Abstract
This work aims to explore the Lower Silurian shale gas and tight sandstone gas accumulation conditions in the Gongtan Syncline, southeastern Sichuan Basin. The sedimentary environment, organic geochemical characteristics, reservoir characteristics, gas content, and preservation conditions of the reservoir were comprehensively analyzed. The results show that the Wufeng–Longmaxi Formation shale formed in a deep-water shelf characterized by a large thickness (50–70 m), appropriate total organic carbon content (0.5–5.47%), high maturity (2.38%), high brittle mineral content (67.10%), and large gas content (0.71–1.64 m3/t), and the formations show the good resource potential of the shale gas. The Xintan Formation formed in a lower shore phase, and the tight sandstone is locally developed with a small thickness. The Xiaoheba Formation formed in an upper-middle shore phase, and the tight sandstone is stably distributed with large thicknesses. The porosity and permeability of the two sets of sandstone are small and some natural fractures are developed in the sandstone, but the fracture filling degree is higher. The results of well logging show that there are abnormally high values of total hydrocarbon in both the Xintan Formation and Xiaoheba Formation; this indicates that tight sandstone gas is developed in the Lower Silurian strata. A comprehensive study indicates that the Lower Silurian of the Gongtan Syncline has the geological conditions for the formation of shale gas and tight sandstone gas, which are the “Two gases” with good co-exploration prospects.
1. Introduction
With the continuous growth in global energy demand and the transition toward a low-carbon society, unconventional natural hydrocarbons have garnered increasing attention from nations worldwide [1,2,3,4,5]. Shale gas and tight sandstone gas have become focal points of research and exploration for unconventional natural gas resources in China. After years of exploration and development, these resources have become a tangible and essential component of China’s energy portfolio [6,7,8]. In recent years, the Chongqing region, as a part of the southeastern Sichuan Basin, has emerged as a primary area for shale gas exploration in China. Breakthroughs have been achieved in the Wufeng–Longmaxi Formation in areas such as Fuling, Yuxi, Pengshui, and Nanchuan, confirming the substantial resource potential of this shale formation in the Chongqing region [9,10,11,12]. Meanwhile, previous studies have also indicated that the Sichuan Basin and surrounding areas harbor abundant tight sandstone gas resources, primarily within the Triassic (Xujiahe Formation), Jurassic, and Ordovician (Hanjiadian Formation and Xiaoheba Formation) strata [13,14,15]. Further, in the Chongqing and adjacent regions, drilling activities targeting the Ordovician Hanjiadian Formation and Xiaoheba Formation have demonstrated active oil and gas shows, with multiple wells achieving industrial gas flows [16,17], underscoring the promising exploration potential for tight sandstone gas in the Ordovician strata of the Chongqing region. However, a significant suite of tight sandstone reservoirs has been identified within the Ordovician strata in the southeastern region of the Sichuan Basin [18,19], but there has been limited foundational research into whether the southeastern region of the Sichuan Basin possesses the geological conditions conducive to the development of tight sandstone gas in the Ordovician strata.
In response to the coexistence of multiple oil and gas resources in the same region, scholars have proposed various methods for joint exploration and development of multiple resources [20,21,22,23]. These approaches not only help in cost-saving during exploration, but also ensure the comprehensive utilization of resources. As of now, successful examples of unconventional gas joint development have been seen around the world. For instance, in Colorado’s Piceance Basin, deep coalbed methane and tight sandstone gas have been jointly extracted in a pioneering experiment [24,25]. In Wyoming’s Wind River Basin, pressure-parted joint production of coalbed methane and sandstone gas has yielded individual well daily production rates of tens of thousands of cubic meters [26]. Similarly, in Canada’s Horseshoe Canyon, coalbed methane along with the overlying and underlying sandstone and shale have been exploited jointly, resulting in higher gas production compared to single-layer extraction methods [27]. In China, regions with coexisting coalbed methane, shale gas, and tight sandstone gas are abundant, and in recent years, several studies have been conducted focusing on the characteristics of unconventional natural gas coexistence, resource potential assessment, and exploration and development strategies. For example, based on the research on unconventional natural gas accumulation conditions in the Qinshui Basin coal series, Li et al. established a model for the coexistence of coalbed methane, shale gas, and tight sandstone gas, indicating promising prospects for the joint exploration and development of these “Three gases” in the region [28]. Cao Daiyong et al. studied the geological conditions of unconventional natural gas accumulation in the coal series on the western margin of the Ordos Basin and established a model for the occurrence of coal-based unconventional natural gas [29]. Zhong Jianhua et al., based on their research on the gas-bearing seal characteristics of the coal series on the eastern margin of the Ordos Basin, proposed a model for the coexistence of tight sandstone gas, shale gas, and coalbed gas [30]. Zhou Yitong et al. conducted a coal series of “Three gases” joint production engineering practices in the Songhe Oilfield in western Guizhou, revealing promising development prospects for the “Three gases” in that area [31]. Previous comprehensive exploration and evaluation studies on the unconventional natural gas in China have often focused on coal-based unconventional gas, with limited research on the coexistence and feasibility of marine unconventional gas. However, in recent years, discoveries of coexisting shale gas and tight sandstone gas have been made in the marine strata of southern China [32,33], suggesting that southern marine strata also possess multiple types of unconventional gas accumulation conditions and configuration relationships, potentially enabling the joint exploration and exploitation of multiple gases. Nevertheless, research evaluating the joint exploration potential of shale gas and tight sandstone gas in the marine strata of southern China has yet to be undertaken.
