Power Hardware-in-the-Loop (PHIL): A Review to Advance Smart Inverter-Based Grid-Edge Solutions
Abstract
1. Introduction
Contribution and Organization of This Review
2. Hardware-in-the-Loop (HIL), CHIL and PHIL in Power System Applications
2.1. Control Hardware-in-the-Loop (CHIL)
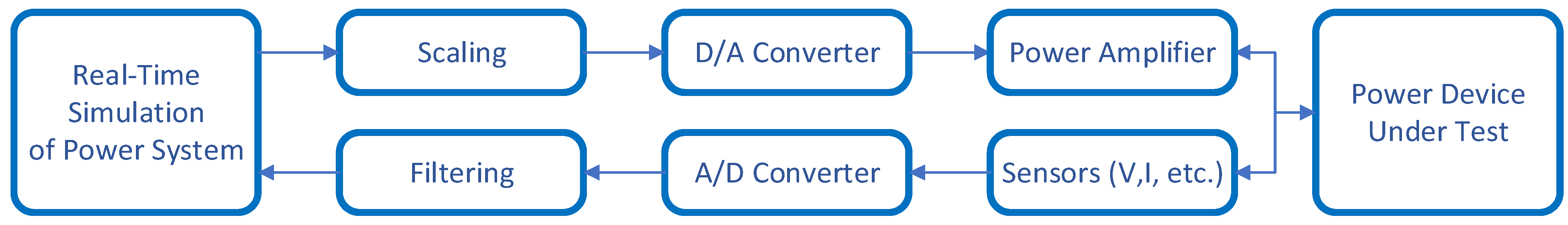
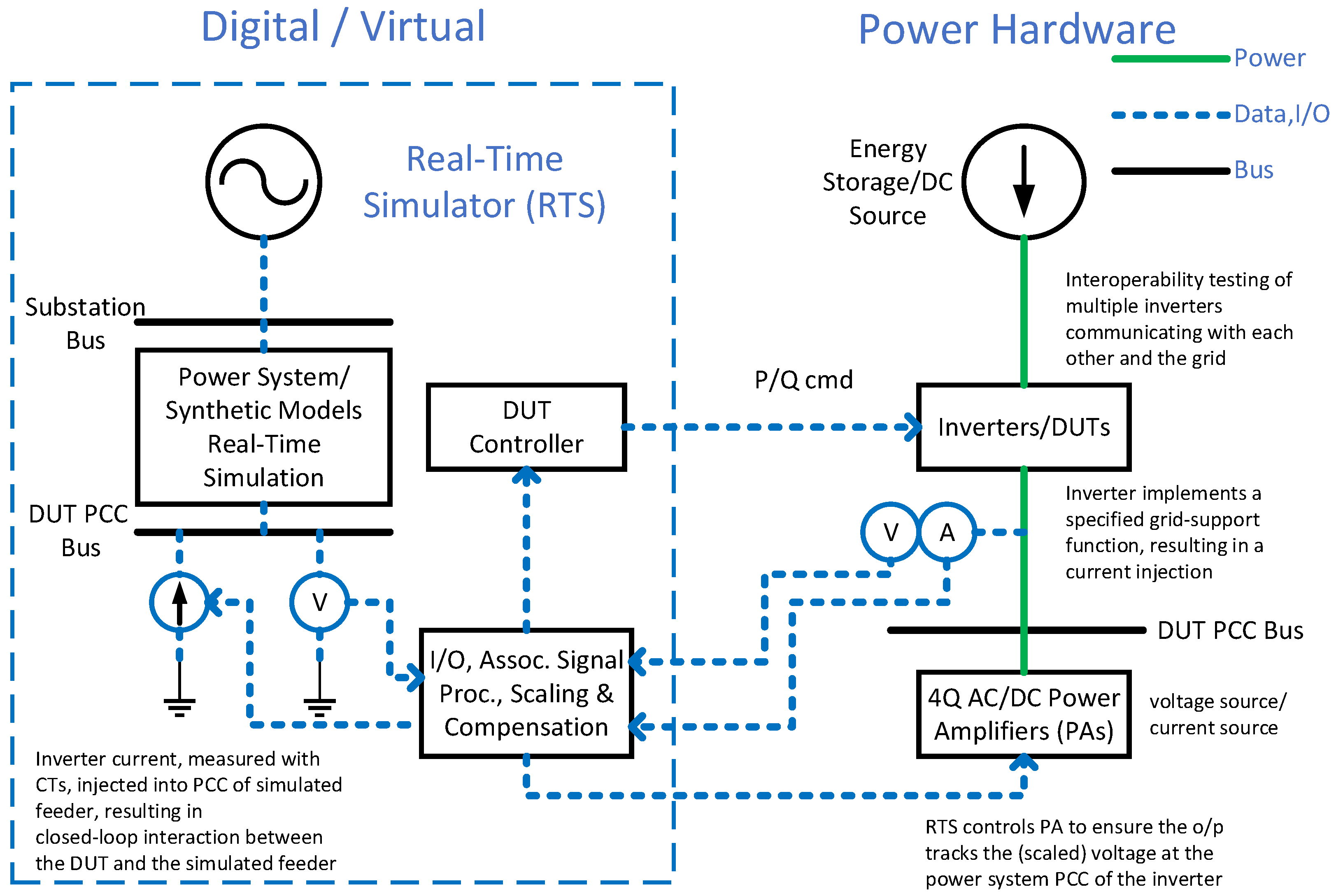
2.2. Power Hardware-in-the-Loop (PHIL)
3. PHIL Setup Requirements and a Detailed Case Study
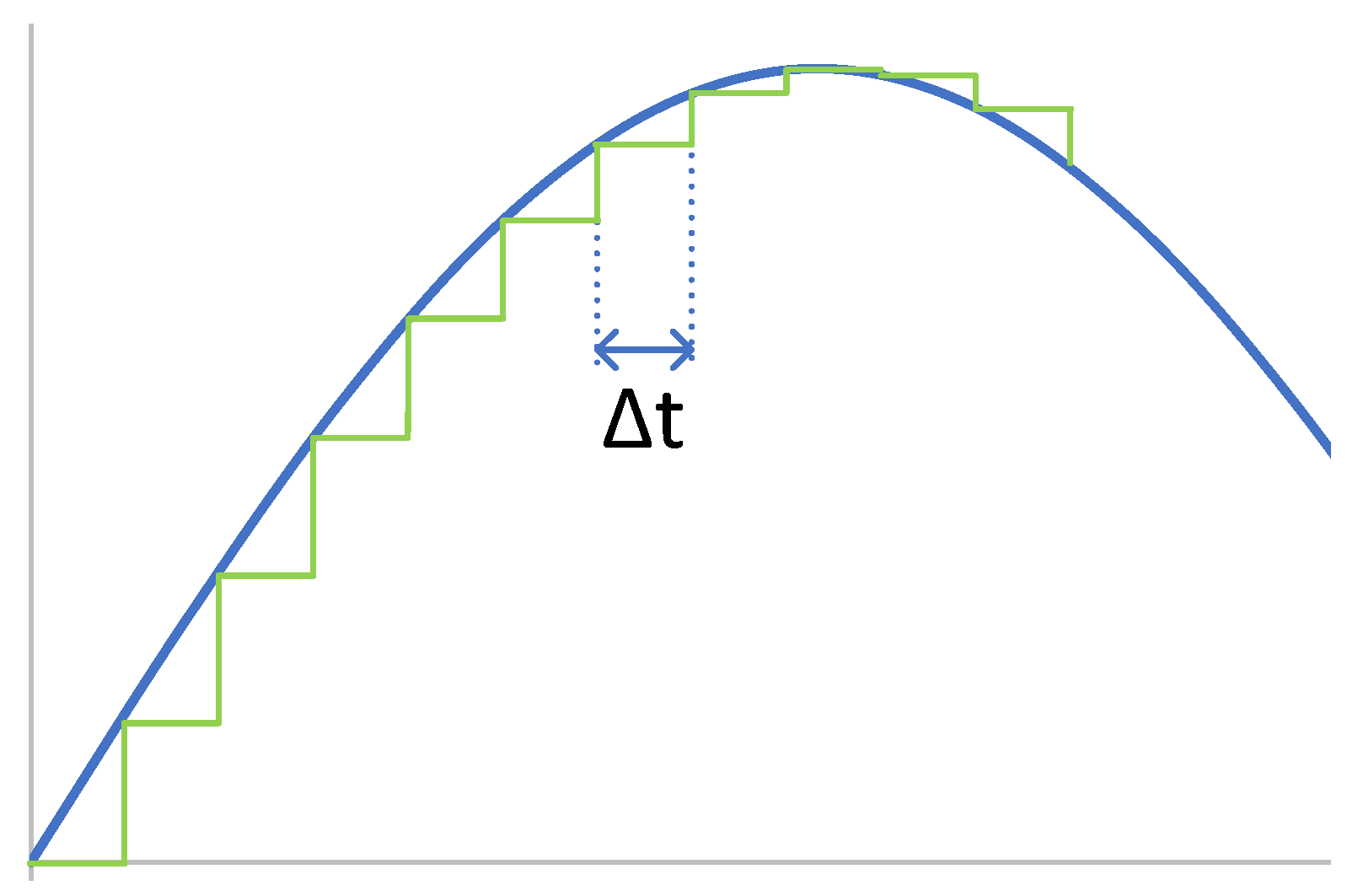
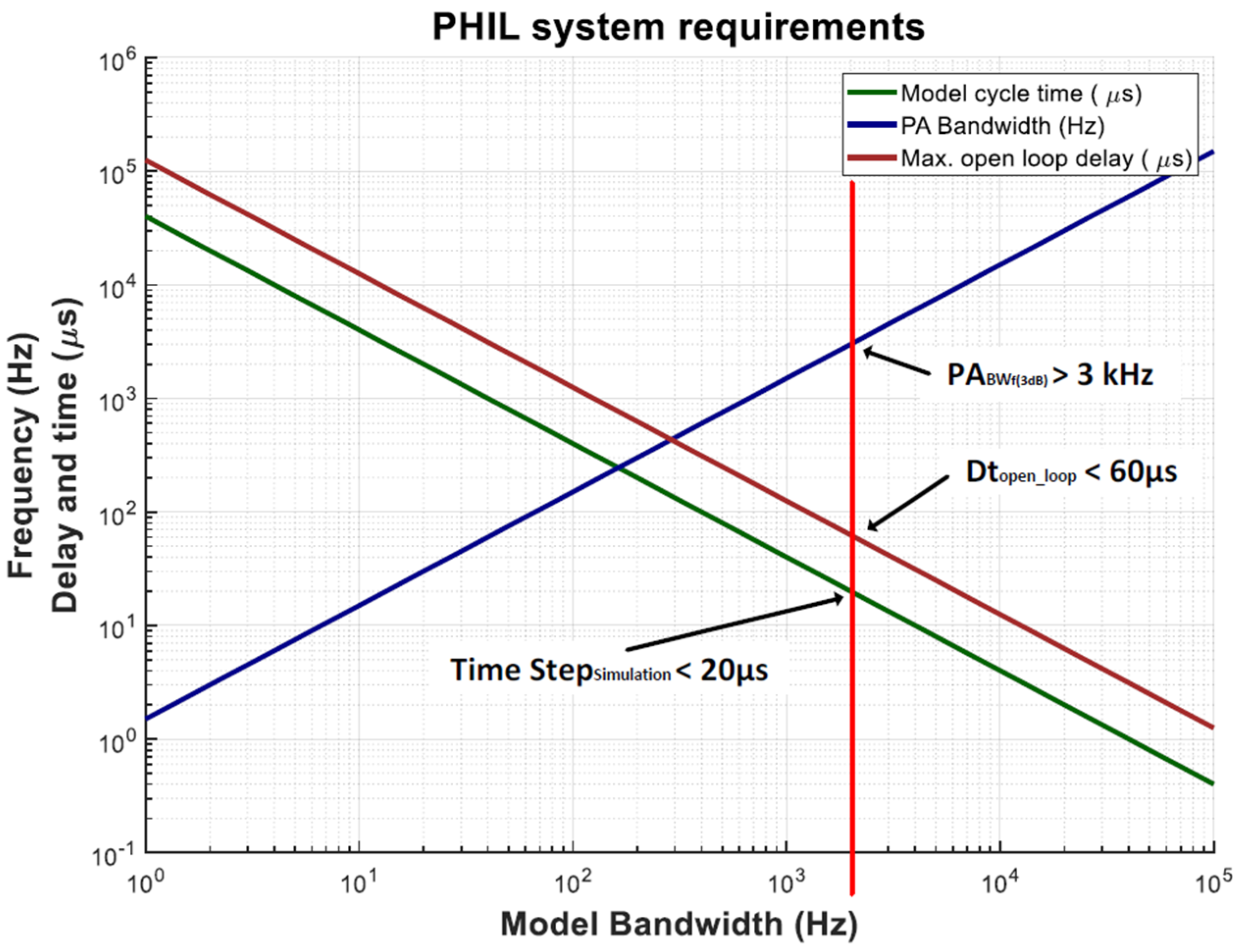
