A VSG Power Decoupling Control with Integrated Voltage Compensation Schemes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
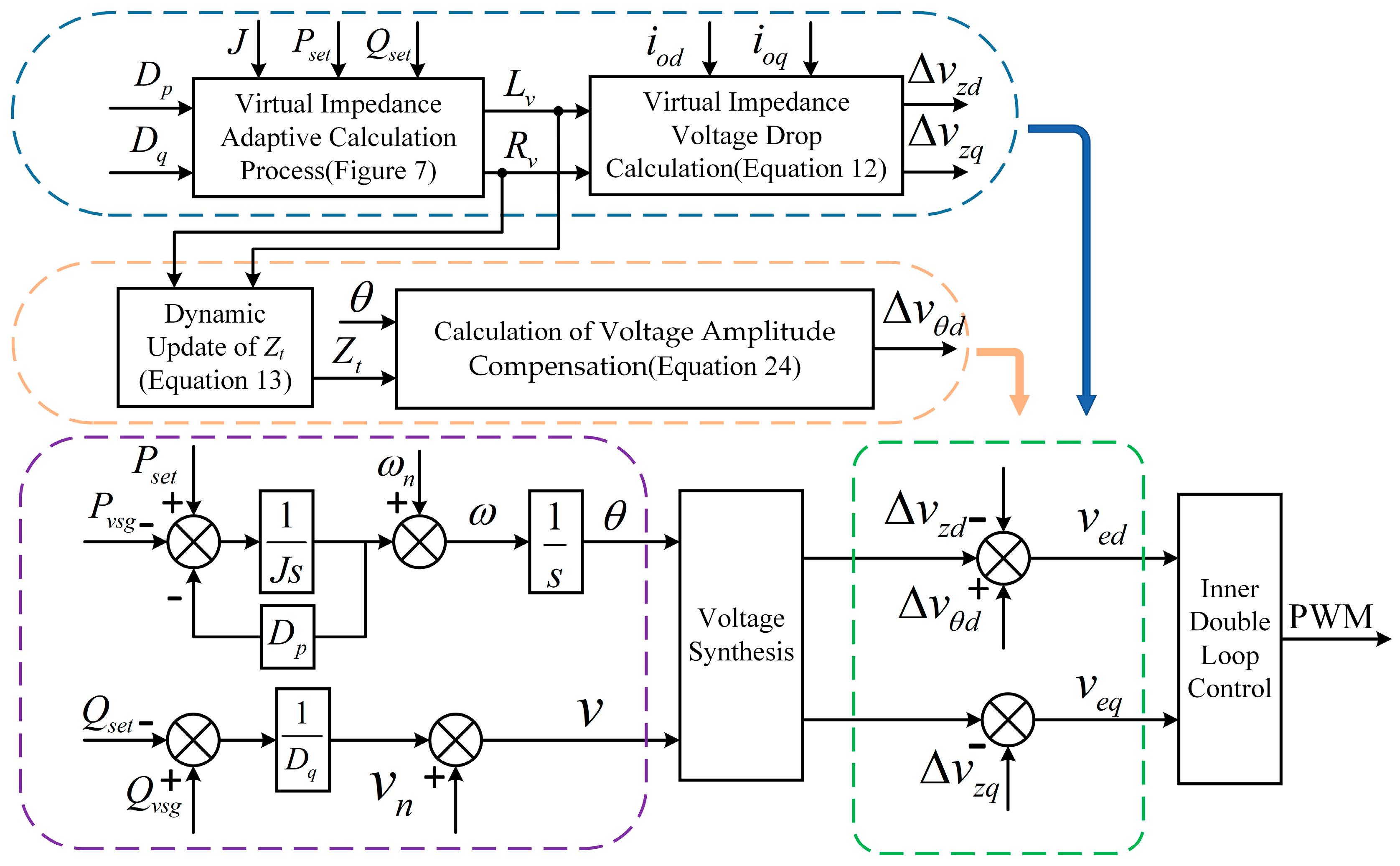
- It introduces the voltage compensation term from virtual resistance and inductance, which are made adaptive to varying operating points by the proposed online parameter adjustments.
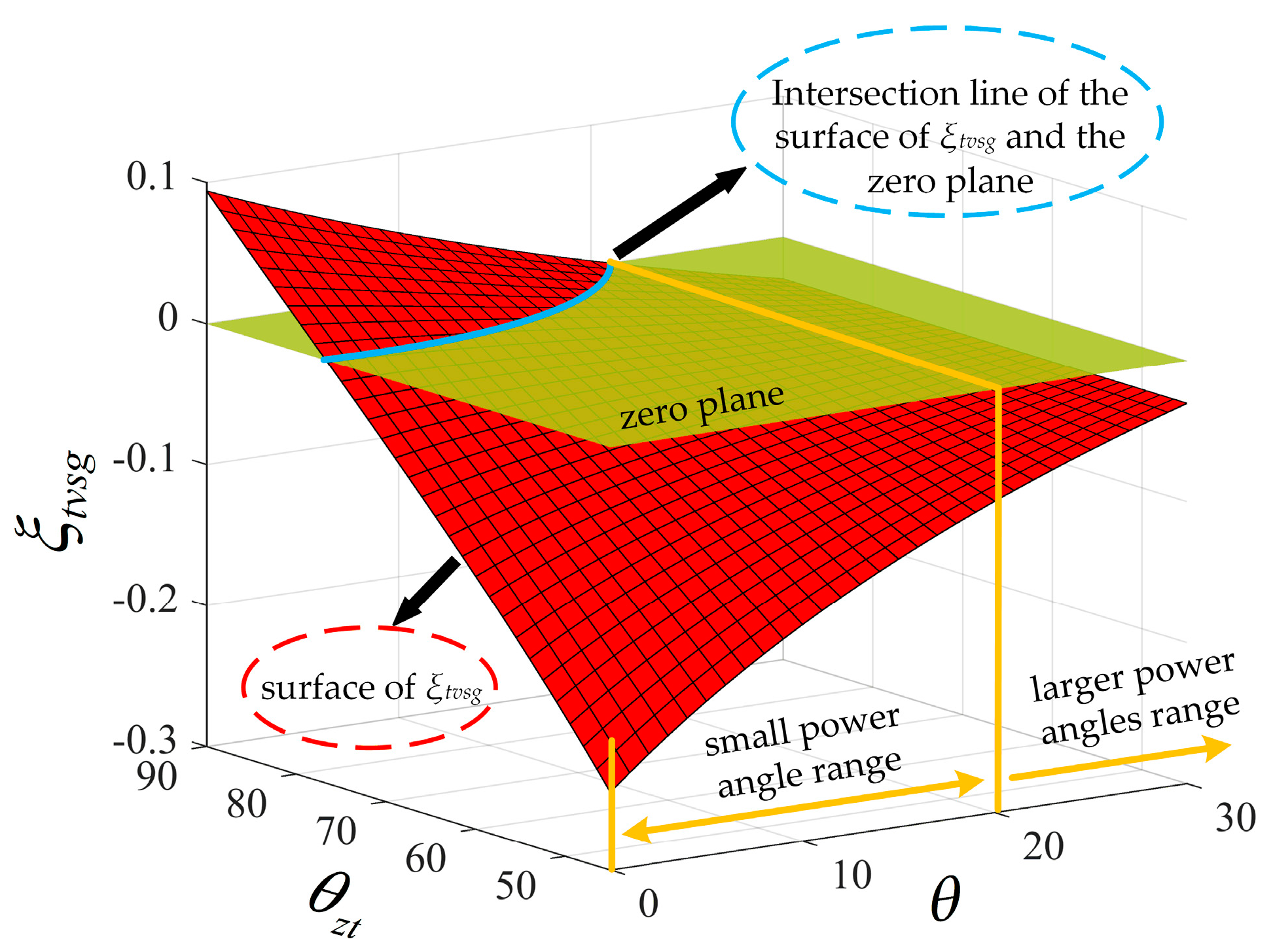
- It is further discovered that total power decoupling limits the full operating range. Therefore, an additional voltage compensation term, Δvθd, in terms of power angle variations, is proposed to eliminate the power coupling at high power ranges.