In recent years, extensive exploration and evaluation of the shale gas in the Wufeng–Longmaxi Formation has been carried out in the southeastern Sichuan Basin. In 2015, during drilling operations at the GD 1 well located in the Gongtan Syncline, besides encountering favorable gas shows in the target Wufeng–Longmaxi Formation layers, gas anomalies were also detected in the overlying Xintan Formation tight sandstone. This discovery represents the first identification of tight sandstone gas in the Silurian strata in the southeastern marginal area of the Sichuan Basin [33], suggesting the potential coexistence of shale gas and tight sandstone gas in the Silurian strata of this region. Therefore, this study aims to analyze the fundamental conditions for the formation of Silurian shale gas and tight sandstone gas in the southeastern region of the Sichuan Basin, elucidate the unconventional natural gas resource potential in the Gongtan Syncline, and provide data support and guiding recommendations for the joint exploration and development of shale gas and tight sandstone gas in the study area.
2. Geological Settings and Sample Collection
2.1. Geological Background
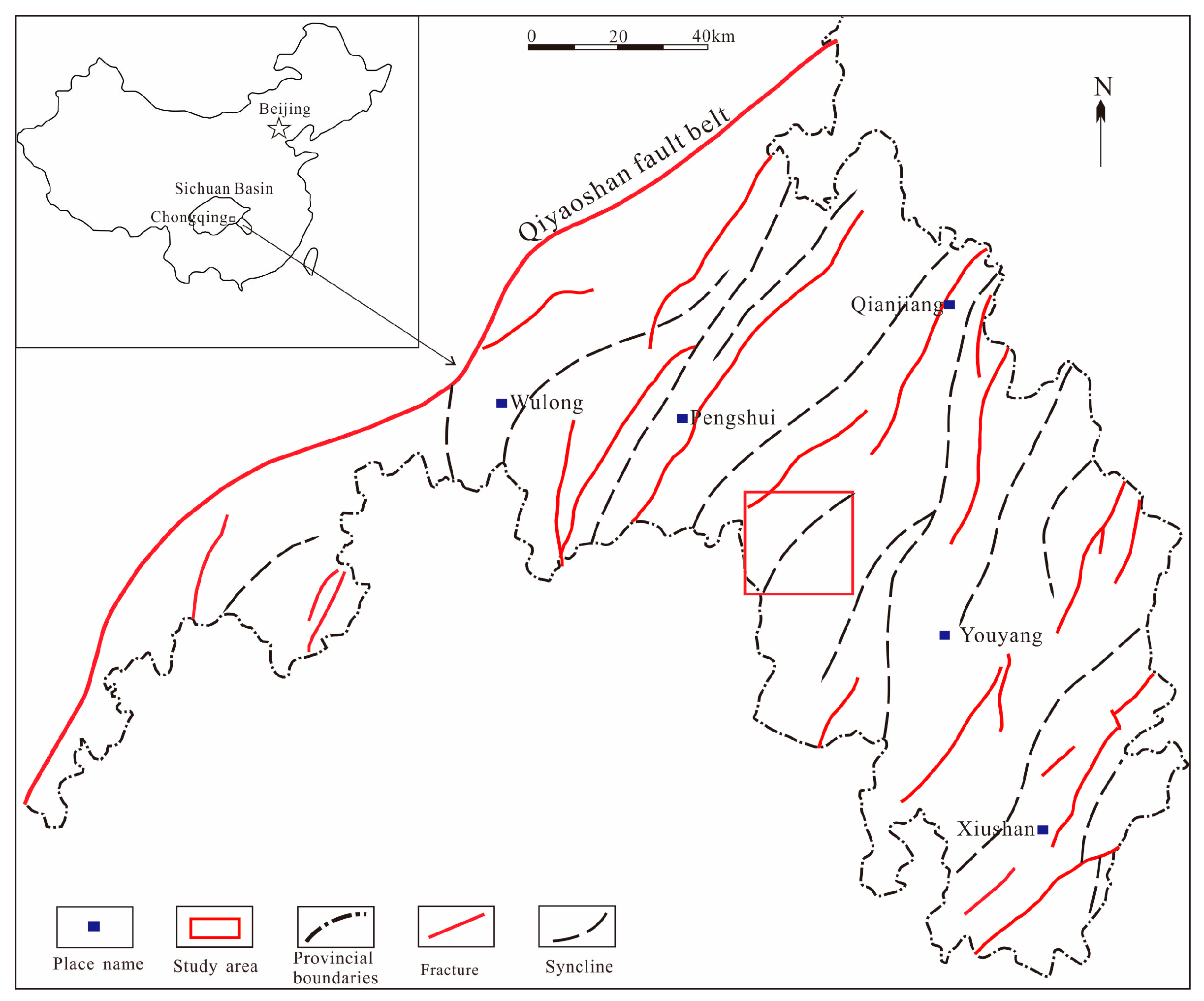
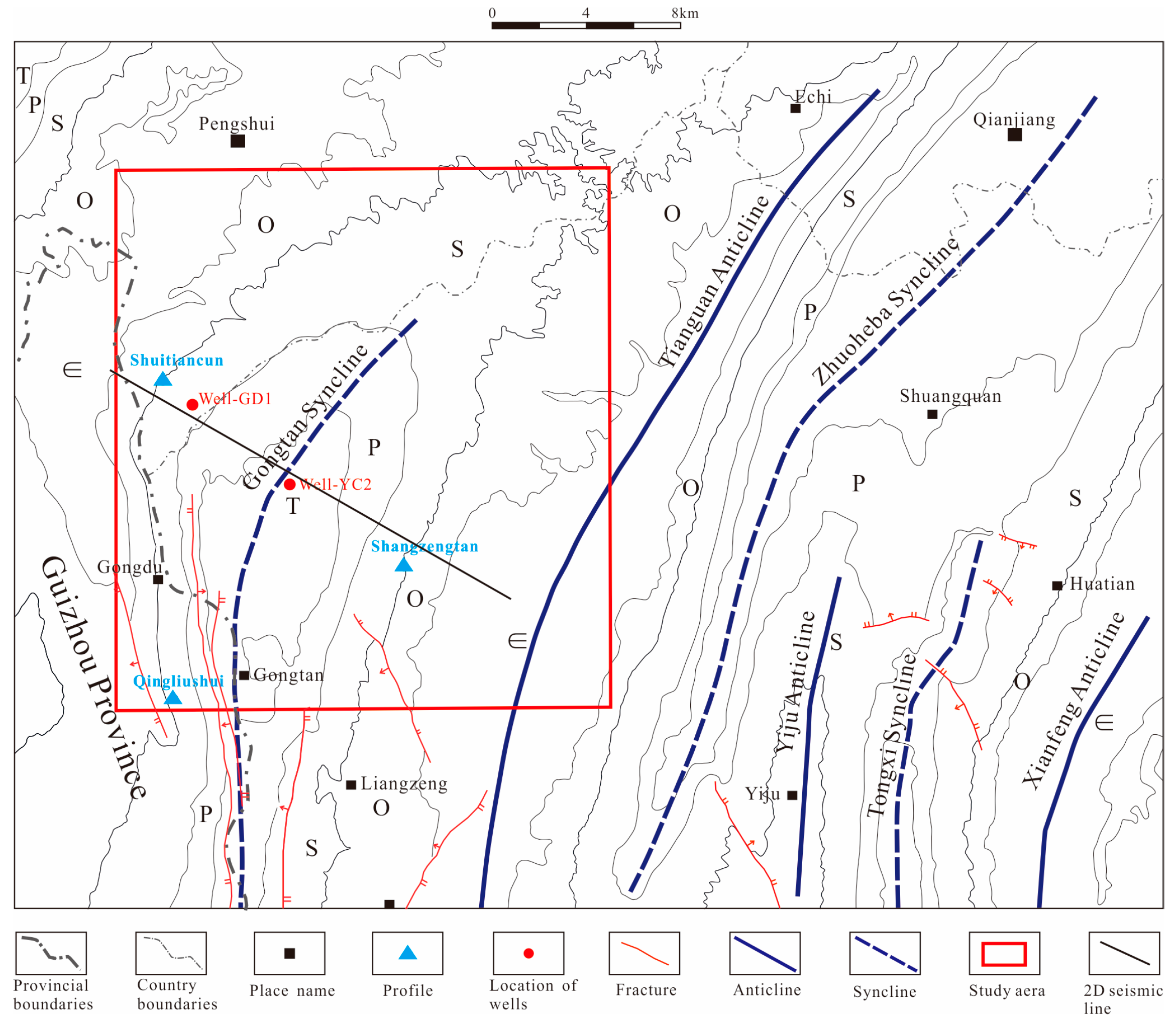
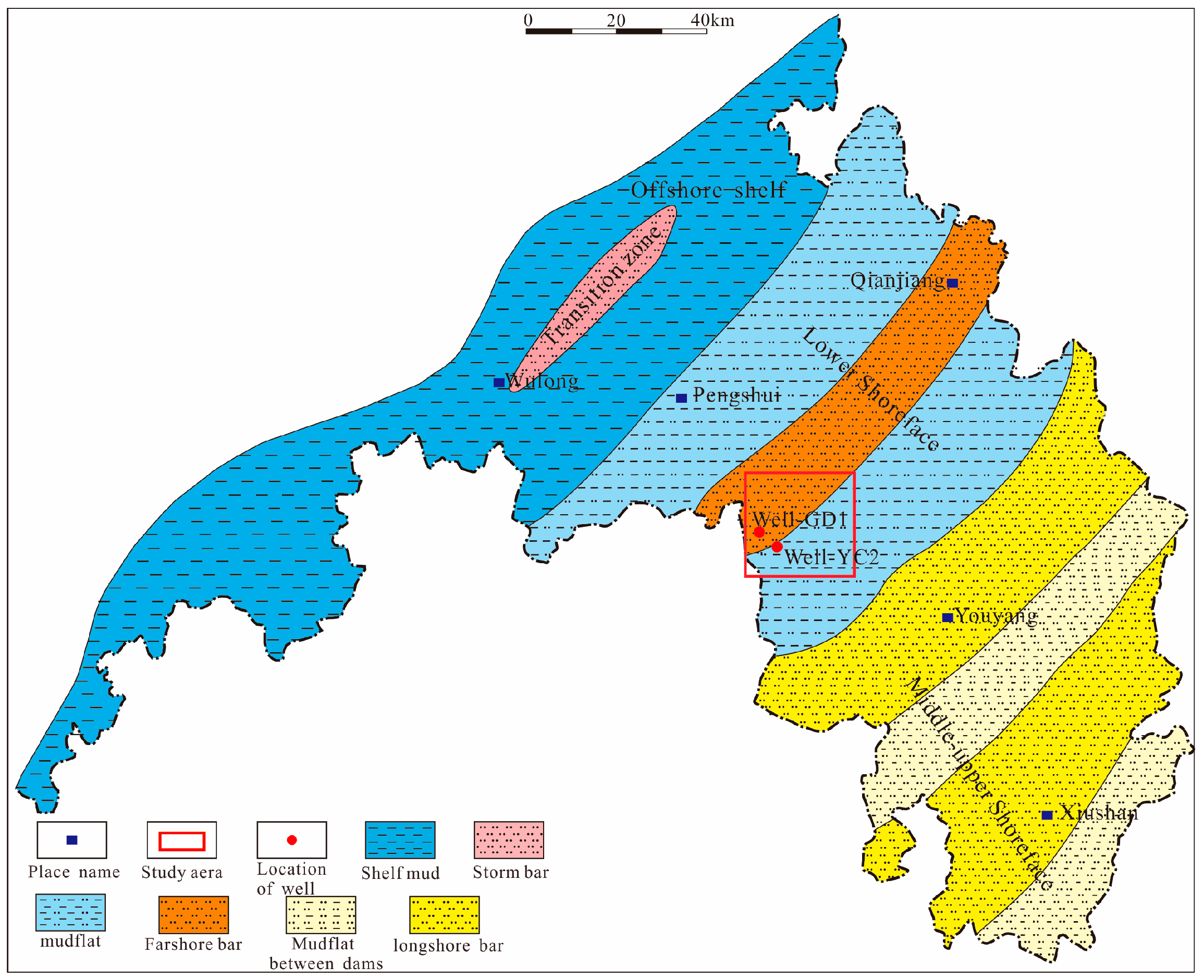
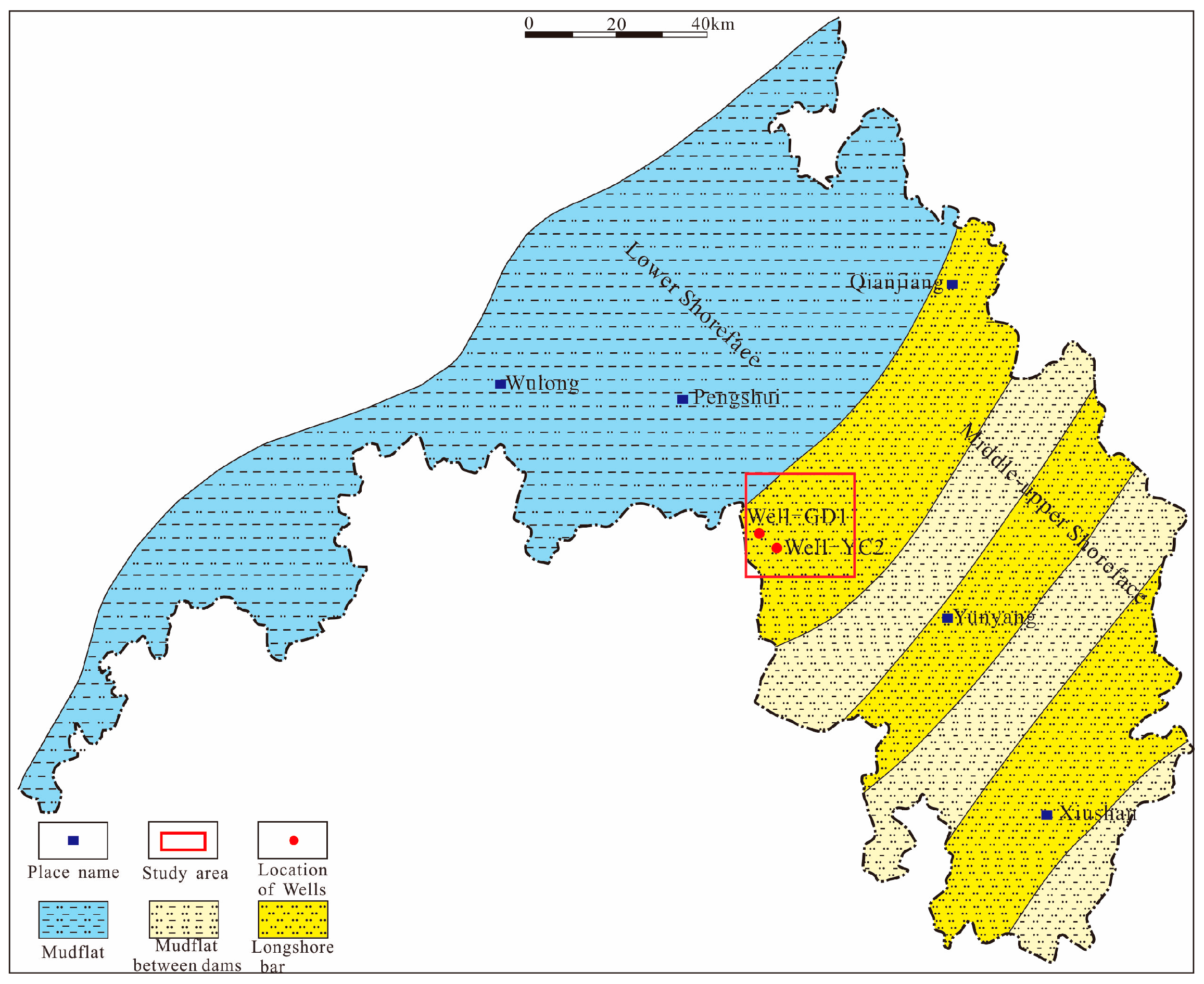
The Gongtan Syncline is situated at the border between the southeastern region of Chongqing and the northern region of Guizhou (Figure 1), and it is a geological unit within the Yangtze Paraplatform (Level I), consisting of the Shangyitai Intra-Basin Depression (Level II) and the Yudongnan Depression and Fold Belt (Level III). The exposed parts of the syncline in the southeastern Sichuan Basin are divided into the northern and central segments, with an exposed length of approximately 20 km. The syncline comprises sedimentary strata from the Neoproterozoic era to the present, and it is dominated by Paleozoic formations. The axis of the syncline is primarily composed of the Lower Triassic Jialingjiang Formation, with Triassic, Permian, Devonian, and Ordovician formations exposed on both flanks. The Gongtan Syncline was mainly formed during the Late Yan Mountain and Himalayan periods. Despite undergoing extensive geological evolution, it exhibits good structural continuity and simplicity, trending in a north–northeast direction. The limbs of the syncline have steep dips, ranging from 30–86° on the northwest limb and 10–65° on the southeast limb. Faults are relatively rare and mostly occur near the fold axis, with short extensions (Figure 2).
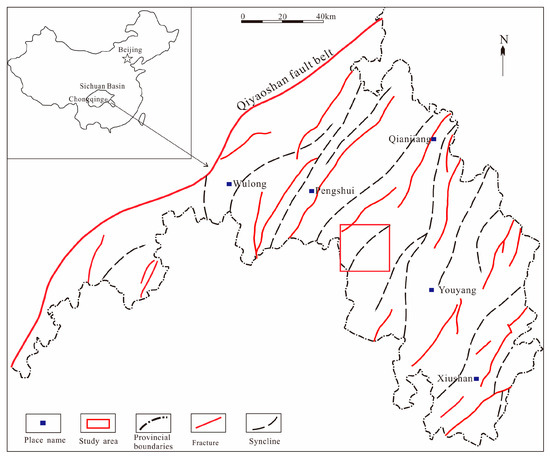
Figure 1.
Regional location of the study area.
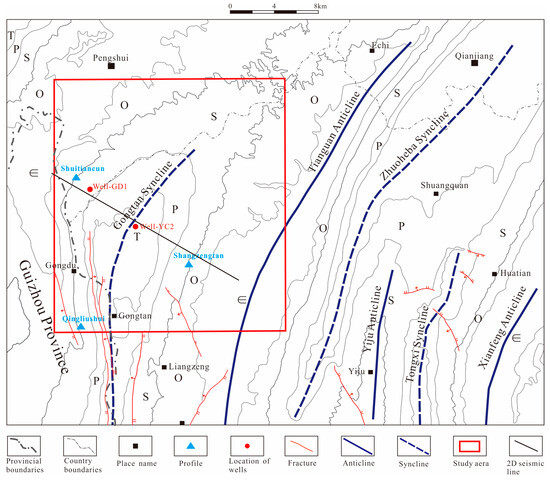
Figure 2.
Regional structure diagram of the Gongtan Syncline. The arrow refers to the tendency of faults.
The Silurian strata in the southeastern Sichuan Basin, where the study area is located, are widely distributed, particularly in the lower and middle series. The upper part of the middle series and the upper series are absent within the regional context. From bottom to top, the stratigraphy consists of the Longmaxi Formation, Xintan Formation, Xiaoheba Formation, and Hanjiadian Formation. The Longmaxi Formation and the underlying Wufeng Formation are characterized by dark shale. Reservoirs of Silurian clastic rocks are mainly distributed in the Middle Silurian Hanjiadian Formation, the Lower Silurian Xiaoheba Formation, and the Xintan Formation. However, the Hanjiadian Formation suffers from severe erosion and extensive exposure within the Gongtan Syncline.
2.2. Sampling and Methodology
Shale samples from the Wufeng and Longmaxi Formations were collected from the cores of shale gas Wells GD 1 and YC 2, as well as from three outcrop profiles within the study area, totaling 100 samples. Additionally, tight sandstone samples from the Xintan and Xiaoheba Formations were collected from Well GD 1, totaling 15 samples. The collected shale samples were subjected to a series of analyses, including TOC, Ro, maceral composition, thin section analysis, whole-rock X-ray diffraction quantitative analysis, scanning electron microscopy, porosity and permeability measurements, and gas desorption. Tight sandstone samples underwent thin section analysis, as well as porosity and permeability measurements.
In this study, the organic geochemical characteristics of shale were characterized using three parameters: TOC, Ro, and organic matter type. The German Leica Instrument Company’s DM4500P optical microscope was employed to measure the Ro and maceral composition, assessing the thermal maturity and organic matter type of the shale. The corresponding analysis methods followed the standards of the Chinese petroleum and natural gas industry, specifically SY/T 5124-2012 [34] and SY/T 5125-2014 [35]. To determine the total organic carbon content of the samples, a China HaiCheng Rock-Eval VIII instrument (produced by HaiCheng Petrochemical Instrument Factory) equipped with a flame ionization detector was employed. The corresponding testing procedures adhered to the Chinese national standard GB/T 18602-2012 [36].
The reservoir characterizations of the shale and tight sandstone in this study primarily involved analyzing mineral composition characteristics, pore structure features, and porosity–permeability characteristics. Mineral composition characteristics were analyzed using X-ray diffraction (XRD) technology with a Bruker D8 Advance X-ray diffractometer from Bruker Corporation, Berlin, Germany, following the guidelines of the Chinese petroleum and natural gas industry standard SY/T 5163-2010 [37]. The pore structure was determined using a JSM-6610LV scanning electron microscope (SEM) from JEOL, Beijing, Chian and an X-max energy dispersive spectrometer from Oxford Instruments, Shanghai, Chian. Corresponding analysis methods adhered to the Chinese national standards GB/T 18295-2001 [38] and GB/T 17359-2012 [39]. Porosity and permeability were determined using an AP-609 porosity–permeability testing instrument from Coretest Systems following the procedures outlined in the Chinese national standard GB/T 29172-2012 [40].
