Analysis of Torque Ripple in V-Shape Interior Permanent Magnet Machine Based on General Airgap Field Modulation Theory
Abstract
:1. Introduction
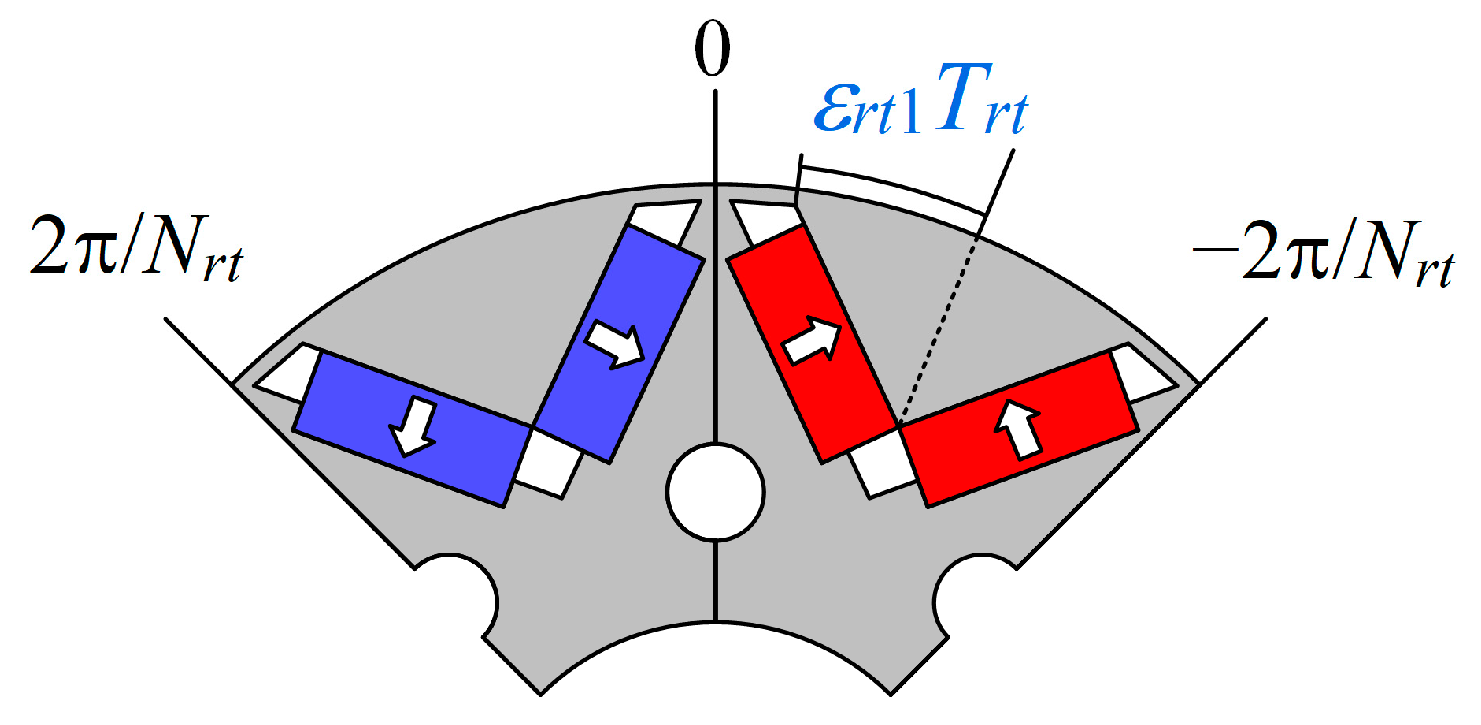
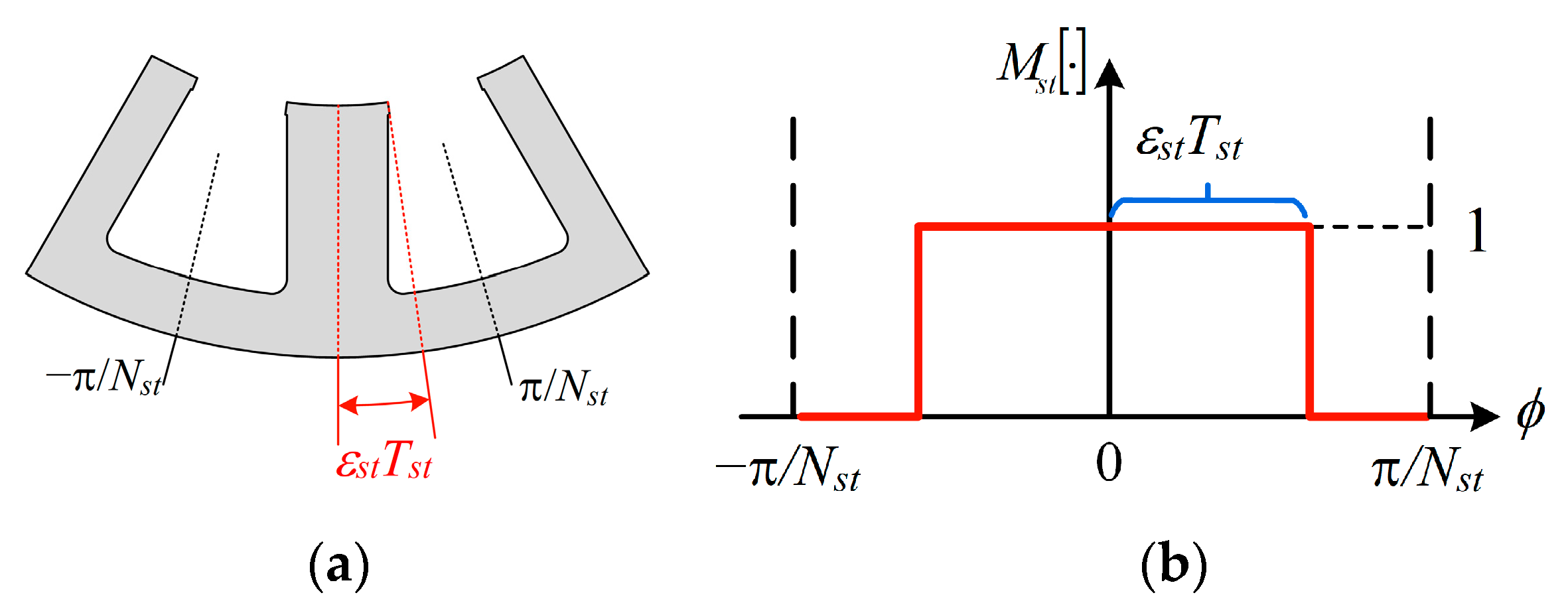
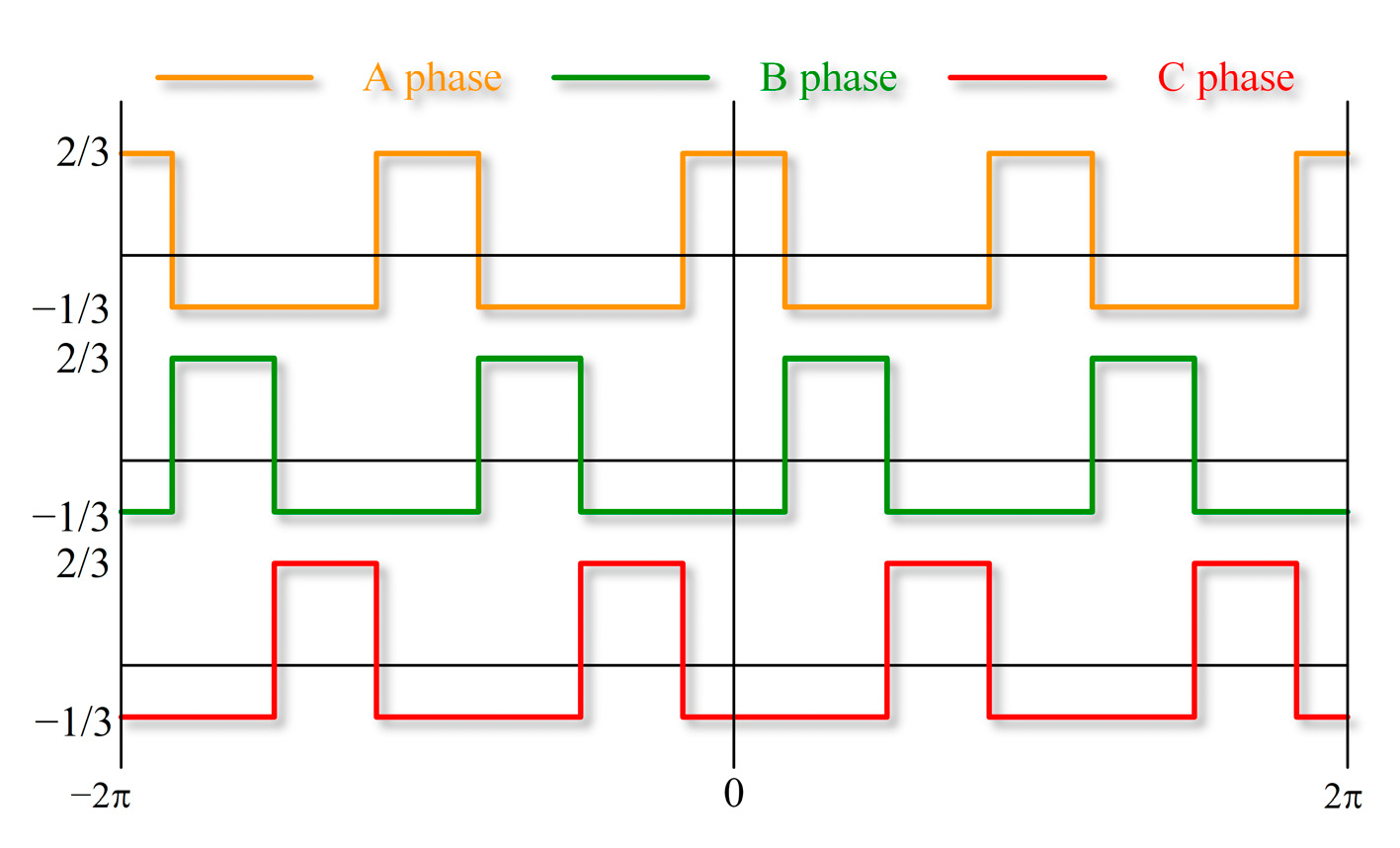
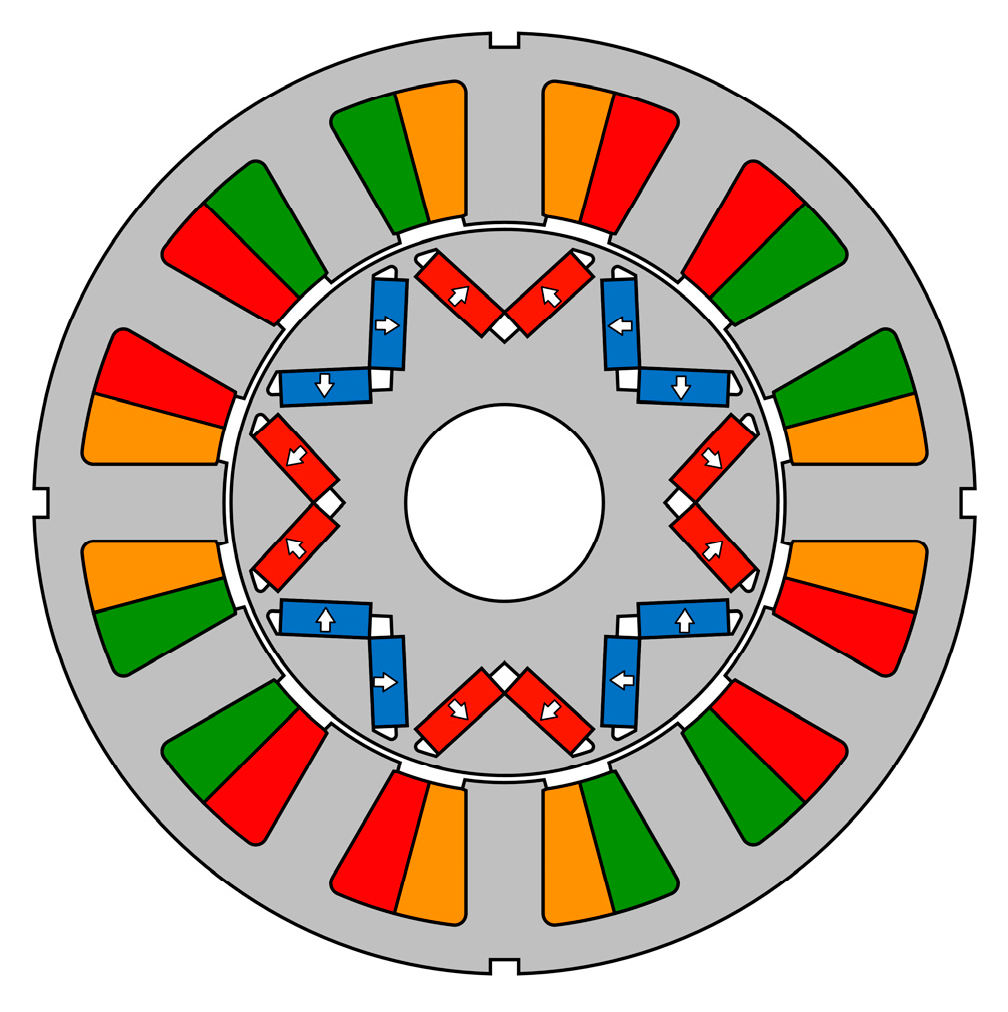
2. Field Modulation Behavior of V-Shape IPM Machine
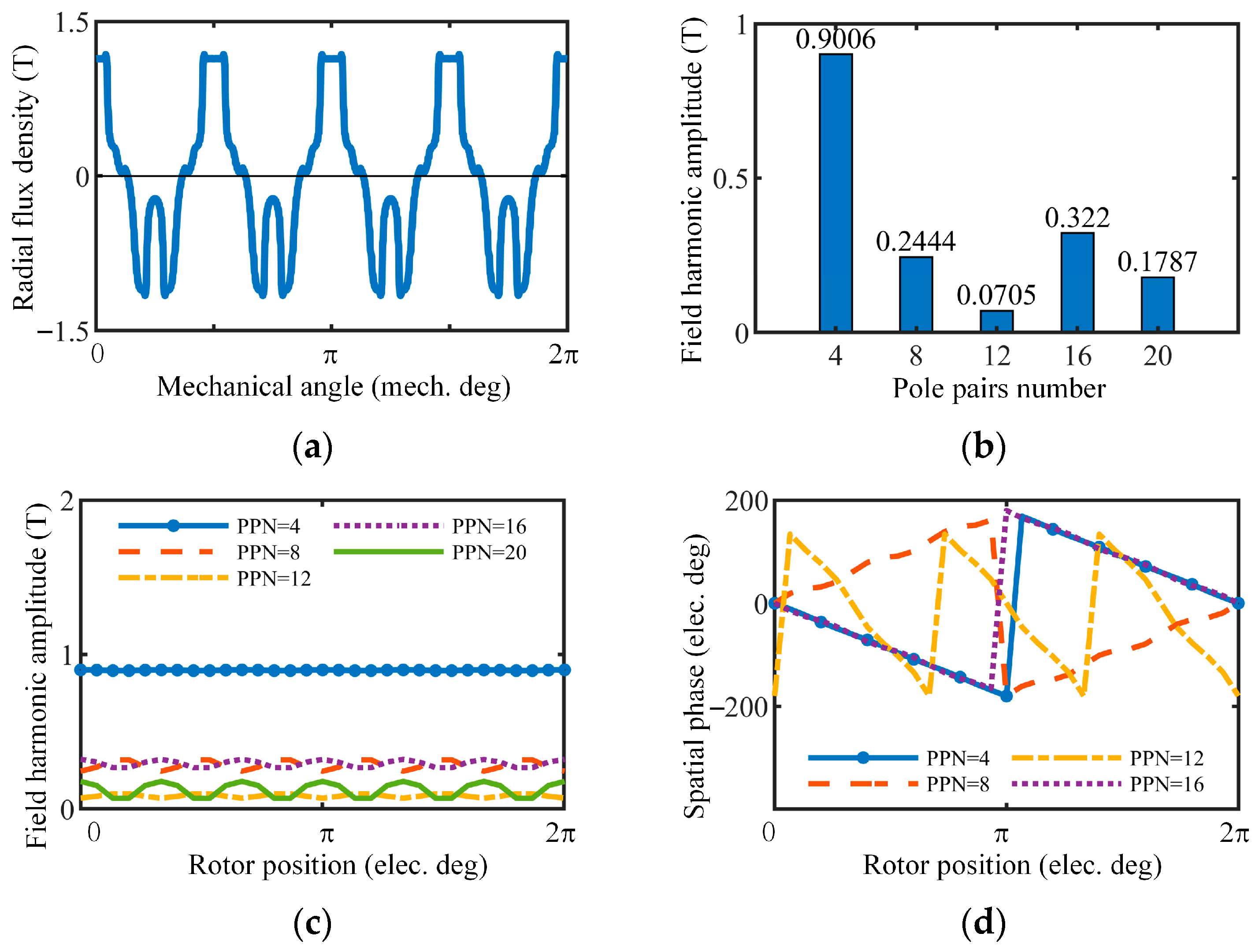
2.1. Rotor Modulation of PM-Excited Field
2.2. Stator Modulation of PM-Excited Field
2.3. Stator Modulation of Armature Field
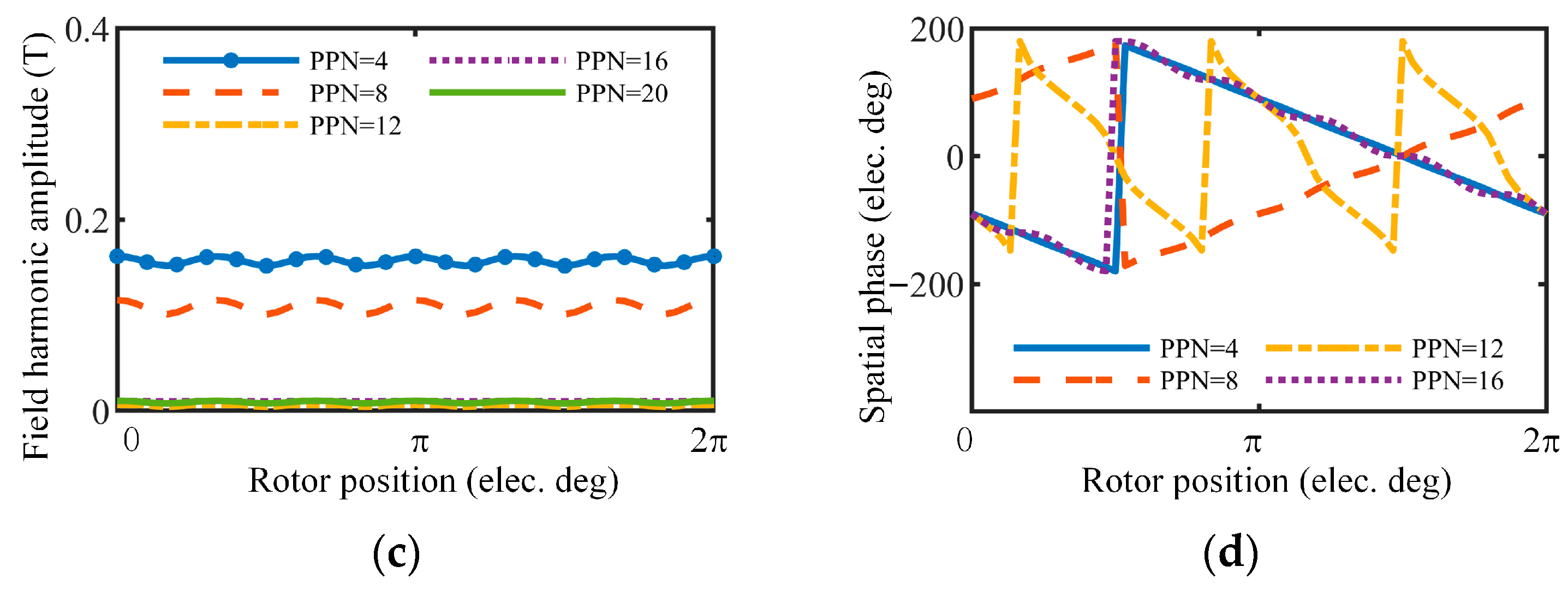
2.4. Rotor Modulation of Armature Field
2.5. Modulated PM-Excited and Armature Fields
3. Torque Ripple Analysis
3.1. Three Torque Ripple Components
3.2. Relationship between the Field Harmonics and Torque Ripple
3.2.1. PM-Excited Cogging Torque and Armature Cogging Torque
3.2.2. Modulation Torque Ripple
4. FEA-Assisted Dual FFT Analysis Method and Torque Ripple Model
