Phosphate Ceramics with Silver Nanoparticles for Electromagnetic Shielding Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
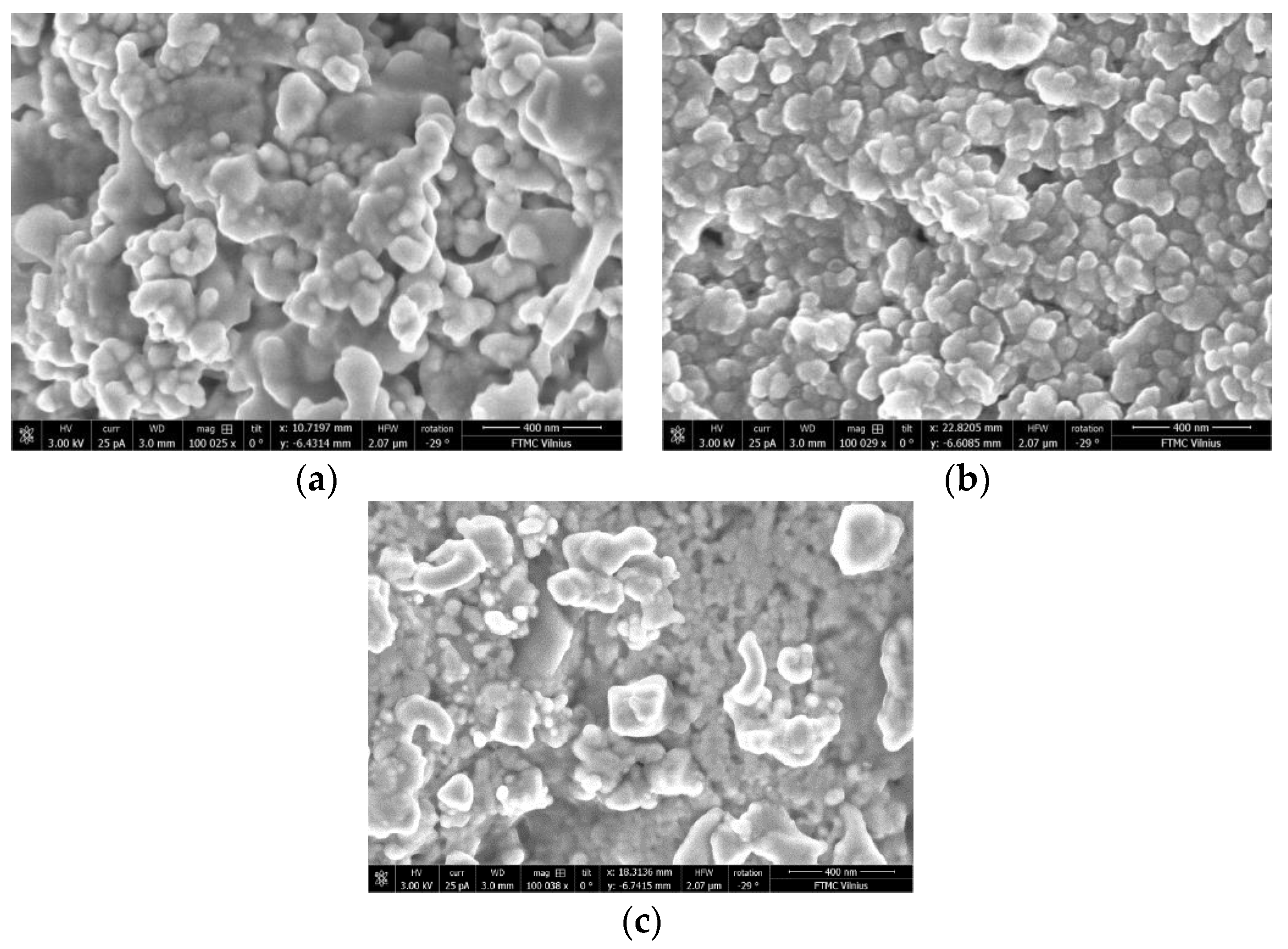
3.1. Structure of Ceramics and Room Temperature Properties
3.2. Electrical Transport at Different Temperatures
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ryu, S.H.; Kim, H.; Park, S.W.; Kwon, S.J.; Kim, S.; Lim, H.R.; Park, B.; Lee, S.B.; Choa, Y.H. Millimeter-scale percolated polyethylene/graphene composites for 5G electromagnetic shielding. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 8429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghdi, S.; Rhee, K.Y.; Hui, D.; Park, S.J. A review of conductive metal nanomaterials as conductive, transparent, and flexible coatings, thin films and conductive fillers: Different deposition methods and applications. Coatings 2018, 8, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plyushch, A.; Macutkevic, J.; Svirskas, S.; Banys, J.; Plausinaitiene, V.; Bychanok, D.; Maksimenko, S.A.; Selskis, A.; Sokal, A.; Lapko, K.N.; et al. Silicon carbide/phosphate ceramics composite for electromagnetic shielding applications whiskers vs. particles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2019, 114, 183105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plyushch, A.; Maciulis, N.; Sokal, A.; Grigalaitis, R.; Macutkevic, J.; Kudlash, A.; Apanasevich, N.; Lapko, K.; Selskis, A.; Maksimenko, S.A.; et al. 0.7Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3-0.3PbTiO3 phosphate composites: Dielectric and ferroelectric properties. Materials 2021, 14, 5065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plyushch, A.; Macutkevic, J.; Kuzhir, P.; Sokal, A.; Lapko, K.; Selskis, A.; Banys, J. Synergy effects in electromagnetic properties of phosphate ceramics with silicon carbide whiskers and carbon nanotubes. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.H.; Cheng, C.B.; Sun, W.J.; Zhang, Z.M.; Ma, R.W.; Zhou, J.X.; Wang, J.; Wang, T.L.; Zheng, Q.J.; Du, Y.; et al. Negative permittivity behavior of carbon fibre/alumina ceramic composites prepared by hot-press sintering. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 10031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ma, P.C.; Chow, W.S.; To, C.K.; Tang, B.C.; Kim, J.K. Correlations between percolation threshold, dispersion state and aspect ratio of carbon nanotubes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2007, 17, 3207–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandler, J.K.W.; Kirk, J.E.; Kinloch, I.A.; Shaffer, M.S.P.; Windle, A.H. Ultra-low electrical percolation threshold in carbon-nanotube-epoxy composites. Polymer 2003, 44, 5893–5899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.L.; Duan, X.Y.; Nie, C.; Jia, Y.C.; Zheng, H.J. The effect of polymer molecular weights on the electrical, reological, and vapor sensing behavior of polycarbonate/multi-walled carbon nanotube nanocomposites. Polym. Compos. 