- The two proposed voltage compensation schemes are seamlessly integrated so that total VSG power decoupling can be achieved.
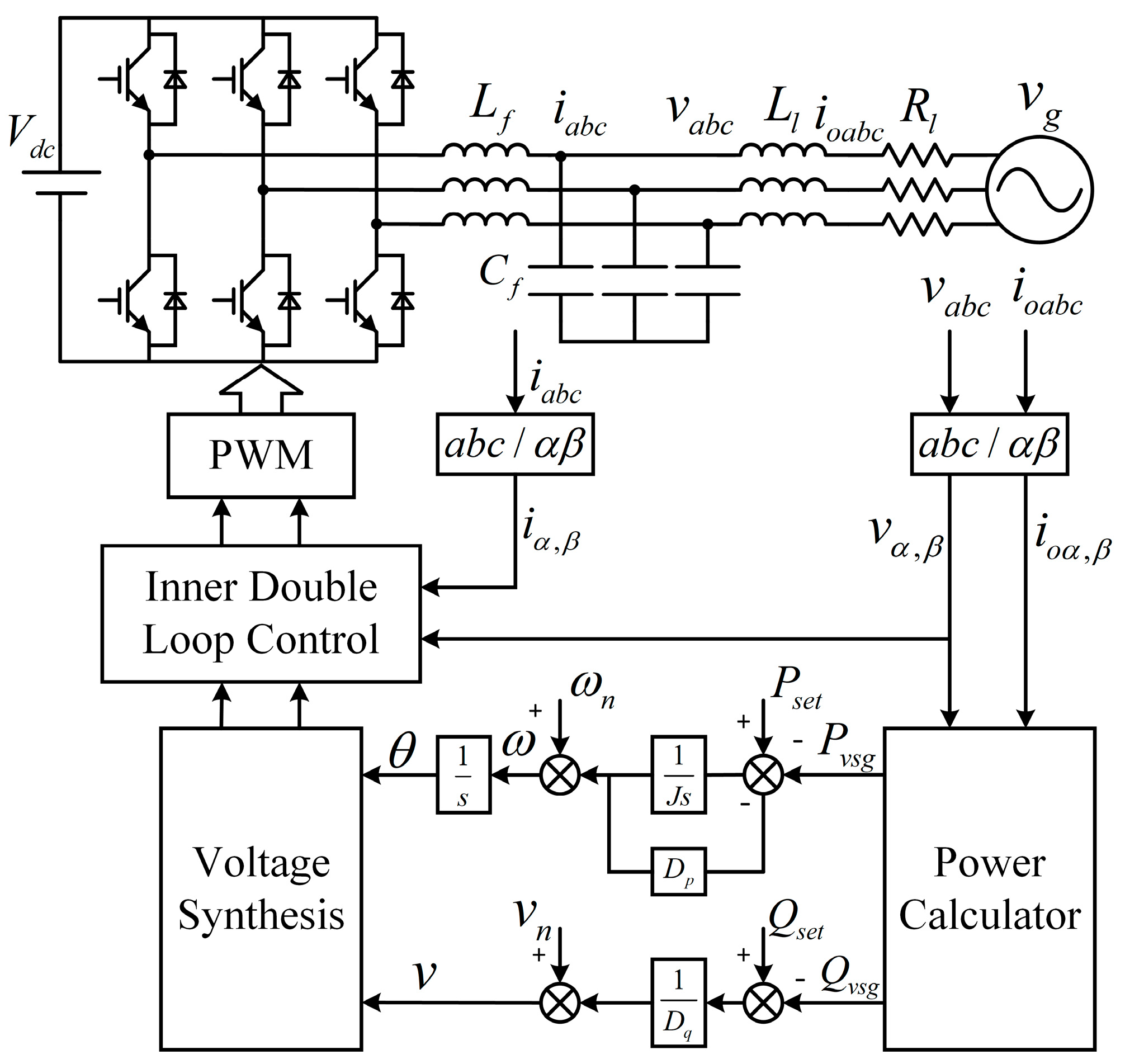
2. VSG Model and Power Coupling Analysis
3. Proposed VSG Power Decoupling Control with Integrated Voltage Compensation Schemes
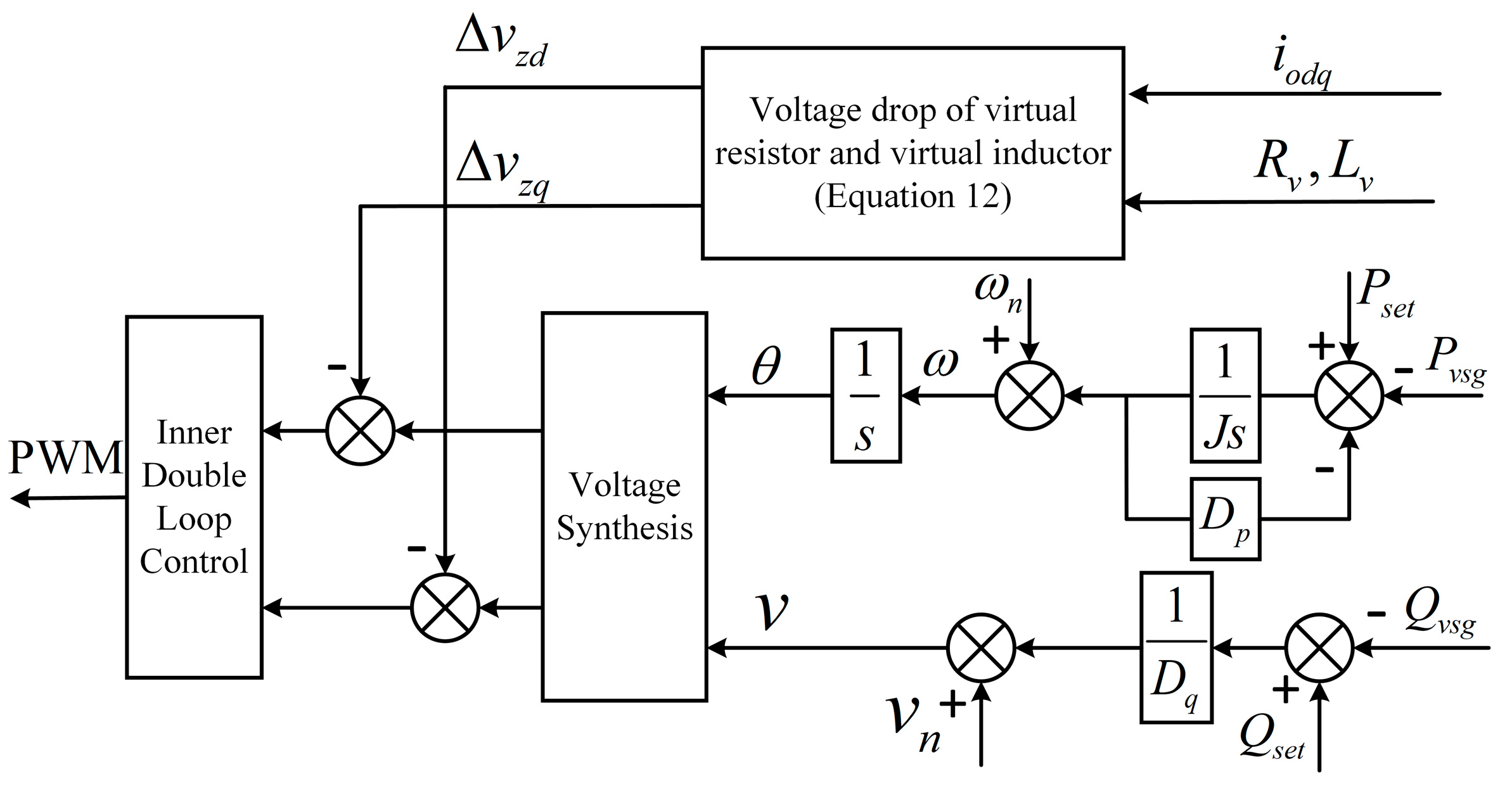
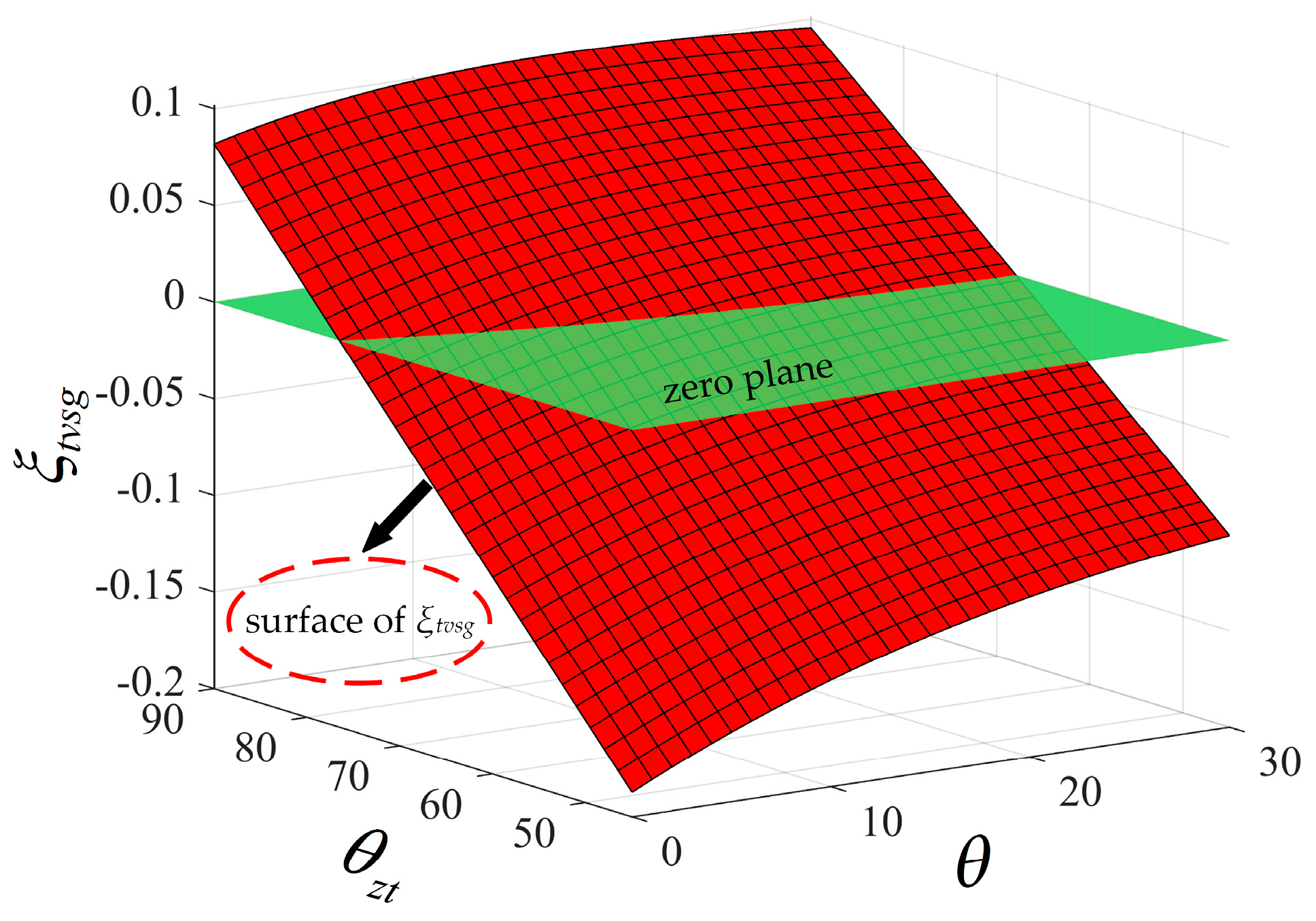
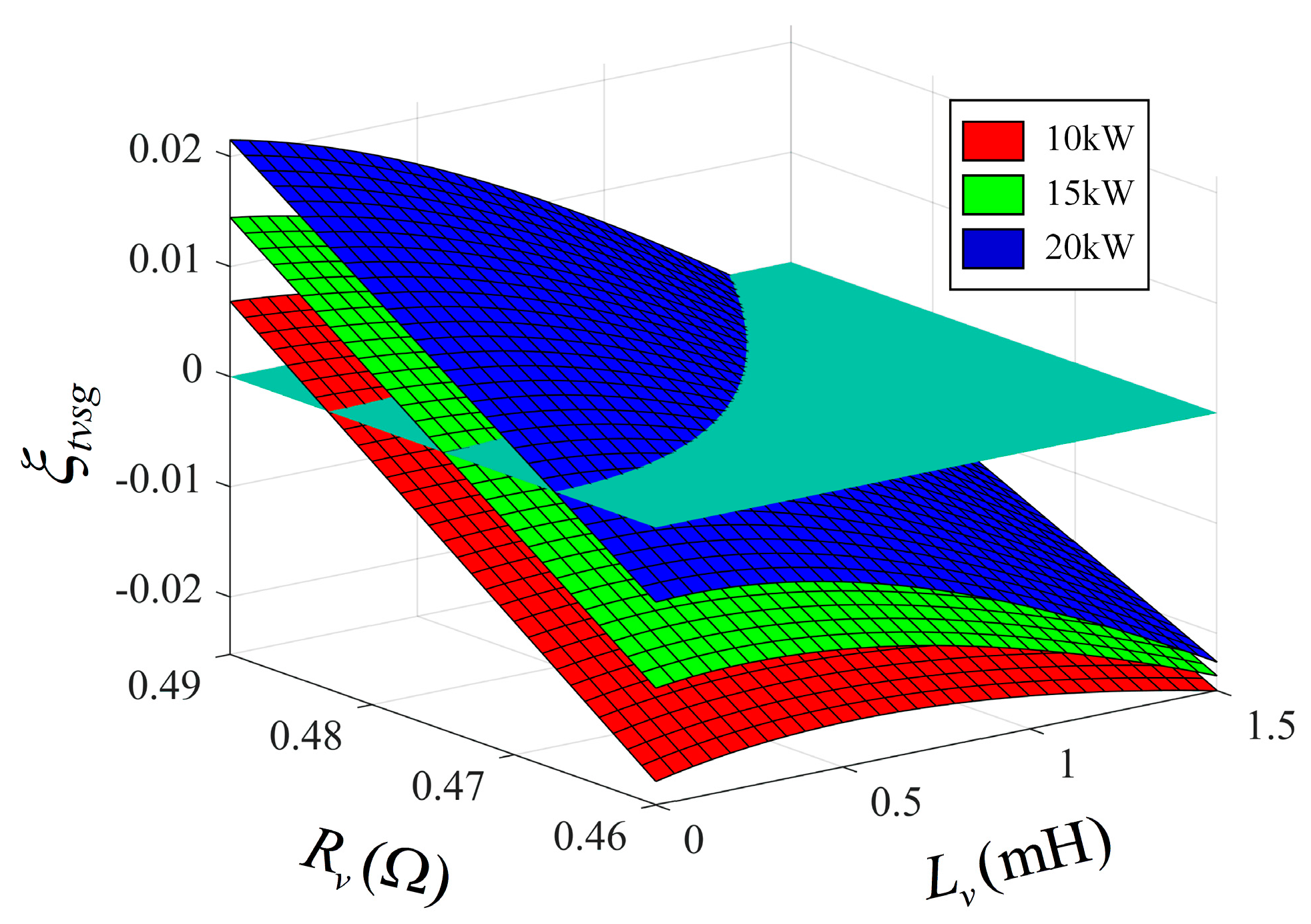
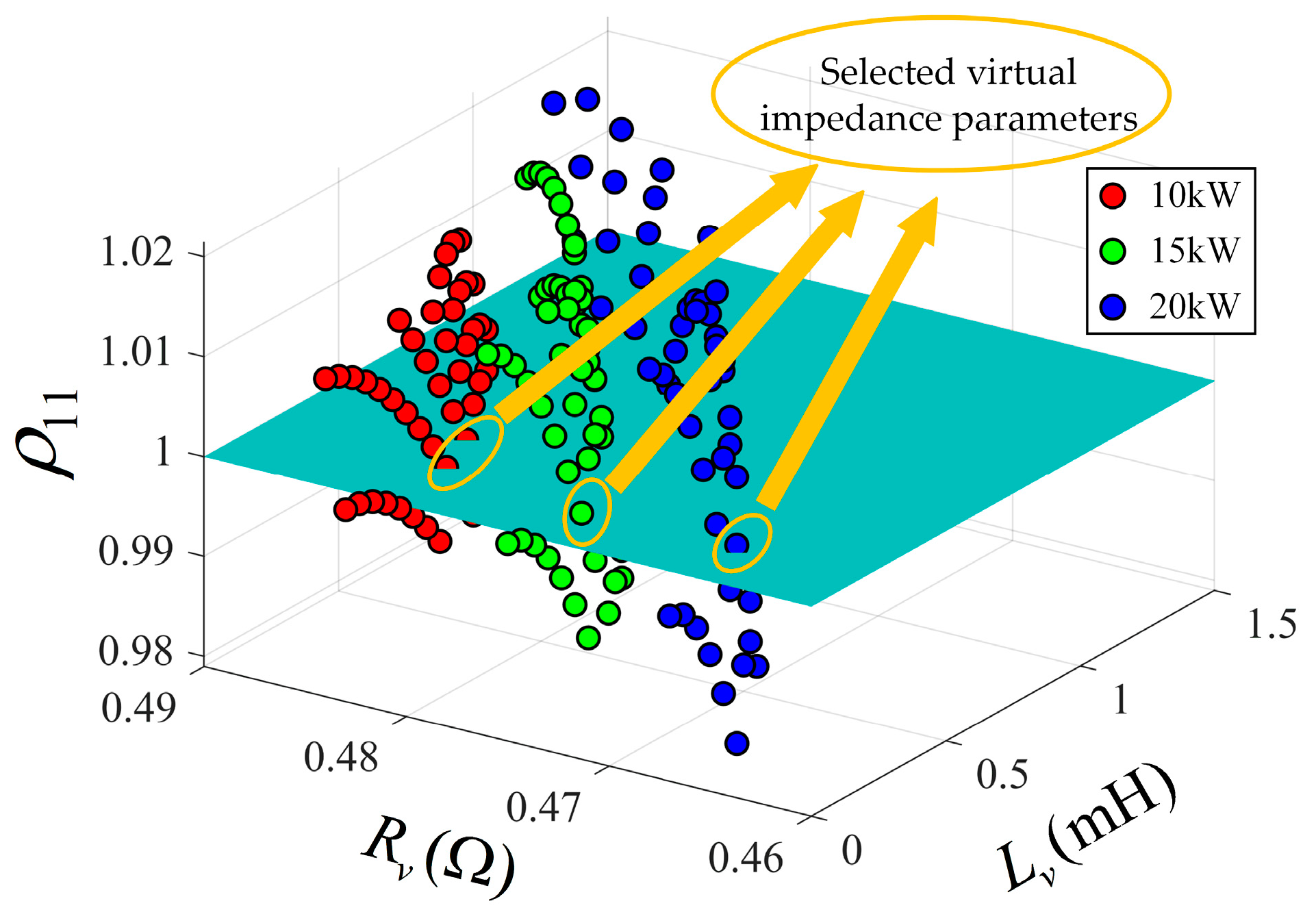
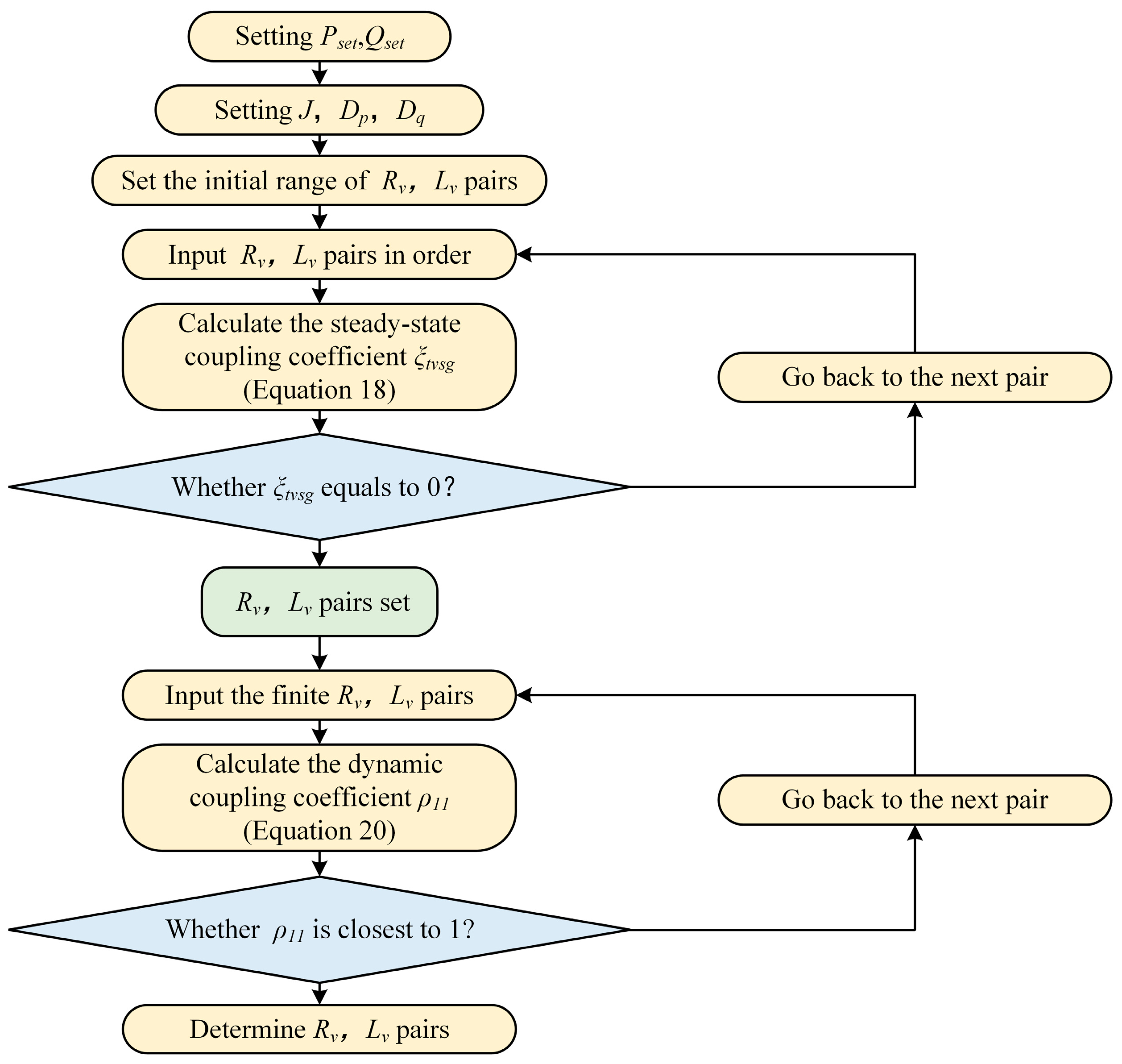
3.1. Proposed Voltage Compensation by Adaptive Virtual Impedance Control
3.2. Integation of Additional Voltage Compensation Term for Power Angle Variations
4. Experimental Verification
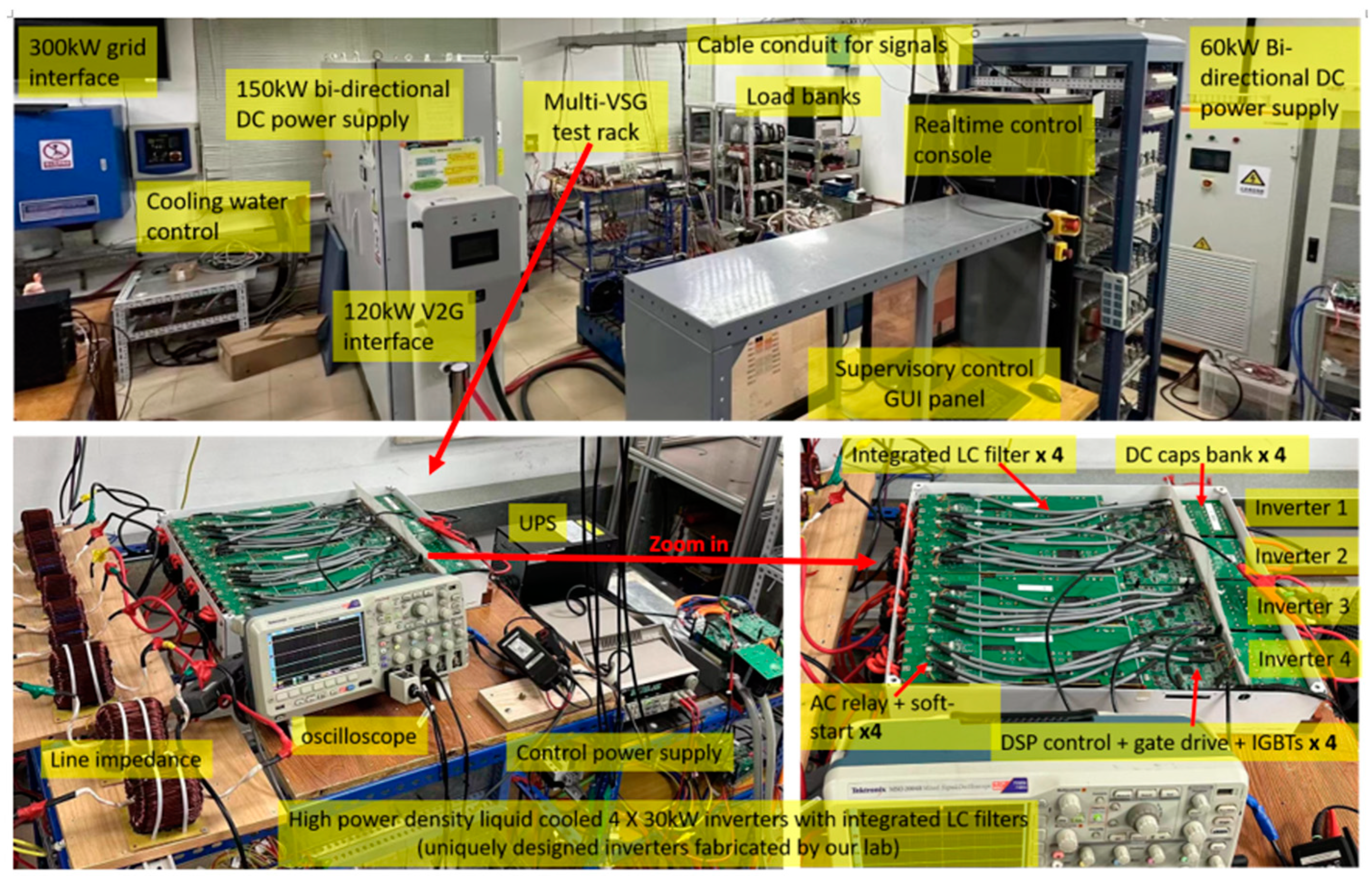
4.1. Experimental Platform
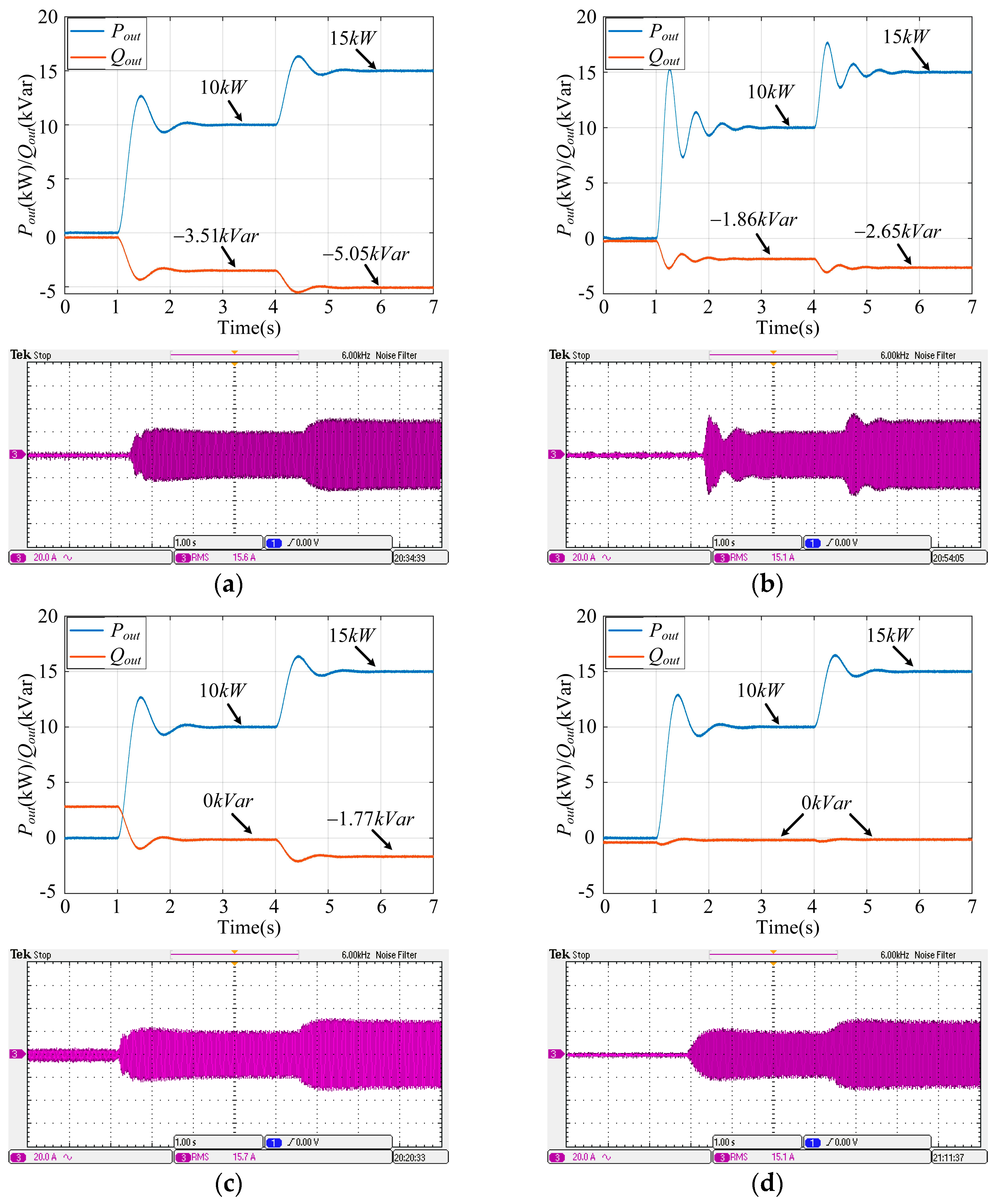
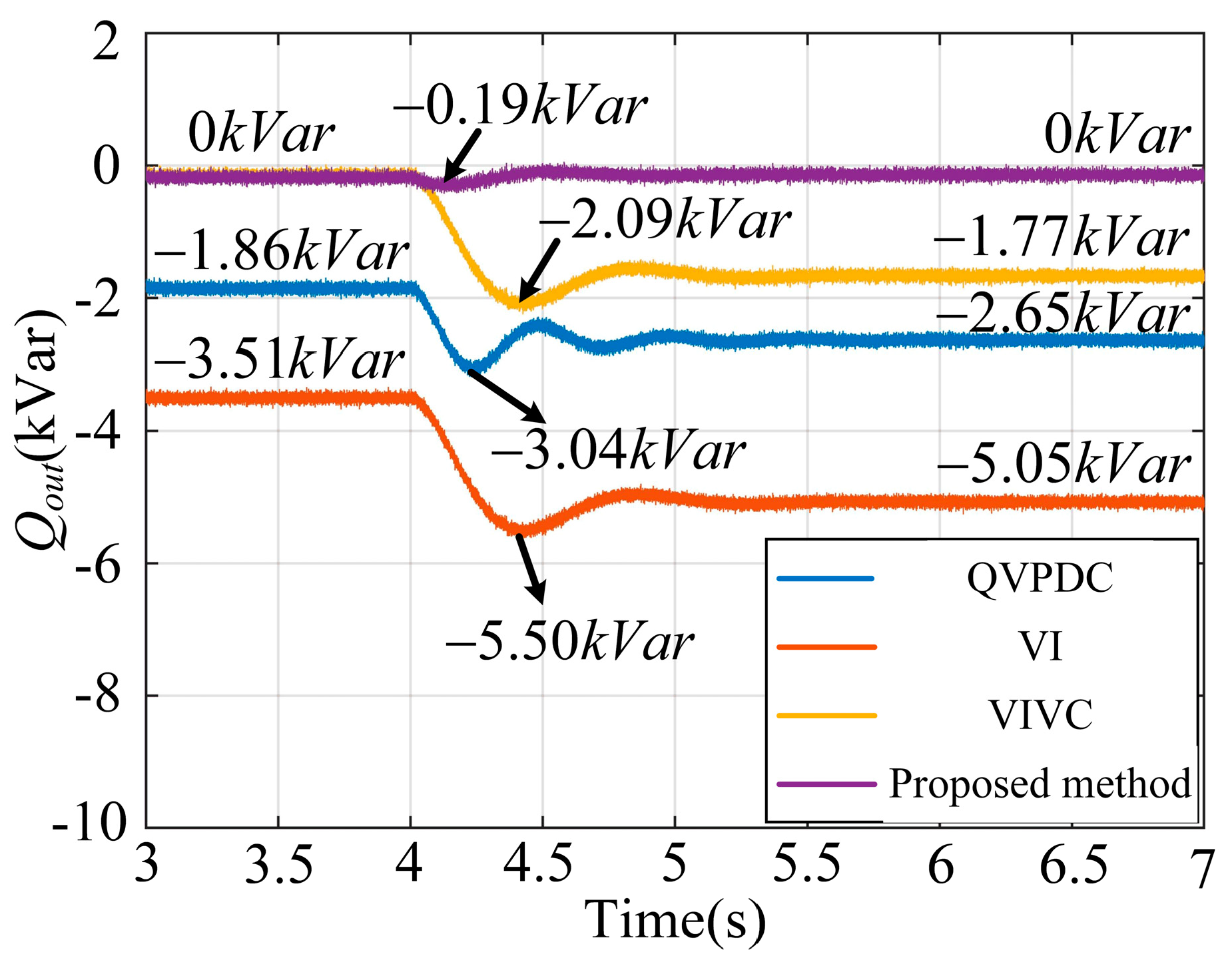
4.2. Experimental Results and Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| APL | Active power loop |
| DESs | Distributed energy sources |
| GCCs | Grid-connected converters |
| MIMO | Multiple-input multiple-output |
| QVPDC | q-axis voltage drop-based power decoupling control |
| RPL | Reactive power loop |
| VI | Virtual inductor |
| VIVC | Virtual inductor and virtual capacitor virtual inductor |
| VSG | Virtual synchronous generator |
References
