Dual-Emission Fluorescent Microspheres for the Detection of Biothiols and Hg2+
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Materials
2.2. Preparation of RBS-Doped Silica Microspheres
2.3. Preparation of CA-AEAPMS Coated Dual-Emission Silica Microspheres
2.4. Fluorescence Assay of Hg2+
2.5. Selectivity and Interference Testing
3. Results and Discussion
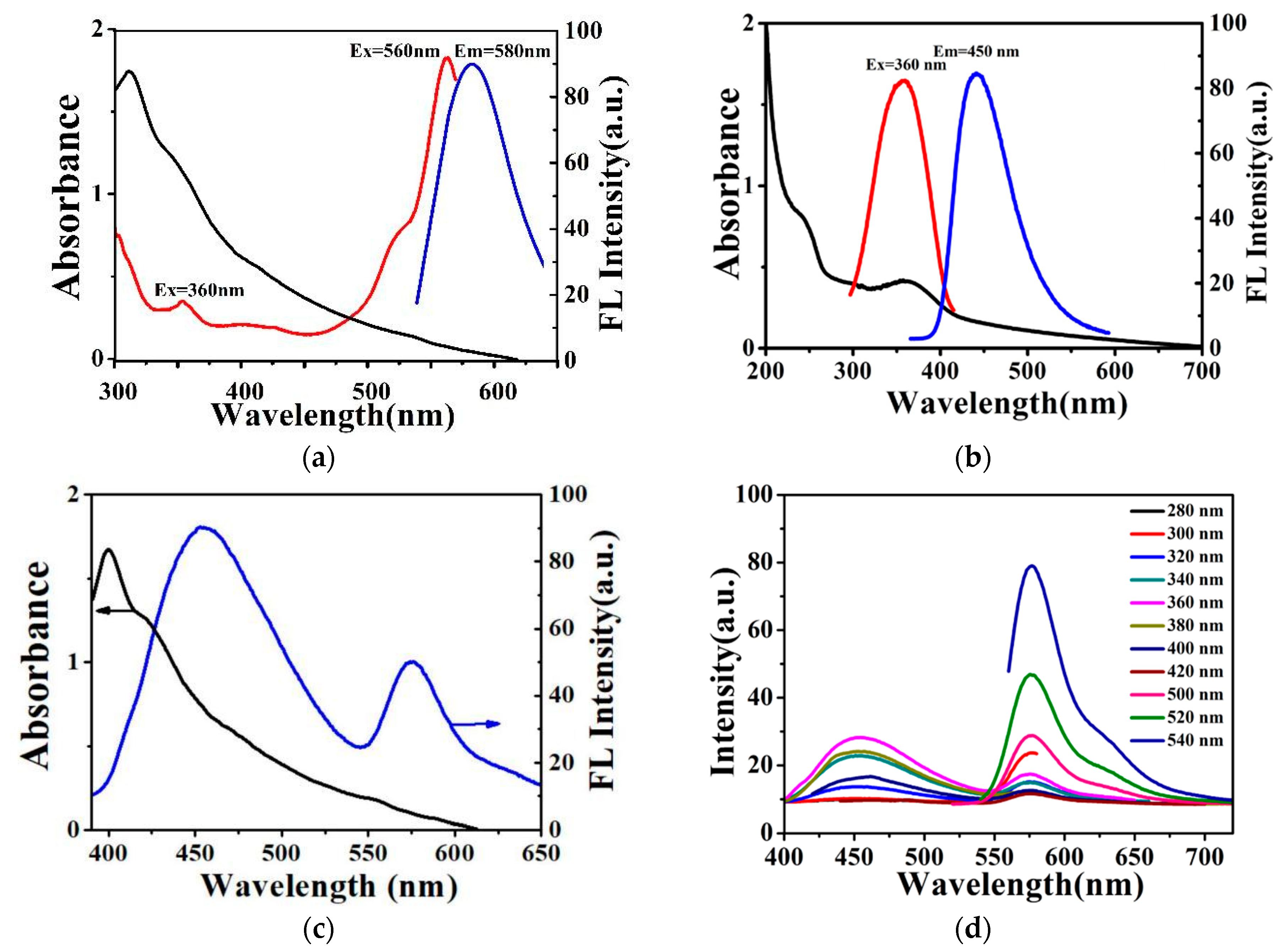
3.1. Preparation and Characterization of the Dual-Emission Silica Microspheres
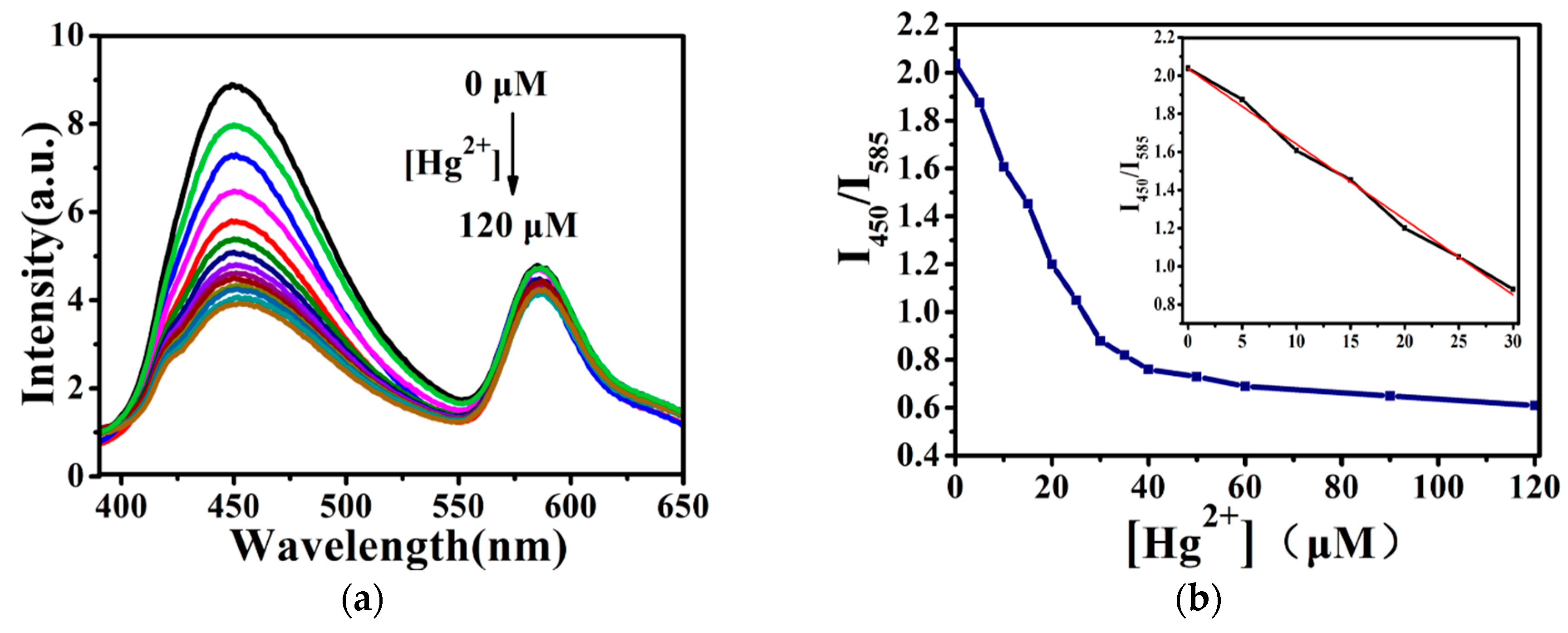
3.2. Fluorescence Detection of Hg2+ and Biothiols Using the Dual-Emission Silica Microspheres
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Takeuchi, T.; Morikawa, N.; Matsumoto, H.; Shiraishi, Y. A pathological study of Minamata disease in Japan. Acta Neuropathol. 1962, 2, 40–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.; Banerjee, A.; Lohar, S.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Sarkar, B.; Mukhopadhyay, S.K.; Sahana, A.; Das, D. Selective sensing of Hg2+ using rhodamine-thiophene conjugate: Red light emission and visual detection of intracellular Hg2+ at nanomolar level. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 261, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grandjean, P.; Weihe, P.; White, R.F.; Debes, F. Cognitive performance of children prenatally exposed to safe levels of methylmercury. Environ. Res. 1998, 77, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, C.M.; Chew, E.H.; Hashemy, S.I.; Lu, J.; Holmgren, A. Inhibition of the human thioredoxin system a molecular mechanism of mercury toxicity. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 11913–11923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, M. Minamata disease: Methylmercury poisoning in Japan caused by environmetal pollution. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 1995, 25, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Huo, F.; Yin, C.; Zheng, A.; Chao, J.; Li, Y.; Nie, Z.; Martínez-Mánez, R.; Liu, D. Thiol–chromene click chemistry: A coumarin-based derivative and its use as regenerable thiol probe and in bioimaging applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 47, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Yu, H.; Hu, Y.; Chen, M.; Shao, S. A gold nanoparticle-based fluorescence sensor for high sensitive and selective detection of thiols in living cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 75, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulsen, C.E.; Carroll, K.S. Cysteine-mediated redox signaling: Chemistry, biology, and tools for discovery. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 4633–4679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.S.; Chen, X.; Kim, J.S.; Yoon, J. Recent progress in luminescent and colorimetric chemosensors for detection of thiols. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6019–6031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Li, X.; Li, L.; Zhou, J.; Ma, H. A simple fluorescent off–on probe for the discrimination of cysteine from glutathione. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 9388–9390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Nam, S.; Park, S.; Yoon, J. A highly selective ratiometric near-infrared Fluorescent cyanine sensor for cysteine with remarkable shift and its application in bioimaging. Chem. Sci. 2012, 3, 2760–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Fan, J.; Peng, X. Colourimetric and fluorescent probes for the optical detection of palladium ions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 7943–7962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; Hu, M.; Fan, J.; Peng, X. Fluorescent chemodosimeters using mild chemical events for the detection of small anions and cations in biological and environmetal media. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 4511–4535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, M.E.; Roy, B.; Ahn, K.H. Turn-on fluorescent sensing with reactive probes. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 7583–7601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andina, D.; Leroux, J.C.; Luciani, P. Ratiometric fluorescent probes to detect reactive oxygen species. Chem.-Eur. J. 2017, 23, 13549–13573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.; Hou, X.; Xu, J.J.; Chen, H.Y. Ratiometric fluorescence, electrochemiluminescence, and photoelectrochemical chemo/biosensing based on semiconductor quantum dots. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 8427–8442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.H.; Kim, J.S.; Sessler, J.L. Small molecule-based ratiometric fluorescence probes for cations anions, and biomolecules. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 44, 4185–4191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ermakova, E.; Michalak, J.; Meyer, M.; Arslanov, V.; Tsivadze, A.; Guilard, R.; Bessmertnykh-Lemeune, A. Colorimetric Hg2+ sensing in water: From molecules toward low-cost solid devices. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 662–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Wang, Y.Z.; Qiu, F.Z. A novel ratiometric fluorescent probe for selective detection of Hg2+, Cr3+ and Al3+ and its bioimaging application in living cells. Sens. Actuators B 2017, 253, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Shen, R.; Wang, Y.Z.; Qiu, F.Z.; Feng, Y. A selective turn-on fluorescent sensor for Hg (II) in living cells and tissues. Sens. Actuators B 2018, 255, 3479–3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L. Synthesis and Characterization of Polyamido-Based Fluorescent Small Molecules. Master’s Thesis, University of Jinan, Jinan, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Nedelčev, T.; Račko, D.; Krupa, I. Preparation and characterization of a new derivative of rhodamine B with an alkoxysilane moiety. Dyes Pigment. 