Green Synthesis of Transition-Metal Nanoparticles and Their Oxides: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
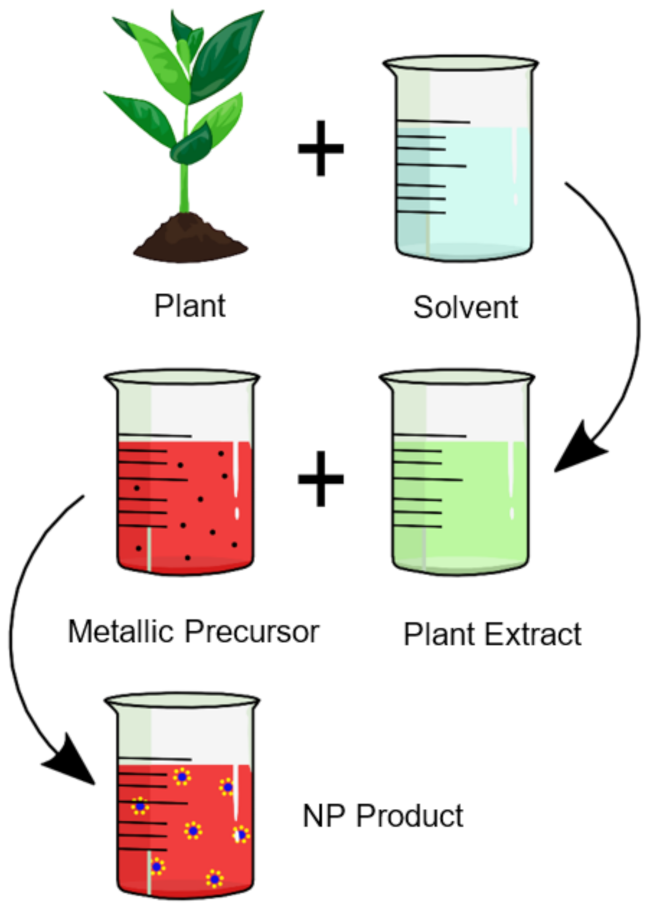
2. Biological Synthesis Techniques
3. Green Synthesis of Transitional Metals and Their Oxides
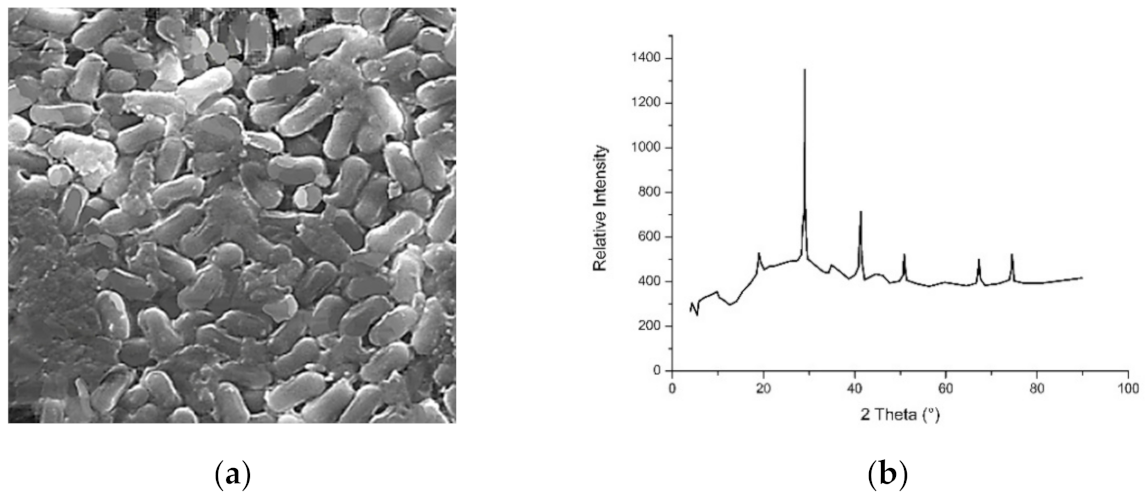
3.1. Titanium and Titanium Dioxide
3.2. Iron and Iron Oxide Nanoparticles
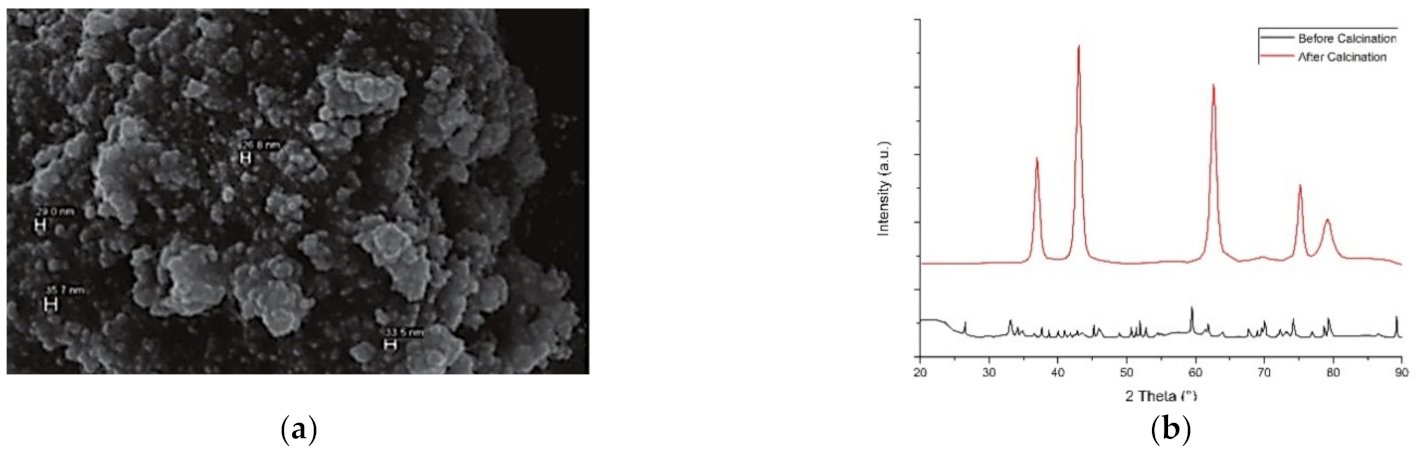
3.3. Cobalt and Cobalt Oxide Nanoparticles
3.4. Nickel and Nickel Oxide Nanoparticles
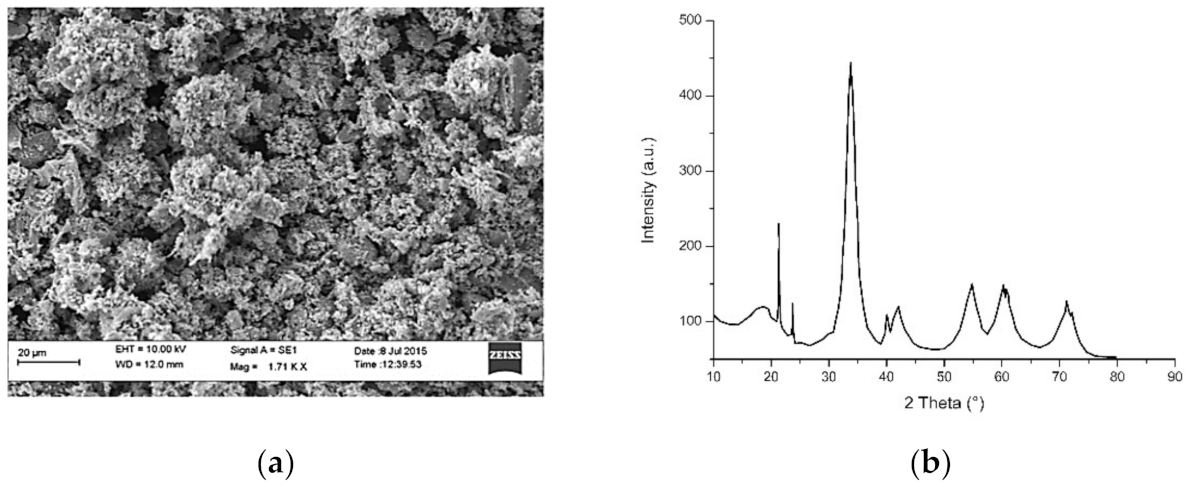
3.5. Copper and Copper Oxide Nanoparticles
3.6. Zinc and Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles
3.7. Palladium and Palladium Oxide Nanoparticles
3.8. Silver and Silver Oxide Nanoparticles
3.9. Platinum Nanoparticles
3.10. Gold Nanoparticles
4. Factors Affecting the Green Synthesis of Nanoparticles