4.1. FEA-Assisted Dual FFT Analysis Method
4.2. Cogging Torque Model
4.3. Modulation Torque Ripple Model
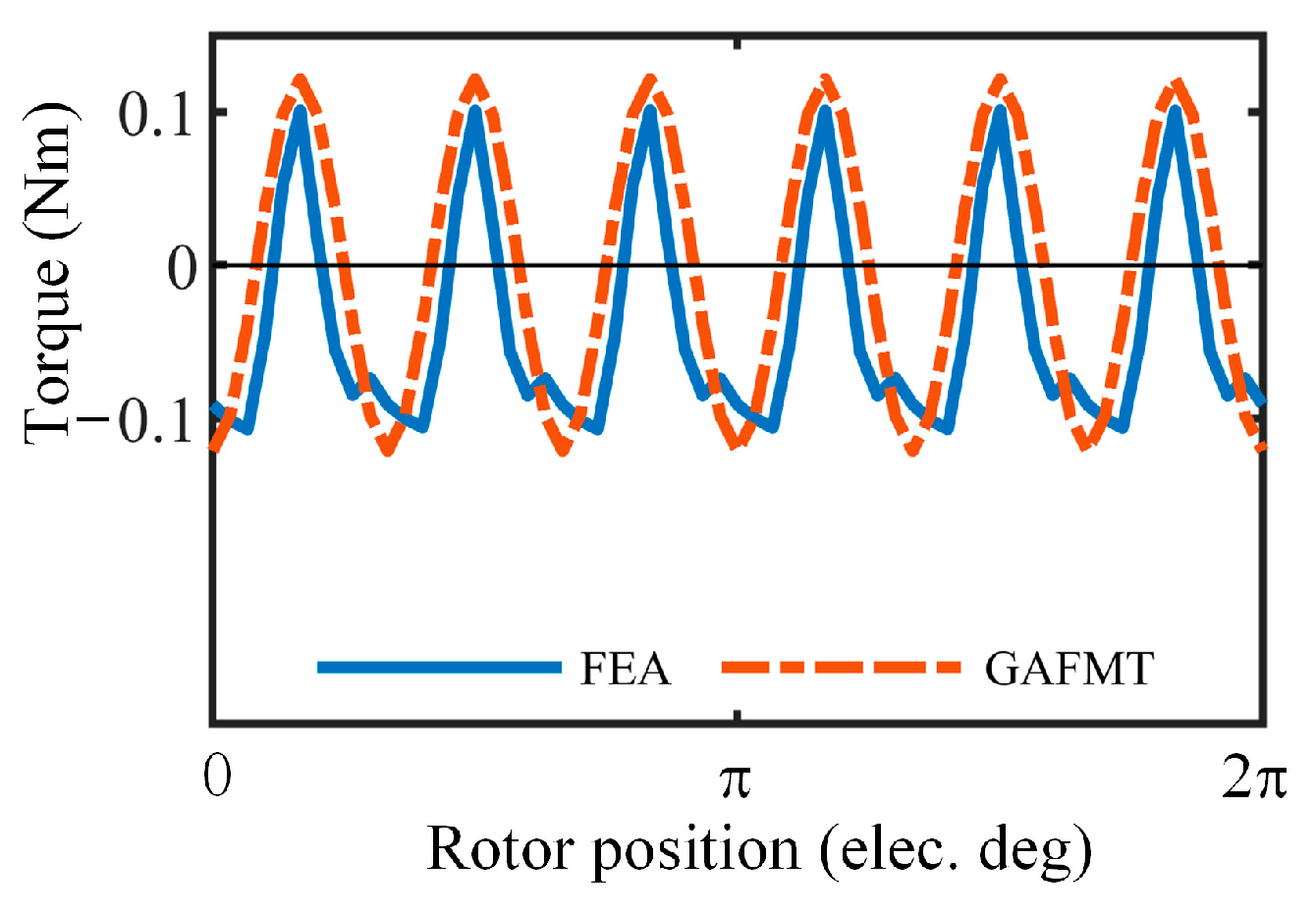
5. Demonstration of Torque Ripple Model
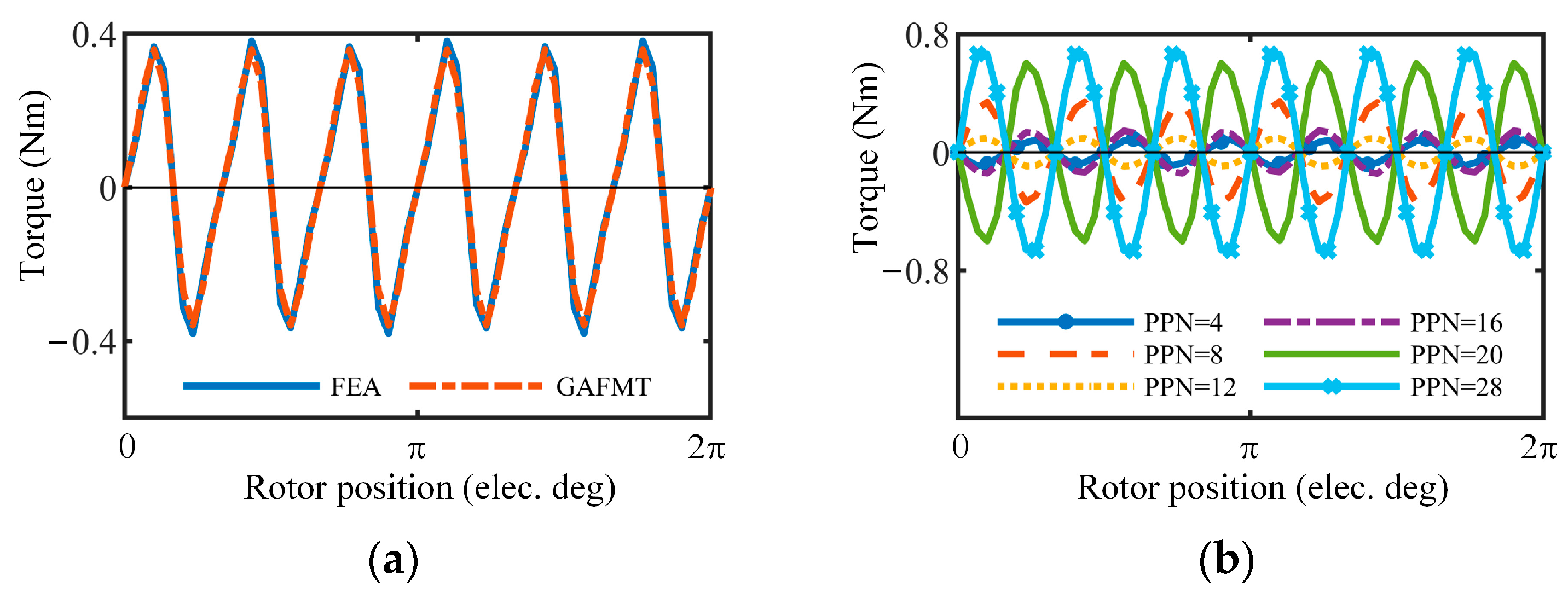
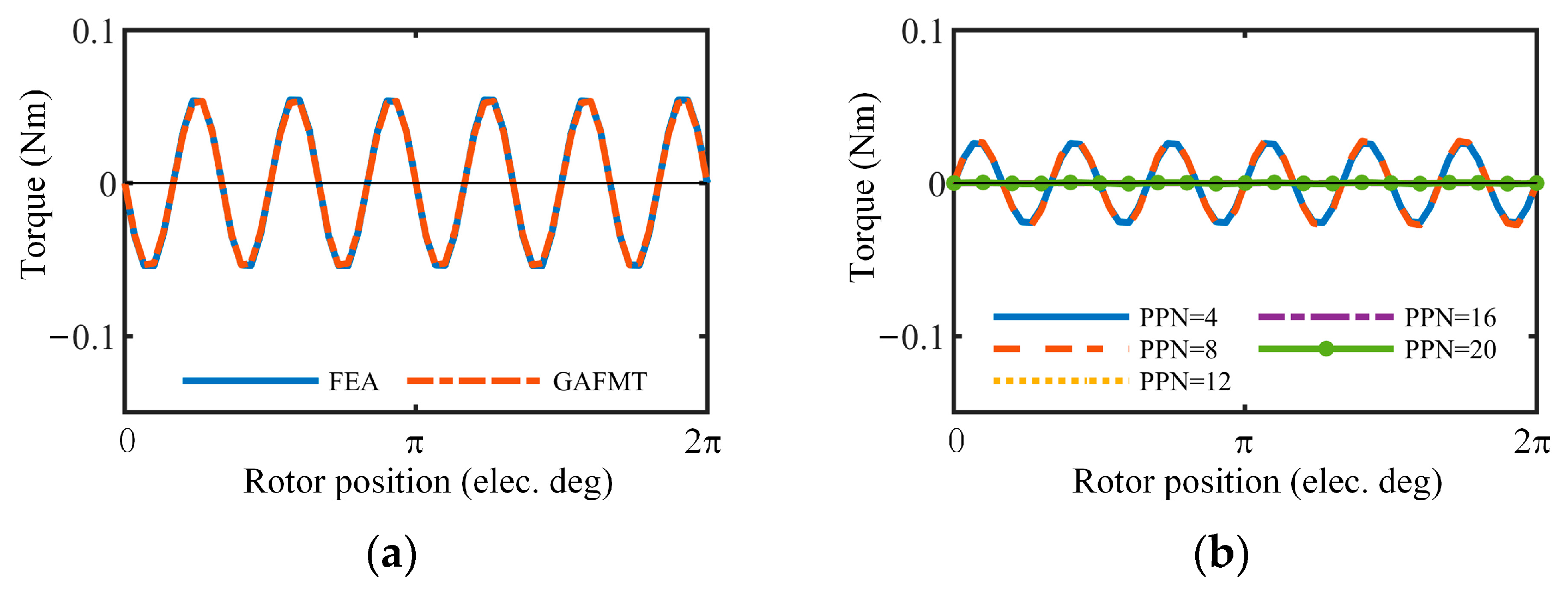
5.1. PM-Excited Cogging Torque
5.2. Armature Cogging Torque
5.3. Modulation Torque Ripple
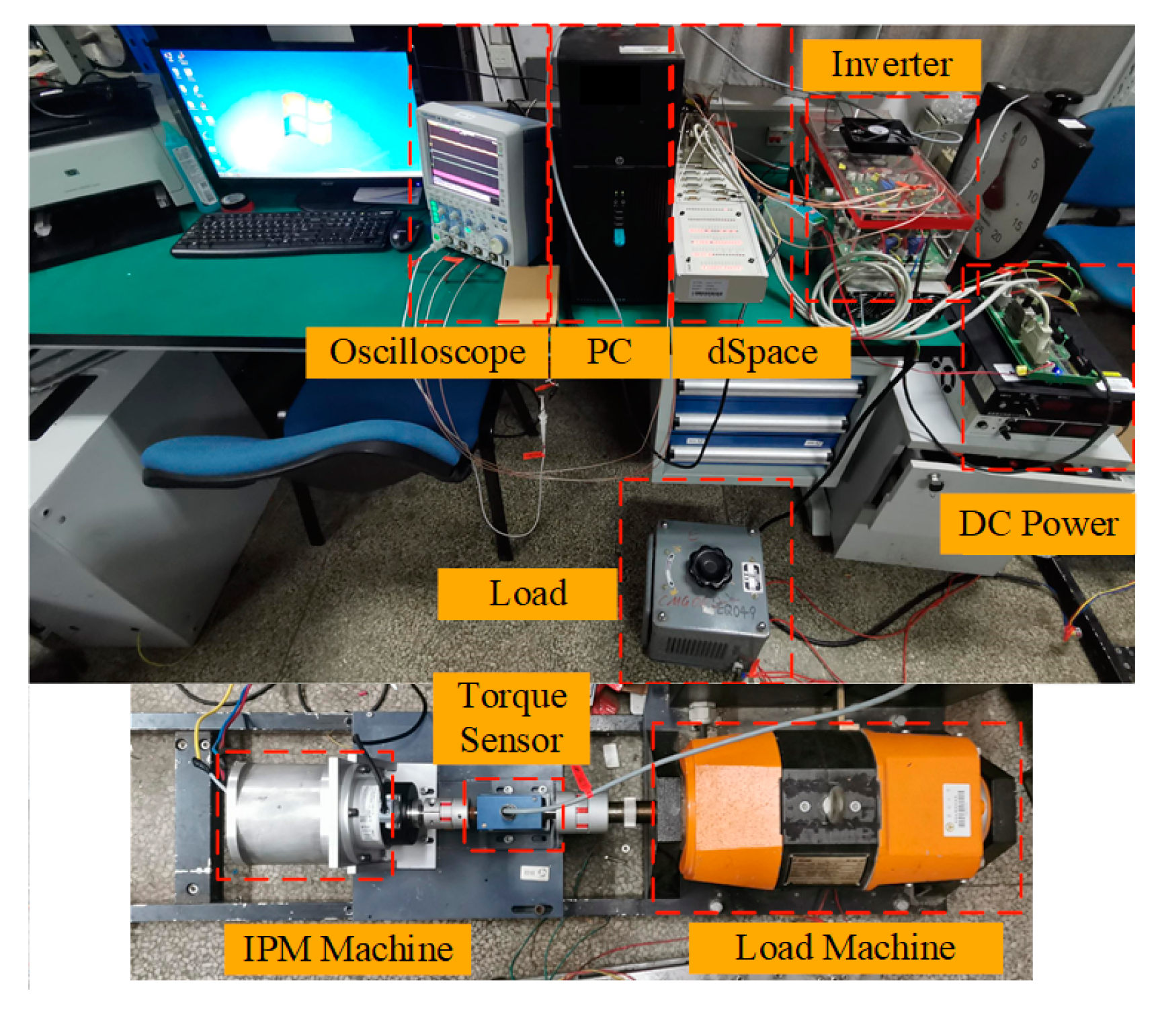
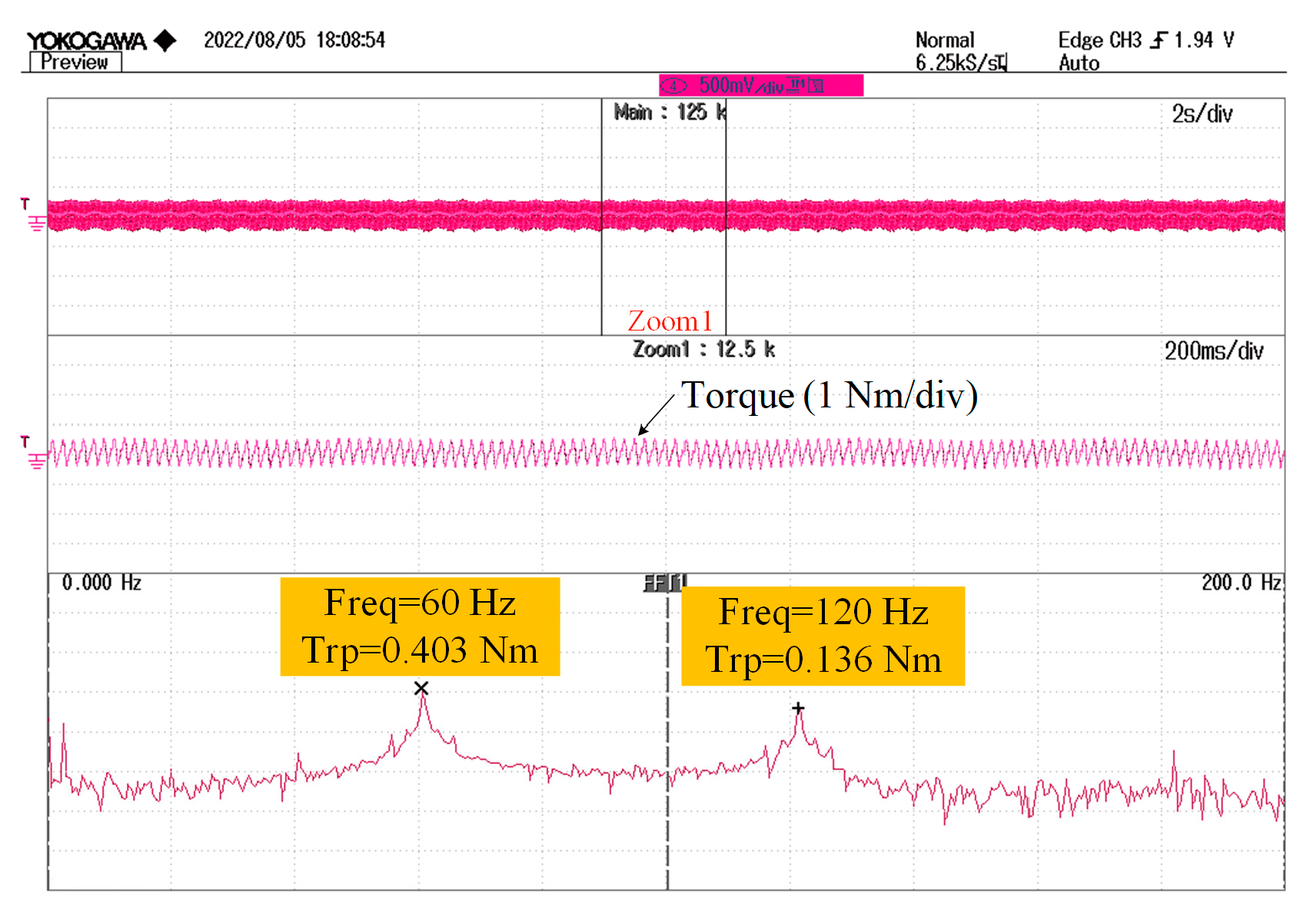
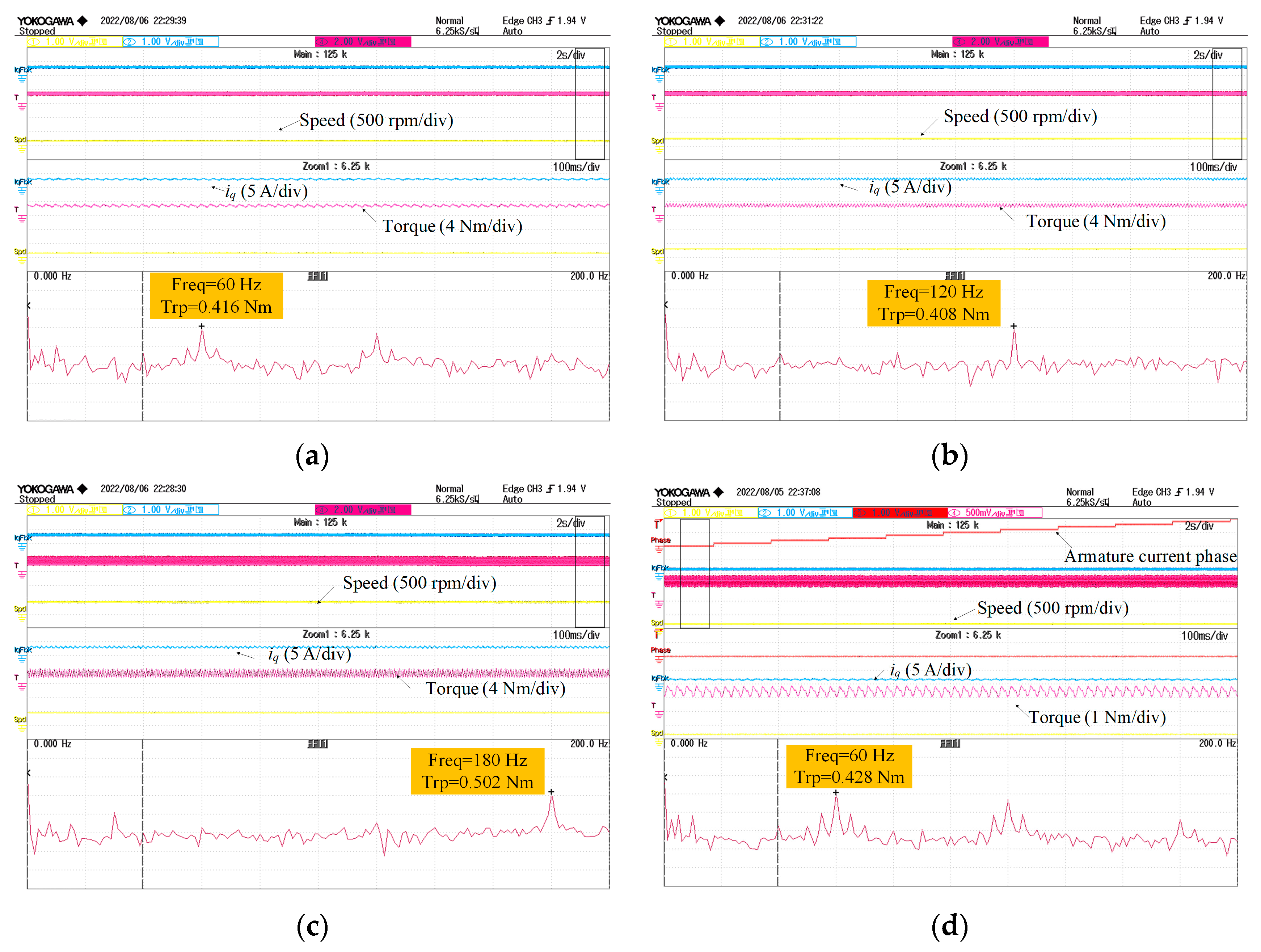
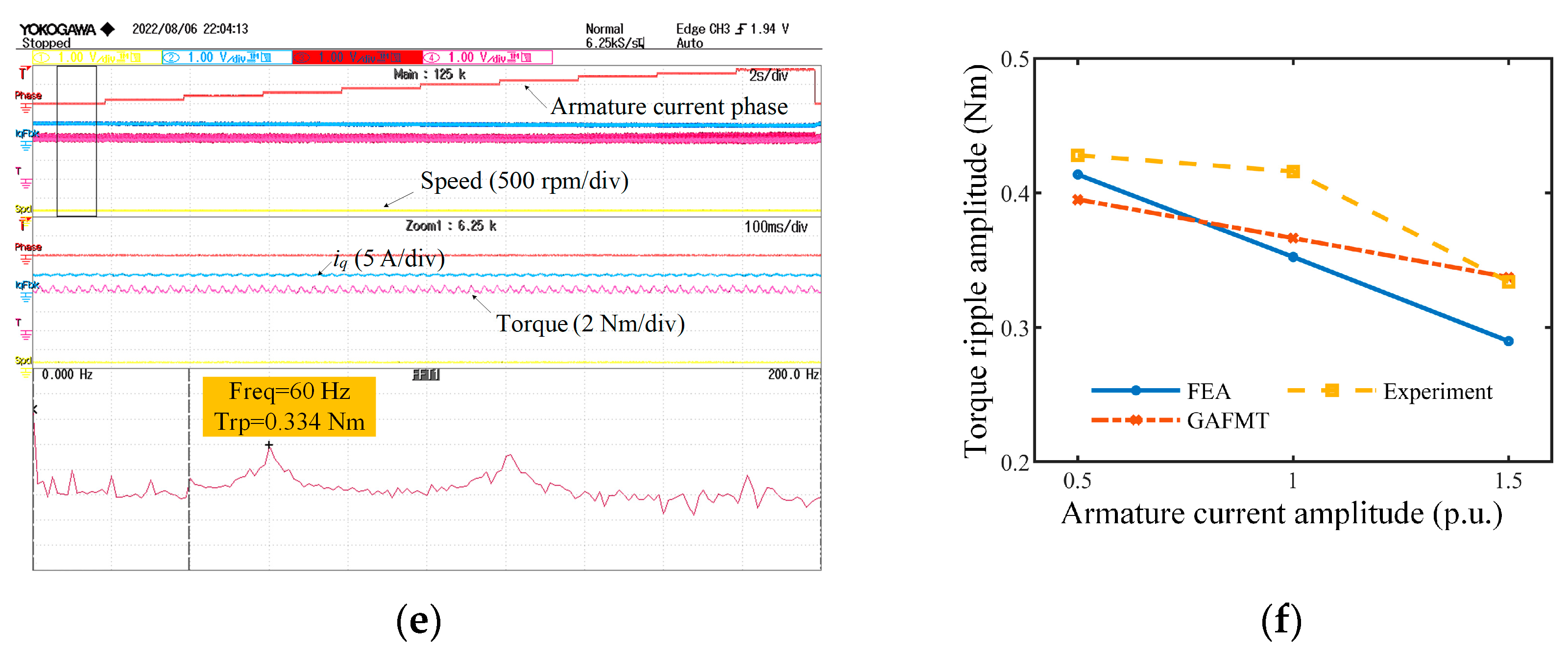
6. Experimental Results
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Q.; Hameyer, K. High-performance adaptive torque control for an IPMSM with real-time MTPA operation. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2017, 32, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, H.; Zhao, J.; Belahcen, A. Research on the performances and parameters of interior PMSM used for electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 