Experimental and Statistical Study on Mechanical Characteristics of Geopolymer Concrete
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiments
2.1. Fly Ash
2.2. Alkaline Liquid
2.3. Mix Design
2.4. Specimens
2.5. Casting
2.6. Curing
2.7. Testing
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Summary of the Mechanical Properties
3.2. Comparison of Microstructures of CFGPC
3.3. Comparison of fc’, ft and Ec of CFGPC and OPCC Specimens
3.4. Correlation between Mechanical Characteristics of CFGPC
3.4.1. Correlation between ft and fc’ in CFGPC
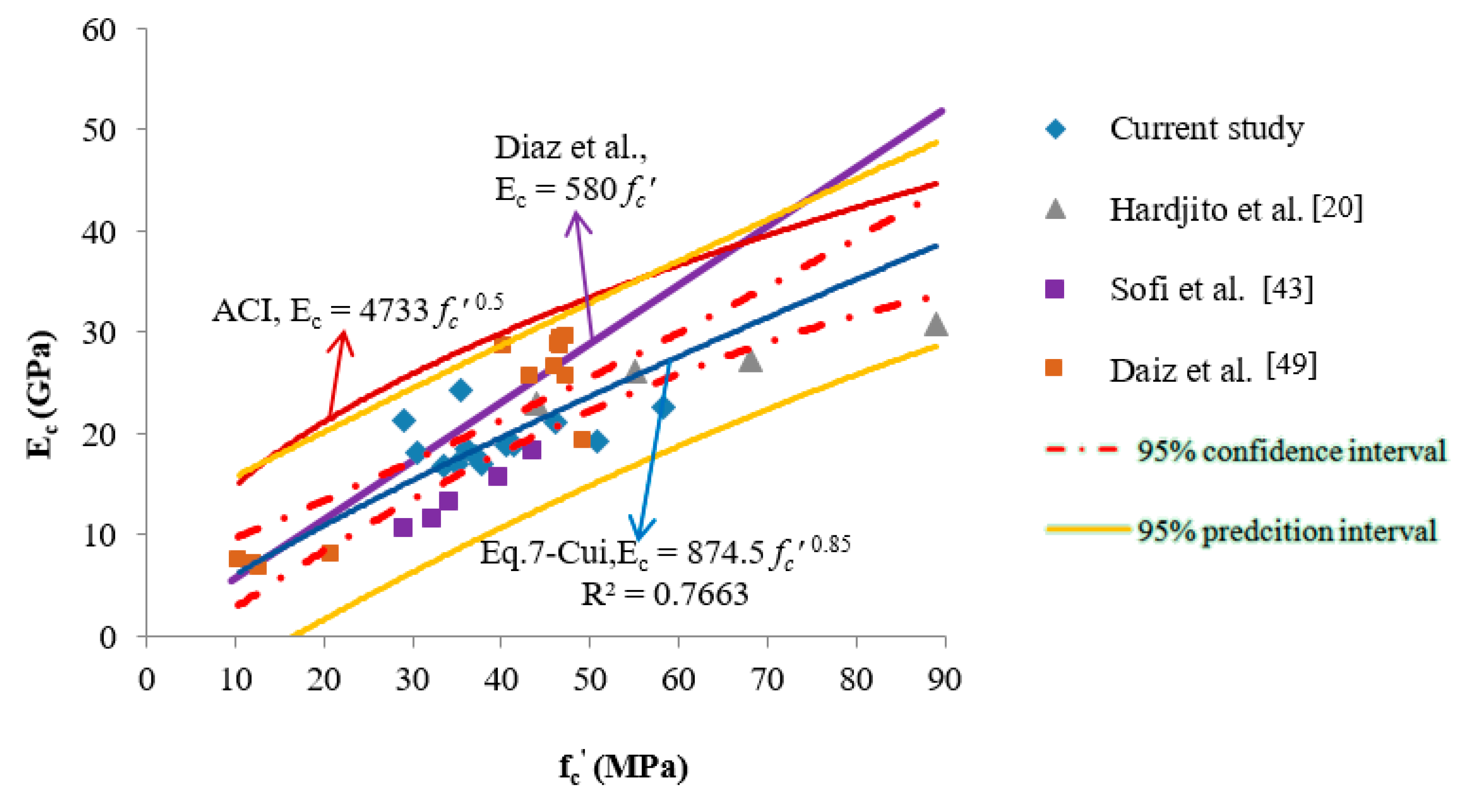
3.4.2. Correlation between fc’ and Ec in CFGPC
3.4.3. Correlation between fc’ Concrete Density w and Ec in CFGPC
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mehta, P.K. Blended cements in construction. Cem. Concr. Compos. 1992, 14, 223–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Geological Survey. USGS Mineral Program Cement Report Mineral Commodity Summaries; U.S. Geological Survey & U.S. Department of the Interior: Washington, DC, USA, 2019.