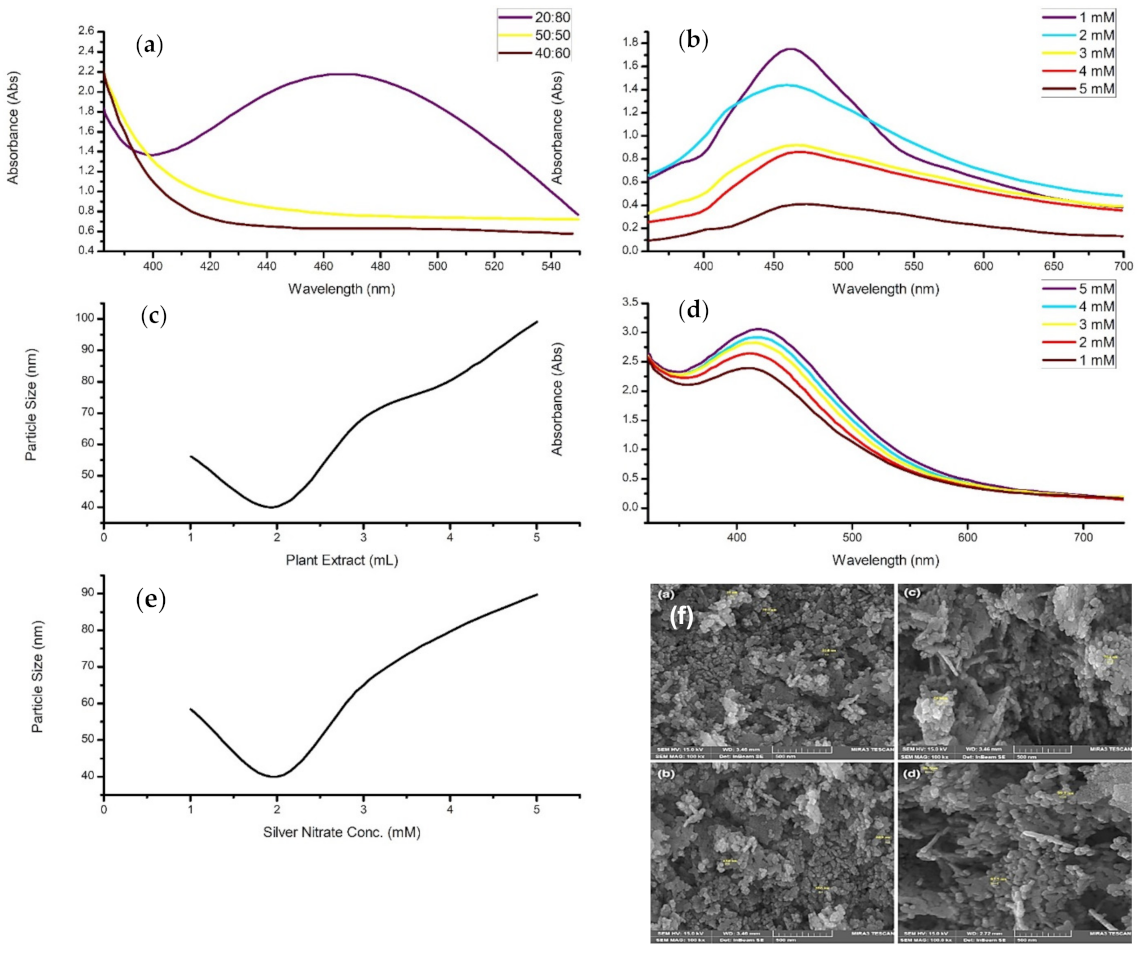
4.1. Concentration
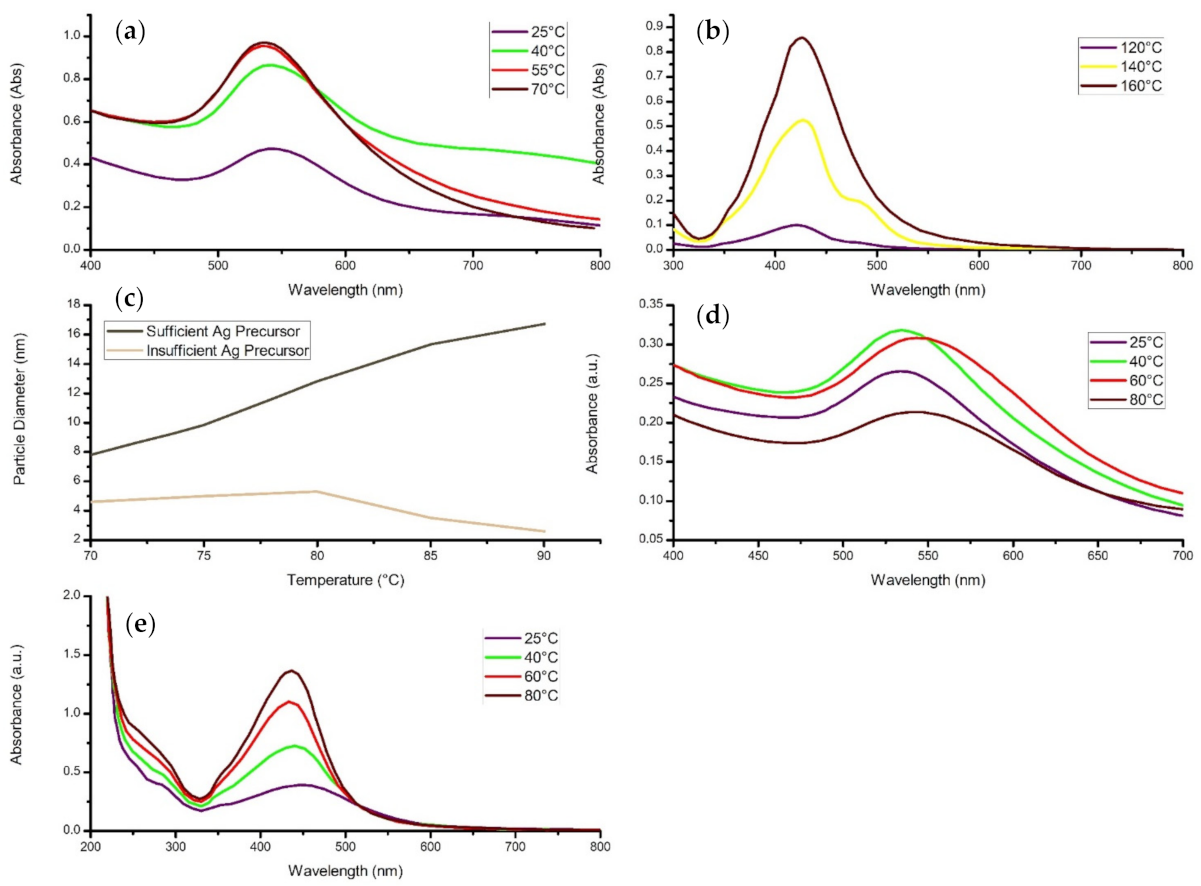
4.2. Reaction Temperature
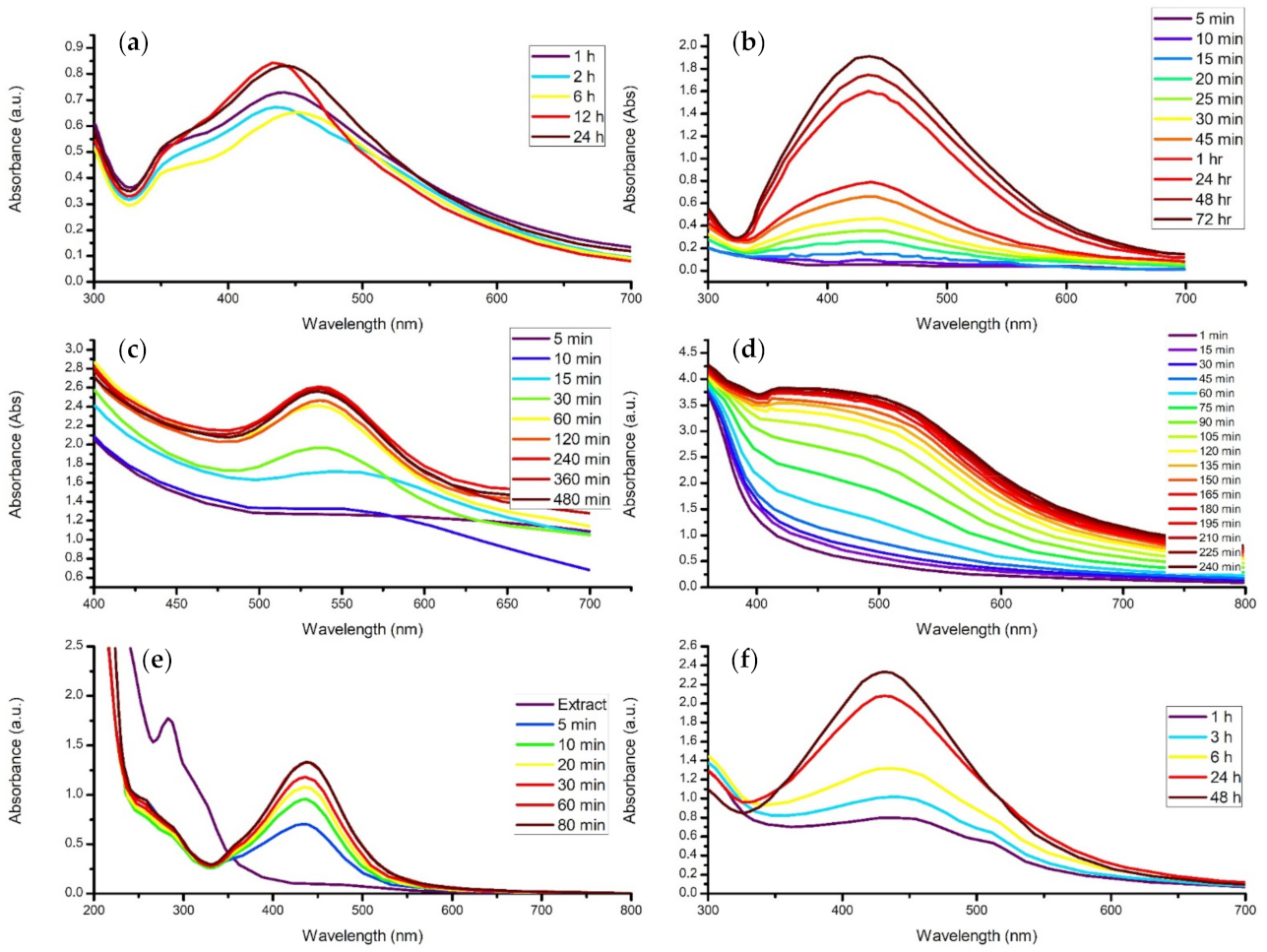
4.3. Contact Time
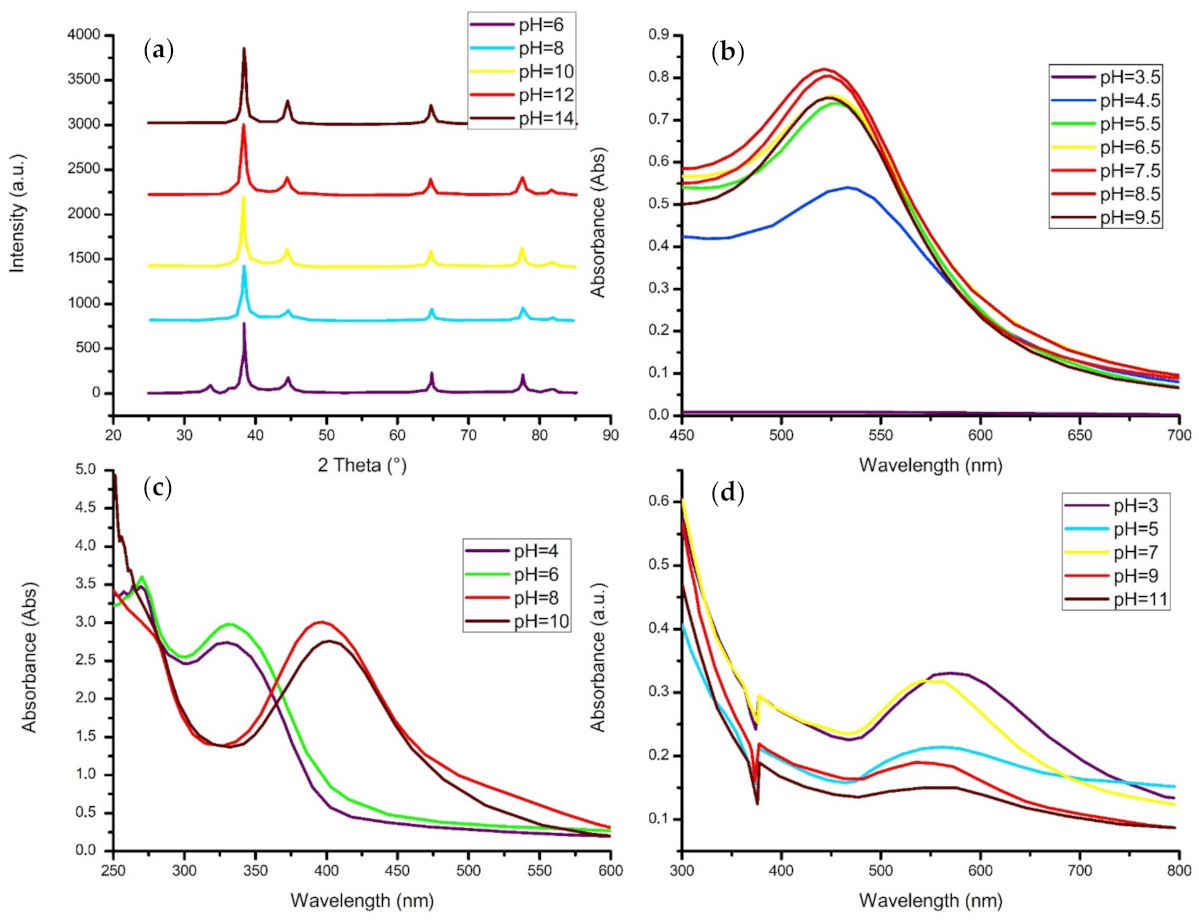
4.4. pH Level
4.5. Calcination Temperature
5. Drawbacks and Future Perspectives
6. Conclusions
- Plant extract-mediated nanoparticles have significant advantages as they reduce the complexity of the procedure, inhibit the use of toxic chemicals and eliminate harmful by-products through the modification of chemical synthesis processes.
- All plants have a reductive capability, with species such as terpenoids, phenols, alkaloids, saponins, and carbohydrates possessing different reducing strengths. This affects the concentration, size, and morphology of the desired nanoparticles.
- Size and morphology give the nanoparticles their unique properties; however, precisely controlling these characteristics is still troublesome.
- Agglomeration is deemed a major issue amongst nanoparticles as it may negatively affect their characteristics by reducing the available surface area; however, this may be avoided with the addition of a surfactant.
- During synthesis, an increase in precursor concentration generally increases particle diameter, concentration, or agglomeration.
- An increase in synthesis temperature increases the reaction rate, thereby increasing the concentration of nanomaterial and narrowing the particle size range, assuming sufficient precursor.
- Increasing the reaction time subsequently increases concentration, size, or agglomeration.
- The reaction solution generally favors a more neutral pH value, although increasing the pH level also increases the crystallinity of the material and may induce clusters to form.
