Incorporation of Silica Particles Attached to Nylon 66 Electrospun Nanofibers with Cement
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Polymer Solution
2.3. Electrospinning Process, Hardened Cement Paste Preparation, and Testing Methods
3. Results and Discussion
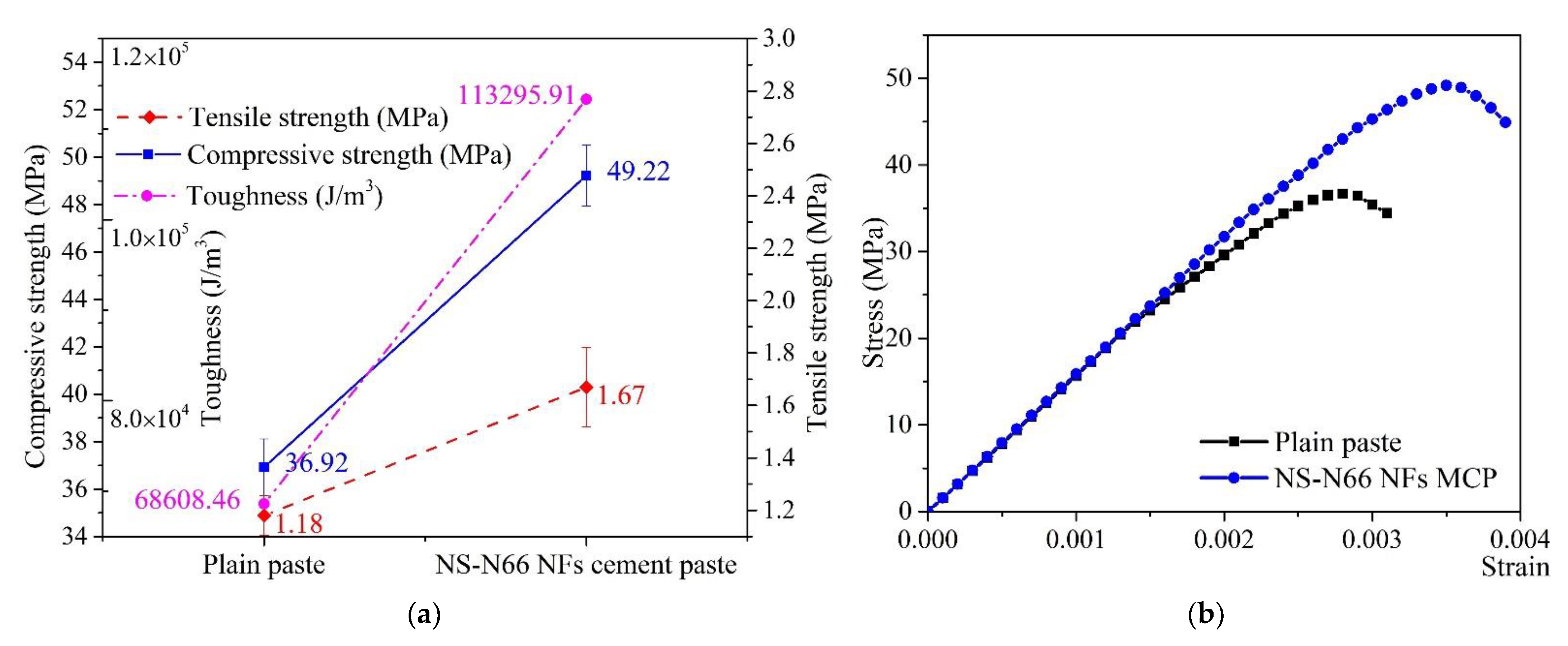
3.1. Mechanical Strength
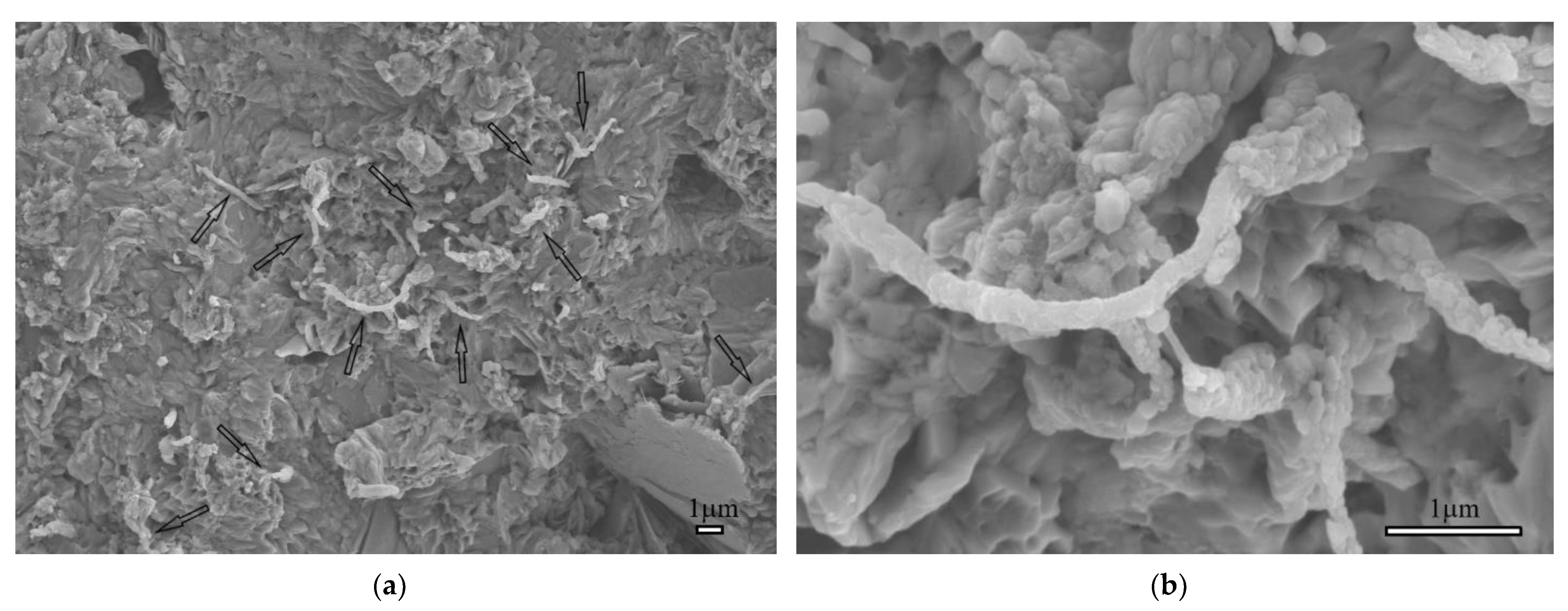
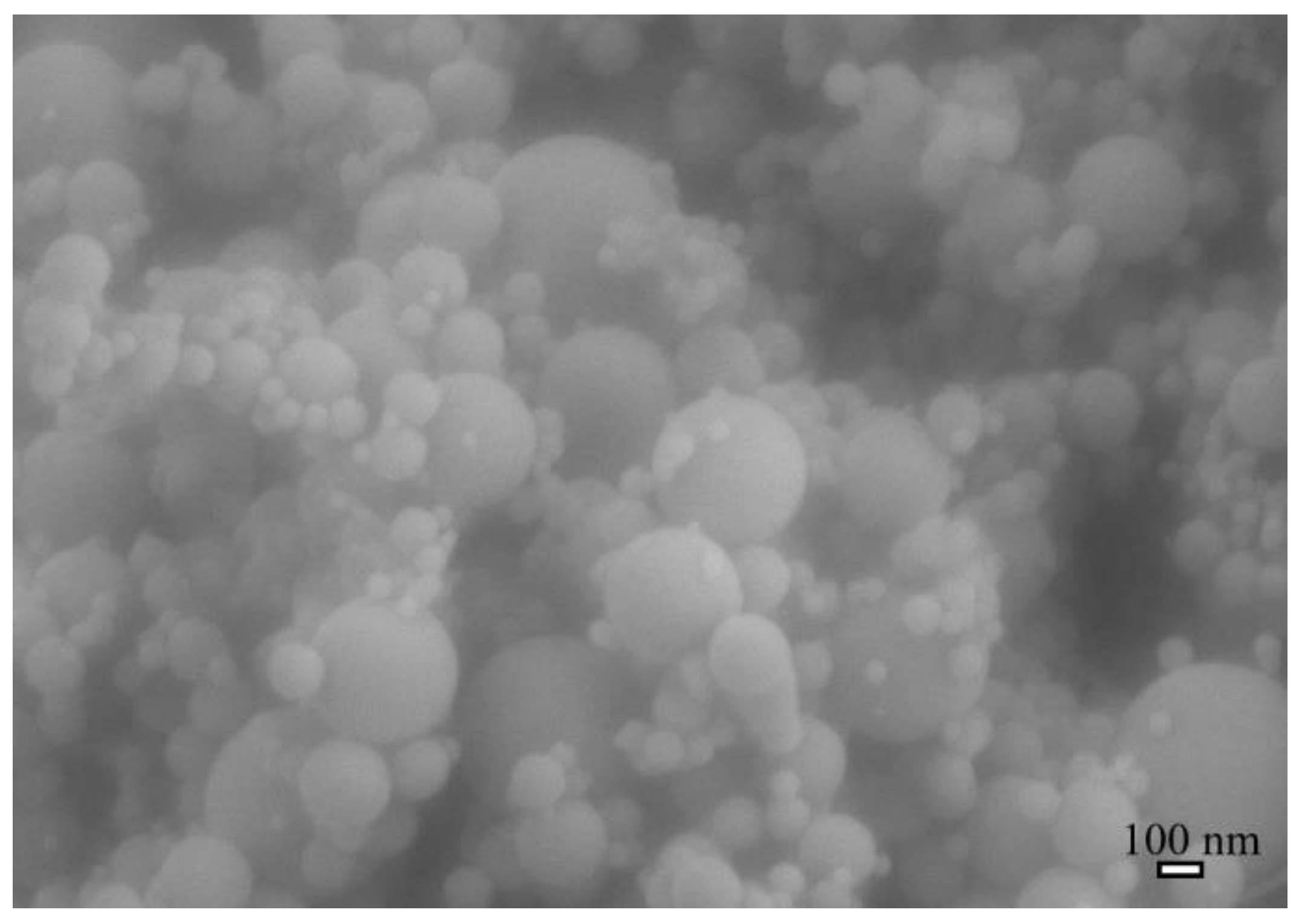
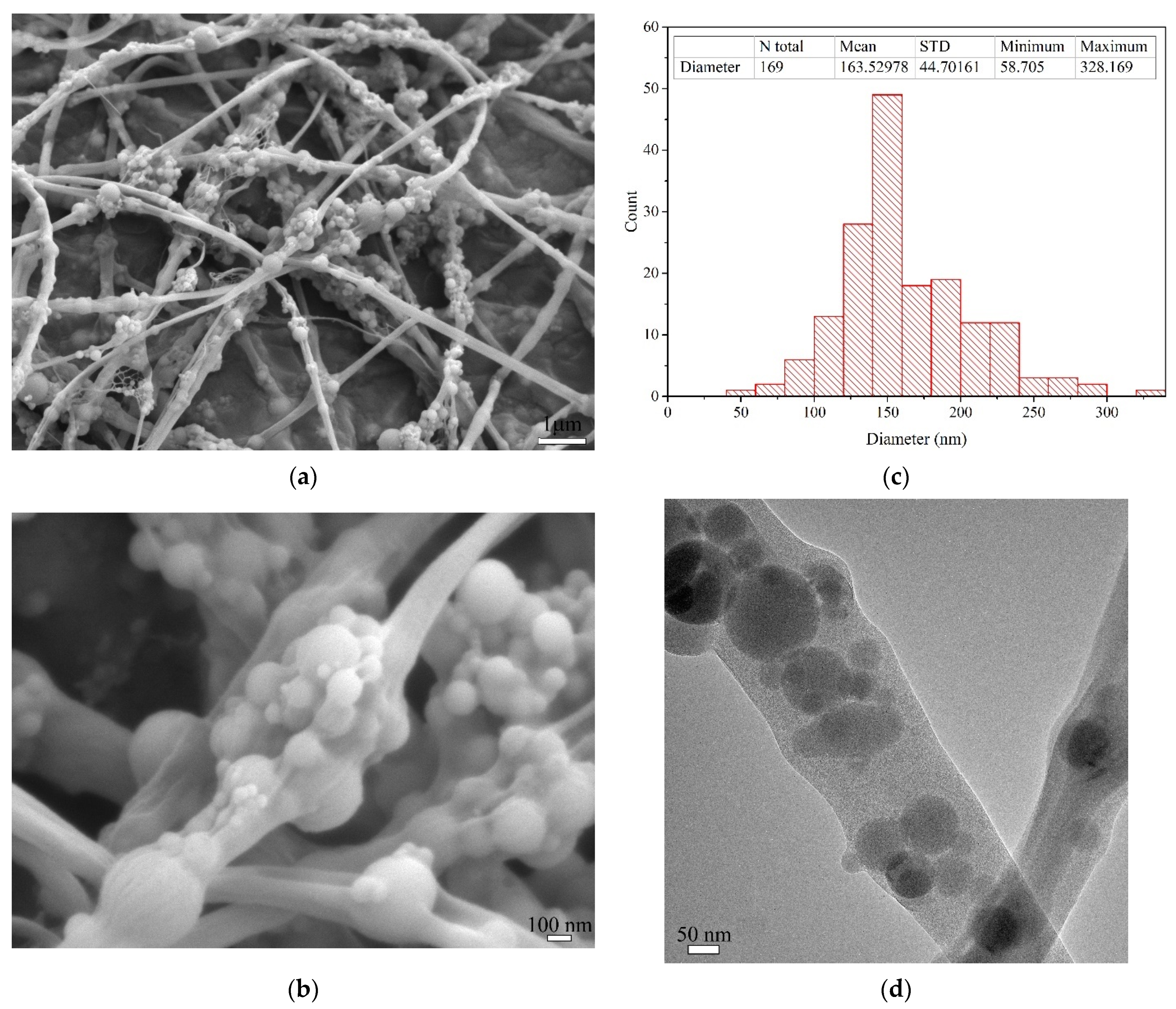
3.2. Morphology and Microstructure of Nanofibers
3.3. Microstructural Characteristic of Hardened Cement Pastes
3.4. XRD Analysis
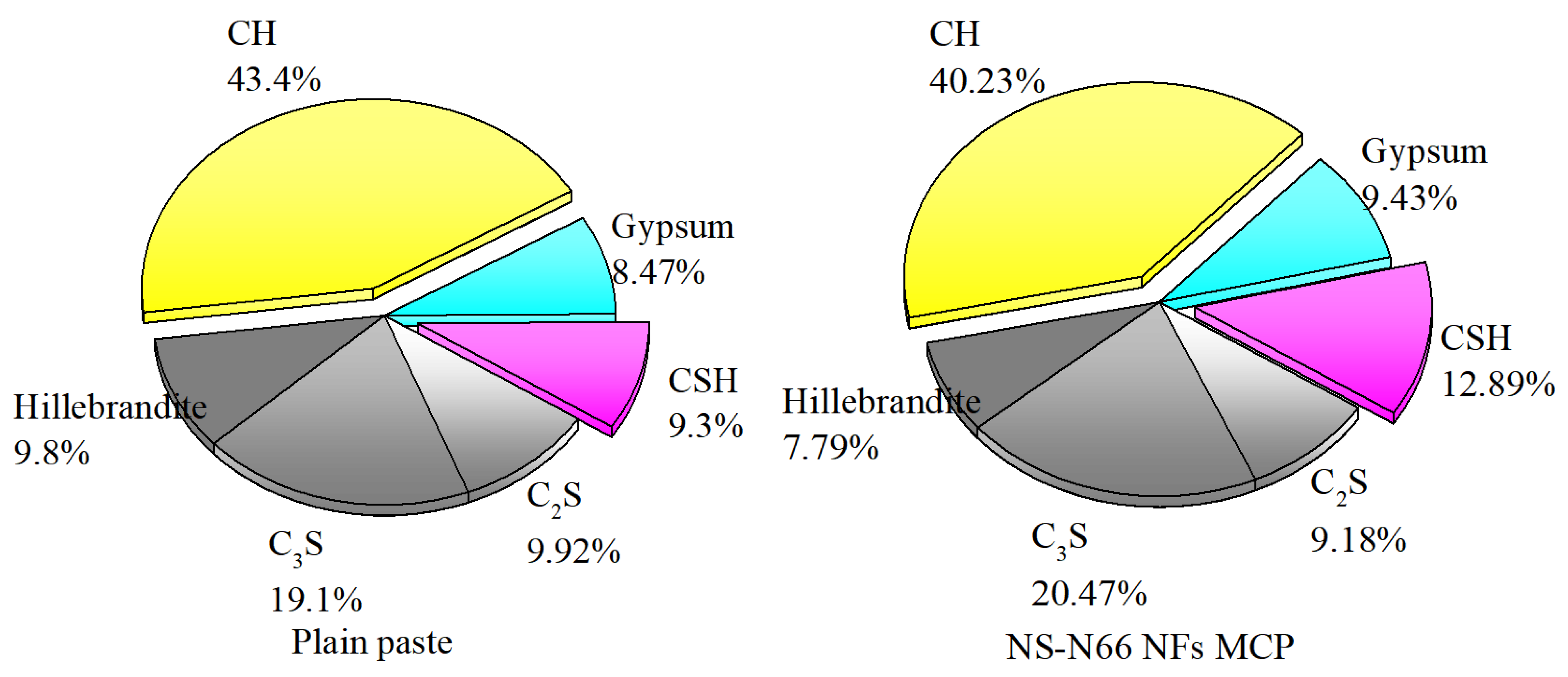
3.5. Thermal Analysis
4. Conclusions and Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mehta, P.K.; Monteiro, P.J.M. Concrete: Microstructure, Properties, and Materials, 4th ed.; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Neville, A.M. Properties of Concrete, 5th ed.; (September 2, 2012); Prentice Hall: Hoboken, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Muller, A.C.A.; Scrivener, K.L.; Skibsted, J.; Gajewicz, A.M.; McDonald, P.J. Influence of silica fume on the microstructure of cement pastes: New insights from 1H NMR relaxometry. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 74, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.; Qian, J.; Cheng, X.; Shah, S.P. Effects of the pozzolanic reactivity of nanoSiO2 on cement-based materials. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2015, 55, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanidou, M.; Papayianni, I. Influence of nano-SiO2 on the Portland cement pastes. Compos. Part B Eng. 2012, 43, 2706–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Land, G.; Stephan, D. The influence of nano-silica on the hydration of ordinary Portland cement. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 1011–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.J.; Rahman, M.K.; Al-Majed, A.A.; Al-Zahrani, M.M.; Taha, M.M.R. Nanosilica effects on composition and silicate polymerization in hardened cement paste cured under high temperature and pressure. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2013, 43, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, J.-Y.; Chang, T.-P.; Hsiao, T.-C. Effect of nanosilica on characterization of Portland cement composite. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 424, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, Y.C.; Cordeiro, G.C.; Filho, R.D.T.; Tavares, L.M. Performance of Portland cement pastes containing nano-silica and different types of silica. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 146, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.; Rafiq, S.; Mahmood, W.; Noaman, R.; AL-Darkazali, H.; Ghafor, K.; Qadir, W. Microstructure characterizations, thermal properties, yield stress, plastic viscosity and compression strength of cement paste modified with nanosilica. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 10941–10956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Xu, J.; Yin, T.; Wang, Y.; Chu, H. Improving electrical and piezoresistive properties of cement-based composites by combined addition of nano carbon black and nickel nanofiber. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 51, 104312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, M.M.; Jian, G.; Zhong, T.; Li, H.; Fernandez, C.A.; Fifield, L.S.; Wolcott, M.; Nassiri, S. Insights into setting time, rheological and mechanical properties of chitin nanocrystals- and chitin nanofibers-cement paste. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2022, 132, 104623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Corr, D.J.; Shah, S.P. Study on mechanical properties of the interfacial transition zone in carbon nanofiber-reinforced cement mortar based on the PeakForce tapping mode of atomic force microscope. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 61, 105248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.-A.; Aakyiir, M.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, A.; Meola, T.R.; Forson, P.; Araby, S.; Zhuge, Y.; Lee, S.-H.; Ma, J. Durable cement/cellulose nanofiber composites prepared by a facile approach. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2022, 125, 104321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen TN, M.; Yoo, D.; Kim, J.J. Cementitious Material Reinforced by Carbon Nanotube-Nylon 66 Hybrid Nanofibers: Mechanical strength and microstructure analysis. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 23, 100845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.N.M.; Moon, J.; Kim, J.J. Microstructure and mechanical properties of hardened cement paste including Nylon 66 nanofibers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 232, 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.N.M.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, J.J. Effect of Electrospun Nanofiber Additive on Selected Mechanical Properties of Hardened Cement Paste. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.J.; Nguyen TN, M.; Nguyen, X.T.; Ta, D.H. Reinforcing Cementitious Material Using Singlewalled Carbon Nanotube-Nylon 66 Nanofibers. Transp. Commun. Sci. J. 2020, 71, 46–55. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM C150/C150M-20; Standard Specification for Portland Cement. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020.