3533–3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Li, J.; Bianchi, F.; Ciuti, G.; Dario, P.; Huang, Q. Analytical magnetic model towards compact design of magnetically-driven capsule robots. IEEE Trans. Med. Rob. Bionics 2020, 2, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zou, J. Reduction of high-frequency vibration noise for dual-branch three-phase permanent magnet synchronous motors. Chin. J. Elect. Eng. 2020, 6, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, K.; Utsunomiya, K.; Ohiwa, H. Mechanism of torque ripple generation by time and space harmonic magnetic fields in permanent magnet synchronous motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 9884–9894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, H.R. The cross-field theory of alternating-current machines. Trans. AIEE 1926, XLV, 466–474. [Google Scholar]
- Fiennes, J. New approach to general theory of electrical machines using magnetic equivalent circuits. Proc. IEE. 1973, 120, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, K.L. The rotating magnetic field theory of AC machines. Trans. AIEE 1925, XLIV, 340–348. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, M.; Han, P.; Hua, W. General airgap field modulation theory for electrical machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 6063–6074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Han, P.; Du, Y.; Wen, H.; Li, X. A tutorial on general air-gap field modulation theory for electrical machines. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Topics Power Electron. 2022, 10, 1712–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Hua, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, W. Overview of stator-permanent magnet brushless machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 58, 5087–5101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toba, A.; Lipo, T.A. Novel dual-excitation permanent