Reformulation of the Used Model to Estimate Soil Temperature
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
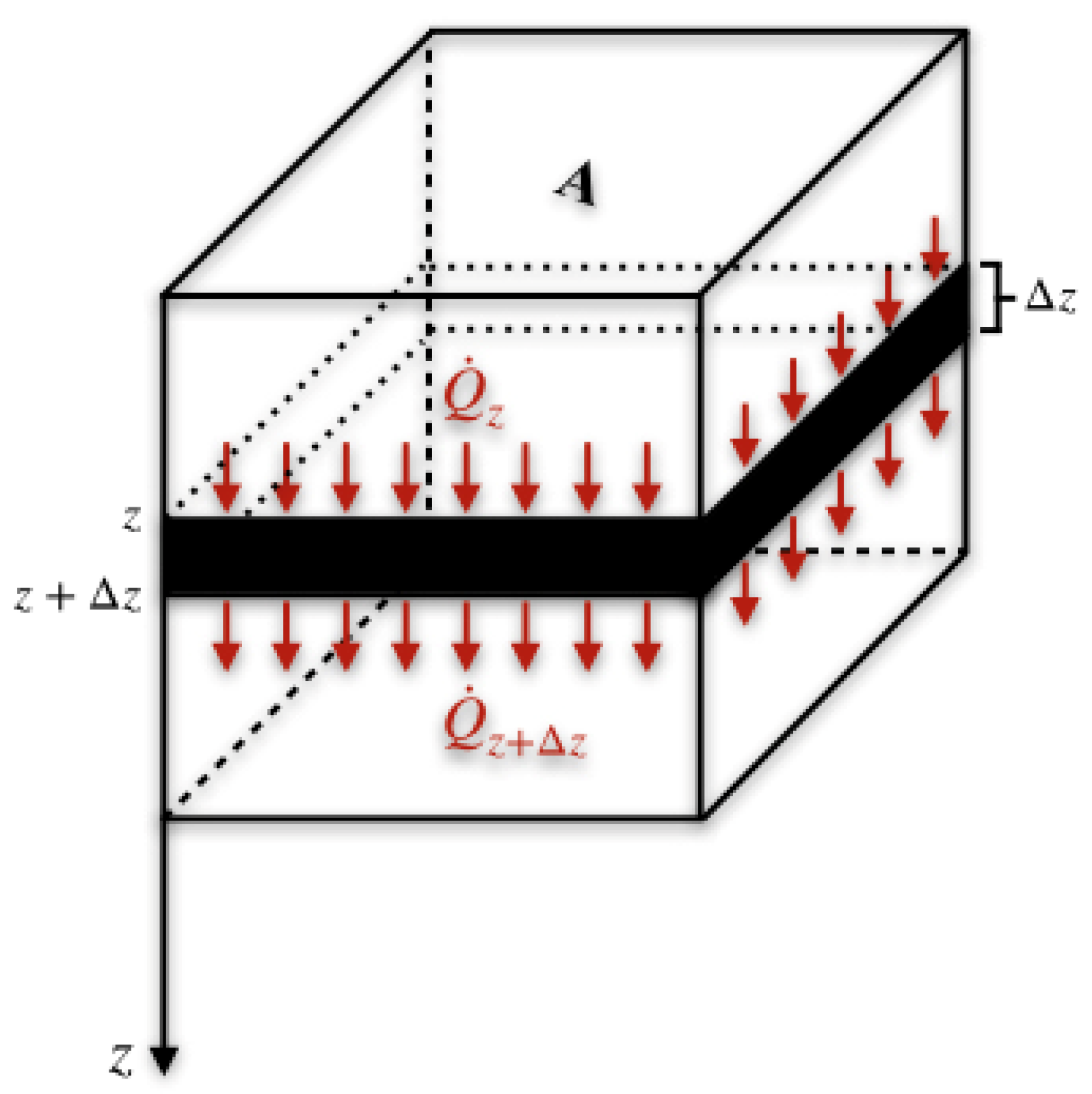
2.1. Soil Heat Flux
2.2. Mathematical Model
2.3. Phase Constant
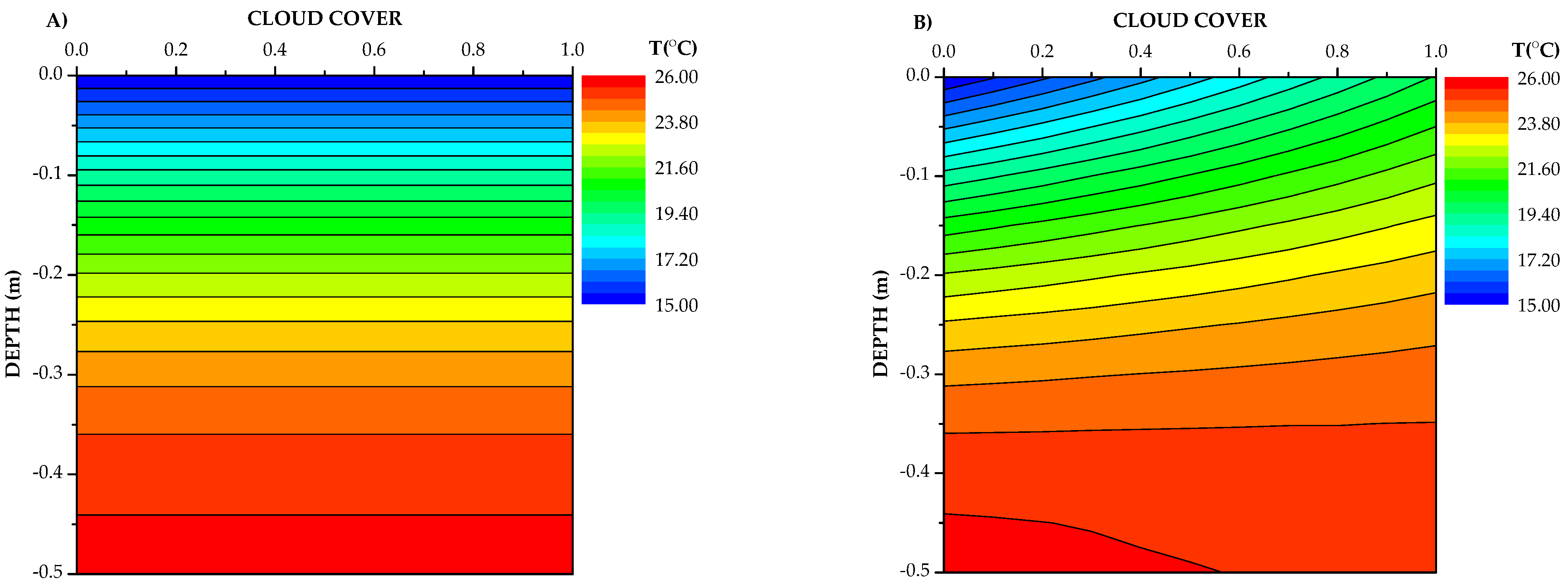
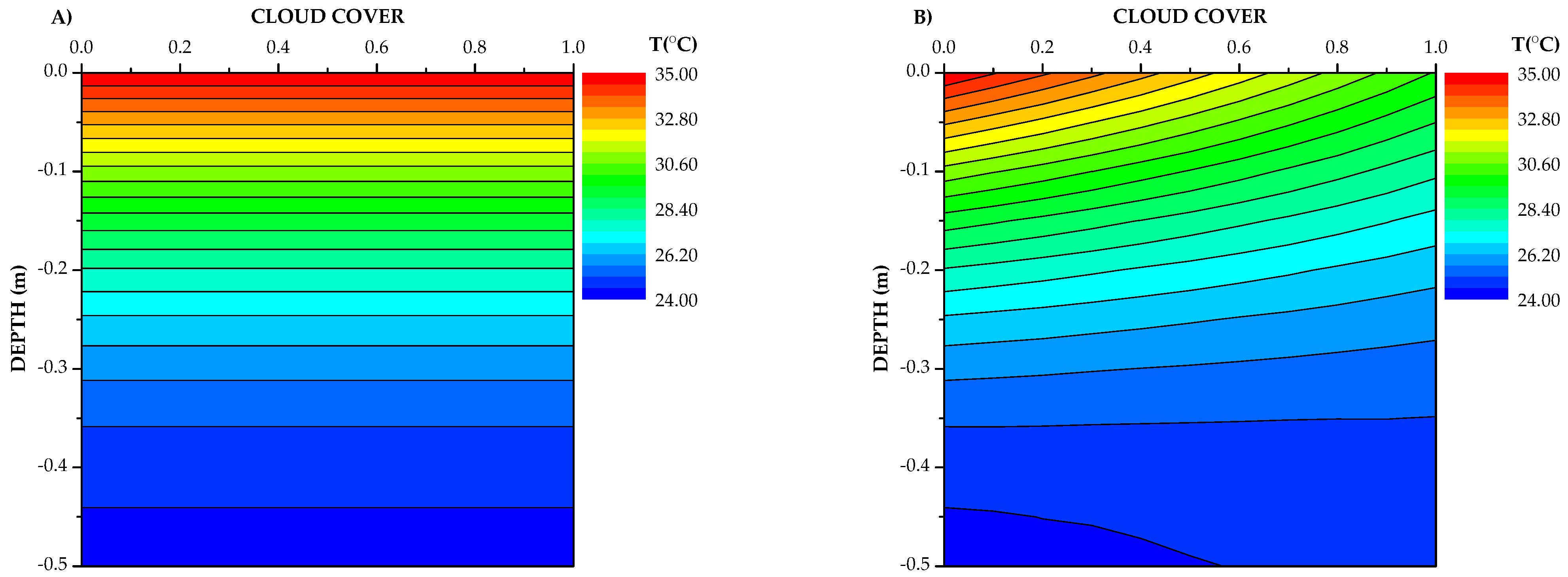
3. Model Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Beruski, G.C.; Pereira, A.B.; Sentelhas, P.C. Desempenho de diferentes modelos de estimativa da radiação solar global em Ponta Grossa, PR. Rev. Bras. Meteorol. 2015, 30, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yildirim, H.B.; Çelik, Ö.; Teke, A.; Barutçu, B. Estimating daily global solar radiation with graphical user interface in Eastern Mediterranean region of Turkey. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2018, 82, 1528–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, D.F.; Silva, D.G.; Souza, A.P.; Gomes, D.P.; Rocha, H.S. Coeficientes da equação de Angström-Prescott e sua influência na evapotranspiração de referência em Seropédica, RJ. Rev. Bras. Eng. Agríc. Ambient. 2011, 15, 838–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dornelas, K.D.S.; Silva, C.L.; Oliveira, C.A.S. Coeficientes médios da equação de Angström-Prescott, radiação solar e evapotranspiração de referência em Brasília. Pesq. Agropec. Bras. 2006, 41, 1213–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Andrade Júnior, A.S.; Noleto, D.H.; Silva, M.E.; Braga, D.L.; Bastos, E.A. Coeficientes da equação de Angström-Prescott para Parnaíba, Piauí. Comun. Sci. 2012, 3, 50–54. [Google Scholar]
- Lal, R.; Shukla, M.K. Principles of Soil Physics; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004; pp. 1–736. [Google Scholar]
- Gasparim, E.; Ricieri, R.P.; Silva, S.L.; Dallacort, R.; Gnoatto, E. Temperatura no perfil do solo utilizando duas densidades de cobertura e solo nu. Acta Sci. Agron. 2005, 27, 107–115. [Google Scholar]