- Gregg, J.S.; Andres, R.J.; Marland, G. China: Emissions pattern of the world leader in CO2 emissions from fossil fuel consumption and cement production. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wittmann, F.H.; Vogel, M.; Müller, H.S.; Zhao, T. Influence of freeze-thaw cycles on capillary absorption and chloride penetration into concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2017, 100, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.R.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, P.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, T.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z. Water absorption and chloride diffusivity of concrete under the coupling effect of uniaxial compressive load and freeze-thaw cycles. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 209, 566–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, J.W.; Li, S.G.; Zhang, P.; Ding, X.; Xue, S.; Cui, Y.; Zhao, T. Influence of the incorporation of recycled coarse aggregate on water absorption and chloride penetration into concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 239, 117845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidovits, J. Properties of geopolymer cements. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Alkaline Cements and Concretes; Kiev State Technical University: Kiev, Ukraine, 1994; pp. 131–149. [Google Scholar]
- Hardjito, D.; Wallah, S.E.; Sumajouw, D.M.; Rangan, B.V. On the development of fly ash-based geopolymer concrete. ACI Mater. J. 2004, 101, 467–472. [Google Scholar]
- Hardjito, D.; Wallah, S.; Sumajouw, D.; Rangan, B. Brief review of development of geopolymer concrete. In Proceedings of the 8th CANMET/ACI International Conference on Fly Ash, Silica Fume, Slag and Natural Pozzolans in Concrete, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 1 May 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Bakharev, T. Geopolymeric materials prepared using Class F fly ash and elevated temperature curing. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 1224–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardjito, D.; Wallah, S.; Sumajouw, D.; Rangan, B. Introducing fly ash-based geopolymer concrete: Manufacture and engineering properties. In Proceedings of the 30th Conference on our World in Concrete and Structures, Singapore, 23–24 August 2005; pp. 23–24. [Google Scholar]
- Bakharev, T. Resistance of geopolymer materials to acid attack. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 658–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakharev, T. Durability of geopolymer materials in sodium and magnesium sulfate solutions. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 1233–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupwade-Patil, K.; Allouche, E.N. Examination of chloride-induced corrosion in reinforced geopolymer concretes. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2012, 25, 1465–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.L.; Sanjayan, J.G. Effect of elevated temperatures on geopolymer paste, mortar and concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2010, 40, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, S.; Zhang, P.; Bao, J.; He, L.; Hu, Y.; Yang, S. Comparison of mercury intrusion porosimetry and multi-scale X-ray CT on characterizing the microstructure of heat-treated cement mortar. Mater. Charact. 