A Review of State Estimation Techniques for Grid-Connected PMSG-Based Wind Turbine Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- A mathematical model of the nonlinear PMSG-based WTS is presented, including the dynamics of the drive train, machine side converter (MSC) control, dc-link voltage control, and grid side converter (GSC) control.
- Principles of state estimation techniques with classical KF, EKF, AEKF, ENKF, UKF, CKF, and ACKF are reviewed with their merits and limitations.
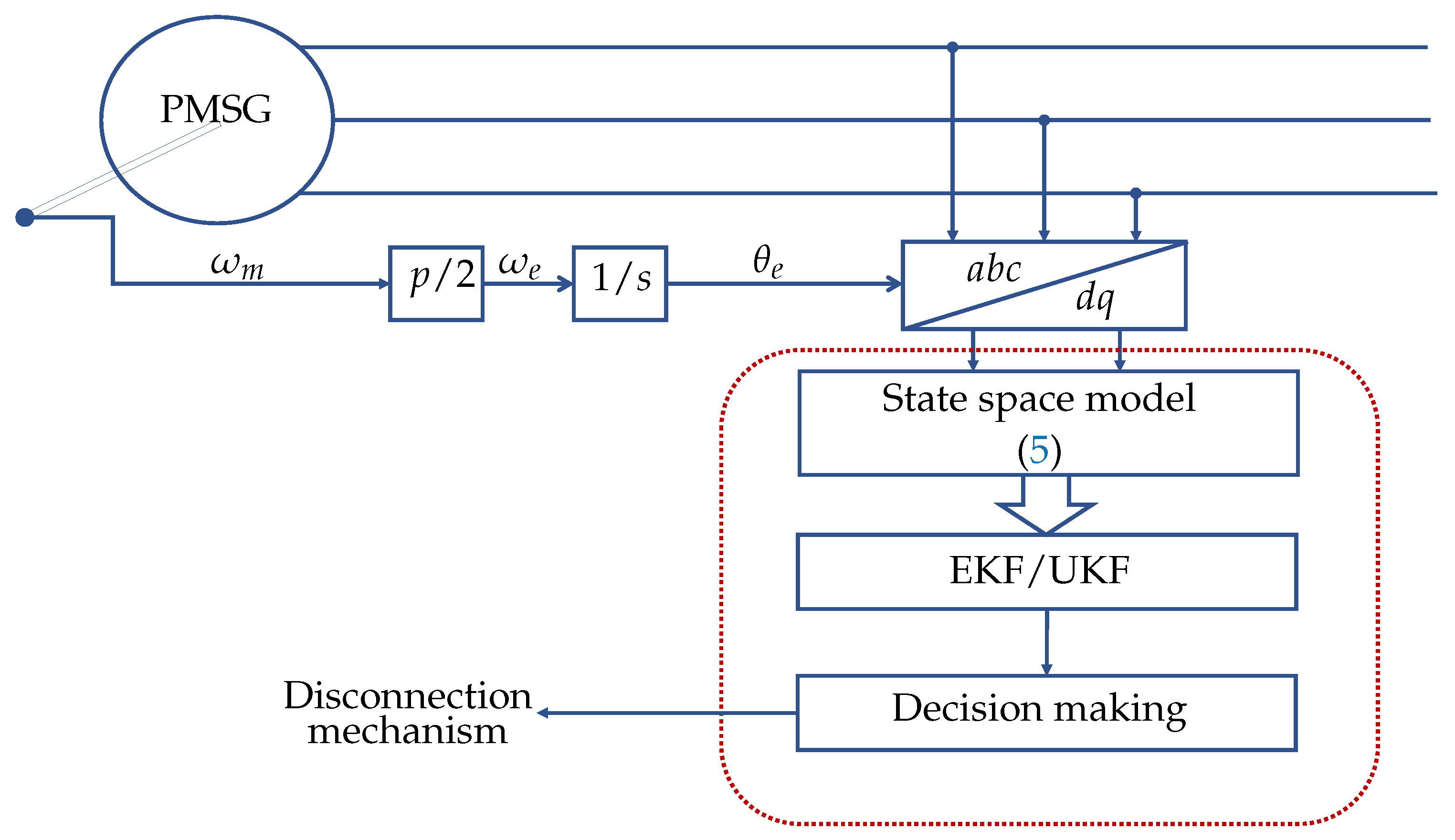
