Study on the Influence of Reinforced Particles Spatial Arrangement on the Neutron Shielding Performance of the Composites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Modeling Methods of Four Models
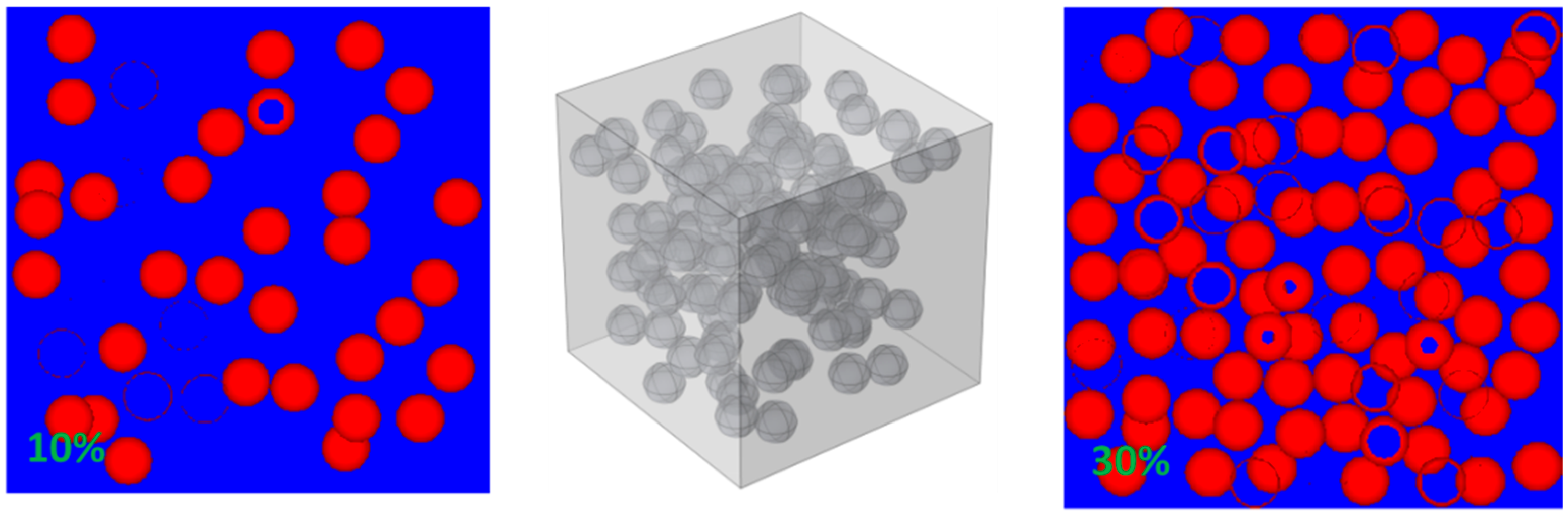
2.2.1. RSA Model
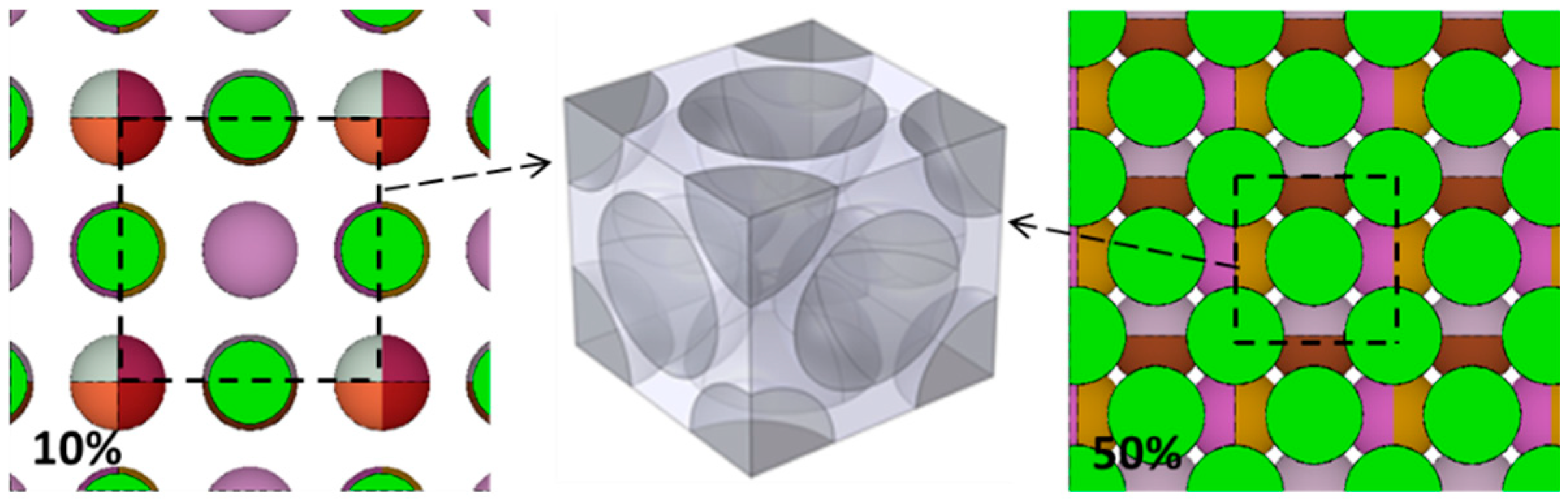
2.2.2. BCC Model and FCC Model
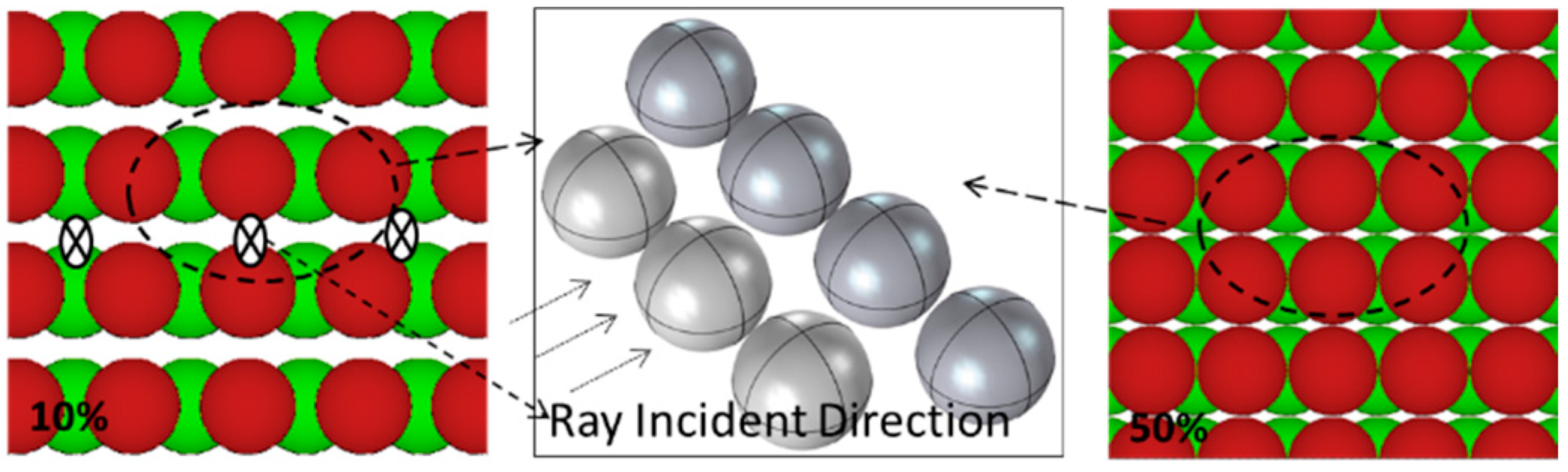
2.2.3. SA Model
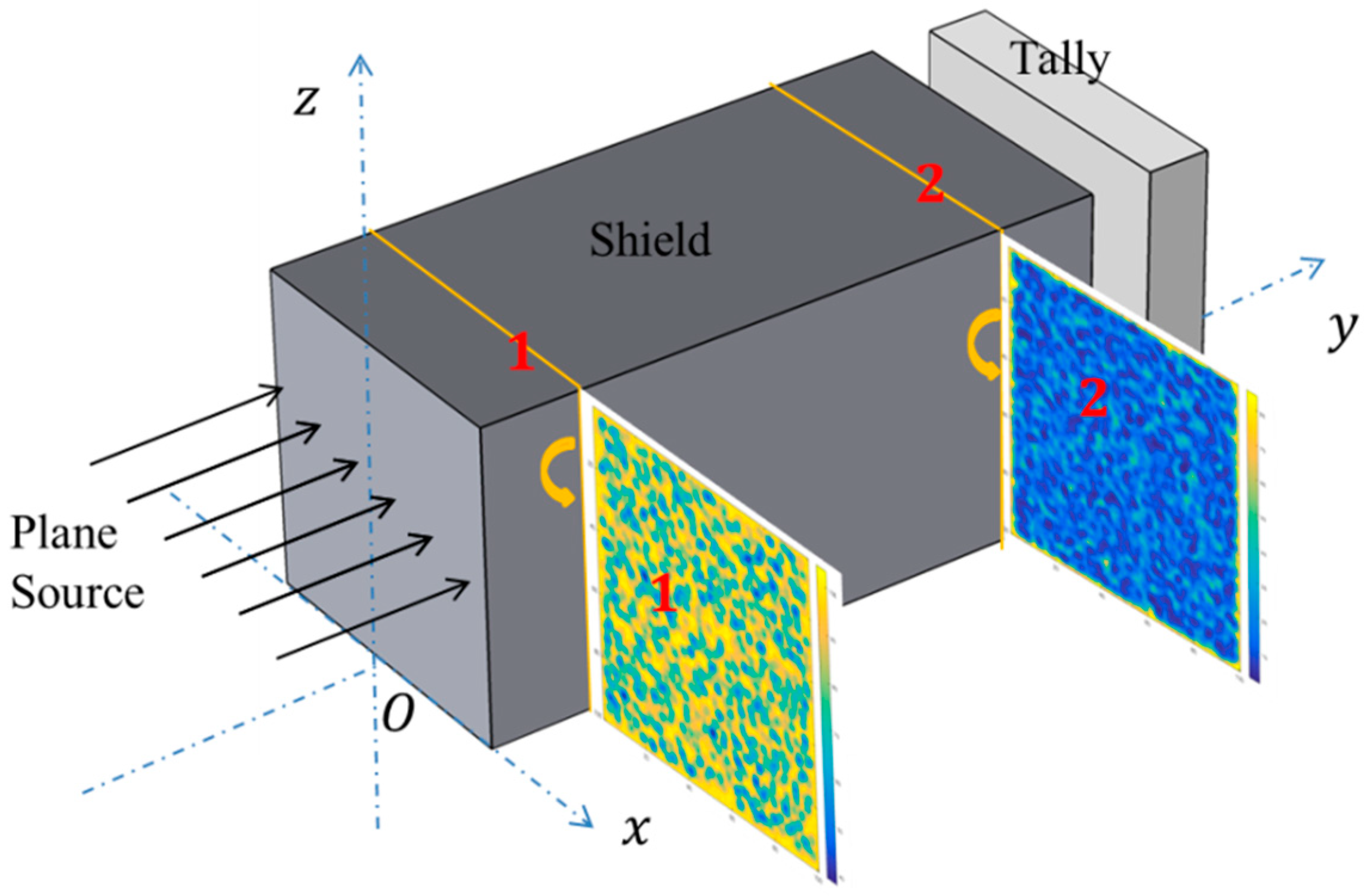
2.3. The Whole Calculation Model
3. Results and Discussion
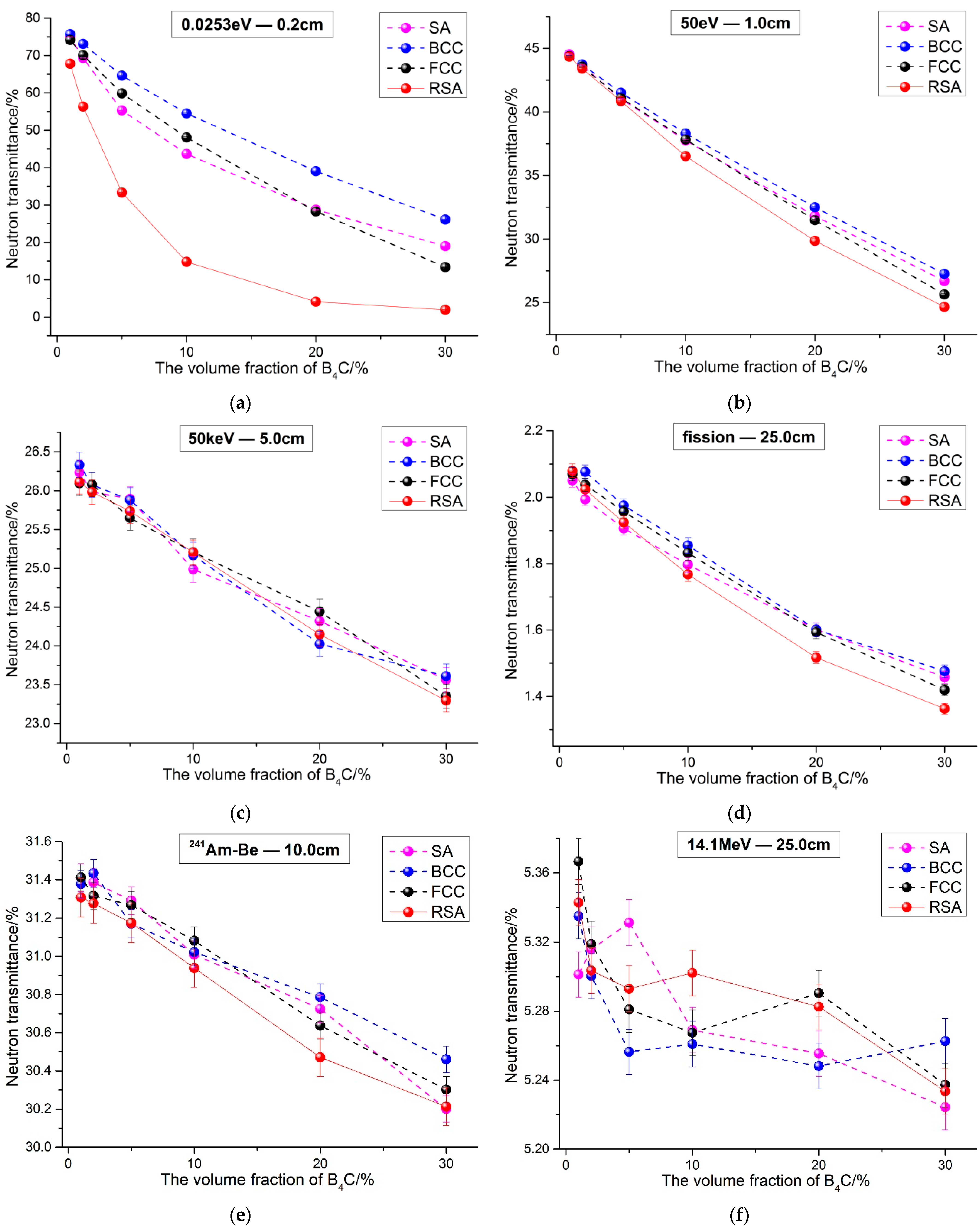
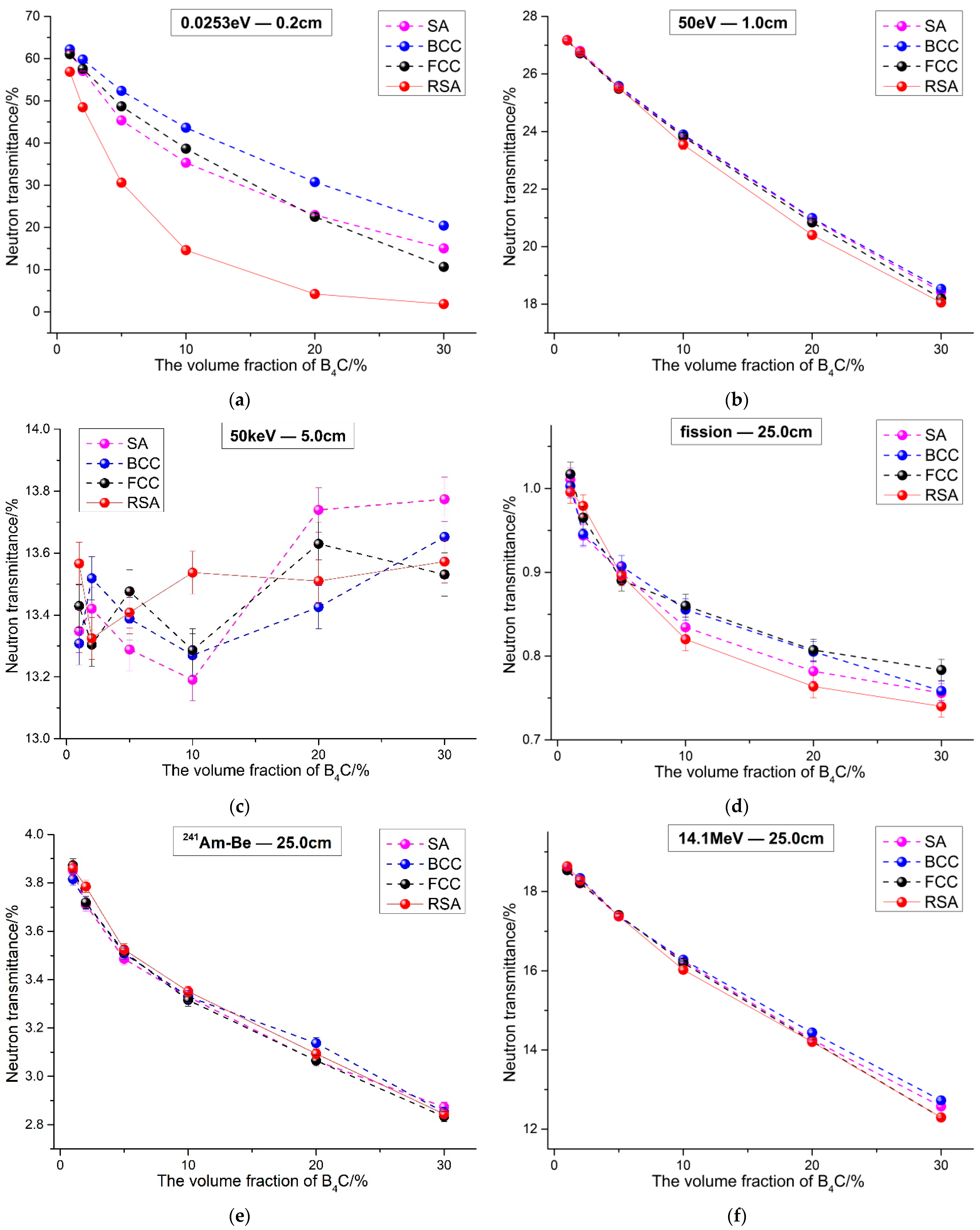
3.1. Neutron Transmittance Results
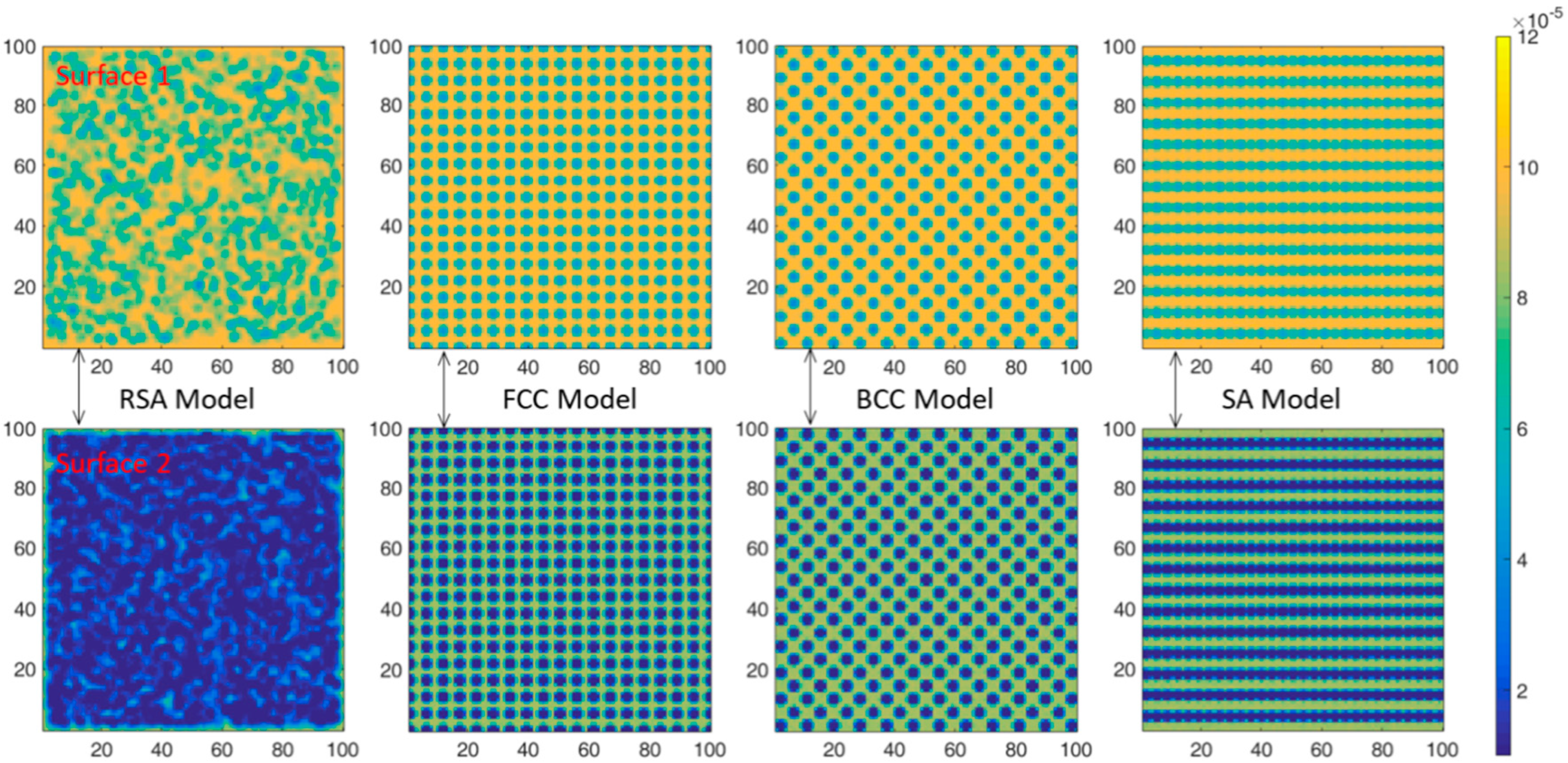
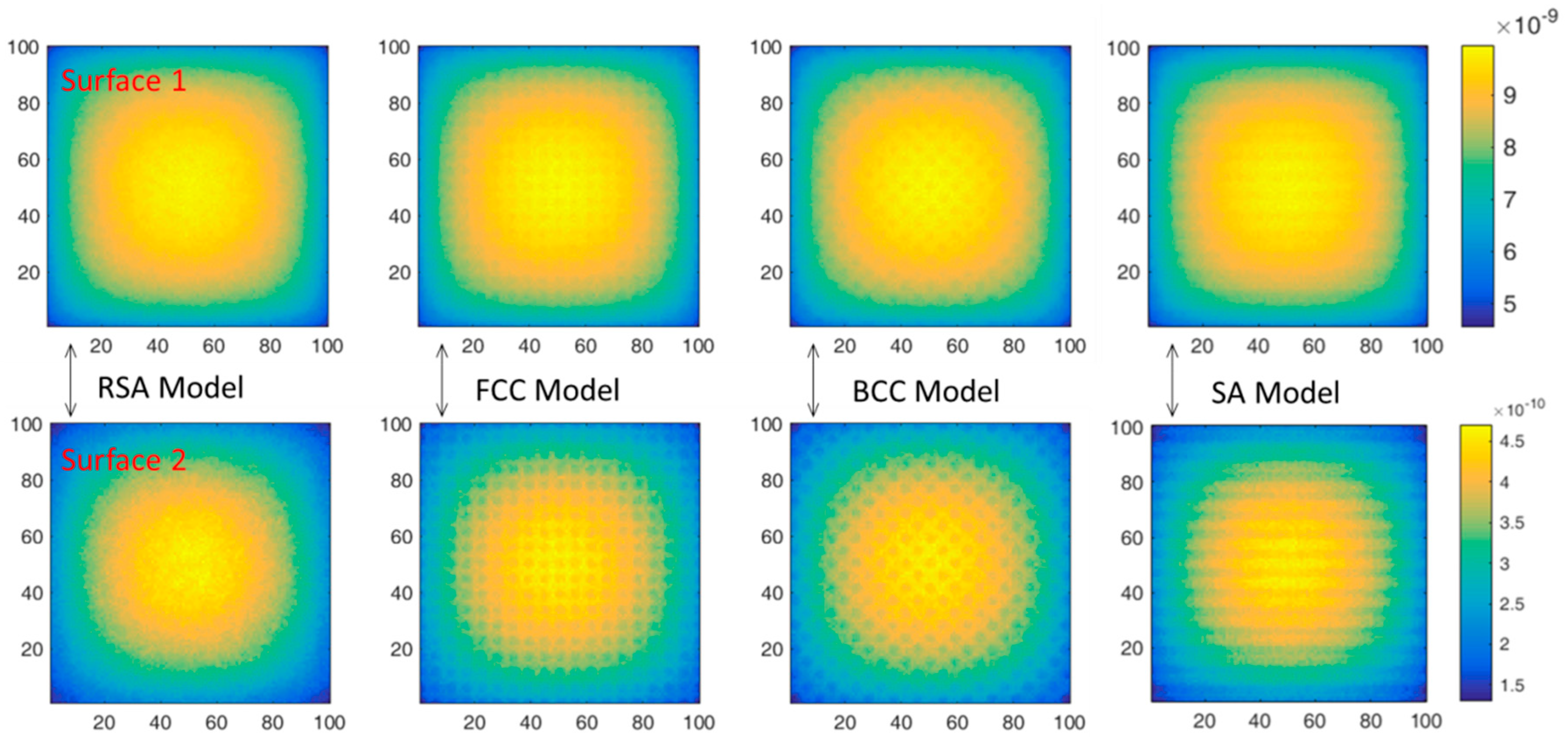
3.2. Neutron Flux Distribution Results
4. Conclusions
- (a)
- The spatial arrangement of B4C has an impact on the neutron shielding performance of the composites. The RSA model composites are roughly better than the other three periodic arrangement composites.
- (b)
- The influence of B4C spatial arrangement on the shielding performance of the composites changes with neutron energies. When the neutron energy is 0.0253 eV and the B4C is 30 vol.