- Cai, Y.; Hou, P.; Cheng, X.; Du, P.; Ye, Z. The effects of nanoSiO2 on the properties of fresh and hardened cement-based materials through its dispersion with silica fume. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 148, 770–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, B.; Chen, S.J.; Korayem, A.H.; Collins, F.; Wang, C.M.; Duan, W.H. Effect of ultrasonication energy on engineering properties of carbon nanotube reinforced cement pastes. Carbon 2015, 85, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konsta-Gdoutos, M.S.; Metaxa, Z.S.; Shah, S.P. Highly dispersed carbon nanotube reinforced cement based materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2010, 40, 1052–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM C307-18; Standard Test Method for Tensile Strength of Chemical-Resistant Mortar, Grouts, and Monolithic Surfacings. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2018.
- ASTM C109/C109M-20b; Standard Test Method for Compressive Strength of Hydraulic Cement Mortars (Using 2-in. or [50 mm] Cube Specimens). ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020.
- ASTM C305-20; Standard Practice for Mechanical Mixing of Hydraulic Cement Pastes and Mortars of Plastic Consistency. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020.
- Timoshenko, S.P.; Gere, J.M. Mechanics of Materials; PWS-Kent Publishing: Boston, MA, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, G.; Zhao, L.Y.; Zhu, L.T.; Deng, X.Y.; Chen, W.L. Effect of Experimental Parameters on Nanofiber Diameter from Electrospinning with Wire Electrodes. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 230, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.; Stylios, G. Effect of Experimental Parameters on the Morphology of Electrospun Nylon 6 fibres. Int. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2010, 10, 70–78. [Google Scholar]