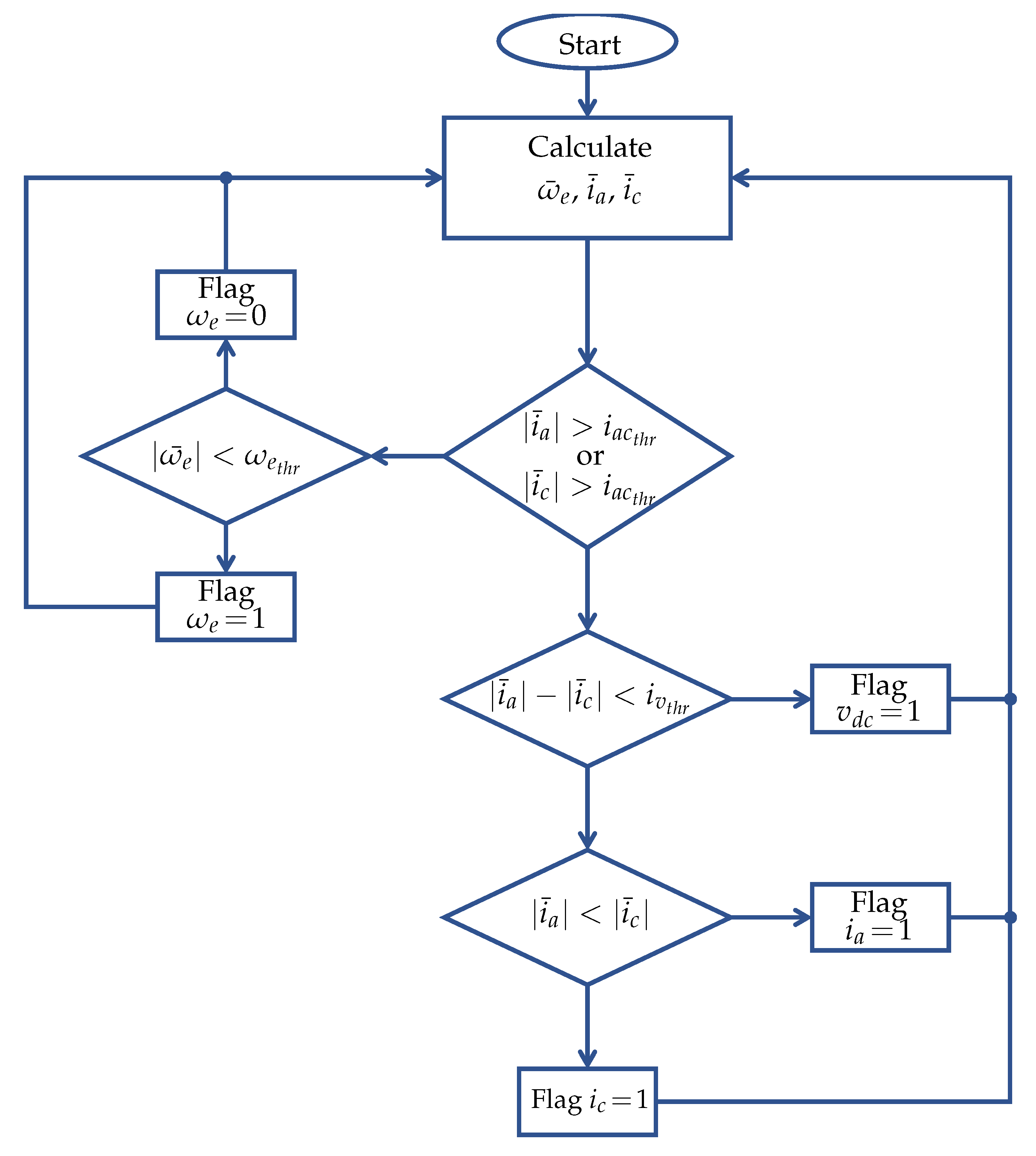
- The application of state estimation techniques for WTS control, fault diagnosis, LVRT operation, and observers for sensorless control of WTS is highlighted.
- State estimation techniques employed in pitch and yaw control of WTSs are discussed.
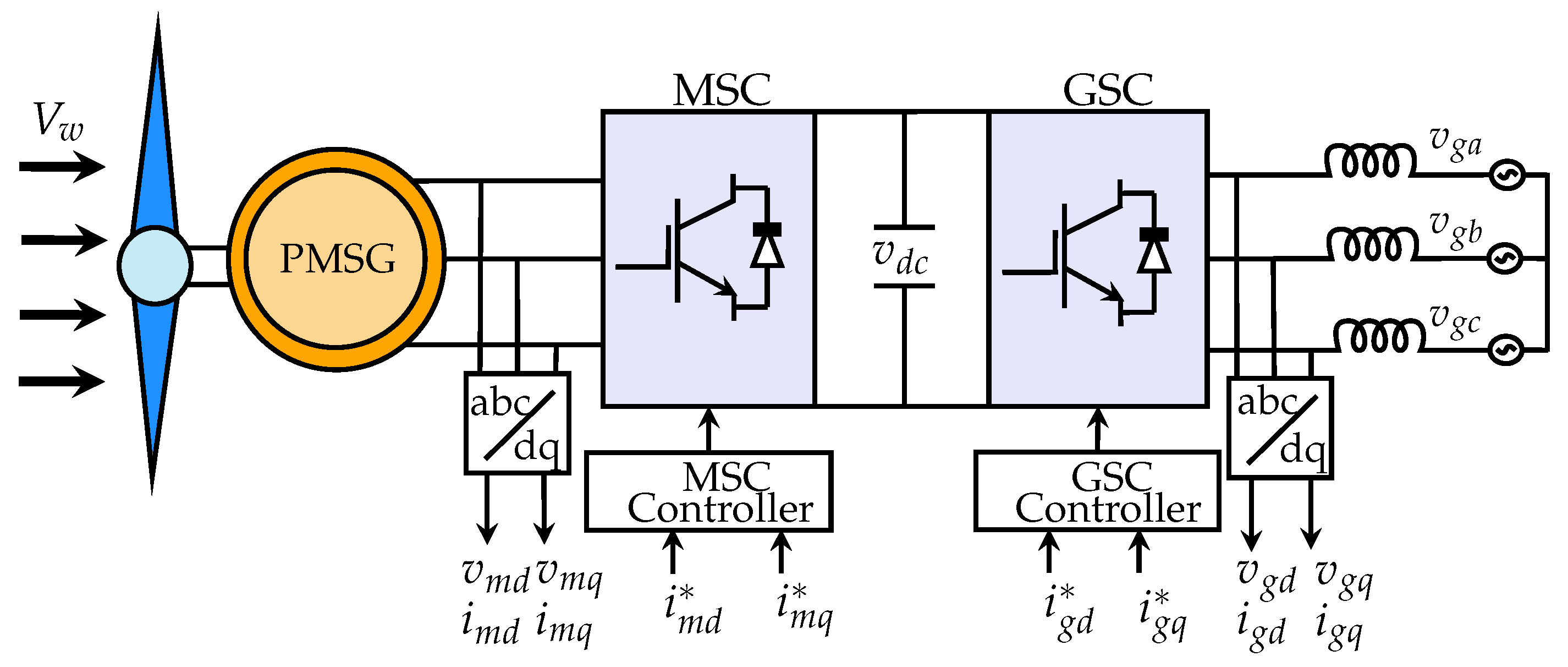
2. Modeling of PMSG-Based WTS Structures
2.1. Mechanical Characteristics of Wind Turbine Systems
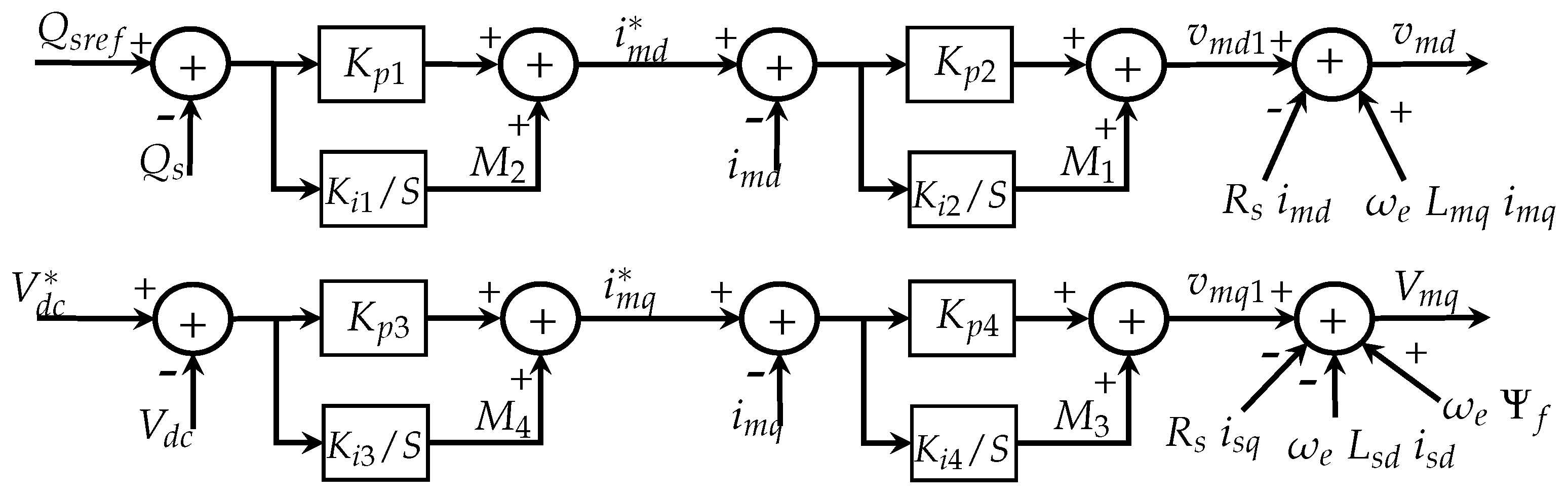
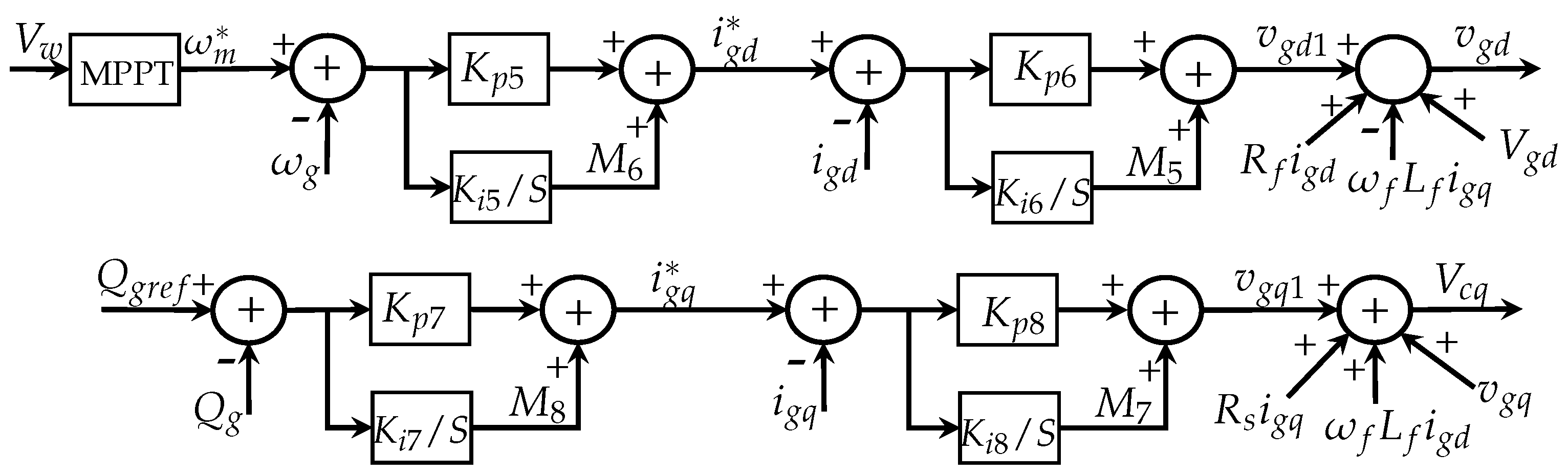
2.2. Modeling of Generator, dc-Link, and Grid
3. State Estimation with Linearized Model of PMSG-Based WTSs
4. State Estimation with Nonlinear Modeling of PMSG-Based WTSs
4.1. Extended Kalman Filter-Based Dynamic State Estimation
- A severe three-phase to ground fault at the PMSG bus with a fault duration of 150 ms is considered case-i.
- The case-i fault is taken in addition to a dc-link measurement noise as case-ii fault. The measurement noise model is expressed as .
- A three-phase to ground fault, which causes the grid voltage to drop 0.15 pu for a longer duration of 625 ms, is assumed as a case-iii.
