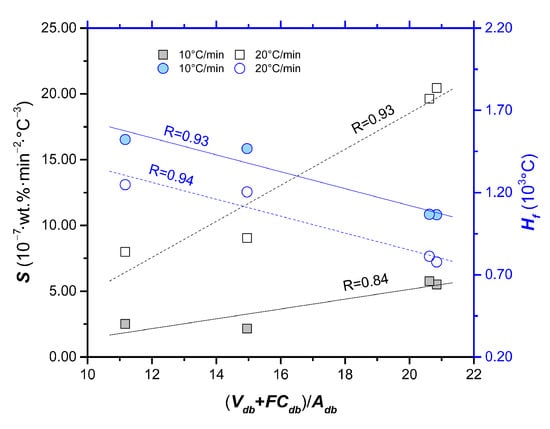
Figure 3.
The relationship between comprehensive indexes (Si and Hf) and (Vad + FCad)/Aad.
3.3. Kinetic and Thermodynamic Analysis
According to different kinetic models, the activation energy of the reaction at different conversion rates was calculated (Figures S2–S5). The obtained Ea value represents the apparent reaction activation energy, since the combustion process is considered to be a complex non-elementary reaction. In the whole conversion range of α = 0.05~0.95, the activation energy in different converted ranges presents the different rule. In the lower converted range (α < 0.6), the activation energy slightly increases with the conversion rate, indicating that the released energy after the ignition behavior of reactant tends to be a steady-output situation in the early-middle stages of combustion. When the conversion rate exceeds 0.60, the activation energy of the combustion system increases significantly, indicating the enhancement of thermal reaction resistance. One of the reasons for this situation is that the coke generated in the initial stage by incomplete combustion contains a large amount of saturated or unsaturated carbon-carbon linkage, which has high bond dissociation energy (BDE). These cokes need to overcome a higher reaction energy barrier to secondary decompose during the re-combustion process. Another reason may be that the higher carbon content increases the calorific value of the residual coke, leading a significant raise of the activation energy. The FWO-based Ea estimate are obviously higher than those calculated by DEAM method and STK method. Based on FWO method, the Ea value of rubber, leather, plastic and cloth reaches to the maximum at α = 0.65, α = 0.75, α = 0.75, and α = 0.80, respectively. The average Ea and R2 corresponding to each reaction model were obtained by statistical integration of the fitting data from whole combustion process, as shown in Table 3. It is obvious that the average activation energy of waste leather and waste cloth during the combustion process is higher than that of waste plastic and waste rubber, which corresponds to the thermogravimetry performance. The results are consistent with results of the combustion index (e.g., Si, Hf), indicating that rubber and plastic have relatively poor combustion performance, while leather and cloth have relatively superior combustion performance. The comprehensive order of the average activation energy of each material are as follow: rubber < plastic < leather < cloth. In the linear fitting process of the four kinetic models, the R2 value of waste leather, waste plastic and waste cloth are higher than 0.95, while the average R2 value of waste rubber is between 0.84 and 0.86.

Table 3.
Average values of activation energy determined by DEAM, FWO, STK and KAS methods for each devolatilization event derived from combustion process of the polymeric wastes.
The FWO model was selected to calculate its combustion thermodynamic parameters under condition of 20 °C/min, and the results are shown in Table S2. The previous study [56] reported that A values lower than 109 s−1 indicate a surface reaction (or the end of complex reaction), while the value higher than 109 s−1 indicate a simple complex reaction. All the FWO-based values of pre-exponential factors of rubber and plastic were less than the critical value, regardless of their conversion rate, so that the surface reaction was the main reaction during their combustion process. The A value of waste leather and waste cloth exceeded 10−9 in the stage of α = 0.6–0.8 and α = 0.55–0.85, respectively. Therefore, both combustion processes underwent some complex reactions, accompanied by the strong bonds cracking that produced intermediate during such multiple stages. The ΔH reflected the heat transfer between the activated complex and the reactants [57]. The trends of ΔH were similar with that of Ea, which indicated the feasibility of the reaction. Lower ΔH than Ea values of the solid waste indicated that more favored products were produced [58]. The entropy changes in the full converted range (Table S3) are almost negative, indicating that the disorder of products formed by the bond breaking was lower than that of initial reactants [56]. A low entropy change meant that the polymeric wastes just underwent some aging process, bringing it close to the state of thermodynamic equilibrium. In this case, the reactant shows little reactivity, increasing the forming time of reactive intermediates. Conversely, the reactant is far from the thermodynamic equilibrium under high entropy change condition, and thus leading the high reactivity and faster producing the reactive intermediates [59]. In the whole range of α, the ΔS of waste rubber is from −137.7 to −195.4, that of waste leather is from −0.001 to −0.164, that of waste plastic is from −80 to −178, and that of waste cloth is from −34 to 232J/mol. The changes in the Gibbs free energy showed that the system energy always increased when approaching reagent and activated complex formation [59,60]. Their ΔG value (135 and 129 kJ/mol) was higher than that of biofuels such as straw (120–168 kJ/mol), para grass (161–171 kJ/mol), spend mushroom substrate (146–147 kJ/mol), pea waste (143–147 kJ/mol), and Wolffia arrhiza (170–172 kJ/mol), etc., [27,57].