An integrated analysis of sedimentary environments was conducted by combining the field outcrop data, drilling logs, well-logging data, and thin section analysis results. The thin section analysis was primarily aimed at identifying rock types and providing data support for the depositional facies division of the target layers. The experiments utilized a Leica Scope.A1 polarizing microscope from Leica Instrument Company, Beijing, China, following the guidelines of national standard GB/T 17412.1~3-1998 [41]. Shale gas content testing was performed using an on-site gas content testing instrument developed by the Chongqing Institute of Geology and Mineral Resources. The test results were primarily used to evaluate the shale gas resource potential, with on-site testing methods following the Chinese national standard GB/T 19559-2008 [42].
3. Gas Accumulation in Shale and Tight Sandstone
3.1. Favorable Geological Condition for Shale Gas
3.1.1. Sedimentary Environment
Previous studies have indicated that the Silurian strata in the southeastern part of the Sichuan Basin were deposited in a shallow marine shelf environment [43,44]. Based on a comprehensive analysis of drilling, outcrop data, and thin-section identification, along with previous research findings, the Wufeng–Longmaxi Formation in the southeastern of the Sichuan Basin can be vertically subdivided into two subfacies and four microfacies sedimentary types. The two subfacies are a shallow-water continental shelf and a deep-water continental shelf. The four microfacies are deep-water argillaceous continental shelf facies, shallow-water mixed continental shelf facies, shallow-water argillaceous continental shelf facies, and shallow-water sandy continental shelf facies. Organic-rich shale mainly develops in the deep-water mudstone shelf sub-facies. On a planar scale, most areas of the southeastern Sichuan Basin are situated in a deep-water shelf environment, with only parts of Youyang County and Xiushan County in a shallow-water shelf environment. The Wufeng–Longmaxi Formation in the Gongtan Syncline is located within a deep-water shelf environment (Figure 3), which represents a favorable sedimentary environment for shale gas development.
Figure 3.
Schematic diagram of the Wufeng–Longmaxi Formation in the southeastern Sichuan Basin (modified by reference [45]).
3.1.2. Hydrocarbon Source Rock Conditions
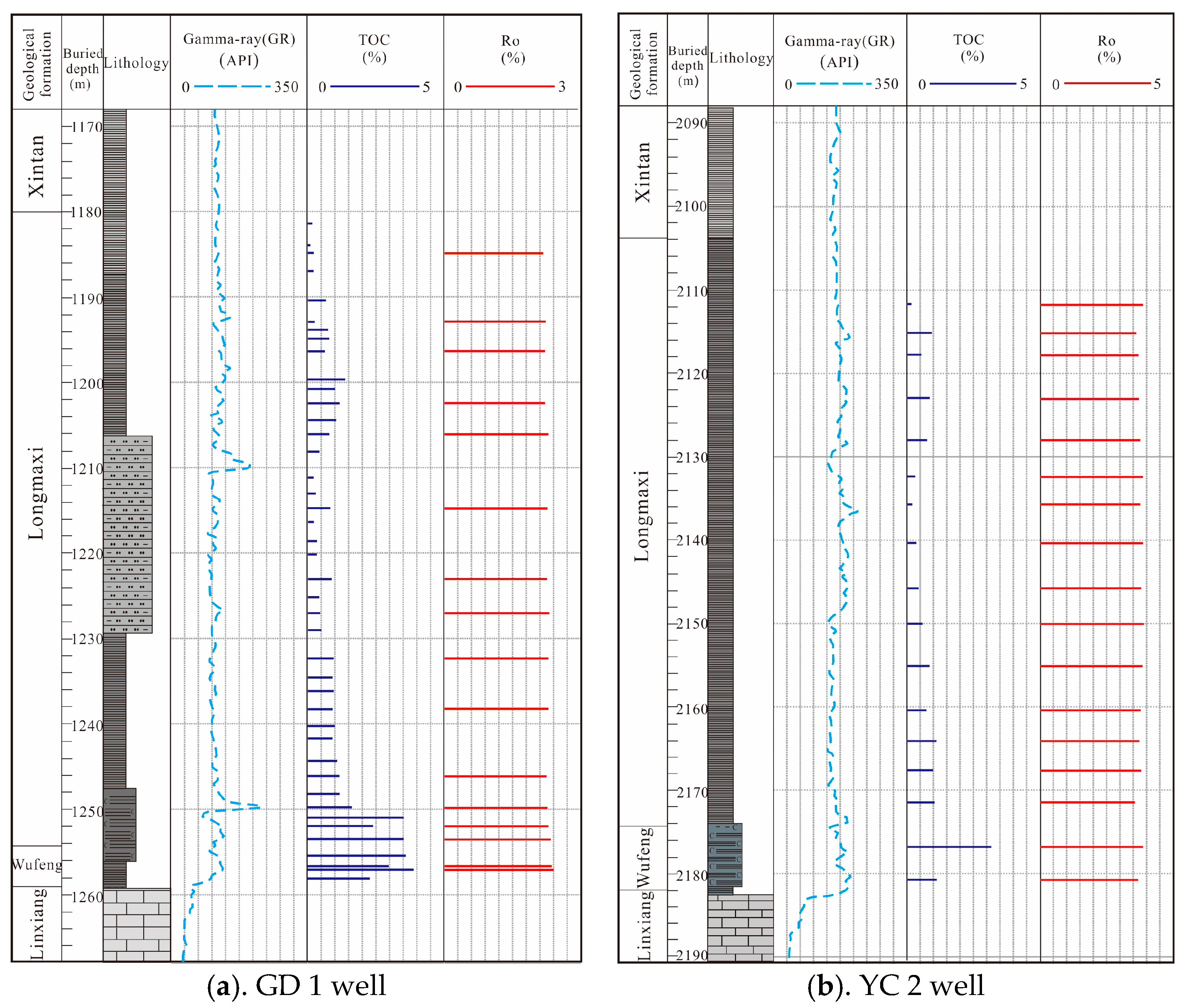
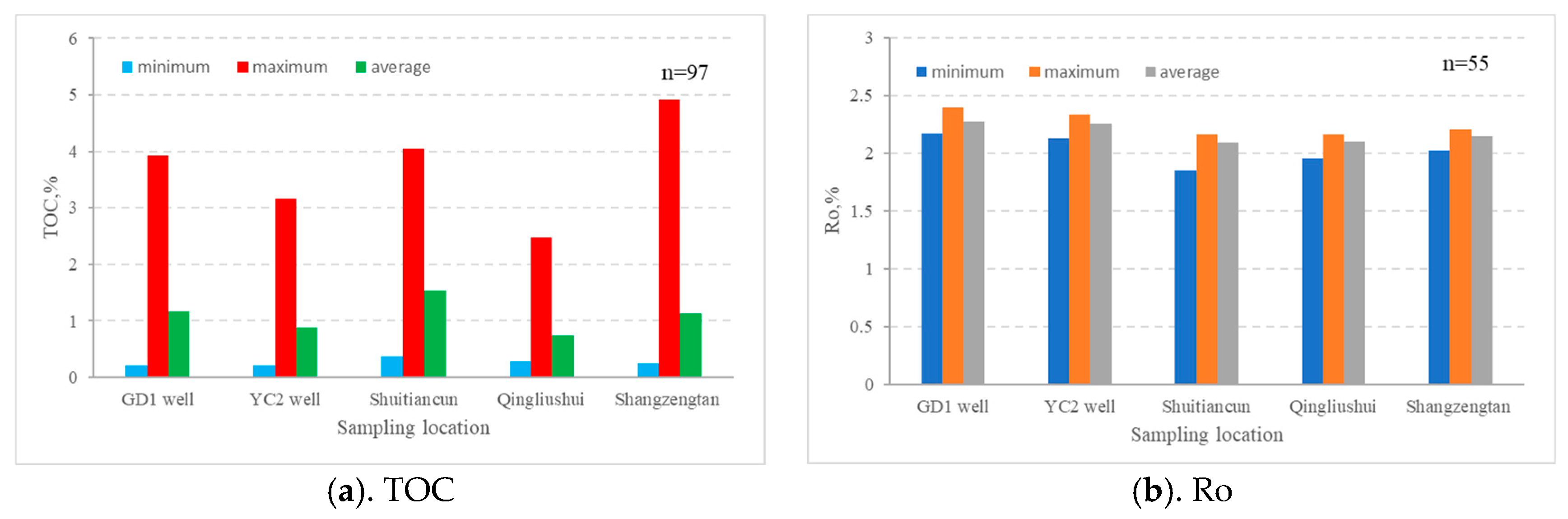
The mud shale of the Wufeng–Longmaxi Formation represents a regionally excellent hydrocarbon source rock [45]. In partial areas of the southeastern Sichuan Basin, this stratigraphic unit has undergone erosion, resulting in significant variations in sediment thickness, ranging from 30 to 120 m, with a gradual thinning trend from northwest to southeast [46]. Drilling and outcrop data reveal that, within the Gongtan Syncline, the distribution of the Wufeng–Longmaxi Formation mud shale is relatively stable, with thickness primarily ranging between 50 to 70 m. Specifically, in the GD 1 well, the thickness ranges from 1180 to 1259 m (a total of 79 m) (refer to Figure 4a), while in the YC 2 well, the thickness ranges from 2104 to 2182 m (a total of 78 m) (refer to Figure 4b). An organic geochemical analysis of 100 samples from drilling and outcrop materials indicates that the organic matter in the Wufeng–Longmaxi Formation shale is predominantly Type I and Type II1, with organic carbon content ranging mainly from 0.21% to 4.91% and averaging at 1.10% (refer to Figure 5a). The organic matter maturity is relatively high, with vitrinite reflectance (Ro) ranging from 1.19% to 2.39% and averaging at 2.18% (refer to Figure 5b), indicating an evolution stage of high to over maturity. The mud shale has reached the peak generation period, facilitating the full generation of shale gas. Consequently, the mud shale of the Wufeng–Longmaxi Formation in the southeastern Sichuan Basin serves as a favorable hydrocarbon source rock, providing conducive conditions for the generation of Lower Silurian shale gas and tight sandstone gas in the region.
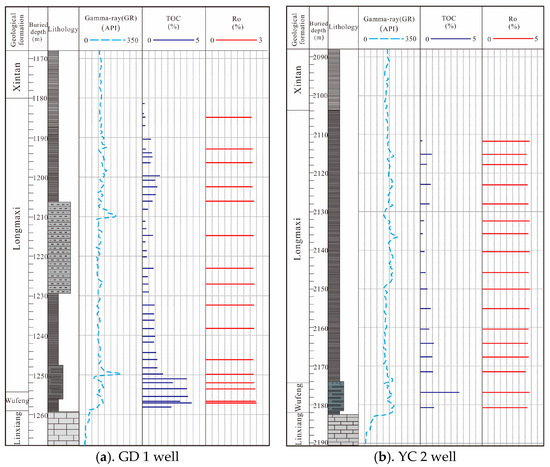
Figure 4.
Columnar diagram of the organic geochemical characteristics of the Wufeng–Longmaxi Formation shales in the study area.
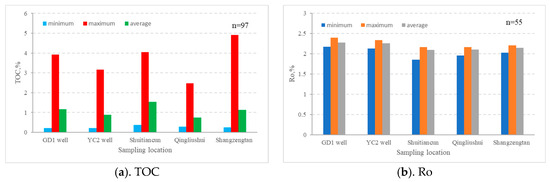
Figure 5.
Histogram of TOC (a) and Ro (b) for the Wufeng–Longmaxi Formation shales in the study area.