- The case-iii fault is taken in addition to a dc-link measurement noise as case-iv fault.
4.2. Adaptive Extended Kalman Filter-Based Dynamic State Estimation
4.3. Ensemble Kalman Filter-Based Dynamic State Estimation
4.4. Unscented Kalman Filter-Based Dynamic State Estimation
4.5. Cubature Kalman Filter-Based Dynamic State Estimation
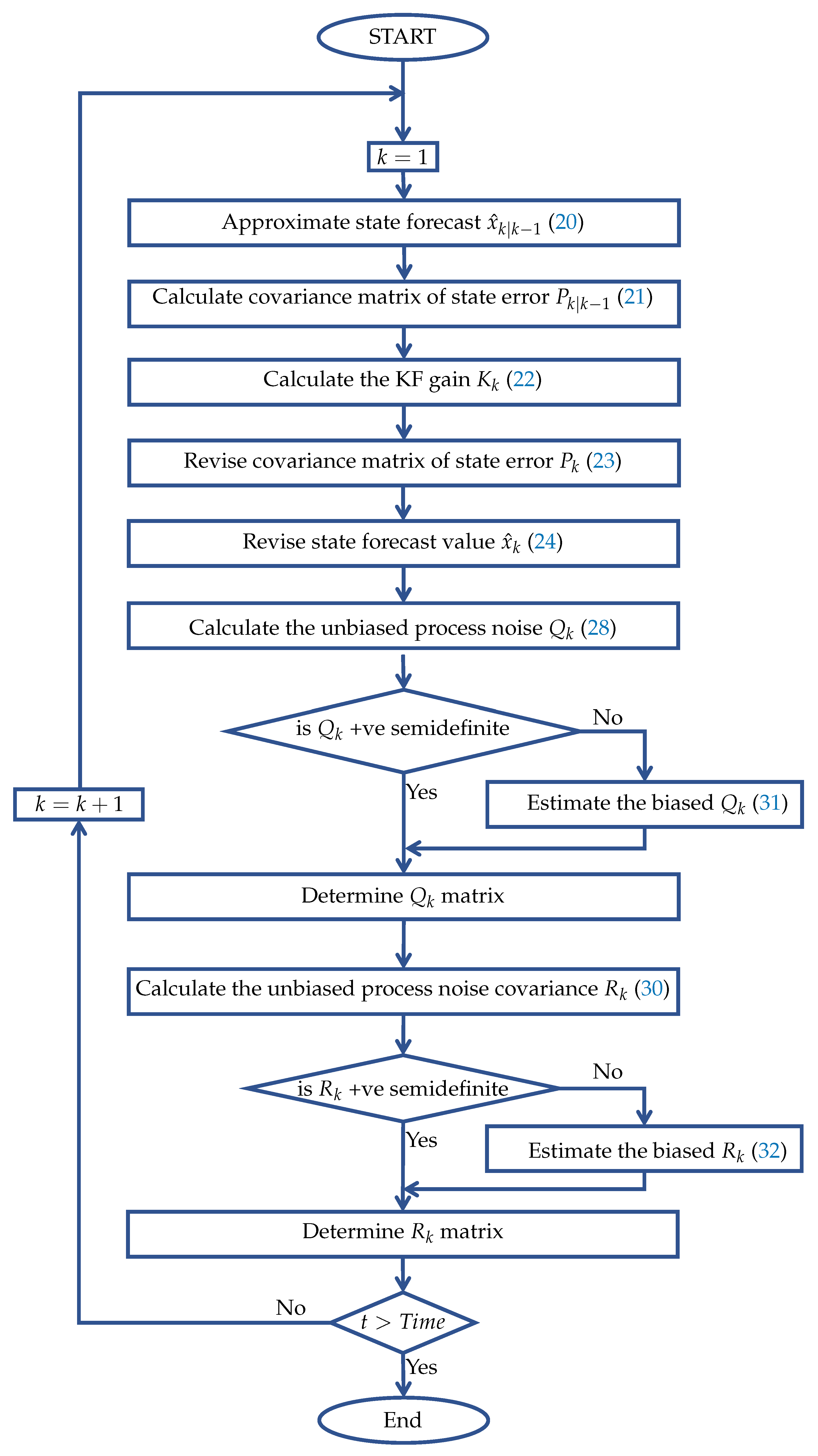
4.6. Adaptive Cubature Kalman Filter-Based Dynamic State Estimation
- It takes more computation to cope with the correlation estimation compared to the CKFs without the correlation on multiplicative noise.
- The filtering technique will inevitably grow a little more complicated in order to account for the multiplicative noise component.
- When the correlation on multiplicative noise is taken into account, the calculation of the suggested filter is likewise increased.
- The filtering process clearly grows difficult because the correlation coefficient is dynamically estimated.
5. Review of State Estimation Techniques for PMSG-Based WTS Fault Diagnosis
6. Observers and Sensorless Control of PMSG-Based WTS
7. State Estimation Techniques for Wind Turbine Pitch and Yaw Control
7.1. Sliding Mode Observer-Based State Estimation for Pitch Actuator
7.2. Estimation of States for Yaw Control of Wind Turbine
- Modeling: The initial step is to represent the system dynamic model in a general format aswhere and are regarded as the state and measurement, respectively; and give the state and measurement noises.
- Measurement updating: The following dynamics can be used as the measurement updatewhere is the Kalman gain, denotes state estimation error covariance, and gives the measurement noise covariance.
- Time update filter gain: The time update is fulfilled bywhere is the state noise covariance. Therefore, all the model parameters of KF-based wind direction estimator are given in detail, refer to [108]. Hence, the proposed KF-estimator offered better results in wind prediction. In the end, the power extraction from the wind turbine using MPC-based yaw control has improved with a KF-based wind direction estimator.