magnet vernier machine. In Proceedings of the IEEE IAS Annual Meeting, Pheonix, AZ, USA, 3–7 October 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Hua, W.; Wang, W.; Huang, W. Analysis of back-EMF in flux-reversal permanent magnet machines by air gap field modulation theory. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 3344–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Cheng, M. Unified analysis of induction machine and synchronous machine based on the general airgap field modulation theory. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 9205–9216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Cheng, M.; Wen, H.; Yan, X.; Tong, M.; Wang, W. Modeling and suppression of torque ripple in PMSM based on the general airgap field modulation theory. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 37, 12502–12512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Wen, H.; Han, P.; Zhu, X. Analysis of airgap field modulation principle of simple salient poles. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 2628–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, K.H.; Choi, J.Y.; Cho, H.W. Characteristic analysis of interior permanent magnet synchronous machine with fractional slot concentrated winding considering nonlinear magnetic saturation. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2016, 26, 5200404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Hua, W.; Zhang, G.; Wang, B.; Cheng, M. Principle of flux-switching permanent magnet machine by magnetic field modulation theory part I: Back-electromotive-force generation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 2370–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Item | PM-Excited Field | Armature Field | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pole Pairs | Rotation Speed | Pole Pairs | Rotation Speed | |
| Primitive modulation | ||||
| Summation modulation | ||||
