Three-Dimensionally Printed Metal-Coated Flow-Field Plate for Lightweight Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
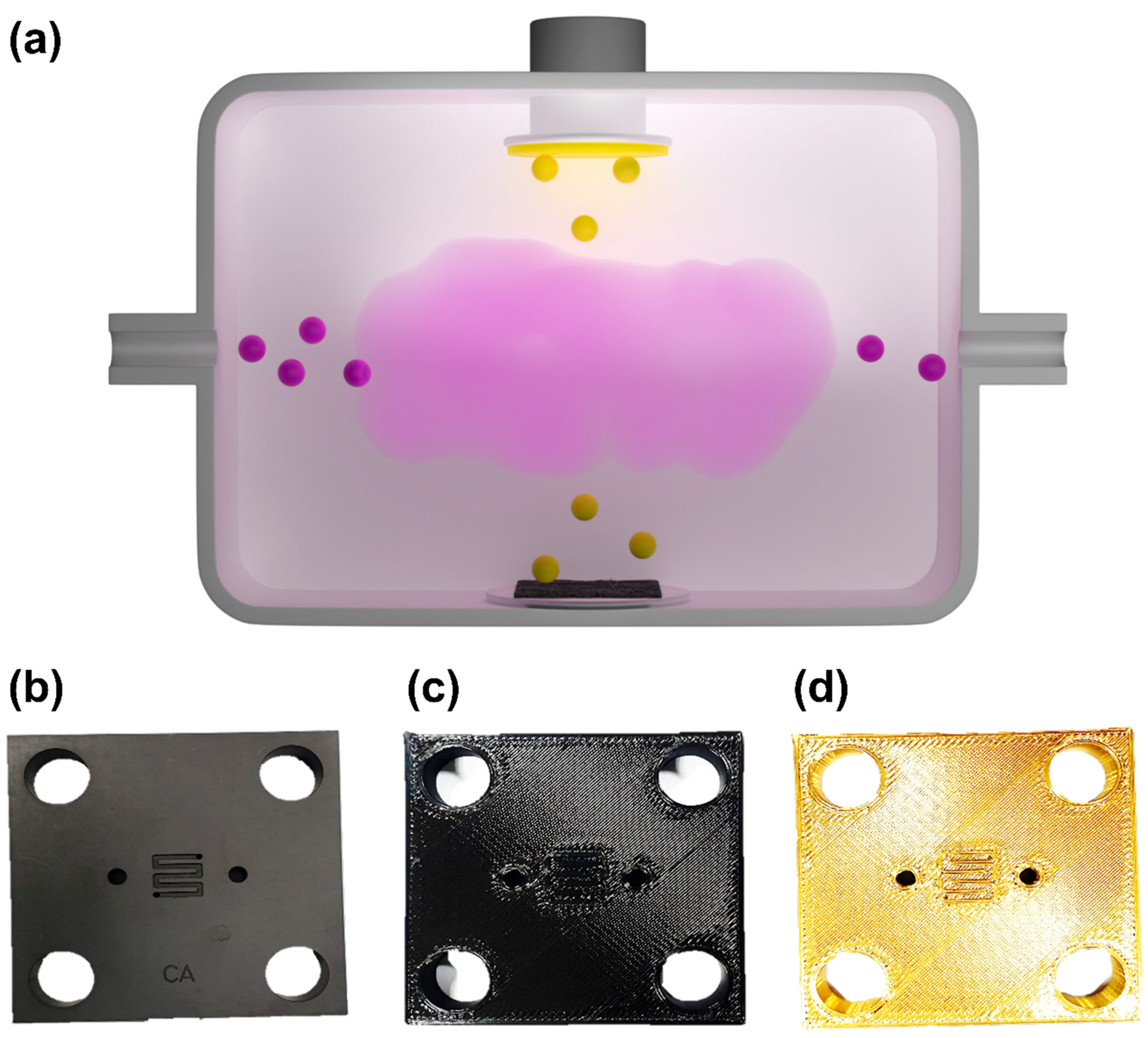
2. Materials and Methods
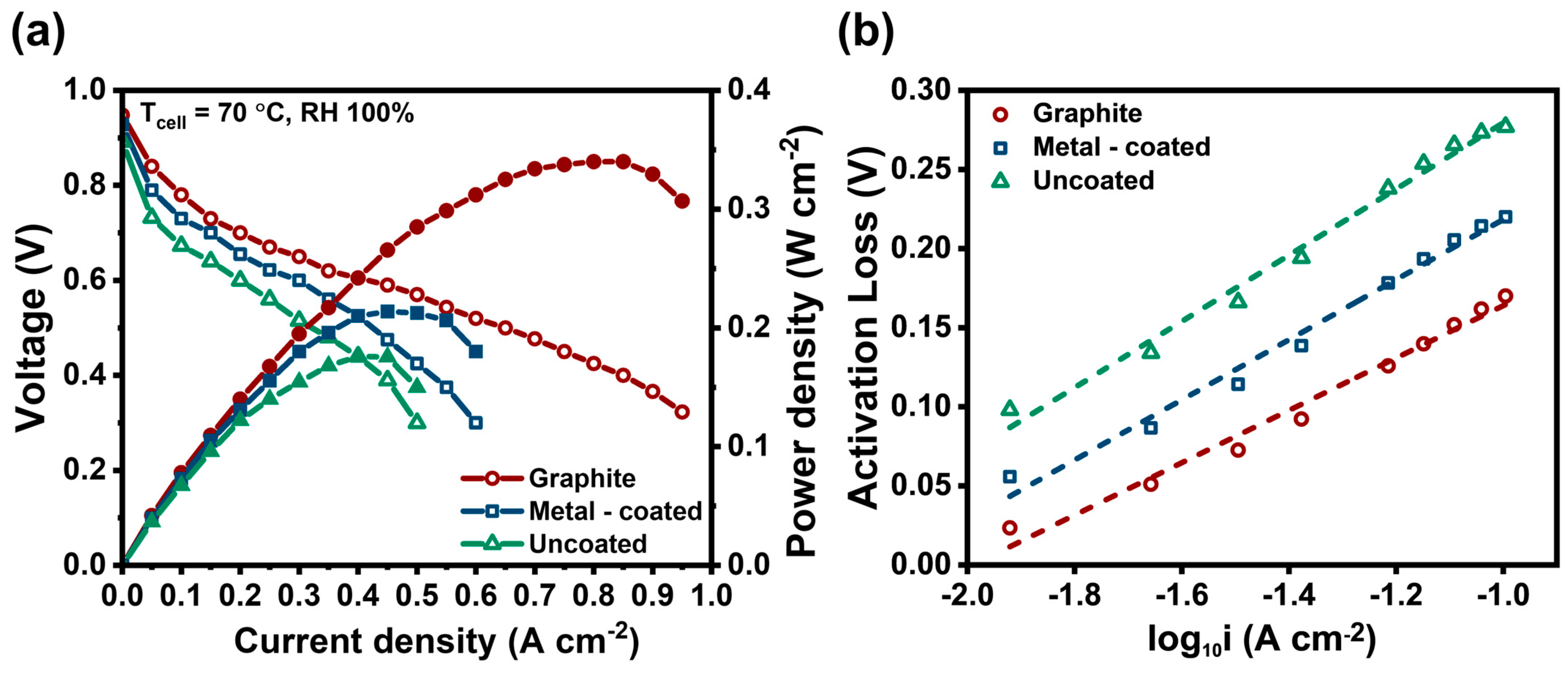
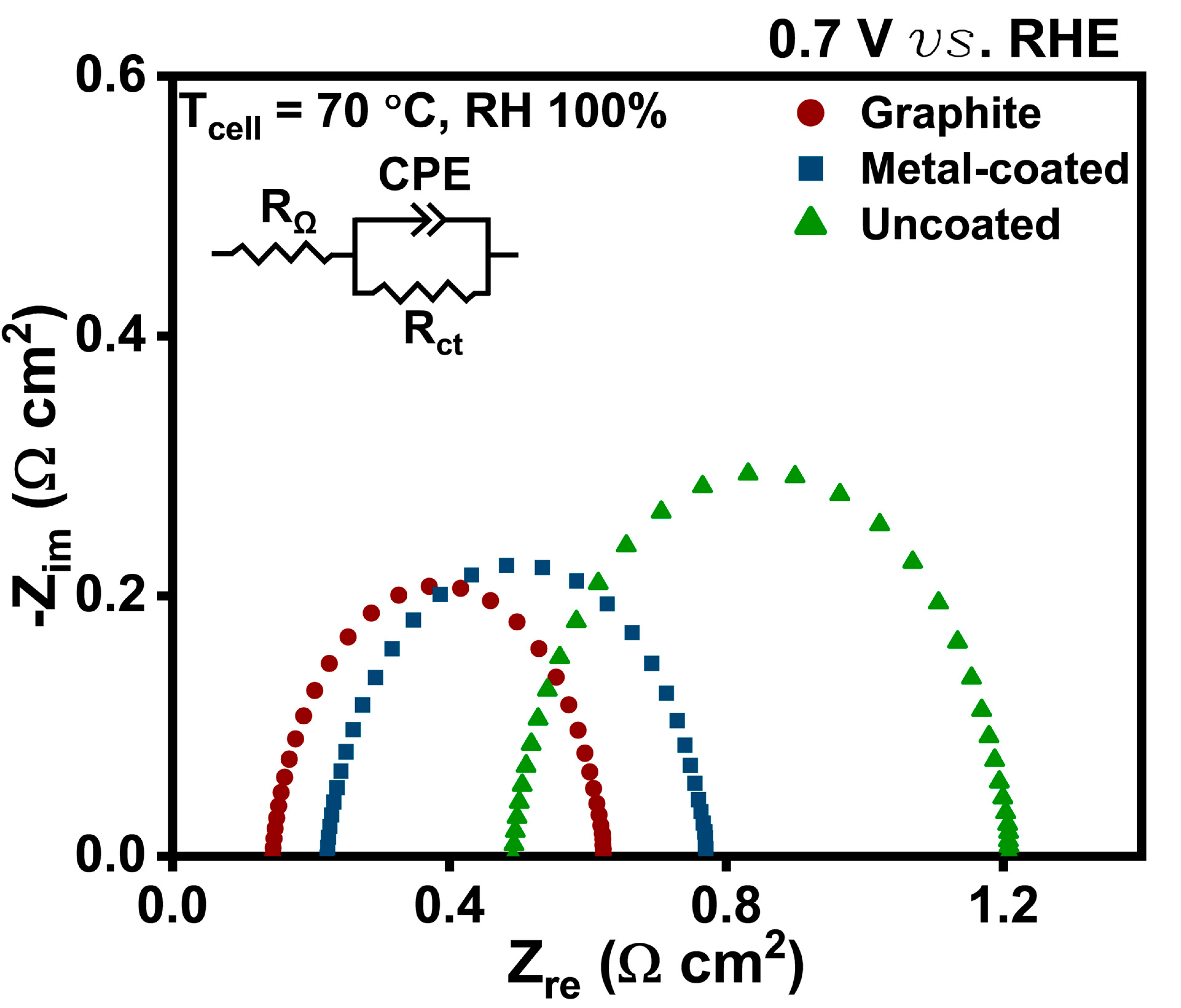
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, D.J.; Jo, M.J.; Nam, S.Y. A review of polymer–nanocomposite electrolyte membranes for fuel cell application. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 21, 36–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, K.S.; Mishler, J.; Cho, S.C.; Adroher, X.C. A review of polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells: Technology, applications, and needs on fundamental research. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 981–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, C.; Knöri, T.; Ribeirinha, P.; Gazdzicki, P. A review on flow field design for proton exchange membrane fuel cells: Challenges to increase the active area for MW applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2024, 192, 114198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parekh, A. Recent developments of proton exchange membranes for PEMFC: A review. Front. Energy Res. 2022, 10, 956132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraytsberg, A.; Ein-Eli, Y. Review of advanced materials for proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Energy Fuels 2014, 28, 7303–7330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Nawaz, T.; Ali, A.; Orhan, M.F.; Samreen, A.; Kannan, A.M. An overview of proton exchange membranes for fuel cells: Materials and manufacturing. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 19086–19131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchiya, H.; Kobayashi, O. Mass production cost of PEM fuel cell by learning curve. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2004, 29, 985–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Chen, J.; Xu, R.; Zhen, Z.; Zeng, X.; Chen, X.; Cui, L. Research progress and prospect of the materials of bipolar plates for proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs). Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 50, 711–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brakni, O.; Kerkoub, Y.; Amrouche, F.; Mohammedi, A.; Ziari, Y.K. CFD investigation of the effect of flow field channel design based on constriction and enlargement configurations on PEMFC performance. Fuel 2024, 357, 129920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasabehi, M.; Jabbary, A.; Shams, M. Cathode side transport phenomena investigation and Multi-Objective optimization of a tapered parallel flow field PEMFC. Energy Convers. Manag. 