Influence of Catalytic Additive Application on the Wood-Based Waste Combustion Process
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Reduction of NO (by CO): the most popular is the rhodium catalyst, but more substances can be effective when oxygen is absent in flue gas:
- Oxidation of CO and hydrocarbons: the most popular is the platinum catalyst (in the presence of a small concentration of oxygen):
2C2H6 + 7O2 = 4CO2 + 6H2O
- Ammonia:
NH2 + NO = N2 + H2O
- Urea:
CO(NH2)2 = NH3 + HNCO
2NO2 + 4NH3 + O2 = 3N2 + 6H2O
SO3 + H2O = H2SO4
2. Materials and Methods
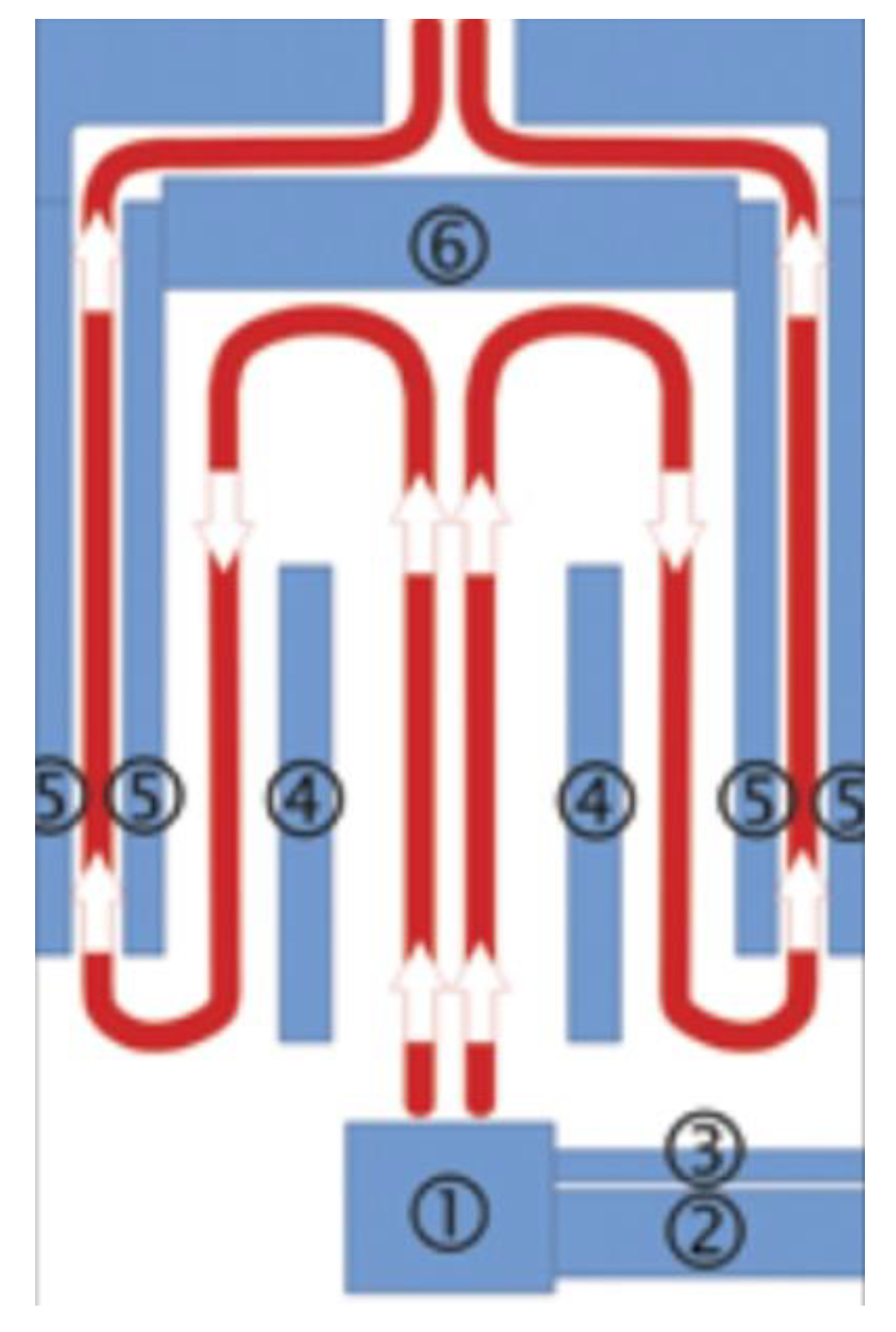
2.1. Research Stand
2.2. Materials
- Pellets made from MDF dust and chipboard waste;
- Pellets made from MDF dust and chipboard waste with the addition of a catalyst (Ad1);
- Pellets made from MDF dust and chipboard waste sprayed with a catalyst mixed with water in a 1:1 ratio (Ad2).