%, for 316 stainless steel composites, the neutron transmittance of the RSA model composite is about 85.31% smaller than the FCC model composite, while for the PE composite, it is about 82.71% at the same case. However, When the neutron is in the fission spectrum and the content of B4C is 30 vol.%, for 316 stainless steel composites, the neutron transmittance of the RSA model composite is about 3.54% smaller than the FCC model composite, while for PE composite, it is only about 2.63%.
- (c)
- For the three periodic arrangement models, the neutron shielding performance of the composites is related to B4C content. In the case of 0.0253 eV neutrons, when B4C is less than 20 vol.%, the neutron transmittance of the SA model composite is smaller than that of the other two models; while B4C is greater than 20 vol.%, the neutron transmittance of the FCC model composite becomes smallest. In the case of fission neutron, the results of 316 stainless steel composites are consistent with the results of 0.0253 eV neutrons. However, for PE composites, the neutron transmittance of the SA model composite is basically smallest.
- (d)
- The more effective alternating shielding is, the fewer ‘neutron channels’ and the better the neutron shielding performance of the composites.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.-R.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, M.-Z.; Wang, L.-Q.; Pan, Q.-F.; Zhang, H.-Z. Research Status in Neutron Shielding Materials with Combined Functional and Structural Performance. J. Netshape Form. Eng. 2019, 11, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miracle, D.B. Metal matrix composites—From science to technological significance. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2005, 65, 2526–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilip, J.J.S.; Ram, G.D.J. Microstructures and Properties of Friction Freeform Fabricated Borated Stainless Steel. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2013, 22, 3034–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.Y.; Soliman, S.E.; Baratta, A.J.; Balliett, T.A. Fracture Mechanism of Borated Stainless Steel. Nucl. Technol. 2000, 130, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Tamaki, H. Developments in Spent Fuel Transport and Storage Caske. Tech. Rev. 2006, 43, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Li, G. International status of the dual purpose cask designed for both transport and storage of spent fuel. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 227, 022005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Cai, Y.