2008, 76, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Li, B.; Zhang, L.M.; Wang, Y.H. Highly selective fluorescent chemosensor for detecting Hg(II) in water based on pyrene functionalized core–shell structured mesoporous silica. J. Lumin. 2012, 132, 1729–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Tang, M.Y.; Shen, H.; Che, G.B.; Qiao, Y.; Liu, B.; Wang, L. Recyclable multifunctional magnetic mesoporous silica nanocomposite for ratiometric detection, rapid adsorption, and efficient removal of Hg(II). ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 1744–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarabadi-Poor, P.Z.; Badiei, A.; Yousefi, A.A.; Barroso-Flores, J. Selective optical sensing of Hg (II) in aqueous media by H-Acid/SBA-15: A combined experimental and theoretical study. J. Phys. Chem. 2013, 117, 9281–9289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.B.; Xu, J.J.; Xue, C.G. Core–shell structured mesoporous silica nanoparticles equipped with pyrene-based chemosensor: Synthesis, characterization, and sensing activity towards Hg (II). J. Lumin. 2011, 131, 2021–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rameshkumar, P.; Manivannan, S.; Ramaraj, R. Silver nanoparticles deposited on amine-functionalized silica spheres and their amalgamation-based spectral and colorimetric detection of Hg (II) ions. J. Nanopart. Res. 2013, 15, 1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.Y.; Zeng, F.; Wu, G.F.; Wu, S.Z. A FRET-based ratiometric sensor for mercury ions in water with multi-layered silica nanoparticles as the scaffold. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 8913–8915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| Materials | Detection Limit | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| SiO2@mSiO2/Py-Si | 1.1 × 10−8 | [23] |
| QDs-MMS-Rh6G | 2.5 × 10−9 | [24] |
| SBA-15-HA | 2.1 × 10−7 | [25] |
| mesoporous silica nanoparticles | 1 × 10−8 | [26] |
| SiO2/AgNPs | 5 × 10−6 | [27] |
| SRhB-NH2 | 5 × 10−7 | [28] |
| dual-emission silica microspheres | 9.7 × 10−8 | This work |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Guan, R. Dual-Emission Fluorescent Microspheres for the Detection of Biothiols and Hg2+. Materials 2018, 11, 2232. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112232
Wang J, Zhang H, Guan R. Dual-Emission Fluorescent Microspheres for the Detection of Biothiols and Hg2+. Materials. 2018; 11(11):2232. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112232
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jiahui, Hao Zhang, and Ruifang Guan. 2018. "Dual-Emission Fluorescent Microspheres for the Detection of Biothiols and Hg2+" Materials 11, no. 11: 2232. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112232
APA StyleWang, J., Zhang, H., & Guan, R. (2018). Dual-Emission Fluorescent Microspheres for the Detection of Biothiols and Hg2+. Materials, 11(11), 2232. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112232