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| P | wind turbine aerodynamic power |
| air density | |
| wind speed | |
| power co-efficient | |
| tip speed ratio | |
| rotor speed | |
| R | radius of turbine blade |
| pitch angle | |
| moment of inertia | |
| aerodynamic torque | |
| electromagnetic torque | |
| B | viscous friction coefficient |
| , | -axes voltage and current of machine |
| stator resistance | |
| stator inductances in frame | |
| magnetic flux | |
| dc-link voltage | |
| C | dc-link capacitance |
| , | stator and grid electric powers |
| , | -axes voltage and current of filter |
| filter resistance | |
| grid inductances in frame | |
| grid voltage angular frequency | |
| grid reactive power | |
| next state of a parameter | |
| present state of a parameter | |
| previous state of a parameter | |
| state, input, and output matrices of a system | |
| sampling period | |
| state covariance, process noise, measurement noise | |
| F | Jacobians of the state functions |
References
- Jones, D. Global Electricity Review 2021; Ember: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Palanimuthu, K.; Mayilsamy, G.; Basheer, A.A.; Lee, S.R.; Song, D.; Joo, Y.H. A Review of Recent Aerodynamic Power Extraction Challenges in Coordinated Pitch, Yaw, and Torque Control of Large-Scale Wind Turbine Systems. Energies 2022, 15, 8161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares-Ramos, E.P.; de Oliveira-Assis, L.; Sarrias-Mena, R.; Fernández-Ramírez, L.M. Current status and future trends of offshore wind power in Europe. Energy 2020, 202, 117787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, A.S.; Al-Dabbagh, R. Wind energy state of the art: Present and future technology advancements. Renew. Energy Environ. Sustain. 2020, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GWEC. Global Offshore Wind Report 2020; GWEC: Brussels, Belgium, 2020; Volume 19, pp. 10–12. [Google Scholar]
- López-Queija, J.; Robles, E.; Jugo, J.; Alonso-Quesada, S. Review of control technologies for floating offshore wind turbines. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 167, 112787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haces-Fernandez, F.; Cruz-Mendoza, M.; Li, H. Onshore Wind Farm Development: Technologies and Layouts. Energies 2022, 15, 2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejad, A.R.; Keller, J.; Guo, Y.; Sheng, S.; Polinder, H.; Watson, S.; Dong, J.; Qin, Z.; Ebrahimi, A.; Schelenz, R.; et al. Wind turbine drivetrains: State-of-the-art technologies and future development trends. Wind Energy Sci. 2022, 7, 387–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, T.Y.; Ding, T.J.; Chang, C.C.W.; Ping, T.J.; Yian, H.C.; Dahari, M. Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generator design optimization for wind energy conversion system: A review. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Xu, H.; Zhang, M.; Cheng, P. Stability analysis of sub/super synchronous oscillation in direct-drive wind farm considering the energy interaction between PMSGs. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2022, 16, 478–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, T.; Song, D.; Joo, Y.H. Non-centralised coordinated optimisation for maximising offshore wind farm power via a sparse communication architecture. Appl. Energy 2022, 324, 119705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Joo, Y.H.; Song, D. Multi-Objective Optimisation for Large-Scale Offshore Wind Farm Based on Decoupled Groups Operation. Energies 2022, 15, 2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padinharu, D.K.K.; Li, G.J.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Clark, R.; Thomas, A.; Azar, Z.; Duke, A. Permanent magnet vernier machines for direct-drive offshore wind power: Benefits and Challenges. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 20652–20668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B. Design method of a direct-drive permanent magnet vernier generator for a wind turbine system. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2019, 55, 4665–4675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.W.; Kang, S.G.; Jung, S.Y.; Yeo, H.K. Design and Analysis of Permanent-Magnet Vernier Machine for Direct-Driven Wind Power Generator Considering Pole-Slot Combinations. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2022, 18, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaheri, A.; Afjei, E.; Torkaman, H. Design optimization of a novel linear transverse flux switching permanent magnet generator for direct drive wave energy conversion. Renew. Energy 2022, 198, 851–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padinharu, D.K.K.; Li, G.J.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Clark, R.; Thomas, A.S.; Azar, Z. System-level investigation of multi-MW direct-drive wind power PM vernier generators. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 191433–191446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tlali, P.M.; Wang, R.J.; Gerber, S.; Botha, C.D.; Kamper, M.J. Design and performance comparison of vernier and conventional PM synchronous wind generators. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020, 56, 2570–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanimuthu, K.; Mayilsamy, G.; Lee, S.R.; Jung, S.Y.; Joo, Y.H. Comparative analysis of maximum power extraction and control methods between PMSG and PMVG-based wind turbine systems. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2022, 143, 108475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, Y.H.; Antonysamy, R.; Ramasamy, T.; Lee, S.R. Stable maximum power extraction and DC link voltage regulation for PMVG-based WECS. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 70, 498–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonysamy, R.P.; Lee, S.R.; Jung, S.Y.; Joo, Y.H. Performance Enhancement Using Robust Sliding Mode Approach-Based Current Control for PMVG-WECS. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkateswaran, R.; Yesudhas, A.A.; Lee, S.R.; Joo, Y.H. Integral sliding mode control for extracting stable output power and regulating DC-link voltage in PMVG-based wind turbine system. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2023, 144, 108482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primadianto, A.; Lu, C.N. A review on distribution system state estimation. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2016, 32, 3875–3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abur, A.; Exposito, A.G. Power System State Estimation: Theory and Implementation; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- NERC. Power Plant Dynamic Model Verification Using PMUs; NERC Reliability: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Berg, J.C.; Miller, K. Sensor Selection for Wind Turbine State Estimation; Technical Report; Sandia National Lab. (SNL-NM): Albuquerque, NM, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, D.H. Least-squares fault detection and diagnosis for networked sensing systems using a direct state estimation approach. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2013, 9, 1670–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhinav, S.; Pal, B.C. Dynamic Estimation and Control of Power Systems; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Rostami, M.; Lotfifard, S. Distributed dynamic state estimation of power systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2017, 14, 3395–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Schneider, K.; Nieplocha, J. Feasibility studies of applying Kalman filter techniques to power system dynamic state estimation. In Proceedings of the 2007 International Power Engineering Conference (IPEC 2007), Singapore, 3–6 December 2007; pp. 376–382. [Google Scholar]
