Study on the Operation Optimization of Medium-Depth U-Type Ground Source Heat Pump Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Method
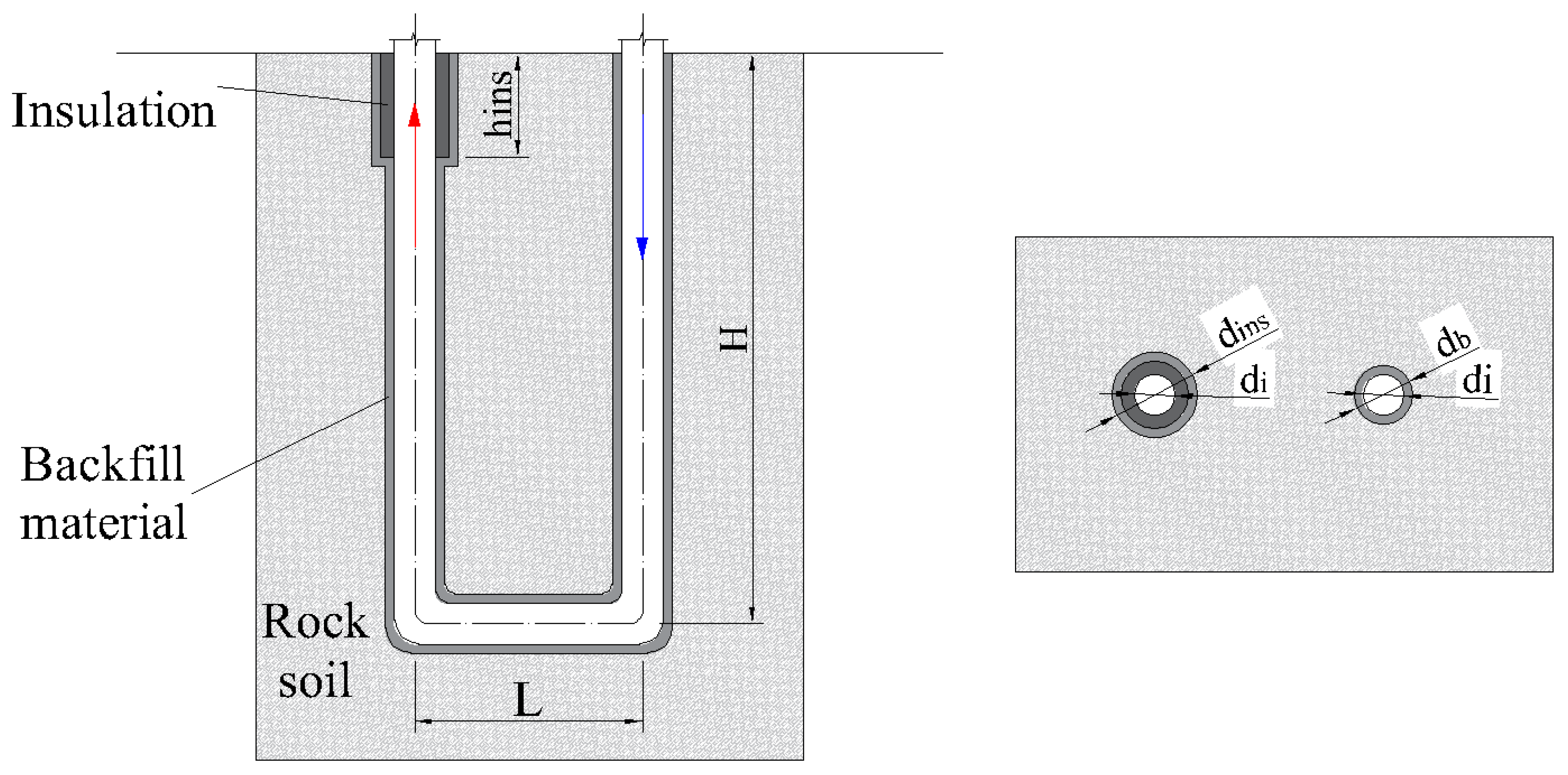
2.1. Basic Assumptions
- (1)
- Neglect the slope of the horizontal pipe section, and consider the initial soil temperature based on the geothermal gradient;
- (2)
- Ignore the heat conduction in the depth direction inside the borehole;
- (3)
- At the same depth, the temperatures of the underground pipe, backfill material, and circulating fluid are equal;
- (4)
- Do not consider the effects of water evaporation, diffusion, condensation, and groundwater seepage on the heat conduction process in the rock and soil;
- (5)
- Each layer of rock and soil has constant and uniform thermal properties, unaffected by temperature.