3.4. Evolution of Gas-Solid Phase
3.4.1. Volatile Component Releasing
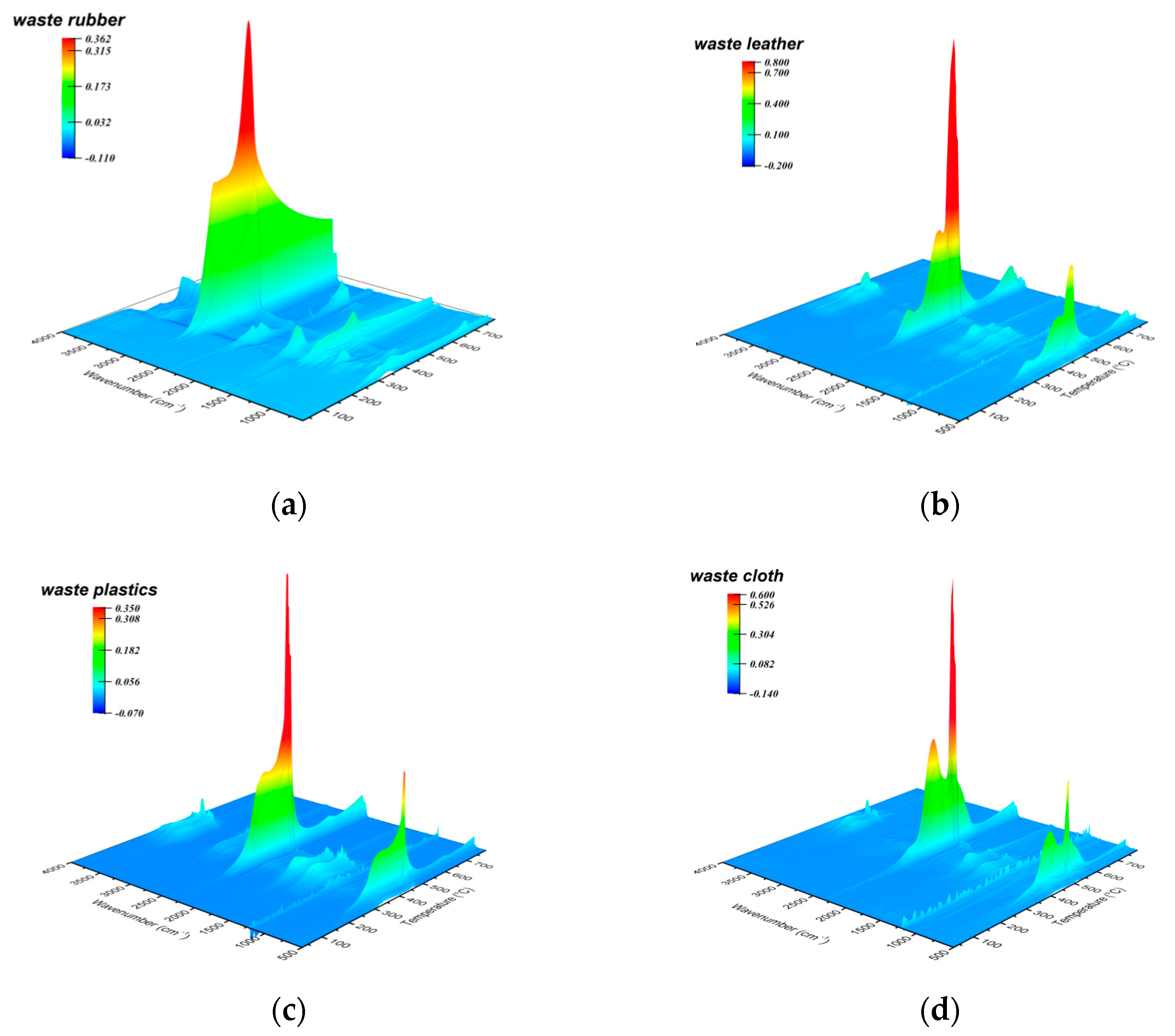
Figure 4 shows the 3D-FTIR spectra of volatile products generated by the combustion of various polymeric solid wastes, from which the intensity of main infrared absorption peaks varies with temperature (Figure S6). It is obvious that the main products generated by the combustion of each solid waste are gases (e.g., CO2, CH4) and small molecule volatile products (e.g., H2O). The volatile products released from waste rubber combustion contained a large amount of alkane rich in methyl (2930 cm−1) and methylene (2862 cm−1). At the initial stage (corresponding to the initial weight loss stage), the infrared absorption intensity of such product reaches the maximum value at 336 °C, indicating that the material underwent ignition behavior. After that, the infrared signal intensity reaches to the maximum value at 451 °C during the subsequent intense combustion stage (main weight loss stage). In contrast, the volatile products generated by combustion of waste leather, waste plastic and waste cloth are mainly carbon dioxide (about 2360 cm−1) and water (670 cm−1 and 3740 cm−1), in addition to some alkane generated at the initial stage (under 500 °C). The combustion products from all solid wastes also contain a small amount of aldehyde and ketone (1760 cm−1), of which the generation temperature is relatively lower than that of CO2. This is a reasonable performance because more carbonyl-containing intermediates are generated in the oxidative pyrolysis reaction of organic compounds before the main combustion stage [61]. Secondly, in the main combustion stage, the intermediate products containing aldehydes and ketones generate carbon dioxide through decarbonylation at the strong oxidation condition, thus reducing the existence of carbonyl group.
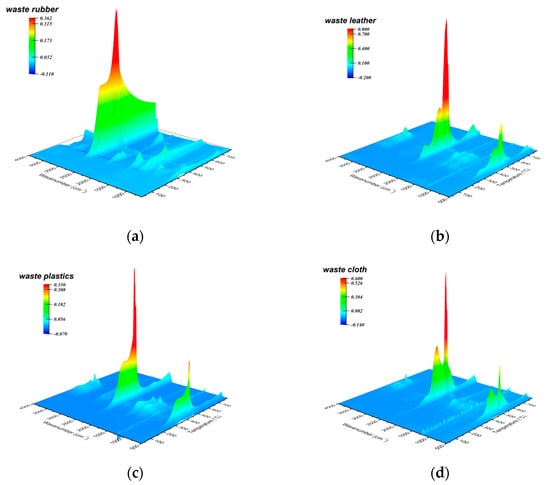
Figure 4.
Three-dimensional FTIR spectra obtained from ex situ observation of gaseous volatiles of waste rubber (a), waste leather (b), waste plastics (c) and waste cloth (d) at temperature ramps of 20 °C/min.
During the whole combustion reaction process, the combustion products distribution of the solid wastes greatly shows rather distinction in various temperature range. Due to its low ignition temperature (303 °C and 289 °C), the generation temperature of the main volatile products of waste rubber and plastic are relatively lower than that of waste leather and waste cloth at the initial combustion/pyrolysis stage, of which generation temperatures are higher than 400 °C. In the initial oxidative pyrolysis stage, a small amount of aldehyde/ketone and alkane are generated in a temperature range similar to that of the main products. These intermediates then undergo a secondary decomposition to generate carbon dioxide and water during subsequent intense combustion process. After the initial stage, the infrared signal intensity of the main products reached the maximum in value during intense combustion stage. In accordance with the thermogravimetric performance, the temperature corresponding to the maximum concentration of main products (CH4 and CO2) of waste rubber and waste plastic are lower than that of waste leather and waste cloth at this stage. The volatile products generated by each solid waste raw material in the secondary combustion stage are mainly carbon dioxide and water. The temperature corresponding to maximum IR signal intensity of the products generated by waste rubber, waste leather and waste plastic in the secondary combustion stage are 674 °C, 741 °C and 642 °C, respectively. The temperature of the products generated by waste cloth in this stage is lower, overlapping with the temperature range corresponding to the product signal in the main combustion stage. To sum, due to the differences in ignition characteristics caused by the inherent properties of each solid waste, they start to generate final products and pyrolysis intermediates at the initial combustion/pyrolysis stage. In the subsequently intense combustion stage, the reactants are rapidly converted into final products, and the intermediate products also undergo a further secondary decomposition, resulting in an increase in Ea. In the secondary combustion stage, the coke and the other stubborn substances, which generated due to incomplete combustion of reactants, overcome the larger energy barrier and crack again to generate the final product, so the reaction activation energy reaches the maximum at this stage.
