Thermal Stability and Flammability Behavior of Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) (PHB) Based Composites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Premilinary Test by PCFC: Screening for Flammability Estimation
3.2. Morphology Investigations (SEM)
3.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
3.4. X-Ray Diffraction
3.5. Size-Exclusion Chromatography (SEC)
3.6. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
3.7. Pyrolysis Combustion Flow Calorimeter (PCFC)
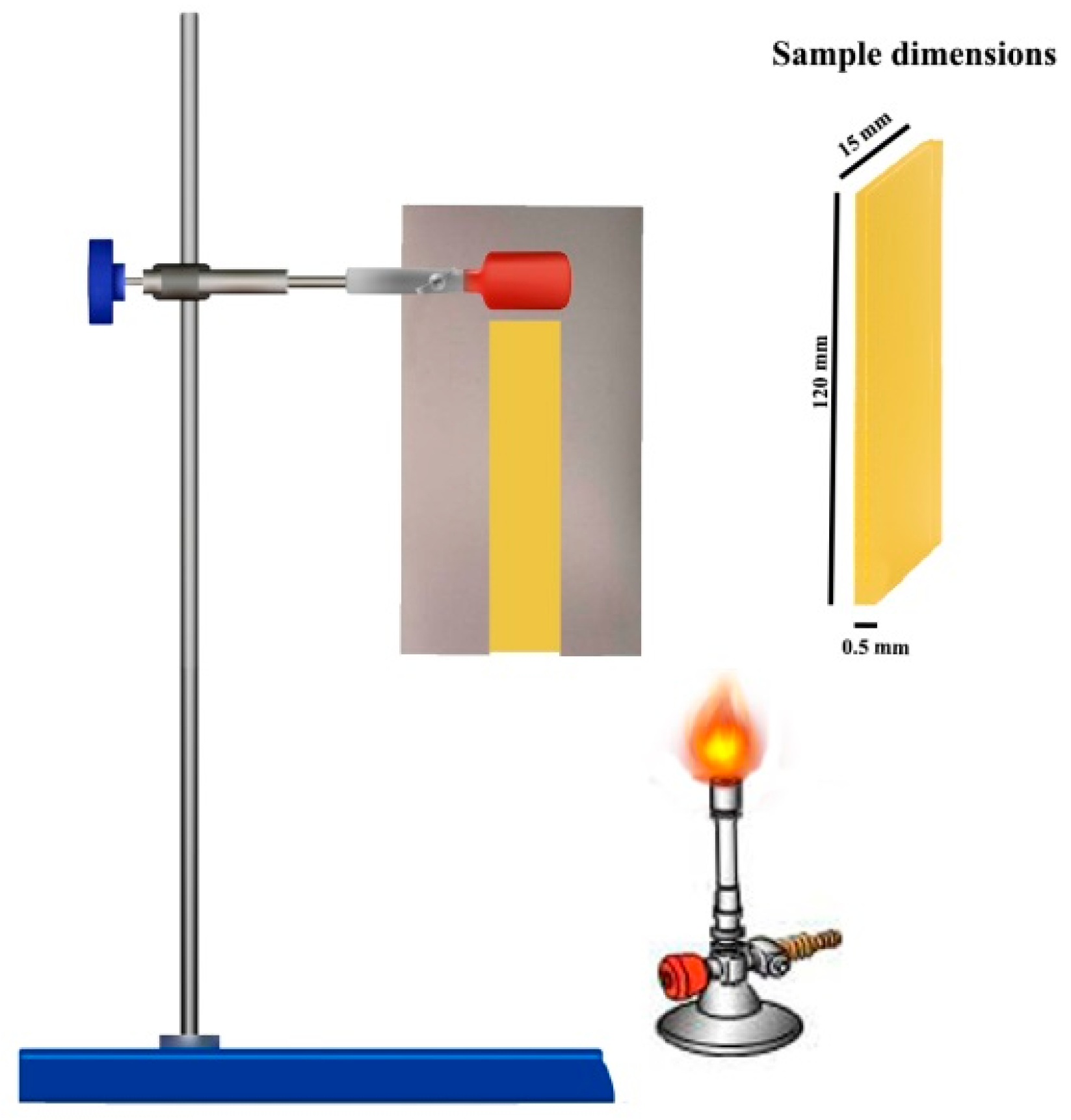
3.8. Vertical Burning Test
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nakajima, H.; Dijkstra, P.; Loos, K.J.P. The recent developments in biobased polymers toward general and engineering applications: Polymers that are upgraded from biodegradable polymers. Analogous to petroleum-derived polymers, and newly developed. Polymers 2017, 9, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luckachan, G.E.; Pillai, C.K.S. Biodegradable polymers-a review on recent trends and emerging perspectives. J. Polym. Environ. 2011, 19, 637–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, R.P.; O’Connor, K.; Seeram, R. Current progress on bio-based polymers and their future trends. Prog. Biomater. 2013, 2, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vahabi, H.; Rohani Rad, E.; Parpaite, T.; Langlois, V.; Saeb, M.R. Biodegradable polyester thin films and coatings in the line of fire: the time of polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA). Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 133, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi-Darani, K.; Bucci, D.Z. Application of poly (hydroxyalkanoate) in food packaging: Improvements by nanotechnology. Chem. Biochem. Eng. Q. 2015, 29, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugnicourt, E.; Cinelli, P.; Lazzeri, A.; Alvarez, V. Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA): Review of synthesis, characteristics, processing and potential applications in packaging. Express Polym. Lett. 2014, 8, 791–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaillé, L.; Albuquerque, M.; Grousseau, E.; Lepeuple, A.-S.; Uribelarrea, J.-L.; Guillermina, H.-R.; Paul, E. Understanding of polyhydroxybutyrate production under carbon and phosphorus-limited growth conditions in non-axenic continuous culture. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 201, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elvers, D.; Song, C.H.; Steinbüchel, A.; Leker, J. Technology Trends in Biodegradable Polymers: Evidence from Patent Analysis. Polym. Rev. 2016, 56, 584–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariffin, H.; Nishida, H.; Shirai, Y.; Hassan, M.A. Determination of multiple thermal degradation mechanisms of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate). Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2008, 93, 1433–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, E.; Schartel, B.; Acierno, D.; Russo, P. Flame retardant biocomposites: Synergism between phosphinate and nanometric metal oxides. Eur. Polym. J. 2011, 47, 1390–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, J.; Loh, J.L. Polyhydroxyalkanoates: Opening doors for a sustainable future. NPG Asia Mater. 2016, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marosi, G.; Szolnoki, B.; Bocz, K.; Toldy, A. Fire-retardant recyclable and biobased polymer composites. In Novel Fire Retardant Polymers and Composite Materials; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2017; Volume 1, pp. 117–146. [Google Scholar]