2022, 43, 5095–5106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrianse, L.J.; Reedijk, J.A.; Teunissen, P.A.A.; Brom, H.B.; Michels, M.A.J.; Broken-Zijp, J.C.M. High-dilution carbon-black/polymer composites: Hierarchical percolation network derived from Hz to THz ac conductivity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1997, 78, 1755–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaimiene, E.; Macutkevic, J.; Banys, J.; Selskis, A.; Fierro, V.; Celzard, A.; Schaefer, S.; Shenderova, O. Ultra-low percolation threshold in epoxy resin-onion-like carbon composites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2018, 113, 033105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Dalal, J.; Kumar, A.; Ohlan, A. Microwave absorption performance of core-shell rGO/Ni0.5Co0.5Fe2O4@PEDOT composite: An effective approach to reduce electromagnetic wave pollution. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2022, 220635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalal, J.; Malik, S.; Dahiya, S.; Punia, R.; Singh, K.; Maan, A.S.; Dhawan, S.K.; Ohlan, A. One pot synthesis and electromagnetic interference shielding behavior of reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites decorated with Ni0.5Co0.5Fe2O4 nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 887, 161472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalal, J.; Lather, S.; Gupta, A.; Dahiya, S.; Maan, A.S.; Singh, K.; Dhawan, S.K.; Ohlan, A. EMI shielding properties of laminated graphene and PbTiO3 reinforced poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2018, 165, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Kim Ch Jiang, P.; Yin, Y.; Li, Z. Influence of aluminum nanoparticle surface treatment on the electrical properties of polyethylene composites. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 105, 014105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tee, D.I.; Mariatti, M.; Azizan, A.; See, C.H.; Chong, K.F. Effect of silane-based coupling agent on the properties of silver nanoparticles filled epoxy composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2007, 67, 2584–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouni, M.; Boudenne, A.; Boiteux, G.; Massardier, V.; Garnier, B.; Serhei, A. Electrical and thermal properties of polyethylene/silver nanoparticle composites. Polym. Compos. 2013, 34, 778–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.H.; Ma, C.C.M.; Teng, C.C.; Huang, Y.L.; Lee, S.H.; Wang, I.; Wei, M.H. Electrical, morphological and electromagnetic interference shielding properties of silver nanowires and nanoparticles conductive composites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2012, 136, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, M.; Li, L.; Shao, X.; Tian, M.; Zou, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, W. Fabrication of highly conductive silver-coated aluminum microspheres based on poly(catechol/polyamine) surface modification. Polymers 2022, 14, 2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.us-nano.com/inc/sdetail/126 (accessed on 11 October 2022).