3.1.3. Reservoir Characteristics
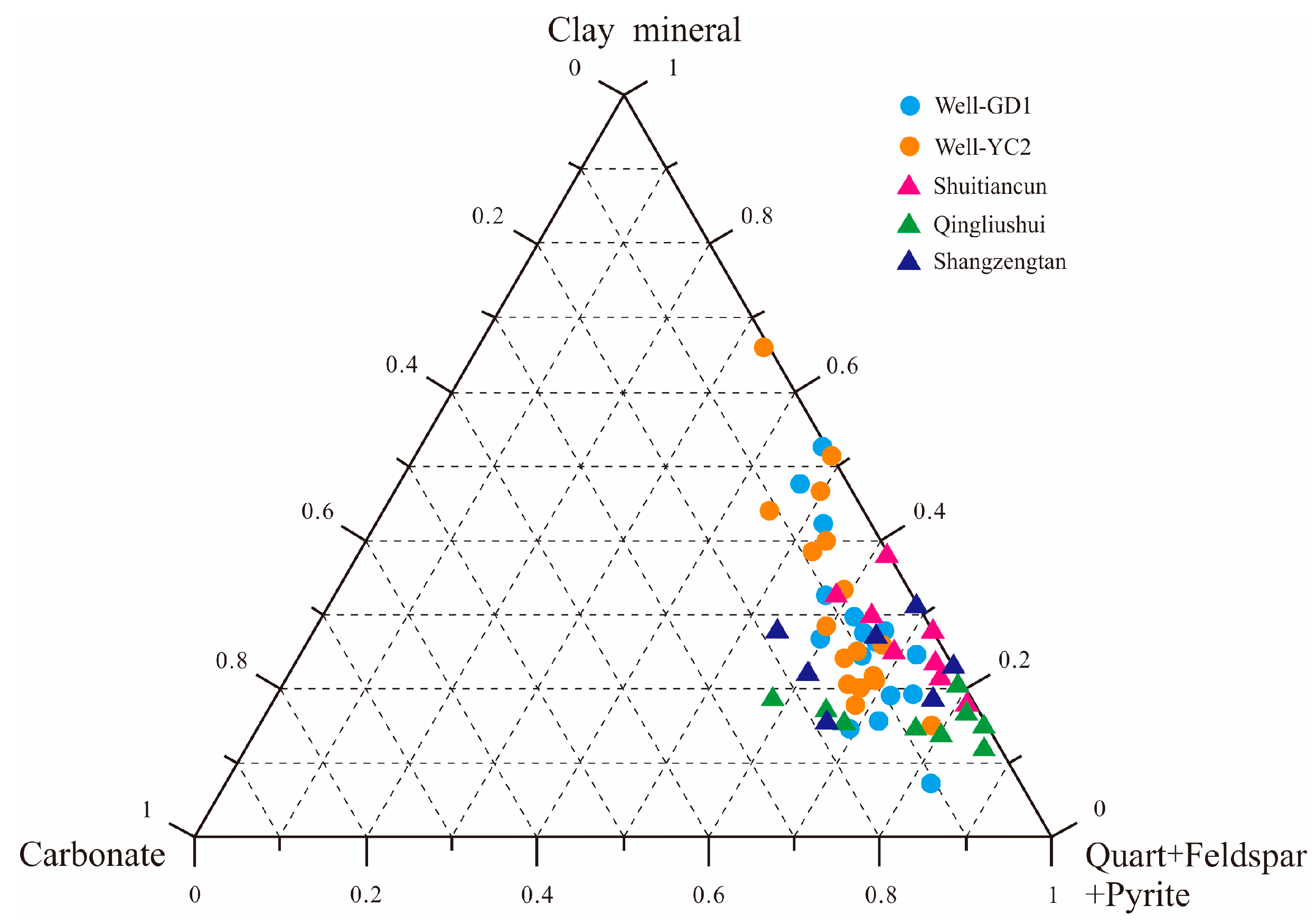
The shale of the Wufeng–Longmaxi Formation constitutes a “source-reservoir unity,” serving as both the hydrocarbon source rock and the reservoir for shale gas [47]. Results from an X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis of 36 drilling and outcrop samples within the Gongtan Syncline indicate that the predominant mineral composition of the Wufeng–Longmaxi Formation shale comprises detrital minerals and clay minerals (refer to Figure 6), with minor quantities of carbonate and pyrite, among other minerals. The shale contains a high content of brittle minerals such as quartz, feldspar, and carbonate, averaging at 67.10%, which is conducive to reservoir fracturing and enhancement. The scanning electron microscope (SEM) results reveal that the matrix pore types in the shale of the Wufeng–Longmaxi Formation in the study area are primarily organic matter pores and interlayer clay mineral pores, with well-developed structural fractures that provide favorable storage space for shale gas enrichment. The porosity and permeability of 47 shale core samples from two wells were tested by the thermal pulse-decay method. The results showed that the porosity of the samples ranged from 0.19 to 5.41%, with an average of 1.21%, and the permeability ranged from 0.0001 to 0.2223 mD, with an average of 0.0082 mD. In general, the Wufeng–Longmaxi Formation in the study area belongs to ultra-low porosity and ultra-low permeability reservoirs.
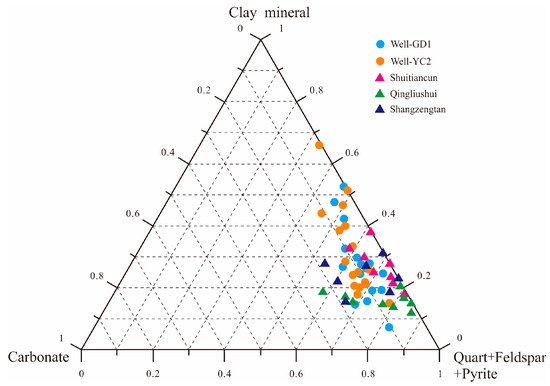
Figure 6.
Mineral triangular diagram of the shale of the Wufeng–Longmaxi Formation in the Gongtan Syncline.
3.1.4. Gas Content
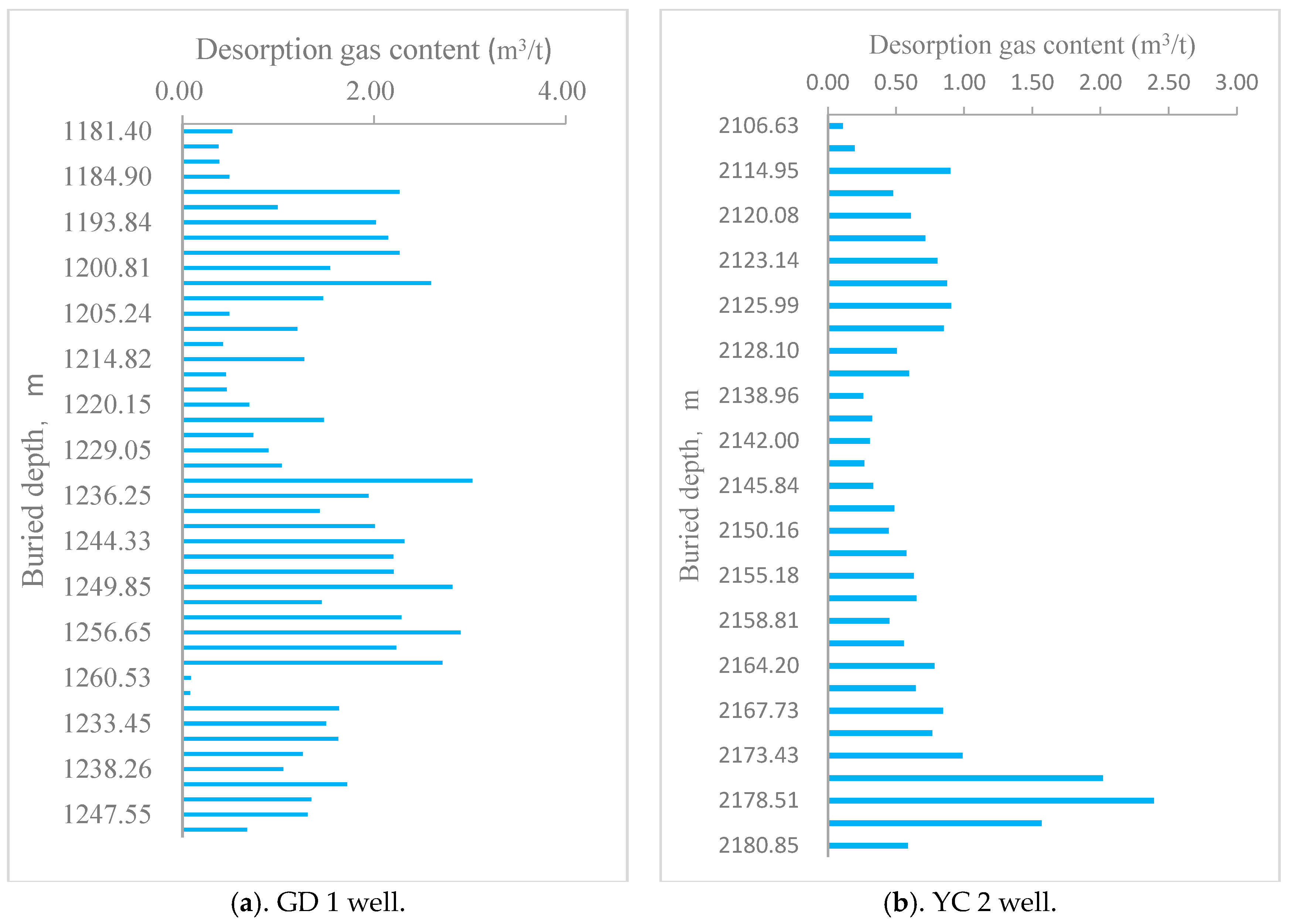
The gas content of shale is a key parameter for evaluating the potential of shale gas reservoirs, and it is crucial for shale gas evaluation, favorable area selection, resource estimation, and calculation [48]. Shale gas content parameters are typically obtained through on-site desorption or isothermal adsorption experiments [49]. In this study, the gas content parameters were primarily obtained using on-site desorption methods, where the desorbed gas quantity was measured using instruments at the drilling site. Statistical analysis of the on-site desorption experiment data from the GD 1 and YC 2 wells within the Gongtan Syncline showed that the Wufeng–Longmaxi Formation shale exhibits good gas content. Vertically, the gas content tends to increase with depth. Specifically, the on-site desorption gas content of the core samples from the GD 1 well ranged from 0.42 to 3.02 m3/ton, averaging 1.64 m3/ton (Figure 7a). For the YC 2 well, the on-site desorption gas content ranged from 0.11 to 2.39 m3/ton, averaging 0.71 m3/ton (Figure 7b). These values are comparable to the on-site analyzed gas content of 0.90 m3/ton at the Jiaoye-1 well in the Reefs Dam area [50], indicating the favorable shale gas resource potential of the Wufeng–Longmaxi Formation within the Gongtan Syncline.
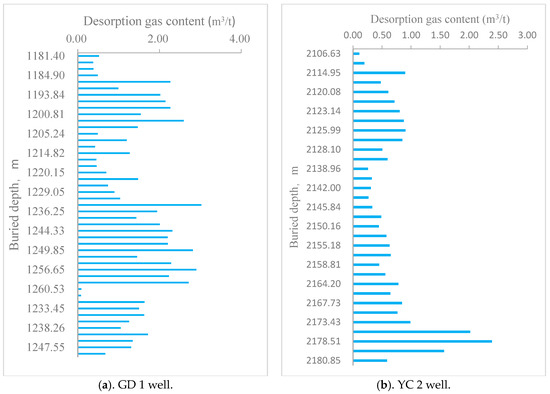
Figure 7.
Variation of the on-site desorption gas content with the buried depth of the Wufeng–Longmaxi Formation in the Gongtan Syncline.
3.2. Favorable Geological Conditions for Tight Sandstone Gas
3.2.1. Sedimentary Environment
Based on the analysis of drilling and logging data in the southeastern Sichuan Basin, the overlying Xintan Formation and Xiaoheba Formation above the Wufeng–Longmaxi Formation primarily exhibit three sedimentary subenvironments: marginal marine (including lower and middle-upper), offshore transition, and outer shelf (Figure 8 and Figure 9). Sandstones are mainly deposited in the middle-upper marginal marine environment, with limited shoreface sand barriers in the lower marginal marine setting and more common occurrences of mudstone interbeds. In the offshore transition zone, there are occasional storm-induced sand barriers, but they are limited in distribution and scale. The Xintan Formation predominantly consists of the sand barriers and mud flats of the lower shoreface within the study area (Figure 8), with tight sandstones developed only in the sand barriers on the western flank of the syncline. The Xiaoheba Formation in the Gongtan Syncline mainly features coastal sand barriers in the middle-upper marginal marine setting (Figure 9), with a relatively developed occurrence of tight sandstones. Therefore, the Xintan Formation and Xiaoheba Formation in the study area represent sedimentary environments conducive to the development of tight sandstones, providing the material basis for the formation of tight sandstone reservoirs in the region.
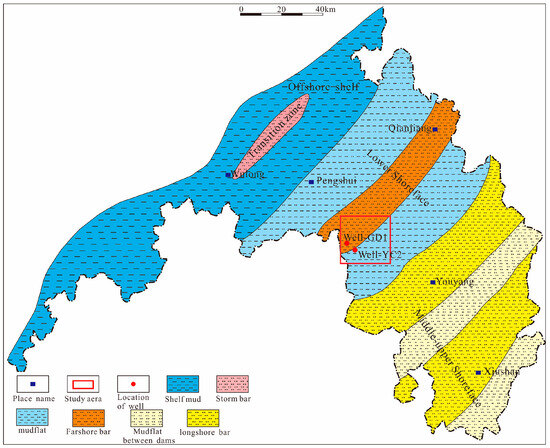
Figure 8.
Schematic diagram of the sediments of the Xintan Formation in the southeastern Sichuan Basin (modified by reference [51]).
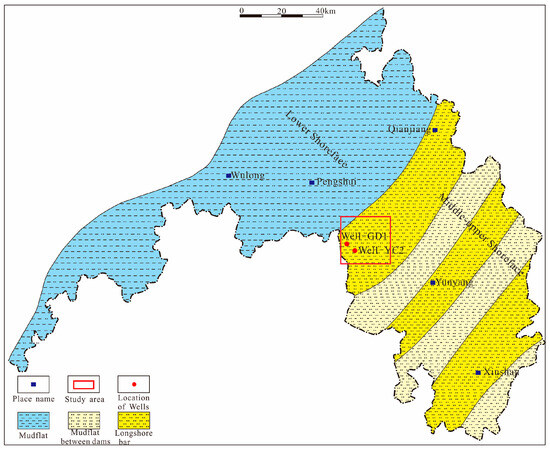
Figure 9.
Schematic diagram of the sediments of the Xiaoheba Formation in the southeastern Sichuan Basin (modified by reference [52,53]).