3.1. Real-Time Simulation Requirements
- -
- -
- -
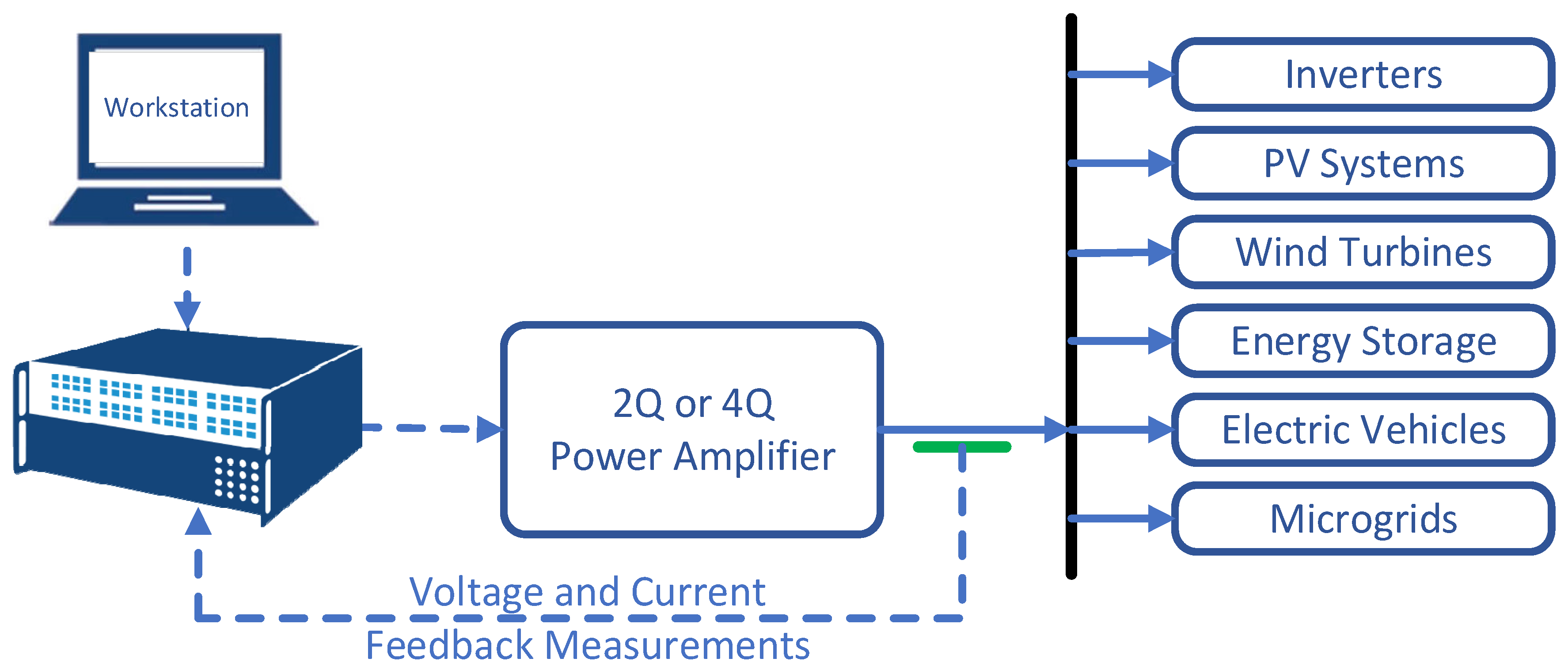
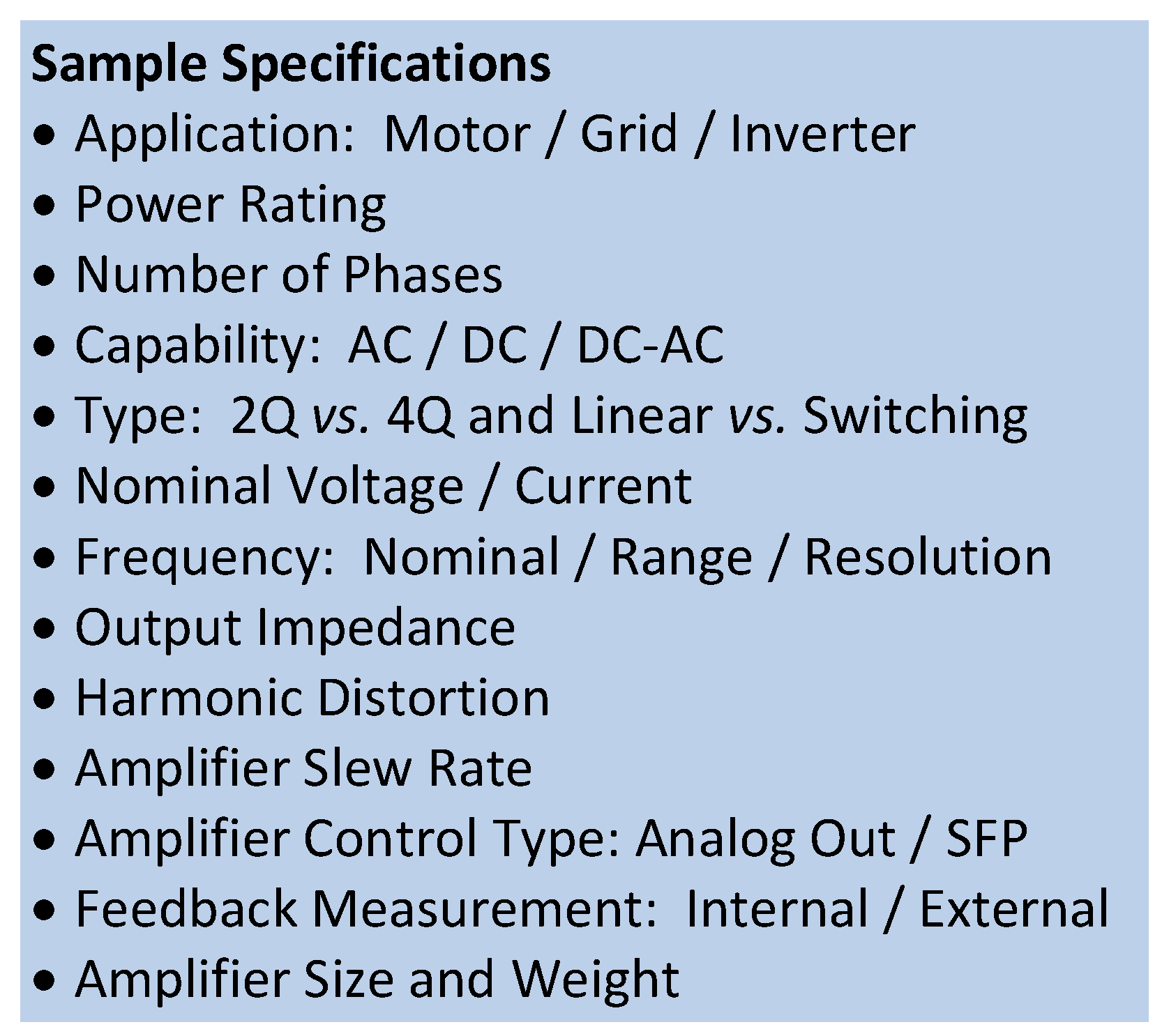
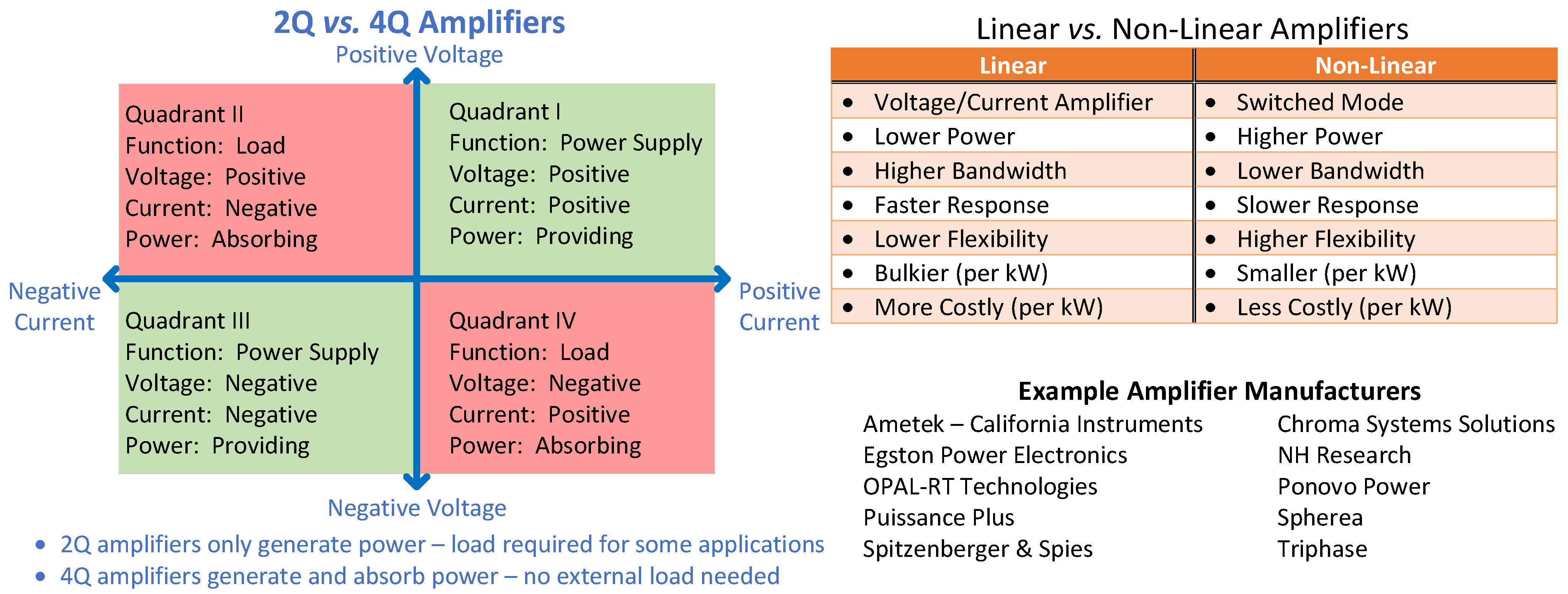
3.2. Power Amplifier Hardware Interface Requirements
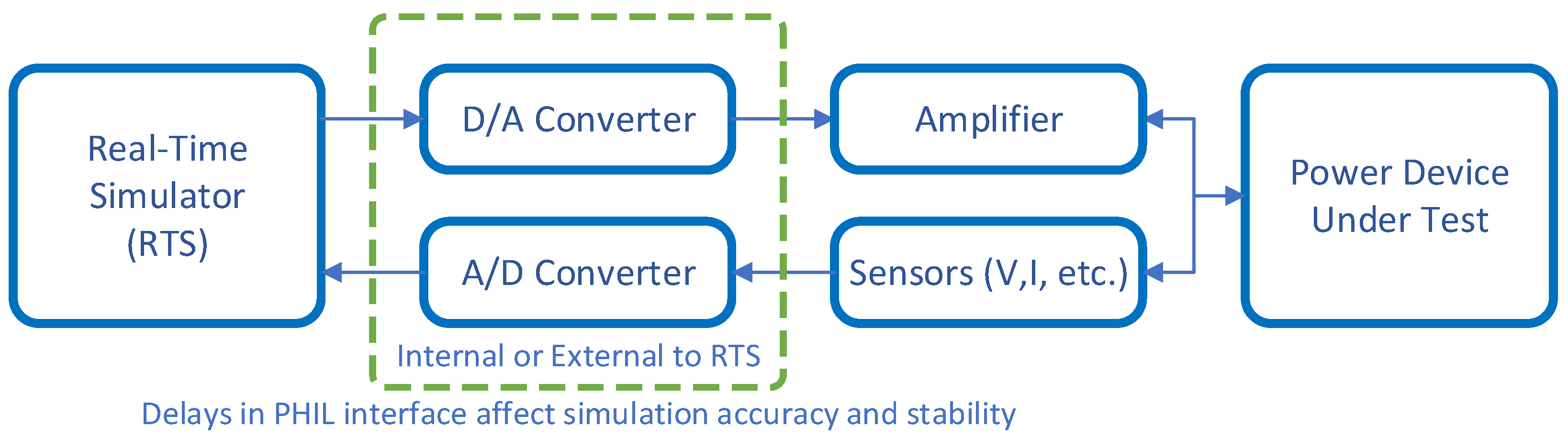
3.3. Interface Algorithms, Communications, Stability and Coordination Considerations for PHIL Testing
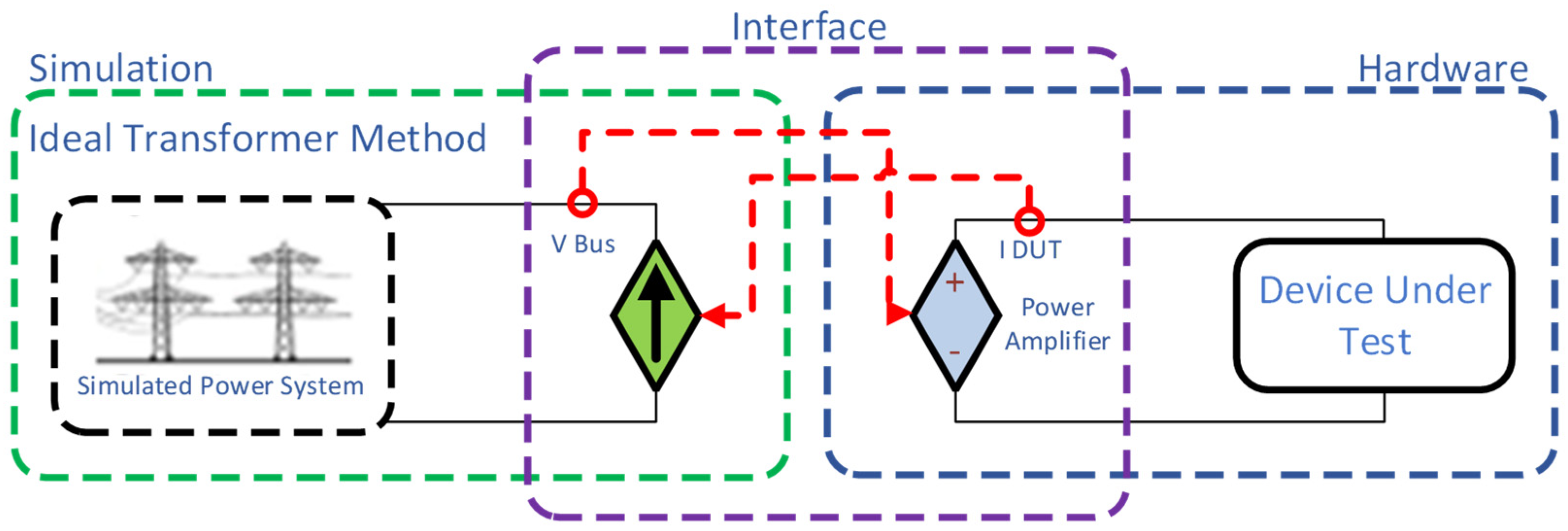
3.3.1. Interface Algorithms
3.3.2. Communications and I/O
3.3.3. Stability and Accuracy
3.3.4. Coordination, Data Management and Real-Time Visualization
3.4. PHIL Case Study
- hardware, including an amplifier (540 kVA AC source) and the DUT (500 kVA PV inverter (AE500)), as shown in Figure 12;
- QSTS simulation of the complete distribution feeder model in the DMS software on a 4-core Windows virtual machine;
- OPAL-RT RTS (4 core) running a reduced-equivalent EMT model of the feeder in eMEGASIM and that also drives the hardware;
- communications link between the DMS and the RTS that includes custom software to coordinate the QSTS and EMT simulations.