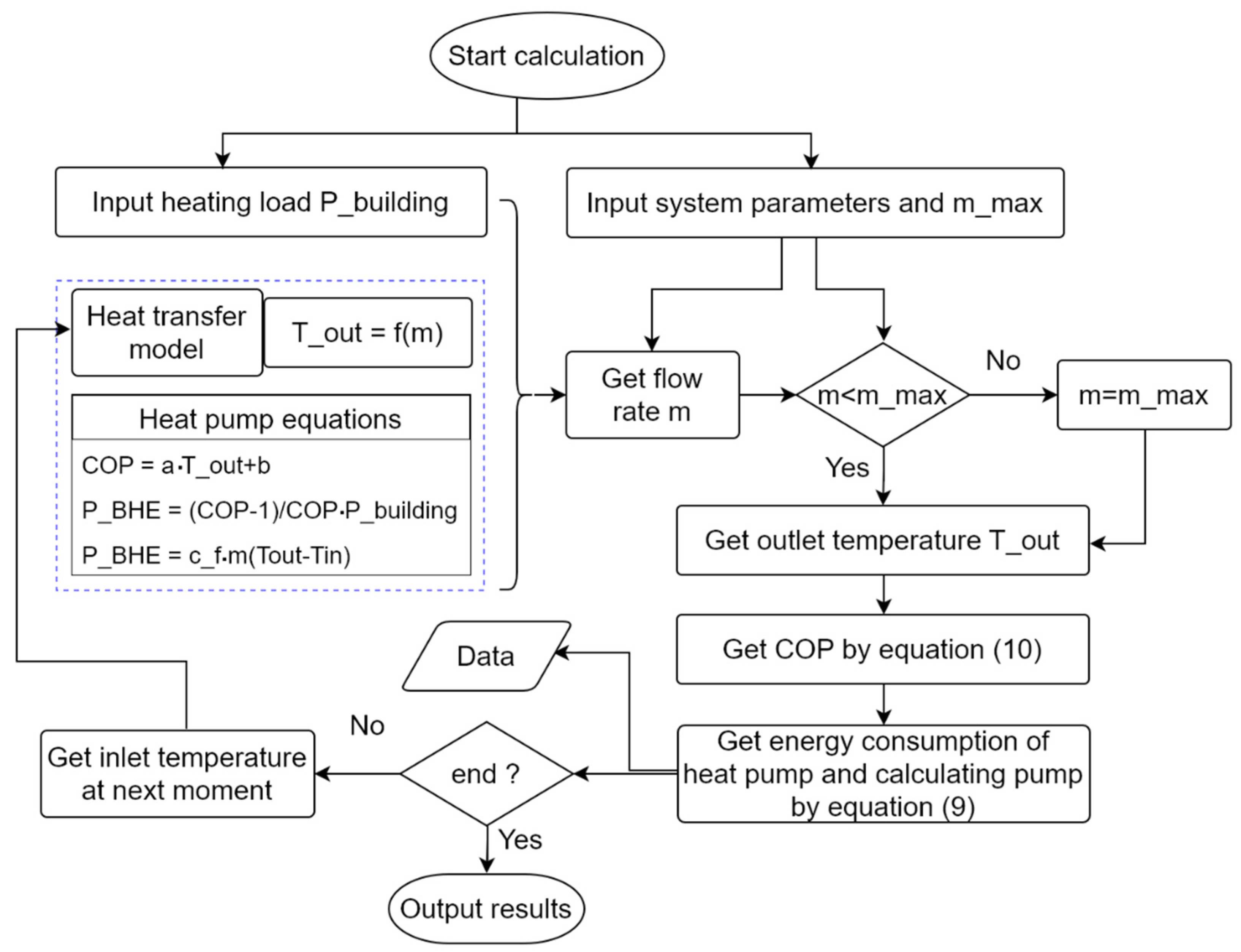
2.2. Mathematical Model
2.3. Model Validation
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Outlook
5.1. Conclusions
- An analytical solution heat transfer model for medium-depth U-type ground heat exchangers is established, and the simulation results align well with experimental data with an average relative error of −3.2%.
