Abstract
The power transformer is one of the most critical assets in power systems; therefore, planning and optimizing the economic investment for its replacement is crucial for the financial efficiency of the utility. A compilation of the main approaches reported in the literature for the replacement of oil-immersed power transformers is presented in this article. A chronological description of procedures presented in the literature for the determination of risk index, useful life evaluation, and transformer replacements is provided. Methodologies that use the theoretical basis of the degree of polymerization of the solid insulation of the units through the oxidation aging process to estimate their condition bring together the best tools currently available to achieve this objective. However, it is important and pertinent to complement these methodologies by considering the aging processes by pyrolysis and hydrolysis together and by incorporating economic analyses for appropriate replacement and management of these aged units.
1. Introduction
The power system infrastructure consists of critical and capital-intensive electrical assets, among which the power transformer (PT) is one of the costliest for power generation and transmission. These assets increase the voltage level at generation centers, allowing the transportation of energy over long distances, thus reducing Joule effect losses. Furthermore, PTs located in substations reduce the voltage to levels suitable for distribution in both industrial and residential areas.
An important and costly decision to be made during the PT lifecycle is its replacement to avoid a final failure and resulting consequences related to unacceptable economic, environmental, and social losses. Therefore, replacement must be optimally planned in order to avoid a hasty decision.
The international standard ISO 55000 [1] recommends that such decisions be made on the basis of risk assessments. The risk index for power transformers is performed through the evaluation of technical aspects that include both the probability of occurrence of a failure that compromises the availability of the unit, and the consequences caused by unavailability [2]. In effect, the final disposition of a PT can be decided based on a risk index that provides a broad overview of the transformer’s condition and the consequences of its failure.
Transmission and sub-transmission transformers have nominal ratings ranging from tens to hundreds of MVA [3] and operate in medium and high voltage networks. Distribution and transmission companies manage PT fleets that can include hundreds of units, each of which costs about 60% of a transformation bay price [4].
Although the average PT service life is approximately 40 years under normal operating conditions [5], it is critical to know its health status.
This is because if the PT needs to be replaced, the production, installation, and commissioning time can range from one to two years, depending on the manufacturer’s availability, time, and production capacity.
Long production and installation times, high acquisition costs, the strategic importance of the transformers within the fleet, maintenance schedules, and the overload of risks PTs can be exposed to mean it is essential to count on these methodologies for asset management. To develop such methodologies, the information available of each unit must be integrated to estimate its current and future condition within certain scenarios. In addition, such an analysis is useful to prevent major system failures or outages by detecting risky situations in timely manner, thereby reducing the likelihood of impacts on services, people, and nearby equipment.
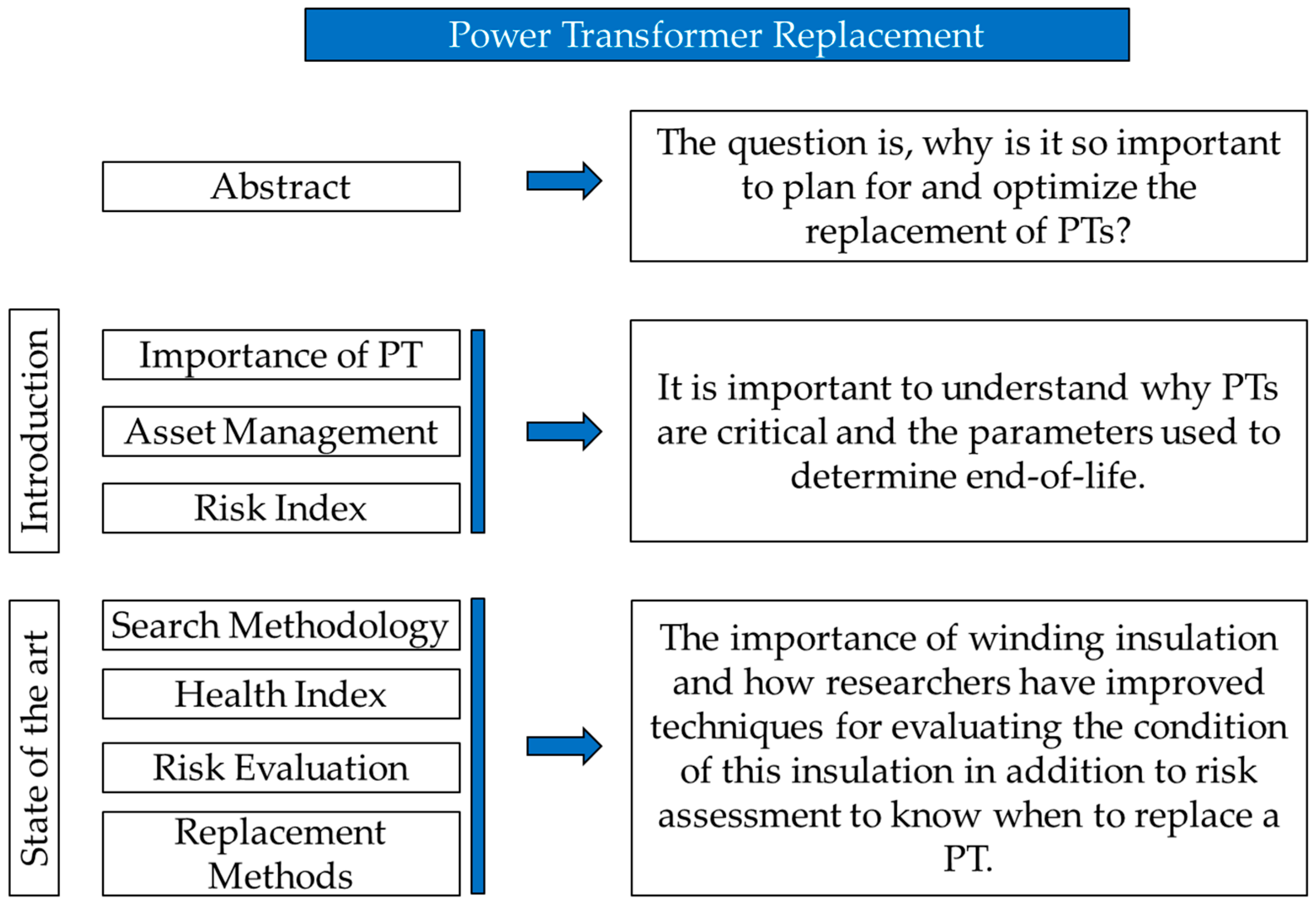
In this context, this article presents a literature review of useful methods for planning PT replacement where the parameters and tests used to determine the PT health index, the risk index, the different methods used over the years to assess the condition of these important assets, and the replacement investments made are known. Figure 1 illustrates how the literature review was approached to understand how the replacement of aging equipment has occurred over the past decade. The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 presents the adopted approach to structure the literature review. The methods for determining risk factors are described in Section 3. In Section 4, methods for calculating a transformer’s useful life are outlined, and Section 5 describes the index to schedule the PT replacement. Finally, conclusions and a synthesis are presented in Section 6.