2022, 265, 115761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafi, M.; Shams, M. The effects of flow-field orientation on water management in PEM fuel cells with serpentine channels. Appl. Energy 2017, 208, 1083–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauermoser, M.; Kizilova, N.; Pollet, B.G.; Kjelstrup, S. Flow field patterns for proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Front. Energy Res. 2020, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafi, M.; Kanani, H.; Shams, M. Numerical and experimental study of two-phase flow uniformity in channels of parallel PEM fuel cells with modified Z-type flow-fields. Energy 2018, 147, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Turner, J. Reviewing metallic PEMFC bipolar plates. Fuel Cells 2010, 10, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Qiu, D.; Yi, P.; Peng, L.; Lai, X. Towards mass applications: A review on the challenges and developments in metallic bipolar plates for PEMFC. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2020, 30, 815–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermann, A.; Chaudhuri, T.; Spagnol, P. Bipolar plates for PEM fuel cells: A review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2005, 30, 1297–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’hayre, R.; Cha, S.-W.; Colella, W.; Prinz, F.B. Fuel Cell Fundamentals; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Yang, W.; Yan, H.; Zuo, X.; Cao, Z.; Li, H.; Shi, M.; Chen, H. A review of modified metal bipolar plates for proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 8672–8701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Sabir, I. Review of bipolar plates in PEM fuel cells: Flow-field designs. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2005, 30, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Qu, Z.; Yang, H.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, C. Collective enhancements on thermal-electrical and mechanical properties of graphite-based composite bipolar plates through the coupled manipulations of molding and impregnation pressures. Membranes 2022, 12, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, K.I.; Oh, J.; Song, S.A.; Lee, D.; Kim, S.S. A review of composite bipolar plates in proton exchange membrane fuel cells: Electrical properties and gas permeability. Compos. Struct. 