2020, 160, 110085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.L.; Sanjayan, J.G. Damage behavior of geopolymer composites exposed to elevated temperatures. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2008, 30, 986–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Jiménez, A.M.; Palomo, A.; López-Hombrados, C. Engineering properties of alkali-activated fly ash concrete. ACI Mater. J. 2006, 103, 106–114. [Google Scholar]
- Junaid, M.T.; Kayali, O.; Khennane, A; Black, J. A mix design procedure for low calcium alkali activated fly ash-based concretes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 79, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardjito, D. Study of Fly-Ash Based Geopolymer Concrete; Curtin University of Technology: Bentley, Australia, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wallah, S.E.; Rangan, B.V. Low-Calcium Fly Ash-Based Geopolymer Concrete: Long-Term Properties; Report-GC2; Curtin University: Bentley, Australia, 2006; pp. 76–80. [Google Scholar]
- Standards Australia. AS3583.3 Method 3: Determination of Loss on Ignition. Methods of Test for Supplementary Cementitious Materials for Use with Portland Cement; Standards Association of Australia: Sydney, Australia, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- De Silva, P.; Sagoe-Crenstil, K.; Sirivivatnanon, V. Kinetics of geopolymerization: Role of Al2O3 and SiO2. Cem. Concr. Res. 2007, 37, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standards Australia. AS 1012.9: Determination of the Compressive Strength of Concrete Specimens; Standards Association of Australia: Sydney, Australia, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Standards Australia. AS1012.10 Method 10: Determination of Indirect Tensile Strength of Concrete Cylinders (‘Brazil’ or Splitting Test); Methods of Testing Concrete; Standards Association of Australia: Sydney, Australia, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Standards Australia. AS 1012.17-1997 (R2014): Determination of the Static Chord Modulus of Elasticity and Poisson’s Ratio of Concrete Specimens; Methods of Testing Concrete; Standards Association of Australia: Sydney, Australia, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM International. ASTM C192/C192M-15: Standard Practice for Making and Curing Concrete Test Specimens in the Laboratory; American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Rangan, V.B. Engineering properties of geopolymer concrete. Geopolymers 2009, 211–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y. Bond Behaviour between Reinforcing Steel Bars and Fly Ash-Based Geopolymer Concrete; University of New South Wales: Sydney, Australia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Standards Australia. AS1012.12.1-1998 Method 12.1: Determination of Mass Per Unit Volume of Hardened Concrete-Rapid Measuring Method; Standards Association of Australia: Sydney, Australia, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Paternoster, R.; Brame, R.; Mazerolle, P.; Piquero, A. Using the correct statistical test for the equality of regression coefficients. Criminology 1998, 36, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trochim, W.M.K. The Research Methods Knowledge Base, 2nd ed.; Atomic dog and Cengage Learning, Cornell University: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Ruxton, G.D. The unequal variance t-test is an underused alternative to Student’s t-test and the Mann–Whitney U test. Behav. Ecol. 2006, 17, 688–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snedecor, G.W.; Cochran, W.G. Statistical Methods, 7th ed.; Iowa State University Press: Ames, IA, USA, 1980; pp. 26–27, 54, 64–65, 96–99. [Google Scholar]
- Stigler, S. Fisher and the 5% level. Chance 2008, 21, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neville, A.M. Properties of Concrete, 4th ed.; Longman: Harlow, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Standards Australia. AS 3600: Australian Standard for Concrete Structures; Standards Association of Australia: Sydney, Australia, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Comité Euro-International du Béton. CEB-FIP Model Code 1990: Design Code; Thomas Telford Ltd.: London, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- ACI Committee 363. ACI 363R-92: State of the Art Report on High-Strength Concrete. ACI Comm. 1992, 81, 364–411. [Google Scholar]
- Rajini, B.; Rao, A.V.N. Mechanical properties of geopolymer concrete with fly ash and GGBS as source materials. Int. J. Innov. Res. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2014, 3, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, E.H. Shear and Bond Behaviour of Reinforced Fly Ash-Based Geopolymer Concrete Beams; Curtin University of Technology: Bentley, Australia, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ryu, G.S.; Lee, Y.B.; Koh, K.T.; Chung, Y.S. The mechanical properties of fly ash-based geopolymer concrete with alkaline activators. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 47, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofi, M.; Van Deventer, J.; Mendis, P.; Lukey, G. Engineering properties of inorganic polymer concretes (IPCs). Cem. Concr. Res. 2007, 37, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verschuuren, G. Part 4: Regression and Curve Fitting in Excel 2013 for Scientists; Excel for Professionals Series; Holy Macro! Books: Chicago, IL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- European Concrete Standard. EN 206-1 Concrete–Part 1: Specification, Performance, Production and Conformity; British Standards Institution: London, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Lamond, J.F. Significance of Tests and Properties of Concrete and Concrete-Making Materials; ASTM International: Herts, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Sarker, P.K. Bond strength of reinforcing steel embedded in fly ash-based geopolymer concrete. Mater. Struct. 2011, 44, 1021–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ACI Committee 318. ACI 318-14: Building Code Requirements for Structural Concrete; American Concrete Institute: Farmington Hills, MI, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Diaz, E.I.; Allouche, E.N.; Vaidya, S. Mechanical properties of fly-ash-based geopolymer concrete. ACI Mater. J. 2011, 108, 300. [Google Scholar]