2.3. Biofuel Physicochemical Analysis
2.4. Measurement of Exhaust Gas Composition
2.5. Measurement of the Temperature in the Biomass Boiler’s Combustion Chamber
3. Results
3.1. Biofuel Physicochemical Analysis
3.2. Measurement of the Temperature in the Biomass Boiler’s Combustion Chamber
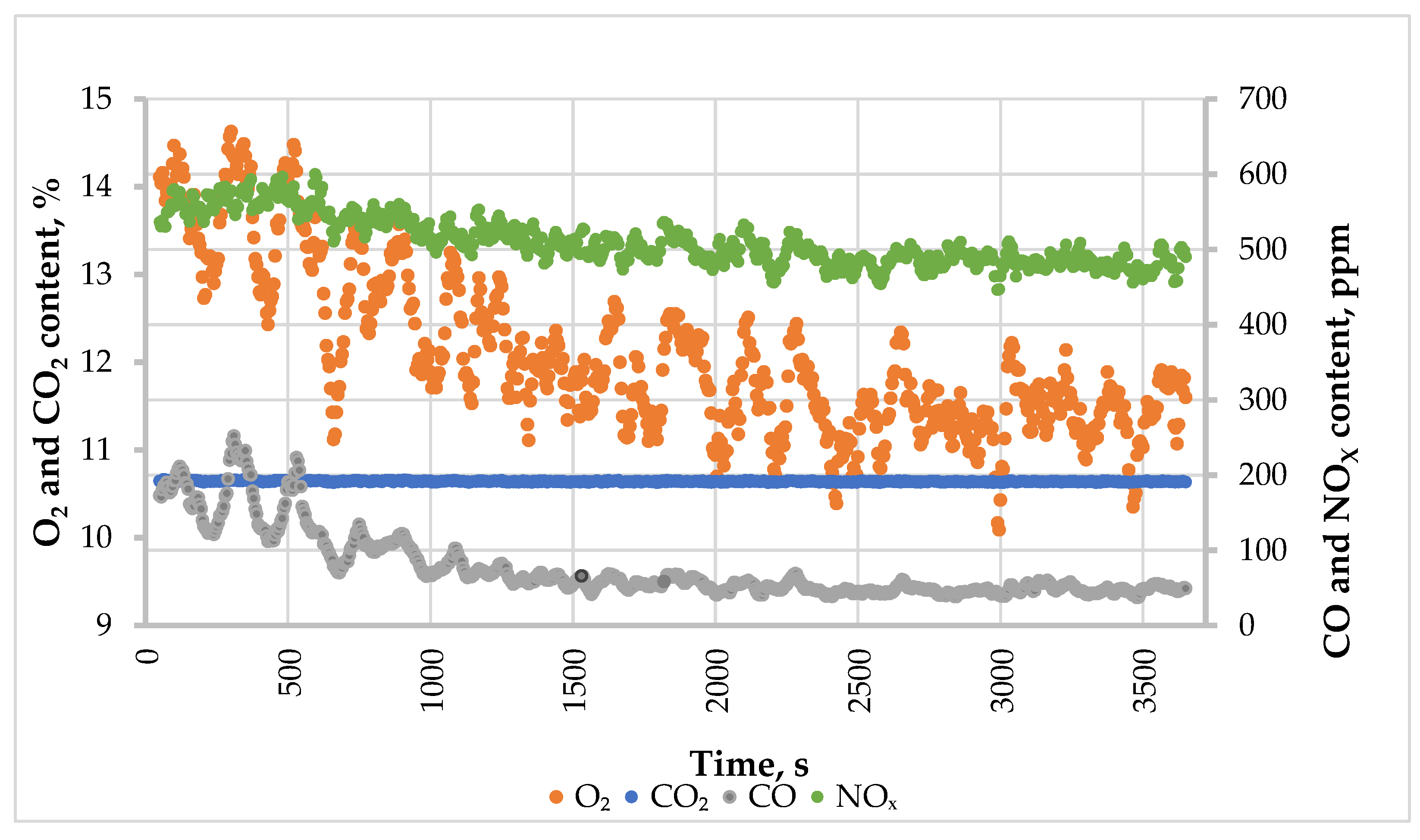
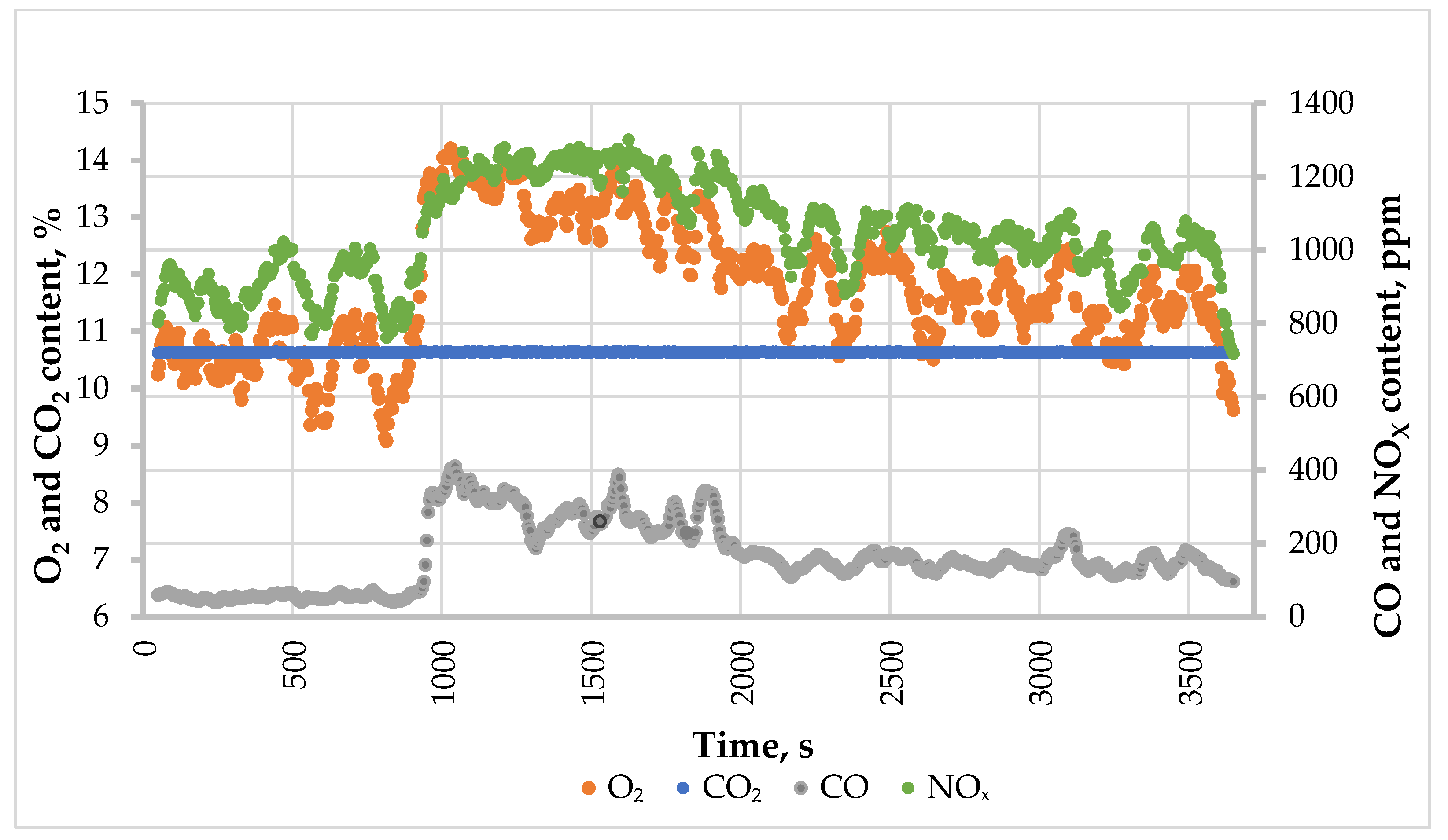
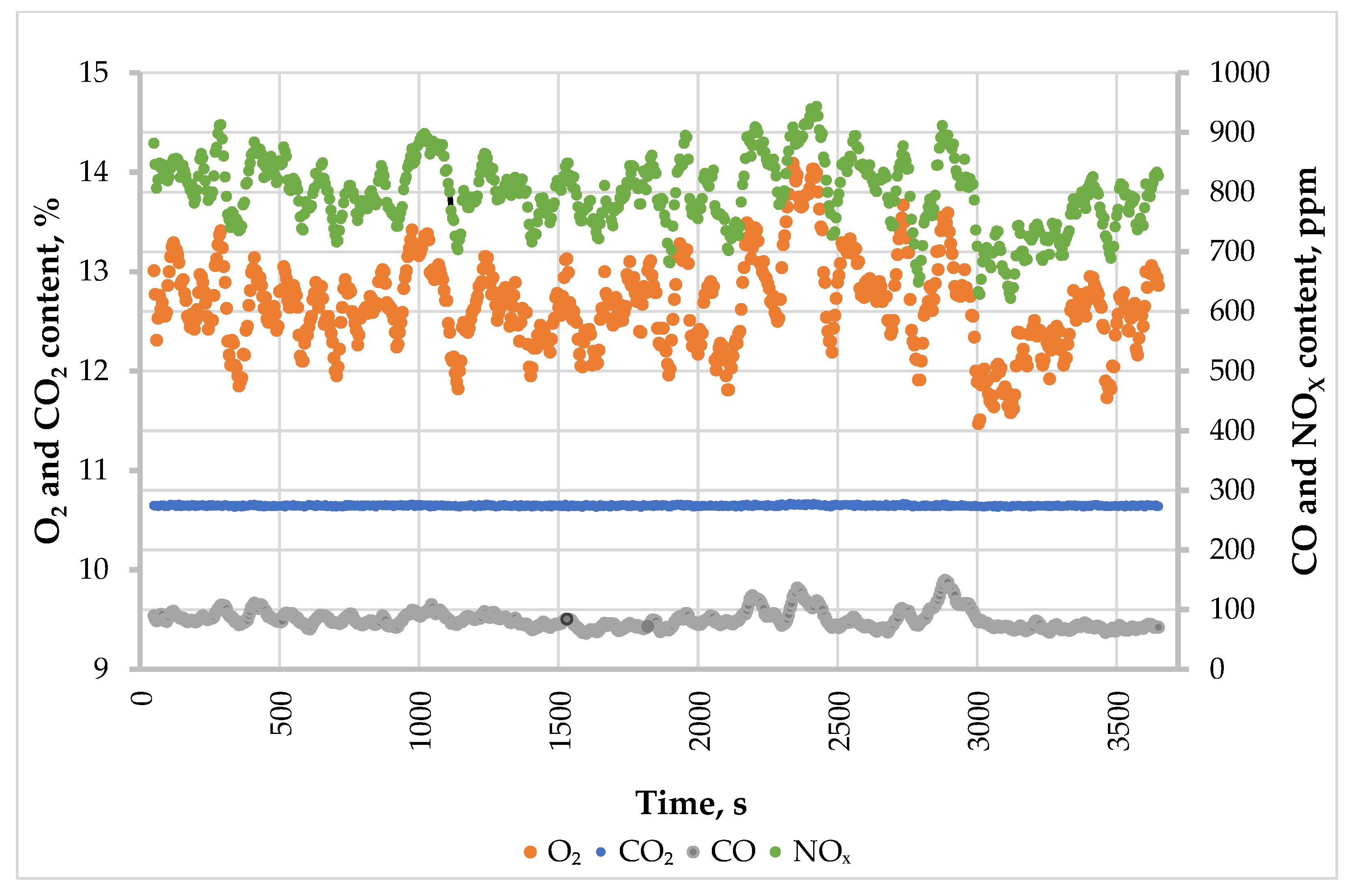
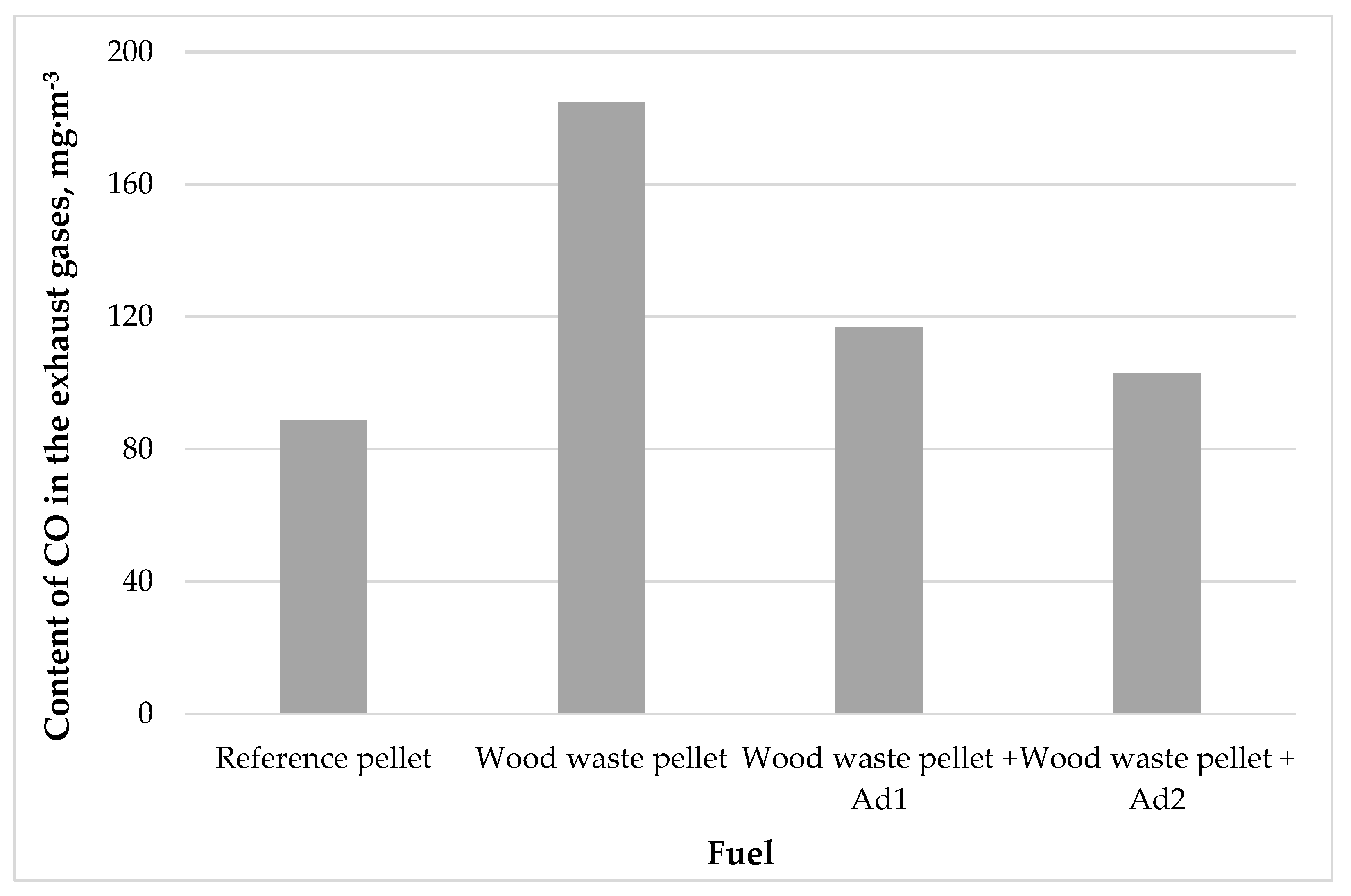
3.3. Measurement of Exhaust Gas Composition
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Waheed, R.; Sarwar, S.; Wei, C. The survey of economic growth, energy consumption and