4. Exemplary and Unique PHIL Testbed Developments around the World
4.1. Austrian Institute of Technology (AIT) PHIL Real-Time Simulation Activities
- “Multiple sources/sinks ranging from high-bandwidth grid simulators/power amplifiers and AC/DC amplification units to an actual PV system
- Specialized equipment for the development of Wide Band Gap (WBG) semiconductor applications
- Multi-level single and three-phase power converter topologies for 4 quadrant converters (Ratings: 35 kVA AC, 35 kW DC/per device)
- High-voltage programmable power supply (Rating: 10 kV)
- Wide range of high-end, high-fidelity measurement equipment” [123]
- The AIT SmartEST Lab Services include [124]:
- “Testing of components and systems with simulated grids and primary energy sources
- “3 independent laboratory grids with variable network impedances for up to 1000 kVA, flexible star point configuration and grounding systems
- Voltage ratings from 300 V to 690 V
- 2 independent high bandwidth grid simulators: 0 to 480 V 3-phase AC, 800 kVA
- 3-phase balanced and unbalanced operation
- Low Voltage Ride-Through (LVRT) capabilities” [125]
4.2. Florida State University (FSU) Center for Advanced Power Systems (CAPS)
4.3. Hydro-Quebec Development of a PHIL Infrastructure
4.4. Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) PHIL Testbed
4.5. National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) PHIL Capabilities
4.6. Sandia National Laboratories PHIL Research
5. PHIL Research Paradigm Considerations to Advance Smart Inverter-Based Grid-Edge Solutions
6. Conclusions
- Interoperability testing of multiple inverters and microinverters, communicating with each other and the grid according to standards (e.g., IEEE 1547), including both grid-following and grid-forming inverters;
- Advance smart inverters providing grid services such as volt-VAR, frequency-Watt, constant PF, black-start capabilities, ride-through etc.
- DERs testing with energy storage or headroom to rapidly increase/decrease output power to provide fast frequency response, address transients and controller interaction instabilities;
- EV fast charging impacts on the grid and microgrids; use of local generation such as PV to support the grid;
- Implement smart inverters optimized to respond based on grid conditions/measurements autonomously, follow standards with the priority to sustain the grid;
- Evaluate control strategies, communication networks, interactions between loads and the grid and test behaviors in both normal adverse conditions;
- Cybersecurity testing to emulate intrusions communications; observe behaviors of inverters detecting the cyber security events;
- PHIL enables multiple cost-benefit analyses and case studies.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IEEE Std. 1547.7-2013; IEEE Guide for Conducting Distribution Impact Studies for Distributed Resource Interconnection. IEEE Std.: New York, NY, USA, February 2014.
- U.S. Department of Energy. Smart Grid Systems Report; U.S. Department of Energy: Washington, DC, USA, January 2022.
- Siano, P. Demand response and smart grids—A survey. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 30, 461–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anttila, S.; Döhler, J.S.; Oliveira, J.G.; Boström, C. Grid Forming Inverters: A Review of the State of the Art of Key Elements for Microgrid Operation. Energies 2022, 15, 5517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strasser, T.; Pröstl Andrén, F.; Lauss, G.; Bründlinger, R.; Brunner, H.; Moyo, C.; Seitl, C.; Rohjans, S.; Lehnhoff, S.; Palensky, P.; et al. Towards holistic power distribution system validation and testing—An overview and discussion of different possibilities. E&I Elektrotechnik Inf. 2017, 134, 71–77. [Google Scholar]
- Bethany, S.; Dheepak, K.; Annabelle, P.; Mark, R.; Hongyu, W. Hardware-in-the-Loop (HIL) Simulations for Smart Grid Impact Studies. In Proceedings of the IEEE PES General Meeting, Portland, OR, USA, 5–9 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Prabakar, K.; Palmintier, B.; Pratt, A.; Hariri, A.; Mendoza, I.; Baggu, M. Improving the Performance of Integrated Power-Hardware-in-the-Loop and Quasi-Static Time-Series Simulations. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 68, 10938–10948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, M.; Abdel Rahman, K.; Niannian, C.; Siddharth, S.R. Advantages of Real-Time Closed-Loop Simulation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Petroleum and Chemical Industry Technical Conference, San Antonio, TX, USA, 13–16 September 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Isermann, R.; Schaffnit, J.; Sinsel, S. Hardware-in-the-Loop Simulation for the Design and Testing of Engine-Control Systems. Control. Eng. Pract. 1999, 7, 643–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacic, M. On Hardware-in-the-Loop Simulation. In Proceedings of the 44th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Seville, Spain, 12–15 December 2005; pp. 3194–3198. [Google Scholar]
- Pratt, A.; Baggu, M.; Ding, F.; Veda, S.; Mendoza, I.; Lightner, E. A Test Bed to Evaluate Advanced Distribution Management Systems for Modern Power Systems. In Proceedings of the IEEE EUROCON 2019—18th International Conference on Smart Technologies, Novi Sad, Serbia, 1–4 July 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barragán-Villarejo, M.; García-López, F.D.P.; Marano-Marcolini, A.; Maza-Ortega, J.M. Power System Hardware in the Loop (PSHIL): A Holistic Testing Approach for Smart Grid Technologies. Energies 2020, 13, 3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariachet, J.E.; Matas, J.; Martín, H.; Li, M.; Guan, Y.; Guerrero, J.M. A power calculation algorithm for single-phase droop-operated-inverters considering linear and nonlinear loads HIL-assessed. Electronics 2019, 8, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y.; Gruosso, G. Ancillary service with grid connected PV: A real-time hardware-in-the-loop approach for evaluation of performances. Electronics 2019, 8, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Paquin, J.; Al Jajeh, F.; Joos, G.; Bouffard, F. Implementation and CHIL Testing of a Microgrid Control System. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Portland, OR, USA, 23–27 September 2018; pp. 2073–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Narayanasamy, D.; Ahn, B.; Ahmad, S.; Zeng, J.; Kim, T. A Real-Time Hardware-in-the-Loop (HIL) Cybersecurity Testbed for Power Electronics Devices and Systems in Cyber-Physical Environments. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 12th International Symposium on Power Electronics for Distributed Generation Systems (PEDG), Chicago, IL, USA, 28 June–1 July 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauss, G.F.; Faruque, M.O.; Schoder, K.; Dufour, C.; Viehweider, A.; Langston, J. Characteristics and Design of Power Hardware-in-the-Loop Simulations for Electrical Power Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 406–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steurer, M.; Bogdan, F.; Ren, W.; Sloderbeck, M.; Woodruff, S. Controller and Power Hardware-in-the-Loop Methods for Accelerating Renewable Energy Integration. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Power Engineering Society General Meeting, Tampa, FL, USA, 24–28 June 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Lundstrom, B.; Chakraborty, S.; Lauss, G.; Brundlinger, R.; Conklin, R. Evaluation of System-Integrated Smart Grid Devices using Software and Hardware-in-the-Loop. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Conference (ISGT), Minneapolis, MN, USA, 6–9 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Guillaud, X.; Faruque, M.O.; Teninge, A.; Hariri, A.H.; Vanfretti, L.; Paolone, M.; Davoudi, A. Applications of real-time simulation technologies in power and energy systems. IEEE Power Energy Technol. Syst. J. 2015, 2, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, S.; Banerjee, A.; Mosier, T. Power Hardware-In-the-Loop Hydropower and Ultracapacitor Hybrid Testbed. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting, Denver, CO, USA, 17–21 July 2022; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Vogel, S.; Stevic, M.; Kadavil, R.; Mohanpurkar, M.; Koralewicz, P.; Gevorgian, V.; Monti, A. Distributed real-time simulation and its applications to wind energy research. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Probabilistic Methods Applied to Power Systems (PMAPS), Boise, ID, USA, 24–28 June 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, A.; Nagarajan, A.; Hoke, A.; Prabakar, K.; Gevorgian, V.; Lundstrom, B.; Nepal, S.; Asano, M.; Ueda, R.; Shindo, J.; et al. Hawaiian Electric Advanced Inverter Grid Support Function Laboratory Validation and Analysis; Technical Report NREL/TP-5D00-67485; NREL: Golden, CO, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, A.; Prabakar, K.; Nagarajan, A.; Nepal, S.; Hoke, A.; Asano, M.; Ueda, R.; Ifuku, E. Power hardware-in-the-loop evaluation of PV inverter grid support on Hawaiian Electric feeders. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Power & Energy Society Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Conference (ISGT), Washington, DC, USA, 23–26 April 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Huerta, F.; Tello, R.L.; Prodanovic, M. Real-time power-hardwarein-the-loop implementation of variable-speed wind turbines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 1893–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelper, B.D.; Dessaint, L.A.; Al-Haddad, K.; Nakra, H. A comprehensive approach to fixed-step simulation of switched circuits. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2002, 17, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufour, C.; Abourida, S.; Belanger, J.; Lapointe, V. InfiniBand based real-time simulation of HVDC, STATCOM, and SVC devices with commercial-off-the-shelf PCs and FPGAs. In Proceedings of the IECON 2006-32nd Annual Conference on IEEE Industrial Electronics, Paris, France, 7–10 November 2006; pp. 5325–5331. [Google Scholar]