Figure 1.
Paper logic structure.
2. Method to Structure the Literature Review
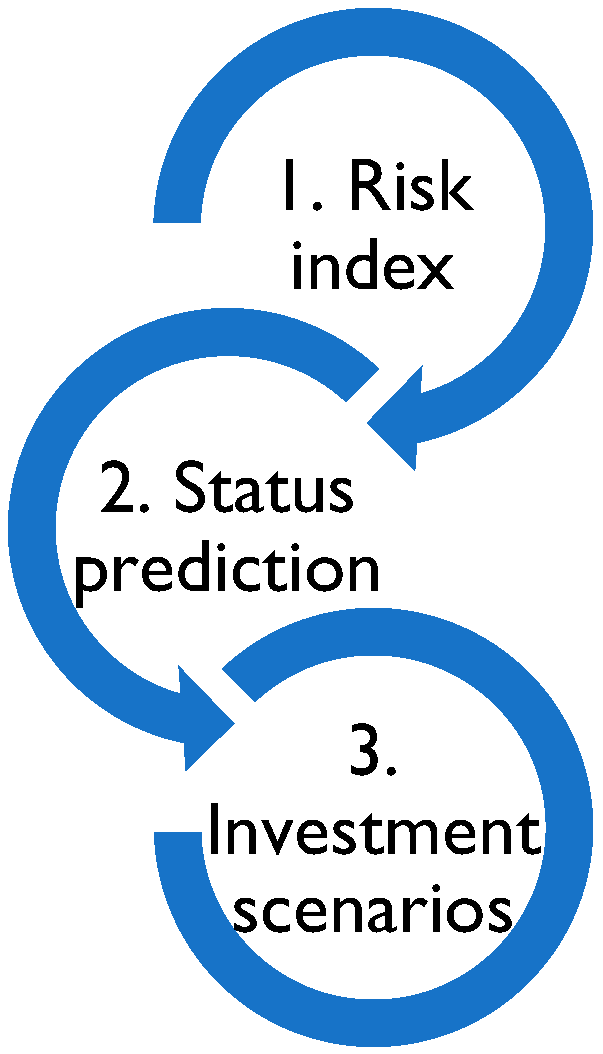
Within the first phase of elaboration of the state of art, the issues necessary to develop a long-term transformer replacement and management scheme were identified: (1) PT risk index, (2) PT status prediction or life index, and (3) investment scenarios in a PT fleet. These are related, as shown in Figure 2, according to their hierarchy. All areas are working in synergy to reach the desired objective, which is an investment scenario, including both the risk and the status of each area related to the PTs fleet.
Figure 2.
Topics to carry out a long-term transformer management scheme.
As performed in [6], each topic was searched using the following search rules, which were applied to titles, abstracts, keywords, and field of academic study as structured in the search catalog in Lens [7]:
- Power transformers risk index = Risk index AND power transformer;
- Power transformers status prediction = Status, power transformer, AND health;
- Investment scenarios in power transformer fleets = Investment AND power transformer;
- Investment scenarios in power transformer fleets considering the risk index = Risk index, power transformer, AND investment.
To apply the aforementioned search rules, each term was defined by a set of synonyms and related concepts, as follows:
- (a)
- Risk index: “risk index” OR “risk assessment”;
- (b)
- Power transformer: “power transformer” OR “power system” OR “power network”;
- (c)
- Status: “life assessment” OR “status”;
- (d)
- Health: “life assessment” OR “health index”;
- (e)
- Investment: “investment” OR “improvement” OR “replacement” OR “economic assessment”.
After applying the above rules, a “subject matter” filter was used to consider only those documents related to the electrical engineering field. The references found are reported in Table 1.

Table 1.
References obtained with Lens searching rules.