- Theron, S.A.; Zussman, E.; Yarin, A.L. Experimental investigation of the governing parameters in the electrospinning of polymer solutions. Polymer 2004, 45, 2017–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rietveld, H.M. A profile refinement method for nuclear and magnetic structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1969, 2, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Li, X.; Lv, Y.; Jiang, D.; Liu, Z.; He, C. Mechanical and hydration properties of low clinker cement containing high volume superfine blast furnace slag and nano silica. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 238, 117683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maagi, M.T.; Jun, G. Effect of the particle size of nanosilica on early age compressive strength in oil-well cement paste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 259, 120393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.K.; Khan MM, R.; Guha, A.K.; Naskar, N. Bio-inspired Fabrication of Silver Nanoparticles on Nanostructure Silica, Characterization and Application as Highly Efficient Hydrogenation Catalyst. Green Chem. 2013, 15, 2548–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, H.F.W. Cement Chemistry, 2nd ed.; Thomas Telford Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.J.; Foley, E.M.; Taha, M.M.R. Nano-mechanical characterization of synthetic calcium–silicate–hydrate (C–S–H) with varying CaO/SiO2 mixture ratios. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2013, 36, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, E.M.; Kim, J.J.; Taha, M.M.R. Synthesis and nano-mechanical characterization of calcium-silicate-hydrate (C-S-H) made with 1.5 CaO/SiO2 mixture. Cem. Concr. Res. 2012, 42, 1225–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.F.; Chen, J.W. The experimental investigation of concrete carbonation depth. Cem. Concr. Res. 2006, 36, 1760–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siverio Lima, M.S.; Hajibabaei, M.; Hesarkazzazi, S.; Sitzenfrei, R.; Buttgereit, A.; Queiroz, C.; Haritonovs, V.; Gschösser, F. Determining the Environmental Potentials of Urban Pavements by Applying the Cradle-to-Cradle LCA Approach for a Road Network of a Midscale German City. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