3.2.2. Reservoir Characteristics
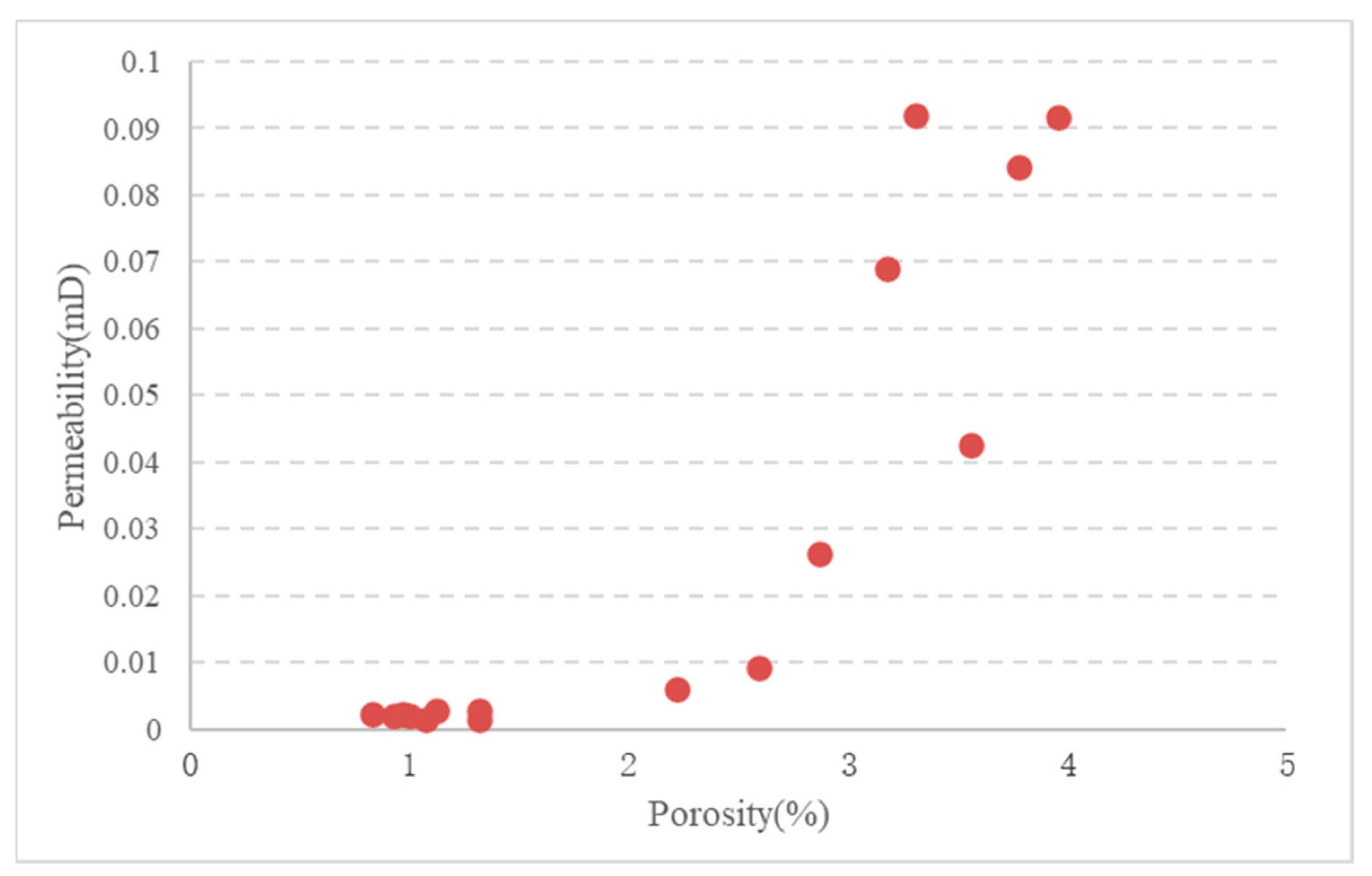
Analysis of the drilling and logging data from Wells GD 1 and YC 2 revealed the presence of discontinuous sand bodies in the middle-upper part of the Xintan Formation within the study area. These sand bodies exhibit unstable single-layer thicknesses ranging from 2 to 15 m, and they are primarily composed of calcareous silty sandstone. The lower part of the Xiaoheba Formation shows continuous and relatively thick-bedded sand bodies, with thicknesses ranging from 26 to 50 m. The lithology of these sand bodies mainly consists of fine-to-silty sandstone and calcareous silty sandstone, exhibiting coarser grain sizes compared to the mudstone–siltstone of the Xintan Formation. Physical property analyses of 15 core samples from the GD1 well (Figure 10) showed low porosity and permeability values for the middle-upper part of the Xintan Formation and the lower part of the Xiaoheba Formation. Porosity values ranged from 0.83% to 3.96%, with an average of 2.12%, while permeability ranged from 0.0015 to 0.0920 mD, with an average of 0.0227 mD. Interpretation of the logging data indicates that, even in the middle-upper Xintan and lower Xiaoheba Formations, the tight sandstone reservoirs exhibit extremely low porosity and low permeability characteristics (Table 1). In summary, the sandstone reservoirs within the Xintan and Xiaoheba Formations exhibit poor physical properties, and they are characterized as having extremely low porosity and low permeability tight sandstone reservoirs.
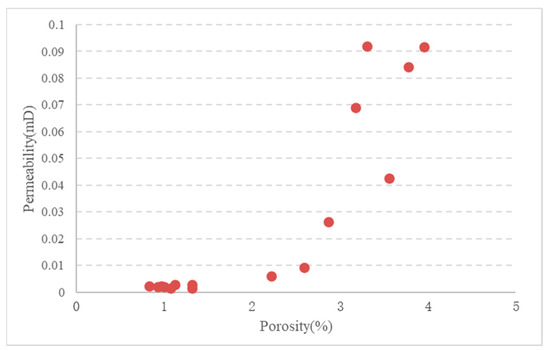
Figure 10.
Porosity and permeability of the Lower Silurian tight sandstone in the GD 1 well.

Table 1.
Reservoir petrophysical parameters of the tight sandstones from the Xintan and Xiaoheba formations. The value of porosity and permeability refers to the minimum-maximum and the average.
3.2.3. Gas Content
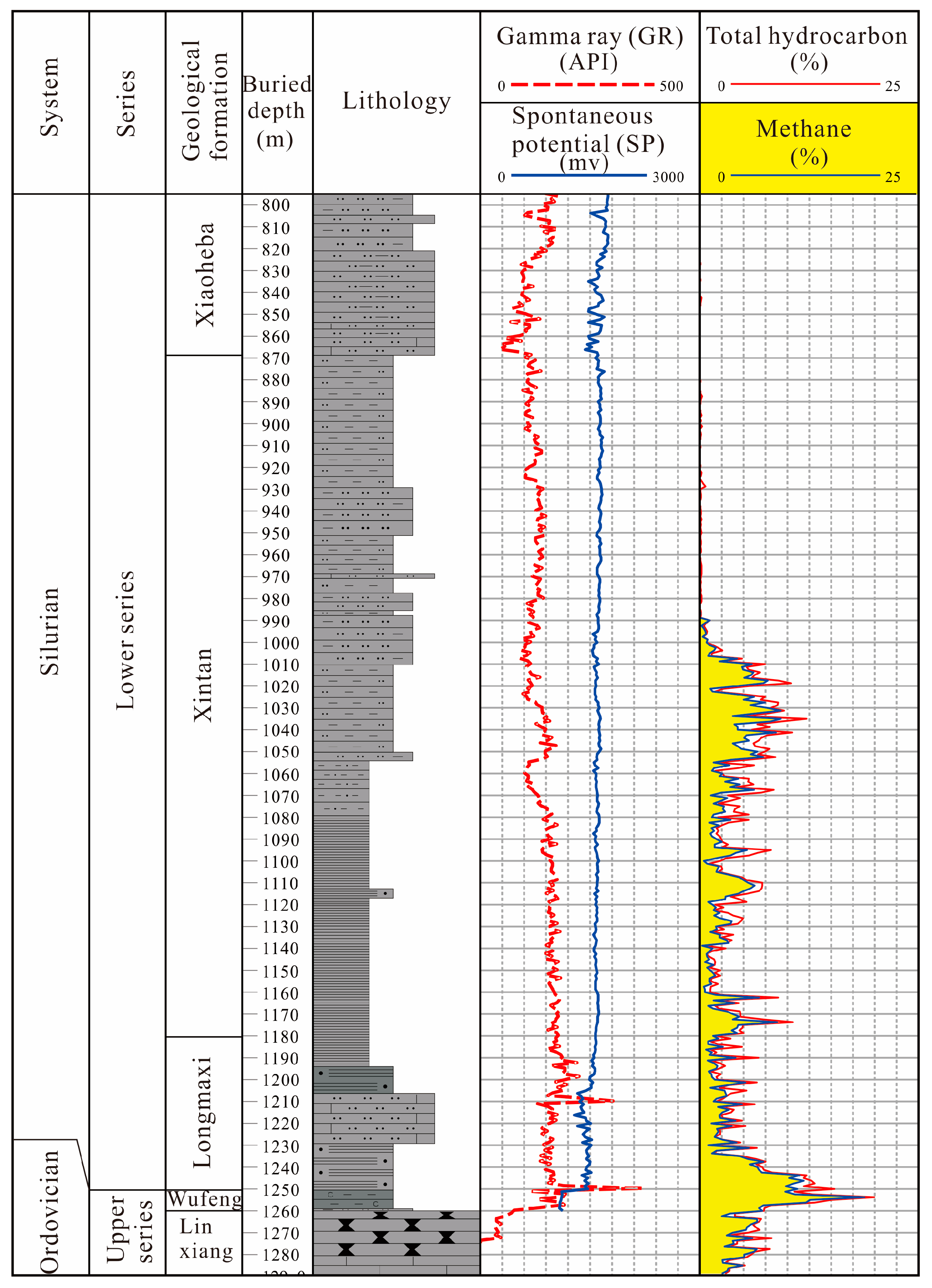
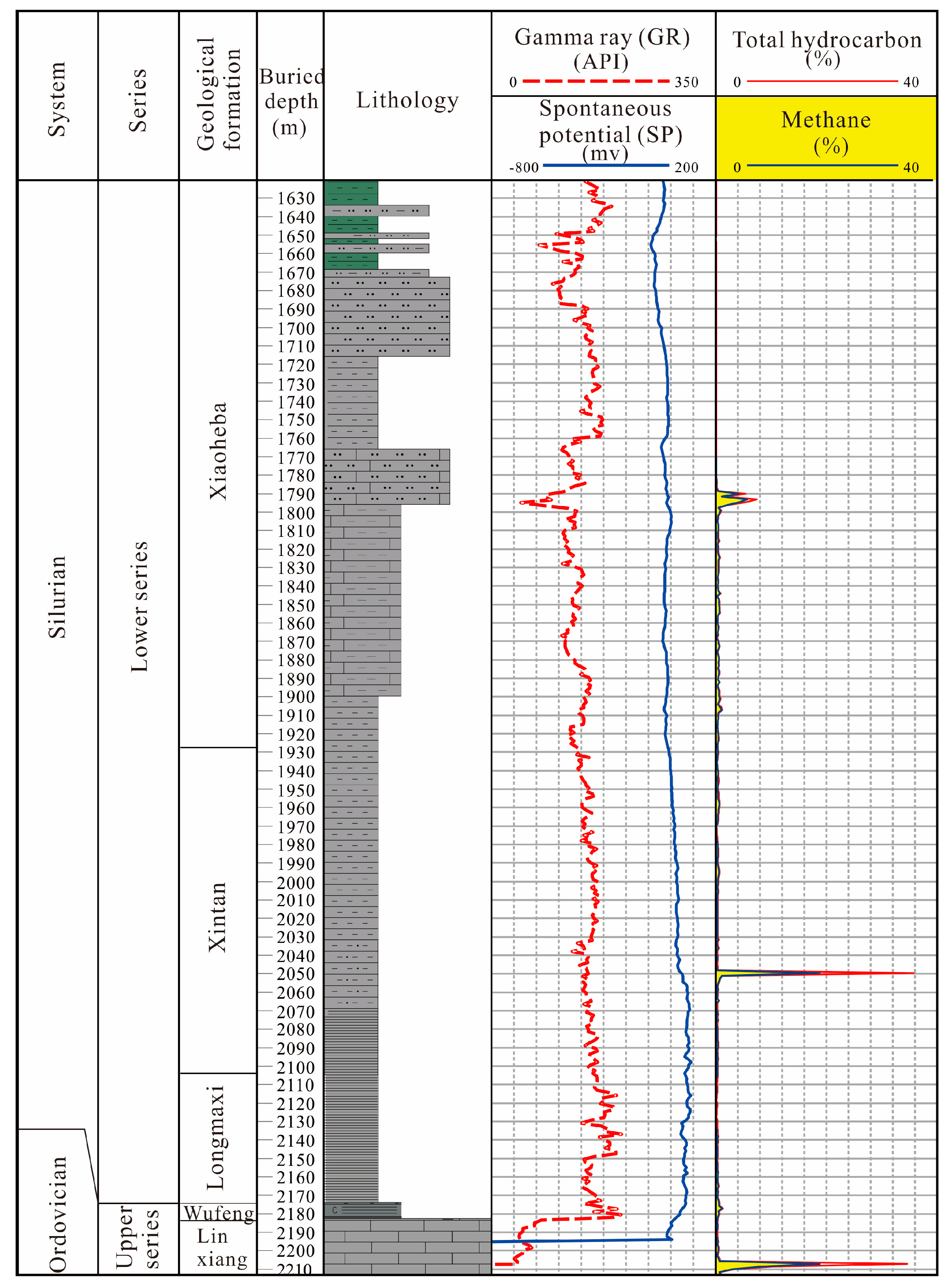
The existing drilling and logging data indicate that the two wells not only exhibit good gas indications within the syncline, but also show gas indications in the overlying Xintan and Xiaoheba formations. The gas logging curves from the GD 1 well revealed consistent gas shows from the lower-middle part of the Xintan Formation (around 1000 m) down to the base of the Wufeng Formation (Figure 11). In the middle section of the Xintan Formation (approximately 1010 m to 1055 m), gas anomalies were detected in silty mudstone and mudstone–siltstone intervals, with total hydrocarbon contents ranging from 1.651% to 12.183%. Logging interpretation of this section indicates the presence of gas-bearing zones, suggesting good gas saturation in the mudstone–siltstone of the Xintan Formation. At the YC 2 well, gas anomalies were identified in the lower part of the calcareous silty sandstone within the Xiaoheba Formation (1788–1796 m), with total hydrocarbon contents ranging from 0.196% to 7.384% (Figure 12). The logging interpretation of this section also confirmed the presence of gas-bearing zones in this interval. These findings from both wells encountering tight sandstone gas within the Xintan and Xiaoheba Formations further confirm the geological characteristic of coexisting “dual-gas” in the lower Silurian strata of the study area.