- Alvalá, R.C.S.; Gielow, R.; Rocha, H.R.; Freitas, H.C.; Lopes, J.M.; Manzi, A.O.; Randow, C.; Dias, M.A.F.S.; Cabral, O.M.R.; Waterloo, M.J. Intradiurnal and seasonal variability of soil temperature, heat flux, soil moisture content, and thermal properties under forest and pasture in Rondônia. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107, LBA-10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prevedello, C.L. Física do Solo Com Problemas Resolvidos; Salesward-Discovery: Curitiba, Brazil, 1996; pp. 1–446. [Google Scholar]
- Hillel, D. Introduction to Environmental Soil Physics; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2004; pp. 1–494. [Google Scholar]
- Echer, M.P.S.; Martins, F.R.; Pereira, E.B. A importância dos dados de cobertura de nuvens e de sua variabilidade: Metodologias para aquisição de dados. Rev. Bras. Ens. Fís. 2006, 28, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz, J.M.T. A Cobertura de Nuvem e a Sua Influência Para a Variabilidade Térmica do solo. Ph.D. Thesis, Federal University of Campina Grande, Campina Grande, Brazil, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Reichardt, K.; Timm, L.C. Solo, Planta e Atmosfera: Conceitos, Processos e Aplicações; Manole: Barueri, Brazil, 2004; pp. 1–478. [Google Scholar]
- Gardner, C.M.K.; Laryea, K.B.; Unger, P.W. Soil Physical Constraints to Plant Growth and Crop Production; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1999; pp. 1–96. [Google Scholar]
- Otunla, T.A.; Oladiran, E.O. Evaluation of soil thermal diffusivity algorithms at two equatorial sites in West Africa. Ann. Geophys. 2013, 56, R0101. [Google Scholar]