- Hardjito, D.; Wallah, S.; Sumajouw, D.; Rangan, B. The stress-strain behaviour of fly ash-based geopolymer concrete. Dev. Mech. Struct. Mater. 2004, 35, 831–834. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, A.M. A step-by-step guide to non-linear regression analysis of experimental data using a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2001, 65, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, R. Quantitative evaluation of elastic modulus of concrete with nanoidentation and homogenization method. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 212, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauw, A. Static modulus of elasticity of concrete as affected by density. ACI J. Proc. 1960, 57, 679–688. [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch, T.J. Modulus of elasticity of concrete affected by elastic moduli of cement paste matrix and aggregate. ACI J. Proc. 1962, 59, 427–452. [Google Scholar]
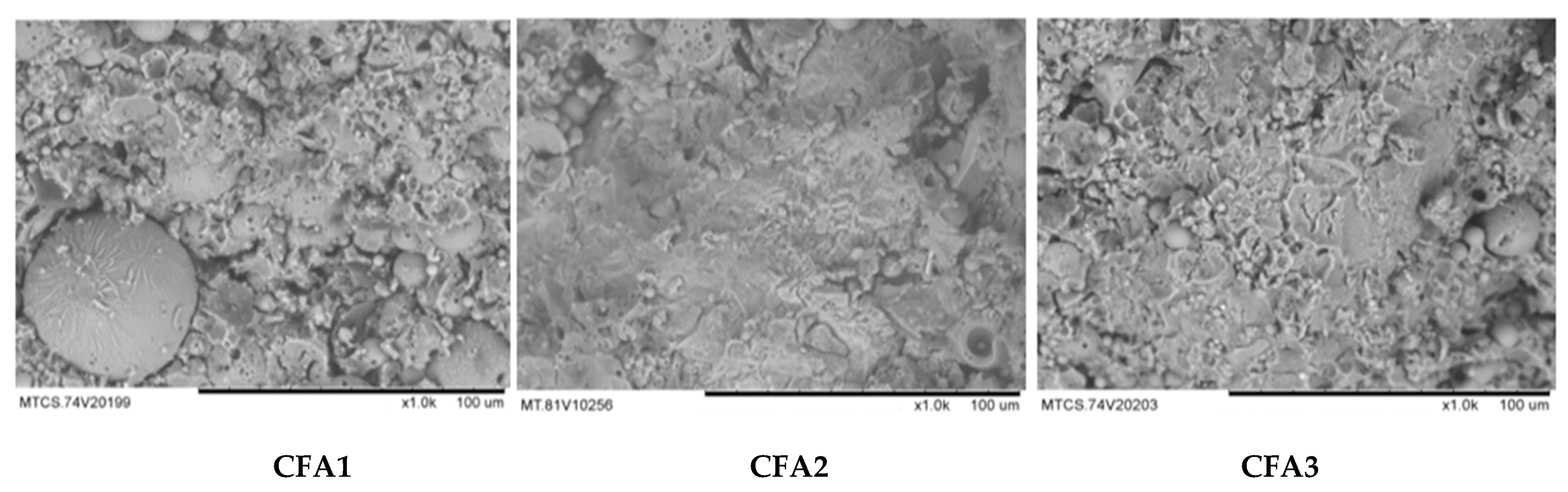



| Fly Ash Batches | CFA1 | CFA2 | CFA3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Component | wt.% | wt.% | wt.% |
| SiO2 | 58.600 | 58.491 | 57.360 |
| Al2O3 | 20.202 | 21.046 | 22.106 |
| Fe2O3 | 9.245 | 8.286 | 8.126 |
| CaO | 4.670 | 3.843 | 4.701 |
| K2O | 3.023 | 3.938 | 3.090 |
| TiO2 | 2.341 | 2.232 | 2.445 |
| SO3 | 1.040 | 1.282 | 1.098 |
| SrO | 0.339 | 0.340 | 0.489 |
| ZrO2 | 0.295 | 0.226 | 0.263 |
| MnO | 0.165 | 0.158 | 0.189 |
| Rb2O | 0.044 | 0.045 | 0.053 |
| Y2O3 | 0.038 | 0.032 | 0.043 |
| Loss of Ignition (AS 3583.3-1991 [22] | 0.97 | 1.6 | 0.91 |
| SiO2/Al2O3(wt) | 2.90 | 2.78 | 2.59 |
| CFGPC 35 | Coarse Aggregate | Fine | CFA | NaOH | Na2SiO3 | Free Water | Total | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14 mm | 10 mm | 7 mm | |||||||
| Mass (kg/m3) | 500 | 310 | 280 | 630 | 420 | 60 | 150 | 31 | 2389 |
| OPCC 35 | Coarse Aggregate | Fine | Free Water | Cement | Total | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14 mm | 10 mm | 7 mm | |||||
| Mass (kg/m3) | 242 | 353 | 349 | 814 | 225 | 357 | 2340 |
| Mixes ID | Concrete Density, w (g/cm3) | Compressive Strength, fc’ (MPa) | Elastic Modulus, Ec (GPa) | Indirect Tensile Strength, ft (MPa) | ft/fc’ | Fly Ash |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.26 | 35.40 | 24.29 | 2.93 | 8.28% | CFA1 |
| 2 | 2.30 | 28.99 | 21.25 | 2.66 | 9.18% | CFA1 |
| 3 | 2.24 | 46.18 | 21.19 | 4.00 | 8.66% | CFA2 |
| 4 | 2.27 | 36.10 | 18.47 | 3.81 | 10.55% | CFA2 |
| 5 | 2.25 | 40.48 | 18.95 | 4.14 | 10.23% | CFA2 |
| 6 | 2.25 | 41.36 | 18.87 | 4.19 | 10.13% | CFA2 |
| 7 | 2.22 | 33.52 | 16.74 | 3.37 | 10.05% | CFA3 |
| 8 | 2.23 | 39.07 | 18.2 | 3.57 | 11.70% | CFA3 |
| 9 | 2.24 | 35.03 | 16.97 | 3.28 | 9.36% | CFA3 |
| 10 | 2.22 | 37.12 | 17.78 | 3.26 | 8.78% | CFA3 |
| 11 | 2.21 | 37.69 | 16.99 | 3.60 | 9.55% | CFA3 |
| 12 | 2.22 | 37.21 | 17.9 | 3.65 | 9.81% | CFA3 |
| Ave | 2.24 | 37.35 | 18.97 | 3.54 | 9.69% |