carbon emission. Energy Rep. 2019, 5, 1103–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roni, M.S.; Chowdhury, S.; Mamun, S.; Marufuzzaman, M.; Lein, W.; Johnson, S. Biomass co-firing technology with policies, challenges, and opportunities: A global review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 78, 1089–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.N.; Techato, K.; Taweekun, J.; Rahman, M.M.; Rasul, M.G.; Mahlia, T.M.I.; Ashrafur, S.M. An Overview of Recent Developments in Biomass Pyrolysis Technologies. Energies 2018, 11, 3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leskinien, P.; Cardellini, G.; Gonzalez-Garcia, S.; Hurmekoski, E.; Sathre, R.; Seppala, J.; Smyth, C.; Stern, T.; Verkerk, P. Substitution Effects of Wood-Based Products in Climate Change Mitigatiom; From Science to Policy 7; EFI: Joensuu, Finland, 2018; ISBN 978-952-5980-69-1. [Google Scholar]
- Kobuszynska, M. Report: Forestry and Wood Products in Poland, Global Agricultural Information Network. 2017. Available online: https://apps.fas.usda.gov/newgainapi/api/report/downloadreportbyfilename?filename=The%20Forestry%20and%20Wood%20Products%20in%20Poland_Warsaw_Poland_3-23-2017.pdf (accessed on 15 December 2022).