- Majumder, R.; Pal, B.C.; Dufour, C.; Korba, P. Design and realtime implementation of robust FACTS controller for damping interarea oscillation. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2006, 21, 809–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sybille, G.; Giroux, P. Simulation of FACTS controllers using the MATLAB power system blockset and hypersim real-time simulator. In Proceedings of the 2002 IEEE Power Engineering Society Winter Meeting, New York, NY, USA, 27–31 January 2002; Volume 1, pp. 488–491. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Lundstrom, B.; Mendoza, I.; Pratt, A. Systematic Characterization of Power Hardware-in-the-Loop Evaluation Platform Stability. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Baltimore, MD, USA, 29 September–3 October 2019; pp. 1068–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainsworth, N.; Hariri, A.; Prabakar, K.; Pratt, A.; Baggu, M. Modeling and compensation design for a power hardware-in-the-loop simulation of an AC distribution system. In Proceedings of the 2016 North American Power Symposium (NAPS), Manhattan, KS, USA, 18–20 September 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashani, M.G.; Pulakhandam, H.; Bhattacharya, S.; Katiraei, F.; Kaiser, D. Design considerations and test setup assessment for power hardware in the loop testing. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Industry Applications Society Annual Meeting, Cincinnati, OH, USA, 1–5 October 2017; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebe, F.; Idlbi, B.; Stakic, D.E.; Chen, S.; Kondzialka, C.; Casel, M.; Heilscher, G.; Seitl, C.; Bründlinger, R.; Strasser, T.I. Comparison of power hardware-in-the-loop approaches for the testing of smart grid controls. Energies 2018, 11, 3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauss, G.; Strunz, K. Accurate and Stable Hardware-in-the-Loop (HIL) Real-Time Simulation of Integrated Power Electronics and Power Systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 36, 10920–10932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; McEntee, C.; Zhang, M.; Lu, N.; Ke, X.; Vallem, M.R.; Samaan, N. Networked HIL Simulation System for Modeling Large-scale Power Systems. In Proceedings of the 2020 52nd North American Power Symposium (NAPS), Tempe, Arizona, 11–13 April 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Carne, G.; Buticchi, G.; Liserre, M. Current-type Power Hardware in the Loop (PHIL) evaluation for smart transformer application. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Electronics for Sustainable Energy Systems (IESES), Madras, India, 31 January–2 February 2018; pp. 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Carne, G.; Langwasser, M.; Gao, X.; Buticchi, G.; Liserre, M. Power-Hardware-In-Loop Setup for Power Electronics Tests. In Proceedings of the PCIM Europe 2017; International Exhibition and Conference for Power Electronics, Intelligent Motion, Renewable Energy and Energy Management, Nuremberg, Germany, 16–18 May 2017; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Bruno, S.; Giannoccaro, G.; Iurlaro, C.; La Scala, M.; Rodio, C. Power Hardware-in-the-Loop Test of a Low-Cost Synthetic Inertia Controller for Battery Energy Storage System. Energies 2022, 15, 3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racewicz, S.; Kutt, F.; Sienkiewicz, Ł. Power Hardware-In-the-Loop Approach for Autonomous Power Generation System Analysis. Energies 2022, 15, 1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Herdt, L.; Shekhar, A.; Yu, Y.; Mouli, G.R.C.; Dong, J.; Bauer, P. Power Hardware-in-the-Loop Demonstrator for Electric Vehicle Charging in Distribution Grids. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference & Expo (ITEC), Chicago, IL, USA, 23–25 June 2021; pp. 679–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinzadehtaher, M.; Tiwari, D.; Kouchakipour, N.; Momeni, A.; Lelic, M.; Wu, Z. Grid Resilience Assessment during Extreme Fast Charging of Electric Vehicles via Developed Power Hardware-in-the-Loop. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference & Expo (ITEC), Anaheim, CA, USA, 15–17 June 2022; pp. 929–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kothandaraman, S.R.; Malekpour, A.; Maigha, M.; Paaso, A.; Zamani, A.; Katiraei, F.; Lelic, M. Utility Scale Microgrid Controller Power Hardware-in-the-Loop Testing. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Electronic Power Grid (eGrid), Auckland, New Zealand, 29 November–2 December 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikusato, H.; Ustun, T.S.; Suzuki, M.; Sugahara, S.; Hashimoto, J.; Otani, K.; Shirakawa, K.; Yabuki, R.; Watanabe, K.; Shimizu, T. Microgrid Controller Testing Using Power Hardware-in-the-Loop. Energies 2020, 13, 2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijay, A.S.; Doolla, S.; Chandorkar, M.C. Real-Time Testing Approaches for Microgrids. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2017, 5, 1356–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoke, A.F.; Nelson, A.; Chakraborty, S.; Bell, F.; McCarty, M. An Islanding Detection Test Platform for Multi-Inverter Islands Using Power HIL. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 7944–7953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao Huang, C.M.D.; Davis, K.R. Real-time Power System Simulation with Hardware Devices through DNP3 in Cyber-Physical Testbed. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Texas Power and Energy Conference (TPEC), College Station, TX, USA, 2–5 February 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faruque, M.D.O.; Strasser, T.; Lauss, G.; Jalili-Marandi, V.; Forsyth, P.; Dufour, C.; Dinavahi, V.; Monti, A.; Kotsampopoulos, P.; Martinez, J.A.; et al. Real-Time Simulation Technologies for Power Systems Design, Testing, and Analysis. IEEE Power Energy Technol. Syst. J. 2015, 2, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Sloderbeck, M.; Steurer, M.; Dinavahi, V.; Noda, T.; Filizadeh, S.; Chevrefils, A.R.; Matar, M.; Iravani, R.; Dufour, C.; et al. Interfacing Issues in Real-Time Digital Simulators. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2011, 26, 1221–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edrington, C.S.; Steurer, M.; Langston, J.; El-Mezyani, T.; Schoder, K. Role of Power Hardware in the Loop in Modeling and Simulation for Experimentation in Power and Energy Systems. Proc. IEEE 2015, 103, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikkili, S.; Panda, A.; Prattipati, J. Review of Real-Time Simulator and the Steps Involved for Implementation of a Model from MATLAB/SIMULINK to Real-Time. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. B 2015, 96, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dargahi, M.; Ghosh, A.; Ledwich, G.; Zare, F. Studies in power hardware in the loop (PHIL) simulation using real-time digital simulator (RTDS). In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Power Electronics, Drives and Energy Systems (PEDES), Bengaluru, India, 16–19 December 2012; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Martínez, E.; Sanz, J.F.; Muñoz-Cruzado, J.; Perié, J.M. A Review of PHIL Testing for Smart Grids—Selection Guide, Classification and Online Database Analysis. Electronics 2020, 9, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Martínez, E.; Sanz, J.F.; Muñoz-Cruzado, J.; Perié, J.M. Online database of Power Hardware In-the-Loop tests. Data Brief 2020, 29, 105128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubschneider, S.; Kochanneck, S.; Bohnet, B.; Suriyah, M.; Mauser, I.; Leibfried, T.; Schmeck, H.; Braun, M. Requirements for Power Hardware-in-the-Loop Emulation of Distribution Grid Challenges. In Proceedings of the 2018 53rd International Universities Power Engineering Conference (UPEC), Glasgow, UK, 4–7 September 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankhe, D.; Sawant, R.; Rao, Y.S. Overview of Power Hardware-in-the-Loop Simulation Towards Implementation of Digital Controller for Resonant Inverters. In Proceedings of the 2018 2nd International Conference on Micro-Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering (ICMETE), Ghaziabad, India, 20–21 September 2018; pp. 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opal-RT Technologies. Available online: https://www.opal-rt.com (accessed on 26 November 2022).