-J.; Li, Q. Research Progress in Radiation Shielding Materials Serving as the Combined Barrier Against Neutron and Gamma-ray. Mater. Rev. 2018, 32, 1107–1113. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Murari, F.D.; de Avillez, R.R. Cold-rolled multiphase boron steels: Microstructure and mechanical properties. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2015, 4, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rodrigues, A.; Filho, T.M.; Filho, W.R. Borated Stainless Steel Storage Project to the Spent Fuel of the IEA-R1 Reactor. In Proceedings of the INAC 2013 Recife, Recife, Brazil, 24–29 November 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, F.; Tang, X.; Huang, H.; Chen, T.; Sun, X. Boracic Polyethylene/polyethylene Wax Blends and Open-Cell Nickel Foams as Neutron-Shielding Composite. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2017, 37, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buyuk, B.; Tugrul, A.B.; Aktop, S.; Addemir, A.O. Investigation on the Effects of Boron Carbide Particle Size on Radiation Shielding Properties of Boron Carbide-Titanium Diboride Composites. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2013, 123, 177–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyawali, T.R. Development of Heavyweight Concrete with 2n Mixing Theory for Shielding Application. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2020, 128, 103465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morioka, A.; Sakurai, S.; Okuno, K.; Sato, S.; Matsukawa, M. Development of 300 °C Heat Resistant Boron-Loaded Resin for Neutron Shielding. J. Nucl. Mater. 2012, 367, 1085–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewkhao, J.; Pokaipisit, A.; Limsuwan, P. Study on Borate Glass System Containing with Bi2O3 and BaO for Gamma-Rays Shielding Materials: Comparison with PbO. J. Nucl. Mater. 2010, 399, 38–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Hu, H.-S.; Yang, Q.-Z.; Yu, B.; Sun, W.-Q. Study on the Design and Experimental Verification of Multilayer Radiation Shield against Mixed Neutrons and γ-rays. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2019, 52, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Wang, Q.; Qin, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Xie, Z.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, G.; Xu, H.; Zheng, X.; et al. Study on Composite Material for Shielding Mixed Neutron and gamma-Rays. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2008, 55, 2376–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, B.C.; Uhm, R.; Miller, W.H. Enhancement of Thermal Neutron Attenuation of Nano-B4C, -BN Dispersed Neutron Shielding Polymer Nanocomposites. J. Nucl. Mater. 2014, 453, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoda, A.; Hossein, T.A. Study on Gamma Shielding Polymer Composites Reinforced with Different Sizes and Proportions of Tungsten Particles using MCNP code. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2019, 115, 91–98. [Google Scholar]
- Shuo, C.; Mohamed, B.; Afsaneh, R. Neutrons Attenuation on Composite Metal Foams and Hybrid Open-Cell Al Foam. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2015, 109, 27–39. [Google Scholar]
- Shuo, C.; Mohamed, B.; Afsaneh, R. Attenuation efficiency of X-ray and comparison to gamma ray and neutrons in composite metal foams. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2015, 117, 12–22. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, W.; Hu, H.; Yu, B.; Sheng, L.; Hu, G.; Cai, Y.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, M.; Yan, Y. Random Model for Radiation Shielding Calculation of Particle Reinforced Metal Matrix Composites and its Application. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2020, 166, 109299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.Q.; Hu, G.; Yu, X.H.; Shi, J.; Xu, H.; Wu, R.J.; He, C.; Yi, Q.; Hu, H.S. Study on a High-Boron-Content Stainless Steel Composite for Nuclear Radiation. Materials 2021, 14, 7004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Booth, T.E.; Avneet, S.; Goorley, T.J.; Jeffrey, S.; Brown, B.F.; Arthure, R. MCNP—A General Monte Carlo N-Particle Transport Code, Version 5: LA-UR-03-1987; Los Alamos National Laboratory: Los Alamos, NM, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Mathworks. MATLAB Programming, Version 2016a; Mathwork: Natick, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Magrab, E.B.; Azarm, S.; Balacandran, B.; Duncan, J.H.; Herold, K.E.; Walsh, G.C. An Engineers Guide to MATLAB, 3rd ed.; Person Press: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.; Hu, H.; Pan, Z.; Hu, G.; Zhang, T. A method to optimize the shield compact and lightweight combining the structure with components together by genetic algorithm and MCNP code. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2018, 139, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evaluated Nuclear Data File. ENDF/B-VIII.0 Released February 2, 2018. Available online: https://www.nndc.bnl.gov/exfor/endf00.jsp (accessed on 25 February 2022).