- The Particle diameter and crystallinity of the nanostructures increases with an increase in calcination temperature.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AFM | Atomic Force Microscopy |
| ATR | Attenuated Total Reflectance |
| BET | Brunauer, Emmett and Teller Analysis |
| CD | Circular Dichroism |
| CV | Cyclic Voltammetry |
| DLS | Dynamic Light Scattering |
| DRS | Differential Reflectance Spectroscopy |
| DSC | Differential Scanning Calorimetry |
| EDS/EDX/EDAX | Energy-Dispersive X-Ray Spectroscopy |
| EELS | Electron Energy Loss Spectroscopy |
| ESI-MS | Electrospray Ionisation Mass Spectroscopy |
| FESEM | Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy |
| FTIR | Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy |
| GC-MS | Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry |
| HRSEM | High Resolution Scanning Electron Microscopy |
| HRTEM | High Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy |
| ICP-OES | Inductively Coupled Plasma-Optical Emission Spectrometry |
| NAA | Neutron Activation Analysis |
| NP | Nanoparticle |
| NTA | Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis |
| PL | Photoluminescence |
| SAED | Selected Area Electron Diffraction |
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscopy |
| TEM | Transmission Electron Microscopy |
| TGA | Thermogravimetric Analysis |
| UV-vis | Ultra Violet-visible spectroscopy |
| VSM | Vibrating-Sample Magnetometer |
| XPS | X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy |
| XRD | X-Ray Powder Diffraction |
References
- Iravani, S. Green synthesis of metal nanoparticles using plants. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 2638–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvardhan, K.; Ahmed, S. (Eds.) Green Metal Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization and Their Applications; Scrivener Publishing: Salem, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sridharan, K. The electromagnetic spectrum. In Spectral Methods in Transition Metal Complexes; 2016; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manchon, A.; Belabbes, A. Spin-Orbitronics at Transition Metal Interfaces. Solid State Phys. 2017, 68, 1–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rastogi, A.; Singh, P.; Haraz, F.A.; Barhoum, A. Biological synthesis of nanoparticles: An environmentally benign approach. Fundam. Nanopart. 2018, 571–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryaidh, A.-H.; Al-Qayim, M.A.J. Bio-Synthesis and Characterizations of Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Mediated By Iraq Propolis Extract. IOSR J. Pharm. Biol. Sci. 2017, 12, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deljou, A.; Goudarzi, S. Green Extracellular Synthesis of the Silver Nanoparticles Using Thermophilic Bacillus Sp. AZ1 and its Antimicrobial Activity against Several Human Pathogenetic Bacteria. Iran. J. Biotechnol. 2016, 14, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molnár, Z.; Bódai, V.; Szakacs, G.; Erdélyi, B.; Fogarassy, Z.; Sáfrán, G.; Varga, T.; Kónya, Z.; Tóth-Szeles, E.; Szűcs, R.; et al. Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles by thermophilic filamentous fungi. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kathiraven, T.; Sundaramanickam, A.; Shanmugam, N.; Balasubramanian, T. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using marine algae Caulerpa racemosa and their antibacterial activity against some human pathogens. Appl. Nanosci. 2015, 5, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niknejad, F.; Nabili, M.; Ghazvini, R.D.; Moazeni, M. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles: Another honor for the yeast model Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Curr. Med. Mycol. 2015, 1, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bar, H.; Bhui, D.K.; Sahoo, G.P.; Sarkar, P.; De, S.P.; Misra, A. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using latex of Jatropha curcas. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2009, 339, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Fang, G.; Cao, Z.; Shang, Y.; Alfarraj, S.; Alharbi, S.A.; Li, J.; Yang, S.; Duan, X. Green synthesis, characterization, cytotoxicity, antioxidant, and anti-human ovarian cancer activities of Curcumae kwangsiensis leaf aqueous extract green-synthesized gold nanoparticles. Arab. J. Chem. 2021, 14, 103000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, P.; Saravanan, K.; Manogar, P.; Johnson, J.; Vinoth, E.; Mayakannan, M. Green synthesis and characterization of biocompatible zinc oxide nanoparticles and evaluation of its antibacterial potential. Sens. Bio Sens. Res. 2021, 31, 100399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yew, Y.P.; Shameli, K.; Miyake, M.; Khairudin, N.B.B.A.; Mohamad, S.E.B.; Naiki, T.; Lee, K.X. Green biosynthesis of superparamagnetic magnetite Fe3O4 nanoparticles and biomedical applications in targeted anticancer drug delivery system: A review. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 2287–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, A.T.; Ovais, M.; Ullah, I.; Ali, M.; Shinwari, Z.K.; Maaza, M. Physical properties, biological applications and biocompatibility studies on biosynthesized single phase cobalt oxide (Co3O4) nanoparticles via Sageretia thea (Osbeck.). Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 606–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudiaf, M.; Messai, Y.; Bentouhami, E.; Schmutz, M.; Blanck, C.; Ruhlmann, L.; Bezzi, H.; Tairi, L.; Mekki, D.E. Green synthesis of NiO nanoparticles using Nigella sativa extract and their enhanced electro-catalytic activity for the 4-nitrophenol degradation. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2021, 153, 110020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, N.; Bin Humayoun, U.; Kumar, M.; Alam Zaidi, S.F.; Yoo, J.H.; Ali, N.; Jeong, D.I.; Lee, J.H.; Yoon, D.H. Citric acid mediated green synthesis of copper nanoparticles using cinnamon bark extract and its multifaceted applications. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 292, 125974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunalan, S.; Sivaraj, R.; Rajendran, V. Green synthesized ZnO nanoparticles against bacterial and fungal pathogens. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2012, 22, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hariharan, D.; Srinivasan, K.; Nehru, L.C. Synthesis and Characterization of Tio2 Nanoparticles Using Cynodon Dactylon Leaf Extract for Antibacterial and Anticancer (A549 Cell Lines) Activity. J. Nanomed. Res. 2017, 5, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gardea-Torresdey, J.L.; Parsons, J.G.; Gomez, E.; Peralta-Videa, J.; Troiani, H.E.; Santiago, P.; Yacaman, M.J. Formation and Growth of Au Nanoparticles inside Live Alfalfa Plants. Nano Lett. 2002, 2, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowshik, M.; Ashtaputre, S.; Kharrazi, S.; Vogel, W.; Urban, J.; Kulkarni, S.K.; Paknikar, K.M. Extracellular synthesis of silver nanoparticles by a silver-tolerant yeast strain MKY3. Nanotechnology 2002, 14, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Purdon, A.M.; Chu, A.V.; Westervelt, R.M. Controlled Assembly of Magnetic Nanoparticles from Magnetotactic Bacteria Using Microelectromagnets Arrays. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 995–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, P.; Senapati, S.; Mandal, D.; Ahmad, A.; Khan, M.I.; Kumar, R.; Sastry, M. Extracellular Synthesis of Gold Nanopar-ticles by the Fungus Fusarium oxysporum. ChemBioChem 2002, 3, 461–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, H.; Chen, Z.-S.; Chen, G. Biosynthesis of Nanoparticles by Microorganisms and Their Applications. J. Nanomater. 2011, 2011, 270974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, P.; Kim, Y.-J.; Zhang, D.; Yang, D.-C. Biological Synthesis of Nanoparticles from Plants and Microorganisms. Trends Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 588–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, I.; Singh, N.B.; Singh, A.; Singh, H.; Singh, S.C. Green synthesis of nanoparticles and its potential application. Biotechnol. Lett. 2016, 38, 545–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharissova, O.V.; Dias, H.R.; Kharisov, B.I.; Pérez, B.O.; Pérez, V.M.J. The greener synthesis of nanoparticles. Trends Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, R.K.; Pachapur, V.L.; Lonappan, L.; Naghdi, M.; Pulicharla, R.; Maiti, S.; Cledon, M.; Dalila, L.M.A.; Sarma, S.J.; Brar, S.K. Biological synthesis of metallic nanoparticles: Plants, animals and microbial aspects. Nanotechnol. Environ. Eng. 2017, 2, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ovais, M.; Khalil, A.T.; Islam, N.U.; Ahmad, I.; Ayaz, M.; Saravanan, M.; Shinwari, Z.K.; Mukherjee, S. Role of plant phytochemicals and microbial enzymes in biosynthesis of metallic nanoparticles. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 6799–6814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böttger, A.; Vothknecht, U.; Bolle, C.; Wolf, A. Lessons on Caffeine, Cannabis & Co.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnasamy, A.; Sundaresan, M.; Velan, P. Rapid phytosynthesis of nano-sized titanium using leaf extract of Azadirachta indica. Int. J. ChemTech Res. 2015, 8, 2047–2052. [Google Scholar]