- Moura, M.A.L.; Querino, C.A.S. Variação sazonal do fluxo de calor no solo dentro de um manguezal tropical. Rev. Bras. Eng. Agríc. Ambient. 2010, 14, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çengel, Y.A.; Ghajar, A.J. Transferência de Calor e Massa: Uma Abordagem Prática; Amgh Editora LTDA: Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2012; pp. 1–904. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z.; Wang, L.; Horton, R. Comparison of six algorithms to determine the soil thermal diffusivity at a site in the Loess Plateau of China. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2009, 6, 2247–2274. [Google Scholar]
- Lier, Q.J.; Durigon, A. Soil thermal diffusivity estimated from data of soil temperature and single soil component properties. Rev. Bras. Cienc. Solo 2013, 37, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silans, A.P.; Silva, F.M.; Barbosa, F.A.R. Determinação in loco da difusividade térmica num solo da região de Caatinga (PB). Rev. Bras. Cienc. Solo 2006, 30, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Horton, R.; Wierenga, P.J.; Nielsen, D.R. Evaluation of methods for determining the apparent thermal diffusivity of soil near the surface. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1983, 47, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zill, D.G. Equações Diferenciais com Aplicações em Modelagem; Cengage Learning: São Paulo, Brazil, 2016; pp. 1–504. [Google Scholar]
- Diniz, J.M.T.; Sousa, E.P.; Wanderley, J.A.C.; Filho, J.F.; Maracajá, P.B. Variabilidade diária da temperatura do solo: Um estudo de caso. Rev. Verde Agroecol. Desenvolv. Sustent. 2013, 8, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz, J.M.T.; Rafael, R.A.; Filho, J.F.; Júnior, J.R.S.; Fernandes, A.A. Características térmicas do solo observadas em cidades distintas do Estado da Paraíba. Rev. Verde Agroecol. Desenvolv. Sustent. 2013, 8, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Diniz, J.M.T.; Dantas, R.T.; Filho, J.F. Variabilidade espaço-temporal da temperatura e difusividade térmica do solo de Lagoa Seca-PB. Rev. Ambient. Água 2014, 9, 722–736. [Google Scholar]