- Parikka, M. Global biomass fuel resources. Biomass Bioenergy 2004, 27, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajda-Szcześniak, M. Evaluation of the basic properties of the wood waste and wood based wastes. Arch. Waste Manag. Environ. Prot. 2013, 15, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho, L.; Magalhães, F.; Ferra, J. Formaldehyde emissions from wood-based panels-Testing methods and industrial perspectives. In Formaldehyde: Chemistry, Applications and Role in Polymerization; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 1–45. [Google Scholar]
- Wasilewski, R.; Hrycko, P. Efekty energetyczno-emisyjne spalania odpadów z przeróbki płyt drewnopochodnych w kotle małej mocy. Arch. Gospod. Odpad. I Ochr. Sr. 2010, 12, 27–34. [Google Scholar]
- De Ligne, L.; Van Acker, J.; Baetens, J.M.; Omar, S.; De Baets, B.; Thygesen, L.G.; Van den Bulcke, J.; Thybring, E.E. Moisture Dynamics of Wood-Based Panels and Wood Fibre Insulation Materials. Front. Plant Sci 2022, 13, 951175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Council Directive 2010/75/EC on Industrial Emissions (Integrated Pollution Prevention and Control). Official Journal of the European Communities. 2010. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2010:334:0017:0119:en:PDF (accessed on 15 December 2022).