- Kalyanasundaram, S.; Prakash, M.J. Biosynthesis and Characterization of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles Using Pithecellobium Dulce and Lagenaria Siceraria Aqueous Leaf Extract and Screening their Free Radical Scavenging and Antibacterial Properties. Int. Lett. Chem. Phys. Astron. 2015, 50, 80–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dobrucka, R. The biological synthesis of anatase titanium dioxide nanoparticles using Arnicae anthodium extract. Bulg. Chem. Commun. 2017, 49, 595–599. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, K.G.; Ashok, C.H.; Rao, K.V.; Chakra, C.S.; Rajendar, V. Synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles from orange fruit waste. Int. J. Multidiscip. Adv. Res. Trends 2015, 2, 82–90. [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee, A.; Nishanthini, D.; Sandhiya, N.; Abraham, J. Biosynthesis of titanium dioxide nanoparticles using Vigna radiata. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2016, 9, 85–88. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, S.-J.; Lei, C.; Xu, M.-W.; Cai, C.-J.; Jia, D.-Z. Environment-friendly biomimetic synthesis of TiO2 nanomaterials for photocatalytic application. Nanotechnology 2012, 23, 205601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, M.; Venkatesan, M.; Arumugam, V.; Natesan, G.; Saravanan, N.; Murugesan, S.; Ramachandran, S.; Ayyasamy, R.; Pugazhendhi, A. Green synthesis and characterization of titanium dioxide nanoparticles (TiO2 NPs) using Sesbania grandiflora and evaluation of toxicity in zebrafish embryos. Process. Biochem. 2019, 80, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahir, A.A.; Chauhan, I.S.; Bagavan, A.; Kamaraj, C.; Elango, G.; Shankar, J.; Arjaria, N.; Roopan, S.M.; Rahuman, A.A.; Singh, N. Green Synthesis of Silver and Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles Using Euphorbia prostrata Extract Shows Shift from Apoptosis to G0/G1Arrest followed by Necrotic Cell Death in Leishmania donovani. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 4782–4799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sahaya, P.; Kumar, M.; Francis, A.P.; Devasena, T. Biosynthesized and Chemically Synthesized Titania Nanoparticles: Comparative Analysis of Antibacterial Activity. J. Environ. Nanotechnol. 2014, 3, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoag, G.E.; Collins, J.B.; Holcomb, J.L.; Hoag, J.R.; Nadagouda, M.N.; Varma, R.S. Degradation of bromothymol blue by ‘greener’ nano-scale zero-valent iron synthesized using tea polyphenols. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 8671–8677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.-C.; Ehrman, S.H. Synthesis of Iron Nanoparticles via Chemical Reduction with Palladium Ion Seeds. Langmuir 2007, 23, 1419–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latha, N.; Gowri, M. Bio Synthesis and Characterization of Fe3O4 Nanoparticles Using Caricaya Papaya Leaves Extract. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2014, 3, 1551–1556. [Google Scholar]
- Pravallika, P.L.; Mohan, G.K.; Rao, K.V.; Shanker, K. Biosynthesis, characterization and acute oral toxicity studies of synthesized iron oxide nanoparticles using ethanolic extract of Centella asiatica plant. Mater. Lett. 2019, 236, 256–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseem, T.; Farrukh, M.A. Antibacterial Activity of Green Synthesis of Iron Nanoparticles Using Lawsonia inermis and Gardenia jasminoides Leaves Extract. J. Chem. 2015, 2015, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salgado, P.; Márquez, K.; Rubilar, O.; Contreras, D.; Vidal, G. The effect of phenolic compounds on the green synthesis of iron nanoparticles (FexOy-NPs) with photocatalytic activity. Appl. Nanosci. 2019, 9, 371–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murgueitio, E.; Debut, A.; Cumbal, J.L.A.L. Synthesis of iron nanoparticles through extracts of native fruits of Ecuador, as capuli (Prunus serotina) and mortiño (Vaccinium floribundum). Biol. Med. 2016, 8, 8–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balamurugan, M.G.; Mohanraj, S.; Kodhaiyolii, S.; Pugalenthi, V. Ocimum sanctum leaf extract mediated green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles: Spectroscopic and microscopic studies. JCHPS 2014, 4, 201–204. [Google Scholar]
- Amutha, S.; Sridhar, S. Green synthesis of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticle using leaves of Glycosmis mauritiana and their antibacterial activity against human pathogens. J. Innov. Pharm. Biol. Sci. 2015, 5, 22–26. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, J.; Srivastava, P.; Singh, G.; Akhtar, M.S.; Ameen, S. Green synthesis of Co3O4 nanoparticles and their applications in thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate and dye-sensitized solar cells. Mater. Sci. Eng. B Solid State Mater. Adv. Technol. 2015, 193, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Yang, D.-P.; Liu, A. Leaf-Templated synthesis of 3D hierarchical porous cobalt oxide nanostructure as direct electrochemical biosensing interface with enhanced electrocatalysis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 63, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K. Green synthesis of cobalt nanoparticles by using methanol extract of plant leaf as reducing agent. Pure Appl. Biol. 2016, 5, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, S.A.; Usami, T.; Kuroda, K.; Okido, M. Synthesis and Characterization of Cobalt Nanoparticles Using Hydrazine and Citric Acid. J. Nanotechnol. 2014, 2014, 525193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ikhuoria, E.; Omorogbe, S.; Sone, B.; Maaza, M. Bioinspired shape controlled antiferromagnetic Co3O4 with prism like-anchored octahedron morphology: A facile green synthesis using Manihot esculenta Crantz extract. Sci. Technol. Mater. 2018, 30, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igwe, O. Biofabrication of cobalt Nanoparticles using leaf extract of Chromolaena odorata and their potential antibacterial application. Res. J. Chem. Sci. 2018, 8, 11–17. [Google Scholar]
- Okwunodulu, F.U.; Chukwuemeka-Okorie, H.O.; Okorie, F.C. Biological Synthesis of Cobalt Nanoparticles from Mangifera indica Leaf Extract and Application by Detection of Manganese (II) Ions Present in Industrial Wastewater. Chem. Sci. Int. J. 2019, 27, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nomura, K.; Terwilliger, P.; Saeed, M.; Akram, N.; Ali, S.; Naqvi, R.; Usman, M.; Abbas, M.A. Green and eco-friendly synthesis of Co3O4 and Ag-Co3O4: Characterization and photo-catalytic activity. Green Process. Synth. 2019, 8, 382–390. [Google Scholar]
- Matinise, N.; Mayedwa, N.; Fuku, X.G.; Mongwaketsi, N.; Maaza, M. Green synthesis of cobalt (II, III) oxide nanoparticles using Moringa Oleifera natural extract as high electrochemical electrode for supercapacitors. In AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing LLC: Melville, NY, USA, 2018; p. 1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, J.; Abbasi, B.A.; Batool, R.; Khalil, A.T.; Hameed, S.; Kanwal, S.; Ullah, I.; Mahmood, T. Biogenic synthesis of green and cost effective cobalt oxide nanoparticles using Geranium wallichianum leaves extract and evaluation of in vitro antioxidant, antimicrobial, cytotoxic and enzyme inhibition properties. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 115407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibi, I.; Nazar, N.; Iqbal, M.; Kamal, S.; Nawaz, H.; Nouren, S.; Safa, Y.; Jilani, K.; Sultan, M.; Ata, S.; et al. Green and eco-friendly synthesis of cobalt-oxide nanoparticle: Characterization and photo-catalytic activity. Adv. Powder Technol. 2017, 28, 2035–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diallo, A.; Beye, A.; Doyle, T.; Park, E.; Maaza, M. Green synthesis of Co3O4 nanoparticles via Aspalathus linearis: Physical properties. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 2015, 8, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sudhasree, S.; Banu, A.S.; Brindha, P.; Kurian, G.A. Synthesis of nickel nanoparticles by chemical and green route and their comparison in respect to biological effect and toxicity. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2014, 96, 743–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibi, I.; Kamal, S.; Ahmed, A.; Iqbal, M.; Nouren, S.; Jilani, K.; Nazar, N.; Amir, M.; Abbas, A.; Ata, S.; et al. Nickel nanoparticle synthesis using Camellia sinensis as reducing and capping agent: Growth mechanism and photo-catalytic activity evaluation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 103, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juibari, N.M.; Eslami, A. Synthesis of nickel oxide nanorods by Aloe vera leaf extract: Study of its electrochemical properties and catalytic effect on the thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 136, 913–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, N.; Yulizar, Y. Spectroscopic, Structural, and Morphology of Nickel Oxide Nanoparticles Prepared Using Physalis angulata Leaf Extract. Mater. Sci. Forum MSF 2018, 917, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahaleh, Y.B.M.; Sadrnezhaad, S.K.; Hosseini, D. NiO Nanoparticles Synthesis by Chemical Precipitation and Effect of Applied Surfactant on Distribution of Particle Size. J. Nanomater. 2008, 2008, 470595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zorkipli, N.N.M.; Kaus, N.H.M.; Mohamad, A.A. Synthesis of NiO Nanoparticles through Sol-gel Method. Procedia Chem. 2016, 19, 626–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pandian, C.J.; Palanivel, R.; Dhananasekaran, S. Green synthesis of nickel nanoparticles using Ocimum sanctum and their application in dye and pollutant adsorption. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2015, 23, 1307–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasseri, M.A.; Ahrari, F.; Zakerinasab, B. A green biosynthesis of NiO nanoparticles using aqueous extract of Tamarix serotinaand their characterization and application. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2016, 30, 978–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helen, S.M.; Rani, M.H.E. Characterization and Antimicrobial Study of Nickel Nanoparticles Synthesized from Dioscorea (Elephant Yam) by Green Route. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2015, 4, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, J.; Abbasi, B.A.; Mahmood, T.; Hameed, S.; Munir, A.; Kanwal, S. Green synthesis and characterizations of Nickel oxide nanoparticles using leaf extract of Rhamnus virgata and their potential biological applications. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2019, 33, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thema, F.; Manikandan, E.; Gurib-Fakim, A.; Maaza, M. Single phase Bunsenite NiO nanoparticles green synthesis by Agathosma betulina natural extract. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 657, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Huang, D.; Chen, X.; Zhu, J.; Sun, D.; Huang, J.; Li, Q. Plant-mediated synthesis of size-controllable Ni nanoparticles with alfalfa extract. Mater. Lett. 2014, 122, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrollahzadeh, M.; Sajadi, S.M.; Khalaj, M. Green synthesis of copper nanoparticles using aqueous extract of the leaves of Euphorbia esula L and their catalytic activity for ligand-free Ullmann-coupling reaction and reduction of 4-nitrophenol. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 47313–47318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caroling, G.; Vinodhini, E.; Ranjitham, A.M.; Shanthi, P. Biosynthesis of Copper Nanoparticles Using Aqueous Phyllanthus embilica—Characterization and Study of Antibacterial Effects. Int. J. Pharm. Biol. Sci. 2015, 5, 25–43. [Google Scholar]
- Muthuvel, A.; Jothibas, M.; Manoharan, C. Synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles by chemical and biogenic methods: Photocatalytic degradation and in vitro antioxidant activity. Nanotechnol. Environ. Eng. 2020, 5, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altikatoglu, M.; Attar, A.; Erci, F.; Cristache, C.M.; Isildak, I. Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using Ocimum ba-silicum extract and their antibacterial activity. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2017, 25, 7832–7837. [Google Scholar]
- Jayarambabu, N.; Akshaykranth, A.; Rao, T.V.; Rao, K.V.; Kumar, R.R. Green synthesis of Cu nanoparticles using Curcuma longa extract and their application in antimicrobial activity. Mater. Lett. 2020, 259, 126813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharmila, G.; Pradeep, R.S.; Sandiya, K.; Santhiya, S.; Muthukumaran, C.; Jeyanthi, J.; Kumar, N.M.; Thirumarimurugan, M. Biogenic synthesis of CuO nanoparticles using Bauhinia tomentosa leaves extract: Characterization and its antibacterial application. J. Mol. Struct. 2018, 1165, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maham, M.; Sajadi, S.M.; Kharimkhani, M.M.; Nasrollahzadeh, M. Biosynthesis of the CuO nanoparticles using Euphorbia chamaesyce leaf extract and investigation of their catalytic activity for the reduction of 4-nitrophenol. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2017, 11, 766–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagar, N.; Devra, V. Green synthesis and characterization of copper nanoparticles using Azadirachta indica leaves. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 213, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, D.; Shaikh, S.; Shulaksana, D.; Kanawade, R. Green synthesis of copper nanoparticles using Gloriosa superba L. leaf extract. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Res. 2017, 203–209. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, K.S.; Patra, A.; Shruthi, G.; Chandan, S. Aqueous Extract of Saraca indica Leaves in the Synthesis of Copper Oxide Nanoparticles: Finding a Way towards Going Green. J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 2017, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, G.M.; Tawfeeq, A.T.; Jaaffer, M.D. Biogenic synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles Usingolea europaea leaf extract and evaluation of their toxicity activities: An in vivo and in vitro study. Biotechnol. Prog. 2018, 34, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awwad, A.M.; Albiss, B.A.; Salem, N.M. Antibacterial Activity of synthesized Copper Oxide Nanoparticles using Malva sylvestris Leaf Extract. SMU Med. J. 2015, 2, 91–101. [Google Scholar]
- Sangeetha, G.; Rajeshwari, S.; Venckatesh, R. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles by aloe barbadensis miller leaf extract: Structure and optical properties. Mater. Res. Bull. 2011, 46, 2560–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narendhran, S.; Sivaraj, R. Biogenic ZnO nanoparticles synthesized using L. aculeata leaf extract and their antifungal activity against plant fungal pathogens. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2016, 39, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aneesh, P.M.; Vanaja, K.A.; Jayaraj, M.K. Synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles by hydrothermal method. Proc. SPIE 2007, 6639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devasenan, S.; Beevi, N.H.; Jayanthi, S.S. Green synthesis and characterization of zinc nanoparticle using Andrographis paniculata leaf extract. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res. 2016, 39, 243–247. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, N.; Syed, A.; Vyawahare, P.; Dakle, R.; Ghuge, B. Green approach for the synthesis of zinc nanoparticles and its antibacterial activity. Int. Res. J. Pharm. 2016, 7, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, M.; Anbuvannan, M.; Viruthagiri, G. Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using Solanum nigrum leaf extract and their antibacterial activity. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 136, 864–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, N.; Khole, E.; Jagtap, S.; Tribhuvan, H.; Kakde, G.; Kuwar, P. Green Synthesis of Zinc Nanowires using Spilanthes acmella Leaf Extract. Pharm. Biosci. J. 2016, 4, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loganathan, K.; Kumar, P.V.; Ahamed, A.J. Biosynthesis of ZnO Nanoparticles using Phyllanthus emblica Seed Powder and its Structural and Optical Characterization Studies. J. Environ. Nanotechnol. 2018, 7, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, A.; Patra, C.; Bharadwaj, H.; Kaur, S.; Dimri, N.; Khajuria, R. Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Parthenium hysterophorus Leaf Extract and Evaluation of their Antibacterial Properties. J. Biotechnol. Biomater. 2017, 7, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, R.; Gayathri, R. Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles by using Hibiscus rosa-sinensis. Int. J. Curr. Eng. Technol. 2014, 44, 2444–2446. [Google Scholar]
- Dobrucka, R.; Długaszewska, J. Biosynthesis and antibacterial activity of ZnO nanoparticles using Trifolium pratense flower extract. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 23, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karnan, T.; Selvakumar, S.A.S. Biosynthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using rambutan (Nephelium lappaceum L.) peel extract and their photocatalytic activity on methyl orange dye. J. Mol. Struct. 2016, 1125, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elumalai, K.; Velmurugan, S.; Ravi, S.; Kathiravan, V.; AshokKumar, S. Facile, eco-friendly and template free photosynthesis of cauliflower like ZnO nanoparticles using leaf extract of Tamarindus indica (L.) and its biological evolution of antibacterial and antifungal activities. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 136, 1052–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathishkumar, M.; Sneha, K.; Kwak, I.S.; Mao, J.; Tripathy, S.; Yun, Y.-S. Phyto-crystallization of palladium through reduction process using Cinnamom zeylanicum bark extract. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 171, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surendra, T.; Roopan, S.M.; Arasu, M.V.; Al-Dhabi, N.A.; Rayalu, G.M. RSM optimized Moringa oleifera peel extract for green synthesis of M. oleifera capped palladium nanoparticles with antibacterial and hemolytic property. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2016, 162, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharmila, G.; Fathima, M.F.; Haries, S.; Geetha, S.; Kumar, N.M.; Muthukumaran, C. Green synthesis, characterization and antibacterial efficacy of palladium nanoparticles synthesized using Filicium decipiens leaf extract. J. Mol. Struct. 2017, 1138, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.L.; Nguyen, D.C.; Hirata, H.; Ohtaki, M.; Hayakawa, T.; Nogami, M. Chemical synthesis and characterization of palladium nanoparticles. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2010, 1, 35012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, E.; Khenfouch, M.; Dhlamini, M.; Dube, S.; Maaza, M. Green palladium and palladium oxide nanoparticles synthesized via Aspalathus linearis natural extract. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 695, 3632–3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauthal, P.; Mukhopadhyay, M. Biosynthesis of Palladium Nanoparticles Using Delonix regia Leaf Extract and Its Catalytic Activity for Nitro-aromatics Hydrogenation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 18131–18139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanchana, A.; Devarajan, S.; Ayyappan, S.R. Green synthesis and characterization of palladium nanoparticles and its conjugates from Solanum trilobatum leaf extract. Nano Micro Lett. 2010, 2, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attar, A.; Yapaoz, M.A. Biosynthesis of palladium nanoparticles using Diospyros kaki leaf extract and determination of antibacterial efficacy. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2018, 48, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikandan, V.; Velmurugan, P.; Park, J.-H.; Lovanh, N.; Seo, S.-K.; Jayanthi, P.; Park, Y.-J.; Cho, M.; Oh, B.-T. Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of palladium nanoparticles from Prunus × yedoensis leaf extract. Mater. Lett. 2016, 185, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinath, V.; MubarakAli, D.; Priyadarshini, S.; Priyadharsshini, N.M.; Thajuddin, N.; Velusamy, P. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles from Tribulus terrestris and its antimicrobial activity: A novel biological approach. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2012, 96, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, N.; Li, D.; Xiaodong, C.; Yasin, S.; Umair, M.; Eede, S.; Wei, Q. Photo-irradiation based biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles by using an ever-green shrub and its antibacterial study. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostruct. 2015, 10, 95–105. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Hussain, M.; Memon, H.; Yasin, S. Solar Irradiation and Nageia Nagi Extract Assisted Rapid Synthesis of Silver Na-noparticles and their Antibacterial Activity. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostruct. 2015, 10, 1019. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, J.; Yasin, S.; Liu, L. Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles by Bamboo Leaves Extract and Their Antimicrobial Activity. J. Fiber Bioeng. Inform. 2013, 6, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasaradhudu, Y.; Srinivasan, M.A. Synthesis and characterization of silver nano particles using co-precipitation method. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 720–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahjahan, M.; Rahman, H.; Hossain, M.S.; Khatun, M.A.; Islam, A.; Begum, M.H.A. Synthesis and Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles by Sol-Gel Technique. Nanosci. Nanometrol. 2017, 3, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rashmi, B.; Harlapur, S.F.; Avinash, B.; Ravikumar, C.; Nagaswarupa, H.; Kumar, M.A.; Gurushantha, K.; Santosh, M. Facile green synthesis of silver oxide nanoparticles and their electrochemical, photocatalytic and biological studies. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2020, 111, 107580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikandan, V.; Velmurugan, P.; Park, J.-H.; Chang, W.-S.; Park, Y.-J.; Jayanthi, P.; Cho, M.; Oh, B.-T. Green synthesis of silver oxide nanoparticles and its antibacterial activity against dental pathogens. 3 Biotech 2017, 7, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ravichandran, S.; Paluri, V.; Kumar, G.; Loganathan, K.; Venkata, B.R.K. A novel approach for the biosynthesis of silver oxide nanoparticles using aqueous leaf extract of Callistemon lanceolatus (Myrtaceae) and their therapeutic potential. J. Exp. Nanosci. 2016, 11, 445–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sadeghi, B.; Gholamhoseinpoor, F. A study on the stability and green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Ziziphora tenuior (Zt) extract at room temperature. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 134, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saware, K.; Venkataraman, A. Biosynthesis and Characterization of Stable Silver Nanoparticles Using Ficus religiosa Leaf Extract: A Mechanism Perspective. J. Clust. Sci. 2014, 25, 1157–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idrees, M.; Batool, S.; Kalsoom, T.; Raina, S.; Sharif, H.M.A.; Yasmeen, S. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Sida acuta extract for antimicrobial actions and corrosion inhibition potential. Environ. Technol. 2019, 40, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alghoraibia, I.; Soukkarieh, C.; Zein, R.; Alahmad, A.; Walter, J.-G.; Daghestani, M. Aqueous extract of Eucalyptus camaldulensis leaves as reducing and capping agent in green synthesis of silver nanoparticles. Curr. Nanomater. 2019, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodarzi, V.; Zamani, H.; Bajuli, L.; Moradshahi, A. Evaluation of antioxidant potential and reduction capacity of some plant extracts in silver nanoparticles’ synthesis. Mol. Boil. Res. Commun. 2014, 3, 165–174. [Google Scholar]
- Karthik, R.; Sasikumar, R.; Chen, S.M.; Govindasamy, M.; Kumar, J.V.; Muthuraj, V. Green Synthesis of Platinum Nanoparticles Using Quercus glauca Extract and Its Electrochemical Oxidation of Hydrazine in Water Samples. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2016, 11, 8245–8255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.V.; Kala, S.M.J.; Prakash, K. Green synthesis derived Pt-nanoparticles using Xanthium strumarium leaf extract and their biological studies. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, K.; Nazir, S.; Ahmad, A.; Li, B.; Khan, A.U.; Khan, Z.U.H.; Khan, F.U.; Khan, Q.U.; Khan, A.; Rahman, A.U. Facile and green synthesis of phytochemicals capped platinum nanoparticles and in vitro their superior antibacterial activity. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2017, 166, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, W.; Qi, W.; Tang, S.; Peng, H.; Li, S. Hydrothermal Synthesis of Ultrasmall Pt Nanoparticles as Highly Active Electrocatalysts for Methanol Oxidation. Nanomaterials 2015, 5, 2203–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pal, A.; Shah, S.; Belochapkine, S.; Tanner, D.; Magner, E.; Devi, S. Room temperature synthesis of platinum nanoparticles in water-in-oil microemulsion. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2009, 337, 205–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrucka, R. Synthesis and Structural Characteristic of Platinum Nanoparticles Using Herbal Bidens tripartitus Extract. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2015, 26, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, L.; Blázquez, M.L.; González, F.; Muñoz, J. Ángel; Ballester, A. Biosynthesis of silver and platinum nanoparticles using orange peel extract: Characterisation and applications. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2015, 9, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyapaul, U.; Kala, M.J.; Bosco, A.J.; Piruthiviraj, P.; Easuraja, M. An Eco-friendly Approach for Synthesis of Platinum Nanoparticles using Leaf Extracts of Jatropa gossypifolia and Jatropa glandulifera and its Antibacterial Activity. Orient. J. Chem. 2018, 34, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dobrucka, R. Biofabrication of platinum nanoparticles using Fumariae herba extract and their catalytic properties. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 26, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, K.P.; Paul, W.; Sharma, C.P. Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles with Zingiber officinale extract: Characterization and blood compatibility. Process. Biochem. 2011, 46, 2007–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.G.; Gokavarapu, S.D.; Rajeswari, A.; Dhas, T.S.; Karthick, V.; Kapadia, Z.; Shrestha, T.; Barathy, I.; Roy, A.; Sinha, S. Facile green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using leaf extract of antidiabetic potent Cassia auriculata. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 87, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jameel, Z.N. Synthesis of The gold Nanoparticles with Novel Shape via Chemical Process and Evaluating The structural, Morphological and Optical Properties. Energy Procedia 2017, 119, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, S.P.; Lahtinen, M.; Särkkä, H.; Sillanpää, M. Bioprospective of Sorbus aucuparia leaf extract in development of silver and gold nanocolloids. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 80, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, B.; Bhuyan, B.; Purkayastha, D.D.; Vadivel, S.; Dhar, S.S. One-pot green synthesis of gold nanoparticles and studies of their anticoagulative and photocatalytic activities. Mater. Lett. 2016, 185, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Cho, C.-W.; Yun, Y.-S. Biosynthesis of Gold Nanoparticles Using Ocimum sanctum Extracts by Solvents with Different Polarity. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 2651–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbagory, A.M.; Cupido, C.N.; Meyer, M.; Hussein, A.A. Large Scale Screening of Southern African Plant Extracts for the Green Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles Using Microtitre-Plate Method. Molecules 2016, 21, 1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noruzi, M.; Zare, D.; Khoshnevisan, K.; Davoodi, D. Rapid green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Rosa hybrida petal extract at room temperature. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2011, 79, 1461–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiri, Y.; Elia, P.; Zach, R.; Hazan, S.; Kolusheva, S.; Porat, Z. Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using plant extracts as reducing agents. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 4007–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dozie-Nwachukwu, S.; Etuk-Udo, G.; Obayemi, J.; Anuku, N.; Odusanya, O.; Malatesta, K.; Chi, C.; Soboyejo, W.; Dozie-Nwachukwu, S. Biosynthesis of Gold Nanoparticles from Nauclea latifolia Leaves. Adv. Mater. Res. 2015, 1132, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Li, Q.; Sun, D.; Lu, Y.; Su, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Shao, W.; He, N.; et al. Biosynthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles by novel sundried Cinnamomum camphora leaf. Nanotechnology 2007, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-S.; Seo, Y.S.; Kim, K.; Han, J.W.; Park, Y.; Cho, S. Concentration Effect of Reducing Agents on Green Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles: Size, Morphology, and Growth Mechanism. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Latif, M.S.; Kormin, F.; Mustafa, M.K.; Mohamad, I.I.; Khan, M.; Abbas, S.; Ghazali, M.I.; Shafie, N.S.; Abu Bakar, M.F.; Sabran, S.F.; et al. Effect of temperature on the synthesis of Centella asiatica flavonoids extract-mediated gold nanoparticles: UV-visible spectra analyses. AIP Conf. Proc. 2018, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darroudi, M.; Bin Ahmad, M.; Zamiri, R.; Zak, A.; Abdullah, A.H.; Ibrahim, N.A. Time-dependent effect in green synthesis of silver nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 677–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Traiwatcharanon, P.; Timsorn, K.; Wongchoosuk, C. Effect of pH on the Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles through Reduction with Pistiastratiotes L. Extract. Adv. Mater. Res. 2015, 1131, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, S.; Mohamad, R.; Bahadoran, A.; Bayat, S.; Rahim, R.A.; Ariff, A.; Saad, W.Z. Effect of annealing temperature on antimicrobial and structural properties of bio-synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles using flower extract of Anchusa italica. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2016, 161, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anigol, L.B.; Charantimath, J.S.; Gurubasavaraj, P.M. Effect of Concentration and pH on the Size of Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized by Green Chemistry. Org. Med. Chem. 2017, 3, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratheema, P. Anti- Inflammatory And Anti-Bacterial Activity of Titanium Nanoparticles Synthesized From Rhizomes of Alpinia calcarata. Int. J. Res. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2018, 6, 2472–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, S.; Upadhyay, L.S.B. Biosynthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles using plant derivatives of Lawsonia inermis (Henna) and its surface modification for biomedical application. Nanotechnol. Environ. Eng. 2019, 4, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faghihi, R.; Larijani, K.; Abdossi, V.; Moradi, P. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles by grapefruit‘s peel and effect on superoxide dismutase enzyme activity and growth of cucumber plants inoculated with Rhizoctonia solani. Orient. J. Chem. 2017, 33, 2810–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asemani, M.; Anarjan, N. Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using Juglans regia leaf extract and assessment of their physico-chemical and biological properties. Green Process. Synth. 2019, 8, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, F.M.; Ghasemi, N. Influence of temperature and concentration on biosynthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles using cherry extract. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 2018, 8, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vanaja, M.; Rajeshkumar, S.; Paulkumar, K.; Gnanajobitha, G.; Malarkodi, C.; Annadurai, G. Kinetic study on green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Coleus aromaticus leaf extract. Pelagia Res. Libr. 2013, 4, 50–55. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, R.; Ghoshal, G.; Jain, A.; Goyal, M. Rapid Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs) Using (Prunus persica) Plants extract: Exploring its Antimicrobial and Catalytic Activities. J. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muniandy, S.S.; Sasidharan, S.; Lee, H.L. Green Synthesis of Ag Nanoparticles and Their Performance towards Antimicrobial Properties. Sains Malays. 2019, 48, 851–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavinskaya, O.; Laguta, I.; Fesenko, T.; Krumova, M. Effect of Temperature on Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Vitex Agnus-castus Extract. Chem. J. Mold. 2019, 14, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Wei, J. Effect of temperature on the size of biosynthesized silver nanoparticle: Deep insight into microscopic kinetics analysis. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 13, 1011–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jon, R.; Martin, N.; Dasari, P.R.; Paul, A.; Singh, V. Effect of Physical Parameters on Green Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles using Zea Mays Extract. Int. J. Eng. Adv. Technol. 2019, 9, 870–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesika, N.S.; Stebe, K.J.; Searson, P.C. Relationship between Absorbance Spectra and Particle Size Distributions for Quantum-Sized Nanocrystals. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 10412–10415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Chan, C.; Huang, S.; Lin, Y. Green biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles using Chenopodium formosanum shell extract and analysis of the particles’ antibacterial properties. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 3693–3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, B.; Tang, R.-C. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles with antibacterial activities using aqueous Eriobotrya japonica leaf extract. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 015014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramli, N.A.; Jai, J.; Yusof, N.M. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Elaeis guineensis (Palm Leaves): An Investigation on the Effect of Reaction Time in Reduction Mechanism and Particle Size. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 575, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behravan, M.; Panahi, A.H.; Naghi Zadeh, A.; Ziaee, M.; Mahdavi, R.; Mirzapour, A. Facile green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Berberis vulgaris leaf and root aqueous extract and its antibacterial activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 124, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, H.M. Green synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using banana peel extract and their antimicrobial activity against representative microorganisms. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2015, 8, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, T.; Irfan, M.; Bustam, M.A.; Bhattacharjee, S. Effect of Reaction Time on Green Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles by Using Aqueous Extract of Elaise guineensis (Oil Palm Leaves). Procedia Eng. 2016, 148, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, A.K.; Srivastava, O.N. One-Step Green Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles Using Black Cardamom and Effect of pH on Its Synthesis. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aziz, W.J.; Jassim, H.A. A novel study of pH influence on Ag nanoparticles size with antibacterial and antifungal activity using green synthesis. World Sci. News 2018, 97, 139–152. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Radadi, N.S. Green synthesis of platinum nanoparticles using Saudi’s Dates extract and their usage on the cancer cell treatment. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 330–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, M.; Ahmad, T.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Abdullah, B. Effect of pH on ionic liquid mediated synthesis of gold nanoparticle using elaiseguineensis (palm oil) kernel extract. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 204, 012002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mfon, R.E.; Hall, S.R.; Sarua, A. Effect of ocimum gratissimum plant leaf extract concentration and annealing temperature on the structure and optical properties of synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles. Educ. J. Sci. Math. Technol. 2020, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Kayani, Z.N.; Saleemi, F.; Batool, I. Effect of calcination temperature on the properties of ZnO nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 2015, 119, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


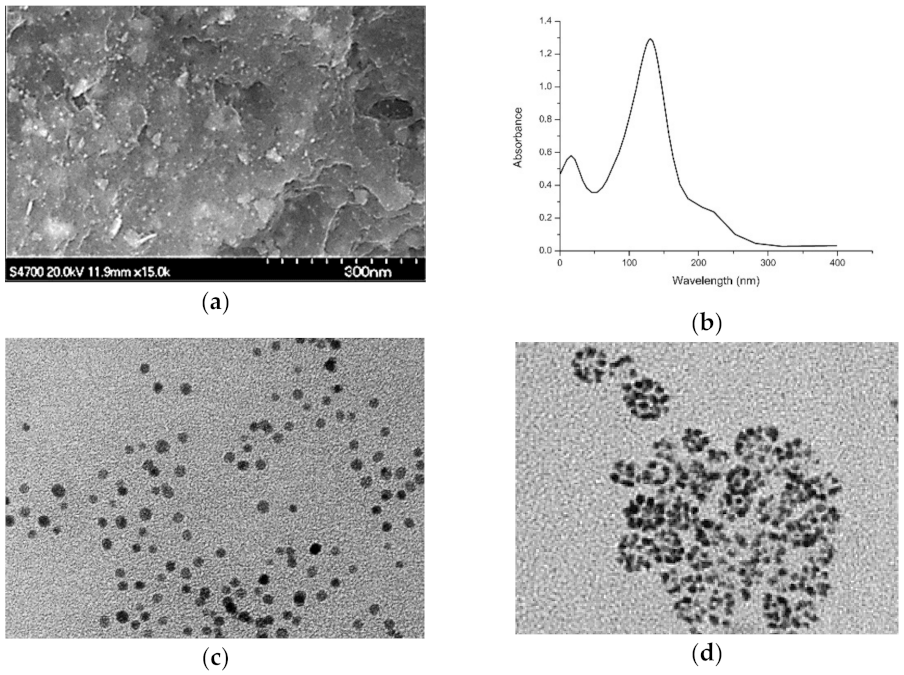
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Drummer, S.; Madzimbamuto, T.; Chowdhury, M. Green Synthesis of Transition-Metal Nanoparticles and Their Oxides: A Review. Materials 2021, 14, 2700. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14112700
Drummer S, Madzimbamuto T, Chowdhury M. Green Synthesis of Transition-Metal Nanoparticles and Their Oxides: A Review. Materials. 2021; 14(11):2700. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14112700
Chicago/Turabian StyleDrummer, Sean, Tafirenyika Madzimbamuto, and Mahabubur Chowdhury. 2021. "Green Synthesis of Transition-Metal Nanoparticles and Their Oxides: A Review" Materials 14, no. 11: 2700. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14112700
APA StyleDrummer, S., Madzimbamuto, T., & Chowdhury, M. (2021). Green Synthesis of Transition-Metal Nanoparticles and Their Oxides: A Review. Materials, 14(11), 2700. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14112700