- Karimipour, H.; Dinavahi, V. Extended Kalman filter-based parallel dynamic state estimation. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2015, 6, 1539–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarzadeh, S.; Lascu, C.; Fadali, M.S. State estimation of induction motor drives using the unscented Kalman filter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 59, 4207–4216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Cagigal, M.; Rosendo-Macías, J.A.; Gómez-Expósito, A. Parameter estimation of wind turbines with PMSM using cubature Kalman filters. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2019, 35, 1796–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Mili, L. A theoretical framework of robust H-infinity unscented Kalman filter and its application to power system dynamic state estimation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2019, 67, 2734–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Sun, K.; Wang, J.; Liu, H. Dynamic state estimation for multi-machine power system by unscented Kalman filter with enhanced numerical stability. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2016, 9, 1184–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.; Meng, D.; Lu, S. Estimation of the dynamic states of synchronous machines using an extended particle filter. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2013, 28, 4152–4161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Kavasseri, R. A particle filter for dynamic state estimation in multi-machine systems with detailed models. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2015, 30, 3377–3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emami, K.; Fernando, T.; Iu, H.H.C.; Trinh, H.; Wong, K.P. Particle filter approach to dynamic state estimation of generators in power systems. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2014, 30, 2665–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, W.; Yuan, P. Distributed dynamic state estimation in active distribution system based on particle filter. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Innovative Smart Grid Technologies-Asia (ISGT Asia), Singapore, 22–25 May 2018; pp. 664–668. [Google Scholar]
- El-Sharafy, M.Z.; Saxena, S.; Farag, H.E. Optimal design of islanded microgrids considering distributed dynamic state estimation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2020, 17, 1592–1603. [Google Scholar]
- Ritter, B.; Schild, A.; Feldt, M.; Konigorski, U. The design of nonlinear observers for wind turbine dynamic state and parameter estimation. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2016, 753, 052029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor-A-Rahim, M.; MO Khyam, X.L.; Pesch, D. Sensor fusion and state estimation of IoT enabled wind energy conversion system. Sensors 2019, 19, 1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mateljak, P.; Petrovic, V.; Baotic, M. Dual kalman estimation of wind turbine states and parameters. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Process Control, Tatranska Lomnica, Slovakia, 14–17 June 2011; pp. 85–91. [Google Scholar]
- Miranda-Blanco, B.N.; Díaz-Dorado, E.; Carrillo, C.; Cidrás, J. State estimation for wind farms including the wind turbine generator models. Renew. Energy 2014, 71, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahriari, S.A.A.; Raoofat, M.; Dehghani, M.; Mohammadi, M.; Saad, M. Dynamic state estimation of a permanent magnet synchronous generator-based wind turbine. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2016, 10, 1278–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Fernando, T.; Emami, K.; Iu, H.H.C. Dynamic state estimation based control strategy for DFIG wind turbine connected to complex power systems. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2016, 32, 1272–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Emami, K.; Fernando, T.; Iu, H.H.; Wong, K.P. State estimation of doubly fed induction generator wind turbine in complex power systems. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2016, 31, 4935–4944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapat, G.P.; Bhui, P.; Senroy, N.; Kar, I.N. Modelling and estimation of gear train backlash present in wind turbine driven DFIG system. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2018, 12, 3527–3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourlis, D.; Bleijs, J. A wind speed estimation method using adaptive Kalman filtering for a variable speed stall regulated wind turbine. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE 11th International Conference on Probabilistic Methods Applied to Power Systems, Singapore, 14–17 June 2010; pp. 89–94. [Google Scholar]
- Sudev, P.; Anita, J.; Sudheesh, P. Nonlinear state estimation of wind turbine. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communications and Informatics (ICACCI), Udupi, India, 13–16 September 2017; pp. 354–358. [Google Scholar]