- Yeo, J.C.C.; Muiruri, J.K.; Thitsartarn, W.; Li, Z.; He, C. Recent advances in the development of biodegradable PHB-based toughening materials: Approaches, advantages and applications. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 92, 1092–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; He, H.; Liu, T.; Wei, R.; Cao, X.; Sun, Q.; Li, R.K. Synergetic enhancement on flame retardancy by melamine phosphate modified lignin in rice husk ash filled P34HB biocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2018, 168, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battegazzore, D.; Noori, A.; Frache, A. Hemp hurd and alfalfa as particle filler to improve the thermo-mechanical and fire retardant properties of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate). Polym. Compos. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Huang, H.; Yang, W.; Xiao, X. Preparation and thermal properties of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate)/aluminum-containing layered double hydroxides nanocomposites. High Perform. Polym. 2013, 25, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, P.; Carfagna, C.; Cimino, F.; Acierno, D.; Persico, P. Biodegradable composites reinforced with kenaf fibers: Thermal, mechanical, and morphological issues. Adv. Polym. Tech. 2013, 32, E313–E322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, E.; Schartel, B.; Acierno, D.; Cimino, F.; Russo, P. Tailoring the flame retardant and mechanical performances of natural fiber-reinforced biopolymer by multi-component laminate. Compos. Part B: Eng. 2013, 44, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, P.; Vetrano, B.; Acierno, D.; Mauro, M. Thermal and structural characterization of biodegradable blends filled with halloysite nanotubes. Polym. Compos. 2013, 34, 1460–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmo, N.; Lizarbe, M.A.; Gavilanes, J.G. Biocompatibility and degradability of sepiolite-collagen complex. Biomaterials 1987, 8, 67–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masood, F.; Haider, H.; Yasin, T. Sepiolite/poly-3-hydroxyoctanoate nanocomposites: Effect of clay content on physical and biodegradation properties. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 175, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajmal, A.W.; Masood, F.; Yasin, T. Influence of sepiolite on thermal, mechanical and biodegradation properties of poly-3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate nanocomposites. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 156, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahabi, H.; Sonnier, R.; Otazaghine, B.; Le Saout, G.; Lopez-Cuesta, J.M. Nanocomposites of polypropylene/polyamide 6 blends based on three different nanoclays: Thermal stability and flame retardancy. Polimery 2013, 58, 350–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.H.; Chen, Z.J.; Wang, J.Q.; Wei, P. Synergistic effects of sepiolite on intumescent flame retardant polypropylene. Express Polym. Lett. 2010, 4, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappalardo, S.; Russo, P.; Acierno, D.; Rabe, S.; Schartel, B. The synergistic effect of organically modified sepiolite in intumescent flame retardant polypropylene. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 76, 196–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Thomas, N.L. Preparation and properties of polyhydroxybutyrate blended with different types of starch. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 116, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godbole, S.; Gote, S.; Latkar, M.; Chakrabarti, T. Preparation and characterization of biodegradable poly-3-hydroxybutyrate–starch blend films. Bioresour. Technol. 2003, 86, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavioun, P.; Halley, P.J.; Doherty, W.O. Thermophysical properties and rheology of PHB/lignin blends. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 50, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertini, F.; Canetti, M.; Cacciamani, A.; Elegir, G.; Orlandi, M.; Zoia, L. Effect of ligno-derivatives on thermal properties and degradation behavior of poly (3-hydroxybutyrate)-based biocomposites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2012, 97, 1979–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyon, R.E.; Walters, R.N.; Stoliarov, S.I. Screening flame retardants for plastics using microscale combustion calorimetry. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2007, 47, 1501–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cogen, J.M.; Lin, T.S.; Lyon, R.E. Correlations between pyrolysis combustion flow calorimetry and conventional flammability tests with halogen-free flame retardant polyolefin compounds. Fire Mater. 2009, 33, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, A.B. Milligram Scale Flammability Testing of Flame Retardant Polyurethane Foams; ACS Symposium Series; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; Volume 1118, pp. 445–458. [Google Scholar]
- Sonnier, R.; Vahabi, H.; Ferry, L.; Lopez-Cuesta, J.M. Pyrolysis-combustion Flow Calorimetry: A Powerful Tool to Evaluate the Flame Retardancy of Polymers; ACS Symposium Series; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; Volume 1118, pp. 361–390. [Google Scholar]
- Murariu, M.; Bonnaud, L.; Yoann, P.; Fontaine, G.; Bourbigot, S.; Dubois, P. New trends in polylactide (PLA)-based materials: ‘‘Green’’ PLA–calcium sulfate (nano) composites tailored with flame retardant properties. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2010, 95, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyagi, Y.; Yamashita, K.; Doi, Y. Thermal degradation of poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate],poly[e-caprolactone], and poly[(S)-lactide]. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2002, 76, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.D.; He, J.D.; Yu, P.; Cheung, M.K. Thermal degradation of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) and poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) as studied by TG, TG–FTIR, and Py–GC/MS. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 89, 1530–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, S.; Yu, G.; Marchessault, R.H. Thermal Degradation of Poly(3-hydroxyalkanoates): Preparation of Well-Defined Oligomers. Biomacromolecules 2002, 3, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, A.; Irusta, L.; Fernandez-Berridi, M.J.; Iriarte, M.; Iruin, J.J. Application of pyrolysis/gas chromatography/Fourier transforminfrared spectroscopy and TGA techniques in the study ofthermal degradation of poly (3-hydroxybutyrate). Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2005, 87, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boryniec, S.; Przygocki, W. Polymer Combustion Processes. 3. Flame Retardants for Polymeric Materials. Prog. Rubber Plast. Recycl. Technol. 2001, 17, 127–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Number | Sample Code | PHB | Sepiolite | APP | Lignin | Starch |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PHB | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | PHB-Sep. | 85 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | PHB-APP | 85 | 0 | 15 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | PHB-Lig. | 85 | 0 | 0 | 15 | 0 |
| 5 | PHB-Starch | 85 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15 |
| 6 | PHB-APP-Lig. | 85 | 0 | 10 | 5 | 0 |
| 7 | PHB-APP-Sep. | 85 | 5 | 10 | 0 | 0 |
| 8 | PHB-APP-Starch | 85 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 5 |
| 9 | PHB-APP-Lig.-Sep. | 85 | 2.5 | 10 | 2.5 | 0 |
| 10 | PHB-APP-Lig.-Starch | 85 | 0 | 10 | 2.5 | 2.5 |