| Differential modulation | ||||
| Parameters | Value | Units | Parameters | Value | Units |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outer diameter of the stator | 100 | mm | Thickness of the PM | 3.6 | mm |
| Inner diameter of the stator | 59.6 | mm | Stack length | 75 | mm |
| Radian of the stator tooth | 8.1 | mm | Nominal torque | 10 | Nm |
| Radian of the stator slot | 7 | mm | Angle of the V-Shape PMs | 95 | deg |
| Thickness of the magnetic bridge | 0.7 | mm | Outer diameter of the rotor | 58.1 | mm |
| PM-Excited Field | Armature Field | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Pole pairs | Rotation speed | Pole pairs | Rotation speed |
| 20 | 20 | ||
| 28 | 28 | ||
| Pole pairs | Pole pairs | ||
| 20 | 0.1223 | 20 | 0.0093 |
| 28 | 0.1075 | 28 | 0.0266 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, J.; Cheng, M.; Yu, W.; Hua, W. Analysis of Torque Ripple in V-Shape Interior Permanent Magnet Machine Based on General Airgap Field Modulation Theory. Energies 2023, 16, 4586. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16124586
Zhou J, Cheng M, Yu W, Hua W. Analysis of Torque Ripple in V-Shape Interior Permanent Magnet Machine Based on General Airgap Field Modulation Theory. Energies. 2023; 16(12):4586. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16124586
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Jiawei, Ming Cheng, Wenfei Yu, and Wei Hua. 2023. "Analysis of Torque Ripple in V-Shape Interior Permanent Magnet Machine Based on General Airgap Field Modulation Theory" Energies 16, no. 12: 4586. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16124586
APA StyleZhou, J., Cheng, M., Yu, W., & Hua, W. (2023). Analysis of Torque Ripple in V-Shape Interior Permanent Magnet Machine Based on General Airgap Field Modulation Theory. Energies, 16(12), 4586. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16124586