| Sample ID | Concrete Density, w (g/cm3) | Compressive Strength, fc’ (MPa) | Elastic Modulus, Ec (GPa) | Indirect Tensile Strength, ft (MPa) | ft/fc’ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.36 | 35.43 | 28.81 | 2.97 | 8.38% |
| 2 | 2.35 | 38.88 | 28.60 | 3.35 | 8.62% |
| 3 | 2.37 | 39.09 | 23.12 | 3.40 | 8.70% |
| 4 | 2.35 | 37.06 | 28.26 | 3.40 | 9.17% |
| 5 | 2.37 | 32.96 | 29.59 | 2.76 | 8.37% |
| 6 | 2.35 | 34.54 | 27.62 | 3.54 | 10.25% |
| 7 | 2.34 | 35.09 | 28.24 | 3.42 | 9.75% |
| 8 | 2.31 | 33.96 | 27.04 | 2.88 | 8.48% |
| 9 | 2.34 | 36.22 | 29.12 | 3.24 | 8.95% |
| 10 | 2.33 | 39.74 | 29.03 | 3.82 | 9.61% |
| 11 | 2.35 | 42.30 | 28.37 | 3.54 | 8.37% |
| 12 | 2.34 | 37.59 | 28.91 | 3.19 | 8.84% |
| Ave | 2.35 | 36.91 | 28.06 | 3.29 | 9.01% |
| Mechanical Characteristics | fc’ (MPa) | ft (MPa) | Ec (GPa) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concrete Type | OPCC | CFGPC | OPCC | CFGPC | OPCC | CFGPC |
| Mean | 36.91 | 37.35 | 3.29 | 3.54 | 28.06 | 18.97 |
| Test date | 28 day | 7 day | 28 day | 7 day | 28 day | 7 day |
| F-test | F = 2.46 < f0.05 = 2.81 | F = 2.37 < f0.05 = 2.81 | F = 1.72 < f0.05 = 2.81 | |||
| Equal variances? | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||
| T-test | ts = 0.30 < t0.05 = 2.07 P = 0.77 > 0.05 | ts = 1.52 < t0.05 = 2.07 P = 0.14 > 0.05 | ts = 11.23 > t0.05 = 2.07 P = 1.4 × 10−10 < 0.05 | |||
| Statistically significant difference? | No | No | Yes | |||
| Researcher | Experimental ft (MPa) | Experimental fc’ (MPa) | AS3600 ft (MPa) | CEB-FIP ft (MPa) | ACI 363 ft (MPa) | Equation (4) ft (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Current study | 5.54 | 58.2 | 3.05 | 4.51 | 2.14 | 5.09 |
| 4.82 | 49.57 | 2.82 | 4.05 | 1.97 | 4.35 | |
| 2.79 | 35.4 | 2.38 | 3.23 | 1.67 | 3.14 | |
| 2.66 | 28.99 | 2.15 | 2.83 | 1.51 | 2.59 | |
| 4.00 | 46.18 | 2.72 | 3.86 | 1.90 | 4.06 | |
| 3.81 | 36.1 | 2.40 | 3.28 | 1.68 | 3.20 | |
| 4.14 | 40.48 | 2.54 | 3.54 | 1.78 | 3.57 | |
| 4.19 | 41.36 | 2.57 | 3.59 | 1.80 | 3.65 | |
| 3.37 | 33.52 | 2.32 | 3.12 | 1.62 | 2.98 | |
| 3.57 | 30.5 | 2.21 | 2.93 | 1.55 | 2.72 | |
| 3.28 | 35.03 | 2.37 | 3.21 | 1.66 | 3.11 | |
| 3.26 | 37.12 | 2.44 | 3.34 | 1.71 | 3.29 | |
| 3.6 | 37.69 | 2.46 | 3.37 | 1.72 | 3.34 | |
| Sofi et al. [43] | 3.2 | 35.2 | 2.37 | 3.22 | 1.66 | 3.12 |
| 2.9 | 44.4 | 2.67 | 3.76 | 1.87 | 3.91 | |
| 2.4 | 37.6 | 2.45 | 3.37 | 1.72 | 3.33 | |
| 3.6 | 41.8 | 2.59 | 3.61 | 1.81 | 3.69 | |
| 3.5 | 42.0 | 2.59 | 3.63 | 1.81 | 3.70 | |
| 2.7 | 38.3 | 2.48 | 3.41 | 1.73 | 3.39 | |
| Hardjito [20] | 7.43 | 89 | 3.77 | 5.98 | 2.64 | 7.71 |
| 5.52 | 68 | 3.30 | 5.00 | 2.31 | 5.92 | |
| 5.45 | 55 | 2.97 | 4.34 | 2.08 | 4.81 | |
| 4.43 | 44 | 2.65 | 3.74 | 1.86 | 3.87 | |
| Rajini and Rao [40] | 1.13 | 10.51 | 1.30 | 1.44 | 0.91 | 1.02 |
| 1.16 | 12.11 | 1.39 | 1.58 | 0.97 | 1.15 | |
| 1.18 | 18.68 | 1.73 | 2.11 | 1.21 | 1.71 | |
| 1.32 | 22.03 | 1.88 | 2.36 | 1.31 | 2.00 | |
| Chang [41] | 3.62 | 37 | 2.43 | 3.33 | 1.70 | 3.30 |
| 2.96 | 30 | 2.19 | 2.90 | 1.53 | 2.69 | |
| 4.96 | 55 | 2.97 | 4.34 | 2.08 | 4.88 | |
| 4.48 | 48 | 2.77 | 3.96 | 1.94 | 4.26 | |
| 2.96 | 30 | 2.19 | 2.90 | 1.53 | 2.69 | |
| 2.93 | 29 | 2.15 | 2.83 | 1.51 | 2.60 | |
| 4.65 | 51 | 2.86 | 4.13 | 2.00 | 4.53 | |