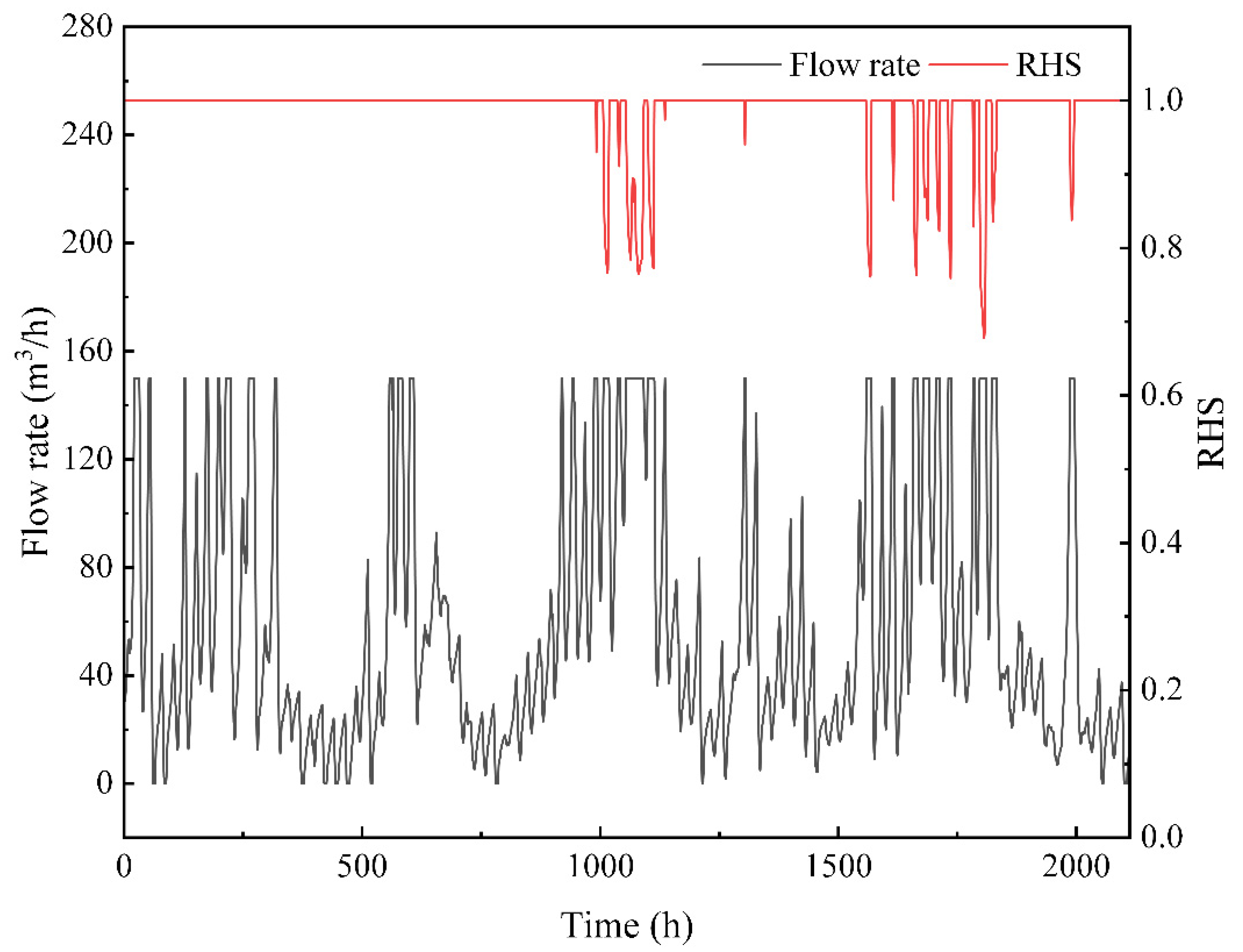
- Operating the system with variable fluid flow can reduce energy consumption. When the heating load decreases, the flow rate becomes smaller and the temperature difference between inlet and outlet will increase. Compared to constant flow operation, the average COP of the heat pump increases from 4.99 to 5.12 