- RTDS Technologies. Available online: https://www.rtds.com (accessed on 26 November 2022).
- Collin, R.; Stephens, M.; Von Jouanne, A. Development of SiC-Based Motor Drive Using Typhoon HIL 402 as System-Level Controller. In Proceedings of the IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition, Detroit, Michigan, 11–15 October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Von Jouanne, A.; Oriti, G.; Julian, A.; Agamloh, E.; Yokochi, A. GaN Four-leg Inverter Implementing Novel Common Mode Elimination using a Hardware-in-the-loop System-Level Controller. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Detroit, Michigan, 9–13 October 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Dommel, H. Digital Computer Solution of Electromagnetic Transients in Single and Multiphase Networks. IEEE Trans. Power Appar. Syst. 1969, 88, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuffel, R.; Giesbrecht, J.; Maguire, T.; Wierckx, R.P.; Mclaren, P. RTDS-a fully digital power system simulator operating in real time. In Proceedings of the 1995 International Conference on Energy Management and Power Delivery (EMPD’95), Singapore, 21–23 November 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Torres-Olguin, R.E.; Endegnanew, A.G.; D’Arco, S. Power-hardware-in-the-loop approach for emulating an offshore wind farm connected with a VSC-based HVDC. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Energy Internet and Energy System Integration (EI2), Beijing, China, 26–28 November 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Amitkumar, K.S.; Kaarthik, R.S.; Pillay, P. A versatile power-hardware-in-the-loop based emulator for rapid testing of electric drives. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Cincinnati, OH, USA, 1–5 October 2017; pp. 5468–5474. [Google Scholar]
- Seitl, C.; Kathan, J.; Lauss, G.; Lehfuss, F. Power hardware-in-the-loop implementation and verification of a real time capable battery model. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE 23rd International Symposium on Industrial Electronics (ISIE), Istanbul, Turkey, 1–4 June 2014; pp. 2285–2290. [Google Scholar]
- Craciun, O.; Florescu, A.; Munteanu, I.; Bratcu, A.I.; Bacha, S.; Radu, D. Hardware-in-the-loop simulation applied to protection devices testing. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2014, 54, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehfuss, F.; Lauss, G.; Strasser, T. Implementation of a multi-rating interface for Power-Hardware-in-the-Loop simulations. In Proceedings of the IECON 2012—38th Annual Conference on IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Montreal, QC, Canada, 25–28 October 2012; pp. 4777–4782. [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood, D.M.; Lim, K.Y.; Patsios, C.; Lyons, P.F.; Lim, Y.S.; Taylor, P.C. Frequency response services designed for energy storage. Appl. Energy 2017, 203, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Delille, G.; Guillaud, X.; Colas, F.; Francois, B. Real-time simulation: The missing link in the design process of advanced grid equipment. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting, Providence, RI, USA, 25–29 July 2010; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Lundstrom, B.; Palmintier, B.; Rowe, D.; Ward, J.; Moore, T. Trans-oceanic remote power hardware-in-the-loop: Multi-site hardware, integrated controller, and electric network co-simulation. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2017, 11, 4688–4701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, A.; Nelson, A.; Prabakar, K.; Hoke, A.; Asano, M.; Ueda, R.; Nepal, S. Network reduction algorithm for developing distribution feeders for real-time simulators. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting, Chicago, IL, USA, 16–20 July 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Lemaire, M.; Sicard, P.; Belanger, J. Prototyping and Testing Power Electronics Systems using Controller Hardware-In-the-Loop (HIL) and Power Hardware-In-the-Loop (PHIL) Simulations. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference (VPPC), Montreal, QC, Canada, 19–22 October 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, G.; Herrera, L.; Alsolami, M.; He, L.; Pu, X.; Xintong, L.; Andong, L.; Jin, W.; Zhijun, L. Design and development of a reconfigurable hybrid Microgrid testbed. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Denver, CO, USA, 15–19 September 2013; pp. 1350–1356. [Google Scholar]
- Craciun, O.; Florescu, A.; Munteanu, I.; Bacha, S.; Bratcu, A.I.; Radu, D. Protection devices testing based on power-hardware-in-the-loop simulation. In Proceedings of the IECON 2011—37th Annual Conference on IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Melbourne, Australia, 7–10 November 2011; pp. 3736–3741. [Google Scholar]
- Seitl, C.; Kathan, J.; Lauss, G.; Lehfuss, F. Selection and implementation of a generic battery model for PHIL applications. In Proceedings of the Industrial Electronics Society, IECON 2013—39th Annual Conference of the IEEE, Vienna, Austria, 10–13 November 2013; pp. 5412–5417. [Google Scholar]
- Yamane, A.; Li, W.; Belanger, J.; Ise, T.; Iyoda, I.; Aizono, T.; Dufour, C. A Smart Distribution Grid Laboratory. In Proceedings of the IECON 2011—37th Annual Conference on IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Melbourne, Australia, 7–10 November 2011; pp. 3708–3712. [Google Scholar]
- Ihrens, J.; Möws, S.; Wilkening, L.; Kern, T.A.; Becker, C. The Impact of Time Delays for Power Hardware-in-the-Loop Investigations. Energies 2021, 14, 3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruhe, S.; Fechner, M.; Nicolai, S.; Bretschneider, P. Simulation of Coupled Components within Power-Hardware-in-the-Loop (PHiL) Test Bench. In Proceedings of the 2020 55th International Universities Power Engineering Conference (UPEC), Torino, Italy, 1–4 September 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W. Accuracy Evaluation of Power Hardware-in-the-Loop Simulation. Ph.D. Thesis, Florida State University, Tallahassee, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Nzimako, O.; Wierckx, R. Stability and accuracy evaluation of a power hardware in the loop (PHIL) interface with a photovoltaic micro-inverter. In Proceedings of the IECON 2015—41st Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Yokohama, Japan, 9–12 November 2015; pp. 5285–5291. [Google Scholar]
- Lauss, G.; Lehfuss, F.; Bletterie, B.; Strasser, T.; Brundlinger, R. Examination of LV grid phenomena by means of PHIL testing. In Proceedings of the IECON 2012—38th Annual Conference on IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Monteral, QC, Canada, 25–28 October 2012; pp. 4771–4776. [Google Scholar]
- Kotsampopoulos, P.; Kleftakis, V.; Messinis, G.; Hatziargyriou, N. Design, development and operation of a PHIL environment for Distributed Energy Resources. In Proceedings of the IECON 2012—38th Annual Conference on IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Monteral, QC, Canada, 25–28 October 2012; pp. 4765–4770. [Google Scholar]
- Pokharel, M.; Ho, C.N.M. Stability study of power hardware in the loop (PHIL)simulations with a real solar inverter. In Proceedings of the IECON 2017—43rd Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Beijing, China, 5–8 November 2017; pp. 2701–2706. [Google Scholar]
- Langston, J.; Schoder, K.; Steurer, M.; Faruque, O.; Hauer, J.; Bogdan, F.; Bravo, R.; Mather, B.; Katiraei, F. Power hardware-in-the-loop testing of a 500 kWphotovoltaic array inverter. In Proceedings of the IECON 2012—38th Annual Conference on IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Monteral, QC, Canada, 25–28 October 2012; pp. 4797–4802. [Google Scholar]
- Kotsampopoulos, P.; Kapetanaki., A.; Messinis., G.; Kleftakis., V.; Hatziargyriou, N. A Power-Hardware-in-the-loop facility for microgrids. Int. J. Renew. Energy Technol. 2012, 9, 89–104. [Google Scholar]
- Karapanos, V.; de Haan, S.; Zwetsloot, K. Real time simulation of a power system with VSG hardware in the loop. In Proceedings of the IECON 2011—37th Annual Conference on IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Melbourne, Australia, 7–10 November 2011; pp. 3748–3754. [Google Scholar]
- Schacherer, C.; Langston, J.; Steurer, M.; Noe, M. Power Hardware-in-the-Loop Testing of a YBCO Coated Conductor Fault Current Limiting Module. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2009, 19, 1801–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langston, J.; Bogdan, F.; Hauer, J.; Schoder, K.; Steurer, M.; Dalessandro, D.; Fikse, T.; Cherry, J.; Gonstead, S. Megawatt-scale power hardware-in-the-loop simulation testing of a power conversion module for naval applications. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Electric Ship Technologies Symposium (ESTS), Old Town Alexandria, VA, USA, 21–24 June 2015; pp. 268–275. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, E.S.; Kim, D.W. Performance testing of Grid-connected photovoltaic inverter based on an integrated electronic protection device. In Proceedings of the 2009 Transmission and Distribution Conference and Exposition: Asia and Pacific, Seoul, Repulic of Korea, 26–30 October 2009; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, C.; Leng, F.; Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, L.; Mo, R.; Wang, D.; Zeng, J.; Chen, X.; An, R.; et al. A 400-V/50-kVA Digital-Physical Hybrid Real-Time Simulation Platform for Power Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 3666–3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vodyakho, O.; Edrington, C.S.; Steurer, M.; Azongha, S.; Fleming, F. Synchronization of three-phase converters and virtual microgrid implementation utilizing the Power-Hardware-in-the-Loop concept. In Proceedings of the 2010 Twenty-Fifth Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC), Palm Springs, CA, USA, 21–25 February 2010; pp. 216–222. [Google Scholar]