- Wasielewski, R. The use of engineered wood wastes for energy production. Arch. Waste Manag. Environ. Prot. 2019, 21, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Igliński, B.; Cichosz, M.; Skrzatek, M.; Buczkowski, R. Technical potential of waste biomass for energy in Poland. Eng. Prot. Environ. 2018, 22, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesprini, E.; Resente, G.; Causin, V.; Urso, T.; Cavalli, R.; Zanetti, M. Energy recovery of glued wood waste–A review. Fuel 2020, 262, 116520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraszkiewicz, A.; Przywara, A.; Parafiniuk, S. Emission of Nitric Oxide during the Combustion of Various Forms of Solid Biofuels in a Low-Power Heating Device. Energies 2022, 15, 5960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kułażyński, M.; Świątek, Ł.; Pstrowska, K. Katalityczna redukcja tlenków azotu ze spalania biomasowych kotłów małej mocy. Logistyka 2015, Nr 5, 289–294. [Google Scholar]
- Radsak, D. Redukcja emisj tlenków azotu w kotłach energetycznych jako konieczność spełniania europejskich standardów emisyjnych. Electr. Eng. 2017, 90, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakawati, R.; Smyth, B.M.; McCullough, G.; De Rosa, F.; Rooney, D. What is the most energy efficient route for biogas utilization: Heat, electricity or transport? Appl. Energy 2017, 206, 1076–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panepinto, D.; Tedesco, V.; Brizio, E.; Genon, G. Environmental performances and energy efficiency for MSW gasification treatment. Waste Biomass Valorization 2015, 6, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordylewski, W. Spalanie i Paliwa; Oficyna Wydawnicza Politechniki Wrocławskiej: Wrocław, Polska, 2008; pp. 10–470. ISBN 978-83-7493-378-0. [Google Scholar]
- Marcewicz-Kuba, A. Effect of the synthetic zeolite modification on its physicochemical and catalytic properties in the preparation of the catalysts effectively removing sulphur dioxide from exhaust gases. Pol. J. Chem. Technol. 2016, 18, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tic, W.J. System poprawy efektywności energetycznej i ekologicznej spalnia paliw stałych. Chemik 2014, 68, 850–855. [Google Scholar]
- Gaze, B.; Romański, L.; Kułażyński, M. Koncepcja wykorzystania mocznika do ograniczenia emisji NOx w kotłach małej mocy. Przemysł Chem. 2020, 99, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standard PN-EN ISO 18134-1; Solid Biofuels—Determination of Moisture Content—Oven Dry Method—Part 1: Total Moisture—Reference Method. Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 2016. Available online: https://standards.globalspec.com/std/9951652/iso-18134-1 (accessed on 24 January 2022).
- Standard PN-EN ISO 18125:2017-07; Solid Biofuels—Determination of Calorific Value. Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 2017. Available online: https://standards.globalspec.com/std/9972508/iso-18125 (accessed on 24 January 2022).
- Standard PN-EN ISO 18122:2016-01; Solid Biofuels—Determination of Ash Content. Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 2016. Available online: https://standards.globalspec.com/std/2051854/iso-18122 (accessed on 24 January 2022).
- Standard PN-EN ISO 18123:2016-01; Solid Biofuels—Determination of the Content of Volatile Matter. Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 2016. Available online: https://standards.globalspec.com/std/2051856/iso-18123 (accessed on 24 January 2022).
- Standard PN-EN ISO 16948:2015-07; Solid Biofuels—Determination of Total Content of Carbon, Hydrogen and Nitrogen. Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 2015. Available online: https://standards.globalspec.com/std/2048180/iso-16948 (accessed on 24 January 2022).