over a simulated runtime of 2112 h. In addition, the power consumption of the heat pump decreases from 171,090 kW·h to 168,043 kW·h, and the circulating pump power consumption decreases from 117,332 kW·h to 56,548 kW·h, with the total power consumption decreasing by 22.1%.
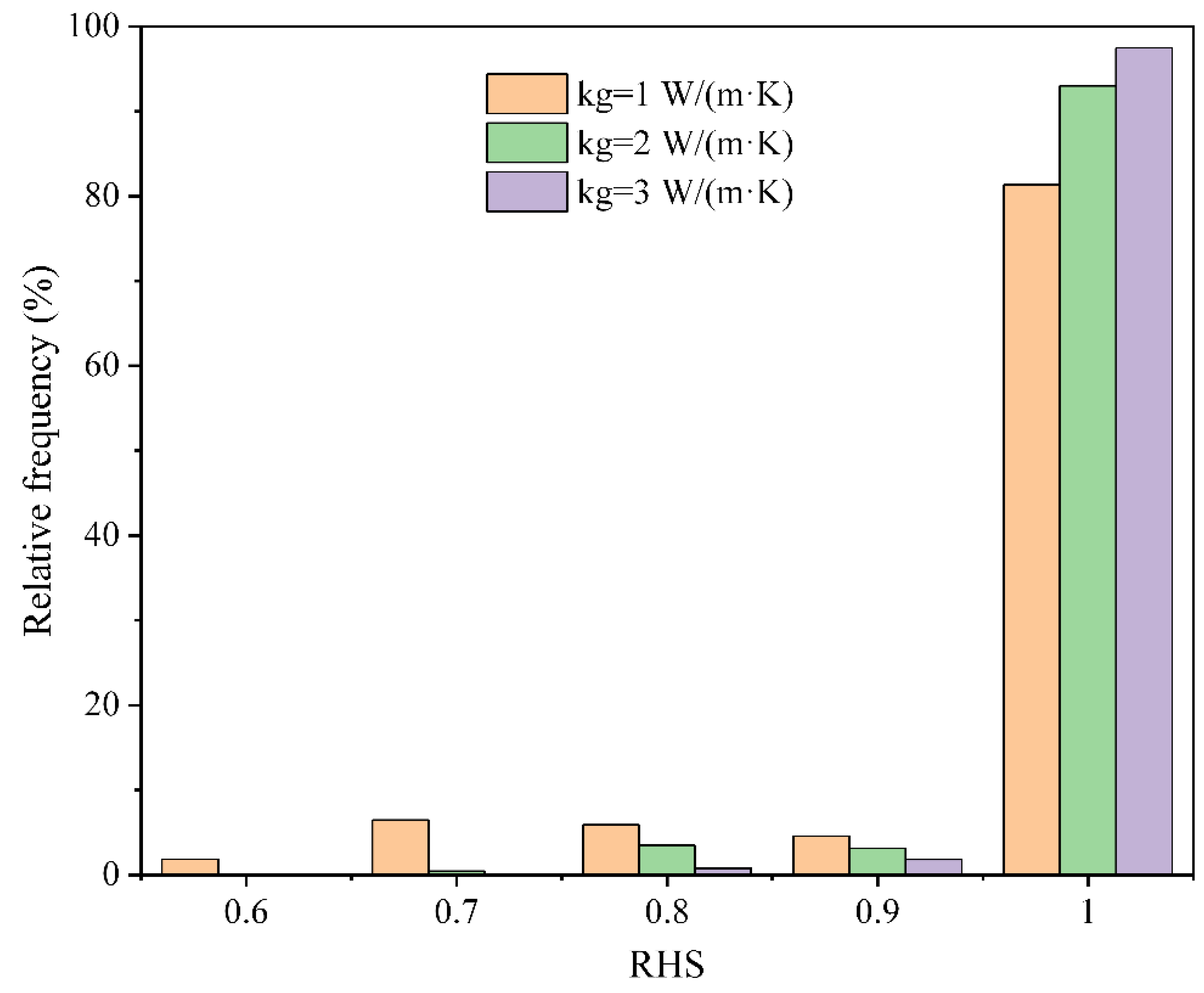
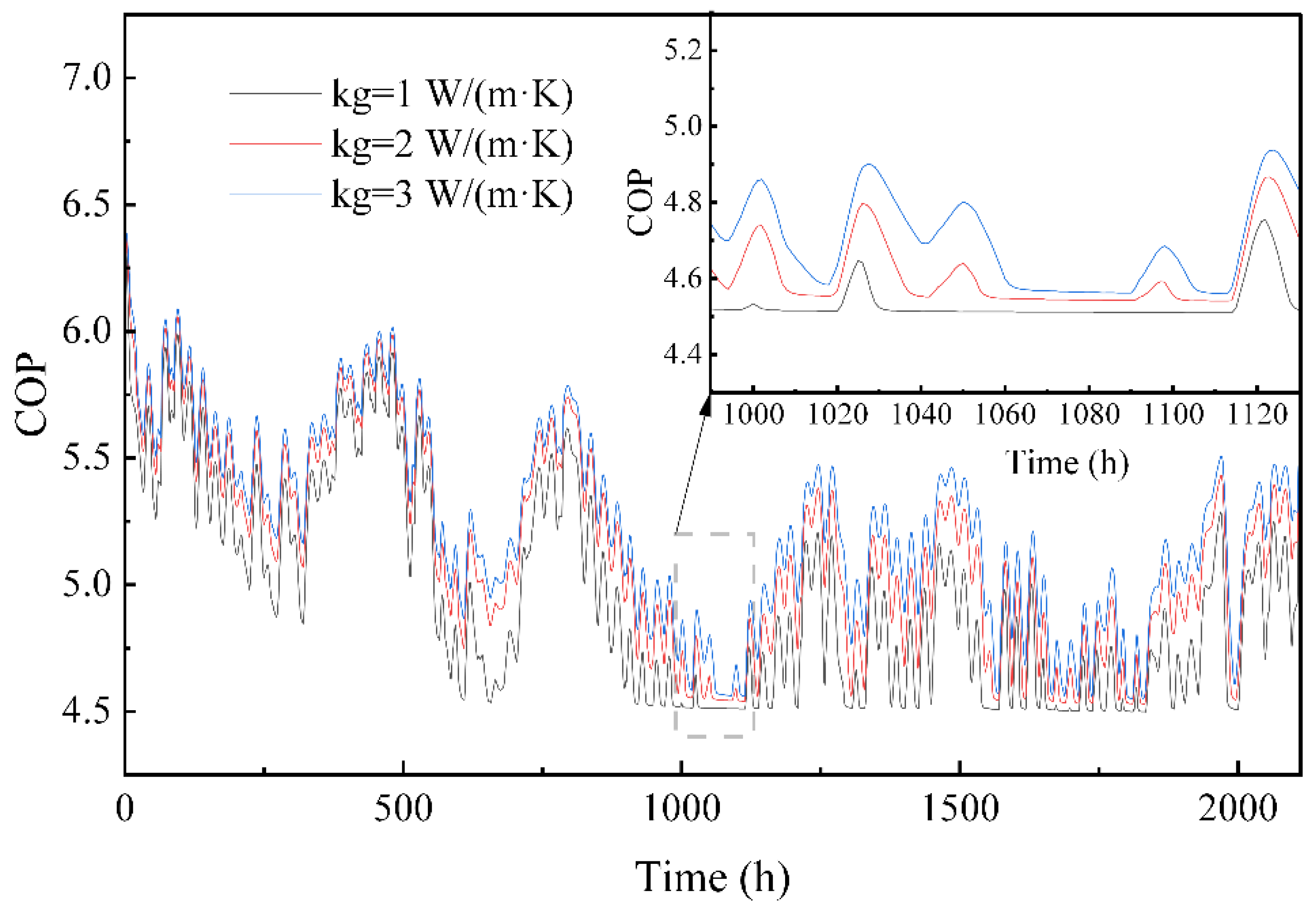