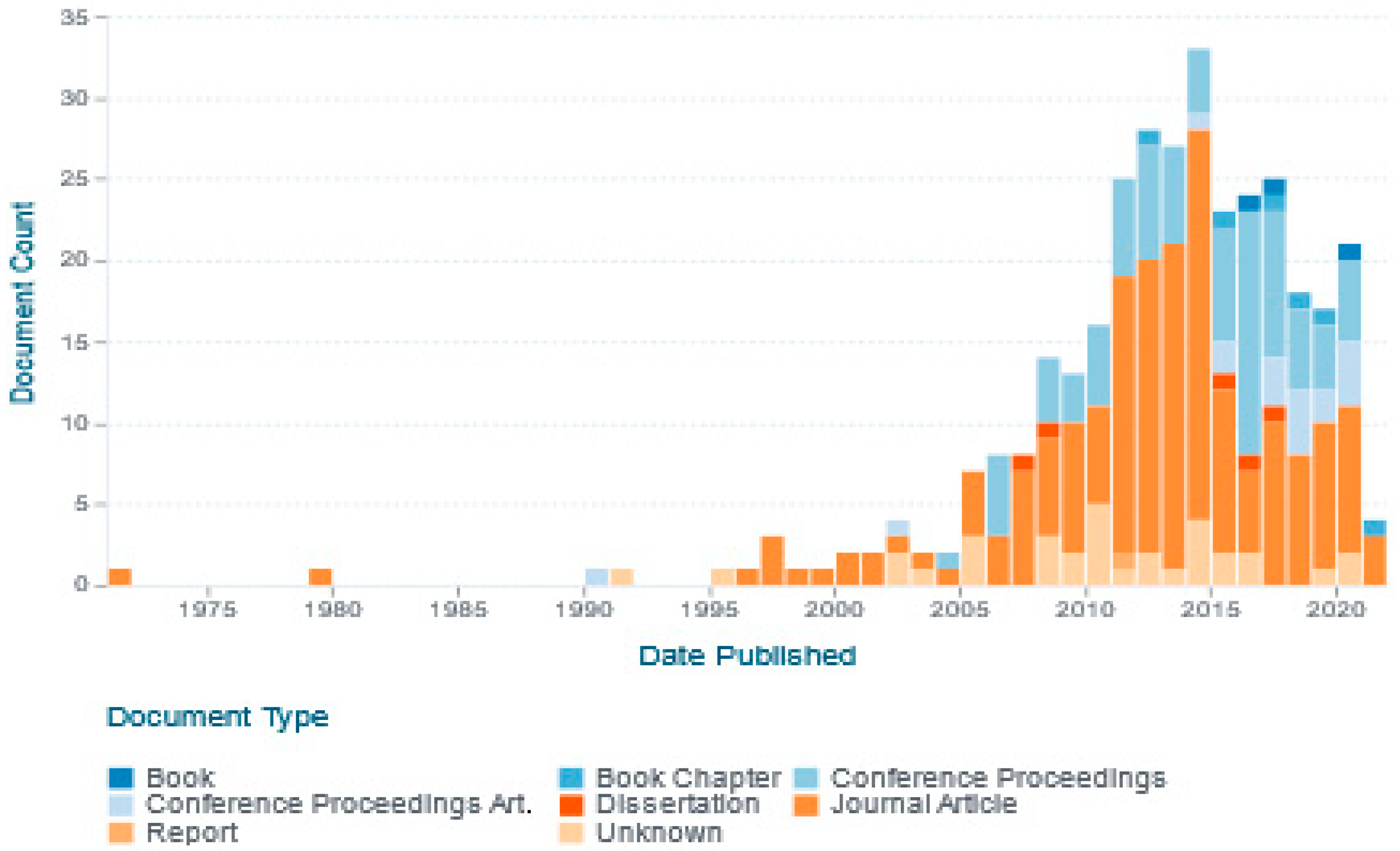
The search for risk index in power transformers returned 333 results, which indicates that it is a recent issue because there are few articles about it (see Figure 3). Conversely, the search rule for investment scenarios in PT fleets based on the risk index only returned five results; among them, only three correspond to journal articles.
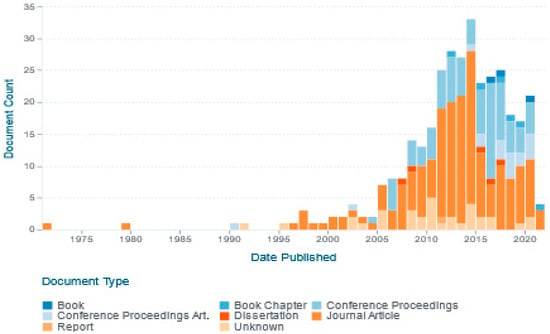
Figure 3.
Risk index works over time.
For this review, journal articles were prioritized because the peer review process guarantees the quality of the research. However, some conference articles were considered because these represent important pieces of information.
A network was created with the bibliographic information of articles on each topic described in the search rules from Lens. The abstracts of the available articles were analyzed, and those with a strong connection to the topic were identified as the primary articles. The co-occurrence method (semantic proximity indicator or two terms interdependence) was used with the WOS viewer [8]. Based on relevance and citation analysis, this method identifies journal articles with several common themes associated with the search rules. The relevance represents the number of quotes the author receives from recognized journals, whereas the citation analysis system provides tools to identify patterns in scientific literatures based on bibliographic data, allowing us to track the evolution of the research over time [9]. The number of citations reflects the document’s impact in the scientific field, while the network of citations reveals the relationships between investigations.
Each network article is discussed in the following sections; their relationships are analyzed, and their contributions are highlighted.
3. Risk Index Methodologies
Researchers have tried a variety of methods to calculate the risk index for PT. Fuzzy logic systems, whose input variables and membership functions can be modified according to the needs of the user, are the most commonly used. Rankings and weights, Markov chains, cluster analysis (k-means), and risk matrices have also been used.
PT diagnosis can be a complex task as there are several parameters to be considered [10,11].
Authors in [12] simulated a series of single-phase and three-phase short circuits to determine the transformer risk index. As the main source of deterioration of the evaluated assets, the authors focused on the damage caused to the winding insulating paper, which is appropriate because this kind of insulation cannot be regenerated. This paper is a pioneer for calculating the risk index using neural networks and fuzzy logic combined with transformed paper condition. The risk index is derived using hierarchical analytical processes of fuzzy logic, such as the speed of response and the minimal information required for operation, in addition to the advantages of neural networks, such as the distributed information storage, parallel processing, and self-learning [13]. The development of these models employs several entry criteria. c, resulting in a numerical value indicating the transformer’s risk. Sun and Wang [14] present a method based on a tree-failure analysis and an improved fuzzy analytical hierarchy process to convert the fuzzy coherence rating into optimization problems, adopting a genetic algorithm to calculate the weight of the failure cause, given as a result of the reliability value of the transformer’s components. The methodology used in [15] integrates the calculation of the oil health index, the paper health index, and the severity and/or type of incipient failure to obtain the total asset health index using fuzzy logic. As a complement to the abovementioned methods, a neuro fuzzy scheme based on DGA which mainly evaluates the carbon ratio (CO2/CO) is presented in [16]. Comparing the results, it is determined that the presented scheme has a better response speed than the fuzzy logic or former propagation of neural network methods.