- Gaze, B.; Knutel, B.; Jajczyk, M.; Wacławek, A.; Bukowski, P.; Dębowski, M. Analysis of the use of catalytic additives for combustion with wood pellets in a low-power boiler. Rynek Energii 2021, 4, 93–98. [Google Scholar]
- Gaze, B. Określenie dominującego mechanizmu powstawania NOX w kotłach małej mocy zasilanych biomasą. Przemysł Chem. 2020, 1, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhler, L.; Görtler, G.; Krail, J.; Kozek, M. Carbon monoxide emission models for small-scale biomass combustion of wooden pellets. Appl. Energy 2019, 254, 113668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piersa, P.; Szufa, S.; Czerwińska, J.; Ünyay, H.; Adrian, Ł.; Wielgosinski, G.; Obraniak, A.; Lewandowska, W.; Marczak-Grzesik, M.; Dzikuć, M.; et al. Pine Wood and Sewage Sludge Torrefaction Process for Production Renewable Solid Biofuels and Biochar as Carbon Carrier for Fertilizers. Energies 2021, 14, 8176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Component | Measurement Method | Range | Precision | Compl. with Standards |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O2 | paramagnetic | 0–25% | ±0.1% abs. or 3% rel. | EN 14789; OTM-13 |
| CO | chemiluminescence | 0–10,000 ppm | ±3 ppm abs. or 3% rel. | EN 15058; METHOD 10 |
| CO2 | chemiluminescence | 0–25% | ±0.03% abs. or 3% rel. | ISO 12039; OTM-13 |
| NOx | chemiluminescence | 0–1000 ppm | ±3 ppm abs. or 3% rel. | EN14792 |
| Parameter | Reference Pellet | Wood-Based Waste Pellet | Wood-Based Waste Pellet + Ad1 | Wood-Based Waste Pellet + Ad2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture content, % | 8.65 | 7.69 | 8.08 | 6.00 |
| Ash content, % | 1.89 | 1.07 | 2.01 | 1.02 |
| Volatile matter content, % | 75.00 | 98.93 | 96.67 | 98.98 |
| Calorific value, MJ · kg−1 | 17.49 | 18.27 | 18.40 | 18.40 |
| Parameter | Reference Pellet | Wood-Based Waste Pellet |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen content, % | 5.70 | 4.00 |
| Carbon content, % | 48.00 | 45.00 |
| Hydrogen content, % | 0.08 | 6.40 |
| Sulfur content, % | 0.02 | 0.03 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gaze, B.; Wojtko, P.; Knutel, B.; Kobel, P.; Bobrowicz, K.; Bukowski, P.; Chojnacki, J.; Kielar, J. Influence of Catalytic Additive Application on the Wood-Based Waste Combustion Process. Energies 2023, 16, 2055. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16042055
Gaze B, Wojtko P, Knutel B, Kobel P, Bobrowicz K, Bukowski P, Chojnacki J, Kielar J. Influence of Catalytic Additive Application on the Wood-Based Waste Combustion Process. Energies. 2023; 16(4):2055. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16042055
Chicago/Turabian StyleGaze, Błażej, Paulina Wojtko, Bernard Knutel, Przemysław Kobel, Kinga Bobrowicz, Przemysław Bukowski, Jerzy Chojnacki, and Jan Kielar. 2023. "Influence of Catalytic Additive Application on the Wood-Based Waste Combustion Process" Energies 16, no. 4: 2055. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16042055
APA StyleGaze, B., Wojtko, P., Knutel, B., Kobel, P., Bobrowicz, K., Bukowski, P., Chojnacki, J., & Kielar, J. (2023). Influence of Catalytic Additive Application on the Wood-Based Waste Combustion Process. Energies, 16(4), 2055. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16042055