- Cieśla, M. Properties of random sequential adsorption of generalized dimers. Phys. Rev. E 2014, 89, 042404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Elements | H | 10B | 11B | C | Si | P | S | Cr | Mn | Fe | Ni | Mo | Density(g·cm−3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | Content (wt%) | ||||||||||||
| B4C | - | 15.7 | 62.6 | 21.7 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2.52 |
| 316 stainless steel | - | - | - | 0.08 | 1.00 | 0.035 | 0.03 | 17.75 | 2 | 63.61 | 13 | 2.5 | 7.62 |
| PE | 14.3 | - | - | 85.7 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.95 | ||
| 1 vol.% B4C/316 stainless steel | - | 0.05 | 0.21 | 0.15 | 1.00 | 0.035 | 0.030 | 17.69 | 1.99 | 63.40 | 12.96 | 2.49 | 7.57 |
| 5 vol.% B4C/316 stainless steel | - | 0.27 | 1.07 | 0.45 | 0.98 | 0.034 | 0.029 | 17.45 | 1.97 | 62.52 | 12.78 | 2.46 | 7.37 |
| 10 vol.% B4C/316 stainless steel | - | 0.56 | 2.22 | 0.78 | 0.96 | 0.034 | 0.029 | 17.12 | 1.93 | 61.36 | 12.54 | 2.41 | 7.11 |
| 20 vol.% B4C/316 stainless steel | - | 1.20 | 4.78 | 1.73 | 0.92 | 0.032 | 0.028 | 16.39 | 1.85 | 58.75 | 12.01 | 2.31 | 6.60 |
| 30 vol.% B4C/316 stainless steel | - | 1.95 | 7.77 | 2.76 | 0.88 | 0.031 | 0.026 | 15.55 | 1.75 | 55.71 | 11.39 | 2.19 | 6.09 |
| 1 vol.% B4C/PE | 13.93 | 0.41 | 1.63 | 84.03 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.97 |
| 5 vol.% B4C/PE | 12.55 | 1.92 | 7.67 | 77.86 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.03 |
| 10 vol.% B4C/PE | 11.04 | 3.57 | 14.25 | 71.13 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.11 |
| 20 vol.% B4C/PE | 8.60 | 6.26 | 24.96 | 60.18 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.26 |
| 30 vol.% B4C/PE | 6.69 | 8.35 | 33.30 | 51.65 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.42 |
| Energy (MeV) | Nuclides | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1H | 10B | 12C | 52Cr | 56Fe | |
| 2.53 × 10−8 | 30.40 | 3846.76 | 4.95 | 3.93 | 14.78 |
| 5 × 10−5 | 20.44 | 88.30 | 4.75 | 3.06 | 11.96 |
| 5 × 10−2 | 15.53 | 5.14 | 4.59 | 36.46 | 4.23 |
| Fission (average: 1.98) | 2.91 | 2.06 | 1.70 | 2.73 | 2.38 |
| 241Am-Be (average: 4.5) | 1.75 | 1.79 | 1.69 | 3.81 | 3.80 |
| 14.1 | 0.69 | 1.49 | 1.30 | 2.41 | 2.59 |
| Energy (MeV) | The Shield Size (cm) | The B4C Radius (cm) | The Plane Source Size (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2.53 × 10−8 | 0.1 × 0.2 × 0.1 | 0.002 | 0.1 × 0.1 |
| 5 × 10−5 | 0.5 × 1.0 × 0.5 | 0.01 | 0.5 × 0.5 |
| 0.05 | 2.5 × 5.0 × 2.5 | 0.05 | 2.5 × 2.5 |
| Fission (average: 1.98) | 12.5 × 25.0 × 12.5 | 0.25 | 12.5 × 12.5 |
| 241Am-Be (average: 4.5) | 12.5 × 10.0/25.0 × 12.5 | 0.25 | 12.5 × 12.5 |
| 14.1 | 12.5 × 25.0 × 12.5 | 0.25 | 12.5 × 12.5 |
| Position | Neutron Flux | 0.0253 eV | Fission Spectrum | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RSA | FCC | BCC | SA | RSA | FCC | BCC | SA | ||
| Surface 1 | maximum | 1.04 × 10−4 | 1.03 × 10−4 | 1.04 × 10−4 | 1.03 × 10−4 | 9.96 × 10−9 | 9.93 × 10−9 | 9.94 × 10−9 | 9.95 × 10−9 |
| minimum | 3.77 × 10−5 | 4.25 × 10−5 | 3.78 × 10−5 | 4.71 × 10−5 | 5.79 × 10−9 | 5.75 × 10−9 | 5.77 × 10−9 | 5.68 × 10−9 | |
| Surface 2 | maximum | 6.50 × 10−5 | 8.65 × 10−5 | 8.61 × 10−5 | 8.69 × 10−5 | 4.56 × 10−10 | 4.71 × 10−10 | 4.75 × 10−10 | 4.71 × 10−10 |
| minimum | 1.20 × 10−6 | 1.12 × 10−6 | 1.11 × 10−6 | 1.41 × 10−6 | 1.65 × 10−10 | 1.61 × 10−10 | 1.61 × 10−10 | 1.60 × 10−10 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, W.; Hu, G.; Xu, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Men, T.; Ji, F.; Lao, W.; Yu, B.; Sheng, L.; et al. Study on the Influence of Reinforced Particles Spatial Arrangement on the Neutron Shielding Performance of the Composites. Materials 2022, 15, 4266. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15124266
Sun W, Hu G, Xu H, Li Y, Wang C, Men T, Ji F, Lao W, Yu B, Sheng L, et al. Study on the Influence of Reinforced Particles Spatial Arrangement on the Neutron Shielding Performance of the Composites. Materials. 2022; 15(12):4266. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15124266
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Weiqiang, Guang Hu, Hu Xu, Yanfei Li, Chao Wang, Tingxuan Men, Fu Ji, Wanji Lao, Bo Yu, Liang Sheng, and et al. 2022. "Study on the Influence of Reinforced Particles Spatial Arrangement on the Neutron Shielding Performance of the Composites" Materials 15, no. 12: 4266. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15124266
APA StyleSun, W., Hu, G., Xu, H., Li, Y., Wang, C., Men, T., Ji, F., Lao, W., Yu, B., Sheng, L., Li, J., Jia, Q., Xiong, S., & Hu, H. (2022). Study on the Influence of Reinforced Particles Spatial Arrangement on the Neutron Shielding Performance of the Composites. Materials, 15(12), 4266. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15124266