3.4.2. Residual Phase Evolution
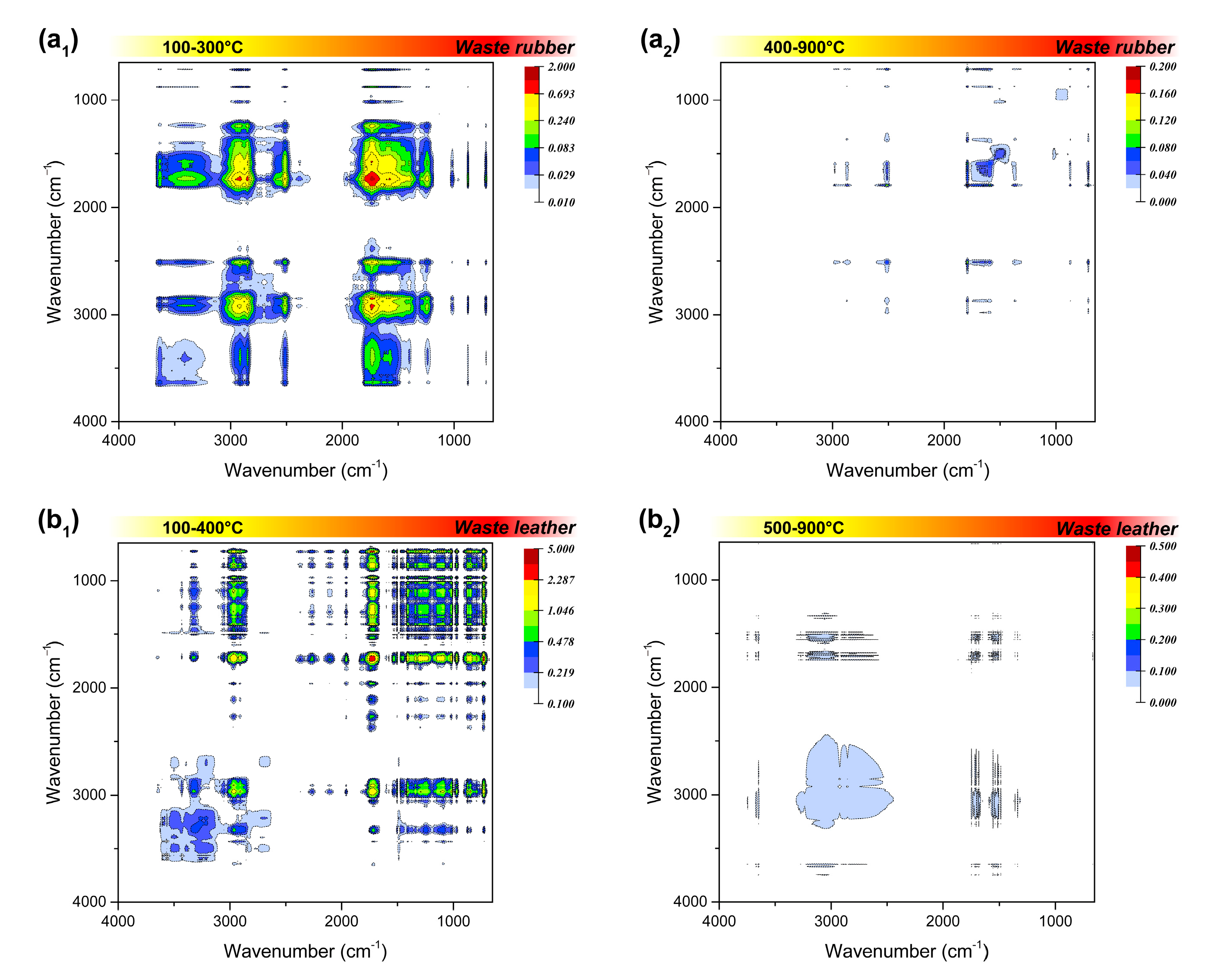
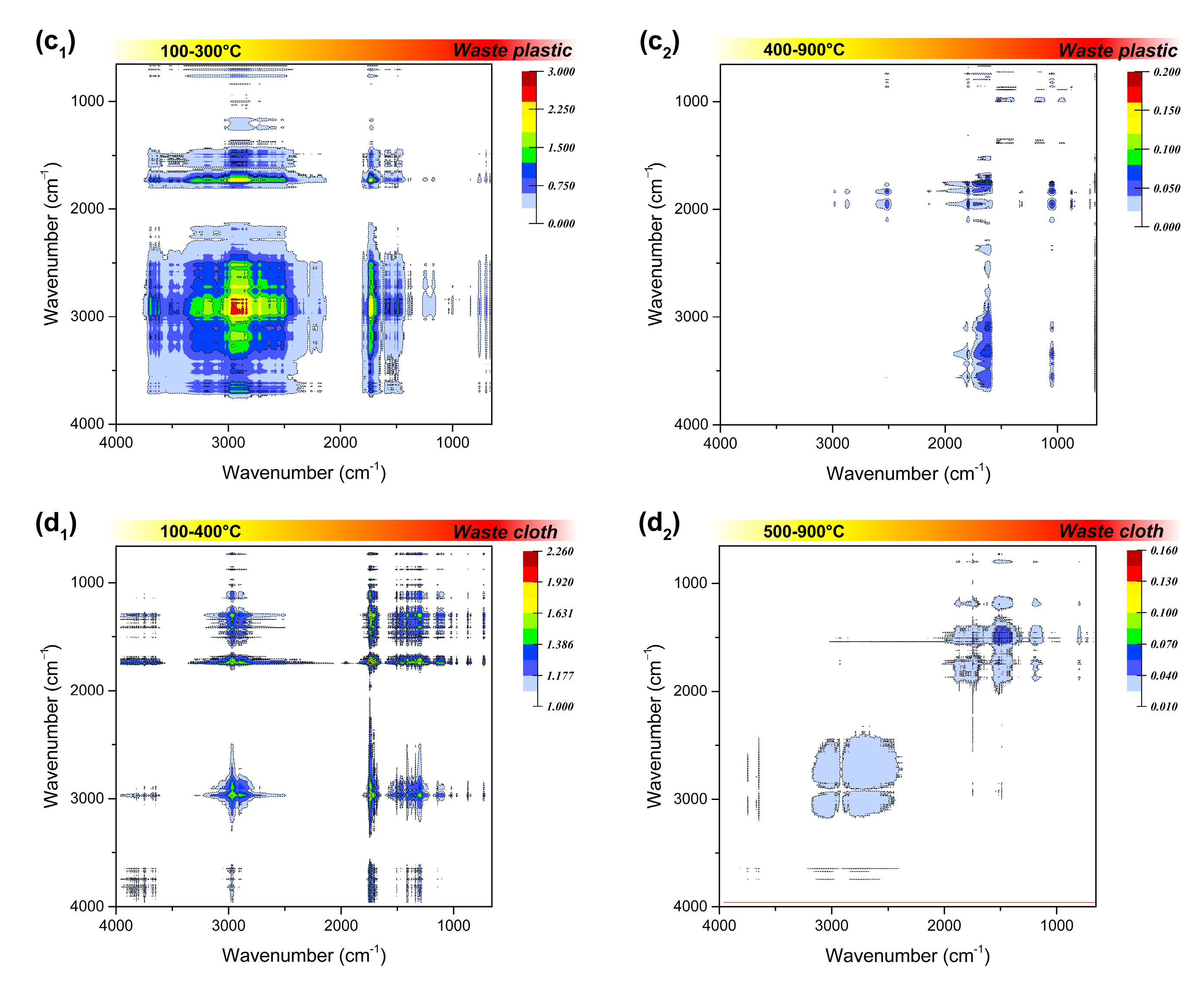
The residual phases at different temperatures were tracked using FTIR analysis, to observe the chemical structure evolution of the solid phase during the combustion, and the results are shown in Figures S7–S10. According to the original infrared spectra, it is found that when the combustion temperature exceeds the ignition temperature, the functional group signal in the residual phase is obviously weakened, indicating quick completion of the combustion in a short time. Based on this, the spectra before and after ignition were synchronously correlated, and the corresponding two-dimensional infrared spectra of the four polymeric wastes were obtained, as shown in Figure 5.