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, N.; Du, E. Review and Countermeasures on Frequency Security Issues of Power Systems with High Shares of Renewables and Power Electronics. Proc. CSEE 2022, 42, 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Cespedes, M.; Sun, J. Impedance Modeling and Analysis of Grid-Connected Voltage-Source Converters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 1254–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Harnefors, L.; Nee, H. Power-Synchronization Control of Grid-Connected Voltage-Source Converters. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2010, 25, 809–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Miura, Y.; Ise, T. Comparison of Dynamic Characteristics Between Virtual Synchronous Generator and Droop Control in Inverter-Based Distributed Generators. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 3600–3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Ruan, X.; Yang, D.; Chen, X.; Zhao, W.; Lv, Z.; Zhong, Q.C. Small-Signal Modeling and Parameters Design for Virtual Synchronous Generators. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 4292–4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Liu, J.; Liu, Z. A Generalized Droop Control for Grid-Supporting Inverter Based on Comparison Between Traditional Droop Control and Virtual Synchronous Generator Control. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 5416–5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Zhao, J.; Zeng, Z.; Mao, L.; Qu, K. Enhanced Power Decoupling Strategy for VSG with Power Control Based on Virtual Power Angle. Proc. CSEE 2024, 44, 8808–8819. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Kao, C. An Accurate Power Control Strategy for Power-Electronics-Interfaced Distributed Generation Units Operating in a Low-Voltage Multibus Microgrid. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2009, 24, 2977–2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Zhang, Y. Power coupling analysis of inverters based on relative gain method and decoupling control based on feedforward compensation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Renewable Power Generation (RPG 2015), Beijing, China, 17–18 October 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Zhou, L.; Yu, X.; Zheng, C.; Liu, J. Improved power decoupling control strategy based on virtual synchronous generator. IET Power Electron. 2017, 10, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, B.; Boroyevich, D.; Mattavelli, P.; Burgos, R.; Shen, Z. Impedance-based analysis of grid-synchronization stability for three-phase paralleled converters. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition—APEC, Fort Worth, TX, USA, 16–20 March 2014; pp. 1233–1239. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, T.; Zou, X.; Guo, X.; Zhu, D.; Peng, L.; Wang, X. Feedforward Compensation Control for Virtual Synchronous Generator to Improve Power Decoupling Capability. In Proceedings of the 14th IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications (ICIEA), Xi’an, China, 19–21 June 2019; pp. 2528–2533. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Raheja, U. An Optimized Virtual Synchronous Generator Control Strategy for Power Decoupling in Grid Connected Inverters. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Baltimore, MD, USA, 29 September–3 October 2019; pp. 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, W.; Xu, Z.; Gerada, C. Dynamic power decoupling for low-voltage ride-through of grid-forming inverters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 37, 3878–3891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wai, R. Adaptive Fuzzy-Neural-Network Power Decoupling Strategy for Virtual Synchronous Generator in Micro-Grid. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 37, 3878–3891. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Davari, M.; Blaabjerg, F. An Effective PQ-Decoupling Control Scheme Using Adaptive Dynamic Programming Approach to Reducing Oscillations of Virtual Synchronous Generators for Grid Connection with Different Impedance Types. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2024, 71, 3763–3775. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Xu, J.; Li, C. A New Virtual Inductance Control Method for Frequency Stabilization of Grid-Forming Virtual Synchronous Generators. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2023, 90, 441–451. [Google Scholar]
- Guerrero, J.; Matas, J.; De Vicuna, L.; Castilla, M.; Miret, J. Decentralized control for parallel operation of distributed generation inverters using resistive output impedance. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2007, 54, 994–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandoorn, T.; Meersman, B.; Kooning, J.; Vandevelde, L. Directly-coupled synchronous generators with converter behavior in islanded microgrids. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2012, 27, 1395–1406. [Google Scholar]
- Guerrero, J.; De Vicuna, L.; Matas, J.; Castilla, M.; Miret, J.; de Vicuna, L.G. Output impedance design of parallel-connected ups inverters with wireless load-sharing control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2005, 52, 1126–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.; Zhu, D.; Zou, X.; Jiang, B.; Peng, L.; Kang, Y. Power Coupling Mechanism Analysis and Improved Decoupling Control for Virtual Synchronous Generator. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 36, 3028–3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Cui, S.; Jia, J. Virtual steady state synchronous negative impedance of a VSG power decoupling strategy. Power Syst. Prot. Control 2020, 48, 102–113. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Wand, Y.; Liu, Y. Enhanced power decoupling strategy for virtual synchronous generator. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 73601–73613. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Shao, Y.; Yang, R.; Long, X. A Configurable Virtual Impedance Method for Grid-Connected Virtual Synchronous Generator to Improve the Quality of Output Current. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2020, 8, 2404–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, B.; Zhu, S.; Rodriguez, J.; Chong, K.T. Enhancement of Power Decoupling for Virtual Synchronous Generator: A Virtual Inductor and Virtual Capacitor Approach. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2023, 70, 6830–6843. [Google Scholar]
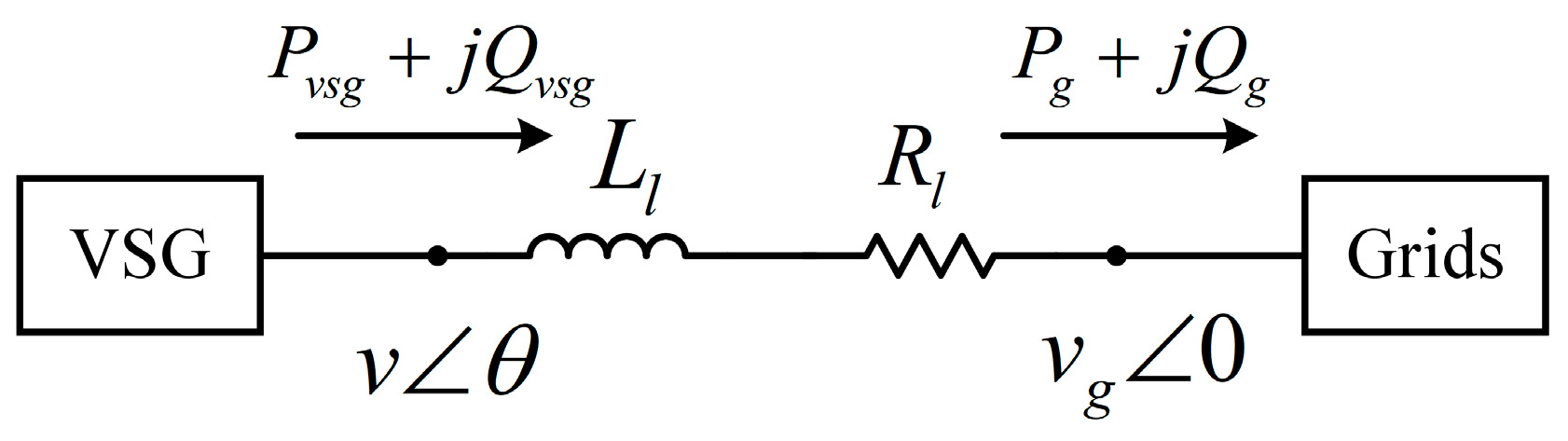

| Symbol | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Vdc | DC voltage | 700 V |
| Vn | Normal value of line voltage | 380 V |
| Sn | Normal value of power | 30 kVA |