In [17], the authors suggest adding the prioritization of risk to different modes of potential failures in the existing methodologies and weighing each factor differently because faults were given the same importance. Initially, the potential failure modes and damaging effects were identified, and then the risk value was defined based on operational impact, environmental, human, and economic losses, and influence in the power system. Finally, according to the probability of occurrence, identification, and severity, the risk index and a potential failure sequence are obtained. Later, Suwanasri et al. [18] add the assessment of the risk index associated with critical loads, its impact on the stability of the system, possibility and consequence of failure, possible damage to nearby properties, and socio-environmental impact. An importance matrix is created where it is classified from lowest to highest risk compared to the actual condition; this is calculated with oil data to decide which equipment to repair and/or change.
The proposal to separately evaluate the health index and the failure consequence factor to obtain the risk index from a technical point of view is presented in [19]. A risk matrix is created whose indices are the consequence versus the probability of occurrence. The numerical calculation of the risk index is carried out with the product between the probability of failure (PF) and the consequence factor (CF), or by evaluating the Euclidean distance between the origin of the risk surface and the point formed by PF and CF in the matrix. The recommendations according to the index obtained are: acquire a new asset, use it normally, perform maintenance, relocate, reduce its working regime, refurbish, repower, or perform the final disposal of the transformer. Lin and Xu [20] propose the use of the Markov approximation principle with the historical operation and maintenance data considering a failure’s influence on the network economy and reliability. For high-risk index transformers, a load reduction is proposed to ensure the safety and availability of the network. This load reduction is calculated by analyzing the power flow, seeking the optimal value where the system is not affected, and minimizing the interruption probability. This is interesting because most companies want to guarantee the quality of the power supply to the user, which means keeping the most critical assets in the fleet in top condition.
On the other hand, Khuntia and Rueda [21] develop a risk optimization model that consists of two assessments: the condition of the transformer, and the criticality of the network to which it belongs. The condition is evaluated with respect to live parts, the oil insulation, the tap changer condition, the bushings, and the surge arrester. Meanwhile, the network is evaluated in terms of load factor, load shedding, expert criterial, and bushings creepage distance. By combining these assessments, a matrix is created where the transformer located at the furthest point, i.e., the one with the highest index in both criteria, requires priority maintenance or repair actions.
Up to this point, several methods disagree with each other and do not use the latest technologies to assess the health of the PT. However, [22] gather the best attributes found in the literature and use a grouping technique of units with similar characteristics, relying on the k-means algorithm to decide what to do with the assets. This demonstrates greater effectiveness compared to a ranking classification.
The authors compare two methodologies to obtain the health index, and large differences are evident because each one uses different weights for the input factor. Using the proposed methodology, similar results are obtained, demonstrating its usefulness for PT fleet management.
In his doctoral thesis, [2] shows a very good approximation of the PT condition by using tools, such as neural networks, differential equations, probability theories and stochastic processes, Monte Carlo approximations, and fuzzy logic. The report first presents the results from the calculation of the degree of polymerization of four transformers under sample to obtain the health index of each unit using the fuzzy integration method. As a second step, it evaluates the consequence factor for the failure of each unit to obtain a risk index individually. Finally, it integrates the two previous factors (health index and the consequence factor) to propose a transformer fleet ranking aimed at providing information for the optimization process of these important assets. These steps are optimized by Cerón [23] in his doctoral thesis, where, in addition to the factors described in [2], he evaluates the future state of the units through a load and temperature forecast to analyze investment alternatives in a transformer fleet. As a result, he presents a methodology for the replacement of these assets, considering technical, economic, safety, environmental, and performance parameters. Using a real example of 102 transformer units, he demonstrates a long-term replacement strategy.
Finally, in [24], the proposed method combines three basic models: the physical degradation of the winding, the health index model, and the statistical model based on the end of the useful life of the asset. First, the individual breakage and the condition-dependent probabilities are obtained to calculate the expected remaining lifetime. As a result, a key decision is obtained for transformer managers to decide whether to perform maintenance or to replace the PT. The model is based on a set of 18 transformers only, and the probability of failure is calculated using active parts that are considered non-repairable, excluding measurements on bushings or tap changers where important failure frequencies must be taken into account for this type of study. However, oil segment replacements are included in the calculations, making the information obtained reliable over time.
Table 2 presents the synthesis of the methodologies described. It presents the input data found in the literature for the calculation of risk indices most commonly used by companies that own fleets of power transformers, showing that each author uses those they consider important or those they have in their test history, confirming that there is no standard for finding the risk index.

Table 2.
Input data to obtain the risk index.
4. Methodologies for Evaluating the Useful Life of Power Transformers
In recent years, the methods for predicting the useful life of PTs have improved as new technologies have been introduced to monitor these important assets. Initial calculations were based on temperature, but alternatives, such as fuzzy logic, neural networks, Bayesian networks, and data mining, have been used to evaluate the parameters derived from insulating paper and oil measurements. Some of the major methods implemented are presented below.
In [25], a first approximation of the transformer’s useful life calculation is presented, mainly using temperature as an indicator of insulation degradation. Guidelines for transformers’ life management are defined, and it is recommended to consider a maintenance strategy, an aging mechanism (insulation degradation), and the condition assessment by technical diagnostics during asset monitoring. One year later, Qian and Yan [26] apply fuzzy logic to a set of oil dissolve gas data to determine whether the transformer is aging normally or rapidly. As a result, the applied methodology indicates the possible cause of the failure. In 2006, Pradhan [27] develops prototype transformers to evaluate aging by increasing the temperature at different scales and performing daily physicochemical tests. At the end of the studies, it is determined that some furans tests, such as “5-Hydroxymethyl 2 Furfural” and “2-Furfuryl alcohol,” are unstable, while “2-Furaldehyde” behavior correlates with the insulation deterioration and the “2-Acetylfuran” helps to determine the assets’ aging. Furthermore, the study concludes that the best insulation aging indicator is the degree of polymerization (DP); however, as it is a destructive test (because samples must be taken from the insulating paper), it must be correlated with DGA, furans, and other diagnostic tests. Based on this information, a team of researchers compared paper degradation tests with the temperature and chargeability data from a decommissioned transformer from 2001 to 2007 and found that the maximum paper degradation can be roughly estimated by using the Arrhenius equation [28].