- Song, D.; Yang, J.; Cai, Z.; Dong, M.; Su, M.; Wang, Y. Wind estimation with a non-standard extended Kalman filter and its application on maximum power extraction for variable speed wind turbines. Appl. Energy 2017, 190, 670–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahriari, S.A.A.; Mohammadi, M.; Raoofat, M. A new method based on state-estimation technique to enhance low-voltage ride-through capability of doubly-fed induction generator wind turbines. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2018, 95, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, R.A.; Zakzouk, N.E. A PMSG Wind Energy System Featuring Low-Voltage Ride-through via Mode-Shift Control. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Ghosh, S.; Das, S.; Singh, A.K.; Singh, N.K. ANFIS-Based Control for Low-Voltage Ride-Through Enhancement of PMSG Tidal Turbine. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Students Conference on Engineering and Systems (SCES), Prayagraj, India, 1–3 July 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Palanimuthu, K.; Mayilsamy, G.; Lee, S.R.; Jung, S.Y.; Joo, Y.H. Fault Ride-through for PMVG-based Wind Turbine System Using Coordinated Active and Reactive Power Control Strategy. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahriari, S.A.A.; Mohammadi, M.; Raoofat, M. Enhancement of low-voltage ride-through capability of permanent magnet synchronous generator wind turbine by applying state-estimation technique. COMPEL Int. J. Comput. Math. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2020, 39, 363–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Jiang, Z.; Pan, L. Recurrent neural network based adaptive integral sliding mode power maximization control for wind power systems. Renew. Energy 2020, 145, 1149–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri, M.; Milimonfared, J.; Fathi, S. A review of low-voltage ride-through enhancement methods for permanent magnet synchronous generator based wind turbines. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 47, 399–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkateswaran, R.; Natesan, B.; Lee, S.R.; Joo, Y.H. Maximum Power Extraction for PMVG-based WECS Using Q-Learning MPPT Algorithm with Finite-time Control Scheme. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2022, 14, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, Y. Integral sliding mode control for increasing maximum power extraction efficiency of variable-speed wind energy system. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2022, 139, 107958. [Google Scholar]
- Mayilsamy, G.; Natesan, B.; Joo, Y.H.; Lee, S.R. Fast Terminal Synergetic Control of PMVG-Based Wind Energy Conversion System for Enhancing the Power Extraction Efficiency. Energies 2022, 15, 2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yesudhas, A.A.; Joo, Y.H.; Lee, S.R. Reference Model Adaptive Control Scheme on PMVG-Based WECS for MPPT under a Real Wind Speed. Energies 2022, 15, 3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuppusamy, S.; Joo, Y.H. Stabilization Criteria for T–S Fuzzy Systems With Multiplicative Sampled-Data Control Gain Uncertainties. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2021, 30, 4082–4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuppusamy, S.; Joo, Y.H. Observer-Based Non-PDC Control Design for PMSG-Based Wind Energy Conversion Systems. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2022, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasamy, T.; Abdul Basheer, A.; Tak, M.H.; Joo, Y.H.; Lee, S.R. An Effective DC-Link Voltage Control Strategy for Grid-Connected PMVG-Based Wind Energy Conversion System. Energies 2022, 15, 2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalman, R.E. A new approach to linear filtering and prediction problems. Trans. ASME J. Basic Eng. 1960, 82, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foo, G.H.B.; Zhang, X.; Vilathgamuwa, D.M. A sensor fault detection and isolation method in interior permanent-magnet synchronous motor drives based on an extended Kalman filter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 3485–3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Mao, C.; Lu, J.; Wang, D. Small-signal modelling and analysis of wind turbine with direct drive permanent magnet synchronous generator connected to power grid. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2012, 6, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.; Xu, Z.; Yang, L.; Østergaard, J.; Xue, Y.; Wong, K.P. A comprehensive LVRT control strategy for DFIG wind turbines with enhanced reactive power support. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2013, 28, 3302–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Huang, S.; Gao, M.; Wang, Z. Adaptive extended Kalman filter based dynamic equivalent method of PMSG wind farm cluster. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2021, 57, 2908–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narasimhappa, M.; Mahindrakar, A.D.; Guizilini, V.C.; Terra, M.H.; Sabat, S.L. MEMS-based IMU drift minimization: Sage Husa adaptive robust Kalman filtering. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 20, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, X. A comparative study of different adaptive extended/unscented Kalman filters for lithium-ion battery state-of-charge estimation. Energy 2022, 246, 123423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrasiabi, S.; Afrasiabi, M.; Rastegar, M.; Mohammadi, M.; Parang, B.; Ferdowsi, F. Ensemble kalman filter based dynamic state estimation of PMSG-based wind turbine. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Texas Power and Energy Conference (TPEC), College Station, TX, USA, 7–8 February 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Rigatos, G.; Siano, P.; Zervos, N. PMSG sensorless control with the Derivative-free nonlinear Kalman Filter for Distributed Generation units. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2013, 46, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigatos, G.; Siano, P.; Zervos, N. Derivative-free nonlinear Kalman filtering for PMSG sensorless control. In Interdisciplinary Mechatronics; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 277–311. [Google Scholar]
- Rigatos, G.; Siano, P.; Zervos, N. PMSG sensorless control with the use of the derivative-free nonlinear Kalman filter. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Clean Electrical Power (ICCEP), Alghero, Italy, 11–13 June 2013; pp. 673–678. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, R.; Rasmussen, C.E. Model based learning of sigma points in unscented Kalman filtering. Neurocomputing 2012, 80, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gliga, L.I.; Chafouk, H.; Popescu, D.; Lupu, C. Comparison of State Estimators for a Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generator. In Proceedings of the 2018 22nd International Conference on System Theory, Control and Computing (ICSTCC), Sinaia, Romania, 10–12 October 2018; pp. 474–479. [Google Scholar]
- Aghamolki, H.G.; Miao, Z.; Fan, L.; Jiang, W.; Manjure, D. Identification of synchronous generator model with frequency control using unscented Kalman filter. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2015, 126, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- LaViola, J.J. A comparison of unscented and extended Kalman filtering for estimating quaternion motion. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 2003 American Control Conference, Denver, CO, USA, 4–6 June 2003; Volume 3, pp. 2435–2440.