2021, 262, 113617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitchiya, A.P.; Le, N.-T.; Putnam, Z.A.; Harrington, M.; Krishnan, S. Microporous graphite composites of tailorable porosity, surface wettability, and water permeability for fuel cell bipolar plates. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 10203–10216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenkai, L.; Zhiyong, X.; Haodong, Z. Current status of research on composite bipolar plates for proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs): Nanofillers and structure optimization. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 7172–7194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, Y.; Tawfik, H.; Mahajan, D. Effect of terminal design and bipolar plate material on PEM fuel cell performance. Smart Grid Renew. Energy 2013, 4, 28123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Xie, Z.; Qiu, S.; Zeng, H.; Liu, M.; Wu, G. Improved performance of composite bipolar plates for PEMFC modified by homogeneously dispersed multi-walled carbon nanotube networks prepared by in situ chemical deposition. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickmann, T.; Zielinski, O. Bipolar Plates: Different Materials and Processing Methods for Their Usage in Fuel Cells. E3S Web of Conf. 2020, 160, 01002. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.H.; Lim, J.W.; Kim, M. Development of carbon fabric/graphite hybrid bipolar plate for PEMFC. Compos. Struct. 2013, 98, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiki, T.; Accary, G.; Charon, W.; Kouta, R. Influence of Local Porosity, Local Permeability, and Contact Resistance Between the Gas Diffusion Layer and the Bipolar Plate, on the Performances of a Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cell. In Proceedings of the CCCA12, Marseille, France, 6–8 December 2012; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, C.-Y.; Chen, S.-K.; Chiu, P.-J.; Chang, M.-H.; Hung, T.-T.; Ko, T.-H. Carbon film-coated 304 stainless steel as PEMFC bipolar plate. J. Power Sources 2008, 176, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakate, S.; Mathur, R.; Kakati, B.; Dhami, T. Properties of graphite-composite bipolar plate prepared by compression molding technique for PEM fuel cell. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2007, 32, 4537–4543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.-D.; Chiou, A.-H. The study on a new method of preparing PMMA forming composite bipolar plate. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, G.