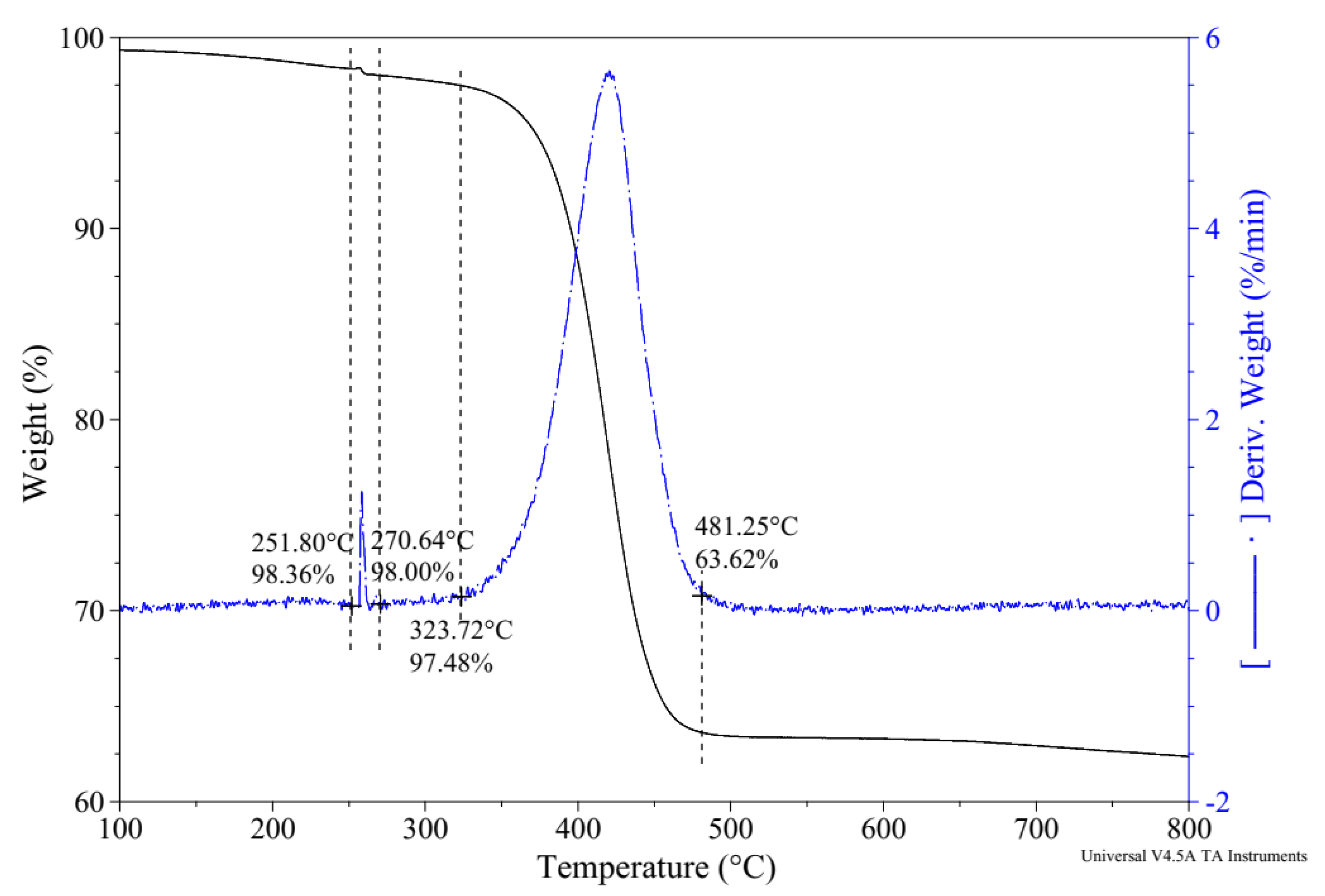
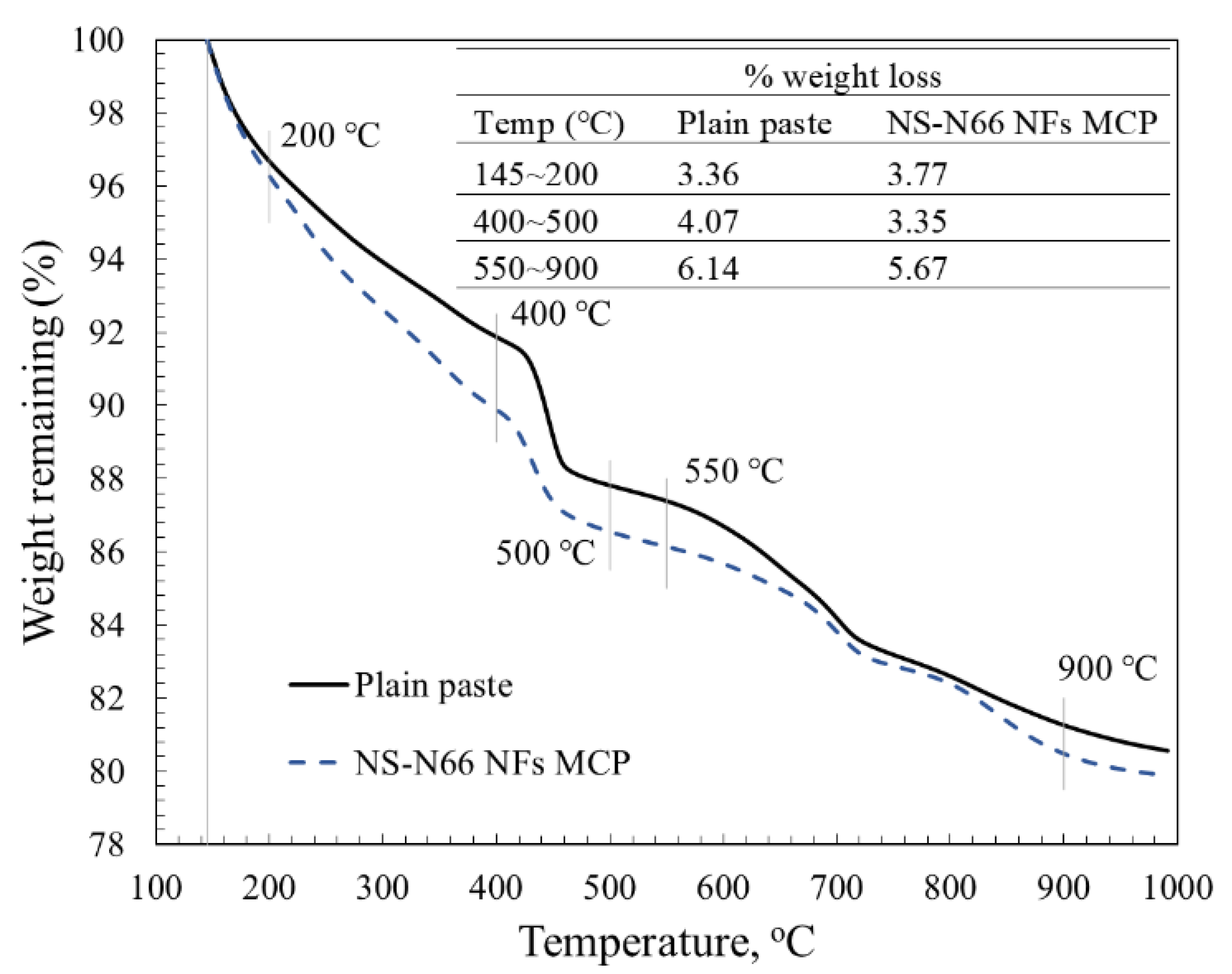
| CaO | Al2O3 | SiO2 | SO3 | MgO | Fe2O3 | Ig. Loss | Specific Surface Area (cm2/g) | Compressive Strength, 28-Day (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 61.33 | 6.40 | 21.01 | 2.30 | 3.02 | 3.12 | 1.40 | 2800 | 36 |
| Previous Study [16] | Present Study | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| N66 NFs MCP (1) | N66 NFs MCP (2) | NS-N66 NFs MCP | |
| Solvent (Volume %) | Formic acid: dichloromethane (4:1) | Formic acid: Chloroform (4:1) | Formic acid: Chloroform (4:1) |
| Polymer solution (Weight %) | N66 10 wt%: solvent 90 wt% | N66 10 wt%: solvent 90 wt% | NS 13 wt%: N66 7 wt%: solvent 80 wt% |
| Tensile strength | 32 | 28 | 41 |
| Compressive strength | 6 | 8 | 33 |
| Toughness | 42 | 49 | 65 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, T.N.M.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, J.J. Incorporation of Silica Particles Attached to Nylon 66 Electrospun Nanofibers with Cement. Materials 2022, 15, 7011. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15197011
Nguyen TNM, Lee DH, Kim JJ. Incorporation of Silica Particles Attached to Nylon 66 Electrospun Nanofibers with Cement. Materials. 2022; 15(19):7011. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15197011
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Tri N. M., Do Hyung Lee, and Jung J. Kim. 2022. "Incorporation of Silica Particles Attached to Nylon 66 Electrospun Nanofibers with Cement" Materials 15, no. 19: 7011. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15197011
APA StyleNguyen, T. N. M., Lee, D. H., & Kim, J. J. (2022). Incorporation of Silica Particles Attached to Nylon 66 Electrospun Nanofibers with Cement. Materials, 15(19), 7011. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15197011