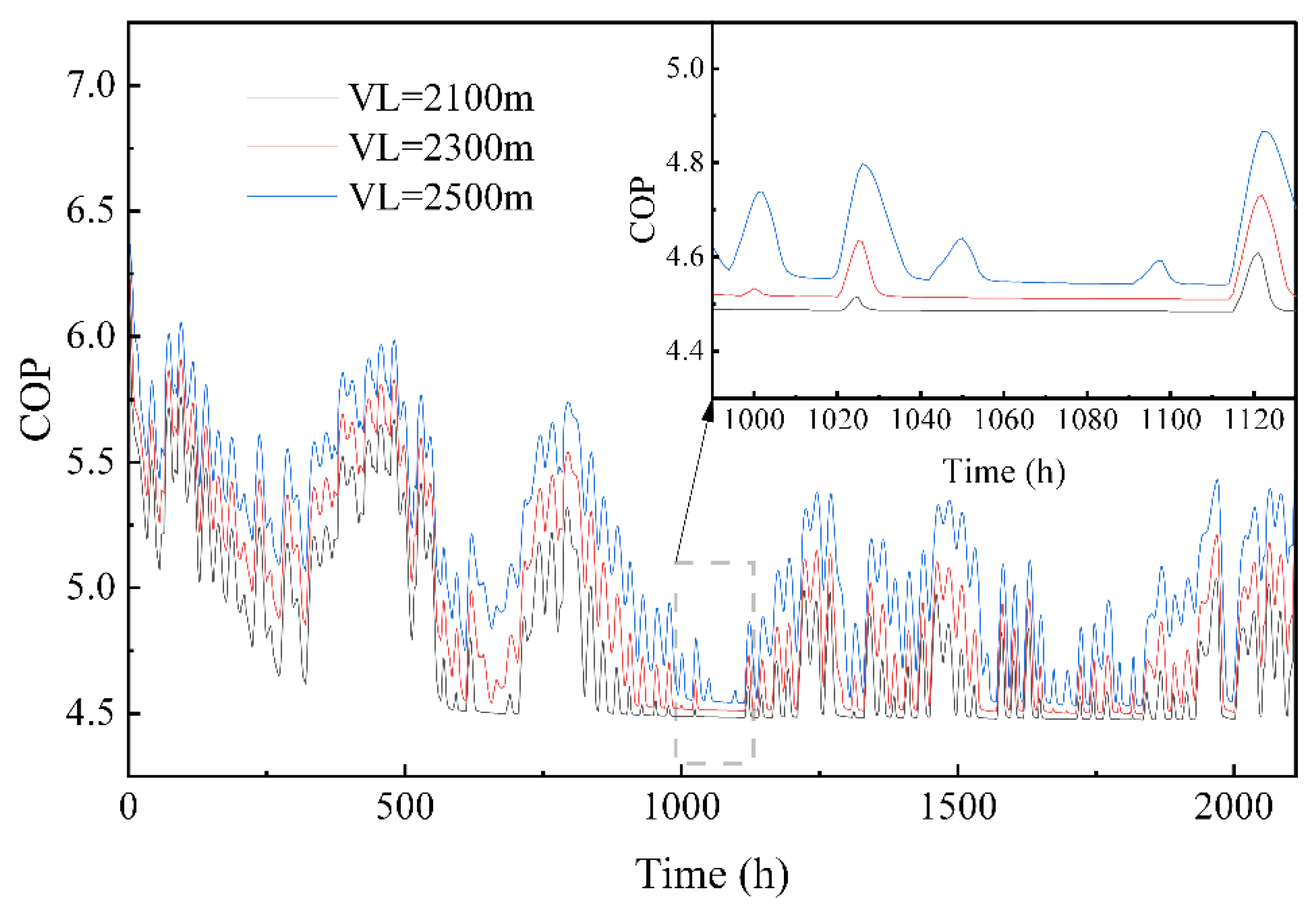
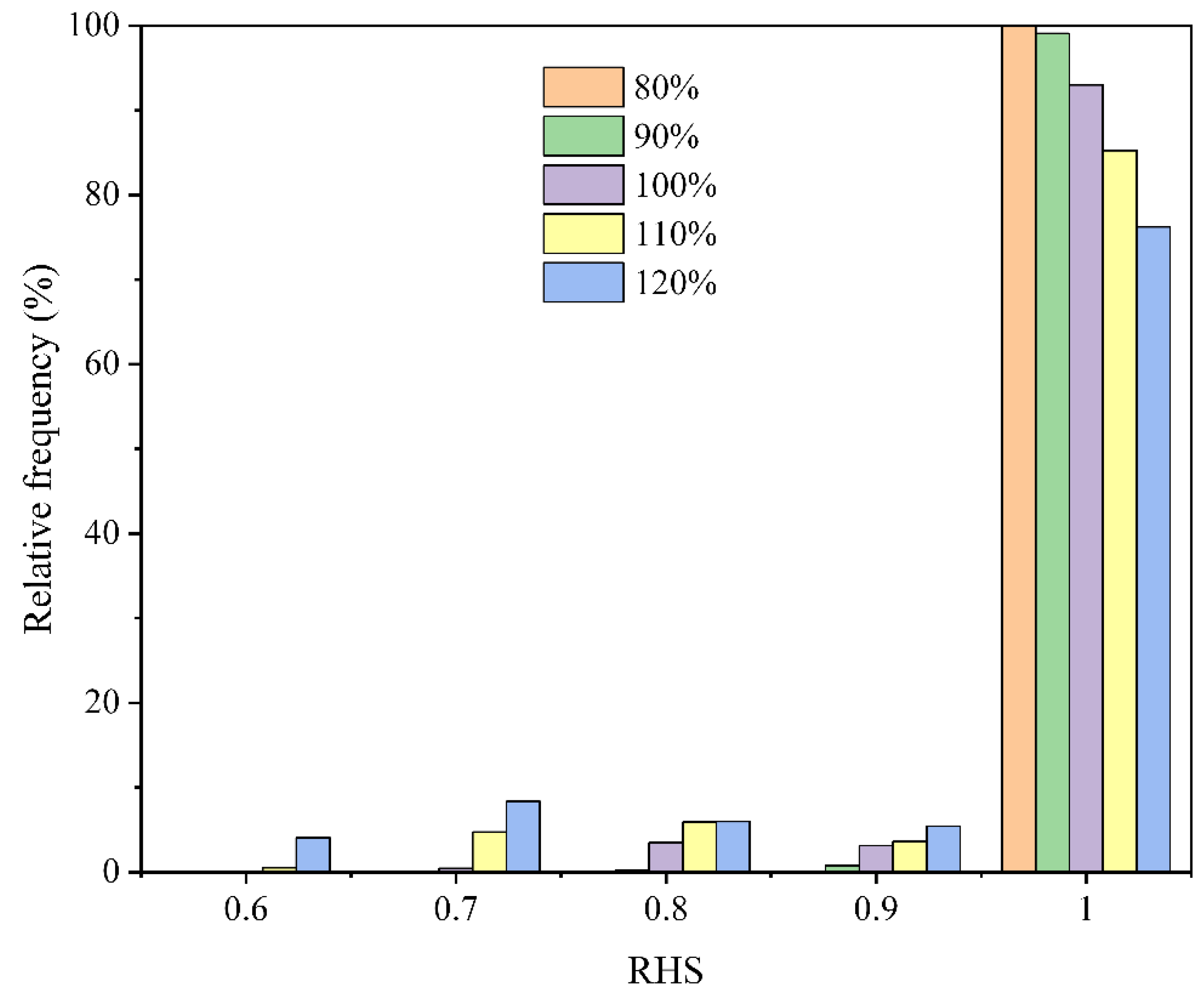
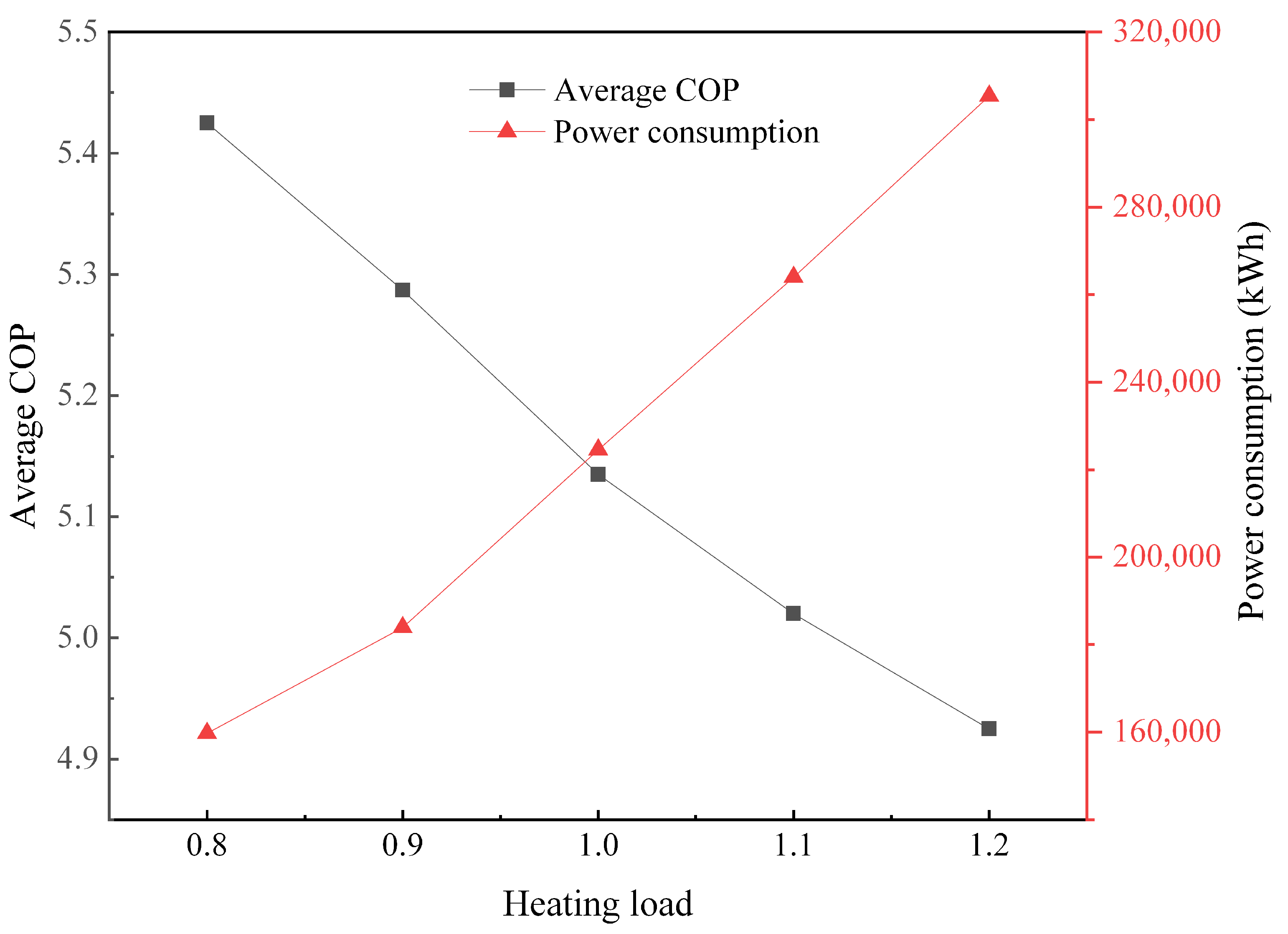
- When the thermal conductivity of the backfill materials increases, the underground heat transfer will be enhanced, so both the RHS and COP of the system will increase accordingly. As the borehole depth increases, the required flow rate decreases, which significantly reduces the energy consumption of the circulating pump. If the depth increases from 2300 m to 2500 m, the value will decrease from 85,844 kW·h to 56,548 kW·h during the 2112 h operation. An increase in the building thermal load leads to a nearly linear decrease in the COP of the heat pump unit and an increase in total power consumption.