In [29,30], Yang compares different PT aging methods and comes to the following important conclusions: (i) The carbon ratio analysis CO2/CO considers a transformer to be aged when the radius of the gas content is greater than seven and, in some cases, greater than ten. (ii) The thermal method evaluates the hot spots of the transformer to estimate its aging. (iii) The methodology based on electrical parameters uses tangent delta tests and defines a maximum value of 0.6% for transformers between 330 kV and 500 kV at 20 °C and, in general, the tangent delta radius and its historical value should not exceed 30% for an unaged transformer. (iv) The solid insulation degree of polymerization method considers a transformer to be aged when it has the value of 150 to 200 ppm. (v) The methodology based on the furan content in transformer oil has a correlation coefficient of 0.9657 with the DP test value.
Knowing all these data, it is not appropriate to calculate the aging of PTs based only on the temperature. The main criteria for determining this parameter is a fusion between the DP, the results of electrical and physicochemical tests, and the asset’s operating history. Lastly, the author recommends taking the first insulation paper sample after 15 years of operation and then at 5-year intervals. However, [31] propose a transformer thermal model in a fault-free operating environment based on a fuzzy neural network, which gives an early indication of any deviation of the transformer from normal operating conditions. The model considers internal measurements at different locations to predict future temperature hot spots. Meanwhile, in [32], the authors perform a method to find a PT’s life index using DGA and temperature data. It is proposed to use DGA instead of furans because the data of the latter are scarce and have a higher probability of sampling errors. The method is divided into three parts: calculation of the reliability of the transformer’s oil–paper insulation during normal operation, calculation while updating during the fault events, and calculation after reparation. Compared with a practical case, the asset’s remaining life increases after proper maintenance is carried out. The “gray target” theory is used for data fitting and calculation of main function parameters.
Li et al. [33] present a self-learning method to estimate the DP value of the transformer insulation using oil parameters. Fuzzy clustering and linear regression are used. The calculations are then compared with actual values obtained from laboratory tests performed every 24 days on paper samples placed in glass bottles filled with different types of oil and exposed to different temperatures for 240 days. The proposed equation is compared with different authors’ calculations and shows a better prediction of the real Partial Discharge (PD) value measured in the laboratory. Hence, this proposal can be used to automate monitoring equipment that shows the PTs’ real-time solid insulation condition. Continuing this research topic, [34] present a Bayesian statistical learning-based methodology that calculates the health index to determine the PTs’ status. This index is compared with a company’s maintenance budget to predict the feasibility of performing maintenance or, conversely, waiting for a signal alarm to intervene in the asset.
Because not all utilities have a complete history of transformer tests, or some of these tests are missing, in [35], a time-updated health index is proposed, which performs the calculation of an asset’s initial state through Markov chains, thereby estimating certain parameters and obtaining acceptable results.
Finally, [36] analyze a PT’s life from an economic point of view, considering maintenance costs and failure penalties. It is concluded that the economic asset life is shorter than the operational life because, after a certain time, the maintenance and failure costs are so expensive that it would be feasible to opt for the transformer’s replacement.
A summary of the methods found in this section is presented in Table 3. Both the input data and the calculation method used to estimate transformer health vary from author to author. Therefore, it is advisable to treat these methods as estimates because there is no standard that defines their general calculation.

Table 3.
Methods used to calculate the useful life of PTs.
5. Assessment Indexes for Power Transformer Replacement
In order to estimate the time when a PT should be replaced, several proposals have been discussed. In [37], the authors present a model that predicts the PT’s remaining lifetime based on the paper insulation degradation to know its replacement time. Data were taken from test equipment at two-hour intervals for two years. Ambient temperature information was reconstructed according to IEC 60076-6 [38], assuming a load increase of 2% per year. The results are considered speculative as not all the necessary input parameters were available. It is noted that redistributing the load in the transformers is disadvantageous because it reduces their useful lifetime. Meanwhile, [39] recommends PT replacement using service classes (condition) and risk of disconnection as criteria. Gas analysis tests are used to determine the asset’s condition through fuzzy logic rules, and the number of disconnected customers in a blackout is used to determine the equipment replacement or maintenance sequence. The data were tested in 10 transformers, resulting in the replacement sequence.
In [40], it was found that PT replacement alternatives could be evaluated using a probabilistic approach to paper insulation thermal degradation. Two scenarios are compared: one where the units are hypothetically replaced, and a second where input data are used, including the asset’s loading history. As a result, by equalizing loads in different transformers, the waiting time for a first failure may be extended, but the unit’s useful life will be considerably reduced. In addition, monitoring it is ideal to avoid calculation errors due to input parameters, as happens in the first scenario. After two years, in [41], gray incidence analysis is used to select a PT replacement based on the lifecycle cost of the asset. This model is good for dealing with uncertain, scarce, or only few data information problems. It uses fuzzy logic to adapt qualitative indices into quantitative ones and the entropy method to determine the weight of each of them. This method is used to select a transformer between two options, showing the best scheme. However, the authors recommend that further research be conducted to address conflicting evidence problems when using evidential reasoning.
Trappey et. al. [42] identify the key factors that influence the PT’s normal operation to predict life expectancy, applying logistic regression based on the Weibull distribution. On the other hand, [43] presents a methodical decision-making system to determine the optimal replacement time for a PT. Two studies are performed: the first considers maintenance effects, and the second does not. Using the bathtub curve as a reference to represent the transformer’s lifetime, the focus is on the spot where the stable zone ends to decide whether to replace or maintain the asset. The authors conclude that to extend a transformer’s useful life, it has been shown to be cost-effective to perform at least one maintenance operation before replacing. The decision is based on an algorithm rather than on the condition of the equipment, which ignores several important factors.