| 11 | PHB-APP-Sep.-Starch | 85 | 2.5 | 10 | 0 | 2.5 |
| Sample Code | PHB | Sepiolite | APP |
|---|---|---|---|
| PHB | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| PHB-APP | 85 | 0 | 15 |
| PHB-Sep. | 85 | 15 | 0 |
| PHB-APP-Sep. | 85 | 5 | 10 |
| Area Number | Elements (%wt.) Normalized at 100 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | O | Si | Mg | P | N | |
| Area 1 | 90.7 | 9.0 | 0.3 | - | - | - |
| Area 2 | 66.4 | 24.9 | 4.6 | 2.5 | 1.6 | - |
| Area 3 | 14.4 | 54.8 | 2.7 | 1.1 | 15.0 | 12.0 |
| Sample | 1st Heating | 2nd Heating | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tm1 (°C) | ΔHTm1 (J/g) | Χc (%) | Tg (°C) | Tcc (°C) | ΔHTcc (J/g) | Tm2 (°C) | |
| PHB | 172.2 | 85.4 | 58.2 | 5.30 | 48.3 | 36.7 | 172.6 |
| PHB-APP | 174.9 | 84.6 | 57.7 | 6.50 | 44.6 | 5.0 | 173.9 |
| PHB-Sep. | 171.9 | 70.8 | 48.3 | 5.70 | 44.6 | 14.2 | 171.5 |
| PHB-APP-Sep. | 175.9 | 73.3 | 50.0 | 4.15 | 45.9 | 2.4 | 172.9 |
| Sample Code | 2θ (°) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (020) | (110) | (021) | (111) | (121) | (040) | |
| PHB | 13.91 | 17.41 | 20.46 | 23.06 | 26.06 | 27.66 |
| PHB-APP | 14.02 | 17.41 | 20.41 | 22.94 | 25.98 | 27.63 |
| PHB-Sep. | 13.75 | 17.26 | 19.93 | 22.66 | 26.07 | 27.04 |
| PHB-APP-Sep. | 14.04 | 17.42 | 20.54 | 23.04 | 26.05 | 27.83 |
| Sample Code | Lattice Constants (Å) & Lattice Volume (Å) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | b | c | v | |
| PHB | 5.54 | 12.88 | 5.87 | 4.19 |
| PHB-APP | 5.54 | 12.90 | 5.92 | 4.23 |
| PHB-Sep. | 5.54 | 13.17 | 5.78 | 4.20 |
| PHB-APP-Sep. | 5.54 | 12.81 | 5.90 | 4.19 |
| Sample Code | Mn (g/mol) | Mw (g/mol) | PDI |
|---|---|---|---|
| PHB | 106,000 | 254,400 | 2.4 |
| PHB-APP | 72,000 | 216,000 | 3.0 |
| PHB-Sep. | 55,000 | 148,500 | 2.7 |
| PHB-APP-Sep. | 69,000 | 186,300 | 2.7 |
| Sample Code | T10% (°C) | Tmax* (°C) | Residue (wt.%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PHB | 265 | 280 | 0 |
| PHB-Sep. | 264 | 278 | 16 |
| PHB-APP | 274 | 292 | 6 |
| PHB-APP-Sep. | 273 | 290 | 11 |
| Sample Code | THR (kJ/g) | TpHRR (°C) | pHRR (W/g) | Reduction in pHRR (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PHB | 22 | 302 | 1064 | - |
| PHB-Sep. | 17 | 291 | 656 | 38 |
| PHB-APP | 20 | 305 | 699 | 34 |
| PHB-APP-Sep. | 18 | 308 | 607 | 42 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vahabi, H.; Michely, L.; Moradkhani, G.; Akbari, V.; Cochez, M.; Vagner, C.; Renard, E.; Saeb, M.R.; Langlois, V. Thermal Stability and Flammability Behavior of Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) (PHB) Based Composites. Materials 2019, 12, 2239. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12142239
Vahabi H, Michely L, Moradkhani G, Akbari V, Cochez M, Vagner C, Renard E, Saeb MR, Langlois V. Thermal Stability and Flammability Behavior of Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) (PHB) Based Composites. Materials. 2019; 12(14):2239. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12142239
Chicago/Turabian StyleVahabi, Henri, Laurent Michely, Ghane Moradkhani, Vahideh Akbari, Marianne Cochez, Christelle Vagner, Estelle Renard, Mohammad Reza Saeb, and Valérie Langlois. 2019. "Thermal Stability and Flammability Behavior of Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) (PHB) Based Composites" Materials 12, no. 14: 2239. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12142239
APA StyleVahabi, H., Michely, L., Moradkhani, G., Akbari, V., Cochez, M., Vagner, C., Renard, E., Saeb, M. R., & Langlois, V. (2019). Thermal Stability and Flammability Behavior of Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) (PHB) Based Composites. Materials, 12(14), 2239. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12142239