- Available online: https://www.us-nano.com/inc/sdetail/470 (accessed on 11 October 2022).
- Grigas, J. Microwave dielectric spectroscopy of ferroelectrics. Ferroelectrics 2009, 380, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balberg, I. Excluded volume explanation of Archies law. Phys. Rev. B 1986, 33, 3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celzard, A.; McRae, E.; Deleuze, C.; Dufort, M.; Furdin, C.; Mareche, J.F. Critical concentration in percolating systems containing a high-aspect-ratio filler. Phys. Rev. B 1996, 53, 6209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tennant, A.; Chambers, B. A single-layer tuneable microwave absorber using an active FSS. IEEE Microw. Absorber Using Act. FSS 2004, 14, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Apanasevich, N.; Sokal, A.; Lapko, K.; Kudlash, A.; Lomonosov, V.; Plyushch, A.; Kuzhir, P.P.; Macutkevic, J.; Banys, J.; Okotrub, A. Phosphate ceramics—Carbon nanotubes composites: Liquid aluminum phosphate vs. solid magnesium phosphate binder. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 12147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonscher, A.K. The universal dielectric response and its physical significance. IEEE Trans. Electr. Insul. 1992, 27, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaimiene, E.; Schaefer, S.; Macutkevic, J.; Banys, J.; Selskis, A.; Fierro, V.; Celzard, A. Electrical percolation and electromagnetic properties of PDMS composites filled with Ag nanoparticles of different sizes. Polym. Compos. 2020, 41, 4750–4756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plyushch, A.; Kuzhir, P.P.; Maksimenko, S.A.; Macutkevic, J.; Banys, J.; Sokal, A.; Lapko, K.N.; Arkhipov, V.; Okotrub, A. Grain size effect in conductive phosphate/carbon nanotube ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 4965–4969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, P.; Sichel, E.K.; Gittleman, I.J. Fluctuation-induced tunneling conduction in carbon-polyvinylcloride composites. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1978, 40, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Concentration and Average Size of Ag Nanoparticles | Reflection | Transmission | Absorption |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20% 30–50 nm | 0.39 | 0.45 | 0.16 |
| 30% 30–50 nm | 0.39 | 0.08 | 0.53 |
| 40% 30–50 nm | 0.59 | 0.07 | 0.35 |
| 50% 30–50 nm | 0.38 | 0.01 | 0.61 |
| 20% 80–100 nm | 0.13 | 0.62 | 0.25 |
| 50% 80–100 nm | 0.75 | 0.08 | 0.17 |
| Ag (wt.%), Size | Temperature Region | E, eV | ln(σ0, Sm−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 30% 30–50 nm | T > Tr | 0.118 | 4.62 |
| T < Tr | 0.086 | 3.62 | |
| 40% 30–50 nm | T > Tr | 0.056 | 8.86 |
| T < Tr | 0.041 | 8.43 | |
| 50% 30–50 nm | T > Tr | 0.077 | 7.57 |
| T < Tr | 0.130 | 9.17 | |
| 50% 80–100 nm | T > Tr | 0.079 | 5.91 |
| T < Tr | 0.037 | 4.76 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Palaimiene, E.; Macutkevič, J.; Banys, J.; Selskis, A.; Apanasevich, N.; Kudlash, A.; Sokal, A.; Lapko, K. Phosphate Ceramics with Silver Nanoparticles for Electromagnetic Shielding Applications. Materials 2022, 15, 7100. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15207100
Palaimiene E, Macutkevič J, Banys J, Selskis A, Apanasevich N, Kudlash A, Sokal A, Lapko K. Phosphate Ceramics with Silver Nanoparticles for Electromagnetic Shielding Applications. Materials. 2022; 15(20):7100. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15207100
Chicago/Turabian StylePalaimiene, Edita, Jan Macutkevič, Jūras Banys, Algirdas Selskis, Natalia Apanasevich, Alexander Kudlash, Aliaksei Sokal, and Konstantin Lapko. 2022. "Phosphate Ceramics with Silver Nanoparticles for Electromagnetic Shielding Applications" Materials 15, no. 20: 7100. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15207100
APA StylePalaimiene, E., Macutkevič, J., Banys, J., Selskis, A., Apanasevich, N., Kudlash, A., Sokal, A., & Lapko, K. (2022). Phosphate Ceramics with Silver Nanoparticles for Electromagnetic Shielding Applications. Materials, 15(20), 7100. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15207100