-E.; Cho, G.-Y. Effects of Ag current collecting layer fabricated by sputter for 3D-printed polymer bipolar plate of ultra-light polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balogh, M.P.; Dadheech, G.V.; Irish, N.P.; Tessema, M.M.; Miller, D.P.; Abd Elhamid, M.H. Method of Depositing Durable Thin Gold Coating on Fuel Cell Bipolar Plates. U.S. Patent No. 8,778,562, 15 July 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Dorjgotov, A.; Jeon, Y.; Hwang, J.; Ulziidelger, B.; Kim, H.S.; Han, B.; Shul, Y.-G. Synthesis of durable small-sized bilayer Au@ Pt nanoparticles for high performance PEMFC catalysts. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 228, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinoiu, A.; Andrulevicius, M.; Tamuleviciene, A.; Tamulevicius, T.; Raceanu, M.; Varlam, M. Synthesis of well dispersed gold nanoparticles on reduced graphene oxide and application in PEM fuel cells. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 504, 144511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.-Q.; Wu, Y.-M.; Su, S.; Shi, D.-D.; Wang, X.-Z.; Behnamian, Y.; Zhang, J.-Y.; Li, Q. Solution acidity and temperature induced anodic dissolution and degradation of through-plane electrical conductivity of Au/TiN coated metal bipolar plates used in PEMFC. Energy 2022, 254, 124453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinoiu, A.; Raceanu, M.; Andrulevicius, M.; Tamuleviciene, A.; Tamulevicius, T.; Nica, S.; Bala, D.; Varlam, M. Low-cost preparation method of well dispersed gold nanoparticles on reduced graphene oxide and electrocatalytic stability in PEM fuel cell. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 3585–3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Schwartzkopf, M.; Roth, S.V.; Müller-Buschbaum, P. State of the art of ultra-thin gold layers: Formation fundamentals and applications. Nanoscale Adv. 2022, 4, 2533–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivera, S.; Muralidhara, H.B.; Venkatesh, K.; Gopalakrishna, K.; Vivek, C.S. Plating on acrylonitrile–butadiene–styrene (ABS) plastic: A review. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 3657–3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronell, D.; Egan, E.; Hamilton, G.; Jain, A.; Venkatraman, R.; Weitzman, B. Monte Carlo simulations of sputter deposition and step coverage of thin films. Thin Solid Film. 1998, 333, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callister, W.D.; Rethwisch, D.G. Materials Science and Engineering: An Introduction; Wiley New York: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, C.; Loh, N.; Khor, K.; Tor, S. Sintering study of 316L stainless steel metal injection molding parts using Taguchi method: Final density. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2001, 311, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari-Rarani, M.; Rafiee-Afarani, M.; Zahedi, A. Mechanical characterization of FDM 3D printing of continuous carbon fiber reinforced PLA composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 175, 107147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, G.Y.; Lee, Y.H.; Hong, S.W.; Bae, J.; An, J.; Kim, Y.B.; Cha, S.W. High-performance thin film solid oxide fuel cells with scandia-stabilized zirconia (ScSZ) thin film electrolyte. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 15704–15708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-H. Surface roughness effect on the metallic bipolar plates of a proton exchange membrane fuel cell. Appl. Energy 2013, 104, 898–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bard, A.J.; Faulkner, L.R.; White, H.S. Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Blunk, R.; Zhong, F.; Owens, J. Automotive composite fuel cell bipolar plates: Hydrogen permeation concerns. J. Power Sources 2006, 159, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, D.; Kim, G.; Na, J.; Kim, H.; Kim, J.; Cho, G.; Park, T. Three-Dimensionally Printed Metal-Coated Flow-Field Plate for Lightweight Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells. Energies 2025, 18, 1533. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18061533
Kim D, Kim G, Na J, Kim H, Kim J, Cho G, Park T. Three-Dimensionally Printed Metal-Coated Flow-Field Plate for Lightweight Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells. Energies. 2025; 18(6):1533. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18061533
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Dasol, Geonhwi Kim, Juho Na, Hyeok Kim, Jaeyeon Kim, Guyoung Cho, and Taehyun Park. 2025. "Three-Dimensionally Printed Metal-Coated Flow-Field Plate for Lightweight Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells" Energies 18, no. 6: 1533. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18061533
APA StyleKim, D., Kim, G., Na, J., Kim, H., Kim, J., Cho, G., & Park, T. (2025). Three-Dimensionally Printed Metal-Coated Flow-Field Plate for Lightweight Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells. Energies, 18(6), 1533. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18061533