- Diniz, J.M.T. Caracterização das Propriedades Térmicas do Solo de Lagoa Seca-PB. Master’s Thesis, Federal University of Campina Grande, Campina Grande, Brazil, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Mendoza, V.; Pazos, M.; Garduño, R.; Mendoza, B. Thermodynamics of climate change between cloud cover, atmospheric temperature and humidity. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, A.; Trenberth, K.E.; Karl, T.R. Effects of clouds, soil moisture, precipitation, and water vapor on diurnal temperature range. J. Clim. 1999, 12, 2451–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Henderson, M.; Liu, B.; Shen, X.; Chen, X.; Lian, L.; Zhou, D. Maximum and minimum soil surface temperature trends over China, 1965–2014. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 2004–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Diniz, J.M.T.; Santos, C.A.C.d.; Silva, J.P.S.d.; Rocha, Á.B.d. Reformulation of the Used Model to Estimate Soil Temperature. Energies 2022, 15, 2905. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15082905
Diniz JMT, Santos CACd, Silva JPSd, Rocha ÁBd. Reformulation of the Used Model to Estimate Soil Temperature. Energies. 2022; 15(8):2905. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15082905
Chicago/Turabian StyleDiniz, Júlio M. T., Carlos A. C. dos Santos, Jean P. S. da Silva, and Álvaro B. da Rocha. 2022. "Reformulation of the Used Model to Estimate Soil Temperature" Energies 15, no. 8: 2905. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15082905
APA StyleDiniz, J. M. T., Santos, C. A. C. d., Silva, J. P. S. d., & Rocha, Á. B. d. (2022). Reformulation of the Used Model to Estimate Soil Temperature. Energies, 15(8), 2905. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15082905