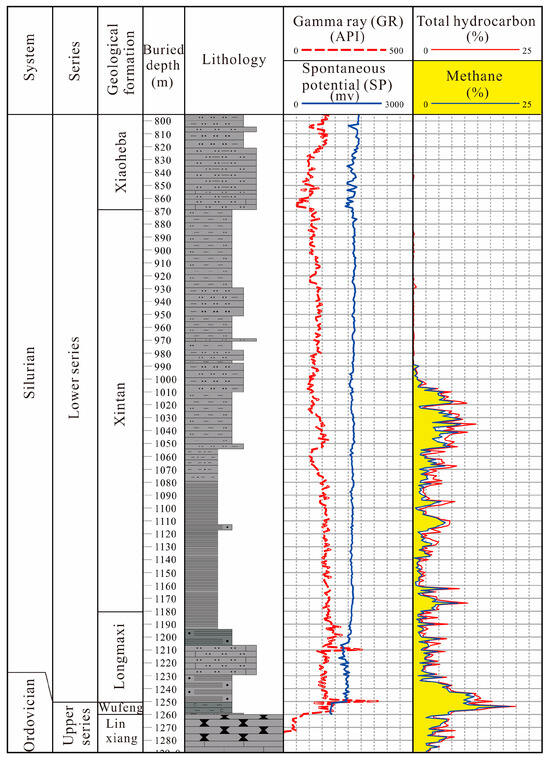
Figure 11.
Histogram of the gas logging of the GD 1 well.
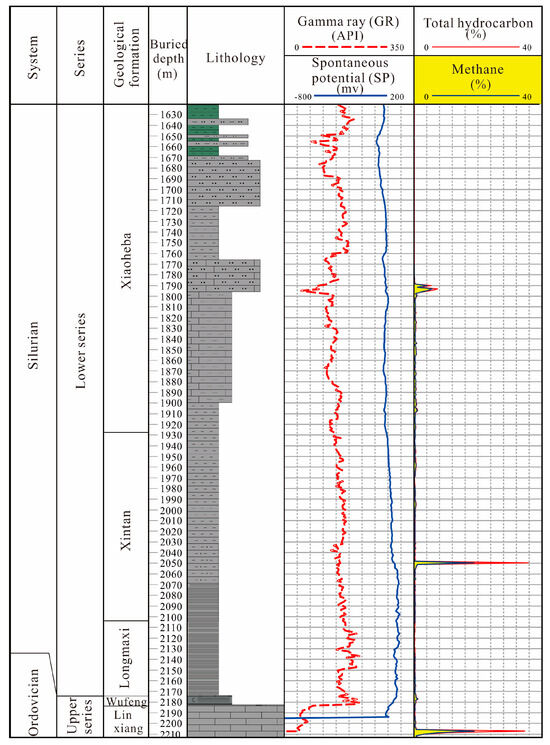
Figure 12.
Histogram of the gas logging of the YC 2 well.
3.2.4. Hydrocarbon Migration Pathways
- (1)
- Reservoir fractures and hydrocarbon accumulation
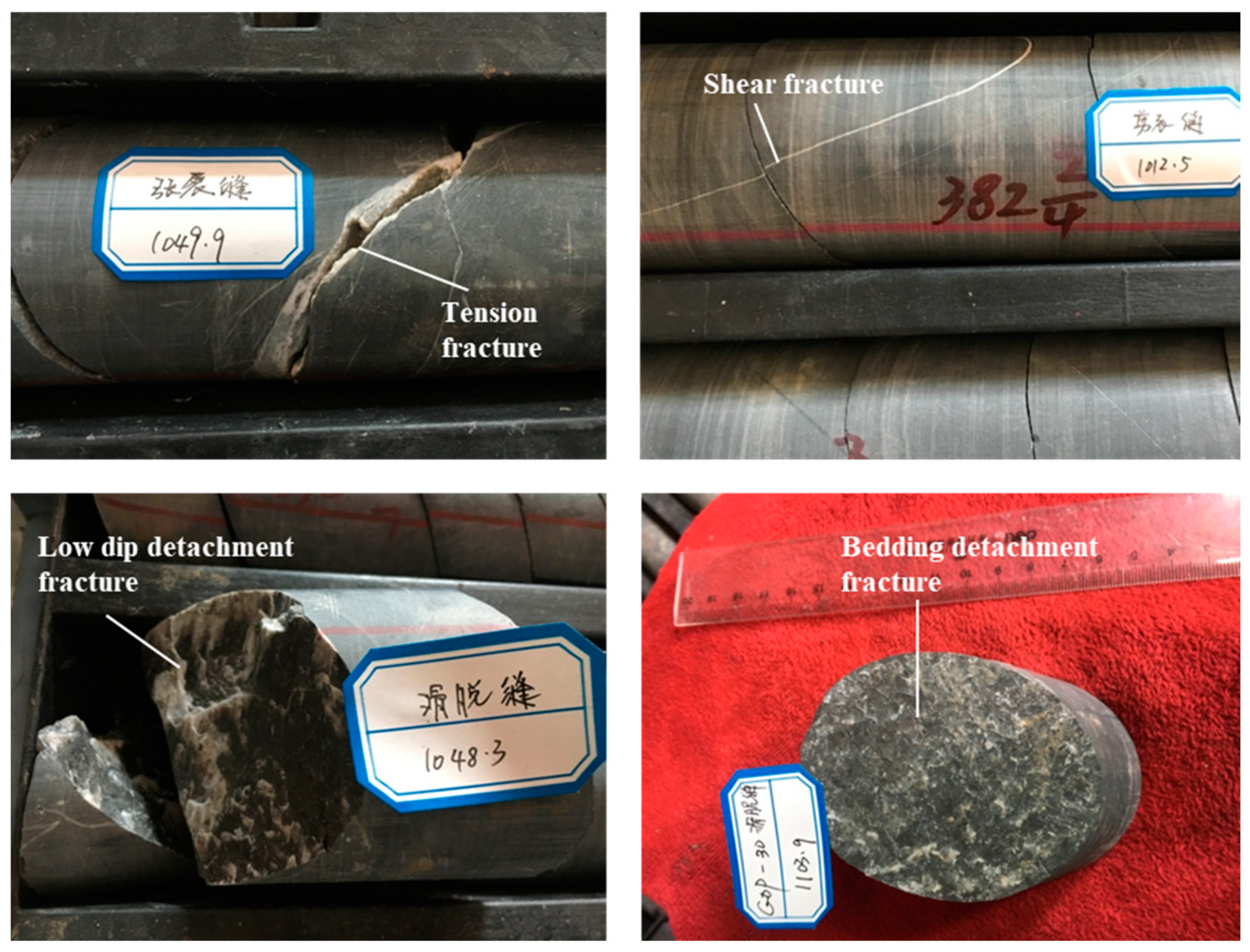
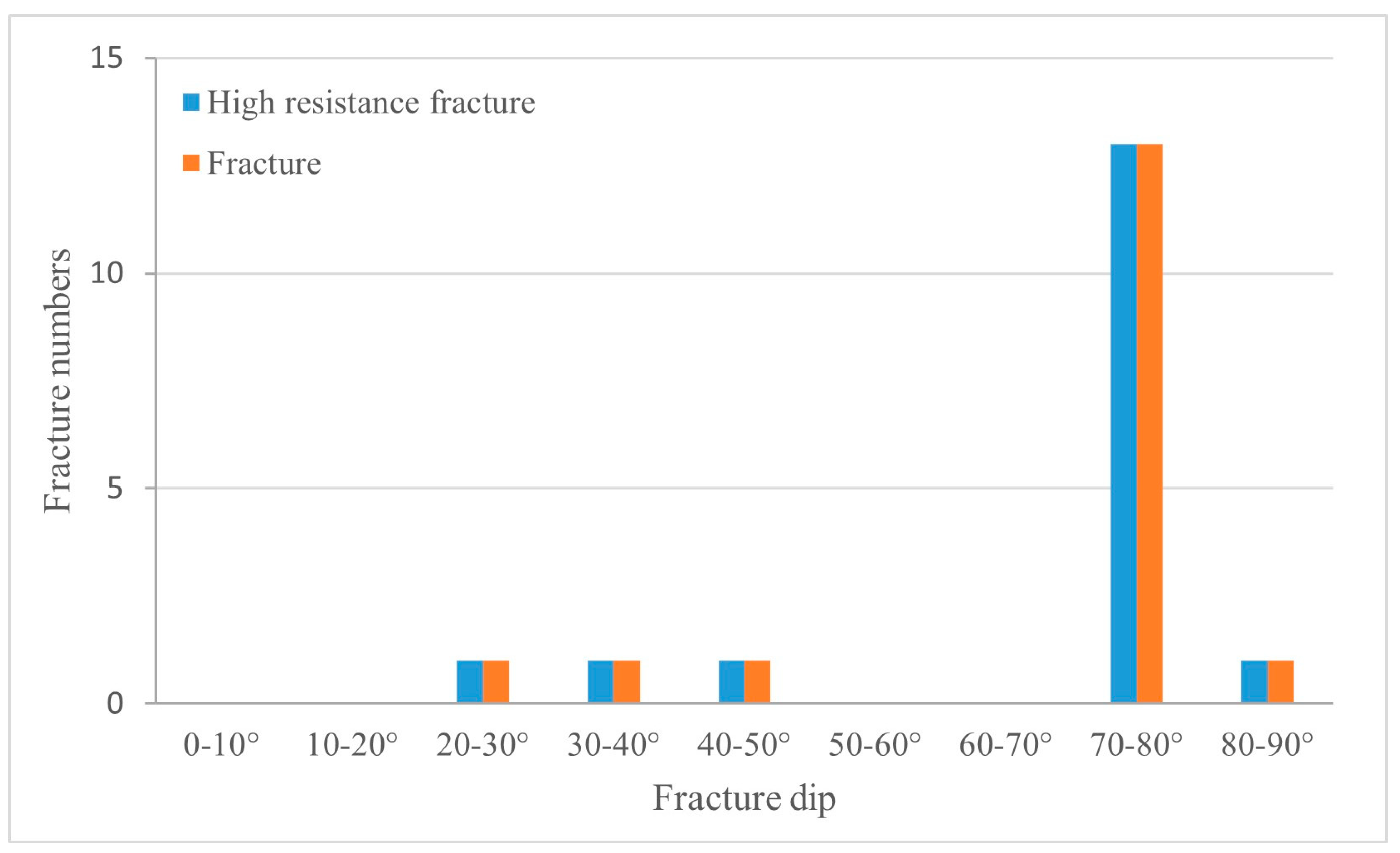
Based on the research results above, it is evident that the high mud content in the tight sandstones of the Xintan and Xiaoheba formations within the study area leads to relatively poor reservoir properties, which are unfavorable for the migration and accumulation of natural gas. Scholars have discovered that natural fractures developed within tight reservoirs can serve as pathways for oil and gas migration and as trapping locations, thereby improving the conditions for oil and gas accumulation in tight reservoirs [54,55]. Through core observations, fractures were identified within the gas-rich intervals of the mudstone–siltstone in the middle-upper part of the Xintan Formation in the GD 1 well (Figure 13). These fractures predominantly consist of low-angle and inclined fractures. The fracture density is relatively low, with an average longitudinal fracture density of only 0.11 fractures per meter, primarily consisting of small fractures. The statistical analysis of fracture filling indicates that most fractures are filled, with fully filled fractures accounting for 87.2% of all fractures. The imaging logging data from Well YC 2 (Figure 14) show that fractures within the tight sandstone of the Xiaoheba Formation mainly consist of high-resistance fractures and drilling-induced fractures, with minimal development of high-conductivity fractures. As a result, natural fractures are developed to a certain extent within the Lower Silurian tight sandstone formations in the study area, but these fractures are predominantly filled, which may partially affect the migration and accumulation of natural gas within the tight sandstone reservoirs.
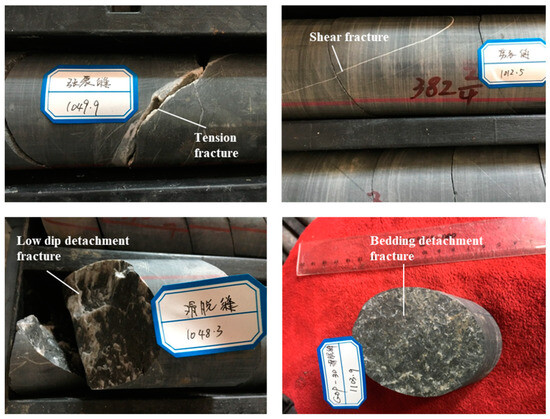

Figure 13.
Fracture characteristics of the tight sandstone of the Xintan Formation in the GD 1 well.
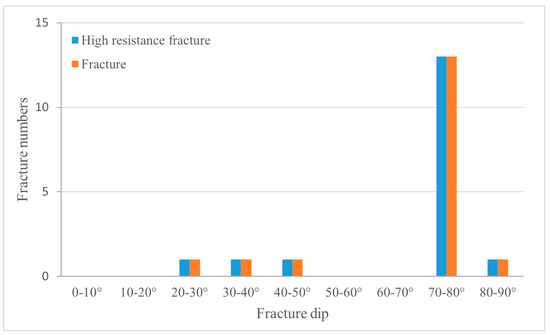
Figure 14.
Dip angles of the natural fractures in the Xiaoheba Formation, Well YC 2.