The effect of changing the PT’s oil on the measurement of furan content is evaluated in [44], because it is one of the most important parameters for determining the asset’s age and whether it needs to be replaced. The oil change reduced the furan content, causing an error in the aging assessment. In order to compensate for this effect, the authors introduce a correction factor. Experimental examples in the laboratory are used to verify the functions with the correction factor, and the results are corroborated by data collected from 44 in-service transformers. This is an important milestone to consider when assessing the aging of insulation paper, as many of the operating transformers have had their oil changed during service.
In [45], the authors use the Monte Carlo method to predict load profiles in different scenarios (constant load, load increase, and load reduction). According to the results of the study, the cost of energy and the regulatory structure are responsible for the decision to replace a transformer. Using other parameters, such as humidity, temperature, transformer capacity, oxygen content, breakdown voltage, and the current age of the asset, a mathematical model is proposed to estimate the PT’s remaining lifetime because these data can be easily and cheaply collected [46]. The authors use the de Pablo equation [47] to calculate DP, replacing the furan content due to its relationship with the above. Linear regression is used for furan content below 0.6 and non-linear regression is used for furan levels above 0.6 because the linear regression produces errors exceeding 160 parts per million (ppm) of DP after this value. The Monte Carlo method is also used in [48] to calculate the power delivered in case of failure, the penalty costs in case of failure, and to estimate the retirement year of aging units. This methodology analyzes the cost–benefit of replacing the PT, considering the system risk under several load steps.
Martin et al. [49] obtained failure and retirement data for 98% of the PTs in Australia in 2016. In this paper, failure cause data for different voltage ranges are presented, and the authors conclude that windings, on-load tap changers (OLTCs), and bushings are the main failure causes. In total, 46% of the withdrawals are attributed to changes or repowering of the network, while only 9% are attributed to insulation problems. It is also confirmed that utilities remove transformers mainly when the cost of maintenance or repair exceeds their budget. Data, such as these, are extremely helpful in the development of a risk-based methodology, such as that presented in [50], which also considers the lifetime of the ventilation and pumping systems and the risk of failure of the unit. This is important for equipment operating close to its load limit or in areas with extreme temperatures.
In [51], a methodology for the classification and replacement of PTs in substations is presented. Furthermore, among the health index classifications widely studied in the literature, the authors present an Operational Vulnerability Indicator (OVI) supported by parallelism (units working together or supporting each other), which identifies the percentage of load insured by the asset in case of a contingency. In this paper, 39 PTs from seven substations are compared to determine the next transformer to be replaced based on its health index, and also due to the risk of not having a backup load in the event of a power outage. The radius of the transformer is another parameter considered by the OVI, because the greater the difference between the primary and secondary voltages, the longer it takes to build the asset. It is concluded that it is possible to postpone the replacement of a transformer if it has a backup transformer prepared for its load.
In the latest development, Cerón [23] provides an optimal methodology for the replacement of transformers, which is achieved by using the risk matrix, whose axes consist of the estimated lifetime and the failure consequences. Key factors, including oil and paper moisture, hot spot temperature, chargeability, and DP, are considered when estimating the life used. Furthermore, Non-Linear Principal Component Analysis (NLPCA) is used to extrapolate the future state of the asset. The consequence of failure is quantified using a methodology that classifies the costs associated with equipment failure into four categories: financial, safety, environmental, and network performance. In addition, the optimization model and risk matrix can be used to determine the order of asset replacement in the future, taking into account both the annual budget and the assets’ CAPEX amounts. This was one of the most complete contributions, although it did not include equipment maintenance in its methodology.
There are other methodologies, such as those found in [24,52], that use the health index to predict the need to replace a PT.
Presented in Table 4 are the advantages and disadvantages of the most common replacement methodologies. The literature indicates that the end of transformer life is directly related to the end of life of the insulation paper. It is not possible to perform direct maintenance on this insulation (except in the case of a complete rebuild of the transformer), so it is considered a primary element in determining the condition of the asset. This is mainly assessed by the DP and is used in conjunction with the failure consequence factor to evaluate the risk of the asset and thus plan for replacement.

Table 4.
A review of PT replacement methodologies.
6. Conclusions
The techniques for evaluating PT life have been refined over the past few years. The process began with estimates of failures, then moved to temperature and hot spot analysis, and finally arrived at its current stage of evaluating insulation of the paper by taking measurements in both the oil and in the insulating paper.
According to the literature, the life of a transformer is directly correlated to the lifespan of the insulating paper. This insulation is extremely difficult to maintain, so it is an essential element in determining the asset’s condition. It is generally assessed by measuring or calculating the degree of polymerization.
Each author uses different input data and calculations to estimate transformer health. The same is true for the probability of failure and the consequence factor. This type of methodology should be treated as an expert opinion due to the lack of standardization of the calculation required.
In the absence of clearly defined asset management policies, utilities could not track the history of tests or data to assess the health of assets. Therefore, it is necessary to develop methods to estimate missing data.
Statistical models were first used to estimate transformer health, then fuzzy logic, then Markov chains and Bayesian networks, and then, finally, neural networks. On the other hand, training neural networks can identify normal operating conditions of transformers and detect changes in input signals that may indicate an early warning.
To present PT replacement models, recent studies have integrated issues, such as risk index, consequence factor, and economic impact. However, there is a lack of a more comprehensive methodology that considers these factors and, at the same time, integrates the maintenance of these assets, as good and scheduled maintenance can significantly affect the health of transformers.
In order to make the best decisions about which assets to replace or maintain, it is necessary to have a methodology for estimating future data. Thus, utility budgets can be estimated to be consistent with a good asset management system.
Table 5 shows the main aspects considered by each methodology.

Table 5.
Main aspects considered by each methodology.