5.2. Outlook
- The model overlooks groundwater seepage but will be further improved to take its influence into account.
- It is necessary to obtain the cost information of drilling and equipment, and to conduct economic and environmental benefit analysis in order to apply the research results to actual engineering design processes.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jolie, E.; Scott, S.; Faulds, J.; Chambefort, I.; Axelsson, G.; Gutiérrez-Negrín, L.C.; Regenspurg, S.; Ziegler, M.; Ayling, B.; Richter, A.; et al. Geological controls on geothermal resources for power generation. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 324–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, J.W.; Toth, A.N. Direct utilization of geothermal energy 2020 worldwide review. Geothermics 2021, 90, 101915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhuyi Nazari, M.; Kumar, R.; Mukhtar, A.; Yasir, A.S.H.M.; Ahmadi, M.H.; Al-Bahrani, M. Geothermal energy for preheating applications: A comprehensive review. J. Cent. South Univ. 2023, 30, 3519–3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, P.; Yang, W.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, K.; Spitler, J.D.; Yu, M. Advances in ground heat exchangers for space heating and cooling: Review and perspectives. Energy Built Environ. 2024, 5, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, M.; Liu, L.; Yang, Q.; Ki-Il, S. Heat Storage/Heat Release of Phase-Change Filling Body with Casing Heat Exchanger for Extracting Geothermal Energy. J. Therm. Sci. 2023, 32, 1171–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, M.; Yan, D.; An, J.; Hong, T.; Spitler, J.D. Evaluation of thermal imbalance of ground source heat pump systems in residential buildings in China. Build. Simul. 2020, 13, 585–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Zhang, K.; Cao, X.; Hu, A.; Cui, P.; Fang, Z. Zoning operation of multiple borehole ground heat exchangers to alleviate the ground thermal accumulation caused by unbalanced seasonal loads. Energy Build. 2016, 110, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Li, R.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, S. Numerical Simulation of Mid-Deep Buried Casing Heat Exchanger and its Heating System Application. J. Therm. Sci. 2023, 32, 1445–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; He, S.; Wei, Q.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H. Field test and optimization of heat pumps and water distribution systems in medium-depth geothermal heat pump systems. Energy Build. 2020, 209, 109724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nian, Y.-L.; Cheng, W.-L. Evaluation of geothermal heating from abandoned oil wells. Energy 2018, 142, 592–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jello, J.; Baser, T. Utilization of existing hydrocarbon wells for geothermal system development: A review. Appl. Energy 2023, 348, 121456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.-L.; Li, T.-T.; Nian, Y.-L.; Wang, C.-L. Studies on geothermal power generation using abandoned oil wells. Energy 2013, 59, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Śliwa, T.; Kruszewski, M.; Zare, A.; Assadi, M.; Sapińska-Śliwa, A. Potential application of vacuum insulated tubing for deep borehole heat exchangers. Geothermics 2018, 75, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, A.; Yao, J.; Fan, D.; Bongole, K.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X. Potential for heat production by retrofitting abandoned gas wells into geothermal wells. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0220128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi Ajarostaghi, S.S.; Javadi, H.; Mousavi, S.S.; Poncet, S.; Pourfallah, M. Thermal performance of a single U-tube ground heat exchanger: A parametric study. J. Cent. South Univ. 2021, 28, 3580–3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, W.; Sørensen, B.R.; Cui, P.; Man, Y.; Yu, M.; Fang, Z. Comparative analysis of heat transfer performance of coaxial pipe and U-type deep borehole heat exchangers. Geothermics 2021, 96, 102220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.S.; Kolo, I.; Banks, D.; Falcone, G. Comparison of the thermal and hydraulic performance of single U-tube, double U-tube and coaxial medium-to-deep borehole heat exchangers. Geothermics 2024, 117, 102888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Li, J.; Zhu, K.; Dong, J.; Jiang, Y. Thermal recovery characteristics of rock and soil around medium and deep U-type borehole heat exchanger. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2023, 224, 120071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Guan, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, G.; Zhou, C.; Xun, Y. Experimental and numerical studies on heat transfer characteristics of vertical deep-buried U-bend pipe to supply heat in buildings with geothermal energy. Energy 2018, 142, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Guan, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhou, C.; Xun, Y.; Gui, L. Experimental and numerical studies on heat transfer characteristics of vertical deep-buried U-bend pipe in intermittent heating mode. Geothermics 2019, 79, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, F.; Lu, W.; Cui, P.; Guan, C.; Yu, M.; Fang, Z. Heat transfer analysis of U-type deep borehole heat exchangers of geothermal energy. Energy Build. 2021, 237, 110794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Wei, L.; Fangfang, Z.; Wenke, Z.; Ping, C.; Zhaohong, F. A novel model and heat extraction capacity of mid-deep buried U-bend pipe ground heat exchangers. Energy Build. 2021, 235, 110723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Cai, W.; Naumov, D.; Tu, K.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Kolditz, O.; Shao, H. Numerical investigation on the capacity and efficiency of a deep enhanced U-tube borehole heat exchanger system for building heating. Renew. Energy 2021, 169, 557–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramey, H.J. Wellbore Heat Transmission. J. Pet. Technol. 