- (2)
- Fractures of the hydrocarbon source rock and hydrocarbon accumulation
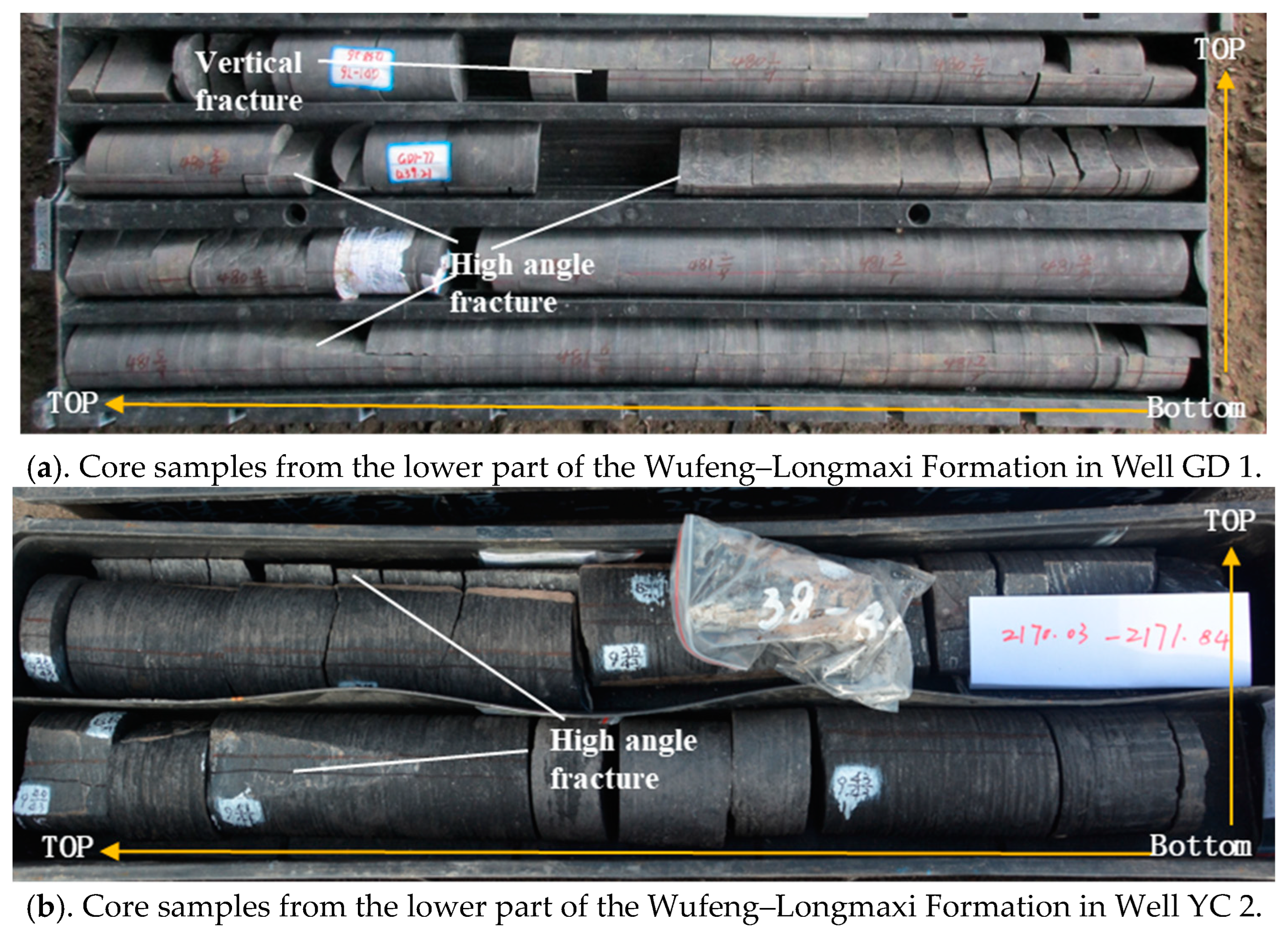
For the tight sandstone gas reservoirs in the Xintan and Xiaoheba Formations within the study area, the organic-rich shale of the Upper Ordovician Wufeng Formation to the Lower Silurian Longmaxi Formation serves as the main source rock for hydrocarbons. Natural gas within shale layers require effective migration pathways for transport [56,57,58], whereas these shale layers exhibited characteristics of self-generation, self-storage, tightness, low porosity, and ultra-low permeability. The presence of natural fractures undoubtedly can provide crucial conditions for the migration of gas within shale layers, facilitating gas expulsion. Through core observations, it was observed that natural fractures are developed within the Wufeng–Longmaxi formations in the wells of GD 1 and YC 2 (Figure 15). These fractures predominantly consist of high-angle cutting and vertical fractures. Such fractures effectively connect different mechanical layers of the rock, forming efficient pathways for natural gas migration. Consequently, natural gas generated within the Wufeng–Longmaxi shale formations can migrate into the overlying Xintan and Xiaoheba formations of tight sandstones through these pathways.
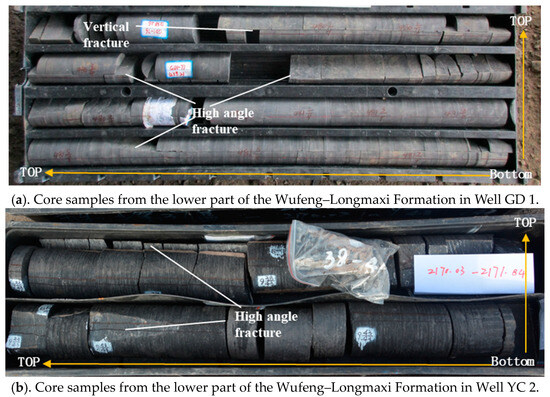
Figure 15.
Fracture characteristics of the Wufeng–Longmaxi Formation in the Gongtan Syncline.
4. Gas Preservation Settings
The Wufeng–Longmaxi Formation shales are extensively distributed within the Gongtan Syncline at moderate burial depths. Overlying these formations are medium-thick layers of silty mudstone, muddy siltstone, and fine sandstone belonging to the Xintan and Xiaoheba formations, serving as both reservoirs of tight sandstone gas and caprocks for Wufeng–Longmaxi Formation shales. The Hanjiadian Formation overlies the Xintan and Xiaoheba Formations. Its lower portion predominantly consists of yellow and yellow-green shales interbedded with a purple-red shale. The middle section is composed of yellow-green, gray-green, and purple-red shales along with thick layers of siltstone. The upper part of the Hanjiadian Formation is characterized by yellow-gray and gray-green shales. The Hanjiadian Formation exhibits significant thickness, ranging from 703 to 783 m, and it is extensively distributed throughout the study area. It is characterized by low porosity, low permeability, and effective sealing properties. Consequently, the development of direct caprocks for shale gas and tight sandstone gas is well established, exhibiting favorable sealing characteristics.
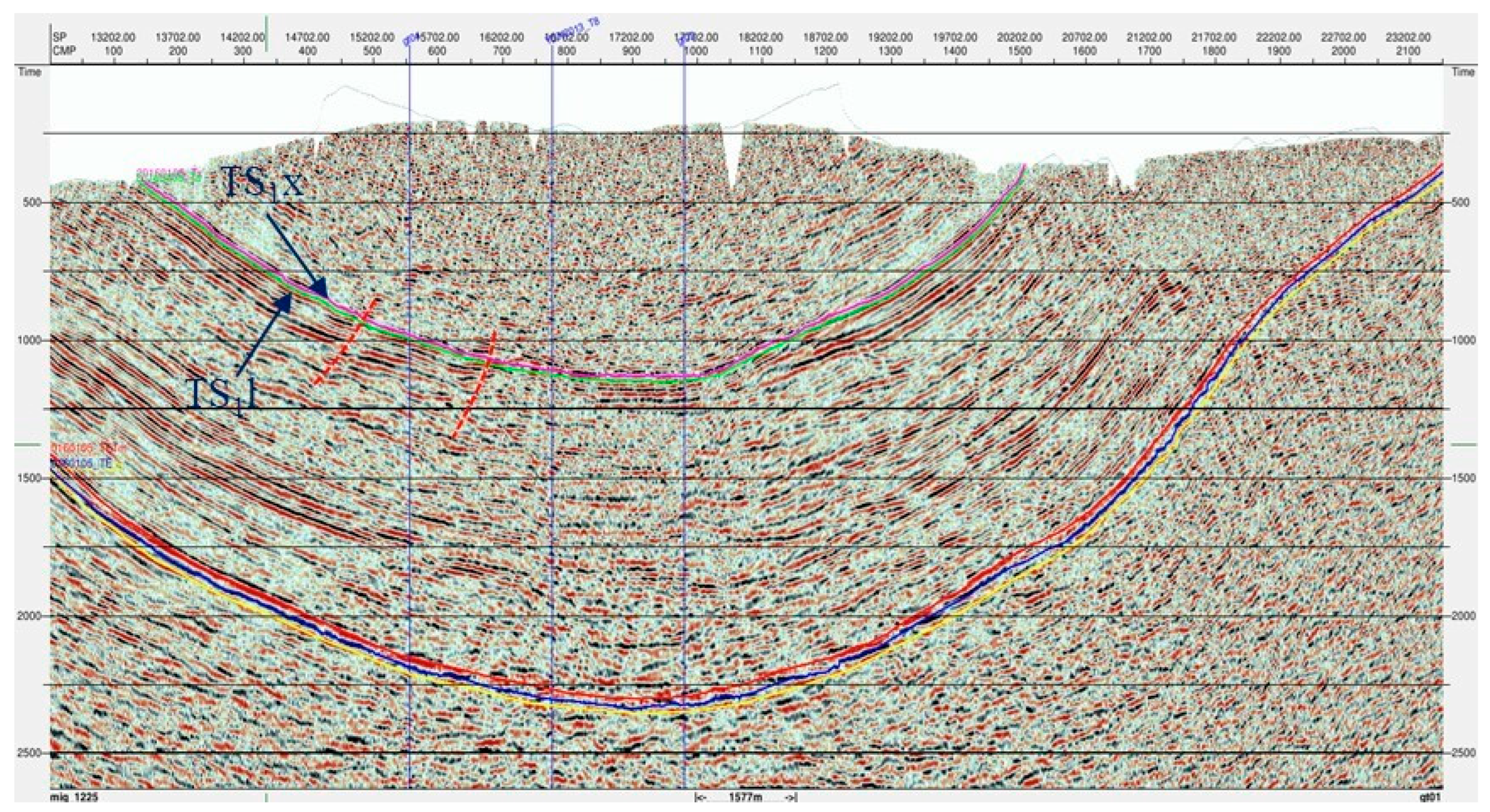
Seismic interpretation results indicate that the Gongtan Syncline is a typical dish-shaped fold with a relatively weak structural deformation. Only a few faults with relatively small fault scales and spacings are present within the Xintan and Longmaxi formations, as well as underlying formations in the syncline. These faults do not breach the overlying layers of the Lower Silurian shale and tight sandstone reservoirs (Figure 16). Overall, the structural style of the Gongtan Syncline is straightforward, and the faults developed within the syncline have minimal impact on the preservation conditions of shale gas and tight sandstone gas, making it an advantageous area for unconventional oil and gas preservation in the southeastern part of the Sichuan Basin.
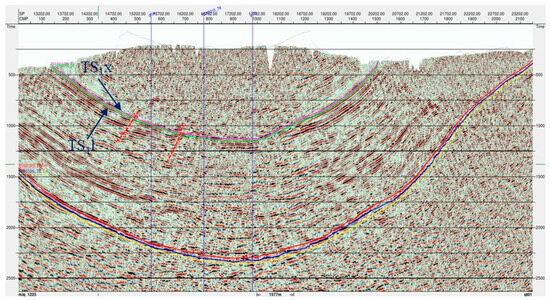
Figure 16.
Structural profile of the Gongtan Syncline (Profile lines are shown in Figure 2). The red dotted lines represent faults in the Gongtan Syncline.
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Within the Gongtan Syncline, the Wufeng–Longmaxi Formation is situated in a deep-water continental shelf depositional environment, characterized by thick organic-rich shale deposits with high organic content, moderate thermal maturity, and good hydrocarbon generation potential. This provides a solid material basis for the accumulation of shale gas and tight sandstone gas. The Wufeng–Longmaxi Formation in the study area exhibits high desorption gas content from organic-rich shale, indicating good gas-bearing properties and significant potential for shale gas resources.
- (2)
- The Xintan Formation primarily comprises offshore sandbars and nearshore mud flats of the lower shoreface, with an unstable distribution of tight sandstone layers. These tight sandstone layers have relatively small individual thicknesses, predominantly developing within the offshore sandbars on the western flank of the syncline. The Xiaoheba Formation is dominated by alongshore sandbars of the upper-middle shore phase, with well-developed tight sandstone that is characterized by thicker individual layer thickness and more stable distribution. Both sets of tight sandstone reservoirs exhibit low porosity, low permeability, and some natural fractures characterized by high fracture filling. These natural fractures may facilitate the extensive migration and accumulation of natural gas in the formations.
- (3)
- The Lower Silurian formations within the Gongtan Syncline are at moderate burial depths, and they are characterized by overall underdeveloped internal faults and a relatively intact cap rock. The structural style is a broad and gentle syncline, providing favorable conditions for hydrocarbon preservation. The geological conditions for shale gas accumulation in the Wufeng–Longmaxi Formation within the syncline are favorable, offering conducive prospects for shale gas exploration. The accumulation conditions for tight sandstone gas in the Xiaoheba Formation are superior to those in the Xintan Formation. The tight sandstone gas in the Xintan Formation is locally accumulated due to the distribution of tight sandstones, which are primarily developing on the western flank of the syncline.