| Ryu et al. [42] | 2.0 | 25.8 | 2.03 | 2.62 | 1.42 | 2.32 |
| 2.2 | 27.5 | 2.10 | 2.73 | 1.47 | 2.47 | |
| 2.4 | 29.4 | 2.17 | 2.86 | 1.52 | 2.63 | |
| 2.5 | 30.3 | 2.20 | 2.92 | 1.54 | 2.71 | |
| 2.5 | 30 | 2.19 | 2.90 | 1.53 | 2.69 | |
| 2.6 | 31.2 | 2.23 | 2.97 | 1.56 | 2.79 |
| Researcher | fc’ (MPa) | w (g/cm3) | Ec (GPa) | ACI 318 Ec (GPa) | Diaz et al. [49] Ec (GPa) | Equation (7) Ec (GPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Current study | 58.20 | 2.26 | 22.54 | 36.11 | 33.76 | 27.13 |
| 50.70 | 2.30 | 19.24 | 33.70 | 29.41 | 24.15 | |
| 35.40 | 2.24 | 24.29 | 28.16 | 20.53 | 17.82 | |
| 28.99 | 2.27 | 21.25 | 25.48 | 16.81 | 15.05 | |
| 46.18 | 2.25 | 21.19 | 32.16 | 26.78 | 22.31 | |
| 36.1 | 2.25 | 18.47 | 28.44 | 20.94 | 18.12 | |
| 40.48 | 2.20 | 18.95 | 30.11 | 23.48 | 19.96 | |
| 41.36 | 2.22 | 18.87 | 30.44 | 23.99 | 20.33 | |
| 33.52 | 2.22 | 16.74 | 27.40 | 19.44 | 30.84 | |
| 39.07 | 2.23 | 18.2 | 26.14 | 17.69 | 17.02 | |
| 35.03 | 2.24 | 16.97 | 28.01 | 20.32 | 15.71 | |
| 37.12 | 2.22 | 17.78 | 28.84 | 21.53 | 17.67 | |
| 37.69 | 2.21 | 16.99 | 29.06 | 21.86 | 18.55 | |
| Diaz et al. [49] | 40.35 | 2.31 | 28.599 | 30.06 | 23.40 | 18.79 |
| 47.35 | 2.29 | 29.475 | 32.57 | 27.46 | 19.91 | |
| 46.69 | 2.32 | 29.358 | 32.34 | 27.08 | 22.79 | |
| 46.79 | 2.31 | 28.517 | 32.38 | 27.14 | 22.52 | |
| 46.11 | 2.29 | 26.455 | 32.14 | 26.74 | 22.56 | |
| 47.44 | 2.24 | 25.635 | 32.60 | 27.52 | 22.28 | |
| 12.20 | 1.99 | 7.04 | 16.53 | 7.08 | 22.83 | |
| 12.82 | 1.97 | 6.812 | 16.95 | 7.44 | 7.24 | |
| 20.86 | 1.99 | 7.96 | 21.62 | 12.10 | 7.55 | |
| 10.34 | 1.89 | 7.46 | 15.22 | 6.00 | 11.40 | |
| 46.56 | 2.37 | 28.744 | 32.30 | 27.00 | 6.30 | |
| 49.24 | 1.91 | 19.278 | 33.21 | 28.56 | 22.47 | |
| 43.38 | 2.29 | 25.607 | 31.17 | 25.16 | 23.56 | |
| Hardjito and Rangan [50] | 89 | 30.8 | 44.65 | 51.62 | 21.16 | |
| 68 | 27.3 | 39.03 | 39.44 | 38.85 | ||
| 55 | 26.1 | 35.10 | 31.90 | 30.95 | ||
| 44 | 23 | 31.40 | 25.52 | 25.87 | ||
| Fernández-Jiménez et al. [18] | 32 | 11.7 | 26.77 | 18.56 | 21.42 | |
| 29 | 10.7 | 25.49 | 16.82 | 16.36 | ||
| 34 | 13.4 | 27.60 | 19.72 | 15.06 | ||
| 43.5 | 18.4 | 31.22 | 25.23 | 17.23 | ||
| 39.5 | 15.8 | 29.75 | 22.91 | 21.21 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, Y.; Gao, K.; Zhang, P. Experimental and Statistical Study on Mechanical Characteristics of Geopolymer Concrete. Materials 2020, 13, 1651. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13071651
Cui Y, Gao K, Zhang P. Experimental and Statistical Study on Mechanical Characteristics of Geopolymer Concrete. Materials. 2020; 13(7):1651. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13071651
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Yifei, Kaikai Gao, and Peng Zhang. 2020. "Experimental and Statistical Study on Mechanical Characteristics of Geopolymer Concrete" Materials 13, no. 7: 1651. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13071651
APA StyleCui, Y., Gao, K., & Zhang, P. (2020). Experimental and Statistical Study on Mechanical Characteristics of Geopolymer Concrete. Materials, 13(7), 1651. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13071651