- Kotsampopoulos, P.; Kleftakis, V.; Hatziargyriou, N. Laboratory Education of Modern Power Systems using PHIL Simulation. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2016, 32, 3992–4001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Averous, N.R.; Stieneker, M.; Kock, S.; Andrei, C.; Helmedag, A.; Doncker, R.W.D.; Hameyer, K.; Jacobs, G.; Monti, A. Development of a 4MWFull-SizeWind-Turbine Test Bench. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2017, 5, 600–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steurer, M.M.; Schoder, K.; Faruque, O.; Soto, D.; Bosworth, M.; Sloderbeck, M.; Bogdan, F.; Hauer, J.; Winkelnkemper, M.; Schwager, L.; et al. Multifunctional Megawatt-Scale Medium Voltage DC Test Bed Based on Modular Multilevel Converter Technology. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2016, 2, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Q.; Abdulhadi, I.; Roscoe, A.; Booth, C. Application of a MW-scale motor-generator set to establish power-hardware-in-the-loop capability. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE PES Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Conference Europe (ISGT-Europe), Torino, Italy, 26–29 September 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Maniatopoulos, M.; Lagos, D.; Kotsampopoulos, P.; Hatziargyriou, N. Combined control and power hardware in-the-loop simulation for testing smart grid control algorithms. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2017, 11, 3009–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashani, M.G.; Bhattacharya, S.; Matamoros, J.; Kaiser, D.; Cespedes, M. Voltage regulation with autonomous distributed smart inverters in a low voltage network. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting, Chicago, IL, USA, 16–20 July 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Roscoe, A.J.; Mackay, A.; Burt, G.M.; McDonald, J.R. Architecture of a Network-in-the-Loop Environment for Characterizing AC Power-System Behavior. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 57, 1245–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Steurer, M.; Baldwin, T.L. Improve the Stability and the Accuracy of Power Hardware-in-the-Loop Simulation by Selecting Appropriate Interface Algorithms. In Proceedings of the Industrial and Commercial Power Systems Technical Conference (ICPS 2007. IEEE/IAS), Edmonton, AB, Canada, 6–11 May 2007; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, W.; Steurer, M.; Woodruff, S. Applying Controller and Power Hardware-in-the-Loop Simulation in Designing and Prototyping Apparatuses for Future All Electric Ship. In Proceedings of the Electric Ship Technologies Symposium (ESTS ’07. IEEE), Arlington, VA, USA, 21–23 May 2007; pp. 443–448. [Google Scholar]
- Fleming, F.; Edrington, C.S.; Steurer, M.; Vodyakho, O. Development and implementation of a 25 kW virtual induction machine test bed utilizing the power-hardware-in-the-loop concept. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Electric Machines and Drives Conference (IEMDC ’09), Miami, FL, USA, 3–6 May 2009; pp. 1161–1166. [Google Scholar]
- Vodyakho, O.; Fleming, F.; Steurer, M.; Edrington, C. Implementation of a virtual induction machine test bed utilizing the power hardware-in-the-loop concept. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Electric Ship Technologies Symposium (ESTS), Alexandria, VA, USA, 10–13 April 2011; pp. 52–55. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Yang, H.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, S.; Gao, X.; Gong, P. A Dynamic Cyber-attack Approach for Real-time Hardware-in-the-loop Simulation of Power Grid. In Proceedings of the 2022 24th International Conference on Advanced Communication Technology (ICACT), Pyeongchang, Repulic of Korea, 13–16 February 2022; pp. 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokharel, M.; Man Ho, C.N. Modelling and Experimental Evaluation of Ideal Transformer Algorithm Interface for Power Hardware in the Loop Architecture. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC), New Orleans, LA, USA, 15–19 March 2020; pp. 1404–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hypersim—Hydro Québec. Available online: https://www.opal-rt.com/systems-hypersim/ (accessed on 26 November 2022).
- Tremblay, O. Contribution to the Design of the Closed-Loop Control of a Real-Time Power Simulator. Ph.D. Thesis, Ecole de Technologie Superieure, Montreal, QC, Canada, 2020. Available online: https://espace.etsmtl.ca/id/eprint/2693 (accessed on 26 November 2022).
- Dione, M.; Sirois, F.; Bonnard, C.H. Evaluation of the Impact of Superconducting Fault Current Limiters on Power System Network Protections Using a RTS-PHIL Methodology. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2011, 21, 2193–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemaire, M.; Pammer, G.; Black, B. Smarter drives need smarter development. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference and Expo (ITEC), Dearborn, MI, USA, 27–29 June 2016; pp. 1–63. [Google Scholar]
- Bélanger, J.; Dufour, C.; Schoen, L. eMEGAsim: An Open High-Performance Architecture and Specification. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Power Systems (ICPS’07), Bangalore, India, 12–14 December 2007; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez-Alvidrez, J.; Gurule, N.S.; Reno, M.J.; Flicker, J.D.; Summers, A.; Ellis, A. Method to Interface Grid-Forming Inverters into Power Hardware in the Loop Setups. In Proceedings of the 2020 47th IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference (PVSC), Calgary, ON, Canada, 15 June–21 August 2020; pp. 1804–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quedan, A.; Wang, W.; Ramasubramanian, D.; Farantatos, E.; Asgarpoor, S. Behavior of a High Inverter-Based Resources Distribution Network with Different Participation Ratios of Grid-Forming and Grid-Following Inverters. In Proceedings of the 2021 North American Power Symposium (NAPS), College Station, TX, USA, 14–16 November 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, S.; Nguyen, H.T.; Stevic, M.; Jensen, T.V.; Heussen, K.; Rajkumar, V.S.; Monti, A. Distributed Power Hardware-in-the-Loop Testing Using a Grid-Forming Converter as Power Interface. Energies 2020, 13, 3770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, M.; Behrends, H.; Geißendörfer, S.; Maydell, K.V.; Agert, C. Power Hardware-in-the-Loop: Response of Power Components in Real-Time Grid Simulation Environment. Energies 2021, 14, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandl, R. Operational Range of Several Interface Algorithms for Different Power Hardware-In-The-Loop Setups. Energies 2017, 10, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, V.; Georg, L.; Lehfuss, F. Stabilization of Power Hardware-in-the-Loop simulations of electric energy systems. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 2011, 19, 1699–1708. [Google Scholar]
- Guillo-Sansano, E.; Syed, M.H.; Roscoe, A.J.; Burt, G.M.; Coffele, F. Characterization of Time Delay in Power Hardware in the Loop Setups. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 68, 2703–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Miller, B.; Pratt, A.; Fossum, J.; Bialek, T.; Mason, S. Diesel Generator Controller Evaluation via Controller-Hardware-in-the-Loop for Various Microgrid Operation Modes. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Innovative Smart Grid Technologies (ISGT), New Orleans, LA, USA, 21–24 February 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Storey, H.L. Implementing an integrated centralized model-based distribution management system. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting, Detroit, Michigan, 24–28 July 2011; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentarzi, H.; Tsebia, M.; Abdelmoumene, A. PMU based SCADA enhancement in smart power grid. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 12th International Conference on Compatibility, Power Electronics and Power Engineering (CPE-POWERENG 2018), Doha, Qatar, 10–12 April 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peak Load Management in Distribution Systems Using Legacy Utility Equipment and Distributed Energy Resources. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Green Technologies Conference (GreenTech), Denver, Colorado, 7–9 April 2021; pp. 435–441. [CrossRef]
- Reno, M.J.; Deboever, J.; Mather, B. Motivation and requirements for quasi-static time series (QSTS) for distribution system analysis. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE power & energy society general meeting, Chicago, IL, USA, 16–20 July 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Villalva, M.; Gazoli, J.; Filho, E. Comprehensive approach to modeling and simulation of photovoltaic arrays. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2009, 24, 1198–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jambrich, G.; Felix, L.; Johannes, S.; Johann, M.; Stephan, L.; Friederich, K. Development of P-HIL test methods and research infrastructure for medium and low voltage DC systems. Elektrotechnik Inf. 2020, 137, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austrian Institute of Technology (AIT). Available online: https://www.ait.ac.at/en/solutions/power-system-technologies-development-validation/power-electronics-lab (accessed on 6 January 2023).