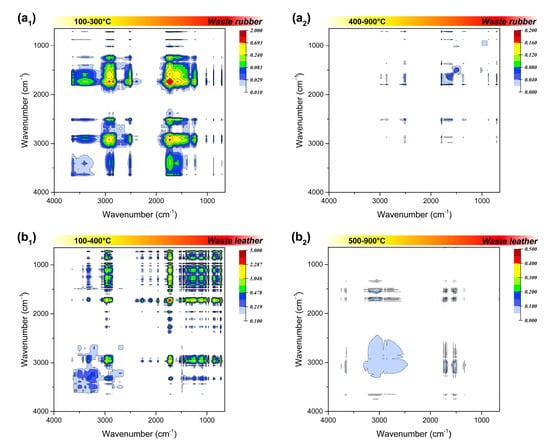
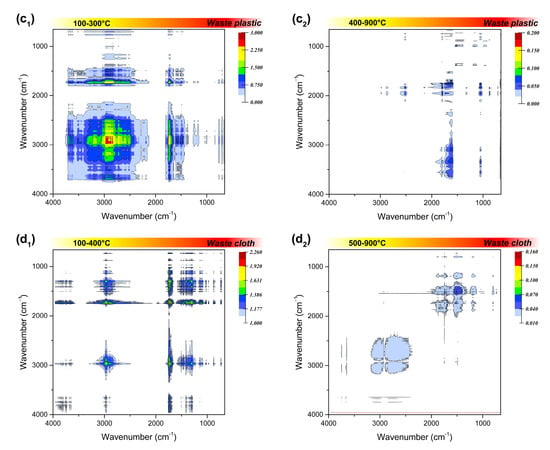
Figure 5.
Synchronous two-dimensional correlation spectrum in 4000–650 cm−1 of the four polymeric wastes before (a1,b1,c1,d1) and after ignition (a2,b2,c2,d2).
The infrared absorption of 2500–2000 cm−1 region can be attributed to the stretching vibration of triple bonds or accumulated double bonds. The triple bond linkage in the combustion residue was not considered in this study, since the addition reaction that generate triple bonds are rarely involved in the combustion process. Among the residual phases, waste rubber has an obvious medium infrared absorption at 2515 cm−1, corresponding to the strong absorption at 1792 cm−1 that always exists, which can be judged to be attributed to the deviation of O-H stretching vibration on the carboxyl group (-COOH). It may also can be due to absorption shift of the carboxyl group on oligomers or polymers. Beside waste rubber, the residual phase of waste plastics also has an inconspicuous carboxyl signal at lower temperatures, and the signal disappears when the temperature exceeds 200 °C, which may be inherent in their raw materials.
The spectral information in the fingerprint region (1800–1000 cm−1) looks more complicated. First of all, in the C=O stretching vibration range of 1820–1600 cm−1, the strong infrared absorption of waste rubber and waste plastic at around 1790 cm−1 is attributed to the C=O stretching vibration in the carboxyl group, while there is no such functional group in waste leather and waste plastic. The related absorption signals at 1745 cm−1, 1712 cm−1, and 1597 cm−1 may be attributed to the C=O stretching vibration in the ester, aldehydes, and ketones, respectively. The residual phases of the four types wastes all have obvious absorption signals at 1745 cm−1, indicating that they are oxidized at a lower temperature in the combustion process, and then rapidly decomposed into small oxygen-containing molecules over the ignition temperature. The infrared absorption in the region of 1500–1300 cm−1 is attributed to the double bond bending vibration. This may be due to the stubborn cracking of C=C bond in the aromatic structure of the two materials, or the stubborn fracture of C=C bond in coke generated by incomplete combustion at a higher temperature.
3.4.3. Final Ash Analysis
The composition and morphology of the final ash of the polymer wastes were investigated due to their higher content (Table 4). The content of inorganic metal shows that there is a considerable variation in the composition of the different final ashes. The content of calcium oxide in waste plastics after combustion is as high as 79.3 wt.%, accounting for the dominant percentage, which may be caused by the mixing of a large amount of sediment in the process of recycling, storage and transportation of the raw material. The secondary elements in ash from waste plastics combustion are Aluminum (9.93 wt.%), Silicon (5.14 wt.%), Natrium (6.58% at 550 °C, but 0.64 wt.% at 900 °C) and Magnesium (up to 3.50% at 550 °C), but their contents are much lower than that of Calcium. In addition, it also contains a small amount of other heavy metals, such as ferrum, kalium, manganese, nickel, and zinc, but all their content is less than 1 wt.%. Similarly, the calcium content in the final ash of waste cloth also accounts for a large proportion (exceeding 30 wt.%) regardless of the temperature, but the difference is that the content is much lower than that of waste plastic. The ash of waste cloth also contains high levels of basic metals such as Natrium (6.88 wt.%), magnesium (up to 19.9 wt.%), ferrum (7.95 wt.%), and other acid metals such as Silicon (10.4 wt.%) and Titanium (14.7 wt.%). There was also a significant amount of Chromium in the cloth ash (up to 8.37%). One possible explanation for such harmful metal is that a small amount of waste leather was mixed into the fabric recycling process, which is chrome-tanned and retains a relatively high amount of chromium. In addition to such an element, the burning ash of waste cloth contain less other heavy metal elements, such as manganese, nickel, cuprum, and zinc.

Table 4.
Ion content in ash from waste plastics and cloth Metal combustion at different temperatures (wt.%).