Author Contributions
Methodology, W.W., Y.Y., Q.W. and D.Z.; Validation, W.W.; Investigation, S.W. and C.Z.; Resources, Y.Z. and D.Z.; Writing—original draft, S.W.; Writing—review & editing, W.W.; Visualization, C.Y. and Y.X.; Project administration, Y.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was financially supported by the Chongqing Natural Science Foundation (cstc2021jcyj-msxmX0624, CSTB2023NSCQ-LZX0036).
Data Availability Statement
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding authors upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors Shengxiu Wang, Wei Wang, Qiaoli Wang, Chuan Yu, Chunlin Zeng and Yao Xu were employed by the Chongqing Huadi Resources and Environment Technology Co., Ltd. Author Yang Yang was employed by the China National Petroleum Corporation Changqing Oilfield Branch Fifth Gas Production Plant. The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
References
- Jarvie, D.M.; Hill, R.J.; Ruble, T.E.; Pollastro, R.M. Unconventional shale-gas systems: The mississippian barnett shale of north-central Texas as one model for thermogenic shale-gas assessment. AAPG Bull. 2007, 91, 475–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marc Bustin, R. Shale gas and shale oil petrology and petrophysics. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2012, 103, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yao, Y.B.; Elsworth, D. Morphological complexity and azimuthal disorder of evolving pore space in low-maturity oil shale during in-situ thermal upgrading and impacts on permeability. Pet. Sci. 2024; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakamatsu, H.; Aruga, K. The impact of the shale gas revolution on the U.S. and Japanese natural gas markets. Energy Policy 2013, 62, 1002–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.N.; Yang, Z.; Zhu, R.K.; Zhang, G.S.; Hou, L.H.; Wu, S.T.; Shizhen, T.A.O.; Yuan, X.J.; Dong, D.Z.; Wang, Y.M.; et al. Progress in China’s Unconventional Oil & Gas Exploration and Development and Theoretical Technologies. Acta Geol. Sin. 2015, 89, 979–1007. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, W.; Zhao, P.; Lu, Y. Variational Reservoir Characteristics of the Wufeng–Longmaxi Formation from Different Sedimentary Region and Its Implications in Southeastern Sichuan Basin, China. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 20684–20696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.; Zhao, Q.; Cong, L.; Wang, H.; Shi, Z.; Wu, J.; Pan, S. Development progress, potential and prospect of shale gas in China. Nat. Gas Ind. 2021, 41, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, A.; Wei, Y.; Guo, Z.; Wang, G.; Meng, D.; Huang, S. Development status and prospect of tight sandstone gas in China. Nat. Gas Ind. 2022, 42, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.L. Discovery and characteristics of the Fuling shale gas field and its enlightment and thinking. Earth Sci. Front. 2016, 23, 29–43. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.P.; Zhang, P.X.; Fang, D.Z.; Mei, J.W.; He, G.S.; Lu, B. Production characteristics of normal pressure shale gas in Pengshui-Wulong area, southeast Chongqing. Pet. Geol. Recovery Effic. 2018, 25, 72–79. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.S. Controlling factors on shale gas accumulations of Wufeng-Longmaxi Formations in Pingqiao shale gas field in Fuling area, Sichuan Basin. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2019, 30, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.R.; Dong, D.Z.; Liao, Q.S.; Sun, S.; Huang, S.; Guan, Q.; Zhang, C.; Guo, W.; Jiang, S.; Shi, P. Geological characteristics and resource prospect of deep marine shale gas in the southern Sichuan Basin. Nat. Gas Ind. 2021, 41, 35–45. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, D.F. Evaluation of Silurian Tight Sandstone Reservoir in Jiannan Gas Field Area, West Hubei-East Chongqing. Mar. Orig. Pet. Geol. 2011, 16, 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, T.L. Key controls on accumulation and high production of large non-marine gas fields in northern Sichuan Basin. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2013, 40, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Li, G.; Li, N.; Chen, S.; Wang, H.; Xu, L. Hydrocarbon accumulation characteristics and enrichment laws of multi-layered reservoirs in the Sichuan Basin. Nat. Gas Ind. B 2017, 4, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.J.; Zhang, Z.B. Depositional system evolution characteristic in the framework of sequences of Silurian and prediction of Favorable zones in eastern Sichuan-Western Hubei. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2016, 16, 13–21. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.K.; Shi, Z.J.; Tian, Y.M.; Wang, Y.; Hu, X.Q.; Li, W.J. Pore types and genesis of tight sandstone of Silurian Xiaoheba Formation in southeastern Sichuan Basin. Lithol. Reserv. 2021, 33, 10–19. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, W.X.; Liu, S.G.; Huang, W.M.; Zhang, C.J.; Zeng, X.L. Reservoir rocks characters of Silurian and its unconventional gas prospection in Western Hubei—Eastern Chongqing. J. Southwest Pet. Univ. Sci. Technol. Ed. 2012, 34, 27–37. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.J.; Zhang, W.J.; Hu, X.W.; Luo, Y.P.; Cheng, L.X. Pore structures of the Xiaoheba Formation tight sandstone reservoirs in southeastern Sichuan Basin, China. J. Chengdu Univ. Technol. 2019, 46, 70–79. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, B.; Shi, Y.S.; Sun, W.J.; Liu, Q. Reservoir forming characteristics of “the three gases” in coal measure and the possibility of commingling in China. J. China Coal Soc. 2016, 41, 167–173. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.Q.; Liu, J.; Li, L.; Kassabi, N.; Hamdi, E. Petrophysical and Geochemical Investigation-Based Methodology for Analysis of the Multilithology of the Permian Longtan Formation in Southeastern Sichuan Basin, SW China. Energies 2024, 17, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.N.; Yang, Z. Resource types, formation, distribution and prospects of coal-meas-ure gas. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2019, 46, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.H.; Wei, P.F.; Zhang, Z.; Nie, S.S.; Lou, X.Q.; Cui, K.X.; Fu, Y.W. Joint exploration and development: A self-salvation road to sustainable development of unconventional oil and gas resources. Nat. Gas Ind. 2017, 37, 126–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, R.; Kaiser, W.R.; Scott, A.R.; Hamilton, D.S.; McMurry, R.G.; Zhou, N. Geologic and Hydrologic Assessment of Natural Gas from Coal Seams in the Mesaverde Group and Fort Union Formation, Great Green River Basin, Wyoming and Colorado; Bu-reau of Economic Geology: Texas City, TX, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Olson, T.; Hobbs, B.; Brooks, R.; Gale, B. Paying off for tom brown in white river dom field’s tight sandstone, deep coals. Am. Oil Gas Rep. 2002, 10, 67–75. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.S.; Li, Z.X.; Zu, B.H. Coalbed Methane (CBM) Project Enrichment Area and Economic Evaluation. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 772, 776–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leshchyshyn, T.T.; Rieb, B.A.; Thomson, J.T. The production suc-cess of proppant stimulation on Horseshoe Canyon coal bed methane and sandstone commingled wells. In Proceedings of the Canadian Interna-Tional Petroleum Conference, Calgary, AB, Canada, 7–9 June 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Zhang, D.; Li, D.; Tang, S.; Zhang, S. Co-accumulating mechanisms of unconventional gas in the coal measure of the Qinshui Basin. J. China Coal Soc. 2018, 43, 1533–1546. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, D.Y.; Yao, Z.; Li, J. Evaluation Status and Development Trend of Unconventional Gas in Coal Measure. Coal Sci. Technol. 2014, 42, 89–92. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, J.H.; Liu, C.; Wu, J.G.; Zhang, S.R.; Yang, G.Q. Symbiotic accumulation characteristics of coal measure gas in Linxing Block, eastern Ordos Basin. J. China Coal Soc. 2018, 43, 1517–1525. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, T.S.; Zhou, X.Z.; Jin, J. Reservoir forming characteristics and co-exploration and concurrent production technology of Longtan coal measure coalbed methane & tight gas in Songhe field, western Guizhou. J. China Coal Soc. 2016, 41, 212–220. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Ren, S.; Bao, S.; Chen, K.; Guo, T.; Xu, Q. The discovery of tight gas and shale gas in Silurian strata in Jianshi, Hubei Province. Geol. China 2018, 45, 855–856. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.; Jin, C.S.; Wang, S.X.; Chen, K.; Pang, F.; Wang, P. A discovery of tight sandstone gas in relict synclinal of southeastern Chongqing. Geol. China 2017, 44, 814–815. [Google Scholar]
- SY/T 5124-2012; Method of Determining Microscopically the Reflctance of Vitrinite in Sedimentary. Petroleum Geology Exploration Standardization Committee: Beijing, China, 2012. (In Chinese)
- SY/T 5125-2014; Method of Identification Microscopically the Macerals of Kerogen and Indivision the Kerogen Type by Transmitted-Light and Fluorescence. Petroleum Geology Exploration Standardization Committee: Beijing, China, 2014. (In Chinese)
- GB/T 18602-2012; Rock Pyrolysis Analysis. Chinese Standard: Beijing, China, 2012. (In Chinese)
- SY/T 5163-2010; Analysis Method for Clay Minerals and Ordinary Non-Clay Minerals in Sedimentary Rocks by the X-ray Diffraction. Petroleum Geology Exploration Standardization Committee: Beijing, China, 2010. (In Chinese)
- GB/T18295-2001; Analysis Method of Sandstone Sample of Petroleum and Gas Reservoir by Scanning Electron Microscope. Chinese Standard: Beijing, China, 2001. (In Chinese)
- GB/T 17359-2012; Microbeam Analysis—Quantitative Analysis Using Energy Dispersive Spectrometry. Chinese Standard: Beijing, China, 2012. (In Chinese)
- GB/T 29172-2012; Practices for Core Analysis. Chinese Standard: Beijing, China, 2012. (In Chinese)
- GB/T 17412.1~3-1998; Classification and Nomenclature Schemes of the Rocks Classification and Nomenclature Schemes of Igneous Rock. Chinese Standard: Beijing, China, 1998. (In Chinese)
- GB/T 21650.1-2008; Pore Size Distribution and Porosity of Solid Materials by Mercury Porosimetry and Gas Adsorption-Part 1:Mercury Porosimetry. Chinese Standard: Beijing, China, 2008. (In Chinese)
- Yan, D.; Wang, H.; Fu, Q.; Chen, Z.; He, J.; Gao, Z. Geochemical characteristics in the Longmaxi Formation(Early Silurian) of South China: Implication for organic matter accumulation. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2015, 65, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.N.; Dong, D.Z.; Wang, Y.M.; Li, X.; Huang, J.; Wang, S.; Guan, Q.; Zhang, C.; Wang, H.; Liu, H.; et al. Shale gas in China: Characteristics, challenges and prospects (I). Pet. Explo-Ration Dev. 2015, 42, 753–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.G.; Guo, T.L.; Bian, L.Z.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, Z. Some Progresses on Studies of Hydrocarbon Generation and Accumulation in Marine Sedimentary Regions, Southern China (Part 3): Controlling Factors on the Sedimentary Facies and Development of Palaeozoic Marine Source Rocks. Mar. Orig. Pet. Geol. 2009, 14, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Jiao, W.; Fang, G.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Q. Geochemical features and genesis of shale gas of Wufeng-Longmaxi Formation in Southeastern Chongqing. Mar. Orig. Pet. Geol. 2017, 22, 77–84. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.C.; Nie, H.K.; Xu, B.; Jiang, S.L.; Zhang, P.X.; Wang, Z.Y. Geological condition of shale gas accumulation in Sichuan Baisin. Nat. Gas Ind. 2008, 172, 151–156. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, H.K.; Zhang, J.C. Shale gas accumulation condition and gas content calculation: A case study of Sichuan Basin and its periphery in the Lower Paleozoic. Acta Geol. Sin. 2012, 86, 349–361. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.; Zhang, J.C.; Liu, Z.J.; Li, L.Z. Use and improvement of the desorption method in shale gas content tests. Nat. Gas Ind. 2011, 31, 108–112. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, T.L.; Zhang, H.R. Formation and enrichment mode of Jiaoshiba shale gas field, Sichuan Basin. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2014, 41, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.Y.; Yang, Z.Q.; Xiang, K.P.; Huang, Y.; Chen, H.G.; He, Y.Z.; Liu, W.; Yu, Q. The geochemical characteristics and significance of the Ordovician—Silurian black shale in northern Guizhou—A case study of the Well Daoye-1 in Daozhen County. Geol. Rev. 2021, 67, 1105–1118. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.J.; Chen, H.D. An analysis of sedimentary characteristics and model of Silurian Xiaoheba Formation in southeastern Sichuan Province. Geol. China 2012, 39, 64–76. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, D.; Shi, Z.Q.; Zhang, X.; Li, C. Characteristics of contourites in the Lower Silurian in southeastern Sichuan Basin, China. J. Palaeogeogr. 2023, 25, 856–871. [Google Scholar]
- Woodworth, J.B. On the fracture system of joints with remarks on certain great fractures. Proc. Boston Soc. Nat. Hist. 1896, 27, 163–183. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, G.H., Jr. Quantitative fracture study: Sanish Pool, Mckenzie County, North Dakota. AAPG Bull. 1968, 52, 57–65. [Google Scholar]
- Curtis, J.B. Fractured Shale-Gas Systems. AAPG Bull. 2002, 86, 1921–1938. [Google Scholar]
- Gale, J.F.; Laubach, S.E.; Olson, J.E.; Eichhubl, P.; Fall, A. Natural fractures in shale: A review and new observations. AAPG Bull. 2014, 98, 2165–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.J.; Zeng, L.B.; Shi, X.W.; Wu, W.; Tian, H.; Xue, M.; Luo, L. Characteristics and Main Controlling Factors of Natural Fractures in Marine Shale in Luzhou Area, Sichuan Basin. Earth Sci. 2023, 48, 2630–2642. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).