- Johnson, J.; Ablinger, R.; Bründlinger, R.; Fox, B.; Flicker, J. Design and Evaluation of SunSpec-Compliant Smart Grid Controller with an Automated Hardware-in-the-Loop Testbed. Technol. Econ. Smart Grids Sustain. Energy 2017, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austrian Institute of Technology (AIT). Available online: https://www.ait.ac.at/en/solutions/power-system-technologies-development-validation/smartest-lab (accessed on 6 January 2023).
- Langston, J.; Schoder, K.; Steurer, M.; Edrington, C.; Roberts, R.G. Analysis of Linear Interface Algorithms for Power Hardware-in-the-Loop Simulation. In Proceedings of the IECON 2018—44th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Washington, DC, USA, 21–23 October 2018; pp. 4005–4012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florida State University—Center for Advanced Power Systems (FSU-CAPS). Available online: https://www.caps.fsu.edu/about-caps/5-mw-advanced-prototype-test-facility/ (accessed on 6 January 2023).
- Ettore, B.; Sergio, B.; Andres, C.-P.; Cesar, D.-L.; Giovanni, G.; Massimo La, S.; Andrea, M.; Enrico, P. Latency and Simulation Stability in a Remote Power Hardware-in-the-Loop Cosimulation Testbed. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2021, 57, 3463–3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gielnik, F.; Geis-Schroer, J.; Eser, D.; Eichhorn, S.; Steinle, S.; Hirsching, C.; Leibfried, T. Establishing a Power Hardware-in-the-Loop Environment with a Smart Energy Complex. In Proceedings of the 2022 57th International Universities Power Engineering Conference (UPEC), Istanbul, Turkey, 30 August–2 September 2022; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochanneck, S.; Mauser, I.; Bohnet, B.; Hubschneider, S.; Schmeck, H.; Braun, M.; Leibfried, T. Establishing a hardware-in-the-loop research environment with a hybrid energy storage system. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Innovative Smart Grid Technologies—Asia (ISGT-Asia), Melbourne, Australia, 28 November–1 December 2016; pp. 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafidehkordi, F.; De Carne, G. Improved Accuracy of the Power Hardware-in-the-Loop Modeling using Multirate Discrete Domain. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 13th International Symposium on Power Electronics for Distributed Generation Systems (PEDG), Kiel, Germany, 26–29 June 2022; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Pratt, A.; Prabakar, K.; Miller, B.; Symko-Davies, M. Development of an Integrated Platform for Hard-ware-in-the-Loop Evaluation of Microgrids Prior to Site Commissioning. Appl. Energy 2021, 290, 116755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabakar, K.; Pratt, A.; Fossum, J.; Wang, J.; Miller, B.; Symko-Davies, M.; Usman, M.U.; Bialek, T. Site-Specific Evaluation of Microgrid Controller Using Controller and Power-Hardware-in-the-Loop. In Proceedings of the 45th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society (IECON), Lisbon, Portugal, 14–17 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- National Renewable Energy Lab (NREL). Available online: https://www.nrel.gov/grid/controllable-grid-interface.html (accessed on 6 January 2023).
- Sandia National Laboratories (SNL). Available online: https://energy.sandia.gov/programs/electric-grid/renewable-energy-integration/distributed-energy-technologies-lab-detl/ (accessed on 6 January 2023).
- Darbali-Zamora, R.; Johnson, J.; Gurule, N.S.; Reno, M.J.; Ninad, N.; Apablaza-Arancibia, E. Evaluation of Photovoltaic Inverters Under Balanced and Unbalanced Voltage Phase Angle Jump Conditions. In Proceedings of the 2020 47th IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference (PVSC), Calgary, ON, Canada, 15 June–21 August 2020; pp. 1562–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darbali-Zamora, R.; Quiroz, J.E.; Hernández-Alvidrez, J.; Johnson, J.; Ortiz-Rivera, E.I. Validation of a Real-Time Power Hardware-in-the-Loop Distribution Circuit Simulation with Renewable Energy Sources. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 7th World Conference on Photovoltaic Energy Conversion (WCPEC) (A Joint Conference of 45th IEEE PVSC, 28th PVSEC & 34th EU PVSEC), Waikele, HI, USA, 10–15 June 2018; pp. 1380–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summers, A.; Johnson, J.; Darbali-Zamora, R.; Hansen, C.; Anandan, J.; Showalter, C. A Comparison of DER Voltage Regulation Technologies Using Real-Time Simulations. Energies 2020, 13, 3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darbali-Zamora, R.; Johnson, J.; Summers, A.; Jones, C.B.; Hansen, C.; Showalter, C. State Estimation-Based Distributed Energy Resource Optimization for Distribution Voltage Regulation in Telemetry-Sparse Environments Using a Real-Time Digital Twin. Energies 2021, 14, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Eto, J.H.; Johnson, B.B.; Flicker, J.D.; Lasseter, R.H.; Pico, H.V.; Ellis, A. Research Roadmap on Grid-Forming Inverters. Golden, CO: National Renewable Energy Laboratory. NREL/TP-5D00-73476; 2020. Available online: https://www.nrel.gov/docs/fy21osti/73 (accessed on 26 November 2022).
- Horowitz, K.A.; Peterson, Z.; Coddington, M.H.; Ding, F.; Sigrin, B.O.; Saleem, D.; Baldwin, S.E.; Lydic, B.; Stanfield, S.C.; Enbar, N.; et al. An Overview of Distributed Energy Resource (DER) Interconnection: Current Practices and Emerging Solutions. Golden, CO: National Renewable Energy Laboratory. NREL/TP-6A20-72102; 2019. Available online: https://www.nrel.gov/docs/fy19osti/72102.pdf (accessed on 26 November 2022).
- Jin, D.; Nicol, D.M.; Yan, G. An event buffer flooding attack in dnp3 controlled scada systems. In Proceedings of the 2011 Winter Simulation Conference (WSC), Phoenix, AZ, USA, 11–14 December 2011; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 2614–2626. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; McLaughlin, K.; Littler, T.; Sezer, S.; Im, E.G.; Yao, Z.Q.; Wang, H.F. Man-in-the-middle attack test-bed investigating cyber-security vulnerabilities in Smart Grid SCADA systems. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Sustainable Power Generation and Supply (SUPERGEN 2012), Hangzhou, China, 8–9 September 2012; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Kim, H.; Kim, K.; Yoo, P.D. Simulated attack on dnp3 protocol in scada system. In Proceedings of the 31th Symposium on Cryptography and Information Security, Kagoshima, Japan, 21–24 January 2014; pp. 21–24. [Google Scholar]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
von Jouanne, A.; Agamloh, E.; Yokochi, A. Power Hardware-in-the-Loop (PHIL): A Review to Advance Smart Inverter-Based Grid-Edge Solutions. Energies 2023, 16, 916. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16020916
von Jouanne A, Agamloh E, Yokochi A. Power Hardware-in-the-Loop (PHIL): A Review to Advance Smart Inverter-Based Grid-Edge Solutions. Energies. 2023; 16(2):916. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16020916
Chicago/Turabian Stylevon Jouanne, Annette, Emmanuel Agamloh, and Alex Yokochi. 2023. "Power Hardware-in-the-Loop (PHIL): A Review to Advance Smart Inverter-Based Grid-Edge Solutions" Energies 16, no. 2: 916. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16020916
APA Stylevon Jouanne, A., Agamloh, E., & Yokochi, A. (2023). Power Hardware-in-the-Loop (PHIL): A Review to Advance Smart Inverter-Based Grid-Edge Solutions. Energies, 16(2), 916. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16020916