1962, 14, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.; Wang, X.; Jin, P.; Cui, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y. An analytical heat transfer model for the mid-deep U-shaped borehole heat exchanger considering groundwater seepage. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 64, 105612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Zhou, C.; Luo, Y.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, S.; Fan, J.; Ling, Z. Comprehensive thermal performance analysis and optimization study on U-type deep borehole ground source heat pump systems based on a new analytical model. Energy 2023, 274, 127367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Sun, W.; Fu, Q.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, P. Semi-analytical and numerical modeling of U-bend deep borehole heat exchanger. Renew. Energy 2024, 222, 119959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Bao, L.; Jin, P.; Zhu, Y. Analytical model of heat transfer of U-shaped borehole heat exchanger under convolution theory and its optimal heat extraction analysis. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2023, 193, 108496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Wang, F.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, J.; Wei, Q.; Cai, W.; Chen, C. Evaluation of the long-term performance of the deep U-type borehole heat exchanger on different geological parameters using the Taguchi method. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 59, 105122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Li, J.; Zhu, K.; Dong, J.; Jiang, Y. Influencing factors analysis for the long-term thermal performance of medium and deep U-type borehole heat exchanger system. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 68, 106152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Li, J.; Zhu, K.; Dong, J.; Jiang, Y. Multifactor optimization of medium and deep U-type borehole heat exchanger design using Taguchi method. Geothermics 2023, 109, 102644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Ma, H.; Liu, S.; Yang, D.; Xu, X.; Fu, M.; Jia, H. Thermal power extraction from a deep, closed-loop, multi-level, multi-branch, U-shaped borehole heat exchanger geothermal system. Renew. Energy 2022, 198, 894–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Guo, H.; Meggers, F.; Zhang, L. Deep coaxial borehole heat exchanger: Analytical modeling and thermal analysis. Energy 2019, 185, 1298–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Guan, Y.; Wang, X. Study on reasonable selection of insulation depth of the outlet section of vertical deep-buried U-bend tube heat exchanger. Energy Build. 2018, 167, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmberg, H.; Acuña, J.; Næss, E.; Sønju, O.K. Thermal evaluation of coaxial deep borehole heat exchangers. Renew. Energy 2016, 97, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casasso, A.; Sethi, R. Efficiency of closed loop geothermal heat pumps: A sensitivity analysis. Renew. Energy 2014, 62, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hein, P.; Kolditz, O.; Görke, U.-J.; Bucher, A.; Shao, H. A numerical study on the sustainability and efficiency of borehole heat exchanger coupled ground source heat pump systems. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 100, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariti, Y.; Hader, A.; Faraji, H.; Boughaleb, Y. Scaling Law of Permeability and Porosity for Fluid Transport Phenomena in Porous PCM Media. J. Appl. Comput. Mech. 2021, 7, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaharra, O.; Choukairy, K.; Faraji, H.; Hamdaoui, S. Improved heating floor thermal performance by adding PCM microcapsules enhanced by single and hybrid nanoparticles. Heat Transfer 2023, 52, 3817–3838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Conditions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Drilling diameter db | 215.9 mm | Density of circulating water ρf | 995.7 kg/m3 |
| Drilling depth H | 2520 m | Thermal conductivity of circulating water λf | 0.618 W/(m·K) |
| Horizontal drilling length L | 210 m | Specific heat capacity of circulating water cf | 4174 J/(kg·°C) |
| Insulation section drilling diameter dbins | 444.5 mm | Insulation material volume heat capacity Cins | 7.74 × 104 J/Km3 |
| Insulation section depth Hins | 350 m | Insulation material thermal conductivity λins | 0.022 W/(m·K) |
| Insulation layer thickness | 40 mm | Heat capacity of backfill material Cg | 2.5 × 106 J/Km3 |
| Outer diameter of descent pipe dor | 139.7 mm | Thermal conductivity of backfill material λg | 1.5 W/(m·K) |
| Wall thickness of descent pipe | 9.17 mm | Spatial step Δx/Δz | 35 m |
| Outer diameter of ascent pipe doc | 177.8 mm | Time step Δτ | 3600 s |
| Wall thickness of ascent pipe | 8.05 mm | - | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, C.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, R.; Luo, Y.; Wang, X.; Luo, H. Study on the Operation Optimization of Medium-Depth U-Type Ground Source Heat Pump Systems. Energies 2024, 17, 3184. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17133184
Zhou C, Hu Y, Liu Y, Liu R, Luo Y, Wang X, Luo H. Study on the Operation Optimization of Medium-Depth U-Type Ground Source Heat Pump Systems. Energies. 2024; 17(13):3184. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17133184
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Chaohui, Yue Hu, Yuce Liu, Rujie Liu, Yongqiang Luo, Xiao Wang, and Huiheng Luo. 2024. "Study on the Operation Optimization of Medium-Depth U-Type Ground Source Heat Pump Systems" Energies 17, no. 13: 3184. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17133184
APA StyleZhou, C., Hu, Y., Liu, Y., Liu, R., Luo, Y., Wang, X., & Luo, H. (2024). Study on the Operation Optimization of Medium-Depth U-Type Ground Source Heat Pump Systems. Energies, 17(13), 3184. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17133184