- Liu, M.; Lai, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, J. An adaptive cubature Kalman filter algorithm for inertial and land-based navigation system. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, D.G.; Vivek, A.; Srikanth, V. Non-linear state estimation of PMSM using derivative-free and square-root Cubature Kalman Filter. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Intelligent Computing, Instrumentation and Control Technologies (ICICICT), Kerala, India, 6–7 July 2017; pp. 126–131. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Bi, T.; Liu, H. Dynamic state estimation of a grid-connected converter of a renewable generation system using adaptive cubature Kalman filtering. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2022, 143, 108470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Lang, Y.; Zargari, N.; Kouro, S. Power Conversion and Control of Wind Energy Systems; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, S.; Huang, R.; Bi, T.; Mili, L.; Huang, Z. Correlation-Aided Robust Decentralized Dynamic State Estimation of Power Systems With Unknown Control Inputs. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2020, 35, 2443–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.; Choi, M.; Gao, Z.; Moan, T. Fault detection and diagnosis of a blade pitch system in a floating wind turbine based on Kalman filters and artificial neural networks. Renew. Energy 2021, 169, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Qin, S.; Liang, M. Time–frequency analysis based on Vold-Kalman filter and higher order energy separation for fault diagnosis of wind turbine planetary gearbox under nonstationary conditions. Renew. Energy 2016, 85, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attallah, O.; Ibrahim, R.A.; Zakzouk, N.E. CAD system for inter-turn fault diagnosis of offshore wind turbines via multi-CNNs & feature selection. Renew. Energy 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gliga, L.I.; Chafouk, H.; Popescu, D.; Lupu, C. Diagnosis of a permanent magnet synchronous generator using the extended Kalman filter and the fast Fourier transform. In Proceedings of the 2018 7th International Conference on Systems and Control (ICSC), Valencia, Spain, 24–26 October 2018; pp. 65–70. [Google Scholar]
- Otava, L.; Buchta, L. Implementation and verification of the PMSM stator interturn short fault detection algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2017 19th European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications (EPE’17 ECCE Europe), Warsaw, Poland, 11–14 September 2017; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El Sayed, W.; Abd El Geliel, M.; Lotfy, A. Fault diagnosis of PMSG stator inter-turn fault using extended Kalman filter and unscented Kalman filter. Energies 2020, 13, 2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Sayed, W.; Aboelhassan, A.; Madi, A.; Hebala, A.; Galea, M. Comparative Analysis Between Unscented and Extended Kalman Filters for PMSG Inter-Turn Fault Detection. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Workshop on Electrical Machines Design, Control and Diagnosis (WEMDCD), Modena, Italy, 8–9 April 2021; pp. 243–248. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, C.; Chen, Z.; Huang, D. Fault diagnosis of voltage sensor and current sensor for lithium-ion battery pack using hybrid system modeling and unscented particle filter. Energy 2020, 191, 116504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carranza, O.; Figueres, E.; Garcerá, G.a.; Gonzalez, L. Comparative study of speed estimators with highly noisy measurement signals for Wind Energy Generation Systems. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 805–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smidl, V.; Peroutka, Z. Advantages of square-root extended Kalman filter for sensorless control of AC drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 59, 4189–4196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Sun, K.; Huang, L.; Li, Y. Online identification of permanent magnet flux based on extended Kalman filter for IPMSM drive with position sensorless control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 59, 4169–4178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaclavek, P.; Blaha, P.; Herman, I. AC drive observability analysis. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 60, 3047–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akrad, A.; Hilairet, M.; Diallo, D. Design of a fault-tolerant controller based on observers for a PMSM drive. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 58, 1416–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantino, R.; Solsona, J.; Busada, C. Nonlinear observer-based control for PMSG wind turbine. Energy 2016, 113, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Yu, T.; Shu, H.; Han, Y.; Cao, P.; Jiang, L. Adaptive fractional-order PID control of PMSG-based wind energy conversion system for MPPT using linear observers. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst. 2019, 29, e2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lan, J.; Patton, R.J.; Zhu, X. Fault-tolerant wind turbine pitch control using adaptive sliding mode estimation. Renew. Energy 2018, 116, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Gao, Z. Pitch control for wind turbine systems using optimization, estimation and compensation. Renew. Energy 2016, 91, 501–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholbrock, A.; Fleming, P.; Wright, A.; Slinger, C.; Medley, J.; Harris, M. Field Test Results from Lidar Measured Yaw Control for Improved Yaw Alignment with the NREL Controls Advanced Research Turbine; Technical Report; National Renewable Energy Lab. (NREL): Golden, CO, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Song, D.; Chang, Q.; Zheng, S.; Yang, S.; Yang, J.; Joo, Y.H. Adaptive model predictive control for yaw system of variable-speed wind turbines. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2020, 9, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Jin, F.; Huang, C.; Xia, E.; Rizk-Allah, R.M.; Yang, J.; Su, M.; Joo, Y.H. Energy capture efficiency enhancement of wind turbines via stochastic model predictive yaw control based on intelligent scenarios generation. Appl. Energy 2022, 312, 118773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakasis, N.; Mesemanolis, A.; Nalmpantis, T.; Mademlis, C. Active yaw control in a horizontal axis wind system without requiring wind direction measurement. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2016, 10, 1441–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Fan, X.; Yang, J.; Liu, A.; Chen, S.; Joo, Y.H. Power extraction efficiency optimization of horizontal-axis wind turbines through optimizing control parameters of yaw control systems using an intelligent method. Appl. Energy 2018, 224, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Yang, J.; Liu, Y.; Su, M.; Liu, A.; Joo, Y.H. Wind direction prediction for yaw control of wind turbines. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2017, 15, 1720–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mayilsamy, G.; Palanimuthu, K.; Venkateswaran, R.; Antonysamy, R.P.; Lee, S.R.; Song, D.; Joo, Y.H. A Review of State Estimation Techniques for Grid-Connected PMSG-Based Wind Turbine Systems. Energies 2023, 16, 634. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16020634
Mayilsamy G, Palanimuthu K, Venkateswaran R, Antonysamy RP, Lee SR, Song D, Joo YH. A Review of State Estimation Techniques for Grid-Connected PMSG-Based Wind Turbine Systems. Energies. 2023; 16(2):634. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16020634
Chicago/Turabian StyleMayilsamy, Ganesh, Kumarasamy Palanimuthu, Raghul Venkateswaran, Ruban Periyanayagam Antonysamy, Seong Ryong Lee, Dongran Song, and Young Hoon Joo. 2023. "A Review of State Estimation Techniques for Grid-Connected PMSG-Based Wind Turbine Systems" Energies 16, no. 2: 634. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16020634
APA StyleMayilsamy, G., Palanimuthu, K., Venkateswaran, R., Antonysamy, R. P., Lee, S. R., Song, D., & Joo, Y. H. (2023). A Review of State Estimation Techniques for Grid-Connected PMSG-Based Wind Turbine Systems. Energies, 16(2), 634. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16020634