Author Contributions
J.Z.B.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing—Original draft preparation. S.R.: Writing—Reviewing, Supervision. A.A.R.: Resources, Writing—Reviewing, Supervision. G.C.: Writing—Reviewing and Editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported in part by the Ministry of Science, Technology, and Innovation of Colombia (MINCIENCIAS), under grant: BPIN 2021000100223—“Implementation of a digital platform to increase the use of the assets that belong to the electrical network of the archipelago of San Andres and Providencia”.
Acknowledgments
Financial supports from the National Council for Scientific and Technical Research (CONICET) and the Deutscher Akademischer Austauschdienst (DAAD) are gratefully acknowledged.
Conflicts of Interest
Our paper currently is not submitted for publication at any other journal. All authors agree with the content of the paper. There are no conflict of interest with any of the authors.
References
- ISO 55000; Asset Management—Overview, Principles and Terminology. International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; p. 25.
- Medina, R.D. Desarrollo de Indicadores Para El Análisis de Riesgo En Parques de Transformadores de Potencia Dentro de Un Contexto de Gestión de Activos Eléctricos. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Nacional de San Juan, San Juan, Puerto Rico, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- IEEE Std C57.12.80-2010 (Revision of IEEE Std C57.12.80-2002); IEEE Standard Terminology for Power and Distribution Transformers. IEEE Standards Association: Manhattan, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 1–60. [CrossRef]
- Jahromi, A.; Piercy, R.; Cress, S.; Service, J.; Fan, W. An Approach to Power Transformer Asset Management Using Health Index. IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag. 2009, 25, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duval, M.; Pablo, A.D.; Atanasova-Hoehlein, I.; Grisaru, M. Significance and Detection of Very Low Degree of Polymerization of Paper in Transformers. IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag. 2017, 33, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caicedo, J.; Mamani, M.; Lopez, S.; Romero, A.A.; Zini, H.; Ratta, G. Impactos de La Conexión de Vehículos Eléctricos En Sistemas de Potencia-Revisión Literaria. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Biennial Congress of Argentina, Bariloche, Argentina, 11–13 June 2014; pp. 645–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambia Lens. Available online: https://www.lens.org/ (accessed on 12 March 2021).
- Lelden University. VOSviewer Version 1.6.11. Available online: https://www.vosviewer.com/ (accessed on 12 March 2021).
- García, A. El Arte de Elaborar El Estado Del Arte En Una Investigación. In Serie Técnica de Manuales Prácticos Para El Investigador; Technological Editorial of Costa Rica: San José, Costa Rica, 2014; ISBN 978-9930-541-06-7. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, U.M.; Reddy, M.V.P.; Jarial, R.K. Fuzzy Logic Based System to Diagnose Internal Faults of Power Transformer. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Communication and Industrial Application, ICCIA 2011, Kolkata, India, 26–28 December 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Equbal, M.D.; Islam, T. A Comprehensive Comparative Study of DGA Based Transformer Fault Diagnosis Using Fuzzy Logic and ANFIS Models. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2015, 22, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, W.C.; Mombello, E.; Jardini, J.A.; Rattá, G. Fuzzy Risk Index for Power Transformer Failures Due to External Short-Circuits. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2009, 79, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.G.; Yu, Q.; Luo, R.C. Application of Fuzzy Analytic Hierarchy Process and Neural Network in Power Transformer Risk Assessment. J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. 2012, 19, 982–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.Y.; Wang, X.; Zheng, Y.H.; Li, L.X.; Xu, Q.S. Application of FTA and Improved FAHP in Power Transformer Risk Assessment. Adv. Mat. Res. 2014, 860–863, 2157–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranga, C.; Chandel, A.K.; Chandel, R. Expert System for Condition Monitoring of Power Transformer Using Fuzzy Logic. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2017, 9, 044901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, H.; Yadav, A.K.; Mishra, S.; Mehto, T. Application of Neuro-Fuzzy Scheme to Investigate the Winding Insulation Paper Deterioration in Oil-Immersed Power Transformer. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2013, 53, 256–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, R.; Bian, J.; Yang, L.; Grzybowski, S. Cloud Model-Based Failure Mode and Effects Analysis for Prioritization of Failures of Power Transformer in Risk Assessment. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst. 2013, 23, 1172–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwanasri, T.Y.; Suwanasri, C.; Phadungthin, R. Risk Assessment Based on Condition and Importance Criteria for Power Transformer in Thailand Transmission Network. IEEJ Trans. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2015, 10, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, R.D.; Morales, D.X.; Toledo, M.A.; Cabrera, J.B. Power Transformer Risk Index Assessment for an Asset Management Plan. In Proceedings of the 2017 CHILEAN Conference on Electrical, Electronics Engineering, Information and Communication Technologies, Pucon, Chile, 18–20 October 2017; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Xu, Y.Y.; Liang, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, N.; Zhang, G.J. A Risk Assessment Method of Transformer Considering the Economy and Reliability of Power Network. In Proceedings of the ICEMPE 2017—1st International Conference on Electrical Materials and Power Equipment, Xi’an, China, 14–17 May 2017; pp. 594–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khuntia, S.R.; Rueda, J.L.; Bouwman, S.; van der Meijden, M.A.M.M. A Literature Survey on Asset Management in Electrical Power [Transmission and Distribution] System. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst. 2016, 26, 2123–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero Quete, A.A.; David, H.; David, J.; Moreno, G. A Practical Method for Risk Assessment in Power Transformer Fleets. Dyna 2017, 84, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerón Piamba, A.F. Metodología Para La Definición de Estrategias de Sustitución En El Largo Plazo Para Transformadores de Potencia; Considerando Criterios Técnicos y Económicos, Universidad del Valle: Cali, Colombia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Foros, J.; Istad, M. Health Index, Risk and Remaining Lifetime Estimation of Power Transformers. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2020, 35, 2612–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumereder, C.; Muhr, M.; Körbler, B. Lifetime Management of Power TransformersLebensdauermanagement von Leistungstransformatoren. E I Elektrotechnik Und Inf. 2003, 120, 420–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Yan, Z. Fuzzy Synthetic Method for Life Assessment of Power Transformer. IEE Proc. Sci. Meas. Technol. 