Solid waste is usually incinerated using specific reactors such as grate incinerators, fluidized bed incinerators, rotary kiln incinerators, and so on. The metal oxides leads to ash accumulation and slagging in the combustion process, which have a serious adverse influence on the operation of a waste incineration plant. For example, the ash accumulation not only resists the heat transfer on the surface of the heat exchange pipe, so as to affect the heat transfer efficiency and increase the exhaust temperature, but also corrodes the surface of the pipe and cause the shutdown of the garbage incinerator [62], which has both safety risks and reduced economic benefits. Therefore, understanding the ash generation has great significance to prolong the operation cycle of garbage incinerator and improve the economy of waste incineration power plant. Slagging hazard depends on the ash properties, which can be described by the fusion temperature of ash [63]: initial deformation temperature (IDT), softening temperature (ST), hemispherical temperature (HT), and flow temperature (FT). The ash adhesion is strongly adhesive over softening temperature and thus results in slagging. Another factor of slagging is caused by the sintering process (e.g., dry-bottom furnaces), which produces deposits that are very difficult to remove over time. The slagging and fouling tendency can be predicted by discriminant index variables commonly used in literature [64,65], such as RB/A, RS, Fu, and SR, etc. Their expressions are as follows:
Base to acid ratio, RB/A:
Slagging index RS:
where Sd is the percentage of sulfur in dry fuel;
Fouling index, Fu:
Slag viscosity index, SR:
Table 4 also shows the discriminant indices for slagging and fouling of the ash. According to previous reports [64,66,67], the slagging or fouling tendency was roughly marked as severe, high, medium, and low. It seems impossible to predict definitively the slagging and fouling properties for a feedstock. It has long been found that so-called basic compounds decrease the melting temperature, while acidic compounds increase it conversely. Therefore, the RB/A in combustion ash can predict the slagging and fouling tendency to a certain extent. It can be found that the ash of polymer waste in this study all have a relatively higher RB/A value, which indicates that they all have a serious slagging tendency according to the discrimination criteria. It is an exception that the RB/A value of cloth ash (1.91) obtained at 900 °C is between 0.75 and 2.0, in which the HT and FT of combustion ash increases with the value. The relatively high B/A ratio indicates that the ash of waste plastics has a more serious slagging tendency than that of waste cloth. Regardless of the waste type, a common trend is that the B/A ratio shows an inverse relationship with the combustion temperature, which is consistent with the previous results on other fuels such as biomass and coal. During the combustion, the alkali metal, such as natrium, kalium, calcium, etc., can notoriously cause slagging and fouling, resulting in lower power plant efficiency [68,69]. Such basic metal reacts with sulfur to form alkali sulfate, which deposits on heat transfer surfaces, reducing the efficiency of the combustion [70]. Hence, the RS value with the influence factor of sulfur content usually was used to evaluate the slagging characteristics of ash. Among the polymeric wastes, the waste plastic, which is the only one to contain sulfur, has a low Rs value, only 0.22 (at 900 °C) and 0.39 (at 550 °C). The slagging is due to the formation of alkali sulfate is classified as low slagging tendency, according to the above-mentioned criterion. The slagging tendency caused by the above reasons can be ignored for other wastes because they do not contain sulfur. The table also shows that the waste plastics have a high Fu value under inadequate combustion condition (at 550 °C), corresponding to extremely high fouling inclination and a tendency to sinter of deposits. With the intensification of combustion (at 900 °C), the Fu value significantly decreased, but still in the range of high fouling inclination (0.6–40). Similarly, the fouling index of waste cloth also decreased with the intensifying of combustion, but its value was still between 0.6 and 40, belonging to a high fouling inclination. The basic metals can also react with silica to form alkali silicates which soften below 700 °C, resulting in undesirable slagging. the slag viscosity index (silica ratio) can be used to distinguish slagging tendency. A high SR value corresponds to high viscosity, thus to low slagging inclination. From the calculated SR value, it can be predicted that the slag viscosity index of waste plastics and waste cloth (both lower than 65) also corresponds to a higher slagging inclination.
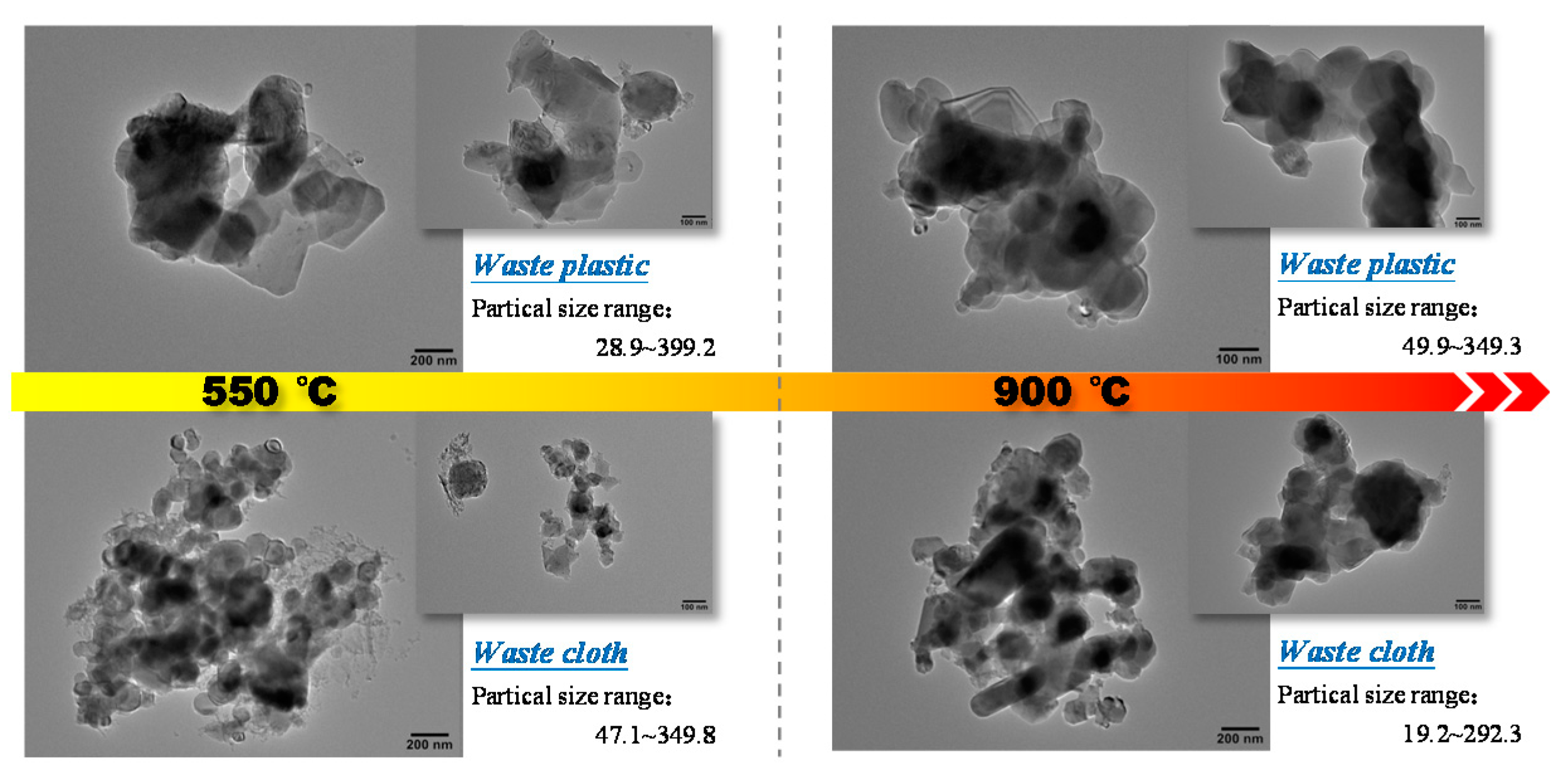
The TEM images of combustion ash, in all temperature conditions for plastic and cloth, are shown in Figure 6. It can be observed that the combustion ash of plastic at 500 °C is irregular non-spherical, with angular edges and large pores. The statistical analysis shows that the average particle size of the ash is 201.12 nm (29.92–399.2 nm), and its particle size distribution is uneven, mainly distributed in the range of 28–140 nm and 214–326 nm. At 900 °C, the ash evolves into smooth and relatively regular spherical particles, which become more compact due to the reduction in porosity. Mostly the ash particles are distributed in the particle size range of 170–290 nm, but less in the size range of <100 nm or >320 nm. The average particle size of combustion at 900 °C (216.3) is obviously higher than that at 500 °C. By comparing of the burning ash of waste plastics at 550 °C and 900 °C, the ash gradually deforms and softens, and the ash particles evolve from irregular flake structure into spherical particles, which adhere to form large pieces and lead to slagging in this process. The combustion ash of waste cloth is irregular spherical particles, and there are a considerable number of fine particles of broom filaments in the ash particles at 550 °C. The average particle size of the ash is 132.4 nm, and the particle size of most ash particles is distributed in the range of 77–168 nm, with less distribution above 200 nm. The fine particles disappear in ash content of 900 °C, and the particle size becomes larger and the edge becomes smoother. The average particle size is 159.38 nm with relatively uniform distribution.