| fn | Normal value of frequency | 50 Hz |
| fsw | Switching frequency | 15 kHz |
| Lf | Inductor of LC filter | 300 μH |
| Cf | Capacitor of LC filter | 25 μF |
| Ll | Inductor of the line | 1600 μH |
| Rl | Resistor of the line | 0.5 Ω |
| Vg | Rated voltage of grid | 380 V |
| Dp | Droop coefficient of active power loop | 10,000 W*s/rad |
| Dq | Droop coefficient of reactive power loop | 2000 A |
| J | The inertial coefficient of active power loop | 10 W*s2/rad |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, L.; Yang, B.; Lu, S. A VSG Power Decoupling Control with Integrated Voltage Compensation Schemes. Energies 2025, 18, 1878. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18081878
Wei L, Yang B, Lu S. A VSG Power Decoupling Control with Integrated Voltage Compensation Schemes. Energies. 2025; 18(8):1878. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18081878
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Longhai, Bo Yang, and Shuai Lu. 2025. "A VSG Power Decoupling Control with Integrated Voltage Compensation Schemes" Energies 18, no. 8: 1878. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18081878
APA StyleWei, L., Yang, B., & Lu, S. (2025). A VSG Power Decoupling Control with Integrated Voltage Compensation Schemes. Energies, 18(8), 1878. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18081878