2004, 151, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, M.K. Assessment of the Status of Insulation during Thermal Stress Accelerated Experiments on Transformer Prototypes. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2006, 13, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, M.A.; Fialho, M.; Martins, J.; Soares, M.; Cristina, M.; Lopes, R.C.; Campelo, H.M.R. Power Transformer End-of-Life Assessment-Pracana Case Study*. IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag. 2011, 27, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C. Research of Ageing and Life Assessment Methods of Power Transformers in Nuclear Power Plants. Adv. Mat. Res. 2013, 614–615, 1109–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C. Life Assessment Methods of Large and Medium-Sized Power Transformers. In Proceedings of the IET International Conference on Information Science and Control Engineering 2012 (ICISCE 2012), Shenzhen, China, 7–9 December 2012; Institution of Engineering and Technology: London, UK, 2012; pp. 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- Rigatos, G.; Siano, P. Power Transformers’ Condition Monitoring Using Neural Modeling and the Local Statistical Approach to Fault Diagnosis. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2016, 80, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Yu, T.; Wang, G.; Yang, B.; Zhou, L. Hot Spot Temperature and Grey Target Theory-Based Dynamic Modelling for Reliability Assessment of Transformer Oil-Paper Insulation Systems: A Practical Case Study. Energies 2018, 11, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Ge, Z.; Abu-Siada, A.; Yang, L.; Li, S.; Wakimoto, K. A New Technique to Estimate the Degree of Polymerization of Insulation Paper Using Multiple Aging Parameters of Transformer Oil. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 157471–157479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarajcev, P.; Jakus, D.; Vasilj, J. Optimal Scheduling of Power Transformers Preventive Maintenance with Bayesian Statistical Learning and Influence Diagrams. J. Clean Prod. 2020, 258, 120850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milosavljevic, S.; Janjic, A. Integrated Transformer Health Estimation Methodology Based on Markov Chains and Evidential Reasoning. Math. Probl. Eng. 2020, 2020, 7291749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fu, L. Power Transformer Life Analysis Based on Lambert W Function. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Power Grid System and Green Energy (PGSGE 2021), Wuhan, China, 26–28 March 2021; Volume 252, p. 01004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wouters, P.A.A.F.; Van Schijndel, A.; Wetzer, J.M. Remaining Lifetime Modeling of Power Transformers: Individual Assets and Fleets. IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag. 2011, 27, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEC 60076-6; Power Transformers—Part 6: Reactors. International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC): Geneva, Switzerland, 2007; p. 242.
- Fischer, M.; Tenbohlen, S.; Schäfer, M.; Haug, R. Determining Power Transformers’ Sequence of Service in Power Grids. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2011, 18, 1789–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Schijndel, A.; Wouters, P.A.A.F.; Wetzer, J.M. Modeling of Replacement Alternatives for Power Transformer Populations. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2012, 27, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liao, R.; Yang, L.; Deng, X.; Cheng, H.; Lv, C. A Cost-Effectiveness Assessment Model Using Grey Correlation Analysis for Power Transformer Selection Based on Life Cycle Cost. Kybernetes 2014, 43, 5–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trappey, C.V.; Trappey, A.J.C.; Ma, L.; Tsao, W.T. Data Driven Modeling for Power Transformer Lifespan Evaluation. J. Syst. Sci. Syst. Eng. 2014, 23, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldhubaib, H.A.; Salama, M.M.A. A Novel Approach to Investigate the Effect of Maintenance on the Replacement Time for Transformers. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2014, 29, 1603–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Yang, L.; Liao, R.; Sun, W.; Zhang, Y. Effect of Oil Replacement on Furfural Analysis and Aging Assessment of Power Transformers. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2015, 22, 2611–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatta, F.M.; Geri, A.; Maccioni, M.; Maiolini, C.; Cresta, M.; Paulucci, M.; Palone, F.; Cannavale, G.; Scaggiante, M. Impact of the Recent EU Regulation on HV/MV Transformers: Possible Technical-Economic Benefits Arising from the Replacement of Old Transformers. Two Case Studies. In Proceedings of the EEEIC 2016—International Conference on Environment and Electrical Engineering, Florence, Italy, 7–10 June 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillary, W.D.A.G.; Jayarathna, K.L.I.M.P.B.; Ranasinghe, L.I.; Samarakoon, S.M.B.P.; Rathnayake, N.M.T.N.; Lucas, J.R.; Samarasinghe, R. A Tool for Estimating Remaining Life Time of a Power Transformer. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Moratuwa Engineering Research Conference, Moratuwa, Sri Lanka, 29–31 May 2017; pp. 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pablo, A. Furfural and Ageing: How Are They Related. In Proceedings of the IEE Colloquium Insulating Liquids, Leatherhead, UK, 27 May 1999; Volume 1999, p. 5. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Z.; Wu, K.; Cheng, C.; Song, W. Replacement of Aging Power Transformers Considering System Risks under Multi-Level Load. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting, Chicago, IL, USA, 16–20 July 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, D.; Marks, J.; Saha, T. Survey of Australian Power Transformer Failures and Retirements. IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag. 2017, 33, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyuboglu, O.H.; Dindar, B.; Gul, O. Risk Assessment by Using Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA) Based on Power Transformer Aging for Maintenance and Replacement Decision. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 2nd Global Power, Energy and Communication Conference, GPECOM 2020, Online, 20–23 October 2020; pp. 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, W.I.; Feil, D.L.P.; Canha, L.N.; Abaide, A.R.; Marchesan, T.B.; Carraro, R. Operational Vulnerability Indicator for Prioritization and Replacement of Power Transformers in Substation. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2018, 102, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harianti, S.; Purnomo, M.H. Determining Priority of Power Transformer Replacement Project by Using Fuzzy AHP Method. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Information and Communication Technology and Systems, ICTS 2019, Surabaya, Indonesia, 18 July 2019; pp. 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).