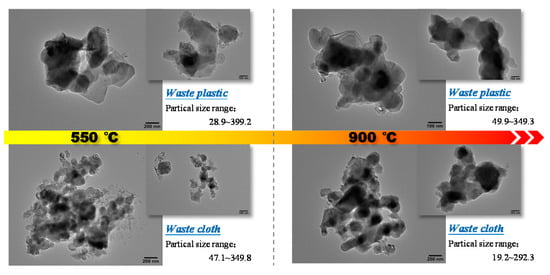
Figure 6.
TEM image of ash sample after combustion of the polymeric wastes.
3.5. Practical Implications of this Study
In this study, we focus on industrial solid wastes commonly used in the refuse incineration power industry. In the process of industrialization development in contemporary China, a huge amount of industrial waste will be generated in the Yangtze River Delta region based on its superior degree of industrialization. The harmless disposal of these industrial wastes has always been a headache for the government. To this end, we carried out comprehensive incineration performance estimation for several typical polymer wastes, and objectively compared the differences of their combustion kinetics and structural evolution. This research is of great significance to the harmless treatment of solid wastes with geographical characteristics. The results are nonnegligible for the actual incineration power manufacturing, and have guiding significance for the rapid judgment of the incineration performance of this waste type. This work also provides a directional database for recycling and resource recovery of organic solid waste.
4. Conclusions
Four typical industrial polymeric wastes were selected as the raw material to simulate polymeric waste combustion behavior based on a series of approaches such as thermogravimetric characteristics, kinetics analysis and TG-Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy analyses. Focused on the combustion behaviors, we drew the following conclusions:
The combustion of polymeric wastes successively experienced initial stage, intense stage and final stage. The average activation energy and enthalpy change in four kinds of solid wastes are in the following order: rubber < Plastic < Leather < cloth. During the combustion process, the surface reaction is the main reaction of waste rubber and waste plastic, while both processes of leather and cloth involved more complex chemical reactions along with the breaking of strong chemical bonds that generated intermediates during the multiple decomposition stages.
The comprehensive combustion performances of leather and cloth are better than the other two samples due to their intrinsic characteristics, while rubber and plastic have a wider combustion temperature range for their higher content of C-H bonds, the intermediate oxidation process, and the stubborn cracking process of C=C bonds.
The volatiles released from rubber combustion contained a large amount of alkane, while the volatile generated from leather, plastic and cloth are mainly CO2 and water. The high levels of basic metals in the industrial waste causes serious slagging and fouling tendency, which have a serious adverse influence on the operation of a waste incineration plant.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/en15072487/s1, Figure S1: Thermogravimetric analysis (TG and DTG curves) of four kinds of industrial polymeric wastes; Figure S2: KAS fitting results for incineration of typical polymeric wastes; Figure S3: FWO fitting results for incineration of typical polymeric wastes; Figure S4: STK fitting results for incineration of typical polymeric wastes; Figure S5: Kissinger fitting results for incineration of typical polymeric wastes; Figure S6: The intensity evolution of main infrared absorption peaks with temperature; Figure S7: FTIR spectra of residual phase of waste rubber at different combustion temperature; Figure S8: FTIR spectra of residual phase of waste leather at different combustion temperature; Figure S9: FTIR spectra of residual phase of waste at different combustion temperature; Figure S10: FTIR spectra of residual phase of waste cloth at different combustion temperature; Table S1: Conventional combustion parameter of four polymeric waste polymers at different heating rates; Table S2: Ea and R2 values of the polymeric wastes according to DAEM, FWO, Starink, and Kissinger; Table S3: Thermodynamic parameters for the polymeric wastes combustions using FWO at 20 °C/min.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis and data curation: S.Y. and M.L. (Ming Lei); validation, M.L. (Ming Lei) and C.L.; investigation: S.Y., M.L. (Ming Lei) and M.L. (Min Li); Resources: R.X. and C.L.; writing—original draft preparation: S.Y.; writing—review and editing: M.L. (Ming Lei); visualization: M.L. (Ming Lei); supervision: R.X.; project administration: B.X. and R.X.; funding acquisition: S.Y., R.X. and C.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key R&D Program of China, grant number 2018YFC1902600 and the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 52106230.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data used for this study is available and will be supplied upon request.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express appreciation for the support of the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (Grant nos. BK20210237 and BK20190363).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Nomenclature
| Mad | Moisture at air dryness condition (ad) |
| Aad | Ash contents at air dryness condition (ad) |
| Vad | Volatile matter at air dryness condition (ad) |
| QLHV | Lower heating value (MJ/kg); |
| QHHV | Higher heating value (MJ/kg); |
| T | Temperature (°C); |
| M0 | The initial sample weight (wt.%); |
| MT | The solid mass at the temperature of T (wt.%); |
| ti | Ignition time (min) |
| Ti | Ignition temperature (°C); |
| Mi | The solid mass at the temperature of Ti (wt.%); |
| ∆t1/2 | The time range of DTG/DTGmax = 0.5, min; |
| ∆T1/2 | The temperature range (half-peak breadth) when (dm/dt)/(dm/dt)max = 1/2 (°C); |
| tp | The time at the maximum mass loss, (min); |
| Tp | The temperature corresponding to the peak (°C); |
| DTGmax | The mass loss rate corresponding to the Tp peak (%/min); |
| tb | Burnout time (min); |
| Tb | Burnout temperature (°C); |
| Mb | The solid mass at the reaction temperature of Tb (wt.%); |
| DTGmean | The average mass loss rate (%/min); |
| Mf | The final sample weight (wt.%); |
| Di | Ignition index, |
| Db | Burnout index, |
| Ci | Lammability index, |
| Si | Comprehensive combustibility index, |
| Hf | Intensity index of combustion process, |
| A | Pre-exponential factor of Arrhenius equation |
| Ea | Reaction activation energy |
| β | Heating rate |
| R | Universal gas constant |
| KB | Boltzmann constant (1.381 × 10−23 J/K) |
| h | Plank constant (6.626 × 10−34 J·s) |
| ∆H | Enthalpy change |
| ∆G | Gibbs free energy |
| ∆S | Entropy production |
| ST | Softening temperature of ash |
| FT | Flow temperature of ash |
| IDT | Initial deformation temperature of ash |
| HT | Hemispherical temperature of ash |
| RB/A | Base to acid ratio |
| Sd | Slagging index |
| RS | Slagging index |
| Fu | Fouling index |
| SR | Slag viscosity index |
References
- Marshall, R.E.; Farahbakhsh, K. Systems approaches to integrated solid waste management in developing countries. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 988–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stachowiak, T.; Łukasik, K. The Management of Polymer and Biodegradable Composite Waste in Relation to Petro-leum-Based Thermoplastic Polymer Waste—In Terms of Energy Consumption and Processability. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suksankraisorn, K.; Patumsawad, S.; Vallikul, P.; Fungtammasan, B.; Accary, A. Co-combustion of municipal solid waste and Thai lignite in a fluidized bed. Energy Convers. Manag. 2004, 45, 947–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolović, D.; Vulic, T.; Kiralj, A.; Hadnadjev-Kostic, M.; Sokolovic, S. Separation efficiency of two waste polymer fibers for oily water treatment. Acta Period. Technol. 2016, 2016, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauve, G.; Van Acker, K. The environmental impacts of municipal solid waste landfills in Europe: A life cycle as-sessment of proper reference cases to support decision making. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 261, 110216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.H.; Yamada, T.; Striebich, R.C.; Graham, J.L.; Giraud, R.J. Investigation of waste incineration of fluorote-lomer-based polymers as a potential source of PFOA in the environment. Chemosphere 2014, 110, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, Y.; Ye, C.; He, X.; Zhang, S. Fate of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes during aerobic co-composting of food waste with sewage sludge. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 784, 146950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, J.M.; Williams, P.T.; Zhang, Y.S.; Yao, D.; Yang, H.; Zhou, H. Comparison of waste plastics pyrolysis under ni-trogen and carbon dioxide atmospheres: A thermogravimetric and kinetic study. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 2021, 156, 105135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zheng, A.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, Q.; Wang, C.; Liu, S.; Huang, Z.; Li, H. External fields enhanced glycerol pre-treatment of forestry waste for producing value-added pyrolytic chemicals. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2021, 168, 113603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, C.; Yuan, H.; Chen, Y. Enhancement of aromatics production via cellulose fast pyrolysis over Ru modi-fied hierarchical zeolites. Renew. Energy 2022, 184, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Salem, S.M.; Kishk, M.W.; Karam, H.J.; Al-Qassimi, M.M.; Al-Wadi, M.H.; Al-Shemmari, A.J. Inducing polymer waste biodegradation using oxo-prodegradant and thermoplastic starch based additives. J. Polym. Res. 2021, 28, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasina, M.; Kajdas, B.; Michalik, M. The leaching potential of sewage sludge and municipal waste incineration ashes in terms of landfill safety and potential reuse. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 791, 148313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Zhao, S.; Liang, Z.; Wang, F.; Sun, F.; Chen, D. Perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in leachate, fly ash, and bottom ash from waste incineration plants: Implications for the environmental release of PFAS. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 795, 148468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusuf, A.A.; Peter, O.; Hassan, A.S.; Tunji, L.A.; Oyagbola, I.; Mustafa, M.M.; Yusuf, D.A. Municipality solid waste management system for Mukono District, Uganda. Procedia Manuf. 2019, 35, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Lu, Q.; Na, Y. N2O and NO emissions from co-firing MSW with coals in pilot scale CFBC. Fuel Process. Technol. 2004, 85, 1539–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthuraman, M.; Namioka, T.; Yoshikawa, K. A comparative study on co-combustion performance of municipal sol-id waste and Indonesian coal with high ash Indian coal: A thermogravimetric analysis. Fuel Process. Technol. 2010, 91, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthuraman, M.; Namioka, T.; Yoshikawa, K. Characteristics of co-combustion and kinetic study on hydrothermally treated municipal solid waste with different rank coals: A thermogravimetric analysis. Appl. Energy 2010, 87, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gug, J.; Cacciola, D.; Sobkowicz, M.J. Processing and properties of a solid energy fuel from municipal solid waste (MSW) and recycled plastics. Waste Manag. 2015, 35, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.H.; Ma, X.Q.; Yu, Z. Experimental and kinetic modeling of oxygen-enriched air combustion of municipal solid waste. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 792–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Z.; Ma, X.; Tang, Y.; Lin, H. A study on municipal solid waste (MSW) combustion in N2/O2 and CO2/O2 atmos-phere from the perspective of TGA. Energy 2011, 36, 819–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, R.; Fernández, C.; Cara, J.; Martínez, O.; Sánchez, M. Differences between combustion and oxy-combustion of corn and corn–rape blend using thermogravimetric analysis. Fuel Process. Technol. 2014, 128, 376–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suksankraisorn, K.; Patumsawad, S.; Fungtammasan, B. Co-firing of Thai lignite and municipal solid waste (MSW) in a fluidised bed: Effect of MSW moisture content. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2010, 30, 2693–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Channiwala, S.; Parikh, P. A unified correlation for estimating HHV of solid, liquid and gaseous fuels. Fuel 2002, 81, 1051–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kök, M.V. Temperature-controlled combustion and kinetics of different rank coal samples. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2005, 79, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Shi, X.; Yang, C.; Wang, W.; Li, Y. Risk evaluation of coal spontaneous combustion on the basis of auto-ignition temperature. Fuel 2018, 233, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, S.; Sarkar, P.; Chakraborty, N.; Adak, A. Thermogravimetric assessment of combustion characteristics of blends of a coal with different biomass chars. Fuel Process. Technol. 2010, 91, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mureddu, M.; Dessì, F.; Orsini, A.; Ferrara, F.; Pettinau, A. Air- and oxygen-blown characterization of coal and bio-mass by thermogravimetric analysis. Fuel 2018, 212, 626–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuanyuan, Z.; Yanxia, G.; Fangqin, C.; Kezhou, Y.; Yan, C. Investigation of combustion characteristics and kinetics of coal gangue with different feedstock properties by thermogravimetric analysis. Thermochim. Acta 2015, 614, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manasrah, A.D.; Hassan, A.; Nassar, N.N. Enhancement of petroleum coke thermal reactivity using Oxy-cracking technique. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 97, 2794–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wnorowska, J.; Ciukaj, S.; Kalisz, S. Thermogravimetric Analysis of Solid Biofuels with Additive under Air Atmos-phere. Energies 2021, 14, 2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lian, W.; Li, P.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, J.; Hao, X.; Huang, W.; Guan, G. Simulation of pyrolysis in low rank coal particle by using DAEM kinetics model: Reaction behavior and heat transfer. Fuel 2017, 207, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Gu, J.; Yuan, H.; Chen, Y. Thermal behaviors and kinetics for fast pyrolysis of chemical pretreated waste cassava residues. Energy 2020, 208, 118192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, T. A New Method of Analyzing Thermogravimetric Data. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1965, 38, 1881–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flynn, J.H.; Wall, L.A. A quick, direct method for the determination of activation energy from thermogravimetric data. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Lett. 1966, 4, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kissinger, H.E. Reaction Kinetics in Differential Thermal Analysis. Anal. Chem. 1957, 29, 1702–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Ma, X.; Fang, S.; Yu, Z.; Lin, Y. Thermogravimetric analysis of the co-combustion of eucalyptus residues and paper mill sludge. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 106, 938–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, I. Chapter 13—Generalized Two-Dimensional Correlation Spectroscopy. In Frontiers of Molecular Spectros-Copy; Laane, J., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 367–381. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, B.; Yang, H.; Yang, Q.; Chen, H. Evolution of functional groups and pore structure during cotton and corn stalks torrefaction and its correlation with hydrophobicity. Fuel 2014, 137, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Yang, H.; Shao, J.; Chen, Y.; Liao, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, H. Generalized two-dimensional correla-tion infrared spectroscopy to reveal mechanisms of CO2 capture in nitrogen enriched biochar. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2017, 36, 3933–3940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, O.R.; Herbert, B.E.; Kuo, L.; Louchouarn, P. Generalized Two-Dimensional Perturbation Correlation Infrared Spectroscopy Reveals Mechanisms for the Development of Surface Charge and Recalcitrance in Plant-Derived Bio-chars. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 10641–10650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulyekeen, K.A.; Umar, A.A.; Patah, M.F.A.; Daud, W.M.A.W. Torrefaction of biomass: Production of enhanced solid biofuel from municipal solid waste and other types of biomass. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 150, 111436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mian, I.; Li, X.; Dacres, O.D.; Wang, J.; Wei, B.; Jian, Y.; Zhong, M.; Liu, J.; Ma, F.; Rahman, N. Combustion kinetics and mechanism of biomass pellet. Energy 2020, 205, 117909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, X.; Li, W.; Zhu, C. Catalytic hydrotreatment of Kraft lignin into liquid fuels over porous ZnCoOx nanoplates. Fuel 2020, 283, 118801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammes, K.; Smernik, R.J.; Skjemstad, J.O.; Schmidt, M.W.I. Characterisation and evaluation of reference materials for black carbon analysis using elemental composition, colour, BET surface area and 13C NMR spectroscopy. Appl. Geochem. 2008, 23, 2113–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, W.; Yang, H.; Chen, H. The structure evolution of biochar from biomass pyrolysis and its correlation with gas pollutant adsorption performance. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 246, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, M.; Wu, S.; Liang, J.; Liu, C. Comprehensive understanding the chemical structure evolution and crucial inter-mediate radical in situ observation in enzymatic hydrolysis/mild acidolysis lignin pyrolysis. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 2019, 138, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Liu, C.; Kong, X.; Han, Y.; Lei, M.; Xiao, R. A new perspective on polyethylene-promoted lignin pyrolysis with mass transfer and radical explanation. Green Energy Environ. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, J.D.; Veses, A.; Mastral, A.M.; Murillo, R.; Navarro, M.V.; Puy, N.; Artigues, A.; Bartrolí, J.; García, T. Co-pyrolysis of biomass with waste tyres: Upgrading of liquid bio-fuel. Fuel Process. Technol. 2014, 119, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, H.; Dong, Z.; Liu, B.; Chen, Y.; Gong, M.; Li, S.; Chen, H. A new insight of lignin pyrolysis mechanism based on functional group evolutions of solid char. Fuel 2020, 288, 119719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kok, M.V. Simultaneous thermogravimetry–calorimetry study on the combustion of coal samples: Effect of heating rate. Energy Convers. Manag. 2012, 53, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Jiang, X.; Li, F.; Lei, Y.; Lin, Q. The thermal behavior and kinetics of co-combustion between sewage sludge and wheat straw. Fuel Process. Technol. 2019, 189, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öner, C.; Altun, S. Improved Combustion of Asphaltite Coals in a Rotating Head Combustor with Various Air Supply Arrangements. Energy Fuel 2014, 28, 2971–2976. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Lv, Y.; Ma, B.; Jian, S.; Tan, H. Thermogravimetric investigation on co-combustion characteristics of tobacco residue and high-ash anthracite coal. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 9783–9787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, J.; Ran, J.; Zhang, L.; Pu, G.; Tang, Q. Experimental study on combustion and kinetic characteristics of mixed industrial sludge. Proc. CSEE 2007, 27, 44–50. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; You, C. Experimental Investigation into the Spontaneous Ignition Behavior of Upgraded Coal Products. Energy Fuels 2014, 28, 2267–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia, A.; de Morais, L.C. Kinetic parameters of red pepper waste as biomass to solid biofuel. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 204, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, L.; Xie, C.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Chang, K.; Kuo, J.; Sun, J.; Xie, W.; Zheng, L.; Sun, S.; et al. Influence of catalysts on co-combustion of sewage sludge and water hyacinth blends as determined by TG-MS analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.S.; Mehmood, M.A.; Liu, C.-G.; Tawab, A.; Bai, F.-W.; Sakdaronnarong, C.; Xu, J.; Rahimuddin, S.A.; Gull, M. Bioenergy potential of Wolffia arrhiza appraised through pyrolysis, kinetics, thermodynamics parameters and TG-FTIR-MS study of the evolved gases. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 253, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turmanova, S.C.; Genieva, S.D.; Dimitrova, A.S.; Vlaev, L.T. Non-isothermal degradation kinetics of filled with rise husk ash polypropene composites. Express Polym. Lett. 2008, 2, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, S.H. Investigation of thermodynamic parameters in the thermal decomposition of plastic waste-waste lube oil compounds. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 5313–5317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Dong, W.; Zhang, J.; Shao, S.; Cai, Y. Preparation of bio-oil derived from catalytic upgrading of biomass vac-uum pyrolysis vapor over metal-loaded HZSM-5 zeolites. J. Energy Inst. 2020, 93, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Du, X.; Yue, M.; Yan, M.; Shi, Y. Heat transfer and ash deposition performance of heat exchange surface in waste incineration flue gas. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2020, 155, 119691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Z.; Cao, X.; Zha, Z.; Ma, Y.; Zeng, M.; Wu, K.; Chu, S.; Tao, Y.; Zhang, H. The mineral transformation and molten behaviors of biomass waste ashes in gasification-melting process. Fuel Process. Technol. 2021, 226, 107095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pronobis, M. Evaluation of the influence of biomass co-combustion on boiler furnace slagging by means of fusibility correlations. Biomass Bioenergy 2005, 28, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizvi, T.; Xing, P.; Pourkashanian, M.; Darvell, L.I.; Jones, J.M.; Nimmo, W. Prediction of biomass ash fusion be-haviour by the use of detailed characterisation methods coupled with thermodynamic analysis. Fuel 2015, 141, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Zhai, M.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, P. Comparison of bituminous coal and lignite during combustion: Combustion performance, coking and slagging characteristics. J. Energy Inst. 2019, 92, 802–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barroso, J.; Ballester, J.; Ferrer, L.; Jiménez, S. Study of coal ash deposition in an entrained flow reactor: Influence of coal type, blend composition and operating conditions. Fuel Process. Technol. 2006, 87, 737–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahmi, R.; Bridgwater, A.; Darvell, L.; Jones, J.; Yates, N.; Thain, S.; Donnison, I. The effect of alkali metals on combustion and pyrolysis of Lolium and Festuca grasses, switchgrass and willow. Fuel 2007, 86, 1560–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saddawi, A.; Jones, J.M.; Williams, A.; Le Coeur, C. Commodity Fuels from Biomass through Pretreatment and Tor-refaction: Effects of Mineral Content on Torrefied Fuel Characteristics and Quality. Energy Fuel 2012, 26, 6466–6474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, T.R.; Baxter, L.L.; Bryers, R.W.; Jenkins, B.M.; Oden, L.L. Boiler deposits from firing biomass fuels. Biomass Bioenergy 1996, 10, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).